
Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a
human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of sh ...
which is distributed in a large region in
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
, extending from
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
and
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
to southern
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
.
While R1a originated c. 22,000 to 25,000 years ago, its
subclade
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup.
Naming convention
Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate syst ...
M417 (R1a1a1) diversified c. 5,800 years ago. The place of origin of the subclade plays a role in the debate about the origins of
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from t ...
.
The SNP mutation R-M420 was discovered after R-M17 (R1a1a), which resulted in a reorganization of the lineage in particular establishing a new
paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers.
In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed ...
(designated R-M420*) for the relatively rare lineages which are not in the R-SRY10831.2 (R1a1) branch leading to R-M17.
Origins
R1a origins
The split of R1a (M420) is computed to c. 22,000 or 25,000 years ago, which is the time of the last glacial maximum. A 2014 study by Peter A. Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eurasia, concluded that there was "a compelling case for the Middle East, possibly near present-day Iran, as the geographic origin of hg R1a". The ancient DNA record has shown the first R1a during the
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
in
Eastern Hunter-Gatherers
In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers ...
(from Eastern Europe), and the earliest case of R* among
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to the ...
s, from which the Eastern Hunter-Gatherers predominantly derive their ancestry.
Diversification of R1a1a1 (M417) and ancient migrations
According to , the downstream R1a-M417 subclade diversified into Z282 and Z93 circa 5,800 years ago "in the vicinity of Iran and Eastern Turkey". Even though R1a occurs as a Y-chromosome haplogroup among various languages such as
Slavic and
Indo-Iranian, the question of the origins of R1a1a is relevant to the
ongoing debate concerning the of the
Proto-Indo-European people
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from t ...
, and may also be relevant to the origins of the
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
. R1a shows a strong correlation with
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
of
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and
Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
,
Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europe. ...
and to some extent
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
being most prevalent in
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
,
West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
. In Europe, Z282 is prevalent particularly while in Asia Z93 dominates. The connection between Y-DNA R-M17 and the spread of Indo-European languages was first noted by T. Zerjal and colleagues in 1999.
Proposed steppe dispersal of R1a1a
proposed
Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
origins, and a postglacial spread of the R1a1 haplogroup during the
Late Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, subsequently magnified by the expansion of the Kurgan culture into Europe and eastward. Spencer Wells proposes Central Asian origins, suggesting that the distribution and age of R1a1 points to an ancient migration corresponding to the spread by the
Kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asi ...
people in their expansion from the
Eurasian steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistri ...
. According to , R1a1a diversified in the Eurasian Steppes or the Middle East and Caucasus region:
Three genetic studies in 2015 gave support to the
Kurgan theory of Gimbutas regarding the
Indo-European Urheimat
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of ...
. According to those studies, haplogroups
R1b and R1a, now the most common in Europe (R1a is also common in South Asia) would have expanded from the Pontic–Caspian steppes, along with the Indo-European languages; they also detected an autosomal component present in modern Europeans which was not present in Neolithic Europeans, which would have been introduced with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as Indo-European languages.
noted that R1a in South Asia most "likely spread from a single
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
n source pool, there do seem to be at least three and probably more R1a founder clades within the
Subcontinent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
, consistent with multiple waves of arrival." According to Martin P. Richards, co-author of , the prevalence of R1a in India was "very powerful evidence for a substantial Bronze Age migration from central Asia that most likely brought Indo-European speakers to India."
Proposed South Asian origins
Kivisild et al. (2003) have proposed either South or
West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, while see support for both South and Central Asia. Sharma et al.(2009) showcased the existence of R1a in India beyond 18,000 years to possibly 44,000 years in origin.
South Asian populations have the highest
STR diversity within R1a1a, and subsequent older
TMRCA
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are Common descent, ...
datings, and R1a1a is present among both higher (
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
) castes and lower castes, although the frequency is higher among Brahmin castes. Nevertheless, the oldest TMRCA datings of the R1a haplogroup occur in the
Saharia tribe, a scheduled caste of the Bundelkhand region. From these findings some researchers have concluded that R1a1a originated in South Asia, excluding a more recent, yet minor, genetic influx from Indo-European migrants in northwestern regions such as Afghanistan, Balochistan, Punjab, and Kashmir.
However, this diversity, and the subsequent older TMRCA-datings, can also be explained by the historically high population numbers, which increases the likelihood of diversification and
microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. ...
variation.
According to Sengupta et al. (2006), "
1a1 and R2could have actually arrived in southern India from a southwestern Asian source region multiple times." However, Sengupta also described in this article:
This suggests that the origins of paternal haplogroup R1a point to the Indian subcontinent and not Central Asia.
Proposed Yamnaya origins


David Anthony considers the
Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура literal translation, lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to ea ...
to be the
Indo-European Urheimat
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of ...
. According to , a massive migration from the Yamnaya culture northwards took place c. 2,500 BCE, accounting for 75% of the genetic ancestry of the
Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a va ...
, noting that R1a and R1b may have "spread into Europe from the
East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
after 3,000 BCE". Yet, all their seven Yamnaya samples belonged to the
R1b-M269 subclade, but no R1a1a has been found in their Yamnaya samples. This raises the question where the R1a1a in the Corded Ware culture came from, if it was not from the Yamnaya culture.
According to Marc Haber, the absence of haplogroup R1a-M458 in Afghanistan does not support a Pontic-Caspian steppe origin for the R1a lineages in modern Central Asian populations. According to
Leo Klejn
Lev Samuilovich Kleyn (; 1 July 1927 – 7 November 2019), better known in English as Leo Klejn, was a Russian Archaeology, archaeologist, anthropologist and philologist.
Early life
Klejn was born in Vitebsk, Belarus, to two Jewish physicians, ...
, the absence of haplogroup R1a in Yamnaya remains (despite its presence in Eneolithic Samara and
Eastern Hunter Gatherer
In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers of ...
populations) makes it unlikely that Europeans inherited haplogroup R1a from Yamnaya. Archaeologist
Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, (born 10 December 1939), known as Barry Cunliffe, is a British archaeologist and academic. He was Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford from 1972 to 2007. Since 2007, he has been an Emeri ...
has said that the absence of haplogroup R1a in Yamnaya specimens is a major weakness in Haak's proposal that R1a has a Yamnaya origin.
do argue for a Yamnaya origin of R1a1a in the Corded Ware culture, noting that several publications point to the presence of R1a1 in the
Comb Ware culture.
Proposed Transcaucasia and West Asian origins and possible influence on Indus Valley Civilization
found that part of the Yamnaya ancestry derived from the Middle East and that neolithic techniques probably arrived at the Yamnaya culture from the
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The
Rössen culture
The Rössen culture or Roessen culture (german: Rössener Kultur) is a Central European culture of the middle Neolithic (4,600–4,300 BC).
It is named after the necropolis of Rössen (part of Leuna, in the Saalekreis district, Saxony-Anhalt). Th ...
(4,600–4,300 BC), which was situated on
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and predates the Corded Ware culture, an old subclade of R1a, namely L664, can still be found.
Part of the South Asian genetic ancestry derives from west Eurasian populations, and some researchers have implied that Z93 may have come to
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
via
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and expanded there during the
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
.
proposed that the roots of Z93 lie in West Asia, and proposed that "Z93 and L342.2 expanded in a southeasterly direction from
Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
into
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
", noting that such an expansion is compatible with "the archeological records of eastward expansion of
West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
n populations in the 4th millennium BCE culminating in the so-called
Kura-Araxes migrations in the post-
Uruk IV period." Yet, Lazaridis noted that sample I1635 of , their
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
n Kura-Araxes sample, carried Y-haplogroup R1b1-M415(xM269) (also called R1b1a1b-CTS3187).
According to the diversification of Z93 and the "early urbanization within the Indus Valley ... occurred at
,600 years agoand the geographic distribution of R1a-M780 (Figure 3d) may reflect this." note that "striking expansions" occurred within R1a-Z93 at c. 4,500–4,000 years ago, which "predates by a few centuries the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation."
However, according to , steppe pastoralists are a likely source for R1a in India.
Phylogeny
The R1a family tree now has three major levels of branching, with the largest number of defined subclades within the dominant and best known branch, R1a1a (which will be found with various names such as "R1a1" in relatively recent but not the latest literature).
Topology
The topology of R1a is as follows (codes
n brackets
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
non-isogg codes):
Tatiana et al. (2014) "rapid diversification process of
K-M526 likely occurred in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, with subsequent westward expansions of the ancestors of haplogroups
R and
Q."
*
P P295/PF5866/S8 (also known as
K2b2).
*
R (R-M207)
**R*
**
R1 (R-M173)
***R1*
***R1a (M420)
(Eastern Europe, Asia)
****R1a*
****
R1a1
Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to southern Siberia and South Asia.
While R1a originated c. 22,000 to 2 ...
