|
Proto-Indo-Europeans
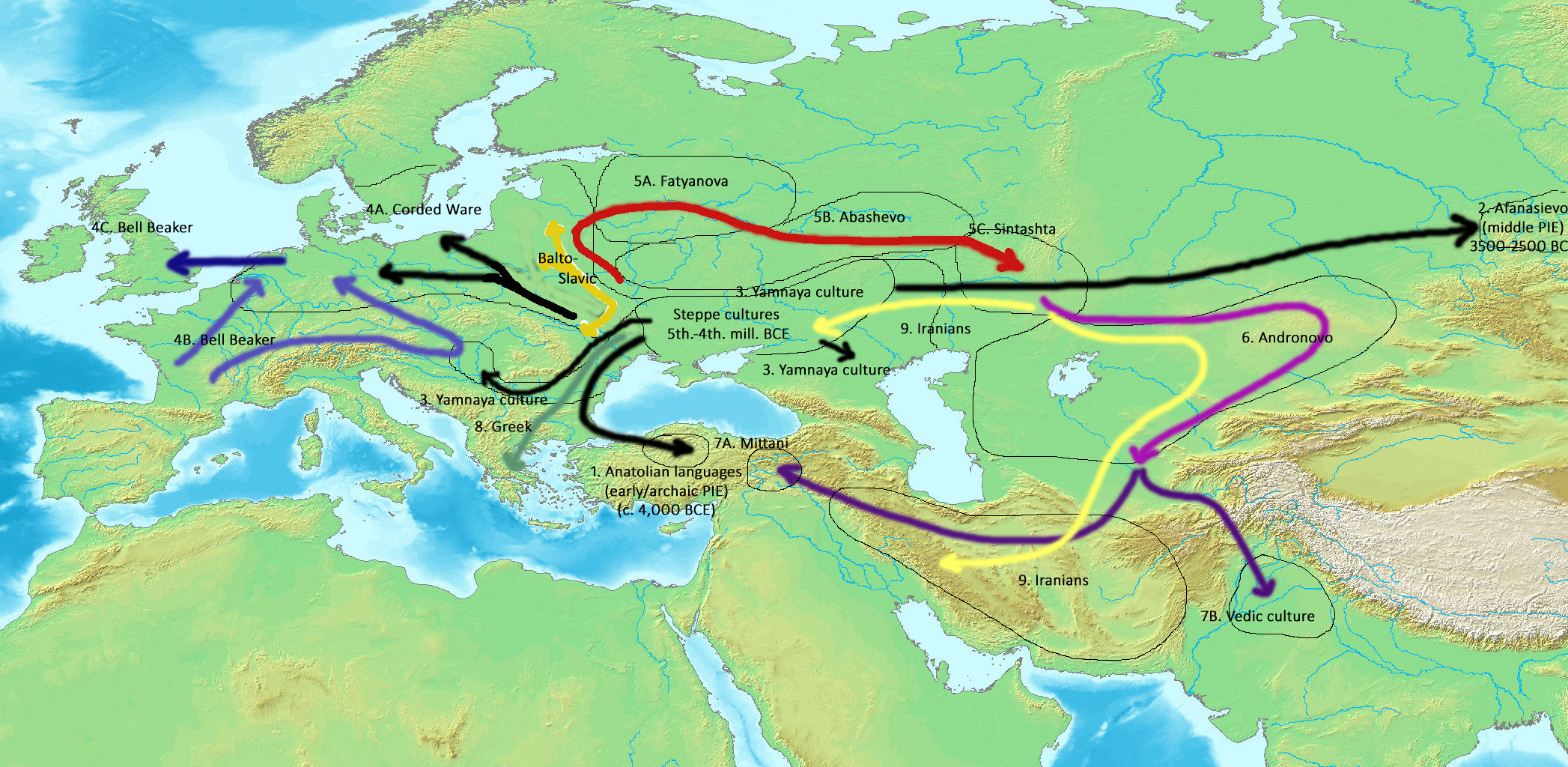
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe ( Cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Urheimat Hypotheses
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of the different branches of the Indo-European language family. The most widely accepted proposal about the location of the Proto-Indo-European homeland is the steppe hypothesis, which puts the archaic, early and late PIE homeland in the Pontic–Caspian steppe around 4,000 BC. The leading competitor is the Anatolian hypothesis, which puts it in Anatolia around 8,000 BC. A notable third possibility, which has gained renewed attraction due to recent aDNA research, is the Armenian hypothesis which situates the homeland for archaic PIE south of the Caucasus. Several other explanations have been proposed, including the outdated but historically prominent North European hypothesis, the Neolithic creolisation hypothesis, the Paleolithic continui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaelogical excavations near Siversky Donets in 1901—1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: (romanization: ) is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits ()', as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli ( kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)The Eastern European hunter-gatherers were themselves mostly descended from ancient North Eurasians, related to the pala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontic–Caspian Steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extends from Dobruja in the northeastern corner of Bulgaria and southeastern Romania, through Moldova and southern and eastern Ukraine, across the Russian Northern Caucasus, the Southern and lower Volga regions to western Kazakhstan, adjacent to the Kazakh steppe to the east, both forming part of the larger Eurasian Steppe. It forms a part of the Palearctic realm and of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. The area corresponds to Cimmeria, Scythia, and Sarmatia of classical antiquity. Across several millennia, numerous tribes of nomadic horsemen used the steppe; many of them went on to conquer lands in the settled regions of Europe, Western Asia, and Southern Asia. The term Ponto-Caspian region is used in biogeograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invasion, it was the eighth-most populous country in Europe, with a population of around 41 million people. It is also bordered by Belarus to the north; by Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; and by Romania and Moldova to the southwest; with a coastline along the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and largest city. Ukraine's state language is Ukrainian; Russian is also widely spoken, especially in the east and south. During the Middle Ages, Ukraine was the site of early Slavic expansion and the area later became a key centre of East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. The state eventually disintegrated into rival regional po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia (around 1650 BC). This empire reached its height during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed an area that included most of Anatolia as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Empire of Hattusa—in modern times conventionally called the Hittite Empire—came into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empire and the empire of Mitanni for control of the Near East. The Middle Assyrian Empire eventually emerged as the dominant power and annexed much of the Hittite Empire, while the remainder was sacked by Phrygian newcomers to the region. After BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse, the Hittites splintered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corded Ware Culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded Ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine on the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The Corded Ware culture is thought to have originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures such as the Globular Amphora and Funnelbeaker cultures, and is considered to be a likely vector for the spread of many of the Indo-European languages in Europe and Asia. Nomenclature The term ''Corded Ware culture'' (german: Schnurkeramik-Kultur) was first introduced by the German archaeologist Friedrich Klopfleisch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoke
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface. The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riven (split lengthwise) into four or six sections. The radial members of a wagon wheel were made by carving a spoke (from a log) into their finished shape. A spokeshave is a tool originally developed for this purpose. Eventually, the term spoke was more commonly applied to the finished product of the wheelwright's work, than to the materials they used. History The spoked wheel was invented to allow the construction of lighter and swifter vehicles. Earliest physical evidence for spoked wheels were found in Sintashta culture, dating to 2000 BC. Soon after this, horse cultures of the Caucasus region used horse-drawn spoked-wheel war chariots for the greater part of three centuries. They moved deep into the Greek peninsula where they joined with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two- wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by light and heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and transport, in processions, for games, and in races. Etymology The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term ''carrus'', a loanword from Gaulish. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a '' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
