
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals".
Analyzing the determinants of
health of a
population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health.
The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a
pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical,
psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
, and
social well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
.
[What is the WHO definition of health?](_blank)
from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19 June - 22 July 1946; signed on 22 July 1946 by the representatives of 61 States (Official Records of WHO, no. 2, p. 100) and entered into force on 7 April 1948. The definition has not been amended since 1948.
Public health is an
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
field. For example,
epidemiology,
biostatistics
Biostatistics (also known as biometry) are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experime ...
,
social sciences and
management of
health services
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wiktionary:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physical and menta ...
are all relevant. Other important sub-fields include
environmental health,
community health Community health refers to simple health services that are delivered by laymen outside hospitals and clinics. Community health is also the subset of public health that is taught to and practiced by clinicians. Community health volunteers and communi ...
,
behavioral health,
health economics,
public policy,
mental health,
health education,
health politics
Health politics or politics of health is an interdisciplinary field of study concerned with the analysis of social and political power over the health status of individuals.
Health politics, incorporating broad perspectives from medical soci ...
,
occupational safety,
disability,
oral health,
gender issues in health, and
sexual and reproductive health.
Public health, together with
primary care, secondary care, and
tertiary care, is part of a country's overall
health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
system. Public health is implemented through the
surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as c ...
of cases and
health indicators, and through the
promotion of healthy behaviors. Common public health initiatives include promotion of
hand-washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands ...
and
breastfeeding, delivery of
vaccinations, promoting ventilation and improved air quality both
indoors and
outdoors
Outdoor(s) may refer to:
*Wilderness
*Natural environment
*Outdoor cooking
*Outdoor education
*Outdoor equipment
*Outdoor fitness
*Outdoor literature
*Outdoor recreation
*Outdoor Channel, an American pay television channel focused on the outdoors
...
,
suicide prevention
Suicide prevention is a collection of efforts to reduce the risk of suicide. Suicide is often preventable, and the efforts to prevent it may occur at the individual, relationship, community, and society level. Suicide is a serious public health ...
,
smoking cessation,
obesity education, increasing
healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
accessibility and distribution of
condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s to control the spread of
sexually transmitted diseases.
There is a significant disparity in access to health care and public health initiatives between
developed countries and
developing countries, as well as within developing countries. In developing countries, public health infrastructures are still forming. There may not be enough trained
healthcare workers, monetary resources, or, in some cases, sufficient knowledge to provide even a basic level of medical care and disease prevention.
A major public health concern in developing countries is poor
maternal and child health, exacerbated by
malnutrition and poverty coupled with governments' reluctance in implementing public health policies.
From the beginnings of
human civilization, communities promoted
health and fought
disease at the population level.
In
complex,
pre-industrialized societies, interventions designed to reduce health risks could be the initiative of different stakeholders, such as army generals, the clergy or rulers. Great Britain became a leader in the development of public health initiatives, beginning in the 19th century, due to the fact that it was the first modern
urban nation worldwide.
The public health initiatives that began to emerge initially focused on
sanitation (for example, the Liverpool and
London sewerage systems), control of
infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
(including vaccination and
quarantine) and an evolving infrastructure of various sciences, e.g. statistics, microbiology, epidemiology, sciences of engineering.
Definitions and purposes

Definition
Public health has been defined as "the science and art of
preventing disease", prolonging life and improving
quality of life through organized efforts and informed choices of
society,
organizations (public and private),
communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place (geography), place, Norm (social), norms, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Identity (social science), identity. Communiti ...
and
individual
An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) of being a person unique from other people and possessing one's own Maslow ...
s.
The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical,
psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
, and
social well-being
Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative ''to'' someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good ''for'' this person, what is in th ...
. As such, according to the
World Health Organization, "health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity".
Related terms

Public health is related to
global health which is the health of populations in the worldwide context. It has been defined as "the area of study,
research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in "
Health for all" people worldwide".
International health is a field of
health care, usually with a public health emphasis, dealing with health across regional or national boundaries. Public health is not the same as public healthcare (
publicly funded health care
Publicly funded healthcare is a form of health care financing designed to meet the cost of all or most healthcare needs from a publicly managed fund. Usually this is under some form of democratic accountability, the right of access to which are se ...
).
The term preventive medicine is related to public health. The American Board of Preventive Medicine separates three categories of preventive medicine: aerospace health,
occupational health, and public health and general preventative medicine. Jung, Boris and Lushniak argue that preventive medicine should be considered the medical specialty for public health but note that the American College of Preventive Medicine and American Board of Preventive Medicine do not prominently use the term "public health".
Preventive medicine specialists are trained as
clinician
A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory or as a researcher. A clinician may diagnose, treat, and otherwise care for pa ...
s and address complex health needs of a population such as by assessing the need for
disease prevention
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
programs, using the best methods to implement them, and assessing their effectiveness.
Since the 1990s many scholars in public health have been using the term population health.
There are no medical specialties directly related to population health.
Valles argues that consideration of
health equity is a fundamental part of population health. Scholars such as Coggon and Pielke express concerns about bringing general issues of wealth distribution into population health. Pielke worries about "stealth issue advocacy" in population health.
Jung, Boris and Lushniak consider population health to be a concept that is the goal of an activity called public health practiced through the specialty preventive medicine.
uses individual lifestyle modification to prevent or revert disease and can be considered a component of preventive medicine and public health. It is implemented as part of
primary care rather than a specialty in its own right.
Valles argues that the term
social medicine has a narrower and more
biomedical
Biomedicine (also referred to as Western medicine, mainstream medicine or conventional medicine) focus than the term population health.
Purposes
The purpose of a
public health intervention
A public health intervention is any effort or policy that attempts to improve mental and physical health on a population level. Public health interventions may be run by a variety of organizations, including governmental health departments and n ...
is to prevent and
mitigate diseases,
injuries and other health conditions. The overall goal is to improve the health of populations and increase
life expectancy.
Characteristics and components
Public health is a complex term, composed of many elements and different practices. It is a multi-faceted,
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
field.
For example,
epidemiology,
biostatistics
Biostatistics (also known as biometry) are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experime ...
,
social sciences and
management of health services are all relevant. Other important sub-fields include
environmental health,
community health Community health refers to simple health services that are delivered by laymen outside hospitals and clinics. Community health is also the subset of public health that is taught to and practiced by clinicians. Community health volunteers and communi ...
,
behavioral health,
health economics,
public policy,
mental health,
health education,
health politics
Health politics or politics of health is an interdisciplinary field of study concerned with the analysis of social and political power over the health status of individuals.
Health politics, incorporating broad perspectives from medical soci ...
,
occupational safety,
disability,
gender issues in health, and
sexual and reproductive health.
Modern public health practice requires
multidisciplinary teams of public health workers and professionals. Teams might include
epidemiologists,
biostatisticians
Biostatistics (also known as biometry) are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experimen ...
,
physician assistant
A physician assistant or physician associate (PA) is a type of Mid-level practitioner, mid-level health care provider. In North America PAs may diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications, and may serve as a pri ...
s,
public health nurses,
midwives,
medical microbiologists,
pharmacist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
s,
economists,
sociologists
This is a list of sociologists. It is intended to cover those who have made substantive contributions to social theory and research, including any sociological subfield. Scientists in other fields and philosophers are not included, unless at least ...