(M459/PF6235,
SRY1532.2/SRY10831.2
)
*****R1a1 (M459)
*****R1a1a (M17, M198)
******R1a1a1 (M417, page7)
*******R1a1a1a (CTS7083/L664/S298)
*******R1a1a1b (S224/Z645, S441/Z647)
********R1a1a1b1 (PF6217/S339/Z283)
*********R1a1a1b1a (Z282)
(Z282)
**********R1a1a1b1a1
(M458)
(M458)
***********
1a1a1g*ref name="snpedia"/>
***********
1a1a1g1(M334)
***********R1a1a1b1a1a (L260/S222)
ref name="snpedia"/>
**********R1a1a1b1a2
(S466/Z280, S204/Z91)
***********R1a1a1b1a2a
***********R1a1a1b1a2b (CTS1211)
(M558)
-CTS1211(V2803/CTS3607/S3363/M558, CTS1211/S3357, Y34/FGC36457)
************R1a1a1b1a2b3* (M417+, Z645+, Z283+, Z282+, Z280+, CTS1211+, CTS3402, Y33+, CTS3318+, Y2613+) (Gwozdz's Cluster K)
************R1a1a1b1a2b3a (L365/S468)
**********R1a1a1b1a3 (Z284)
(Z284)
********R1a1a1b2 (F992/S202/Z93)
(Z93, M746)
*********R1a1a1b2a (F3105/S340/Z94, L342.2/S278.2)
(Z95) R-Z94 (Z94/F3105/S340, Z95/F3568)
**********R-Z2124 (Z2121/S3410, Z2124)
***********
1a1b2a*(Z2125)
************
1a1b2a*(M434)
1a1a1f(M434)
************
1a1b2a*(M204)
**********
1a1b2a1*(M560)
**********
1a1b2a2*(M780, L657) (India)
**********
1a1b2a3*(Z2122, M582)
*******
1a1a1c(M64.2, M87, M204)
*******
1a1a1d(P98)
********
1a1a1d2a*******
1a1a1e(PK5)
***
R1b (M343) (Western Europe)
**
R2 (India)
Haplogroup R
R-M173 (R1)
R1a is distinguished by several unique markers, including the M420 mutation. It is a subclade of
Haplogroup R-M173
Haplogroup R1, or R-M173, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. A primary subclade of Haplogroup R (R-M207), it is defined by the SNP M173. The other primary subclade of Haplogroup R is Haplogroup R2 (R-M479).
Males carrying R-M173 in modern populat ...
(previously called R1). R1a has the sister-subclades
Haplogroup R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central A ...
-M343, and the paragroup R-M173*.
R-M420 (R1a)
R-M420, defined by the mutation M420, has two branches: R-SRY1532.2, defined by the mutation SRY1532.2, which makes up the vast majority; and R-M420*, the
paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers.
In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed ...
, defined as M420 positive but SRY1532.2 negative. (In the 2002 scheme, this SRY1532.2 negative minority was one part of the relatively rare group classified as the paragroup R1*.) Mutations understood to be equivalent to M420 include M449, M511, M513, L62, and L63.
Only isolated samples of the new
paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers.
In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed ...
R-M420* were found by Underhill 2009, mostly in the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
: 1/121
Omanis
Omanis ( ar, الشعب العماني) are the nationals of Sultanate of Oman, located in the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Omanis have inhabited the territory that is now Oman. In the eighteenth century, an alliance of traders a ...
, 2/150
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ians, 1/164 in the
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (The Middle East). It is located at th ...
, and 3/612 in
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Testing of 7224 more males in 73 other Eurasian populations showed no sign of this category.
This paragroup is now known as R1a2 (R-YP4141). It then has two branches R1a2a (R-YP5018) and R1a2b (R-YP4132).
R-SRY1532.2 (R1a1)
R1a1 is defined by SRY1532.2 or SRY10831.2 (understood to always include SRY10831.2, M448, L122, M459, and M516). This family of lineages is dominated by M17 and M198. In contrast,
paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers.
In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed ...
R-SRY1532.2* lacks either the M17 or M198 markers.
The R-SRY1532.2* paragroup is apparently less rare than R1*, but still relatively unusual, though it has been tested in more than one survey. Underhill et al. (2009) reported 1/51 in
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, 3/305 in
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, 1/57
Greek Macedonians
Macedonians ( el, Μακεδόνες, ''Makedónes''), also known as Greek Macedonians or Macedonian Greeks, are a regional and historical population group of ethnic Greeks, inhabiting or originating from the Greek region of Macedonia, in Nor ...
, 1/150 Iranians, 2/734 ethnic
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, and 1/141
Kabardians
The Kabardians ( Highland Adyghe: Къэбэрдей адыгэхэр; Lowland Adyghe: Къэбэртай адыгэхэр; russian: Кабардинцы) or Kabardinians are one of the twelve major Circassian tribes, representing one of th ...
. reported R-SRY1532.2* for 1/15
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
Rajput samples.
R-M17/M198 (R1a1a)
The following SNPs are associated with R1a1a:
R-M417 (R1a1a1)
R1a1a1 (R-M417) is the most widely found subclade, in two variations which are found respectively in Europe (R1a1a1b1 (R-Z282) (
1a1a1a*(R-Z282) (Underhill 2014)) and Central and South Asia (R1a1a1b2 (R-Z93) (
1a1a2*(R-Z93) Underhill 2014)).
R-Z282 (R1a1a1b1a) (Eastern Europe)
This large subclade appears to encompass most of the R1a1a found in Europe.
* R1a1a1b1a
1a1a1a* (Underhill (2014))(R-Z282*) occurs in northern Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia at a frequency of c. 20%.
* R1a1a1b1a3
1a1a1a1 (Underhill (2014))(R-Z284) occurs in Northwest Europe and peaks at c. 20% in Norway.
* R1a1a1c (M64.2, M87, M204) is apparently rare: it was found in 1 of 117 males typed in southern Iran.
