Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one
race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
over another.
It may also mean
prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's per ...
,
discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
, or antagonism directed against other people because they are of a different race or
ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
.
Modern variants of racism are often based in social perceptions of biological differences between peoples. These views can take the form of
social actions
In sociology, social action, also known as Weberian social action, is an act which takes into account the actions and reactions of individuals (or ' agents'). According to Max Weber, "Action is 'social' insofar as its subjective meaning takes ac ...
, practices or beliefs, or
political systems
In political science, a political system means the type of political organization that can be recognized, observed or otherwise declared by a state.
It defines the process for making official government decisions. It usually comprizes the govern ...
in which different races are ranked as inherently superior or inferior to each other, based on presumed shared inheritable traits, abilities, or qualities.
There have been attempts to legitimize racist beliefs through scientific means, such as
scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
, which have been overwhelmingly shown to be unfounded. In terms of political systems (e.g.
apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
) that support the expression of prejudice or aversion in discriminatory practices or laws, racist ideology may include associated social aspects such as
nativism,
xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
,
otherness,
segregation Segregation may refer to:
Separation of people
* Geographical segregation, rates of two or more populations which are not homogenous throughout a defined space
* School segregation
* Housing segregation
* Racial segregation, separation of humans ...
,
hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
ranking, and
supremacism
Supremacism is the belief that a certain group of people is superior to all others. The supposed superior people can be defined by age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, language, social class, ideology, nation, culture, ...
.
While the concepts of race and ethnicity are considered to be separate in contemporary
social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ...
, the two terms have a long history of equivalence in popular usage and older social science literature. "Ethnicity" is often used in a sense close to one traditionally attributed to "race", the division of human groups based on qualities assumed to be essential or innate to the group (e.g. shared
ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
or shared behavior). ''Racism'' and ''
racial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
'' are often used to describe discrimination on an ethnic or cultural basis, independent of whether these differences are described as racial. According to the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
's
, there is no distinction between the terms "racial" and "ethnic" discrimination. It further concludes that superiority based on racial differentiation is
scientifically false
The expression junk science is used to describe scientific data, research, or analysis considered by the person using the phrase to be wikt:spurious, spurious or fraudulent. The concept is often invoked in political and legal contexts where fact ...
, morally condemnable, socially
unjust, and dangerous. The convention also declared that there is no justification for racial discrimination, anywhere, in theory or in practice.
Racism is a relatively modern concept, arising in the European
age of imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
, the subsequent growth of
capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
, and especially the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
,
of which it was a major driving force. It was also a major force behind
racial segregation in the United States
In the United States, racial segregation is the systematic separation of facilities and services such as Housing in the United States, housing, Healthcare in the United States, healthcare, Education in the United States, education, Employment in ...
in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and of
apartheid in South Africa
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
; 19th and 20th-century racism in
Western culture
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
is particularly well documented and constitutes a reference point in studies and discourses about racism.
Racism has played a role in
genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
s such as
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
, the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
, the
Rwandan genocide
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed Hutu ...
, and the
, as well as colonial projects including the
European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
of
the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
,
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
,
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, and the
population transfer in the Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
including deportations of indigenous minorities.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have been—and are—often subject to racist attitudes.
Etymology, definition, and usage

In the 19th century, many scientists subscribed to the belief that the human population can be divided into races. The term ''racism'' is a noun describing the state of being racist, i.e., subscribing to the belief that the human population can or should be classified into races with differential abilities and dispositions, which in turn may motivate a political ideology in which rights and privileges are differentially distributed based on racial categories. The term "racist" may be an adjective or a noun, the latter describing a person who holds those beliefs.
The origin of the root word "race" is not clear. Linguists generally agree that it came to the English language from
Middle French
Middle French (french: moyen français) is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the 14th to the 16th century. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from t ...
, but there is no such agreement on how it generally came into Latin-based languages. A recent proposal is that it derives from the Arabic ''ra's'', which means "head, beginning, origin" or the
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
''rosh'', which has a similar meaning. Early race theorists generally held the view that some races were inferior to others and they consequently believed that the differential treatment of races was fully justified.
These early theories guided
pseudo-scientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
research assumptions; the collective endeavors to adequately define and form hypotheses about racial differences are generally termed
scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
, though this term is a misnomer, due to the lack of any actual science backing the claims.
Most
biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
s,
anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and v ...
, and
sociologists
This is a list of sociologists. It is intended to cover those who have made substantive contributions to social theory and research, including any sociological subfield. Scientists in other fields and philosophers are not included, unless at least ...
reject a
taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
of races in favor of more specific and/or empirically verifiable criteria, such as
geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
, ethnicity, or a history of
endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships.
Endogamy is common in many cultu ...
.
Human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the n ...
research indicates that race is not a meaningful genetic classification of humans.
An entry in the ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
'' (2008) defines
racialism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies can be more ...
as "
earlier term than racism, but now largely superseded by it", and cites the term "racialism" in a 1902 quote. The revised ''Oxford English Dictionary'' cites the shorter term "racism" in a quote from the year 1903. It was defined by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (2nd edition 1989) as "
e theory that distinctive human characteristics and abilities are determined by race"; the same dictionary termed ''racism'' a
synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
of ''racialism'': "belief in the superiority of a particular race". By the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, ''racism'' had acquired the same supremacist connotations formerly associated with ''racialism'': ''racism'' by then implied racial
discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
, racial
supremacism
Supremacism is the belief that a certain group of people is superior to all others. The supposed superior people can be defined by age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, language, social class, ideology, nation, culture, ...
, and a harmful intent. The term "race hatred" had also been used by sociologist
Frederick Hertz
Frederick Hertz (until 1946 Friedrich (Otto) Hertz, a pseudonym also: Germanus Liber; * 26 March 1878 in Vienna, † 20 November 1964 in London) was a British sociologist, economist and historian of Austrian origin.
Life and work
Hertz attended ...
in the late 1920s.
As its history indicates, the popular use of the word ''racism'' is relatively recent. The word came into widespread usage in the
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania. in the 1930s, when it was used to describe the social and political ideology of
Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
, which treated "race" as a naturally given political unit. It is commonly agreed that racism existed before the coinage of the word, but there is not a wide agreement on a single definition of what racism is and what it is not.
Today, some scholars of racism prefer to use the concept in the plural ''racisms'', in order to emphasize its many different forms that do not easily fall under a single definition. They also argue that different forms of racism have characterized different historical periods and geographical areas.
Garner (2009: p. 11) summarizes different existing definitions of racism and identifies three common elements contained in those definitions of racism. First, a historical, hierarchical
power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
relationship between groups; second, a set of ideas (an ideology) about racial differences; and, third, discriminatory actions (practices).
Legal
Though many countries around the globe have passed
law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
s related to race and discrimination, the first significant international
human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
instrument developed by the United Nations (UN) was the
Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal De ...
(UDHR),
which was adopted by the
United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
in 1948. The UDHR recognizes that if people are to be treated with dignity, they require
economic rights
Economic, social and cultural rights, (ESCR) are socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and culture. Econ ...
,
social rights
Economic, social and cultural rights, (ESCR) are socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and culture. Eco ...
including education, and the rights to
cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
and political participation and
civil liberty
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may ...
. It further states that everyone is entitled to these rights "without distinction of any kind, such as race,
colour
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion,
national
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
or
social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
origin, property, birth or other status".
The UN does not define "racism"; however, it does define "racial discrimination". According to the 1965 UN
,
The term "racial discrimination" shall mean any distinction, exclusion, restriction, or preference based on race, colour, descent
Descent may refer to:
As a noun Genealogy and inheritance
* Common descent, concept in evolutionary biology
* Kinship, one of the major concepts of cultural anthropology
**Pedigree chart or family tree
** Ancestry
** Lineal descendant
**Heritag ...
, or national or ethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
origin that has the purpose or effect of nullifying or impairing the recognition, enjoyment or exercise, on an equal footing, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural or any other field of public life.
In their 1978
United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Declaration on Race and Racial Prejudice (Article 1), the UN states, "All human beings belong to a single species and are descended from a common stock. They are born equal in dignity and rights and all form an integral part of humanity."
The UN definition of racial discrimination does not make any distinction between
discrimination based on ethnicity and race, in part because the distinction between the two has been a matter of debate among
academics
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, ...
, including
anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and v ...
. Similarly, in
British law
The United Kingdom has four legal systems, each of which derives from a particular geographical area for a variety of historical reasons: English and Welsh law, Scots law, Northern Ireland law, and, since 2007, purely Welsh law (as a result of ...
, the phrase ''racial group'' means "any group of people who are defined by reference to their race, colour, nationality (including citizenship) or ethnic or national origin".
In Norway, the word "race" has been removed from national laws concerning discrimination because the use of the phrase is considered problematic and unethical. The Norwegian Anti-Discrimination Act bans discrimination based on ethnicity, national origin, descent, and skin color.
Social and behavioral sciences
Sociologists
This is a list of sociologists. It is intended to cover those who have made substantive contributions to social theory and research, including any sociological subfield. Scientists in other fields and philosophers are not included, unless at least ...
, in general, recognize "race" as a
social construct
Social constructionism is a theory in sociology, social ontology, and communication theory which proposes that certain ideas about reality, physical reality arise from collaborative consensus, instead of pure observation of said reality. The ...
. This means that, although the concepts of race and racism are based on observable biological characteristics, any conclusions drawn about race on the basis of those observations are heavily influenced by cultural ideologies. Racism, as an ideology, exists in a society at both the individual and institutional level.
While much of the research and work on racism during the last half-century or so has concentrated on "white racism" in the Western world, historical accounts of race-based social practices can be found across the globe.
[Gossett, Thomas F. ''Race: The History of an Idea in America''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1997. ] Thus, racism can be broadly defined to encompass individual and group prejudices and acts of discrimination that result in material and cultural advantages conferred on a majority or a dominant social group. So-called "white racism" focuses on societies in which white populations are the majority or the dominant social group. In studies of these majority white societies, the aggregate of material and cultural advantages is usually termed "
white privilege
White privilege, or white skin privilege, is the societal privilege that benefits white people over non-white people in some societies, particularly if they are otherwise under the same social, political, or economic circumstances. With roots ...
".
Race and race relations are prominent areas of study in
sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of Empirical ...
and
economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and intera ...
. Much of the sociological literature focuses on white racism. Some of the earliest sociological works on racism were penned by sociologist
W. E. B. Du Bois, the first African American to earn a doctoral degree from
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
. Du Bois wrote, "
e problem of the twentieth century is the problem of the
color line."
Wellman (1993) defines racism as "culturally sanctioned beliefs, which, regardless of intentions involved, defend the advantages whites have because of the subordinated position of racial minorities".
In both sociology and economics, the outcomes of racist actions are often measured by the
inequality
Inequality may refer to:
Economics
* Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy
* Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups
* ...
in
income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For ...
,
wealth
Wealth is the abundance of Value (economics), valuable financial assets or property, physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for financial transaction, transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the ...
,
net worth
Net worth is the value of all the non-financial and financial assets owned by an individual or institution minus the value of all its outstanding liabilities. Since financial assets minus outstanding liabilities equal net financial assets, net ...
, and access to other cultural resources (such as education), between racial groups.
In sociology and
social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the r ...
,
racial identity
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
and the acquisition of that identity, is often used as a variable in racism studies. Racial ideologies and racial identity affect individuals' perception of race and discrimination. Cazenave and Maddern (1999) define racism as "a highly organized system of 'race'-based group privilege that operates at every level of society and is held together by a sophisticated ideology of color/'race' supremacy. Racial centrality (the extent to which a culture recognizes individuals' racial identity) appears to affect the degree of discrimination African-American young adults perceive whereas racial ideology may buffer the detrimental emotional effects of that discrimination."
Sellers and Shelton (2003) found that a relationship between racial discrimination and emotional distress was moderated by racial ideology and social beliefs.
Some sociologists also argue that, particularly in the West, where racism is often
negatively sanctioned in society, racism has changed from being a blatant to a more covert expression of racial prejudice. The "newer" (more hidden and less easily detectable) forms of racism—which can be considered embedded in social processes and structures—are more difficult to explore and challenge. It has been suggested that, while in many countries overt or explicit racism has become increasingly
taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
, even among those who display egalitarian explicit attitudes, an
implicit
Implicit may refer to:
Mathematics
* Implicit function
* Implicit function theorem
* Implicit curve
* Implicit surface
* Implicit differential equation
Other uses
* Implicit assumption, in logic
* Implicit-association test, in social psychology
...
or
aversive racism
Aversive racism is a theory proposed by Samuel L. Gaertner & John F. Dovidio (1986), according to which negative evaluations of racial/ethnic minorities are realized by a persistent avoidance of interaction with other racial and ethnic groups. As ...
is still maintained subconsciously.
This process has been studied extensively in social psychology as implicit associations and
implicit attitude
Implicit attitudes are evaluations that occur without conscious awareness towards an attitude object or the self. These evaluations are generally either favorable or unfavorable and come about from various influences in the individual experience. T ...
s, a component of
implicit cognition
Implicit cognition refers to unconscious influences such as knowledge, perception, or memory, that influence a person's behavior, even though they themselves have no conscious awareness whatsoever of those influences.
Overview
Implicit cognition i ...
. Implicit attitudes are evaluations that occur without conscious awareness towards an attitude object or the self. These evaluations are generally either favorable or unfavorable. They come about from various influences in the individual experience. Implicit attitudes are not consciously identified (or they are inaccurately identified) traces of past experience that mediate favorable or unfavorable feelings, thoughts, or actions towards social objects.
These feelings, thoughts, or actions have an influence on behavior of which the individual may not be aware.
Therefore, subconscious racism can influence our visual processing and how our minds work when we are subliminally exposed to faces of different colors. In thinking about crime, for example,
social psychologist
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the re ...
Jennifer L. Eberhardt (2004) of
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
holds that, "blackness is so associated with crime you're ready to pick out these crime objects."
Such exposures influence our minds and they can cause subconscious racism in our behavior towards other people or even towards objects. Thus, racist thoughts and actions can arise from stereotypes and fears of which we are not aware.
For example, scientists and activists have warned that the use of the stereotype "Nigerian Prince" for referring to
advance-fee scam
An advance-fee scam is a form of fraud and is one of the most common types of confidence tricks. The scam typically involves promising the victim a significant share of a large sum of money, in return for a small up-front payment, which the frauds ...
mers is racist, i.e. "reducing Nigeria to a nation of scammers and fraudulent princes, as some people still do online, is a
stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example ...
that needs to be called out".
Humanities
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
,
linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
, and
discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. ...
are active areas of study in the
humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at the t ...
, along with literature and the arts.
Discourse analysis
Discourse analysis (DA), or discourse studies, is an approach to the analysis of written, vocal, or sign language use, or any significant semiotic event.
The objects of discourse Analysis ( discourse, writing, conversation, communicative event ...
seeks to reveal the meaning of race and the actions of racists through careful study of the ways in which these factors of human society are described and discussed in various written and oral works. For example, Van Dijk (1992) examines the different ways in which descriptions of racism and racist actions are depicted by the perpetrators of such actions as well as by their victims. He notes that when descriptions of actions have negative implications for the majority, and especially for white elites, they are often seen as controversial and such controversial interpretations are typically marked with quotation marks or they are greeted with expressions of distance or doubt. The previously cited book, ''
The Souls of Black Folk
''The Souls of Black Folk: Essays and Sketches'' is a 1903 work of American literature by W. E. B. Du Bois. It is a seminal work in the history of sociology and a cornerstone of African-American literature.
The book contains several essays on r ...
'' by W.E.B. Du Bois, represents early
African-American literature
African American literature is the body of literature produced in the United States by writers of African descent. It begins with the works of such late 18th-century writers as Phillis Wheatley. Before the high point of slave narratives, African ...
that describes the author's experiences with racism when he was traveling in the
South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
as an African American.
Much American fictional literature has focused on issues of racism and the black "racial experience" in the US, including works written by whites, such as ''
Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U. ...
'', ''
To Kill a Mockingbird
''To Kill a Mockingbird'' is a novel by the American author Harper Lee. It was published in 1960 and was instantly successful. In the United States, it is widely read in high schools and middle schools. ''To Kill a Mockingbird'' has become ...
'', and ''
Imitation of Life'', or even the non-fiction work ''
Black Like Me
''Black Like Me'', first published in 1961, is a nonfiction book by journalist John Howard Griffin recounting his journey in the Deep South of the United States, at a time when African-Americans lived under racial segregation. Griffin was a nat ...
''. These books, and others like them, feed into what has been called the "
white savior narrative in film
The white savior is a cinematic trope in which a white central character rescues non-white (often less prominent) characters from unfortunate circumstances. This recurs in an array of genres in American cinema, wherein a white protagonist is port ...
", in which the heroes and heroines are white even though the story is about things that happen to black characters.
Textual analysis
Content analysis is the study of documents and communication artifacts, which might be texts of various formats, pictures, audio or video. Social scientists use content analysis to examine patterns in communication in a replicable and systematic ...
of such writings can contrast sharply with black authors' descriptions of African Americans and their experiences in US society. African-American writers have sometimes been portrayed in
African-American studies as retreating from racial issues when they write about "
whiteness", while others identify this as an African-American literary tradition called "the literature of white estrangement", part of a multi-pronged effort to challenge and dismantle
white supremacy
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White su ...
in the US.
Popular usage
According to dictionaries, the word is commonly used to describe prejudice and discrimination based on race.
Racism can also be said to describe a condition in society in which a dominant racial group benefits from the
oppression
Oppression is malicious or unjust treatment or exercise of power, often under the guise of governmental authority or cultural opprobrium. Oppression may be overt or covert, depending on how it is practiced. Oppression refers to discrimination w ...
of others, whether that group wants such benefits or not. Foucauldian scholar Ladelle McWhorter, in her 2009 book, ''Racism and Sexual Oppression in Anglo-America: A Genealogy'', posits modern racism similarly, focusing on the notion of a dominant group, usually whites, vying for racial purity and progress, rather than an overt or obvious ideology focused on the oppression of nonwhites.
In popular usage, as in some academic usage, little distinction is made between "racism" and "
ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
". Often, the two are listed together as "racial and ethnic" in describing some action or outcome that is associated with prejudice within a majority or dominant group in society. Furthermore, the meaning of the term racism is often conflated with the terms prejudice,
bigotry
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
, and discrimination. Racism is a complex concept that can involve each of those; but it cannot be equated with, nor is it synonymous, with these other terms.
The term is often used in relation to what is seen as prejudice within a minority or subjugated group, as in the concept of
reverse racism
Reverse racism, sometimes referred to as reverse discrimination, is the concept that affirmative action and similar color-conscious programs for redressing racial inequality are a form of anti-white racism. The concept is often associated wi ...
. "Reverse racism" is a concept often used to describe acts of discrimination or hostility against members of a dominant racial or ethnic group while favoring members of minority groups.
This concept has been used especially in the United States in debates over
color-conscious Color consciousness is a theory stating that equality under the law is insufficient to address racial inequalities in society. It rejects the concept of fundamental racial differences, but holds that physical differences such as skin color can and d ...
policies (such as
affirmative action) intended to remedy racial inequalities. However, many experts and other commenters view reverse racism as a myth rather than a reality. Scholars commonly define racism not only in terms of individual prejudice, but also in terms of a power structure that protects the interests of the dominant culture and actively discriminates against ethnic minorities. From this perspective, while members of ethnic minorities may be prejudiced against members of the dominant culture, they lack the political and economic power to actively oppress them, and they are therefore not practicing "racism".
Aspects
The ideology underlying racism can manifest in many aspects of social life. Such aspects are described in this section, although the list is not exhaustive.
Aversive racism
Aversive racism is a form of implicit racism, in which a person's unconscious negative evaluations of racial or ethnic minorities are realized by a persistent avoidance of interaction with other racial and ethnic groups. As opposed to traditional, overt racism, which is characterized by overt hatred for and explicit discrimination against racial/ethnic minorities, aversive racism is characterized by more complex,
ambivalent expressions and attitudes.
Aversive racism is similar in implications to the concept of symbolic or modern racism (described below), which is also a form of implicit, unconscious, or covert attitude which results in unconscious forms of discrimination.
The term was coined by Joel Kovel to describe the subtle racial behaviors of any ethnic or racial group who rationalize their aversion to a particular group by appeal to rules or stereotypes.
People who behave in an aversively racial way may profess egalitarian beliefs, and will often deny their racially motivated behavior; nevertheless they change their behavior when dealing with a member of another race or ethnic group than the one they belong to. The motivation for the change is thought to be implicit or subconscious. Experiments have provided empirical support for the existence of aversive racism. Aversive racism has been shown to have potentially serious implications for decision making in employment, in legal decisions and in helping behavior.
Color blindness
In relation to racism, color blindness is the disregard of racial characteristics in
social interaction
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
, for example in the rejection of affirmative action, as a way to address the results of past patterns of discrimination. Critics of this attitude argue that by refusing to attend to racial disparities, racial color blindness in fact unconsciously perpetuates the patterns that produce racial inequality.
Eduardo Bonilla-Silva
Eduardo Bonilla-Silva (born February 6, 1962) is an American sociologist and professor of sociology at Duke University. He was the 2018 president of the American Sociological Association.
Early influences
Bonilla-Silva was educated in Puert ...
argues that color blind racism arises from an "abstract
liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostility to autocracy, cultural distaste for c ...
, biologization of culture, naturalization of racial matters, and minimization of racism".
Color blind practices are "subtle,
institution
Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions a ...
al, and apparently nonracial"
because race is explicitly ignored in decision-making. If race is disregarded in predominantly white populations, for example, whiteness becomes the
normative
Normative generally means relating to an evaluative standard. Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A norm in ...
standard, whereas
people of color
The term "person of color" ( : people of color or persons of color; abbreviated POC) is primarily used to describe any person who is not considered "white". In its current meaning, the term originated in, and is primarily associated with, the U ...
are
othered, and the racism these individuals experience may be minimized or erased.
At an individual level, people with "color blind prejudice" reject racist ideology, but also reject systemic policies intended to fix
institutional racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, health ...
.
Cultural
Cultural racism manifests as societal beliefs and customs that promote the assumption that the products of a given culture, including the language and traditions of that culture, are superior to those of other cultures. It shares a great deal with
xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
, which is often characterized by fear of, or aggression toward, members of an
outgroup by members of an
ingroup
In sociology and social psychology, an in-group is a social group to which a person self-categorization theory, psychologically identifies as being a member. By contrast, an out-group is a social group with which an individual does not identify. ...
.
In that sense it is also similar to
communalism
Communalism may refer to:
* Communalism (Bookchin), a theory of government in which autonomous communities form confederations
* , a historical method that follows the development of communities
* Communalism (South Asia), violence across ethnic ...
as used in South Asia.
Cultural racism exists when there is a widespread acceptance of stereotypes concerning diverse ethnic or population groups. Whereas racism can be characterised by the belief that one race is inherently superior to another, cultural racism can be characterised by the belief that one culture is inherently superior to another.
Economic
Historical economic or social disparity is alleged to be a form of
discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
caused by past racism and historical reasons, affecting the present generation through deficits in the formal education and kinds of preparation in previous generations, and through primarily unconscious racist attitudes and actions on members of the general population.
Economic discrimination
Economic discrimination is discrimination based on economic factors. These factors can include job availability, wages, the prices and/or availability of goods and services, and the amount of capital investment funding available to minorities for ...
may lead to choices that perpetuate racism. For example, color photographic film was tuned for white skin as are automatic soap dispensers and
facial recognition system
A facial recognition system is a technology capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and wo ...
s.
In 2011,
Bank of America
The Bank of America Corporation (often abbreviated BofA or BoA) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in Charlotte, North Carolina. The bank w ...
agreed to pay $335 million to settle a federal government claim that its mortgage division, Countrywide Financial,
discriminated against black and Hispanic homebuyers.
Institutional