,
geneticists,
data managers,
environmental health officer
Environmental Health Officers (also known as Public Health Inspectors or Environmental Health Practitioners) are responsible for carrying out measures for protecting public health, including administering and enforcing legislation related to enviro ...
s (
public health inspector
Environmental Health Officers (also known as Public Health Inspectors or Environmental Health Practitioners) are responsible for carrying out measures for protecting public health, including administering and enforcing legislation related to enviro ...
s),
bioethicists, gender experts, sexual and reproductive health specialists,
physicians
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
, and
veterinarians.
The elements and priorities of public health have evolved over time, and are continuing to evolve.
Different regions in the world can have different public health concerns at a given time.
Common public health initiatives include promotion of
hand-washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands ...
and
breastfeeding, delivery of
vaccinations,
suicide prevention
Suicide prevention is a collection of efforts to reduce the risk of suicide. Suicide is often preventable, and the efforts to prevent it may occur at the individual, relationship, community, and society level. Suicide is a serious public health ...
,
smoking cessation,
obesity education, increasing
healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
accessibility and distribution of
condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s to control the spread of
sexually transmitted diseases.
Methods

Public health aims are achieved through surveillance of cases and the
promotion of healthy behaviors,
communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place (geography), place, Norm (social), norms, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Identity (social science), identity. Communiti ...
and
environments
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
. Analyzing the determinants of
health of a
population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health.
Many diseases are
preventable through simple, nonmedical methods. For example, research has shown that the simple act of
handwashing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands ...
with soap can prevent the spread of many
contagious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmiss ...
. In other cases, treating a disease or controlling a
pathogen can be vital to preventing its spread to others, either during an outbreak of
infectious disease or through
contamination of food or
water supplies.
Public health communications programs,
vaccination programs and distribution of
condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s are examples of common preventive public health measures.
Public health, together with
primary care, secondary care, and
tertiary care, is part of a country's overall
health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
system. Many interventions of public health interest are delivered outside of
health facilities, such as
food safety
Food safety (or food hygiene) is used as a scientific method/discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent food-borne illness. The occurrence of two or more cases of a similar illness resulting from t ...
surveillance, distribution of
condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
s and
needle-exchange programs for the prevention of transmissible diseases.
Public health plays an important role in disease prevention efforts in both the developing world and in developed countries through local health systems and
non-governmental organizations.
Public health requires
Geographic Information Systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a br ...
(GIS) because risk, vulnerability and exposure involve geographic aspects.
Ethics
A dilemma in public health ethics is dealing with the conflict between
individual rights and maximizing
right to health.
Public health is justified by
consequentialist
In ethical philosophy, consequentialism is a class of normative ethics, normative, Teleology, teleological ethical theories that holds that the wikt:consequence, consequences of one's Action (philosophy), conduct are the ultimate basis for judgm ...
utilitarian ideas,
but is constrained and critiqued by
liberal,
,
principlist
Principlism is an applied ethics approach to the examination of moral dilemmas that is based upon the application of certain ethical principles. This approach to ethical decision-making has been adopted enthusiastically in many different professio ...
and
libertarian
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's e ...
philosophies
Stephen Holland argues that it can be easy to find a particular framework to justify any viewpoint on public health issues, but that the correct approach is to find a framework that best describes a situation and see what it implies about public health policy.
The definition of
health is vague and there are many conceptualizations. Public health practitioners definition of health can different markedly from members of the public or
clinician
A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory or as a researcher. A clinician may diagnose, treat, and otherwise care for pa ...
s. This can mean that members of the public view the values behind public health interventions as alien which can cause resentment amongst the public towards certain interventions.
Such vagueness can be a problem for
health promotion.
Critics have argued that public health tends to place more focus on individual factors associated with health at the expense of factors operating at the population level.
Historically, public health campaigns have been criticized as a form of "
healthism
Medicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions, and thus become the subject of medical study, diagnosis, prevention, or treatment. Medicalization can be driven by new evid ...
", as moralistic in nature rather than being focused on health. Medical doctors, Petr Shkrabanek and James McCormick wrote a series of publications on this topic in the late 1980s and early 1990s criticizing the UK's ''the Health of The Nation'' campaign. These publications exposed abuse of epidemiology and statistics by the public health movement to support lifestyle interventions and screening programs.
A combination of inculcating a fear of ill-health and a strong notion of individual responsibility has been criticized as a form of "health fascism" by a number of scholars, objectifying the individual with no considerations of emotional or social factors.
Priority areas
Original focal areas
When public health initiatives began to emerge in England in modern times (18th century onwards) there were three core strands of public health which were all related to statecraft: Supply of clean water and
sanitation (for example
London sewerage system); control of
infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
(including
vaccination and
quarantine); an evolving infrastructure of various sciences, e.g. statistics, microbiology, epidemiology, sciences of engineering.
Great Britain was a leader in the development of public health during that time period out of necessity: Great Britain was the first modern
urban nation (by 1851 more than half of the population lived in settlements of more than 2000 people).
This led to a certain type of distress which then led to public health initiatives.
Later that particular concern faded away.
Changing and differing focal areas
With the onset of the
epidemiological transition
In demography and medical geography, epidemiological transition is a theory which "describes changing population patterns in terms of fertility, life expectancy, mortality, and leading causes of death." For example, a phase of development marked ...
and as the prevalence of
infectious diseases decreased through the 20th century, public health began to put more focus on
chronic diseases such as
cancer and
heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
. Previous efforts in many developed countries had already led to dramatic reductions in the
infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
using preventive methods. In Britain, the infant mortality rate fell from over 15% in 1870 to 7% by 1930.
A major public health concern in
developing countries is poor
maternal and child health, exacerbated by
malnutrition and poverty. The
WHO reports that a lack of
exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months of life contributes to over a million avoidable child deaths each year.
Public health surveillance has led to the identification and prioritization of many public health issues facing the world today, including
HIV/AIDS,
diabetes,
waterborne diseases,
zoonotic diseases, and
antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
leading to the reemergence of infectious diseases such as
tuberculosis.
Antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
, also known as drug resistance, was the theme of
World Health Day 2011.
For example, the WHO reports that at least 220 million people worldwide have diabetes. Its incidence is increasing rapidly, and it is projected that the number of diabetes deaths will double by 2030. In a June 2010 editorial in the medical journal ''
The Lancet'', the authors opined that "The fact that type 2 diabetes, a largely preventable disorder, has reached epidemic proportion is a public health humiliation." The risk of
type 2 diabetes is closely linked with the growing problem of
obesity. The WHO's latest estimates highlighted that globally approximately 1.9 billion adults were
overweight
Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with mo ...
in 2014, and 41 million children under the age of five were overweight in 2014. Once considered a problem in high-income countries, it is now on the rise in low-income countries, especially in urban settings.