=R-M458 (R1a1a1b1a1)
=
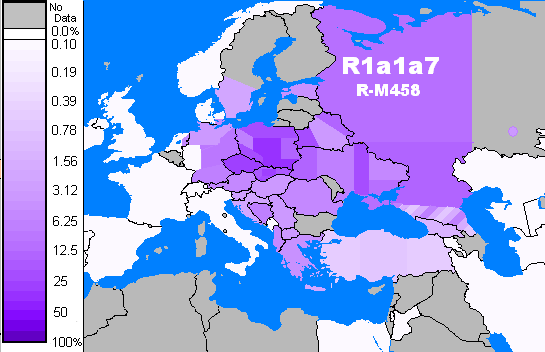
R-M458 is a mainly
Slavic SNP, characterized by its own mutation, and was first called ''cluster N.'' Underhill et al. (2009) found it to be present in modern European populations roughly between the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
catchment and the
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
and traced it to "a founder effect that ... falls into the early Holocene period, 7.9±2.6 KYA." M458 was found in one skeleton from a 14th-century grave field in
Usedom
Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It is north of the Szczecin ...
, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. The paper by Underhill et al. (2009) also reports a surprisingly high frequency of M458 in some
Northern Caucasian populations (for example 27.5% among
Karachays
The Karachays ( krc, Къарачайлыла, Qaraçaylıla or таулула, , 'Mountaineers') are an indigenous Caucasian Turkic ethnic group in the North Caucasus. They speak Karachay-Balkar, a Turkic language. They are mostly situated ...
and 23.5% among
Balkars
The Balkars ( krc, Малкъарлыла, Malqarlıla or Таулула, , 'Mountaineers') are a Turkic people of the Caucasus region, one of the titular populations of Kabardino-Balkaria. Their Karachay-Balkar language is of the Ponto-Casp ...
, 7.8% among
Karanogays and 3.4% among
Abazas).
R-L260 (R1a1a1b1a1a)
R1a1a1b1a1a (R-L260), commonly referred to as
West Slavic or
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
, is a subclade of the larger parent group R-M458, and was first identified as an STR cluster by . In 2010 it was verified to be a haplogroup identified by its own mutation (SNP). It apparently accounts for about 8% of Polish men, making it the most common subclade in Poland. Outside of Poland it is less common. In addition to Poland, it is mainly found in the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, and is considered "clearly West Slavic". The founding ancestor of R-L260 is estimated to have lived between 2000 and 3000 years ago, i.e. during the
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, with significant population expansion less than 1,500 years ago.
R-M334
R-M334 (
1a1a1g1 a subclade of
1a1a1g(M458)
c.q. R1a1a1b1a1 (M458)
) was found by Underhill et al. (2009) only in one Estonian man and may define a very recently founded and small clade.
=R1a1a1b1a2 (S466/Z280, S204/Z91)
=
R1a1a1b1a2b3* (Gwozdz's Cluster K)
R1a1a1b1a2b3* (M417+, Z645+, Z283+, Z282+, Z280+, CTS1211+, CTS3402, Y33+, CTS3318+, Y2613+) (Gwozdz's Cluster K)
is a STR based group that is R-M17(xM458). This cluster is common in Poland but not exclusive to Poland.
R1a1a1b1a2b3a (R-L365)
R1a1a1b1a2b3a (R-L365)
was early called ''Cluster G''.
R1a1a1b2 (R-Z93) (Asia)
This large subclade appears to encompass most of the R1a1a found in Asia, being related to
Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expla ...
(including
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved f ...
,
Indo-Aryan migrations
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
and so on).
* R-Z93* or R1a1a1b2* (R1a1a2* in Underhill (2014)) is most common (>30%) in the South Siberian Altai region of Russia, cropping up in Kyrgyzstan (6%) and in all Iranian populations (1-8%).
* R-Z2125 occurs at highest frequencies in Kyrgyzstan and in Afghan Pashtuns (>40%). At a frequency of >10%, it is also observed in other Afghan ethnic groups and in some populations in the Caucasus and Iran.
** R-M434 is a subclade of Z2125. It was detected in 14 people (out of 3667 people tested), all in a restricted geographical range from
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
to
Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
. This likely reflects a recent mutation event in Pakistan.
* R-M560 is very rare and was only observed in four samples: two Burushaski speakers (north Pakistan), one Hazara (Afghanistan), and one Iranian Azerbaijani.
* R-M780 occurs at high frequency in South Asia: India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and the Himalayas. The group also occurs at >3% in some Iranian populations and is present at >30% in Roma from Croatia and Hungary.
Geographic distribution of R1a1a

Pre-Historical
In Mesolithic Europe, R1a is characteristic of
Eastern Hunter-Gatherer
In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers of ...
s (EHGs). A male EHG of the
Veretye culture
Veretye (russian: Веретье) is a rural locality (a village) in Prigorodnoye Rural Settlement, Sokolsky District, Vologda Oblast, Russia. The population was 13 as of 2002.