Institutional racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, health ...
(also known as
structural racism
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
,
state racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, healt ...
or systemic racism) is racial discrimination by governments, corporations, religions, or educational institutions or other large organizations with the power to influence the lives of many individuals.
Stokely Carmichael
Kwame Ture (; born Stokely Standiford Churchill Carmichael; June 29, 1941November 15, 1998) was a prominent organizer in the civil rights movement in the United States and the global pan-African movement. Born in Trinidad, he grew up in the Unite ...
is credited for coining the phrase ''institutional racism'' in the late 1960s. He defined the term as "the collective failure of an organization to provide an appropriate and professional service to people because of their colour, culture or ethnic origin".
Maulana Karenga
Maulana Ndabezitha Karenga (born Ronald McKinley Everett, July 14, 1941), previously known as Ron Karenga, is an American activist, author, and professor of Africana studies, best known as the creator of the pan-African and African-American holi ...
argued that racism constituted the destruction of culture, language, religion, and human possibility and that the effects of racism were "the morally monstrous destruction of human possibility involved redefining African humanity to the world, poisoning past, present and future relations with others who only know us through this stereotyping and thus damaging the truly human relations among peoples".
Othering
Othering is the term used by some to describe a system of discrimination whereby the characteristics of a group are used to distinguish them as separate from the norm.
Othering plays a fundamental role in the history and continuation of racism. To
objectify
In social philosophy, objectification is the act of treating a person, as an object or a thing. It is part of dehumanization, the act of disavowing the humanity of others. Sexual objectification, the act of treating a person as a mere object of sex ...
a culture as something different, exotic or underdeveloped is to generalize that it is not like 'normal' society. Europe's colonial attitude towards the Orientals exemplifies this as it was thought that the East was the opposite of the West; feminine where the West was masculine, weak where the West was strong and traditional where the West was progressive.
[Said, Edward. (1978) ''Orientalism''. New York: Pantheon Books. p. 357] By making these generalizations and othering the East, Europe was simultaneously defining herself as the norm, further entrenching the gap.
Much of the process of othering relies on imagined difference, or the expectation of difference. Spatial difference can be enough to conclude that "we" are "here" and the "others" are over "there".
Imagined differences serve to categorize people into groups and assign them characteristics that suit the imaginer's expectations.
Racial discrimination
Racial discrimination refers to
discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
against someone on the basis of their race.
Racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of humans into
socially-constructed racial groups in daily life. It may apply to activities such as eating in a restaurant, drinking from a water fountain, using a bathroom, attending school, going to the movies, or in the rental or purchase of a home. Segregation is generally outlawed, but may exist through social norms, even when there is no strong individual preference for it, as suggested by
Thomas Schelling
Thomas Crombie Schelling (April 14, 1921 – December 13, 2016) was an American economist and professor of foreign policy, national security, nuclear strategy, and arms control at the School of Public Policy at University of Maryland, College ...
's models of segregation and subsequent work.
Supremacism

Centuries of
European colonialism
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turkish people, Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the mode ...
in the Americas, Africa and Asia were often justified by
white supremacist
White supremacy or white supremacism is the belief that white people are superior to those of other Race (human classification), races and thus should dominate them. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any Power (social and polit ...
attitudes. During the early 20th century, the phrase "
The White Man's Burden
"The White Man's Burden" (1899), by Rudyard Kipling, is a poem about the Philippine–American War (1899–1902) that exhorts the United States to assume colonial control of the Filipino people and their country.Hitchens, Christopher. ''Bloo ...
" was widely used to justify an
imperialist
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
policy as a noble enterprise. A justification for the policy of conquest and subjugation of
Native Americans emanated from the stereotyped perceptions of the indigenous people as "merciless Indian savages", as they are described in the
United States Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House ...
. Sam Wolfson of ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' writes that "the declaration's passage has often been cited as an encapsulation of the
dehumanizing attitude toward indigenous Americans that the US was founded on." In an 1890 article about colonial expansion onto Native American land, author
L. Frank Baum
Lyman Frank Baum (; May 15, 1856 – May 6, 1919) was an American author best known for his children's books, particularly ''The Wonderful Wizard of Oz'' and its sequels. He wrote 14 novels in the ''Oz'' series, plus 41 other novels (not includ ...
wrote: "The Whites, by law of conquest, by justice of civilization, are masters of the American continent, and the best safety of the frontier settlements will be secured by the total annihilation of the few remaining Indians." In his ''
Notes on the State of Virginia
''Notes on the State of Virginia'' (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jeffers ...
'', published in 1785,
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
wrote: "blacks, whether originally a distinct race, or made distinct by time or circumstances, are inferior to the whites in the endowments of both body and mind." Attitudes of
black supremacy,
Arab supremacy
Racism in the Arab world covers an array of forms of intolerance against non-Arabs and the expat majority of the Arab states of the Persian Gulf coming from ( Sri Lanka, Pakistan, India and Bangladesh) groups as well as Black, European, and Asian ...
, and
East Asian supremacy also exist.
Symbolic/modern

Some scholars argue that in the US, earlier violent and aggressive forms of racism have evolved into a more subtle form of prejudice in the late 20th century. This new form of racism is sometimes referred to as "modern racism" and it is characterized by outwardly acting unprejudiced while inwardly maintaining prejudiced attitudes, displaying subtle prejudiced behaviors such as actions informed by attributing qualities to others based on racial stereotypes, and evaluating the same behavior differently based on the race of the person being evaluated. This view is based on studies of prejudice and discriminatory behavior, where some people will act ambivalently towards black people, with positive reactions in certain, more public contexts, but more negative views and expressions in more private contexts. This ambivalence may also be visible for example in hiring decisions where job candidates that are otherwise positively evaluated may be unconsciously disfavored by employers in the final decision because of their race. Some scholars consider modern racism to be characterized by an explicit rejection of stereotypes, combined with resistance to changing structures of discrimination for reasons that are ostensibly non-racial, an ideology that considers opportunity at a purely individual basis denying the relevance of race in determining individual opportunities and the exhibition of indirect forms of micro-aggression toward and/or avoidance of people of other races.
Subconscious biases
Recent research has shown that individuals who consciously claim to reject racism may still exhibit race-based subconscious biases in their decision-making processes. While such "subconscious racial biases" do not fully fit the definition of racism, their impact can be similar, though typically less pronounced, not being explicit, conscious or deliberate.
International law and racial discrimination
In 1919, a
proposal
Proposal(s) or The Proposal may refer to:
* Proposal (business)
* Research proposal
* Proposal (marriage)
* Proposition, a proposal in logic and philosophy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* The Proposal (album), ''The Proposal'' (album)
Films
...
to include a racial equality provision in the
Covenant of the League of Nations
The Covenant of the League of Nations was the charter of the League of Nations. It was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920.
Creation
Early d ...
was supported by a majority, but not adopted in the
Paris Peace Conference in 1919. In 1943, Japan and its allies declared work for the abolition of racial discrimination to be their aim at the
Greater East Asia Conference
was an international summit held in Tokyo from 5 to 6 November 1943, in which the Empire of Japan hosted leading politicians of various component members of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. The event was also referred to as the Tokyo ...
. Article 1 of the 1945
UN Charter
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the ...
includes "promoting and encouraging respect for human rights and for fundamental freedoms for all without distinction as to race" as UN purpose.
In 1950,
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
suggested in ''
The Race Question
The Race Question is the first of four UNESCO statements about issues of race. It was issued on 18 July 1950 following World War II and Nazi racism to clarify what was scientifically known about race, and as a moral condemnation of racism.< ...
''—a statement signed by 21 scholars such as
Ashley Montagu
Montague Francis Ashley-Montagu (June 28, 1905November 26, 1999) — born Israel Ehrenberg — was a British-American anthropologist who popularized the study of topics such as race and gender and their relation to politics and development. He ...
,
Claude Lévi-Strauss
Claude Lévi-Strauss (, ; 28 November 1908 – 30 October 2009) was a French anthropologist and ethnologist whose work was key in the development of the theories of structuralism and structural anthropology. He held the chair of Social Anthro ...
,
Gunnar Myrdal
Karl Gunnar Myrdal ( ; ; 6 December 1898 – 17 May 1987) was a Swedish economist and sociologist. In 1974, he received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences along with Friedrich Hayek for "their pioneering work in the theory of money a ...
,
Julian Huxley
Sir Julian Sorell Huxley (22 June 1887 – 14 February 1975) was an English evolutionary biologist, eugenicist, and internationalist. He was a proponent of natural selection, and a leading figure in the mid-twentieth century modern synthesis. ...
, etc.—to "drop the term ''race'' altogether and instead speak of
ethnic groups
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
". The statement condemned
scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
theories that had played a role in
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. It aimed both at debunking scientific racist theories, by popularizing modern knowledge concerning "the race question", and morally condemned racism as contrary to the philosophy of the
Enlightenment and its assumption of
equal rights for all. Along with Myrdal's ''
An American Dilemma: The Negro Problem and Modern Democracy'' (1944), ''The Race Question'' influenced the 1954 U.S. Supreme Court
desegregation
Desegregation is the process of ending the separation of two groups, usually referring to races. Desegregation is typically measured by the index of dissimilarity, allowing researchers to determine whether desegregation efforts are having impact o ...
decision in ''
Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision by the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segrega ...
''.
["Toward a World without Evil: Alfred Métraux as UNESCO Anthropologist (1946–1962)"](_blank)
by Harald E.L. Prins, UNESCO Also, in 1950, the
European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by t ...
was adopted, which was widely used on racial discrimination issues.
The United Nations use the definition of racial discrimination laid out in the ''
'', adopted in 1966:
... any distinction, exclusion, restriction or preference based on race, color, descent, or national or ethnic origin that has the purpose or effect of nullifying or impairing the recognition, enjoyment or exercise, on an equal footing, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural or any other field of public life. (Part 1 of Article 1 of the U.N. International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination)
In 2001, the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
explicitly banned racism, along with many other forms of social discrimination, in the
Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union
The Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (CFR) enshrines certain political, social, and economic rights for European Union (EU) citizens and residents into EU law. It was drafted by the European Convention and solemnly proclaim ...
, the legal effect of which, if any, would necessarily be limited to
Institutions of the European Union
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and the Euratom. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty on European Union:
* the European Parliament,
* the European Counci ...
: "Article 21 of the charter prohibits discrimination on any ground such as race, color, ethnic or social origin, genetic features, language, religion or belief, political or any other opinion, membership of a national minority, property, disability, age or sexual orientation and also discrimination on the grounds of nationality."
Ideology