Many public health programs are increasingly dedicating attention and resources to the issue of obesity, with objectives to address the underlying causes including
healthy diet
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
A healthy ...
and
physical exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
. The
National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) has published a review of research on what
local authorities can do to tackle obesity. The review covers interventions in the food environment (what people buy and eat), the
built and
natural environments, schools, and the community, as well as those focussing on
active travel
Active mobility, soft mobility, active travel, active transport or active transportation is the transport of people or goods, through non-motorized means, based around human physical activity. The best-known forms of active mobility are walking a ...
,
leisure services and public sports,
weight management programmes, and
system-wide approaches.
Current practice
Organizations
World Health Organization (WHO)
The
World Health Organization (WHO) is a
specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health.
The WHO Constitution, which establishes the agency's governing structure and principles, states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". The WHO's broad mandate includes advocating for universal healthcare, monitoring public health risks, coordinating responses to health emergencies, and promoting human health and well-being. The WHO has played a leading role in several public health achievements, most notably the
eradication of
smallpox, the near-
eradication of polio
The word "Eradication" is derived from Latin word "radix" which means "root". It may refer to:
*Eradication of infectious diseases (human), the reduction of the global incidence of an infectious disease in humans to zero
*Eradication of infectiou ...
, and the development of an
Ebola vaccine. Its current priorities include
communicable disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
s, particularly
HIV/AIDS,
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
,
COVID-19,
malaria and
tuberculosis;
non-communicable diseases such as heart disease and cancer;
healthy diet
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
A healthy ...
, nutrition, and
food security;
occupational health; and
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
.
Others
Most countries have their own governmental public health agency, often called the ministry of health, with responsibility for domestic health issues.
For example, in the
United States, state and local
health department
A health department or health ministry is a part of government which focuses on issues related to the general health of the citizenry. Subnational entities, such as states, counties and cities, often also operate a health department of their ow ...
s are on the front line of public health initiatives. In addition to their national duties, the
United States Public Health Service (PHS), led by the
Surgeon General of the United States Public Health Service, and the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, headquartered in
Atlanta, are also involved with international health activities.
Public health programs
Most governments recognize the importance of public health programs in reducing the incidence of disease, disability, and the effects of
aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
and other physical and mental health conditions. However, public health generally receives significantly less government funding compared with medicine. Although the collaboration of local health and government agencies is considered best practice to improve public health, the pieces of evidence available to support this is limited. Public health programs providing
vaccinations have made major progress in promoting health, including substantially reducing the occurrence of
cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
and
polio and eradicating
smallpox, diseases that have plagued humanity for thousands of years.

The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies core functions of public health programs including:
* providing leadership on matters critical to health and engaging in partnerships where joint action is needed;
* shaping a
research agenda and stimulating the generation, translation and
dissemination of valuable knowledge;
* setting norms and standards and promoting and monitoring their implementation;
* articulating ethical and
evidence-based policy
Evidence-based policy is an idea in public policy proposing that policy decisions should be based on, or informed by, rigorously established objective evidence. The implied contrast is with policymaking based on ideology, 'common sense,' anecd ...
options;
* monitoring the health situation and assessing health trends.
In particular, public health surveillance programs can:
* serve as an
early warning system for impending public health emergencies;
* document the impact of an intervention, or track progress towards specified goals; and
* monitor and clarify the epidemiology of health problems, allow priorities to be set, and inform
health policy
Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society".World Health Organization''Health Policy'' accessed 22 March 2011(Web archive)/ref> According to the ...
and strategies.
* diagnose, investigate, and monitor health problems and health hazards of the community
Behavior change
Many health problems are due to maladaptive personal behaviors. From an
evolutionary psychology perspective, over consumption of novel substances that are harmful is due to the activation of an evolved
reward system
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
for substances such as drugs, tobacco,
alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
,
refined salt,
fat, and
carbohydrates. New technologies such as modern transportation also cause reduced
physical activity. Research has found that
behavior is more effectively changed by taking evolutionary motivations into consideration instead of only presenting information about health effects. The marketing industry has long known the importance of associating products with high status and attractiveness to others. Films are increasingly being recognized as a public health tool. In fact,
film festivals
A film festival is an organized, extended presentation of films in one or more cinemas or screening venues, usually in a single city or region. Increasingly, film festivals show some films outdoors. Films may be of recent date and, depending upon ...
and
competitions have been established to specifically promote films about health. Conversely, it has been argued that emphasizing the harmful and undesirable effects of tobacco smoking on other persons and imposing smoking bans in public places have been particularly effective in reducing tobacco smoking.
Applications in health care
As well as seeking to improve population health through the implementation of specific population-level interventions, public health contributes to medical care by identifying and assessing population needs for health care services, including:
* Assessing current services and evaluating whether they are meeting the objectives of the
health care system
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, Mental health, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World H ...
* Ascertaining requirements as expressed by
health professionals
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
, the public and other stakeholders
* Identifying the most appropriate interventions
* Considering the effect on resources for proposed interventions and assessing their cost-effectiveness
* Supporting decision making in health care and planning health services including any necessary changes.
* Informing, educating, and empowering people about health issues
Conflicting aims
Some programs and policies associated with public
health promotion and prevention can be controversial. One such example is programs focusing on the prevention of
HIV transmission through
safe sex
Safe sex is sexual activity using methods or contraceptive devices (such as condoms) to reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially HIV. "Safe sex" is also sometimes referred to as safer se ...
campaigns and
needle-exchange program
A needle and syringe programme (NSP), also known as needle exchange program (NEP), is a social service that allows Injection (medicine), injecting drug users (IDUs) to obtain clean and unused hypodermic needles and associated paraphernalia at l ...
s. Another is the control of
tobacco smoking. Changing smoking behavior requires long-term strategies, unlike the fight against
communicable diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, which usually takes a shorter period for effects to be observed. Many nations have implemented
major initiatives to cut smoking, such as increased taxation and bans on smoking in some or all public places. Supporters argue by presenting evidence that smoking is one of the major killers, and that therefore governments have a duty to reduce the death rate, both through limiting
passive (second-hand) smoking and by providing fewer opportunities for people to smoke. Opponents say that this undermines individual freedom and personal responsibility, and worry that the state may be encouraged to remove more and more choice in the name of better population health overall.
Psychological research confirms this tension between concerns about public health and concerns about personal liberty: (i) the best predictor of complying with public health recommendations such as hand-washing, mask-wearing, and staying at home (except for essential activity) during the
COVID-19 pandemic was people's perceived duties to prevent harm but (ii) the best predictor of flouting such public health recommendations was valuing liberty more than equality.
Simultaneously, while communicable diseases have historically ranged uppermost as a
global health priority,
non-communicable diseases and the underlying behavior-related risk factors have been at the bottom. This is changing, however, as illustrated by the
United Nations hosting its first General Assembly Special Summit on the issue of non-communicable diseases in September 2011.
Global perspectives

Disparities in service and access
There is a significant disparity in access to health care and public health initiatives between
developed countries and
developing countries, as well as within developing countries. In developing countries, public health infrastructures are still forming. There may not be enough trained
health workers
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
, monetary resources or, in some cases, sufficient knowledge to provide even a basic level of medical care and disease prevention.