Geography
Veretye is located 15 km southeast of Sokol
The S ...
buried at
Peschanitsa
Peschanitsa (russian: Песчаница) is a rural locality (a village) in Cheryomushskoye Rural Settlement of Kotlassky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. The population was 12 as of 2010.
Geography
Peschanitsa is located 18 km south of Ko ...
near
Lake Lacha
Lake Lacha (russian: Ла́ча, Ла́че) is a freshwater lake, located in the south of Kargopolsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast in Russia, south of the town of Kargopol. It is the largest lake in Arkhangelsk Oblast, with a surface area of ...
in
Arkhangelsk Oblast
Arkhangelsk Oblast (russian: Арха́нгельская о́бласть, ''Arkhangelskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It includes the Arctic Ocean, Arctic archipelagos of Franz Josef Land ...
, Russia c. 10,700 BCE was found to be a carrier of the paternal haplogroup R1a5-YP1301 and the maternal haplogroup
U4a. A Mesolithic male from
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
c. 8,800 BCE to 7950 BCE has been found to be carrying haplogroup R1a. A
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
male buried at
Deriivka c. 7000 BCE to 6700 BCE carried the paternal haplogroup R1a and the maternal
U5a2a. Another male from Karelia from c. 5,500 to 5,000 BC, who was considered an EHG, carried haplogroup R1a. A male from the
Comb Ceramic culture
The Comb Ceramic culture or Pit-Comb Ware culture, often abbreviated as CCC or PCW, was a northeast European culture characterised by its Pit–Comb Ware. It existed from around 4200 BCE to around 2000 BCE. The bearers of the Comb Ceramic cultu ...
in
Kudruküla
Kudruküla is a village in Narva-Jõesuu, Ida-Viru County in northeastern Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across ...
c. 5,900 BCE to 3,800 BCE has been determined to be a carrier of R1a and the maternal
U2e1. According to archaeologist David Anthony, the paternal
R1a-Z93 was found at Alexandria,
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
c. 4000 BCE,
Sredny Stog culture
The Sredny Stog culture (, romanized: ''Serednʹostohivsʹka kulʹtura'') is a pre-Kurgan archaeological culture from the 5th millennium BC. It is named after the Russian term for the Dnieper river islet of today's Seredny Stih, Ukraine, where i ...
, "the earliest known sample to show the genetic adaptation to lactase persistence (13910-T)." R1a has been found in the
Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a va ...
, in which it is predominant. Examined males of the Bronze Age
Fatyanovo culture
Fatyanovo (russian: Фатьяново) is a rural locality (a village) in Klyazminskoye Rural Settlement, Kovrovsky District, Vladimir Oblast, Russia. The population was 4 as of 2010.
Geography
Fatyanovo is located 45 km east of Kovrov
...
belong entirely to R1a, specifically subclade R1a-Z93.
Haplogroup R1a has later been found in ancient fossils associated with the
Urnfield culture
The Urnfield culture ( 1300 BC – 750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and p ...
; as well as the burial of the remains of the
Sintashta
Sintashta (russian: Синташта́) is an archaeological site in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the remains of a fortified settlement dating to the Bronze Age, ''c''. 2800–1600 BC, and is the type site of the Sintashta culture. The site ha ...
,
Andronovo, the
Pazyryk,
Tagar,
Tashtyk, and
Srubnaya cultures, the inhabitants of ancient
Tanais
Tanais ( el, Τάναϊς ''Tánaïs''; russian: Танаис) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in the Don River (Russia), Don river delta, called the Maeotian Swamp, Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana ...
, in the
Tarim mummies
The Tarim mummies are a series of mummies discovered in the Tarim Basin in present-day Xinjiang, China, which date from 1800 BC to the first centuries BC, with a new group of individuals recently dated to between c. 2100 and 1700 BC.School of Li ...
, and the aristocracy of
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
. The skeletal remains of a father and his two sons, from an archaeological site discovered in 2005 near Eulau (in
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it the ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
) and dated to about 2600 BCE, tested positive for the Y-SNP marker SRY10831.2. The
Ysearch
A Y-STR is a short tandem repeat (STR) on the Y-chromosome. Y-STRs are often used in forensics, paternity, and genealogical DNA testing.
Y-STRs are taken specifically from the male Y chromosome. These Y-STRs provide a weaker analysis than autosoma ...
number for the Eulau remains is 2C46S. The ancestral clade was thus present in Europe at least 4600 years ago, in association with one site of the widespread
Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a va ...
.
Historical to recent Europe
In Europe, the R1a1 sub-clade is found at highest levels among peoples of
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
an descent, with results ranging from 35% to 65% among
Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, c ...
,
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
,
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
,
Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
,
western Ukrainians (particularly
Rusyns
Rusyns (), also known as Carpatho-Rusyns (), or Rusnaks (), are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic languages, East Slavi ...
),
Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
,
Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians ( ro, moldoveni , Moldovan Cyrillic: молдовень), are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and the largest ethnic group of the Republic of Moldova (75.1% of the population as of 2014) and a sign ...