Racism existed during the 19th century as "
scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
", which attempted to provide a
racial classification
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of variou ...
of humanity. In 1775
Johann Blumenbach
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840) was a German physician, naturalist, physiologist, and anthropologist. He is considered to be a main founder of zoology and anthropology as comparative, scientific disciplines. He wa ...
divided the world's population into five groups according to skin color (Caucasians, Mongols, etc.), positing the view that the non-Caucasians had arisen through a process of degeneration. Another early view in scientific racism was the
polygenist view, which held that the different races had been separately created. Polygenist
Christoph Meiners
Christoph Meiners (31 July 1747 – 1 May 1810) was a German racialist, philosopher, historian, and writer born in Warstade. He supported the polygenist theory of human origins. He was a member of the Göttingen School of History.
Biogra ...
for example, split mankind into two divisions which he labeled the "beautiful White race" and the "ugly Black race". In Meiners' book, ''The Outline of History of Mankind'', he claimed that a main characteristic of race is either beauty or ugliness. He viewed only the white race as beautiful. He considered ugly races to be inferior, immoral and animal-like.
Anders Retzius
Anders Adolph Retzius (13 October 1796 – 18 April 1860), was a Swedish professor of anatomy and a supervisor at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Biography
Retzius was born in Lund, Sweden, in 1796. He enrolled at Lund University in 18 ...
demonstrated that neither Europeans nor others are one "pure race", but of mixed origins. While
discredited, derivations of Blumenbach's taxonomy are
still widely used for the classification of the population in the United States.
Hans Peder Steensby
Hans Peder Steensby (25 March 1875, Steensby, Skamby Sogn, Funen Island – 20 October 1920, aboard ship Frederik VIII) was an ethnographer, geographer and professor at the University of Copenhagen.H. P. Steensby: Racestudier i Danmark' (PDF; 1,22 ...
, while strongly emphasizing that all humans today are of mixed origins, in 1907 claimed that the origins of human differences must be traced extraordinarily far back in time, and conjectured that the "purest race" today would be the
Australian Aboriginals
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the T ...
.

Scientific racism fell strongly out of favor in the early 20th century, but the origins of fundamental human and societal differences are still researched within
academia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
, in fields such as
human genetics
Human genetics is the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings. Human genetics encompasses a variety of overlapping fields including: classical genetics, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, population gene ...
including
paleogenetics Paleogenetics is the study of the past through the examination of preserved genetic material from the remains of ancient organisms. Emile Zuckerkandl and Linus Pauling introduced the term in 1963, long before the sequencing of DNA, in reference t ...
,
social anthropology
Social anthropology is the study of patterns of behaviour in human societies and cultures. It is the dominant constituent of anthropology throughout the United Kingdom and much of Europe, where it is distinguished from cultural anthropology. In t ...
,
comparative politics
Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the ''comparative method'' or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relatin ...
,
history of religions
The history of religion refers to the written record of human religious feelings, thoughts, and ideas. This period of religious history begins with the invention of writing about 5,200 years ago (3200 BC). The prehistory of religion involves th ...
,
history of ideas
Intellectual history (also the history of ideas) is the study of the history of human thought and of intellectuals, people who conceptualize, discuss, write about, and concern themselves with ideas. The investigative premise of intellectual histor ...
,
prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
,
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
,
ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns m ...
, and
psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry.
Initial psych ...
. There is widespread rejection of any methodology based on anything similar to Blumenbach's races. It is more unclear to which extent and when
ethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
and national
stereotypes
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example ...
are accepted.
Although after
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
, racist ideologies were discredited on ethical, political and scientific grounds, racism and
racial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
have remained widespread around the world.
Du Bois observed that it is not so much "race" that we think about, but culture: "... a common history, common laws and religion, similar habits of thought and a conscious striving together for certain ideals of life". Late 19th century nationalists were the first to embrace contemporary discourses on "race", ethnicity, and "
survival of the fittest
"Survival of the fittest" is a phrase that originated from Darwinian evolutionary theory as a way of describing the mechanism of natural selection. The biological concept of fitness is defined as reproductive success. In Darwinian terms, th ...
" to shape new nationalist doctrines. Ultimately, race came to represent not only the most important traits of the human body, but was also regarded as decisively shaping the character and personality of the nation. According to this view, culture is the physical manifestation created by ethnic groupings, as such fully determined by racial characteristics. Culture and race became considered intertwined and dependent upon each other, sometimes even to the extent of including nationality or language to the set of definition. Pureness of race tended to be related to rather superficial characteristics that were easily addressed and advertised, such as blondness. Racial qualities tended to be related to nationality and language rather than the actual geographic distribution of racial characteristics. In the case of
Nordicism
Nordicism is an ideology of racism which views the historical race concept of the "Nordic race" as an endangered and superior racial group. Some notable and seminal Nordicist works include Madison Grant's book ''The Passing of the Great Race'' ...
, the denomination "
Germanic" was equivalent to superiority of race.
Bolstered by some
nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
and
ethnocentric
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
values and achievements of choice, this concept of racial superiority evolved to distinguish from other cultures that were considered inferior or impure. This emphasis on culture corresponds to the modern mainstream definition of racism: "
cism does not originate from the existence of 'races'. It ''creates'' them through a process of social division into categories: anybody can be racialised, independently of their somatic, cultural, religious differences."
This definition explicitly ignores the biological concept of race, which is still subject to scientific debate. In the words of
David C. Rowe
David C. Rowe (27 September 1949 – 2 February 2003) was an American psychology professor known for his work studying genetic and environmental influences on adolescent onset behaviors such as delinquency and smoking.J. L. Rodgers, K. Jacobs ...
, "
racial concept, although sometimes in the guise of another name, will remain in use in biology and in other fields because scientists, as well as lay persons, are fascinated by human diversity, some of which is captured by race."
Racial prejudice became subject to international legislation. For instance, the
, adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on November 20, 1963, addresses racial prejudice explicitly next to discrimination for reasons of race, colour or ethnic origin (Article I).
Ethnicity and ethnic conflicts

Debates over the origins of racism often suffer from a lack of clarity over the term. Many use the term "racism" to refer to more general phenomena, such as
xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
and
ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
, although scholars attempt to clearly distinguish those phenomena from racism as an
ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
or from scientific racism, which has little to do with ordinary xenophobia. Others conflate recent forms of racism with earlier forms of ethnic and national conflict. In most cases, ethno-national conflict seems to owe itself to conflict over land and strategic resources. In some cases,
ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
and
nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
were harnessed in order to rally
combatant
Combatant is the legal status of an individual who has the right to engage in hostilities during an armed conflict. The legal definition of "combatant" is found at article 43(2) of Additional Protocol I (AP1) to the Geneva Conventions of 1949. It ...
s in wars between great religious empires (for example, the Muslim Turks and the Catholic Austro-Hungarians).
Notions of race and racism have often played central roles in
ethnic conflict
An ethnic conflict is a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups. While the source of the conflict may be political, social, economic or religious, the individuals in conflict must expressly fight for their ethnic group's positi ...
s. Throughout history, when an adversary is identified as "other" based on notions of race or ethnicity (in particular when "other" is interpreted to mean "inferior"), the means employed by the self-presumed "superior" party to appropriate territory, human chattel, or material wealth often have been more ruthless, more brutal, and less constrained by
moral
A moral (from Latin ''morālis'') is a message that is conveyed or a lesson to be learned from a story or event. The moral may be left to the hearer, reader, or viewer to determine for themselves, or may be explicitly encapsulated in a maxim. A ...
or
ethical
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns ma ...
considerations. According to historian Daniel Richter,
Pontiac's Rebellion
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
saw the emergence on both sides of the conflict of "the novel idea that all Native people were 'Indians,' that all Euro-Americans were 'Whites,' and that all on one side must unite to destroy the other".
Basil Davidson
Basil Risbridger Davidson (9 November 1914 – 9 July 2010) was a British journalist and historian who wrote more than 30 books on African history and politics. According to two modern writers, "Davidson, a campaigning journalist whose fir ...
states in his documentary, ''Africa: Different but Equal'', that racism, in fact, only just recently surfaced as late as the 19th century, due to the need for a justification for slavery in the Americas.
Historically, racism was a major driving force behind the
Transatlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
. It was also a major force behind
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
, especially in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, and South Africa under
apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
; 19th and 20th century racism in the
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania. is particularly well documented and constitutes a reference point in studies and discourses about racism.
Racism has played a role in
genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
s such as the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
, and the
Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
, and colonial projects like the European
colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although Norse colonization of North America, the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizin ...
,
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have been—and are—often subject to racist attitudes. Practices and ideologies of racism are condemned by the United Nations in the
Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, i ...
.
Ethnic and racial nationalism

After the
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, Europe was confronted with the new "
nationalities
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction over the person and affords the person the protection of the ...
question", leading to reconfigurations of the European map, on which the frontiers between the states had been delineated during the 1648
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
.
Nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
had made its first appearance with the invention of the ''
levée en masse
''Levée en masse'' ( or, in English, "mass levy") is a French term used for a policy of mass national conscription, often in the face of invasion.
The concept originated during the French Revolutionary Wars, particularly for the period followi ...
'' by the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
aries, thus inventing mass
conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
in order to be able to defend the newly founded
Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
against the ''
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
'' order represented by the European monarchies. This led to the
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
(1792–1802) and then to the conquests of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, and to the subsequent European-wide debates on the concepts and realities of
nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by those ...
s, and in particular of
nation-state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
s. The
Westphalia Treaty
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
had divided Europe into various empires and kingdoms (such as the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, the
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
, the
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
, etc.), and for centuries wars were waged between princes (''
Kabinettskriege
Cabinet wars, derived from the German expression ''Kabinettskriege'' (, singular ''Kabinettskrieg''), were the type of wars which affected Europe during the period of absolute monarchies, from the 1648 Peace of Westphalia to the 1789 French Revolu ...
'' in German).
Modern
nation-state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
s appeared in the wake of the French Revolution, with the formation of
patriotic
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to one's country. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings, language relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or histor ...
sentiments for the first time in
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
during the
Peninsula War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, ...
(1808–1813, known in Spain as the Independence War). Despite the restoration of the previous order with the 1815
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
, the "nationalities question" became the main problem of Europe during the
Industrial Era
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, leading in particular to the
1848 Revolutions
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in Europe ...
, the
Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
completed during the 1871
Franco-Prussian War, which itself culminated in the proclamation of the
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in the Hall of Mirrors in the
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
, thus achieving the
German unification
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
.
Meanwhile, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the "
sick man of Europe
"Sick man of Europe" is a label given to a nation which is located in some part of Europe and experiencing a time of economic difficulty or impoverishment.
Emperor Nicholas I of the Russian Empire is considered to be the first to use the term " ...
", was confronted with endless nationalist movements, which, along with the dissolving of the
Austrian-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1 ...
, would lead to the creation, after
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, of the various nation-states of the
Balkan
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
s, with "national
minorities" in their borders.
Ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politi ...
, which advocated the belief in a hereditary membership of the nation, made its appearance in the historical context surrounding the creation of the modern nation-states.
One of its main influences was the
Romantic nationalist
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
movement at the turn of the 19th century, represented by figures such as
Johann Herder
Johann Gottfried von Herder ( , ; 25 August 174418 December 1803) was a German philosopher, theologian, poet, and literary critic. He is associated with the Enlightenment, ''Sturm und Drang'', and Weimar Classicism.
Biography
Born in Mohrun ...
(1744–1803),
Johan Fichte (1762–1814) in the ''Addresses to the German Nation'' (1808),
Friedrich Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends ...
(1770–1831), or also, in France,
Jules Michelet
Jules Michelet (; 21 August 1798 – 9 February 1874) was a French historian and an author on other topics whose major work was a history of France and its culture. His aphoristic style emphasized his anti-clerical republicanism.
In Michelet's ...
(1798–1874). It was opposed to
liberal nationalism
Civic nationalism, also known as liberal nationalism, is a form of nationalism identified by political philosophers who believe in an inclusive form of nationalism that adheres to traditional liberal values of freedom, tolerance, equality, in ...
, represented by authors such as
Ernest Renan
Joseph Ernest Renan (; 27 February 18232 October 1892) was a French Orientalist and Semitic scholar, expert of Semitic languages and civilizations, historian of religion, philologist, philosopher, biblical scholar, and critic. He wrote influe ...
(1823–1892), who conceived of the nation as a community, which, instead of being based on the ''
Volk
The German noun ''Volk'' () translates to people,
both uncountable in the sense of ''people'' as in a crowd, and countable (plural ''Völker'') in the sense of '' a people'' as in an ethnic group or nation (compare the English term ''folk'') ...
'' ethnic group and on a specific, common language, was founded on the subjective will to live together ("the nation is a daily
plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
", 1882) or also
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
(1806–1873).
Ethnic nationalism blended with scientific racist discourses, as well as with "continental
imperialist
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
" (
Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, 1951
Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, ''The Origins of Totalitarianism
''The Origins of Totalitarianism'', published in 1951, was Hannah Arendt's first major work, wherein she describes and analyzes Nazism and Stalinism as the major totalitarian political movements of the first half of the 20th century.
History
...
'' (1951)) discourses, for example in the
pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism (german: Pangermanismus or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify all the German-speaking people – and possibly also Germanic-speaking ...
discourses, which postulated the racial superiority of the German ''
Volk
The German noun ''Volk'' () translates to people,
both uncountable in the sense of ''people'' as in a crowd, and countable (plural ''Völker'') in the sense of '' a people'' as in an ethnic group or nation (compare the English term ''folk'') ...
'' (people/folk). The
Pan-German League (''Alldeutscher Verband''), created in 1891, promoted
German imperialism and "
racial hygiene
The term racial hygiene was used to describe an approach to eugenics in the early 20th century, which found its most extensive implementation in Nazi Germany (Nazi eugenics). It was marked by efforts to avoid miscegenation, analogous to an animal ...
", and was opposed to intermarriage with
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
. Another popular current, the ''
Völkisch movement
The ''Völkisch'' movement (german: Völkische Bewegung; alternative en, Folkist Movement) was a German ethno-nationalist movement active from the late 19th century through to the Nazi era, with remnants in the Federal Republic of Germany af ...
'', was also an important proponent of the German ethnic nationalist discourse, and it combined Pan-Germanism with modern
racial antisemitism
Racial antisemitism is prejudice against Jews based on a belief or assertion that Jews constitute a distinct race that has inherent traits or characteristics that appear in some way abhorrent or inherently inferior or otherwise different from ...
. Members of the Völkisch movement, in particular the
Thule Society
The Thule Society (; german: Thule-Gesellschaft), originally the ''Studiengruppe für germanisches Altertum'' ("Study Group for Germanic Antiquity"), was a German occultist and '' Völkisch'' group founded in Munich shortly after World War I, ...
, would participate in the founding of the
German Workers' Party
The German Workers' Party (german: Deutsche Arbeiterpartei, DAP) was a short-lived far-right political party established in Weimar Germany after World War I. It was the precursor of the Nazi Party, which was officially known as the National Soci ...
(DAP) in Munich in 1918, the predecessor of the
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that crea ...
. Pan-Germanism played a decisive role in the
interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the World War I, First World War to the beginning of the World War II, Second World War. The in ...
of the 1920s–1930s.
These currents began to associate the idea of the nation with the biological concept of a "
master race
The master race (german: Herrenrasse) is a Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific concept in Nazism, Nazi ideology in which the putative "Aryan race" is deemed the pinnacle of Race (classification of human beings), human racial hierarchy. Members wer ...
" (often the "
Aryan race
The Aryan race is an obsolete historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people of Proto-Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern I ...
" or the "
Nordic race
The Nordic race was a racial concept which originated in 19th century anthropology. It was considered a race or one of the putative sub-races into which some late-19th to mid-20th century anthropologists divided the Caucasian race, claiming th ...
") issued from the scientific racist discourse. They conflated nationalities with ethnic groups, called "races", in a radical distinction from previous racial discourses that posited the existence of a "race struggle" inside the nation and the state itself. Furthermore, they believed that political boundaries should mirror these alleged racial and ethnic groups, thus justifying
ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
, in order to achieve "racial purity" and also to achieve ethnic homogeneity in the nation-state.
Such racist discourses, combined with nationalism, were not, however, limited to pan-Germanism. In France, the transition from Republican liberal nationalism, to ethnic nationalism, which made nationalism a characteristic of
far-right movements in France, took place during the
Dreyfus Affair
The Dreyfus affair (french: affaire Dreyfus, ) was a political scandal that divided the French Third Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. "L'Affaire", as it is known in French, has come to symbolise modern injustice in the Francop ...
at the end of the 19th century. During several years, a nationwide crisis affected French society, concerning the alleged treason of
Alfred Dreyfus
Alfred Dreyfus ( , also , ; 9 October 1859 – 12 July 1935) was a French artillery officer of Jewish ancestry whose trial and conviction in 1894 on charges of treason became one of the most polarizing political dramas in modern French history. ...
, a French Jewish military officer. The country polarized itself into two opposite camps, one represented by
Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
, who wrote ''
J'Accuse…!
"''J'Accuse...!''" (; "I Accuse...!") is an open letter that was published on 13 January 1898 in the newspaper ''L'Aurore'' by Émile Zola in response to the Dreyfus affair. Zola addressed President of France Félix Faure and accused his Govern ...
'' in defense of Alfred Dreyfus, and the other represented by the nationalist poet,
Maurice Barrès
Auguste-Maurice Barrès (; 19 August 1862 – 4 December 1923) was a French novelist, journalist and politician. Spending some time in Italy, he became a figure in French literature with the release of his work ''The Cult of the Self'' in 1888. ...
(1862–1923), one of the founders of the ethnic nationalist discourse in France. At the same time,
Charles Maurras
Charles-Marie-Photius Maurras (; ; 20 April 1868 – 16 November 1952) was a French author, politician, poet, and critic. He was an organizer and principal philosopher of ''Action Française'', a political movement that is monarchist, anti-parl ...
(1868–1952), founder of the monarchist ''
Action française
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 f ...
'' movement, theorized the "anti-France", composed of the "four confederate states of Protestants, Jews, Freemasons and foreigners" (his actual word for the latter being the pejorative ''
métèques''). Indeed, to him the first three were all "internal foreigners", who threatened the ethnic unity of the
French people
The French people (french: Français) are an ethnic group and nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common French culture, history, and language, identified with the country of France.
The French people, especially the nati ...
.
History
Ethnocentrism and proto-racism