As a result, a large majority of disease and mortality in developing countries results from and contributes to extreme
poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
. For example, many African governments spend less than
US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
10 per person per year on health care, while, in the United States, the
federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
spent approximately US$4,500 per capita in 2000. However, expenditures on health care should not be confused with spending on public health. Public health measures may not generally be considered "health care" in the strictest sense. For example, mandating the use of seat belts in cars can save countless lives and contribute to the health of a population, but typically money spent enforcing this rule would not count as money spent on health care.
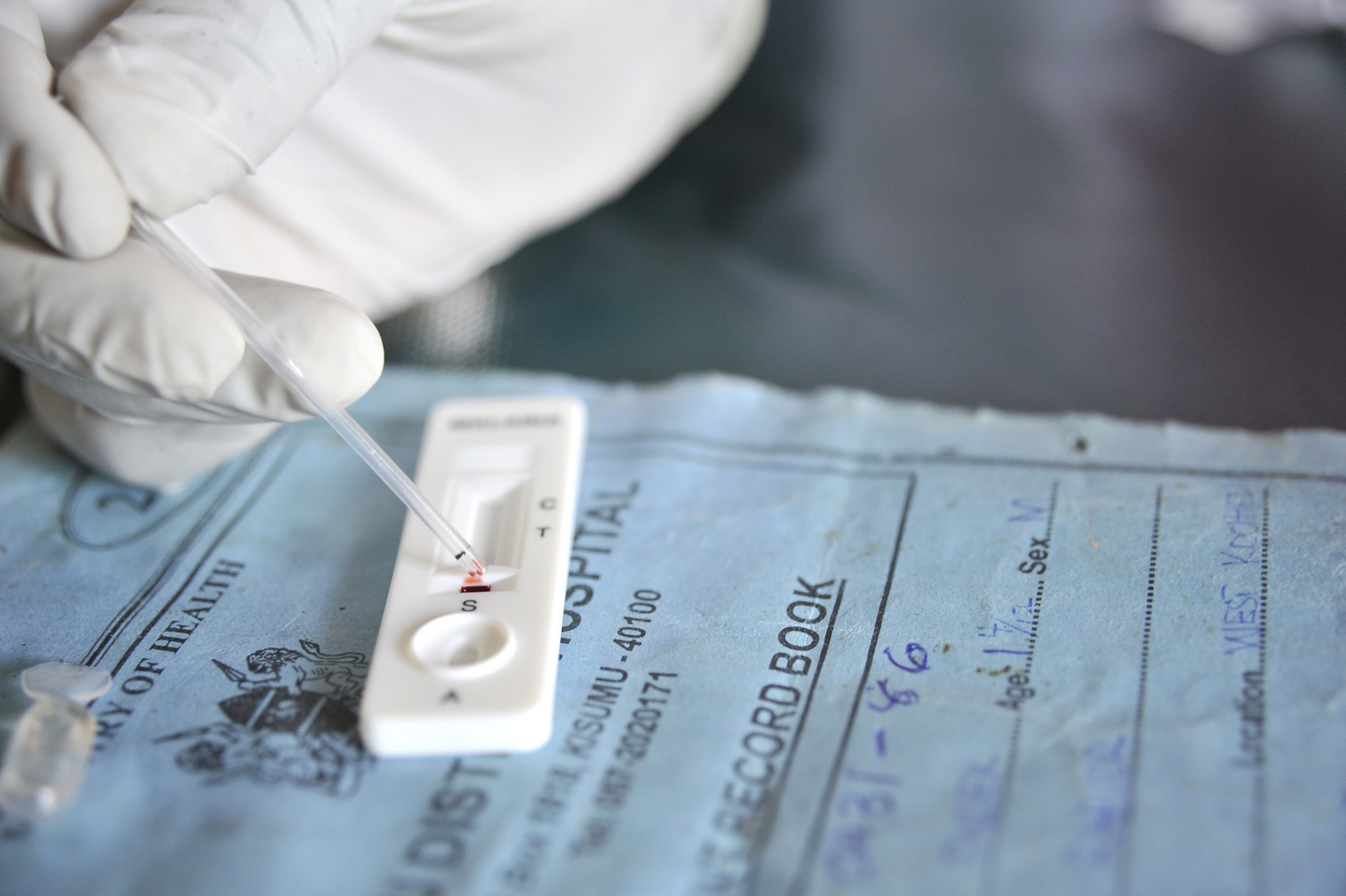
Large parts of the world remained plagued by largely preventable or treatable infectious diseases. In addition to this however, many developing countries are also experiencing an
epidemiological shift and
polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:
Mathematics
*Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds
*Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by ...
in which populations are now experiencing more of the effects of chronic diseases as life expectancy increases, the poorer communities being heavily affected by both chronic and infectious diseases.
Another major public health concern in the developing world is poor
maternal and child health, exacerbated by
malnutrition and poverty. The
WHO reports that a lack of
exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months of life contributes to over a million avoidable child deaths each year.
aimed at treating and preventing
malaria episodes among pregnant women and young children is one public health measure in
endemic countries.
Since the 1980s, the growing field of
population health has broadened the focus of public health from individual behaviors and
risk factors to population-level issues such as
inequality, poverty, and education. Modern public health is often concerned with addressing determinants of health across a population. There is a recognition that health is affected by many factors including class, race, income, educational status, region of residence, and
social relationships; these are known as "
social determinants of health
The social determinants of health (SDOH) are the economic and social conditions that influence individual and group differences in health status. They are the health promoting factors found in one's living and working conditions (such as the d ...
". The upstream drivers such as environment, education, employment, income, food security, housing,
social inclusion and many others effect the distribution of health between and within populations and are often shaped by policy. A social gradient in health runs through society. The poorest generally have the worst health, but even the middle classes will generally have worse health outcomes than those of a higher social level. The new public health advocates for population-based policies that improve health in an equitable manner.
Health aid in developing countries
Health aid to developing countries is an important source of public health funding for many developing countries.
Health aid to developing countries has shown a significant increase after World War II as concerns over the spread of disease as a result of
globalization increased and the HIV/AIDS epidemic in sub-Saharan Africa surfaced.
From 1990 to 2010, total health aid from developed countries increased from 5.5 billion to 26.87 billion with wealthy countries continuously donating billions of dollars every year with the goal of improving population health.
Some efforts, however, receive a significantly larger proportion of funds such as HIV which received an increase in funds of over $6 billion between 2000 and 2010 which was more than twice the increase seen in any other sector during those years.
Health aid has seen an expansion through multiple channels including private philanthropy,
non-governmental organizations, private foundations such as the
Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The second-oldest major philanthropic institution in America, after the Carneg ...
or the
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), a merging of the William H. Gates Foundation and the Gates Learning Foundation, is an American private foundation founded by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates. Based in Seattle, Washington, it was l ...
, bilateral donors, and multilateral donors such as the
World Bank or
UNICEF.
The result has been a sharp rise in uncoordinated and fragmented funding of an ever-increasing number of initiatives and projects. To promote better strategic cooperation and coordination between partners, particularly among bilateral development agencies and funding organizations, the
Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency
The Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency ( sv, Styrelsen för internationellt utvecklingssamarbete, ) is a government agency of the Swedish Ministry for Foreign Affairs. Sida is responsible for organization of the bulk of Swede ...
(Sida) spearheaded the establishment of ESSENCE, an initiative to facilitate dialogue between donors/funders, allowing them to identify synergies. ESSENCE brings together a wide range of funding agencies to coordinate funding efforts.
In 2009 health aid from the
OECD amounted to $12.47 billion which amounted to 11.4% of its total bilateral aid.
In 2009, Multilateral donors were found to spend 15.3% of their total aid on bettering public healthcare.
International health aid debates
Debates exist questioning the efficacy of international health aid. Supporters of aid claim that health aid from wealthy countries is necessary in order for developing countries to escape the
poverty trap. Opponents of health aid claim that international health aid actually disrupts developing countries' course of development, causes dependence on aid, and in many cases the aid fails to reach its recipients.
For example, recently, health aid was funneled towards initiatives such as financing new technologies like
antiretroviral medication,
insecticide-treated mosquito nets, and new vaccines. The positive impacts of these initiatives can be seen in the eradication of smallpox and
polio; however, critics claim that misuse or misplacement of funds may cause many of these efforts to never come into achievement.
Economic modeling based on the
Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation and the
World Health Organization has shown a link between international health aid in developing countries and a reduction in adult mortality rates.
However, a 2014–2016 study suggests that a potential confounding variable for this outcome is the possibility that aid was directed at countries once they were already on track for improvement.
That same study, however, also suggests that 1 billion dollars in health aid was associated with 364,000 fewer deaths occurring between ages 0 and 5 in 2011.
Sustainable development goals for 2030
To address current and future challenges in addressing health issues in the world, the
United Nations have developed the
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
to be completed by 2030. These goals in their entirety encompass the entire spectrum of development across nations, however Goals 1–6 directly address
health disparities, primarily in developing countries.
These six goals address key issues in
global public health,
poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
, hunger and
food security, health, education,
gender equality and
women's empowerment, and
water and
sanitation.
Public health officials can use these goals to set their own agenda and plan for smaller scale initiatives for their organizations. These goals are designed to lessen the burden of disease and inequality faced by developing countries and lead to a healthier future. The links between the various sustainable development goals and public health are numerous and well established.
History
Until the 18th century

From the beginnings of
human civilization, communities promoted
health and fought
disease at the population level.
Definitions of health as well as methods to pursue it differed according to the medical, religious and natural-
philosophical ideas groups held, the resources they had, and the changing circumstances in which they lived. Yet few early societies displayed the hygienic stagnation or even apathy often attributed to them. The latter reputation is mainly based on the absence of present-day
bioindicators, especially
immunological
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there ...
and
statistical
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industria ...
tools developed in light of the
germ theory of disease transmission.
Public health was born neither in
Europe nor as a response to the
Industrial Revolution. Preventive health interventions are attested almost anywhere historical communities have left their mark. In
Southeast Asia, for instance,
Ayurvedic
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
medicine and subsequently
Buddhism fostered occupational, dietary and sexual regimens that promised balanced bodies, lives and communities, a notion strongly present in
Traditional Chinese Medicine as well. Among the
Mayans,
Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
and other early civilizations in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, population centers pursued hygienic programs, including by holding
medicinal herbal markets. And among
Aboriginal Australians, techniques for preserving and protecting water and food sources, micro-zoning to reduce pollution and fire risks, and screens to protect people against
flies were common, even in temporary camps.
Western European,
Byzantine and
Islamicate civilizations, which generally adopted a
Hippocratic,
Galenic or
humoral medical system, fostered preventive programs as well. These were developed on the basis of evaluating the quality of local
climates, including
topography, wind conditions and exposure to the sun, and the properties and availability of water and food, for both
humans and nonhuman
animals. Diverse authors of
medical,
architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings o ...
,
engineering and
military manuals explained how to apply such theories to groups of different origins and under different circumstances. This was crucial, since under Galenism bodily constitutions were thought to be heavily shaped by their material
environments
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
, so their balance required specific regimens as they traveled during different
seasons and between climate zones.
In
complex,
pre-industrialized societies, interventions designed to reduce health risks could be the initiative of different stakeholders. For instance, in
Greek and
Roman antiquity
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
, army generals learned to provide for soldiers' wellbeing, including off the
battlefield, where most combatants died prior to the twentieth century. In
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
monasteries across the
Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
and western Europe since at least the fifth century
CE,
monks and
nuns pursued strict but balanced regimens, including nutritious
diets, developed explicitly to extend their lives. And
royal, princely and
papal courts, which were often mobile as well, likewise adapted their behavior to suit environmental conditions in the sites they occupied. They could also choose sites they considered salubrious for their members and sometimes had them modified.
In
cities, residents and rulers developed measures to benefit the general
population, which faced a broad array of recognized
health risks. These provide some of the most sustained evidence for preventive measures in earlier civilizations. In numerous sites the upkeep of
infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
s, including roads, canals and marketplaces, as well as
zoning policies, were introduced explicitly to preserve residents' health. Officials such as the
muhtasib in the Middle East and the
Road master
The road master (Latin: ''viarius''; Italian: ''Maestro delle Strade'') was a middle- to high-ranking urban official common across the central and northern regions of Italy between c . 1250-1550, that is the communal and despotic era. Often part o ...
in Italy, fought the combined threats of
pollution through
sin,
ocular intromission and
miasma. Craft
guilds were important agents of waste disposal and promoted
harm reduction through honesty and
labor safety among their members. Medical practitioners, including public physicians, collaborated with urban governments in predicting and preparing for calamities and identifying and isolating people perceived as
lepers, a disease with strong moral connotations.
Neighborhoods were also active in safeguarding local people's health, by monitoring at-risk sites near them and taking appropriate social and legal action against artisanal polluters and neglectful owners of animals. Religious institutions, individuals and charitable organizations in both
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and Christianity likewise promoted moral and physical wellbeing by endowing urban amenities such as wells, fountains, schools and bridges, also in the service of
pilgrims. In western Europe and Byzantium, religious
processions commonly took place, which purported to act as both preventive and curative measures for the entire community.
Urban residents and other groups also developed preventive measures in response to calamities such as
war,
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
,
floods and
widespread disease. During and after the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
(1346–53), for instance, inhabitants of the
Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
and
Western Europe reacted to massive population decline in part on the basis of existing medical theories and protocols, for instance concerning meat consumption and burial, and in part by developing new ones. The latter included the establishment of
quarantine facilities and health boards, some of which eventually became regular urban (and later national) offices. Subsequent measures for protecting cities and their regions included issuing health
passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that contains a person's identity. A person with a passport can travel to and from foreign countries more easily and access consular assistance. A passport certifies the personal ...
s for travelers, deploying guards to create
sanitary cordons for protecting local inhabitants, and gathering morbidity and mortality statistics. Such measures relied in turn on better transportation and communication networks, through which news on human and animal disease was efficiently spread.