, and
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
. In the
Baltics
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
, R1a1a frequencies decrease from Lithuania (45%) to Estonia (around 30%).
There is a significant presence in peoples of
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
n descent, with highest levels in
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, where between 20 and 30% of men are in R1a1a.
Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
s and
Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
may have also carried the R1a1a lineage further out, accounting for at least part of the small presence in the
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, and
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. In
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, Haplogroup R1a1a averages between 20 and 30%, with a peak in
Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, c ...
at 31.3%, it.
In Southern Europe R1a1a is not common, but significant levels have been found in pockets, such as in the
Pas Valley
Valles Pasiegos is an administrative ''comarca'' in Cantabria, Spain. It is formed by the valleys of the Pas and Miera rivers, each one being a natural ''comarca'' of its own.
History
In the whole valley, the repopulation allowed by the found ...
in Northern
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, areas of
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, and
Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
in
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
. The
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
shows wide variation between areas with significant levels of R1a1a, for example 36–39% in
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, 27–34% in
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
,
and over 30% in
Greek Macedonia
Macedonia (; el, Μακεδονία, Makedonía ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and Greek geographic region, with a population of 2.36 million in 2020. It is ...
, but less than 10% in
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
,
Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
and parts of
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
south of Olympus gorge.
R1a is virtually composed only of the Z284 subclade in
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
. In Slovenia, the main subclade is Z282 (Z280 and M458), although the Z284 subclade was found in one sample of a Slovenian. There is a negligible representation of Z93 in each region other than Turkey.
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic langu ...
and
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
are characterized by a high frequency of the subclade M458 and a low Z92, a subclade of Z280. Hundreds of Slovenian samples and Czechs lack the Z92 subclade of Z280, while Poles, Slovaks, Croats and Hungarians only show a very low frequency of Z92. The
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
,
East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert H ...
,
Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Bulgarians and Romanians demonstrate a ratio Z280>M458 and a high, up to a prevailing share of Z92. Balts and East Slavs have the same subclades and similar frequencies in a more detailed phylogeny of the subclades. The Russian geneticist Oleg Balanovsky speculated that there is a predominance of the assimilated pre-Slavic substrate in the genetics of East and West Slavic populations, according to him the common genetic structure which contrasts East Slavs and Balts from other populations may suggest the explanation that the pre-Slavic substrate of the East Slavs consisted most significantly of Baltic-speakers, which at one point predated the Slavs in the cultures of the
Eurasian steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistri ...
according to archaeological and toponymic references.
Asia
Central Asia
found R1a1a in 64% of a sample of the Tajiks of Tajikistan and 63% of a sample of the Kyrgyz people, Kyrgyz of Kyrgyzstan.
found R1a1a-M17 in 26.0% (53/204) of a set of samples from Afghanistan, including 60% (3/5) of a sample of Nuristani people, Nuristanis, 51.0% (25/49) of a sample of Pashtuns, 30.4% (17/56) of a sample of Tajiks, 17.6% (3/17) of a sample of Uzbeks, 6.7% (4/60) of a sample of Hazaras, and in the only sampled Turkmen individual.
found R1a1a-M198/M17 in 56.3% (49/87) of a pair of samples of Pashtuns from Afghanistan (including 20/34 or 58.8% of a sample of Pashtuns from Baghlan Province, Baghlan and 29/53 or 54.7% of a sample of Pashtuns from Kunduz Province, Kunduz), 29.1% (37/127) of a pool of samples of Uzbeks from Afghanistan (including 28/94 or 29.8% of a sample of Uzbeks from Jawzjan Province, Jawzjan, 8/28 or 28.6% of a sample of Uzbeks from Sar-e Pol Province, Sar-e Pol, and 1/5 or 20% of a sample of Uzbeks from Balkh Province, Balkh), 27.5% (39/142) of a pool of samples of Tajiks from Afghanistan (including 22/54 or 40.7% of a sample of Tajiks from Balkh Province, Balkh, 9/35 or 25.7% of a sample of Tajiks from Takhar Province, Takhar, 4/16 or 25.0% of a sample of Tajiks from Samangan Province, Samangan, and 4/37 or 10.8% of a sample of Tajiks from Badakhshan Province, Badakhshan), 16.2% (12/74) of a sample of Turkmens from Jawzjan Province, Jawzjan, and 9.1% (7/77) of a pair of samples of Hazara people, Hazara from Afghanistan (including 7/69 or 10.1% of a sample of Hazara from Bamyan Province, Bamiyan and 0/8 or 0% of a sample of Hazara from Balkh Province, Balkh).
found R1a1-SRY10831.2 in 30.0% (12/40) of a sample of Tajiks from Tajikistan.
found R1a-M198 in 6.03% (78/1294) of a set of samples of Kazakhs from Kazakhstan. R1a-M198 was observed with greater than average frequency in the study's samples of the following Kazakh tribes: 13/41 = 31.7% of a sample of Suan, 8/29 = 27.6% of a sample of Oshaqty, 6/30 = 20.0% of a sample of Qozha, 4/29 = 13.8% of a sample of Qypshaq, 1/8 = 12.5% of a sample of Tore, 9/86 = 10.5% of a sample of Jetyru, 4/50 = 8.0% of a sample of Argyn, 1/13 = 7.7% of a sample of Shanyshqyly, 8/122 = 6.6% of a sample of Alimuly, 3/46 = 6.5% of a sample of Alban. R1a-M198 also was observed in 5/42 = 11.9% of a sample of Kazakhs of unreported tribal affiliation.