Aristotle
Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, (31 May 1916 – 19 May 2018) was a British American historian specialized in Oriental studies. He was also known as a public intellectual and political commentator. Lewis was the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near E ...
has cited the
Greek philosopher
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
who, in his discussion of slavery, stated that while Greeks are free by nature, "
barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by som ...
s" (non-Greeks) are slaves by nature, in that it is in their nature to be more willing to submit to a
despotic
Despotism ( el, Δεσποτισμός, ''despotismós'') is a form of government in which a single entity rules with absolute power. Normally, that entity is an individual, the despot; but (as in an autocracy) societies which limit respect an ...
government.
Though Aristotle does not specify any particular races, he argues that people from nations outside Greece are more prone to the burden of slavery than those from
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. While Aristotle makes remarks about the most natural slaves being those with strong bodies and slave souls (unfit for rule, unintelligent) which would seem to imply a physical basis for discrimination, he also explicitly states that the right kind of souls and bodies do not always go together, implying that the greatest determinate for inferiority and natural slaves versus natural masters is the soul, not the body. This proto-racism is seen as an important precursor to modern racism by classicist
Benjamin Isaac
Benjamin Henri Isaac (Ben Isaac; he, בנימין איזק; born May 10, 1945) is the Fred and Helen Lessing Professor of Ancient History Emeritus at Tel Aviv University. He is a member of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities and of the A ...
.
Such proto-racism and ethnocentrism must be looked at within context, because a modern understanding of racism based on hereditary inferiority (with modern racism based on
eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or ...
and scientific racism) was not yet developed and it is unclear whether Aristotle believed the natural inferiority of Barbarians was caused by environment and climate (like many of his contemporaries) or by birth.
Historian Dante A. Puzzo, in his discussion of Aristotle, racism, and the ancient world writes that:
Racism rests on two basic assumptions: that a correlation exists between physical characteristics and moral qualities; that mankind is divisible into superior and inferior stocks. Racism, thus defined, is a modern conception, for prior to the XVIth century there was virtually nothing in the life and thought of the West that can be described as racist. To prevent misunderstanding a clear distinction must be made between racism and ethnocentrism
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
... The Ancient Hebrews
The terms ''Hebrews'' (Hebrew: / , Modern: ' / ', Tiberian: ' / '; ISO 259-3: ' / ') and ''Hebrew people'' are mostly considered synonymous with the Semitic-speaking Israelites, especially in the pre-monarchic period when they were still no ...
, in referring to all who were not Hebrews as Gentile
Gentile () is a word that usually means "someone who is not a Jew". Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, sometimes use the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is generally used as a synonym for ...
s, were indulging in ethnocentrism, not in racism. ... So it was with the Hellenes
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other ...
who denominated all non-Hellenes—whether the wild Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
or the Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
whom they acknowledged as their mentors in the arts of civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Ci ...
—Barbarians, the term denoting that which was strange or foreign.
Medieval Arab writers
Bernard Lewis has also cited historians and geographers of the
Middle East and North Africa
MENA, an acronym in the English language, refers to a grouping of countries situated in and around the Middle East and North Africa. It is also known as WANA, SWANA, or NAWA, which alternatively refers to the Middle East as Western Asia (or a ...
region,
including
Al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
,
Al-Jahiz
Abū ʿUthman ʿAmr ibn Baḥr al-Kinānī al-Baṣrī ( ar, أبو عثمان عمرو بن بحر الكناني البصري), commonly known as al-Jāḥiẓ ( ar, links=no, الجاحظ, ''The Bug Eyed'', born 776 – died December 868/Jan ...
,
Al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
,
Abu Rayhan Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
,
Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Muhammad ibn Muhammad ibn al-Hasan al-Tūsī ( fa, محمد ابن محمد ابن حسن طوسی 18 February 1201 – 26 June 1274), better known as Nasir al-Din al-Tusi ( fa, نصیر الدین طوسی, links=no; or simply Tusi in the West ...
, and
Ibn Qutaybah
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muslim ibn Qutayba al-Dīnawarī al-Marwazī better known simply as Ibn Qutaybah ( ar-at, ابن قتيبة, Ibn Qutaybah; c. 828 – 13 November 889 CE / 213 – 15 Rajab 276 AH) was an Islamic scholar of Persian ...
.
Though the
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing. ...
expresses no racial prejudice, Lewis argues that ethnocentric prejudice later developed among
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s, for a variety of reasons:
their
extensive conquests and
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
; the influence of
Aristotelian ideas regarding slavery, which some
Muslim philosophers
Muslim philosophers both profess Islam and engage in a style of philosophy situated within the structure of the Arabic language and Islam, though not necessarily concerned with religious issues. The sayings of the companions of Muhammad contained ...
directed towards
Zanj
Zanj ( ar, زَنْج, adj. , ''Zanjī''; fa, زنگی, Zangi) was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is also ...
(
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
) and
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
;
and the influence of
Judeo-Christian
The term Judeo-Christian is used to group Christianity and Judaism together, either in reference to Christianity's derivation from Judaism, Christianity's borrowing of Jewish Scripture to constitute the "Old Testament" of the Christian Bible, or ...
ideas regarding divisions among humankind. By the eighth century, anti-black prejudice among Arabs resulted in discrimination. A number of medieval Arabic authors argued against this prejudice, urging respect for all black people and especially
Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
. By the 14th century, a significant number of slaves came from
sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
; Lewis argues that this led to the likes of Egyptian historian Al-Abshibi (1388–1446) writing that "
is said that when the
lack
Lack may refer to:
Places
* Lack, County Fermanagh, a townland in Northern Ireland
* Lack, Poland
* Łąck, Poland
* Lack Township, Juniata County, Pennsylvania, US
Other uses
* Lack (surname)
* Lack (manque), a term in Lacan's psychoanalyti ...
slave is sated, he fornicates, when he is hungry, he steals." According to Lewis, the 14th-century Tunisian scholar
Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (; ar, أبو زيد عبد الرحمن بن محمد بن خلدون الحضرمي, ; 27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732-808 AH) was an Arab
The Historical Muhammad', Irving M. Zeitlin, (Polity Press, 2007), p. 21; "It is, of ...
also wrote:
...beyond nown peoples of black West Africato the south there is no civilization in the proper sense. There are only humans who are closer to dumb animals than to rational beings. They live in thickets and caves, and eat herbs and unprepared grain. They frequently eat each other. They cannot be considered human beings. Therefore, the Negro nations are, as a rule, submissive to slavery, because (Negroes) have little that is (essentially) human and possess attributes that are quite similar to those of dumb animals, as we have stated.
According to
Wesleyan University
Wesleyan University ( ) is a Private university, private liberal arts college, liberal arts university in Middletown, Connecticut. Founded in 1831 as a Men's colleges in the United States, men's college under the auspices of the Methodist Epis ...
professor Abdelmajid Hannoum, French
Orientalists
In art history, literature and cultural studies, Orientalism is the imitation or depiction of aspects in the Eastern world. These depictions are usually done by writers, designers, and artists from the Western world. In particular, Orientalist p ...
projected racist and
colonialist
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
views of the 19th century into their translations of medieval Arabic writings, including those of Ibn Khaldun. This resulted in the translated texts
racializing
In sociology, racialization or ethnicization is a political process of ascribing ethnic or racial identities to a relationship, social practice, or group that did not identify itself as such. Racialization or ethnicization often arises out of th ...
Arabs and
Berber people, when no such distinction was made in the originals. James E. Lindsay argues that the concept of an
Arab identity
Arab identity ( ar, الهوية العربية ) is the objective or subjective state of perceiving oneself as an Arab and as relating to being Arab. Like other cultural identities, it relies on a common culture, a traditional lineage, the com ...
itself did not exist until modern times, though others like
Robert Hoyland
Robert G. Hoyland (born 1966) is a historian, specializing in the medieval history of the Middle East. He is a former student of historian Patricia Crone and was a Leverhulme Fellow at Pembroke College, Oxford. He is currently Professor of Late ...
have argued that a common sense of
Arab identity
Arab identity ( ar, الهوية العربية ) is the objective or subjective state of perceiving oneself as an Arab and as relating to being Arab. Like other cultural identities, it relies on a common culture, a traditional lineage, the com ...
already existed by the 9th century.
''Limpieza de sangre''
With the
Umayyad Caliphate's conquest of Hispania, Muslim Arabs and
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
overthrew the previous
Visigothic
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is kno ...
rulers and created
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, ...
, which contributed to the
Golden age of Jewish culture, and lasted for six centuries. It was followed by the centuries-long ''
Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid ...
'', during which Christian Iberian kingdoms contested Al-Andalus and progressively conquered the divided Muslim kingdoms, culminating in the
fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492 and the rise of
Ferdinand V Ferdinand V is the name of:
* Ferdinand II of Aragon, Ferdinand V of Castile, ''the Catholic'' king of Castile, Aragon and Naples
*Ferdinand I of Austria
en, Ferdinand Charles Leopold Joseph Francis Marcelin
, image = Kaiser Ferdinand I.j ...
and
Isabella I
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...
as
Catholic monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
of Spain. The legacy Catholic
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex Hist ...
then formulated the ''
limpieza de sangre
The concept of (), (, ) or (), literally "cleanliness of blood" and meaning "blood purity", was an early system of Racial discrimination, racialized discrimination used in Spanish Empire, early modern Spain and Portuguese Empire, Portugal.
T ...
'' ("cleanliness of blood") doctrine. It was during this time in history that the Western concept of aristocratic "
blue blood" emerged in a racialized, religious and feudal context,
so as to stem the upward social mobility of the converted
New Christians
New Christian ( es, Cristiano Nuevo; pt, Cristão-Novo; ca, Cristià Nou; lad, Christiano Muevo) was a socio-religious designation and legal distinction in the Spanish Empire and the Portuguese Empire. The term was used from the 15th century ...
. Robert Lacey explains:
It was the Spaniards who gave the world the notion that an aristocrat's blood is not red but blue. The Spanish nobility started taking shape around the ninth century in classic military fashion, occupying land as warriors on horseback. They were to continue the process for more than five hundred years, clawing back sections of the peninsula from its Moorish occupiers, and a nobleman demonstrated his pedigree by holding up his sword arm to display the filigree of blue-blooded veins beneath his pale skin—proof that his birth had not been contaminated by the dark-skinned enemy. Sangre azul, blue blood, was thus a euphemism for being a white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
man—Spain's own particular reminder that the refined footsteps of the aristocracy through history carry the rather less refined spoor of racism.
Following the expulsion of the Arabic
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
and most of the
Sephardic Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefar ...
from the
Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, the remaining
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s were forced to
convert
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* "Conversion" (''Stargate Atlantis''), an episode of the television series
* "The Conversion" ...
to Roman Catholicism, becoming "
New Christian
New Christian ( es, Cristiano Nuevo; pt, Cristão-Novo; ca, Cristià Nou; lad, Christiano Muevo) was a socio-religious designation and legal distinction in the Spanish Empire and the Portuguese Empire. The term was used from the 15th century ...
s", who were sometimes discriminated against by the "
Old Christian
Old Christian ( es, cristiano viejo, pt, cristão-velho, ca, cristià vell) was a social and law-effective category used in the Iberian Peninsula from the late 15th and early 16th century onwards, to distinguish Portuguese and Spanish people atte ...
s" in some cities (including
Toledo), despite condemnations by the Church and the State, which both welcomed the new flock.
The
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
was carried out by members of the
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Cal ...
in order to weed out the converts who still practiced
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
and
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
in secret. The system and ideology of the ''limpieza de sangre'' ostracized false Christian converts from society in order to protect it against
treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
. The remnants of such legislation persevered into the 19th century in military contexts.
In
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, the legal distinction between New and Old Christian was only ended through a legal decree issued by the
Marquis of Pombal
Count of Oeiras () was a Portuguese title of nobility created by a royal decree, dated July 15, 1759, by King Joseph I of Portugal, and granted to Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, head of the Portuguese government.
Later, through another roy ...
in 1772, almost three centuries after the implementation of the racist discrimination. The ''limpieza de sangre'' legislation was common also during the
colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although Norse colonization of North America, the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizin ...
, where it led to the racial and feudal separation of peoples and social strata in the colonies. It was however often ignored in practice, as the new colonies needed skilled people.