After the 18th century
With the onset of the
Industrial Revolution, living standards amongst the working population began to worsen, with cramped and unsanitary urban conditions. In the first four decades of the 19th century alone,
London's population doubled and even greater growth rates were recorded in the new industrial towns, such as
Leeds and
Manchester. This rapid
urbanization exacerbated the spread of disease in the large
conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
s that built up around the
workhouses and
factories. These settlements were cramped and primitive with no organized
sanitation. Disease was inevitable and its incubation in these areas was encouraged by the poor lifestyle of the inhabitants. Unavailable housing led to the rapid growth of
slum
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily inh ...
s and the
per capita death rate began to rise alarmingly, almost doubling in
Birmingham and
Liverpool.
Thomas Malthus warned of the dangers of overpopulation in 1798. His ideas, as well as those of
Jeremy Bentham, became very influential in government circles in the early years of the 19th century.
The latter part of the century brought the establishment of the basic pattern of improvements in public health over the next two centuries: a social evil was identified, private philanthropists brought attention to it, and changing public opinion led to government action.
The 18th century saw rapid growth in voluntary hospitals in
England.
The practice of
vaccination began in the 1800s, following the pioneering work of
Edward Jenner in treating
smallpox.
James Lind's discovery of the causes of
scurvy amongst sailors and its mitigation via the introduction of
fruit on lengthy voyages was published in 1754 and led to the adoption of this idea by the
Royal Navy. Efforts were also made to promulgate health matters to the broader public; in 1752 the British physician Sir
John Pringle published ''Observations on the Diseases of the Army in Camp and Garrison'', in which he advocated for the importance of adequate ventilation in the
military barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
and the provision of
latrines for the soldiers.
Public health legislation in England

The first attempts at sanitary reform and the establishment of public health institutions were made in the 1840s.
Thomas Southwood Smith
Thomas Southwood Smith (17881861) was an English physician and sanitary reformer.
Early life
Smith was born at Martock, Martock, Somerset, into a strict Baptist family, his parents being William Smith and Caroline Southwood. In 1802 he won a sc ...
, physician at the
London Fever Hospital
The London Fever Hospital was a voluntary hospital financed from public donations in Liverpool Road in London. It was one of the first fever hospitals in the country.
History
Originally established with 15 beds in 1802 in Gray's Inn Road, it mov ...
, began to write papers on the importance of public health, and was one of the first physicians brought in to give evidence before the
Poor Law Commission in the 1830s, along with
Neil Arnott and
James Phillips Kay
Sir James Phillips Kay-Shuttleworth, 1st Baronet (20 July 1804 – 26 May 1877, born James Kay) of Gawthorpe Hall, Lancashire, was a British politician and educationist. He founded a further-education college that would eventually become Plymo ...
. Smith advised the government on the importance of
quarantine and sanitary improvement for limiting the spread of infectious diseases such as
cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
and
yellow fever.
The Poor Law Commission reported in 1838 that "the expenditures necessary to the adoption and maintenance of measures of prevention would ultimately amount to less than the cost of the disease now constantly engendered". It recommended the implementation of large scale government
engineering projects to alleviate the conditions that allowed for the propagation of disease.
[ The Health of Towns Association was formed at Exeter Hall London on 11 December 1844, and vigorously campaigned for the development of public health in the United Kingdom.]Edwin Chadwick
Sir Edwin Chadwick KCB (24 January 18006 July 1890) was an English social reformer who is noted for his leadership in reforming the Poor Laws in England and instituting major reforms in urban sanitation and public health. A disciple of Uti ...
, which produced a series of reports on poor and insanitary conditions in British cities.[
These national and local movements led to the ]Public Health Act
Public Health Act is a stock short title used in the United Kingdom for legislation relating to public health.
List
*The Public Health Act 1848 (11 & 12 Vict c 63)
*The Sanitary Act 1866 (29 & 30 Vict c 90) is sometimes called the Public Health Ac ...
, finally passed in 1848. It aimed to improve the sanitary condition of towns and populous places in England and Wales by placing the supply of water, sewerage, drainage, cleansing and paving under a single local body with the General Board of Health as a central authority. The Act was passed by the Liberal government of Lord John Russell, in response to the urging of Edwin Chadwick. Chadwick's seminal report on ''The Sanitary Condition of the Labouring Population'' was published in 1842 and was followed up with a supplementary report a year later. During this time, James Newlands
James Newlands (28 July 1813 – 15 July 1871) was a Scottish civil engineer who worked in Liverpool as the first Borough Engineer appointed in the United Kingdom, and is credited with designing and implementing the first integrated sewerage sy ...
(appointed following the passing of the 1846 Liverpool Sanatory Act championed by the Borough of Liverpool Health of Towns Committee) designed the world's first integrated sewerage system, in Liverpool (1848-1869), with Joseph Bazalgette
Sir Joseph William Bazalgette CB (; 28 March 181915 March 1891) was a 19th-century English civil engineer. As chief engineer of London's Metropolitan Board of Works, his major achievement was the creation (in response to the Great Stink of 1 ...
later creating London's sewerage system (1858-1875).
The Vaccination Act 1853 introduced compulsory smallpox vaccination in England and Wales. By 1871 legislation required a comprehensive system of registration run by appointed vaccination officers.
Further interventions were made by a series of subsequent Public Health Acts
Public Health Act is a stock short title used in the United Kingdom for legislation relating to public health.
List
*The Public Health Act 1848 (11 & 12 Vict c 63)
*The Sanitary Act 1866 (29 & 30 Vict c 90) is sometimes called the Public Health Ac ...
, notably the 1875 Act. Reforms included the building of sewers, the regular collection of garbage followed by incineration or disposal in a landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
, the provision of clean water and the draining of standing water to prevent the breeding of mosquitoes.
The Infectious Disease (Notification) Act 1889 mandated the reporting of infectious diseases to the local sanitary authority, which could then pursue measures such as the removal of the patient to hospital and the disinfection of homes and properties.
Public health legislation in other countries
In the United States, the first public health organization based on a state health department and local boards of health was founded in New York City in 1866.
In Germany during The Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a Constitutional republic, constitutional federal republic for the first time in his ...
the country faced many public health catastrophes. The Nazi Party formed with a goal of modernizing health care with ''The Volksgesundheit'', German for ''public health folk''; this modernization was based on the growing field of eugenics and measures prioritizing group health over any care for the health of individuals. The end of World War 2 led to the Nuremberg Code, a set of research ethics concerning human experimentation.
Epidemiology
 The science of epidemiology was founded by
The science of epidemiology was founded by John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the so ...
's identification of a polluted public water well as the source of an 1854 cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
outbreak in London. Snow believed in the germ theory
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade ...
of disease as opposed to the prevailing miasma theory
The miasma theory (also called the miasmatic theory) is an obsolete medical theory that held that diseases—such as cholera, chlamydia, or the Black Death—were caused by a ''miasma'' (, Ancient Greek for 'pollution'), a noxious form of "bad ...
. By talking to local residents (with the help of Reverend Henry Whitehead
Henry Whitehead (22 September 1825 – 5 March 1896) was a Church of England priest and the assistant curate of St Luke's Church in Soho, London, during the 1854 cholera outbreak.
A former believer in the miasma theory of disease, Whitehead ...
), he identified the source of the outbreak as the public water pump on Broad Street (now Broadwick Street
Broadwick Street (formerly Broad Street) is a street in Soho, City of Westminster, London. It runs for 0.18 miles (0.29 km) approximately west–east between Marshall Street and Wardour Street, crossing Berwick Street.