South Asia
In South Asia, R1a1a has often been observed in a number of demographic groups.
In
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, high frequencies of this haplogroup is observed in Bengali Brahmins, West Bengal Brahmins (72%) to the east, Lohana, Gujarat Lohanas (60%) to the west, Khatris (67%) in the north and Iyengar, Iyengar Brahmins (31%) in the south. It has also been found in several South Indian Dravidian languages, Dravidian-speaking Adivasis including the Chenchu (26%) and the Valmikis of Andhra Pradesh, Kota people (India), Kota (22.58%) and the Kallar(caste), Kallar of Tamil Nadu suggesting that R1a1a is widespread in Tribal Southern Indians.
Besides these, studies show high percentages in regionally diverse groups such as Meitei people, Manipuris (50%) to the extreme North East and among Punjabis (47%) to the extreme North West.
In
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
it is found at 71% among the Mohana (tribe), Mohanna tribe in Sindh province to the south and 46% among the Balti people, Baltis of Gilgit-Baltistan to the north. Among the Sinhalese people, Sinhalese of Sri Lanka, 23% were found to be R1a1a (R-SRY1532) positive. Hindus of Chitwan District in the Terai region Nepal show it at 69%.
East Asia
The frequency of R1a1a is comparatively low among some Turkic languages, Turkic-speaking groups like Yakuts, yet levels are higher (19 to 28%) in certain Turkic or Mongolic languages, Mongolic-speaking groups of Northwestern China, such as the Bonans, Bonan, Dongxiang people, Dongxiang, Salar people, Salar, and Uyghur people, Uyghurs.
A Chinese paper published in 2018 found R1a-Z94 in 38.5% (15/39) of a sample of Keriyalik Uyghurs from Darya Boyi / Darya Boye Village, Yutian County, Xinjiang, Yutian County, Xinjiang (于田县达里雅布依乡), R1a-Z93 in 28.9% (22/76) of a sample of Dolan people, Dolan Uyghurs from Horiqol township, Awat County, Xinjiang (阿瓦提县乌鲁却勒镇), and R1a-Z93 in 6.3% (4/64) of a sample of Loplik Uyghurs from Karquga / Qarchugha Village, Yuli County, Xinjiang (尉犁县喀尔曲尕乡). R1a(xZ93) was observed only in one of 76 Dolan Uyghurs. Note that Darya Boyi Village is located in a remote oasis formed by the Keriya River in the Taklamakan Desert. A 2011 Y-DNA study found Y-dna R1a1 in 10% of a sample of southern Hui people from Yunnan, 1.6% of a sample of Tibetan people from Xizang (Tibet Autonomous Region), 1.6% of a sample of Xibe people from Xinjiang, 3.2% of a sample of northern Hui from Ningxia, 9.4% of a sample of Hazak (Kazakhs in China, Kazakhs) from Xinjiang, and rates of 24.0%, 22.2%, 35.2%, 29.2% in 4 different samples of Uyghurs from Xinjiang, 9.1% in a sample of Mongols in China, Mongols from Inner Mongolia, 10% of a sample of Northern Han Chinese from Gansu and 8.9% of a sample of Northern Han from western Henan. A different subclade of R1 was also found in 1.5% of a sample of northern Hui from Ningxia. in the same study there were no cases of R1a detected at all in 6 samples of Han Chinese in Yunnan, 1 sample of Han in Guangxi, 5 samples of Han in Guizhou, 2 samples of Han in Guangdong, 2 samples of Han in Fujian, 2 samples of Han in Zhejiang, 1 sample of Han in Shanghai, 1 samples of Han in Jiangxi, 2 samples of Han in Hunan, 1 sample of Han in Hubei, 2 samples of Han in Sichuan, 1 sample of Han in Chongqing, 3 samples of Han in Shandong, 5 samples of Han in Gansu, 3 samples of Han in Jilin and 2 samples of Han in Heilongjiang. In a 2014 paper, R1a1a has been detected in 1.8% (2/110) of Chinese samples. These two samples (R-M17, R-M198, R-M434, R-M458 for both) belonged to Han Chinese, Han individuals from Fujian and Shanxi provinces. 40% of Salars, 45.2% of Tajiks of Xinjiang, 54.3% of Dongxiang, 60.6% of Tatars in China, Tatars and 68.9% of Kyrgyz in China, Kyrgyz in Xinjiang in northwestern China tested in one sample had R1a1-M17. Bao'an (Bonan) had the most haplogroup diversity of 0.8946±0.0305 while the other ethnic minorities in northwestern China had a high haplogroup diversity like Central Asians, of 0.7602±0.0546.
In Eastern
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, R1a1a is found among certain indigenous ethnic groups including Kamchatkans and Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Chukotkans, and peaking in Itel'man at 22%.
West Asia
R1a1a has been found in various forms, in most parts of
Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, in widely varying concentrations, from almost no presence in areas such as Jordan, to much higher levels in parts of Kuwait and
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The Shimar (Shammar) Bedouin tribe in Kuwait show the highest frequency in the Middle East at 43%.
, noted that in the western part of the country, Iranians show low R1a1a levels, while males of eastern parts of Iran carried up to 35% R1a1a. found R1a1a in approximately 20% of Iranian males from the cities of Tehran and Isfahan. in a study of
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, noted much higher frequencies in the south than the north.
A newer study has found 20.3% R-M17* among Kurds, Kurdish samples which were taken in the Kurdistan Province in western Iran, 19% among Iranian Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijanis in West Azerbaijan Province, West Azerbaijan, 9.7% among Mazandaranis in North Iran in the province of Mazandaran Province, Mazandaran, 9.4% among Gilaks in province of Gilan Province, Gilan, 12.8% among Persian and 17.6% among Zoroastrians in Yazd Province, Yazd, 18.2% among Persians in Isfahan Province, Isfahan, 20.3% among Persians in Khorasan Province, Khorasan, 16.7% Afro-Iranians, 18.4% Qeshmi "Gheshmi", 21.4% among Persian Bandari people in Hormozgan Province, Hormozgan and 25% among the Baloch people in Sistan and Baluchestan Province.
found haplogroup R1a in 9.68% (18/186) of a set of samples from Iran, though with a large variance ranging from 0% (0/18) in a sample of Iranians from Tehran to 25% (5/20) in a sample of Iranians from Khorasan and 27% (3/11) in a sample of Iranians of unknown provenance. All Iranian R1a individuals carried the M198 and M17 mutations except one individual in a sample of Iranians from Gilan (''n''=27), who was reported to belong to R1a-SRY1532.2(xM198, M17).
found R1a1-SRY10831.2 in 20.8% (16/77) of a sample of Persians collected in the provinces of Khorasan Province, Khorasan and Kerman Province, Kerman in eastern Iran, but they did not find any member of this haplogroup in a sample of 25 Kurds collected in the province of Kermanshah Province, Kermanshah in western Iran.
Further to the north of these Western Asian regions on the other hand, R1a1a levels start to increase in the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
, once again in an uneven way. Several populations studied have shown no sign of R1a1a, while highest levels so far discovered in the region appears to belong to speakers of the Karachay-Balkar language among whom about one quarter of men tested so far are in haplogroup R1a1a.
Historic naming of R1a
The historic naming system commonly used for R1a was inconsistent in different published sources, because it changed often; this requires some explanation.
In 2002, the Y Chromosome Consortium (YCC) proposed a new naming system for haplogroups , which has now become standard. In this system, names with the format "R1" and "R1a" are "phylogeny, phylogenetic" names, aimed at marking positions in a family tree. Names of single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP mutations can also be used to name clades or haplogroups. For example, as M173 is currently the Unique-event polymorphism, defining mutation of R1, R1 is also R-M173, a "mutational" clade name. When a new branching in a tree is discovered, some phylogenetic names will change, but by definition all mutational names will remain the same.
The widely occurring haplogroup defined by mutation M17 was known by various names, such as "Eu19", as used in in the older naming systems. The 2002 YCC proposal assigned the name R1a to the haplogroup defined by mutation SRY1532.2. This included Eu19 (i.e. R-M17) as a subclade, so Eu19 was named R1a1. Note, SRY1532.2 is also known as SRY10831.2 The discovery of M420 in 2009 has caused a reassignment of these phylogenetic names.( and ) R1a is now defined by the M420 mutation: in this updated tree, the subclade defined by SRY1532.2 has moved from R1a to R1a1, and Eu19 (R-M17) from R1a1 to R1a1a.
More recent updates recorded at the ISOGG reference webpage involve branches of R-M17, including one major branch, R-M417.
See also
Y-DNA R-M207 subclades
Y-DNA backbone tree
Notes
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* also at
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* See als
Supplementary Material
* A copy can be found her
* A copy can be found her
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
;DNA Tree
FTDNA R1a Y-chromosome Haplogroup ProjectR1a1a1 and Subclades Y-DNA Project – BackgroundFamily Tree DNA R1a1a1
;TMRCA
TMRCA = Time to Most Recent Common Ancestor;Various
Danish Demes Regional DNA Project: Y-DNA Haplogroup R1a* Eurogenes Blog
* Avotaynu Online
''The Y-DNA Fingerprint of the Shpoler Zeida, a Tzaddik Who Touched the World''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Haplogroup R1a (Y-Dna)
Haplogroup R, R
Indo-European genetics
Human Y-DNA haplogroups, R
 Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a
Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a 