At the end of the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, the
Valladolid debate
The Valladolid debate (1550–1551) was the first moral debate in European history to discuss the rights and treatment of an indigenous people by European colonizers. Held in the Colegio de San Gregorio, in the Spanish city of Valladolid, it was ...
(1550–1551), concerning the treatment of the
natives
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
of the "
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
" pitted the Dominican friar and Bishop of Chiapas,
Bartolomé de Las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar ...
, to another Dominican and Humanist
philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
,
Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda
Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda (11 June 1494 – 17 November 1573) was a Spanish Renaissance humanist, philosopher, and theologian.
Biography
In 1533 and 1534 Sepúlveda wrote to Desiderius Erasmus from Rome concerning differences between Eras ...
. The latter argued that the
Indians practiced
human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein ...
of innocents,
cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
, and other such "crimes against nature"; they were unacceptable and should be suppressed by any means possible including war, thus reducing them to slavery or serfdom was in accordance with Catholic theology and
natural law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacte ...
. To the contrary, Bartolomé de Las Casas argued that the Amerindians were free men in the natural order and deserved the same treatment as others, according to
Catholic theology
Catholic theology is the understanding of Catholic doctrine or teachings, and results from the studies of theologians. It is based on canonical scripture, and sacred tradition, as interpreted authoritatively by the magisterium of the Catholic ...
. It was one of the many controversies concerning racism, slavery, religion, and European morality that would arise in the following centuries and which resulted in the legislation protecting the natives.
The marriage between Luisa de Abrego, a free black domestic servant from Seville and Miguel Rodríguez, a white segovian conquistador in 1565 in St. Augustine (Spanish Florida), is the first known and recorded Christian marriage anywhere in the continental United States.
In the Spanish colonies, Spaniards developed a complex
caste system
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
based on race, which was used for social control, and which also determined a person's importance in society.
While many Latin American countries have long since rendered the system officially illegal through legislation, usually at the time of their independence,
prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's per ...
based on degrees of perceived racial distance from European ancestry combined with one's socioeconomic status remain, an echo of the colonial caste system.
Racism as a modern phenomenon
Although
antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
has a long history, related to
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and
native Egyptian or
Greek religions (
anti-Judaism
Anti-Judaism is the "total or partial opposition to Judaism as a religion—and the total or partial opposition to Jews as adherents of it—by persons who accept a competing system of beliefs and practices and consider certain genuine Judai ...
), racism itself is sometimes described as a ''modern'' phenomenon. In the view of the French philosopher and historian
Michel Foucault
Paul-Michel Foucault (, ; ; 15 October 192625 June 1984) was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationship between power and knowledge, and how ...
, the first formulation of racism emerged in the
Early Modern period as the "
discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. ...
of race struggle", and a historical and political discourse, which Foucault opposed to the philosophical and juridical discourse of
sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
. On the other hand, e.g. Chinese self-identification as a "yellow race" predated such European racial concepts.
This European analysis, which first appeared in
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, was then carried on in
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
by such people as
Boulainvilliers,
Nicolas Fréret
Nicolas Fréret (; 15 February 1688 – 8 March 1749) was a French scholar.
Life
He was born at Paris on 15 February 1688. His father was ''procureur'' to the ''parlement'' of Paris, and destined him to the profession of the law. His first tutor ...
, and then, during the 1789
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
,
Sieyès, and afterwards,
Augustin Thierry
Augustin Thierry (or ''Jacques Nicolas Augustin Thierry''; 10 May 179522 May 1856) was a French historian. Although originally a follower of Henri de Saint-Simon, he later developed his own approach to history. A committed liberal, his approach ...
and
Cournot. Boulainvilliers, who created the matrix of such racist discourse in
medieval France
The Kingdom of France in the Middle Ages (roughly, from the 10th century to the middle of the 15th century) was marked by the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and West Francia (843–987); the expansion of royal control by the House of C ...
, conceived of the "race" as being something closer to the sense of a "nation", that is, in his time, the "race" meant the "people".
He conceived of France as being divided between various nations—the unified
nation-state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
is an
anachronism
An anachronism (from the Ancient Greek, Greek , 'against' and , 'time') is a chronology, chronological inconsistency in some arrangement, especially a juxtaposition of people, events, objects, language terms and customs from different time per ...
here—which themselves formed different "races". Boulainvilliers opposed the
absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitut ...
, which tried to bypass the
aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At t ...
by establishing a direct relationship to the
Third Estate
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into estates developed and ...
. Thus, he developed the theory that the French aristocrats were the descendants of foreign invaders, whom he called the "
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
", while according to him, the Third Estate constituted the autochthonous, vanquished
Gallo-Romans
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization (cultural), Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, Roman culture, language, morals and wa ...
, who were dominated by the Frankish aristocracy as a consequence of the
right of conquest
The right of conquest is a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the aftermath of Worl ...
. Early modern racism was opposed to nationalism and the nation-state: the
Comte de Montlosier, in exile during the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, who borrowed Boulainvilliers' discourse on the "Nordic race" as being the French aristocracy that invaded the plebeian "Gauls", thus showed his contempt for the Third Estate, calling it "this new people born of slaves ...
mixture of all races and of all times".
19th century

While 19th-century racism became closely intertwined with nationalism, leading to the
ethnic nationalist
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentrism , ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocracy, ethnocratic) ...
discourse that identified the "race" with the "
folk
Folk or Folks may refer to:
Sociology
*Nation
*People
* Folklore
** Folk art
** Folk dance
** Folk hero
** Folk music
*** Folk metal
*** Folk punk
*** Folk rock
** Folk religion
* Folk taxonomy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Folk Plus or Fol ...
", leading to such movements as
pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism (german: Pangermanismus or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify all the German-speaking people – and possibly also Germanic-speaking ...
,
pan-Turkism
Pan-Turkism is a political movement that emerged during the 1880s among Turkic intellectuals who lived in the Russian region of Kazan (Tatarstan), Caucasus (modern-day Azerbaijan) and the Ottoman Empire (modern-day Turkey), with its aim bei ...
,
pan-Arabism
Pan-Arabism ( ar, الوحدة العربية or ) is an ideology that espouses the unification of the countries of North Africa and Western Asia from the Atlantic Ocean to the Arabian Sea, which is referred to as the Arab world. It is closely c ...
, and
pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled ...
, medieval racism precisely divided the nation into various non-biological "races", which were thought to be the consequence of historical conquests and
social conflict
Social conflict is the Conflict (process), struggle for Agency (sociology), agency or Power (sociology), power in society.
Social conflict occurs when two or more people oppose each other in social interaction, and each exerts social power with re ...
s. Michel Foucault traced the genealogy of modern racism to this medieval "historical and political discourse of race struggle". According to him, it divided itself in the 19th century according to two rival lines: on one hand, it was incorporated by racists, biologists and
eugenicists
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or ...
, who gave it the modern sense of "race", and they also transformed this popular discourse into a "
state racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, healt ...
" (e.g., Nazism). On the other hand,
Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
also seized this discourse founded on the assumption of a political struggle that provided the real
engine of history and continued to act underneath the apparent peace. Thus, Marxists transformed the
essentialist
Essentialism is the view that objects have a set of attributes that are necessary to their identity. In early Western thought, Plato's idealism held that all things have such an "essence"—an "idea" or "form". In ''Categories'', Aristotle si ...
notion of "race" into the historical notion of "
class struggle
Class conflict, also referred to as class struggle and class warfare, is the political tension and economic antagonism that exists in society because of socio-economic competition among the social classes or between rich and poor.
The forms ...
", defined by socially structured positions: capitalist or proletarian. In ''
The Will to Knowledge
''The History of Sexuality'' (french: L'Histoire de la sexualité) is a four-volume study of sexuality in the Western world by the French historian and philosopher Michel Foucault, in which the author examines the emergence of "sexuality" as a di ...
'' (1976), Foucault analyzed another opponent of the "race struggle" discourse:
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies explained as originatin ...
's
psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might b ...
, which opposed the concept of "blood
heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
", prevalent in the 19th century racist discourse.
Authors such as
Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, in her 1951 book ''
The Origins of Totalitarianism
''The Origins of Totalitarianism'', published in 1951, was Hannah Arendt's first major work, wherein she describes and analyzes Nazism and Stalinism as the major totalitarian political movements of the first half of the 20th century.
History
...
'', have said that the racist ideology (''popular racism'') which developed at the end of the 19th century helped legitimize the
imperialist conquests of foreign territories and the atrocities that sometimes accompanied them (such as the
Herero and Namaqua Genocide
The Herero and Namaqua genocide or the Herero and Nama genocide was a campaign of ethnic extermination and collective punishment waged by the German Empire against the Herero (Ovaherero) and the Nama in German South West Africa (now Namibia). ...
of 1904–1907 or the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
of 1915–1917).
Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's poem, ''
The White Man's Burden
"The White Man's Burden" (1899), by Rudyard Kipling, is a poem about the Philippine–American War (1899–1902) that exhorts the United States to assume colonial control of the Filipino people and their country.Hitchens, Christopher. ''Bloo ...
'' (1899), is one of the more famous illustrations of the belief in the inherent superiority of the
European culture
The culture of Europe is rooted in its art, architecture, film, different types of music, economics, literature, and philosophy. European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage".
Definition ...
over the rest of the world, though it is also thought to be a satirical appraisal of such imperialism. Racist ideology thus helped legitimize the conquest and incorporation of foreign territories into an empire, which were regarded as a humanitarian obligation partially as a result of these racist beliefs.

However, during the 19th century, Western European colonial powers were involved in the suppression of the
Arab slave trade
History of slavery in the Muslim world refers to various periods in which a slave trade has been carried out under the auspices of Arab peoples or Arab countries. Examples include:
* Trans-Saharan slave trade
* Indian Ocean slave trade
* Barbary sl ...
in Africa, as well as in the suppression of the
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in West Africa. Some Europeans during the time period objected to injustices that occurred in some colonies and lobbied on behalf of
aboriginal peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
. Thus, when the
Hottentot Venus
Sarah Baartman (; 1789– 29 December 1815), also spelt Sara, sometimes in the diminutive form Saartje (), or Saartjie, and Bartman, Bartmann, was a Khoikhoi woman who was exhibited as a freak show attraction in 19th-century Europe under the n ...
was displayed in England in the beginning of the 19th century, the African Association publicly opposed itself to the exhibition. The same year that Kipling published his poem,
Joseph Conrad
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, ; 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Poles in the United Kingdom#19th century, Polish-British novelist and short story writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest writers in t ...
published ''
Heart of Darkness
''Heart of Darkness'' (1899) is a novella by Polish-English novelist Joseph Conrad in which the sailor Charles Marlow tells his listeners the story of his assignment as steamer captain for a Belgian company in the African interior. The novel ...
'' (1899), a clear criticism of the
Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leopo ...
, which was owned by Leopold II of Belgium.
Examples of racial theories used include the creation of the Hamitic ethno-linguistic group during the European exploration of Africa. It was then restricted by Karl Friedrich Lepsius (1810–1877) to non-Semitic languages, Semitic Afro-Asiatic languages.
The term ''Hamite'' was applied to different populations within North Africa, mainly comprising Ethiopians, Demographics of Eritrea, Eritreans, Somali people, Somalis, Berber people, Berbers, and the ancient Egyptians. Hamites were regarded as Caucasoid peoples who probably originated in either Arabia or Asia on the basis of their cultural, physical and linguistic similarities with the peoples of those areas. Europeans considered Hamites to be more civilized than Black people, Sub-Saharan Africans, and more akin to themselves and Semitic peoples. In the first two-thirds of the 20th century, the Hamitic race was, in fact, considered one of the branches of the Caucasian race, along with the Aryan race, Indo-Europeans, Semitic people, Semites, and the Mediterranean race, Mediterraneans.
However, the Hamitic peoples themselves were often deemed to have failed as rulers, which was usually ascribed to miscegenation, interbreeding with Negroes. In the mid-20th century, the German scholar Carl Meinhof (1857–1944) claimed that the
Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
race was formed by a merger of Hamitic and Negroid, Negro races. The Hottentots (Nama people, Nama or Khoi) were formed by the merger of Hamitic and Bushmen (San) races—both being termed nowadays as Khoisan peoples.

In the United States in the early 19th century, the American Colonization Society was established as the primary vehicle for proposals to return black Americans to greater freedom and equality in Africa. The colonization effort resulted from a mixture of motives with its founder Henry Clay stating that "unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off". Racism spread throughout the New World in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Whitecapping, which started in Indiana in the late 19th century, soon spread throughout all of North America, causing many African laborers to flee from the land they worked on. In the US, during the 1860s, racist posters were used during election campaigns. In one of these racist posters (see above), a black man is depicted lounging idly in the foreground as one white man ploughs his field and another chops wood. Accompanying labels are: "In the sweat of thy face shalt thou eat thy bread", and "The white man must work to keep his children and pay his taxes." The black man wonders, "Whar is de use for me to work as long as dey make dese appropriations." Above in a cloud is an image of the "Freedman's Bureau! Negro Estimate of Freedom!" The bureau is pictured as a large domed building resembling the U.S. Capitol and is inscribed "Freedom and No Work". Its columns and walls are labeled, "Candy", "Rum, Gin, Whiskey", "Sugar Plums", "Indolence", "White Women", "Apathy", "White Sugar", "Idleness", and so on.
On June 5, 1873, Sir Francis Galton, distinguished English explorer and cousin of Charles Darwin, wrote in a letter to ''The Times'':
20th century


The Nazi party, which seized power in the German federal election, March 1933, 1933 German elections and maintained a dictatorship over much of Europe until the End of World War II in Europe, End of World War II on the European continent, deemed the Germans to be part of an Aryan "
master race
The master race (german: Herrenrasse) is a Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific concept in Nazism, Nazi ideology in which the putative "Aryan race" is deemed the pinnacle of Race (classification of human beings), human racial hierarchy. Members wer ...
" (''Herrenvolk''), who therefore had the right to expand their territory and enslave or kill members of other races deemed inferior.
The racial ideology conceived by the Nazis graded humans on a scale of pure Aryan to non-Aryan, with the latter viewed as subhuman. At the top of the scale of pure Aryans were Germans and other Germanic peoples including the Dutch, Scandinavians, and the English people, English as well as other peoples such as some northern Italians and the French, who were said to have a suitable admixture of Germanic blood.
[Davies, Norman (2006). ''Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. Macmillan Pubs (pp. 167, 4).] Nazi policies labeled Romani people, Black people, people of color, and Slavs (mainly Poles, Serbs, Russians, Belarusians, Ukrainians and Czechs) as inferior non-Aryan subhumans.
[''Operation Barbarossa: Ideology and Ethics against Human Dignity'', by André Mineau, (Rodopi, 2004) p. 180] Jews were at the bottom of the hierarchy, considered inhuman and thus life unworthy of life, unworthy of life.
[''The Czechs under Nazi Rule: The Failure of National Resistance, 1939–1942'', Vojtěch Mastný, Columbia University Press ][''The Politics of Fertility in Twentieth-Century Berlin'', p. 118 Annette F. Timm. 2010. The Nazis' singleminded desire to "purify" the German race through the elimination of non-Aryans (particularly Jews, Gypsies, and Slavs)] In accordance with Nazi racial ideology, approximately six million Jews were killed in the
Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. 2.5 million Nazi crimes against the Polish nation, ethnic Poles, 0.5 million Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, ethnic Serbs and 0.2–0.5 million Porajmos, Romani were killed by the regime and its collaborators.
The Nazis considered most Slavs to be non-Aryan ''Untermenschen''. The Nazi Party's chief racial theorist, Alfred Rosenberg, adopted the term from Klansman Lothrop Stoddard's 1922 book ''The Revolt Against Civilization: The Menace of the Under-man''. In the secret plan Generalplan Ost ("Master Plan East") the Nazis resolved to expel, enslave, or exterminate most Slavic people to provide "Lebensraum, living space" for Germans,
but Nazi policy towards Slavs changed during World War II due to manpower shortages which necessitated limited Slavic participation in the Waffen-SS.
[Norman Davies. ''Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory''. pp. 167, 209.] Significant war crimes were committed against Slavs, particularly Nazi crimes against the Polish nation, Poles, and German mistreatment of Soviet prisoners of war, Soviet POWs had a far higher mortality rate than their American and British counterparts due to deliberate neglect and mistreatment. Between June 1941 and January 1942, the Nazis killed an estimated 2.8 million Red Army POWs, whom they viewed as "subhuman".
In the years 1943–1945, around 120,000 Polish people, mostly women and children, became the victims of massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia, ethnicity-based massacres by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, which was then operating in the territory of Occupation of Poland (1939–45), occupied Poland.
[Norman Davies, ''Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory'' Publisher: Pan Books, 2007, 544 pages, ] In addition to Poles who represented the vast majority of the murdered people, the victims also included Jews, Armenians, Russians, and Ukrainians who were married to Poles or attempted to help them.
During the intensification of ties with Nazi Germany in the 1930s, Ante Pavelić and the Ustaše and their idea of the Croats, Croatian nation became increasingly race-oriented.
The Ustaše view of national and racial identity, as well as the theory of Serbs as an inferior race, was influenced by Croatian nationalism, Croatian nationalists and intellectuals from the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century.
Serbs were primary targets of racial laws and murders in the puppet Independent State of Croatia (NDH); Jews and Roma were also targeted. The Ustaše introduced laws to strip Serbs of their citizenship, livelihoods, and possessions. During the Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, genocide in the NDH, Serbs suffered among the highest casualty rates in Europe during the World War II, and the NDH was one of the most lethal regimes in the 20th century.
German praise for America's institutional racism was continuous throughout the early 1930s, and Nazi lawyers were advocates of the use of American models.
Race based U.S. citizenship laws and anti-miscegenation laws (no race mixing) directly inspired the Nazi's two principal Nuremberg Laws, Nuremberg racial laws—the Citizenship Law and the Blood Law.
Hitler's 1925 memoir ''Mein Kampf'' was full of admiration for America's treatment of "coloreds". Nazi expansion eastward was accompanied with invocation of America's colonial expansion westward, with the accompanying actions toward the Native Americans.
In 1928, Hitler praised Americans for having "gunned down the millions of Redskins to a few hundred thousand, and now keeps the modest remnant under observation in a cage." On Nazi Germany's expansion eastward, in 1941 Hitler stated, "Our Mississippi [the line beyond which Thomas Jefferson wanted all Indians expelled] must be the Volga."
White supremacy was dominant in the U.S. from its founding up to the civil rights movement. On the U.S. immigration laws prior to 1965, sociologist Stephen Klineberg cited the law as clearly declaring "that Northern Europeans are a superior subspecies of the white race."
While anti-Asian racism was embedded in U.S. politics and culture in the early 20th century, Indian people, Indians were also racialized for their anticolonialism, with U.S. officials, casting them as a "Hindu" menace, pushing for Western imperial expansion abroad. The Naturalization Act of 1790 limited U.S. citizenship to whites only, and in the 1923 case, ''United States v. Bhagat Singh Thind'', the Supreme Court ruled that high caste Hindus were not "white persons" and were therefore racially ineligible for naturalized citizenship. It was after the Luce–Celler Act of 1946 that a quota of 100 Indians per year could immigrate to the U.S. and become citizens. The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 dramatically opened entry to the U.S. to immigrants other than traditional Northern European and Germanic peoples, Germanic groups, and as a result would significantly alter the demographic mix in the U.S.
Serious Durban Riot, race riots in Durban between Indian South Africans, Indians and Zulus erupted in 1949. Ne Win's rise to power in Burma in 1962 and his relentless persecution of "resident aliens" led to an exodus of some 300,000 Burmese Indians. They migrated to escape Racial Discrimination against Burmese Indians, racial discrimination and wholesale nationalisation of private enterprises a few years later, in 1964. The Zanzibar Revolution of January 12, 1964, put an end to the local
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
dynasty.
Thousands of Arabs and Indians in Zanzibar were massacred in riots, and thousands more were detained or fled the island. In August 1972, Ugandan President Idi Amin started the expropriation of properties owned by Asians and Europeans. In the same year, Amin ethnically cleansed Expulsion of Asians in Uganda in 1972, Uganda's Asians, giving them 90 days to leave the country.
Shortly after World War II, the South African National Party (South Africa), National Party took control of the government in South Africa. Between 1948 and 1994, the
apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
regime took place. This regime based its ideology on the racial separation of whites and non-whites, including the unequal rights of non-whites. Several protests and violence occurred during the Internal resistance to South African apartheid, struggle against apartheid, the most famous of these include the Sharpeville Massacre in 1960, the Soweto uprising in 1976, the Church Street bombing of 1983, and the Cape Town peace march of 1989.
Contemporary

During the Second Congo War, Congo Civil War (1998–2003), Pygmy people were hunted down like game animals and eaten. Both sides in the war regarded them as "subhuman" and some say their flesh can confer magical powers. UN human rights activists reported in 2003 that rebels had carried out acts of
cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
. Sinafasi Makelo, a representative of the Mbuti pygmies, has asked the UN Security Council to recognise cannibalism as both a Crimes against humanity, crime against humanity and an act of
genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
. A report released by the United Nations Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination condemns Botswana's treatment of the 'Bushmen' as racist. In 2008, the tribunal of the 15-nation Southern African Development Community (SADC) accused Zimbabwean President Robert Mugabe of having a racist attitude towards white people.
The Nanjing Anti-African protests, mass demonstrations and riots against African students in Nanjing, China, lasted from December 1988 to January 1989. In November 2009, British newspaper ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' reported that Lou Jing, of mixed Chinese and African parentage, had emerged as the most famous talent show contestant in China and has become the subject of intense debate because of her skin color.
Her attention in the media opened serious debates about racism in China and racial prejudice.
Some 70,000 black African Mauritanians were expelled from Mauritania in the late 1980s. In the Sudan, black African captives in the civil war were often Slavery in contemporary Africa, enslaved, and female prisoners were often sexually abused. The Darfur conflict has been described by some as a racial matter. In October 2006, Niger announced that it would deport the approximately 150,000 Arabs living in the Diffa region of eastern Niger to Chad. While the government collected Arabs in preparation for the deportation, two girls died, reportedly after fleeing Government forces, and three women suffered miscarriages.

The Jakarta riots of May 1998 Discrimination against Chinese Indonesians, targeted many Chinese Indonesians. The Anti-Chinese legislation in Indonesia, anti-Chinese legislation was in the Indonesian constitution until 1998. Resentment against Overseas Chinese, Chinese workers has led to violent confrontations in Africa and Oceania.
Anti-Chinese rioting, involving tens of thousands of people, broke out in Papua New Guinea in May 2009. Indians in Fiji, Indo-Fijians suffered violent attacks after the 2000 Fijian coup d'état, Fiji coup in 2000. Non-indigenous citizens of Fiji are subject to discrimination. Racial divisions also exist in Guyana, Malaysia, Trinidad and Tobago, Madagascar, and South Africa. In Malaysia such racist state policies are codified on many levels, see Bumiputera (Malaysia), Bumiputera.
Peter Bouckaert, the Human Rights Watch's emergencies director, said in an interview that "racist hatred" is the chief motivation behind the persecution of Muslims in Myanmar, violence against Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar.
One form of racism in the United States was enforced racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, which existed until the 1960s, when it was outlawed in the Civil Rights Act of 1964. It has been argued that this separation of races continues to exist ''de facto'' today in different forms, such as lack of access to loans and resources or discrimination by police and other government officials.
The 2016 Pew Research Center, Pew Research poll found that Italians, in particular, hold strong Anti-Romanyism, anti-Romani views, with 82% of Italians expressing negative opinions about Romani people, Romani. In Greece, there are 67%, in Hungary, 64%, in France, 61%, in Spain, 49%, in Poland, 47%, in the UK, 45%, in Sweden, 42%, in Germany, 40%, and in the Netherlands, 37%, that have an unfavourable view of Roma. A survey conducted by
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
found the Czech Republic, Lithuania, Belarus and Ukraine had the strongest racial bias against black people in Europe, while Serbia, Slovenia and Bosnia and Herzegovina had the weakest racial bias, followed by Croatia and Ireland.
Scientific racism

The modern biological definition of race developed in the 19th century with scientific racist theories. The term ''scientific racism'' refers to the use of science to justify and support racist beliefs, which goes back to the early 18th century, though it gained most of its influence in the mid-19th century, during the New Imperialism period. Also known as academic racism, such theories first needed to overcome the Roman Catholic Church, Church's resistance to positivism, positivist accounts of history and its support of monogenism, the concept that all human beings were originated from the same ancestors, in accordance with creationist accounts of history.
These racist theories put forth on scientific hypothesis were combined with unilineal evolution, unilineal theories of social progress, which postulated the superiority of the European civilization over the rest of the world. Furthermore, they frequently made use of the idea of "
survival of the fittest
"Survival of the fittest" is a phrase that originated from Darwinian evolutionary theory as a way of describing the mechanism of natural selection. The biological concept of fitness is defined as reproductive success. In Darwinian terms, th ...
", a term coined by Herbert Spencer in 1864, associated with ideas of competition, which were named social Darwinism in the 1940s. Charles Darwin himself opposed the idea of rigid racial differences in ''The Descent of Man'' (1871), in which he argued that humans were all of one species, sharing common descent. He recognised racial differences as varieties of humanity, and emphasised the close similarities between people of all races in mental faculties, tastes, dispositions and habits, while still contrasting the culture of the "lowest savages" with European civilization.
At the end of the 19th century, proponents of scientific racism intertwined themselves with
eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or ...
discourses of "Social degeneration, degeneration of the race" and "blood
heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
". Henceforth, scientific racist discourses could be defined as the combination of polygenism, unilinealism, social Darwinism, and eugenism. They found their scientific legitimacy on physical anthropology, anthropometry, craniometry, phrenology, physiognomy, and others now discredited disciplines in order to formulate racist prejudices.
Before being disqualified in the 20th century by the American school of cultural anthropology (Franz Boas, etc.), the British school of
social anthropology
Social anthropology is the study of patterns of behaviour in human societies and cultures. It is the dominant constituent of anthropology throughout the United Kingdom and much of Europe, where it is distinguished from cultural anthropology. In t ...
(Bronisław Malinowski, Alfred Radcliffe-Brown, etc.), the French school of ethnology (
Claude Lévi-Strauss
Claude Lévi-Strauss (, ; 28 November 1908 – 30 October 2009) was a French anthropologist and ethnologist whose work was key in the development of the theories of structuralism and structural anthropology. He held the chair of Social Anthro ...
, etc.), as well as the discovery of the Modern synthesis (20th century), neo-Darwinian synthesis, such sciences, in particular anthropometry, were used to deduce behaviours and psychological characteristics from outward, physical appearances.
The neo-Darwinian synthesis, first developed in the 1930s, eventually led to a gene-centered view of evolution in the 1960s. According to the Human Genome Project, the most complete mapping of human DNA to date indicates that there is no clear Race and genetics, genetic basis to racial groups. While some genes are more common in certain populations, there are no genes that exist in all members of one population and no members of any other.
Heredity and eugenics
The first theory of
eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or ...
was developed in 1869 by Francis Galton (1822–1911), who used the then-popular concept of ''Social degeneration, degeneration''. He applied statistics to study human differences and the alleged "inheritance of intelligence", foreshadowing future uses of "intelligence testing" by the anthropometry school. Such theories were vividly described by the writer
Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
(1840–1902), who started publishing in 1871, a twenty-novel cycle, ''Les Rougon-Macquart'', where he linked
heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
to behavior. Thus, Zola described the high-born Rougons as those involved in politics (''Son Excellence Eugène Rougon'') and medicine (''Le Docteur Pascal'') and the low-born Macquarts as those fatally falling into alcoholism (''L'Assommoir''), prostitution (''Nana (novel), Nana''), and homicide (''La Bête humaine'').
During the rise of Nazi Germany, Nazism in Germany, some scientists in Western nations worked to debunk the regime's racial theories. A few argued against racist ideologies and discrimination, even if they believed in the alleged existence of biological races. However, in the fields of anthropology and biology, these were minority positions until the mid-20th century. According to the 1950 UNESCO statement, ''
The Race Question
The Race Question is the first of four UNESCO statements about issues of race. It was issued on 18 July 1950 following World War II and Nazi racism to clarify what was scientifically known about race, and as a moral condemnation of racism.< ...
'', an international project to debunk racist theories had been attempted in the mid-1930s. However, this project had been abandoned. Thus, in 1950, UNESCO declared that it had resumed:
...up again, after a lapse of fifteen years, a project that the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation has wished to carry through but that it had to abandon in deference to the Appeasement of Hitler, appeasement policy of the pre-war period. The race question had become one of the pivots of Nazi ideology and policy. Tomáš Masaryk, Masaryk and Edvard Beneš, Beneš took the initiative of calling for a conference to re-establish in the minds and consciences of men everywhere the truth about race ... Nazi propaganda was able to continue its baleful work unopposed by the authority of an international organisation.
The Third Reich's racial policies, its Nazi eugenics, eugenics programs and the extermination of Jews in
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
, as well as the Romani people in the Porrajmos (the Porajmos, Romani Holocaust) and others minorities led to a change in opinions about scientific research into race after the war. Changes within scientific disciplines, such as the rise of the Franz Boas, Boasian school of anthropology in the United States contributed to this shift. These theories were strongly denounced in the 1950 UNESCO statement, signed by internationally renowned scholars, and titled ''
The Race Question
The Race Question is the first of four UNESCO statements about issues of race. It was issued on 18 July 1950 following World War II and Nazi racism to clarify what was scientifically known about race, and as a moral condemnation of racism.< ...
''.
Polygenism and racial typologies
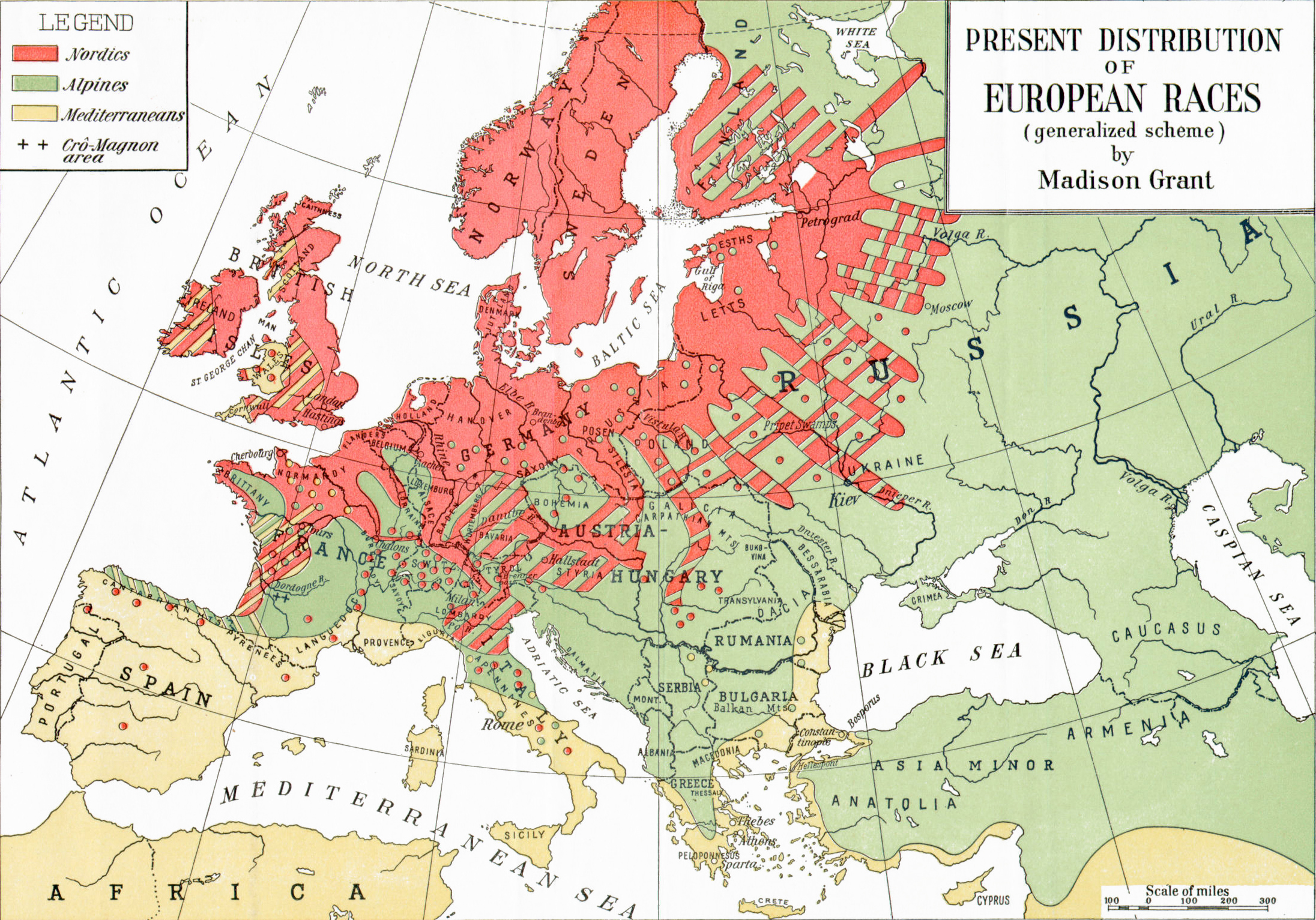
Works such as Arthur de Gobineau's ''An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races'' (1853–1855) may be considered one of the first theorizations of this new racism, founded on an essentialist notion of race, which opposed the former racial discourse, of
Boulainvilliers for example, which saw in races a fundamentally historical reality, which changed over time. Gobineau, thus, attempted to frame racism within the terms of biological differences among humans, giving it the legitimacy of biology.
Gobineau's theories would be expanded in France by Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936)'s typology (anthropology), typology of races, who published in 1899 ''The Aryan and his Social Role'', in which he claimed that the white "Aryan race" "Cephalic index, dolichocephalic", was opposed to the "brachycephalic" race, of whom the "Jew" was the archetype. Vacher de Lapouge thus created a hierarchical classification of races, in which he identified the "''Nordic race, Homo europaeus'' (Teutonic, Protestant, etc.), the "''Homo alpinus''" (Auvergne (province), Auvergnat, Turkish people, Turkish, etc.), and finally the "''Homo mediterraneus''" (Naples, Neapolitan, Andalusia, Andalus, etc.) He assimilated races and social classes, considering that the French upper class was a representation of the ''Homo europaeus'', while the lower class represented the ''Homo alpinus''. Applying Galton's eugenics to his theory of races, Vacher de Lapouge's "selectionism" aimed first at achieving the annihilation of trade unionists, considered to be a "degenerate"; second, creating types of man each destined to one end, in order to prevent any contestation of labour conditions. His "anthroposociology" thus aimed at blocking
social conflict
Social conflict is the Conflict (process), struggle for Agency (sociology), agency or Power (sociology), power in society.
Social conflict occurs when two or more people oppose each other in social interaction, and each exerts social power with re ...
by establishing a fixed, hierarchical social order.
The same year, William Z. Ripley used identical racial classification in ''The Races of Europe (Ripley), The Races of Europe'' (1899), which would have a great influence in the United States. Other scientific authors include Houston Stewart Chamberlain, H.S. Chamberlain at the end of the 19th century (a British citizen who naturalization, naturalized himself as German because of his admiration for the "Aryan race") and Madison Grant, a eugenicist and author of ''The Passing of the Great Race'' (1916). Madison Grant provided statistics for the Immigration Act of 1924, which severely restricted immigration of Jews, Slavs, and Southern Europeans, who were subsequently hindered in seeking to escape Nazi Germany.
Human zoos
Human zoos (called "People Shows"), were an important means of bolstering ''popular racism'' by connecting it to scientific racism: they were both objects of public curiosity and of anthropology and anthropometry. Joice Heth, an African-American slave, was displayed by Phineas Taylor Barnum, P.T. Barnum in 1836, a few years after the exhibition of Saartjie Baartman, the "Hottentot Venus", in England. Such exhibitions became common in the New Imperialism period, and remained so until World War II. Carl Hagenbeck, inventor of the modern zoos, exhibited animals beside humans who were considered "savages".
[Human Zoos](_blank)
by Nicolas Bancel, Pascal Blanchard and Sandrine Lemaire, in ''Le Monde diplomatique'', August 200
French – free
/ref>
Congolese Pygmies, pygmy Ota Benga was displayed in 1906 by eugenicist Madison Grant, head of the Bronx Zoo, as an attempt to illustrate the "missing link" between humans and orangutans: thus, racism was tied to Darwinism, creating a social Darwinism, social Darwinist ideology that tried to ground itself in Charles Darwin, Darwin's scientific discoveries. The 1931 Paris Colonial Exhibition displayed Kanaks from New Caledonia. A "Congolese village" was on display as late as 1958 at the Expo '58, Brussels' World Fair.
Theories about the origins of racism
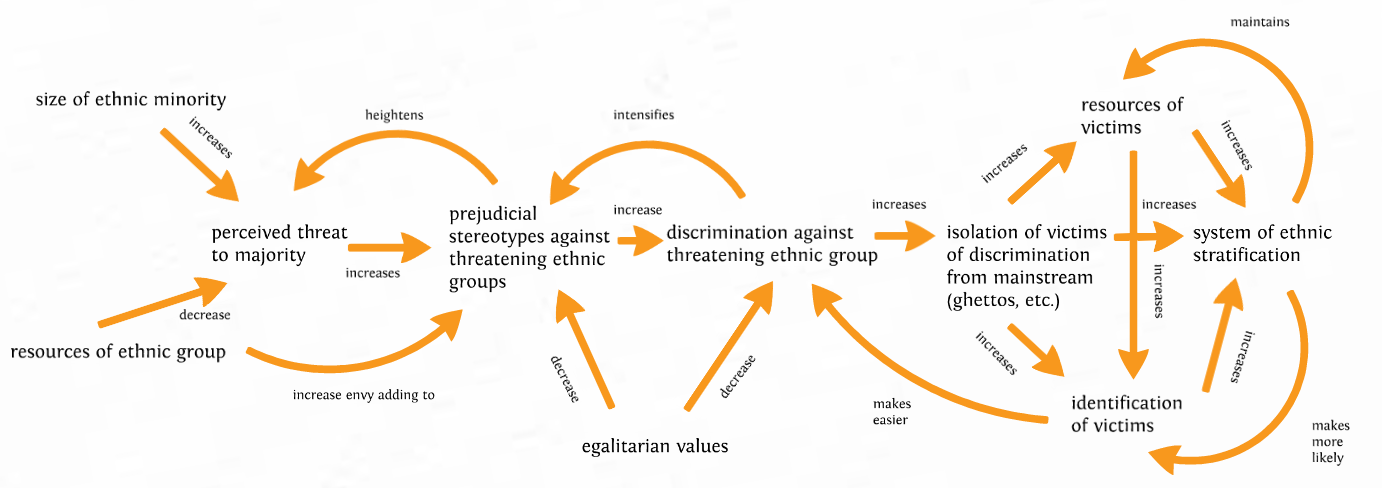 Evolutionary psychologists John Tooby and Leda Cosmides were puzzled by the fact that in the US, race is one of the three characteristics most often used in brief descriptions of individuals (the others are age and sex). They reasoned that natural selection would not have favoured the evolution of an instinct for using race as a classification, because for most of human history, humans almost never encountered members of other races. Tooby and Cosmides hypothesized that modern people use race as a proxy (rough-and-ready indicator) for coalition membership, since a better-than-random guess about "which side" another person is on will be helpful if one does not actually know in advance.
Their colleague Robert Kurzban designed an experiment whose results appeared to support this hypothesis. Using the memory confusion protocol, they presented subjects with pictures of individuals and sentences, allegedly spoken by these individuals, which presented two sides of a debate. The errors that the subjects made in recalling who said what indicated that they sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker of the same race as the "correct" speaker, although they also sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker "on the same side" as the "correct" speaker. In a second run of the experiment, the team also distinguished the "sides" in the debate by clothing of similar colors; and in this case the effect of racial similarity in causing mistakes almost vanished, being replaced by the color of their clothing. In other words, the first group of subjects, with no clues from clothing, used race as a visual guide to guessing who was on which side of the debate; the second group of subjects used the clothing color as their main visual clue, and the effect of race became very small.
Evolutionary psychologists John Tooby and Leda Cosmides were puzzled by the fact that in the US, race is one of the three characteristics most often used in brief descriptions of individuals (the others are age and sex). They reasoned that natural selection would not have favoured the evolution of an instinct for using race as a classification, because for most of human history, humans almost never encountered members of other races. Tooby and Cosmides hypothesized that modern people use race as a proxy (rough-and-ready indicator) for coalition membership, since a better-than-random guess about "which side" another person is on will be helpful if one does not actually know in advance.
Their colleague Robert Kurzban designed an experiment whose results appeared to support this hypothesis. Using the memory confusion protocol, they presented subjects with pictures of individuals and sentences, allegedly spoken by these individuals, which presented two sides of a debate. The errors that the subjects made in recalling who said what indicated that they sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker of the same race as the "correct" speaker, although they also sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker "on the same side" as the "correct" speaker. In a second run of the experiment, the team also distinguished the "sides" in the debate by clothing of similar colors; and in this case the effect of racial similarity in causing mistakes almost vanished, being replaced by the color of their clothing. In other words, the first group of subjects, with no clues from clothing, used race as a visual guide to guessing who was on which side of the debate; the second group of subjects used the clothing color as their main visual clue, and the effect of race became very small.[. The authors provide a summary and other comments at ]
Some research suggests that ethnocentric thinking may have actually contributed to the development of cooperation. Political scientists Ross Hammond and Robert Axelrod created a computer simulation wherein virtual individuals were randomly assigned one of a variety of skin colors, and then one of a variety of trading strategies: be color-blind, favor those of your own color, or favor those of other colors. They found that the ethnocentric individuals clustered together, then grew, until all the non-ethnocentric individuals were wiped out.
In ''The Selfish Gene'', evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins writes that "Blood-feuds and inter-clan warfare are easily interpretable in terms of W. D. Hamilton, Hamilton's kin selection, genetic theory." Dawkins writes that racial prejudice, while not evolutionarily adaptive, "could be interpreted as an irrational generalization of a kin-selected tendency to identify with individuals physically resembling oneself, and to be nasty to individuals different in appearance."
State-sponsored racism
State racism—the institutions and practices of a nation-state that are grounded in racist ideology—has played a major role in all instances of settler colonialism, from the United States to Australia. It also played a prominent role in the Nazi Germany, Nazi German regime, in Fascism, fascist regimes throughout Europe, and during the early years of Japan's Shōwa period. These governments advocated and implemented ideologies and policies that were racist, xenophobic, and, in the case of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
, genocidal. Legislative state racism is known to have been enforced by the National Party (South Africa), National Party of South Africa during its Apartheid regime between 1948 and 1994. Here, a series of Apartheid legislation in South Africa, Apartheid legislation was passed through the legal systems to make it legal for white South Africans to have rights which were superior to those of non-white South Africans. Non-white South Africans were not allowed involvement in any governing matters, including voting; access to quality healthcare; the provision of basic services, including clean water; electricity; as well as access to adequate schooling. Non-white South Africans were also prevented from accessing certain public areas, from using certain public transportation, and were required to live only in certain designated areas. Non-white South Africans were taxed differently than white South Africans and they were also required to carry on them at all times additional documentation, which later became known as "dom passes", to certify their non-white South African citizenship. All of these legislative racial laws were abolished through a series of equal
Legislative state racism is known to have been enforced by the National Party (South Africa), National Party of South Africa during its Apartheid regime between 1948 and 1994. Here, a series of Apartheid legislation in South Africa, Apartheid legislation was passed through the legal systems to make it legal for white South Africans to have rights which were superior to those of non-white South Africans. Non-white South Africans were not allowed involvement in any governing matters, including voting; access to quality healthcare; the provision of basic services, including clean water; electricity; as well as access to adequate schooling. Non-white South Africans were also prevented from accessing certain public areas, from using certain public transportation, and were required to live only in certain designated areas. Non-white South Africans were taxed differently than white South Africans and they were also required to carry on them at all times additional documentation, which later became known as "dom passes", to certify their non-white South African citizenship. All of these legislative racial laws were abolished through a series of equal human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
laws which were passed at the end of the Apartheid era in the early 1990s.
Anti-racism
Anti-racism includes beliefs, actions, movements, and policies which are adopted or developed in order to oppose racism. In general, it promotes an egalitarian society in which people are not discriminated against on the basis of race. Examples of anti-racist movements include the civil rights movement, the Anti-Apartheid Movement and Black Lives Matter. Nonviolent resistance is sometimes embraced as an element of anti-racist movements, although this was not always the case. Hate crime laws, affirmative action, and bans on racist speech are also examples of government policy which is intended to suppress racism.
See also
* Afrophobia
* Allport's Scale
* Aporophobia
* Christian Identity
* Creativity (religion)
* Curse and mark of Cain
* Discrimination based on skin color
* Environmental racism
* Environmental racism in Europe
* Ethnic hatred
* Hipster racism
* Identitarianism
* Index of racism-related articles
* In-group favoritism
* Labeling theory
* Minority stress
* Nigger
* Racial bias in criminal news
* Racial bias on Wikipedia
* Racial fetishism
* Racial literacy
* Racialization
* Raciolinguistics
* Pre-Adamite#Racist pre-Adamism, Racist pre-Adamism
* Racism in horror films
* Racism in the LGBT community
* Reverse discrimination
* Romantic racism
* Social interpretations of race
* Spiritual racism
* Stereotype threat
* Tatarophobia
* Tragic mulatto
* Yellow Peril
References and notes
Further reading
* Theodore W. Allen, Allen, Theodore. (1994). ''The Invention of the White Race: Volume 1'' London: Verso.
* Allen, Theodore. (1997). ''The Invention of the White Race: Volume 2'' London: Verso.
* Barkan, Elazar (1992), ''The Retreat of Scientific Racism : Changing Concepts of Race in Britain and the United States between the World Wars'', Cambridge University Press, New York.
* Barth, Boris
nbn:de:0159-2010092173 ''Racism ''
European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011, retrieved: November 16, 2011.
*
* Bonilla-Silva, Eduardo. 2018.
Racism without Racists: Color-Blind Racism and the Persistence of Racial Inequality in the United States
'. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
*
* Dain, Bruce (2002), ''A Hideous Monster of the Mind : American Race Theory in the Early Republic'', Harvard University Press, Cambridge. (18th century US racial theory)
* Daniels, Jessie (1997), ''White Lies: Race, Class, Gender and Sexuality in White Supremacist Discourse'', Routledge, New York.
* Daniels, Jessie (2009), ''Cyber Racism: White Supremacy Online and the New Attack on Civil Rights'', Rowman & Littlefield, Lanham, MD.
* Ehrenreich, Eric (2007), ''The Nazi Ancestral Proof: Genealogy, Racial Science, and the Final Solution'', Indiana University Press, Bloomington.
* Ewen & Ewen (2006), "Typecasting: On the Arts and Sciences of Human Inequality", Seven Stories Press, New York.
* Joe Feagin, Feagin, Joe R. (2006). ''Systemic Racism: A Theory of Oppression'', Routledge: New York.
* Feagin, Joe R. (2009). ''Racist America: Roots, Current Realities, and Future Reparations, 2nd Edition.''Routledge: New York.
* Eliav-Feldon, Miriam, Isaac, Benjamin & Ziegler, Joseph. 2009. ''The Origins of Racism in the West'', Cambridge University Press: Cambridge
Gibson, Rich (2005) Against Racism and Irrationalism
* Graves, Joseph. (2004) ''The Race Myth'' NY: Dutton.
* Ignatiev, Noel. 1995. ''How the Irish Became White'' NY: Routledge.
* Isaac, Benjamin. 1995 ''The Invention of Racism in Classical Antiquity'' Princeton: Princeton University Press
* Lentin, Alana. (2008) ''Racism: A Beginner's Guide'' Oxford: One World.
* Claude Lévi-Strauss, Lévi-Strauss, Claude (1952), ''Race and History'', (UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
).
*
*
* Rocchio, Vincent F. (2000), ''Reel Racism : Confronting Hollywood's Construction of Afro-American Culture'', Westview Press.
*
* Smedley, Audrey. 2007. ''Race in North America: Origins and Evolution of a World View''. Boulder, CO: Westview.
* (historiography of race and racism)
* Pierre-André Taguieff, Taguieff, Pierre-André (1987), ''La Force du préjugé : Essai sur le racisme et ses doubles'', Tel Gallimard, La Découverte.
* Leon Poliakov, Poliakov, Leon. The Aryan Myth: A History of Racist and Nationalistic Ideas In Europe (Barnes & Noble Books (1996)) .
* Trepagnier, Barbara. 2006. ''Silent Racism: How Well-Meaning White People Perpetuate the Racial Divide''. Paradigm Publishers.
* France Winddance Twine, Twine, France Winddance (1997), ''Racism in a Racial Democracy: The Maintenance of White Supremacy in Brazil'', Rutgers University Press.
* UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, ''The Race Question
The Race Question is the first of four UNESCO statements about issues of race. It was issued on 18 July 1950 following World War II and Nazi racism to clarify what was scientifically known about race, and as a moral condemnation of racism.< ...
'', 1950
Tali Farkash, "Racists among us" in Y-Net (Yediot Aharonot), "Jewish Scene" section, April 20, 2007
* Howard Winant, Winant, Howard ''The New Politics of Race'' (2004)
* Winant, Howard and Michael Omi, Omi, Michael ''Racial Formation in the United States'' Routeledge (1986); Second Edition (1994).
*
* Wright W.D. (1998) ''"Racism Matters"'', Westport, CT: Praeger.
External links
Being a Black Male in Cuba
– By Lucia Lopez, ''Havana Times'' May 5, 2009.
Race, history and culture – Ethics – March 1996
– Extract of two articles by Claude Lévi-Strauss
Claude Lévi-Strauss (, ; 28 November 1908 – 30 October 2009) was a French anthropologist and ethnologist whose work was key in the development of the theories of structuralism and structural anthropology. He held the chair of Social Anthro ...
.
Race, Racism and the Law
– Information about race, racism and racial distinctions in the law.
RacismReview
– Created and maintained by American sociologists Joe Feagin, PhD and Jessie Daniels, PhD, provides a research-based analysis of racism.
The Impact of Racism on Child and Adolescent Health
{{Authority control
Racism,
Prejudice and discrimination by type
Politics and race
 In the 19th century, many scientists subscribed to the belief that the human population can be divided into races. The term ''racism'' is a noun describing the state of being racist, i.e., subscribing to the belief that the human population can or should be classified into races with differential abilities and dispositions, which in turn may motivate a political ideology in which rights and privileges are differentially distributed based on racial categories. The term "racist" may be an adjective or a noun, the latter describing a person who holds those beliefs. The origin of the root word "race" is not clear. Linguists generally agree that it came to the English language from
In the 19th century, many scientists subscribed to the belief that the human population can be divided into races. The term ''racism'' is a noun describing the state of being racist, i.e., subscribing to the belief that the human population can or should be classified into races with differential abilities and dispositions, which in turn may motivate a political ideology in which rights and privileges are differentially distributed based on racial categories. The term "racist" may be an adjective or a noun, the latter describing a person who holds those beliefs. The origin of the root word "race" is not clear. Linguists generally agree that it came to the English language from 
 Centuries of
Centuries of  Some scholars argue that in the US, earlier violent and aggressive forms of racism have evolved into a more subtle form of prejudice in the late 20th century. This new form of racism is sometimes referred to as "modern racism" and it is characterized by outwardly acting unprejudiced while inwardly maintaining prejudiced attitudes, displaying subtle prejudiced behaviors such as actions informed by attributing qualities to others based on racial stereotypes, and evaluating the same behavior differently based on the race of the person being evaluated. This view is based on studies of prejudice and discriminatory behavior, where some people will act ambivalently towards black people, with positive reactions in certain, more public contexts, but more negative views and expressions in more private contexts. This ambivalence may also be visible for example in hiring decisions where job candidates that are otherwise positively evaluated may be unconsciously disfavored by employers in the final decision because of their race. Some scholars consider modern racism to be characterized by an explicit rejection of stereotypes, combined with resistance to changing structures of discrimination for reasons that are ostensibly non-racial, an ideology that considers opportunity at a purely individual basis denying the relevance of race in determining individual opportunities and the exhibition of indirect forms of micro-aggression toward and/or avoidance of people of other races.
Some scholars argue that in the US, earlier violent and aggressive forms of racism have evolved into a more subtle form of prejudice in the late 20th century. This new form of racism is sometimes referred to as "modern racism" and it is characterized by outwardly acting unprejudiced while inwardly maintaining prejudiced attitudes, displaying subtle prejudiced behaviors such as actions informed by attributing qualities to others based on racial stereotypes, and evaluating the same behavior differently based on the race of the person being evaluated. This view is based on studies of prejudice and discriminatory behavior, where some people will act ambivalently towards black people, with positive reactions in certain, more public contexts, but more negative views and expressions in more private contexts. This ambivalence may also be visible for example in hiring decisions where job candidates that are otherwise positively evaluated may be unconsciously disfavored by employers in the final decision because of their race. Some scholars consider modern racism to be characterized by an explicit rejection of stereotypes, combined with resistance to changing structures of discrimination for reasons that are ostensibly non-racial, an ideology that considers opportunity at a purely individual basis denying the relevance of race in determining individual opportunities and the exhibition of indirect forms of micro-aggression toward and/or avoidance of people of other races.
 Racism existed during the 19th century as "
Racism existed during the 19th century as " Scientific racism fell strongly out of favor in the early 20th century, but the origins of fundamental human and societal differences are still researched within
Scientific racism fell strongly out of favor in the early 20th century, but the origins of fundamental human and societal differences are still researched within  Debates over the origins of racism often suffer from a lack of clarity over the term. Many use the term "racism" to refer to more general phenomena, such as
Debates over the origins of racism often suffer from a lack of clarity over the term. Many use the term "racism" to refer to more general phenomena, such as  After the
After the 
 While 19th-century racism became closely intertwined with nationalism, leading to the
While 19th-century racism became closely intertwined with nationalism, leading to the  However, during the 19th century, Western European colonial powers were involved in the suppression of the
However, during the 19th century, Western European colonial powers were involved in the suppression of the  In the United States in the early 19th century, the American Colonization Society was established as the primary vehicle for proposals to return black Americans to greater freedom and equality in Africa. The colonization effort resulted from a mixture of motives with its founder Henry Clay stating that "unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off". Racism spread throughout the New World in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Whitecapping, which started in Indiana in the late 19th century, soon spread throughout all of North America, causing many African laborers to flee from the land they worked on. In the US, during the 1860s, racist posters were used during election campaigns. In one of these racist posters (see above), a black man is depicted lounging idly in the foreground as one white man ploughs his field and another chops wood. Accompanying labels are: "In the sweat of thy face shalt thou eat thy bread", and "The white man must work to keep his children and pay his taxes." The black man wonders, "Whar is de use for me to work as long as dey make dese appropriations." Above in a cloud is an image of the "Freedman's Bureau! Negro Estimate of Freedom!" The bureau is pictured as a large domed building resembling the U.S. Capitol and is inscribed "Freedom and No Work". Its columns and walls are labeled, "Candy", "Rum, Gin, Whiskey", "Sugar Plums", "Indolence", "White Women", "Apathy", "White Sugar", "Idleness", and so on.
On June 5, 1873, Sir Francis Galton, distinguished English explorer and cousin of Charles Darwin, wrote in a letter to ''The Times'':
In the United States in the early 19th century, the American Colonization Society was established as the primary vehicle for proposals to return black Americans to greater freedom and equality in Africa. The colonization effort resulted from a mixture of motives with its founder Henry Clay stating that "unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off". Racism spread throughout the New World in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Whitecapping, which started in Indiana in the late 19th century, soon spread throughout all of North America, causing many African laborers to flee from the land they worked on. In the US, during the 1860s, racist posters were used during election campaigns. In one of these racist posters (see above), a black man is depicted lounging idly in the foreground as one white man ploughs his field and another chops wood. Accompanying labels are: "In the sweat of thy face shalt thou eat thy bread", and "The white man must work to keep his children and pay his taxes." The black man wonders, "Whar is de use for me to work as long as dey make dese appropriations." Above in a cloud is an image of the "Freedman's Bureau! Negro Estimate of Freedom!" The bureau is pictured as a large domed building resembling the U.S. Capitol and is inscribed "Freedom and No Work". Its columns and walls are labeled, "Candy", "Rum, Gin, Whiskey", "Sugar Plums", "Indolence", "White Women", "Apathy", "White Sugar", "Idleness", and so on.
On June 5, 1873, Sir Francis Galton, distinguished English explorer and cousin of Charles Darwin, wrote in a letter to ''The Times'':