Broad Street was no ...
). Although Snow's chemical and microscope examination of a water sample from the Broad Street pump did not conclusively prove its danger, his studies of the pattern of the disease were convincing enough to persuade the local council to close the well pump by removing its handle.
Snow later used a dot map to illustrate the cluster of cholera cases around the pump. He also used statistics to illustrate the connection between the quality of the water source and cholera cases. He showed that the Southwark and Vauxhall Waterworks Company was taking water from sewage-polluted sections of the Thames and delivering the water to homes, leading to an increased incidence of cholera. Snow's study was a major event in the history of public health and geography. It is regarded as the founding event of the science of epidemiology.
Control of infectious diseases
 With the pioneering work in bacteriology of French chemist
With the pioneering work in bacteriology of French chemist Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization, the latter of which was named afte ...
and German scientist Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( , ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera (though the Vibrio ...
, methods for isolating the bacteria responsible for a given disease and vaccines for remedy were developed at the turn of the 20th century. British physician Ronald Ross identified the mosquito as the carrier of malaria and laid the foundations for combating the disease. Joseph Lister revolutionized surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
by the introduction of antiseptic surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
to eliminate infection. French epidemiologist Paul-Louis Simond
Paul-Louis Simond (30 July 1858 – 3 March 1947) was a French physician, chief medical officer and biologist whose major contribution to science was his demonstration that the intermediates in the transmission of bubonic plague from rats to h ...
proved that plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
was carried by fleas on the back of rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
s, and Cuban scientist Carlos J. Finlay
Carlos Juan Finlay (December 3, 1833 – August 20, 1915) was a Cuban epidemiologist recognized as a pioneer in the research of yellow fever, determining that it was transmitted through mosquitoes ''Aedes aegypti''.
Biography
Early life and ...
and U.S. Americans Walter Reed and James Carroll demonstrated that mosquitoes carry the virus responsible for yellow fever. Brazilian scientist Carlos Chagas
Carlos Justiniano Ribeiro Chagas, or Carlos Chagas (; July 9, 1879 – November 8, 1934), was a Brazilian sanitary physician, scientist, and bacteriologist who worked as a clinician and researcher. He discovered Chagas disease, also called ''Ame ...
identified a tropical disease and its vector.
Society and culture
Education and training
Education and training of public health professionals is available throughout the world in Schools of Public Health, Medical Schools, Veterinary Schools, Schools of Nursing, and Schools of Public Affairs. The training typically requires a university degree with a focus on core disciplines of biostatistics
Biostatistics (also known as biometry) are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experime ...
, epidemiology, health services administration
The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services located in North Bethesda, Maryland. It is the primary federal agency for improving access to health care services for peopl ...
, health policy
Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society".World Health Organization''Health Policy'' accessed 22 March 2011(Web archive)/ref> According to the ...
, health education, behavioral science, gender issues, sexual and reproductive health, public health nutrition, and occupational
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a co ...
and environmental health.
Schools of public health: a US perspective
In the United States, the Welch-Rose Report of 1915 has been viewed as the basis for the critical movement in the history of the institutional schism between public health and medicine because it led to the establishment of schools of public health supported by the Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The second-oldest major philanthropic institution in America, after the Carneg ...
.Wickliffe Rose
Wickliffe Rose (November 19, 1862 in Saulsbury, Tennessee – September 5, 1931 in British Columbia) was the first director of the International Health Board of the Rockefeller Foundation and won the Public Welfare Medal The Public Welfare Me ...
of the Rockefeller Foundation. The report focused more on research than practical education.Samuel Zemurray
Samuel Zemurray (born Schmuel Zmurri; January 18, 1877 – November 30, 1961), nicknamed "Sam the Banana Man", was an American businessman who made his fortune in the banana trade. He founded the Cuyamel Fruit Company and later became president ...
instituted the School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine at Tulane University in 1912 conferring its first doctor of public health degree in 1914. The Yale School of Public Health
The Yale School of Public Health (YSPH) was founded in 1915 by Charles-Edward Amory Winslow and is one of the oldest public health masters programs in the United States. It is consistently rated among the best schools of public health in the cou ...
was founded by Charles-Edward Amory Winslow in 1915. The Johns Hopkins School of Hygiene and Public Health
The Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health is the public health graduate school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. As the second independent, degree-granting institution for research in epi ...
was founded in 1916 and became an independent, degree-granting institution for research and training in public health, and the largest public health training facility in the United States. By 1922, schools of public health were established at Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in ...
and Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
on the Hopkins model. By 1999 there were twenty nine schools of public health in the US, enrolling around fifteen thousand students.medical professionals
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (su ...
. However, in 1978, 69% of American students enrolled in public health schools had only a bachelor's degree.
Degrees in public health
 Schools of public health offer a variety of degrees generally fall into two categories: professional or academic. The two major postgraduate degrees are the
Schools of public health offer a variety of degrees generally fall into two categories: professional or academic. The two major postgraduate degrees are the Master of Public Health
The Master of Public Health or Master of Philosophy in Public Health (M.P.H.), Master of Science in Public Health (MSPH), Master of Medical Science in Public Health (MMSPH) and the Doctor of Public Health (Dr.P.H.), International Masters for Healt ...
(MPH) or the Master of Science in Public Health (MSPH). Doctoral studies in this field include Doctor of Public Health (DrPH) and Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in a subspecialty of greater Public Health disciplines. DrPH is regarded as a professional degree and PhD as more of an academic degree.
Professional degrees are oriented towards practice in public health settings. The Master of Public Health
The Master of Public Health or Master of Philosophy in Public Health (M.P.H.), Master of Science in Public Health (MSPH), Master of Medical Science in Public Health (MMSPH) and the Doctor of Public Health (Dr.P.H.), International Masters for Healt ...
, Doctor of Public Health, Doctor of Health Science (DHSc/DHS) and the Master of Health Care Administration are examples of degrees which are geared towards people who want careers as practitioners of public health in health departments, managed care and community-based organizations, hospitals and consulting firms, among others. Master of Public Health degrees broadly fall into two categories, those that put more emphasis on an understanding of epidemiology and statistics as the scientific basis of public health practice and those that include a more wide range of methodologies. A Master of Science of Public Health is similar to an MPH but is considered an academic degree (as opposed to a professional degree) and places more emphasis on scientific methods and research. The same distinction can be made between the DrPH and the DHSc. The DrPH is considered a professional degree and the DHSc is an academic degree.
Academic degrees are more oriented towards those with interests in the scientific basis of public health and preventive medicine who wish to pursue careers in research, university teaching in graduate programs, policy analysis and development, and other high-level public health positions. Examples of academic degrees are the Master of Science, Doctor of Philosophy, Doctor of Science (ScD), and Doctor of Health Science (DHSc). The doctoral programs are distinct from the MPH and other professional programs by the addition of advanced coursework and the nature and scope of a dissertation research project.
Notable people
* John Graunt (1620–1674) was a British citizen scientist who laid the foundations for epidemiology.
* Edward Jenner (1749–1823) created the smallpox vaccine, the first vaccine in the world. He is often known as "the father of immunology."
* Benjamin Waterhouse
Benjamin Waterhouse (March 4, 1754, Newport, Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations – October 2, 1846, Cambridge, Massachusetts) was a physician, co-founder and professor of Harvard Medical School. He is most well known for being ...
(1753–1846) introduced the smallpox vaccine in the United States.
* Lemuel Shattuck
Lemuel Shattuck (15 October 1793, Ashby, Massachusetts – 17 January 1859, Boston, Massachusetts) was a Boston politician, historian, bookseller and publisher.
Biography
He taught at Troy and Albany, NY and from 1818 to 1821 at the frontier ou ...
(1793–1859) has been described as an "architect" and "prophet" of American public health
* Sir Joseph William Bazalgette
Sir Joseph William Bazalgette CB (; 28 March 181915 March 1891) was a 19th-century English civil engineer. As chief engineer of London's Metropolitan Board of Works, his major achievement was the creation (in response to the Great Stink of 1 ...
(1819–1891) created a sewer network for central London in response to the Great Stink
The Great Stink was an event in Central London during July and August 1858 in which the hot weather exacerbated the smell of untreated human waste and industrial effluent that was present on the banks of the River Thames. The problem had been m ...
of 1858. This proved instrumental in relieving the city from cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
epidemics.
* Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization, the latter of which was named afte ...
(1822–1895) conducted research that laid the foundation for our understanding of the causes and preventions of diseases.
* Charles V. Chapin
Charles Value Chapin (January 17, 1856 – January 31, 1941) was an American pioneer in public health research and practice during the Progressive Era. He was superintendent of health for Providence, Rhode Island between 1884 and 1932. He est ...
(1856–1941) public health advocate and researcher credited with planting "the roots of quality in public health" in the United StatesNora Wattie
Nora Wattie (1900–1994) MBChB (Aberdeen), DPH (Cambridge) was a pioneer of social medicine, setting up Glasgow’s internationally renowned ante-natal care service (both before and after the creation of the National Health Service).
Throughou ...
(1900–1994) led the development of public health services and sanitation, and education in improving women and child health in the poorest slum
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily inh ...
s of Glasgow, for which she received the OBE
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations,
and public service outside the civil service. It was established o ...
.
* Jonas Salk (1914–1995) developed one of the first polio vaccines and campaigned vigorously for mandatory vaccinations.
* Ruth Huenemann (1910-2005) She became a pioneer in the study of childhood obesity in the 1960s studying the diet and exercise habits of Berkeley teenagers.
Country examples
Canada
In Canada, the Public Health Agency of Canada is the national agency responsible for public health, emergency preparedness and response, and infectious and chronic disease control and prevention.
Cuba
Since the 1959 Cuban Revolution the Cuban government has devoted extensive resources to the improvement of Healthcare in Cuba, health conditions for its entire population via universal access to health care. Infant mortality has plummeted. Cuban medical internationalism as a policy has seen the Cuban government sent doctors as a form of aid and export to countries in need in Latin America, especially Mission Barrio Adentro, Venezuela, as well as Oceania and Africa countries.
Colombia and Bolivia
Public health was important elsewhere in Latin America in consolidating state power and integrating marginalized populations into the nation-state. In Colombia, public health was a means for creating and implementing ideas of citizenship. In Bolivia, a similar push came after their 1952 revolution.
Ghana
Though curable and preventive, malaria remains a major public health issue and is the third leading cause of death in Ghana.
France
Mexico
United States
The United States lacks a coherent system for the governmental funding of public health, relying on a variety of agencies and programs at the federal, state and local levels.
See also
* Effects of climate change on human health
* European Public Health Association (EUPHA) is an umbrella organization for public health associations and institutes in Europe
* List of national public health agencies
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Public Health
Public health,
Euthenics
Health economics
Health policy
Medical humanities
Sanitation
 Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a 
 Public health is related to global health which is the health of populations in the worldwide context. It has been defined as "the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in " Health for all" people worldwide". International health is a field of health care, usually with a public health emphasis, dealing with health across regional or national boundaries. Public health is not the same as public healthcare (
Public health is related to global health which is the health of populations in the worldwide context. It has been defined as "the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in " Health for all" people worldwide". International health is a field of health care, usually with a public health emphasis, dealing with health across regional or national boundaries. Public health is not the same as public healthcare ( Public health aims are achieved through surveillance of cases and the promotion of healthy behaviors,
Public health aims are achieved through surveillance of cases and the promotion of healthy behaviors,  The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies core functions of public health programs including:
* providing leadership on matters critical to health and engaging in partnerships where joint action is needed;
* shaping a research agenda and stimulating the generation, translation and dissemination of valuable knowledge;
* setting norms and standards and promoting and monitoring their implementation;
* articulating ethical and
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies core functions of public health programs including:
* providing leadership on matters critical to health and engaging in partnerships where joint action is needed;
* shaping a research agenda and stimulating the generation, translation and dissemination of valuable knowledge;
* setting norms and standards and promoting and monitoring their implementation;
* articulating ethical and 
 Large parts of the world remained plagued by largely preventable or treatable infectious diseases. In addition to this however, many developing countries are also experiencing an epidemiological shift and
Large parts of the world remained plagued by largely preventable or treatable infectious diseases. In addition to this however, many developing countries are also experiencing an epidemiological shift and  From the beginnings of human civilization, communities promoted health and fought disease at the population level. Definitions of health as well as methods to pursue it differed according to the medical, religious and natural- philosophical ideas groups held, the resources they had, and the changing circumstances in which they lived. Yet few early societies displayed the hygienic stagnation or even apathy often attributed to them. The latter reputation is mainly based on the absence of present-day bioindicators, especially
From the beginnings of human civilization, communities promoted health and fought disease at the population level. Definitions of health as well as methods to pursue it differed according to the medical, religious and natural- philosophical ideas groups held, the resources they had, and the changing circumstances in which they lived. Yet few early societies displayed the hygienic stagnation or even apathy often attributed to them. The latter reputation is mainly based on the absence of present-day bioindicators, especially  Western European, Byzantine and Islamicate civilizations, which generally adopted a Hippocratic, Galenic or humoral medical system, fostered preventive programs as well. These were developed on the basis of evaluating the quality of local climates, including topography, wind conditions and exposure to the sun, and the properties and availability of water and food, for both humans and nonhuman animals. Diverse authors of medical,
Western European, Byzantine and Islamicate civilizations, which generally adopted a Hippocratic, Galenic or humoral medical system, fostered preventive programs as well. These were developed on the basis of evaluating the quality of local climates, including topography, wind conditions and exposure to the sun, and the properties and availability of water and food, for both humans and nonhuman animals. Diverse authors of medical,  The first attempts at sanitary reform and the establishment of public health institutions were made in the 1840s.
The first attempts at sanitary reform and the establishment of public health institutions were made in the 1840s.  The science of epidemiology was founded by
The science of epidemiology was founded by  With the pioneering work in bacteriology of French chemist
With the pioneering work in bacteriology of French chemist  Schools of public health offer a variety of degrees generally fall into two categories: professional or academic. The two major postgraduate degrees are the
Schools of public health offer a variety of degrees generally fall into two categories: professional or academic. The two major postgraduate degrees are the