|
R-M17
Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to southern Siberia and South Asia. While R1a originated c. 22,000 to 25,000 years ago, its subclade M417 (R1a1a1) diversified c. 5,800 years ago. The place of origin of the subclade plays a role in the debate about the origins of Proto-Indo-Europeans. The SNP mutation R-M420 was discovered after R-M17 (R1a1a), which resulted in a reorganization of the lineage in particular establishing a new paragroup (designated R-M420*) for the relatively rare lineages which are not in the R-SRY10831.2 (R1a1) branch leading to R-M17. Origins R1a origins The split of R1a (M420) is computed to c. 22,000 or 25,000 years ago, which is the time of the last glacial maximum. A 2014 study by Peter A. Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eurasia, concluded that there was "a compelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R1
Haplogroup R1, or R-M173, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. A primary subclade of Haplogroup R (R-M207), it is defined by the SNP M173. The other primary subclade of Haplogroup R is Haplogroup R2 (R-M479). Males carrying R-M173 in modern populations appear to comprise two subclades: R1a and R1b, which are found mainly in populations native to Eurasia (except East and Southeast Asia). R-M173 contains the majority of representatives of haplogroup R in the form of its subclades, R1a and R1b (, , and ). Structure Origins The origins of haplogroup R1 remain unclear. It and its sibling clade R2 (R-M79) are the only immediate descendants of Haplogroup R (R-M207). R is a direct descendant of Haplogroup P1 (P-M45), and a sibling clade, therefore, of Haplogroup Q (Q-M242). No examples of the basal subclade, R1* have yet been identified in living individuals or ancient remains. However, the parent clade, R* was evidently present in upper paleolithic-era individuals (24,000 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
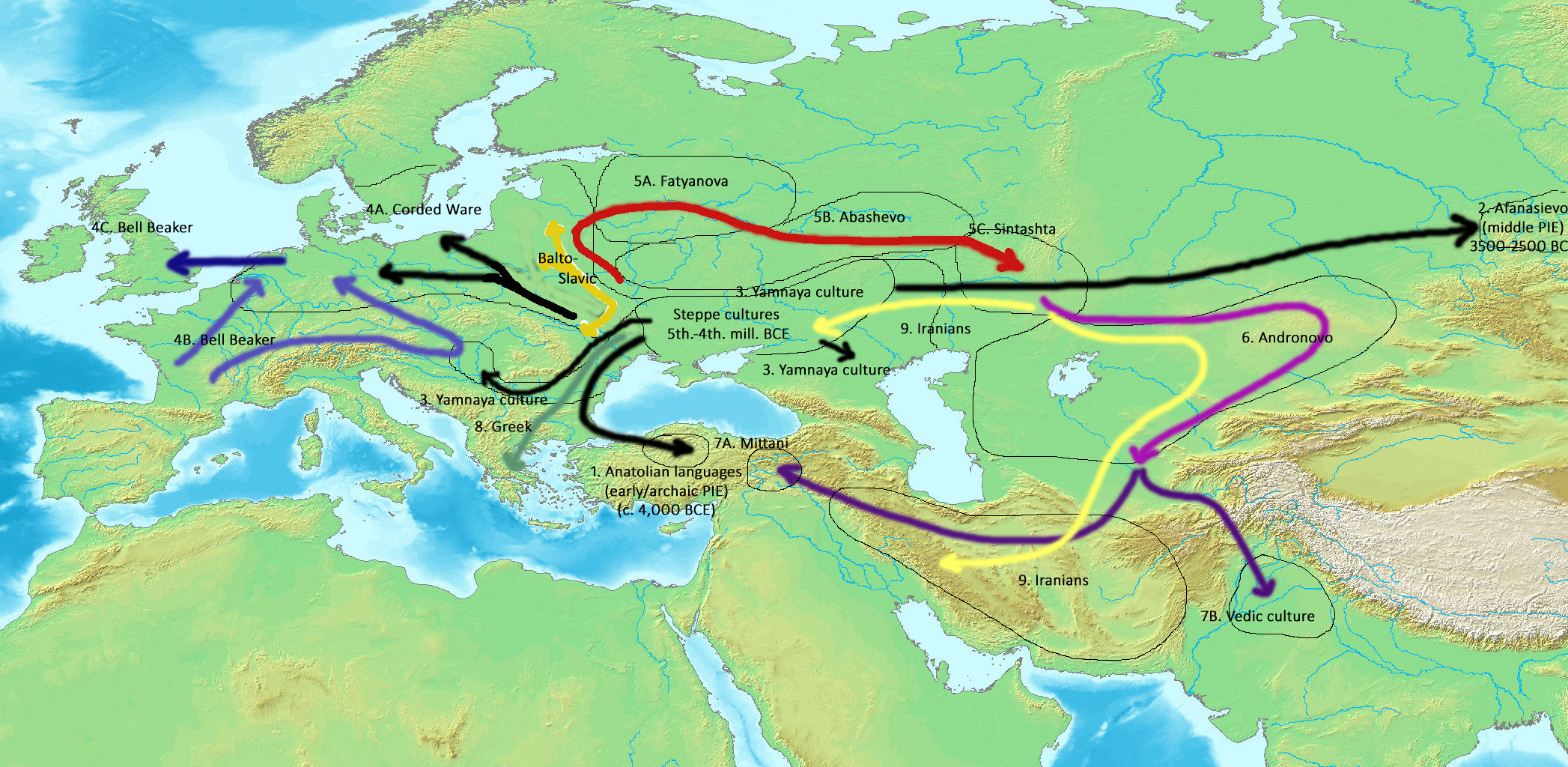
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Urheimat Hypotheses
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of the different branches of the Indo-European language family. The most widely accepted proposal about the location of the Proto-Indo-European homeland is the steppe hypothesis, which puts the archaic, early and late PIE homeland in the Pontic–Caspian steppe around 4,000 BC. The leading competitor is the Anatolian hypothesis, which puts it in Anatolia around 8,000 BC. A notable third possibility, which has gained renewed attraction due to recent aDNA research, is the Armenian hypothesis which situates the homeland for archaic PIE south of the Caucasus. Several other explanations have been proposed, including the outdated but historically prominent North European hypothesis, the Neolithic creolisation hypothesis, the Paleolithic continuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Y-chromosome DNA Haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation. "one mutation in every 30 million base pairs" Y-DNA haplogroups represent major branches of the Y-chromosome phylogenetic tree that share hundreds or even thousands of mutations unique to each haplogroup. The Y-chromosomal most recent common ancestor (Y-MRCA, informally known as Y-chromosomal Adam) is the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) from whom all currently living humans are descended patrilineally. Y-chromosomal Adam is estimated to have lived roughly 236,000 years ago in Africa. By examining other bottlenecks most Eurasian men (men from populations outside of Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European People