 The Nazi party, which seized power in the German federal election, March 1933, 1933 German elections and maintained a dictatorship over much of Europe until the End of World War II in Europe, End of World War II on the European continent, deemed the Germans to be part of an Aryan "
The Nazi party, which seized power in the German federal election, March 1933, 1933 German elections and maintained a dictatorship over much of Europe until the End of World War II in Europe, End of World War II on the European continent, deemed the Germans to be part of an Aryan " During the Second Congo War, Congo Civil War (1998–2003), Pygmy people were hunted down like game animals and eaten. Both sides in the war regarded them as "subhuman" and some say their flesh can confer magical powers. UN human rights activists reported in 2003 that rebels had carried out acts of
During the Second Congo War, Congo Civil War (1998–2003), Pygmy people were hunted down like game animals and eaten. Both sides in the war regarded them as "subhuman" and some say their flesh can confer magical powers. UN human rights activists reported in 2003 that rebels had carried out acts of  The modern biological definition of race developed in the 19th century with scientific racist theories. The term ''scientific racism'' refers to the use of science to justify and support racist beliefs, which goes back to the early 18th century, though it gained most of its influence in the mid-19th century, during the New Imperialism period. Also known as academic racism, such theories first needed to overcome the Roman Catholic Church, Church's resistance to positivism, positivist accounts of history and its support of monogenism, the concept that all human beings were originated from the same ancestors, in accordance with creationist accounts of history.
These racist theories put forth on scientific hypothesis were combined with unilineal evolution, unilineal theories of social progress, which postulated the superiority of the European civilization over the rest of the world. Furthermore, they frequently made use of the idea of "
The modern biological definition of race developed in the 19th century with scientific racist theories. The term ''scientific racism'' refers to the use of science to justify and support racist beliefs, which goes back to the early 18th century, though it gained most of its influence in the mid-19th century, during the New Imperialism period. Also known as academic racism, such theories first needed to overcome the Roman Catholic Church, Church's resistance to positivism, positivist accounts of history and its support of monogenism, the concept that all human beings were originated from the same ancestors, in accordance with creationist accounts of history.
These racist theories put forth on scientific hypothesis were combined with unilineal evolution, unilineal theories of social progress, which postulated the superiority of the European civilization over the rest of the world. Furthermore, they frequently made use of the idea of " Works such as Arthur de Gobineau's ''An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races'' (1853–1855) may be considered one of the first theorizations of this new racism, founded on an essentialist notion of race, which opposed the former racial discourse, of Boulainvilliers for example, which saw in races a fundamentally historical reality, which changed over time. Gobineau, thus, attempted to frame racism within the terms of biological differences among humans, giving it the legitimacy of biology.
Gobineau's theories would be expanded in France by Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936)'s typology (anthropology), typology of races, who published in 1899 ''The Aryan and his Social Role'', in which he claimed that the white "Aryan race" "Cephalic index, dolichocephalic", was opposed to the "brachycephalic" race, of whom the "Jew" was the archetype. Vacher de Lapouge thus created a hierarchical classification of races, in which he identified the "''Nordic race, Homo europaeus'' (Teutonic, Protestant, etc.), the "''Homo alpinus''" (Auvergne (province), Auvergnat, Turkish people, Turkish, etc.), and finally the "''Homo mediterraneus''" (Naples, Neapolitan, Andalusia, Andalus, etc.) He assimilated races and social classes, considering that the French upper class was a representation of the ''Homo europaeus'', while the lower class represented the ''Homo alpinus''. Applying Galton's eugenics to his theory of races, Vacher de Lapouge's "selectionism" aimed first at achieving the annihilation of trade unionists, considered to be a "degenerate"; second, creating types of man each destined to one end, in order to prevent any contestation of labour conditions. His "anthroposociology" thus aimed at blocking
Works such as Arthur de Gobineau's ''An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races'' (1853–1855) may be considered one of the first theorizations of this new racism, founded on an essentialist notion of race, which opposed the former racial discourse, of Boulainvilliers for example, which saw in races a fundamentally historical reality, which changed over time. Gobineau, thus, attempted to frame racism within the terms of biological differences among humans, giving it the legitimacy of biology.
Gobineau's theories would be expanded in France by Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1854–1936)'s typology (anthropology), typology of races, who published in 1899 ''The Aryan and his Social Role'', in which he claimed that the white "Aryan race" "Cephalic index, dolichocephalic", was opposed to the "brachycephalic" race, of whom the "Jew" was the archetype. Vacher de Lapouge thus created a hierarchical classification of races, in which he identified the "''Nordic race, Homo europaeus'' (Teutonic, Protestant, etc.), the "''Homo alpinus''" (Auvergne (province), Auvergnat, Turkish people, Turkish, etc.), and finally the "''Homo mediterraneus''" (Naples, Neapolitan, Andalusia, Andalus, etc.) He assimilated races and social classes, considering that the French upper class was a representation of the ''Homo europaeus'', while the lower class represented the ''Homo alpinus''. Applying Galton's eugenics to his theory of races, Vacher de Lapouge's "selectionism" aimed first at achieving the annihilation of trade unionists, considered to be a "degenerate"; second, creating types of man each destined to one end, in order to prevent any contestation of labour conditions. His "anthroposociology" thus aimed at blocking  Evolutionary psychologists John Tooby and Leda Cosmides were puzzled by the fact that in the US, race is one of the three characteristics most often used in brief descriptions of individuals (the others are age and sex). They reasoned that natural selection would not have favoured the evolution of an instinct for using race as a classification, because for most of human history, humans almost never encountered members of other races. Tooby and Cosmides hypothesized that modern people use race as a proxy (rough-and-ready indicator) for coalition membership, since a better-than-random guess about "which side" another person is on will be helpful if one does not actually know in advance.
Their colleague Robert Kurzban designed an experiment whose results appeared to support this hypothesis. Using the memory confusion protocol, they presented subjects with pictures of individuals and sentences, allegedly spoken by these individuals, which presented two sides of a debate. The errors that the subjects made in recalling who said what indicated that they sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker of the same race as the "correct" speaker, although they also sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker "on the same side" as the "correct" speaker. In a second run of the experiment, the team also distinguished the "sides" in the debate by clothing of similar colors; and in this case the effect of racial similarity in causing mistakes almost vanished, being replaced by the color of their clothing. In other words, the first group of subjects, with no clues from clothing, used race as a visual guide to guessing who was on which side of the debate; the second group of subjects used the clothing color as their main visual clue, and the effect of race became very small.. The authors provide a summary and other comments at
Some research suggests that ethnocentric thinking may have actually contributed to the development of cooperation. Political scientists Ross Hammond and Robert Axelrod created a computer simulation wherein virtual individuals were randomly assigned one of a variety of skin colors, and then one of a variety of trading strategies: be color-blind, favor those of your own color, or favor those of other colors. They found that the ethnocentric individuals clustered together, then grew, until all the non-ethnocentric individuals were wiped out.
In ''The Selfish Gene'', evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins writes that "Blood-feuds and inter-clan warfare are easily interpretable in terms of W. D. Hamilton, Hamilton's kin selection, genetic theory." Dawkins writes that racial prejudice, while not evolutionarily adaptive, "could be interpreted as an irrational generalization of a kin-selected tendency to identify with individuals physically resembling oneself, and to be nasty to individuals different in appearance." Simulation-based experiments in evolutionary game theory have attempted to provide an explanation for the selection of ethnocentric-strategy phenotypes.
Despite support for evolutionary theories relating to an innate origin of racism, various studies have suggested racism is associated with lower intelligence and less diverse peer groups during childhood. A neuroimaging study on amygdala activity during racial matching activities found increased activity to be associated with adolescent age as well as less racially diverse peer groups, which the author conclude suggest a learned aspect of racism. A meta analysis of neuroimaging studies found amygdala activity correlated to increased scores on implicit measures of racial bias. It was also argued amygdala activity in response to racial stimuli represents increased threat perception rather than the traditional theory of the amygdala activity represented ingroup-outgroup processing. Racism has also been associated with lower childhood IQ in an analysis of 15,000 people in the UK.
Evolutionary psychologists John Tooby and Leda Cosmides were puzzled by the fact that in the US, race is one of the three characteristics most often used in brief descriptions of individuals (the others are age and sex). They reasoned that natural selection would not have favoured the evolution of an instinct for using race as a classification, because for most of human history, humans almost never encountered members of other races. Tooby and Cosmides hypothesized that modern people use race as a proxy (rough-and-ready indicator) for coalition membership, since a better-than-random guess about "which side" another person is on will be helpful if one does not actually know in advance.
Their colleague Robert Kurzban designed an experiment whose results appeared to support this hypothesis. Using the memory confusion protocol, they presented subjects with pictures of individuals and sentences, allegedly spoken by these individuals, which presented two sides of a debate. The errors that the subjects made in recalling who said what indicated that they sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker of the same race as the "correct" speaker, although they also sometimes mis-attributed a statement to a speaker "on the same side" as the "correct" speaker. In a second run of the experiment, the team also distinguished the "sides" in the debate by clothing of similar colors; and in this case the effect of racial similarity in causing mistakes almost vanished, being replaced by the color of their clothing. In other words, the first group of subjects, with no clues from clothing, used race as a visual guide to guessing who was on which side of the debate; the second group of subjects used the clothing color as their main visual clue, and the effect of race became very small.. The authors provide a summary and other comments at
Some research suggests that ethnocentric thinking may have actually contributed to the development of cooperation. Political scientists Ross Hammond and Robert Axelrod created a computer simulation wherein virtual individuals were randomly assigned one of a variety of skin colors, and then one of a variety of trading strategies: be color-blind, favor those of your own color, or favor those of other colors. They found that the ethnocentric individuals clustered together, then grew, until all the non-ethnocentric individuals were wiped out.
In ''The Selfish Gene'', evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins writes that "Blood-feuds and inter-clan warfare are easily interpretable in terms of W. D. Hamilton, Hamilton's kin selection, genetic theory." Dawkins writes that racial prejudice, while not evolutionarily adaptive, "could be interpreted as an irrational generalization of a kin-selected tendency to identify with individuals physically resembling oneself, and to be nasty to individuals different in appearance." Simulation-based experiments in evolutionary game theory have attempted to provide an explanation for the selection of ethnocentric-strategy phenotypes.
Despite support for evolutionary theories relating to an innate origin of racism, various studies have suggested racism is associated with lower intelligence and less diverse peer groups during childhood. A neuroimaging study on amygdala activity during racial matching activities found increased activity to be associated with adolescent age as well as less racially diverse peer groups, which the author conclude suggest a learned aspect of racism. A meta analysis of neuroimaging studies found amygdala activity correlated to increased scores on implicit measures of racial bias. It was also argued amygdala activity in response to racial stimuli represents increased threat perception rather than the traditional theory of the amygdala activity represented ingroup-outgroup processing. Racism has also been associated with lower childhood IQ in an analysis of 15,000 people in the UK.
 Legislative state racism is known to have been enforced by the National Party (South Africa), National Party of South Africa during its Apartheid regime between 1948 and 1994. Here, a series of Apartheid legislation in South Africa, Apartheid legislation was passed through the legal systems to make it legal for white South Africans to have rights which were superior to those of non-white South Africans. Non-white South Africans were not allowed involvement in any governing matters, including voting; access to quality healthcare; the provision of basic services, including clean water; electricity; as well as access to adequate schooling. Non-white South Africans were also prevented from accessing certain public areas, from using certain public transportation, and were required to live only in certain designated areas. Non-white South Africans were taxed differently than white South Africans and they were also required to carry on them at all times additional documentation, which later became known as "dom passes", to certify their non-white South African citizenship. All of these legislative racial laws were abolished through a series of equal
Legislative state racism is known to have been enforced by the National Party (South Africa), National Party of South Africa during its Apartheid regime between 1948 and 1994. Here, a series of Apartheid legislation in South Africa, Apartheid legislation was passed through the legal systems to make it legal for white South Africans to have rights which were superior to those of non-white South Africans. Non-white South Africans were not allowed involvement in any governing matters, including voting; access to quality healthcare; the provision of basic services, including clean water; electricity; as well as access to adequate schooling. Non-white South Africans were also prevented from accessing certain public areas, from using certain public transportation, and were required to live only in certain designated areas. Non-white South Africans were taxed differently than white South Africans and they were also required to carry on them at all times additional documentation, which later became known as "dom passes", to certify their non-white South African citizenship. All of these legislative racial laws were abolished through a series of equal