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, which spans roughly 40% of the continent's landmass while accounting for approximately 15% of its total population."The Balkans" , ''Global Perspectives: A Remote Sensing and World Issues Site''. Wheeling Jesuit University/Center for Educational Technologies, 1999–2002. It represents a significant part of Culture of Europe, European culture; the main socio-cultural characteristics of Eastern Europe have historically been defined by the traditions of Slavs and Greeks, as well as by the influence of Eastern Christianity as it developed through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread. Its sites spanned an area from much of Pakistan, to northeast Afghanistan, and northwestern India. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan. The term ''Harappan'' is sometimes applied to the Indus civilisation after its type site Harappa, the first to be excavated early in the 20th century in what was then the Punjab province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family. The Slavic languages are conventionally (that is, also on the basis of extralinguistic features) divided into three subgroups: East, South, and West, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Of these, 10 have at least one million speakers and official status as the national languages of the countries in which they are predominantly spoken: Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian (of the East group), Polish, Czech and Slovak (of the West group) and Bulgarian and Macedonian (eastern dialects of the South group), and Serbo-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranian Languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family (with over 400 languages), predominantly spoken in the Subregion, geographical subregion of United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern_Asia, Southern Asia. They have more than 1.5 billion speakers, stretching from Europe (Romani language, Romani), Mesopotamia (Kurdish languages, Zaza–Gorani languages, Zaza–Gorani and Kurmanji#Dialect continuum, Kurmanji Dialect continuum) and the Caucasus (Ossetian language, Ossetian, Tat language (Caucasus), Tat and Talysh language, Talysh) eastward to Xinjiang (Sarikoli language, Sarikoli) and Assam (Assamese language, Assamese), and south to Sri Lanka (Sinhala language, Sinhala) and the Maldives (Maldivian language, Maldivian), with branches stretching as far out as Oceania and the Caribbean for Fiji Hindi and Caribbean Hindustani respectively. Fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. Western Asia covers an area of , with a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to them, such as from Afontova Gora and the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site, and populations descended from them. ANE ancestry developed from a sister lineage of West-Eurasians with significant admixture from early East Asians. ANE ancestry has spread throughout Eurasia and the Americas in various migrations since the Upper Paleolithic, and more than half of the world's population today derives between 5 to 40% of their genomes from the Ancient North Eurasians. Significant ANE ancestry can be found in the indigenous peoples of the Americas, as well as in regions of Europe, South Asia, Central Asia, and Siberia. It has been suggested that their mythology may have included a narrative, found in both Indo-European and some Native American fables, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |