|
Thomas Southwood Smith
Thomas Southwood Smith (17881861) was an English physician and sanitary reformer. Early life Smith was born at Martock, Somerset, into a strict Baptist family, his parents being William Smith and Caroline Southwood. In 1802 he won a scholarship to the Bristol Baptist College to train as a minister, but in 1807 funds were abruptly withdrawn, on the grounds that he was 'entertaining opinions widely different from us on most of the doctrines we consider to be essential to Evangelical Religion'. At 19 years old he was already showing the courage and independence of mind that were to characterise his life, however it led to a break with his parents who never spoke to him again. Over the following four years Smith turned to Unitarianism, influenced by William Blake, a minister at Crewkerne, Somerset: Blake put him in touch with John Prior Estlin at Lewin's Mead, Bristol. Another friend, and Unitarian convert from Baptism who became a physician, was Benjamin Spencer. These associatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
James Charles Armytage
James Charles Armytage ( – 28 April 1897Devon Libraries Local Studies ServiceBiographical dictionary of printmakers: A-D. URL last accessed 2020-10-21.) was an England, English engraver of the 19th century. He produced over 200 plates. References External Links * An engraving of by Charles Bentley (painter), Charles Bentley with a poetical illustration by Letitia Elizabeth Landon. Further reading *Hunnisett, B.: ''Dictionary of British Steel Engravers''; F. Lewis, 1981. . English engravers 1800s births 1897 deaths Year of birth uncertain {{England-artist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
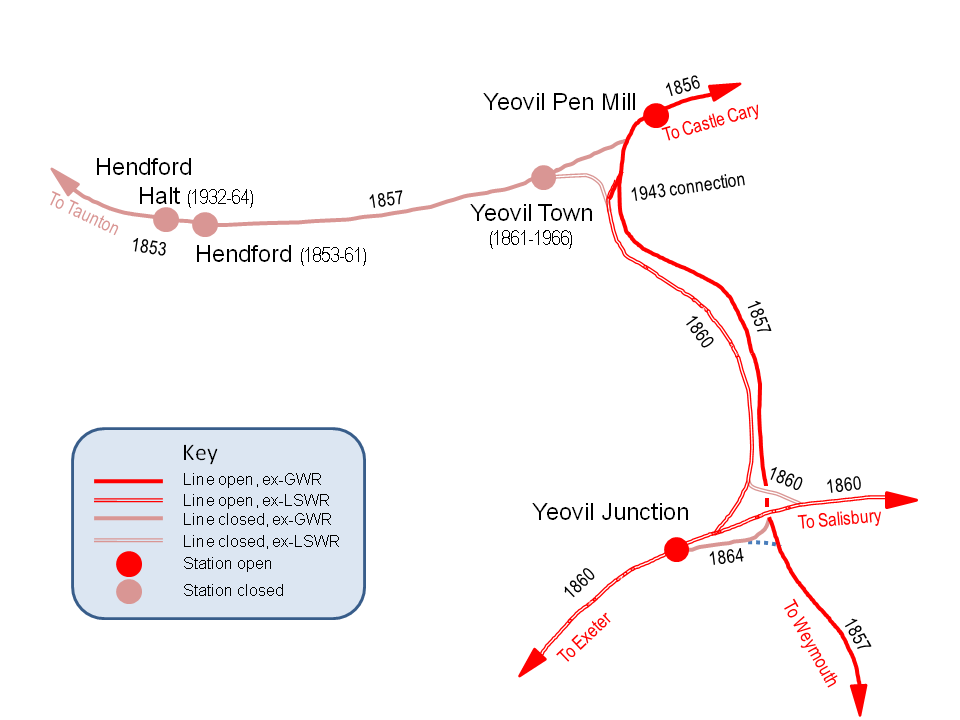 |
Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol, from Sherborne and from Taunton. The aircraft and defence industries which developed in the 20th century made it a target for bombing in the Second World War; they are still major employers. Yeovil Country Park, which includes Ninesprings, is one of several open spaces with educational, cultural and sporting facilities. Religious sites include the 14th-century Church of St John the Baptist. The town is on the A30 and A37 roads and has two railway stations. History Archaeological surveys have yielded Palaeolithic burial and settlement sites mainly to the south of the modern town, particularly in Hendford, where a Bronze Age golden torc (twisted collar) was found. Yeovil is on the main Roman roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Edward Seymour, 12th Duke Of Somerset
Edward Adolphus Seymour (later St. Maur), 12th Duke of Somerset, etc., (20 December 180428 November 1885), styled Lord Seymour until 1855, was a British Whig aristocrat and politician, who served in various cabinet positions in the mid-19th century, including that of First Lord of the Admiralty. Background and education Somerset was the eldest son of Edward St. Maur, 11th Duke of Somerset, and Lady Charlotte, daughter of Archibald Hamilton, 9th Duke of Hamilton. He was baptized on 16 February 1805 at St. George's, Hanover Square, London. He was educated at Eton and Christ Church, Oxford. Political career Somerset sat as Member of Parliament as Lord Seymour for Okehampton between 1830 and 1831 and for Totnes between 1834 and 1855. He served under Lord Melbourne as a Lord of the Treasury between 1835 and 1839, as Joint Secretary to the Board of Control between 1839 and 1841 and as Under-Secretary of State for the Home Department between June and August 1841 and was a membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Central Board Of Health
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Miasma Theory
The miasma theory (also called the miasmatic theory) is an Superseded scientific theories#Biology, obsolete medical theory that opinion, held that diseases—such as cholera, Chlamydia infection, chlamydia, or the Black Death—were caused by a ''miasma'' (, Ancient Greek for 'pollution'), a noxious form of "bad air", also known as night air. The theory held that epidemics were caused by miasma, emanating from rotting organic matter. Though miasma theory is typically associated with the spread of contagious diseases, some academics in the early nineteenth century suggested that the theory extended to other conditions as well, e.g. one could become obese by inhaling the odor of food. The miasma theory was advanced by Hippocrates in the fourth century B.C. and accepted from ancient times in Europe and China. The theory was eventually abandoned by scientists and physicians after 1880, replaced by the germ theory of disease: specific germs, not miasma, caused specific diseases. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Edwin Chadwick
Sir Edwin Chadwick KCB (24 January 18006 July 1890) was an English social reformer who is noted for his leadership in reforming the Poor Laws in England and instituting major reforms in urban sanitation and public health. A disciple of Utilitarian philosopher Jeremy Bentham, he was most active between 1832 and 1854; after that he held minor positions, and his views were largely ignored. Chadwick pioneered the use of scientific surveys to identify all phases of a complex social problem, and pioneered the use of systematic long-term inspection programmes to make sure the reforms operated as planned. Early life Edwin Chadwick was born on 24 January 1800 at Longsight, Manchester. His mother died when he was still a young child, yet to be named. His father, James Chadwick, tutored the scientist John Dalton in music and botany and was considered to be an advanced liberal politician, thus exposing young Edwin to political and social ideas. His grandfather, Andrew Chadwick, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Metropolitan Association For Improving The Dwellings Of The Industrious Classes
In London, the Metropolitan Association for Improving the Dwellings of the Industrious Classes (MAIDIC) was a Victorian-era, philanthropically-motivated model dwellings company. The association, established in 1841, was fore-runner of the modern housing association which sought to provide affordable housing for the working classes on a privately run basis, with a financial return for investors. Although not the first society to build such homes, the Association was the first to be founded expressly for this purpose.Tarn, J. N. (1973) Five Per Cent Philanthropy. London: CUP As such it was one of the earliest adopters of the principal of the five per cent philanthropy model, outlined in the Company's resolution: "that an association be formed for the purpose of providing the labouring man with an increase of the comforts and conveniences of life, with full return to the capitalist." History The association was formed in 1841 by a group including Thomas Southwood Smith, Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Housing Association
In Ireland and the United Kingdom, housing associations are private, non-profit making organisations that provide low-cost " social housing" for people in need of a home. Any budget surplus is used to maintain existing housing and to help finance new homes and it cannot be used for personal benefit of directors or shareholders. Although independent, they are regulated by the state and commonly receive public funding. They are now the United Kingdom's major providers of new housing for rent, while many also run shared ownership schemes to help those who cannot afford to buy a home outright. Housing associations provide a wide range of housing, some managing large estates of housing for families, while the smallest may perhaps manage a single scheme of housing for older people. Much of the supported accommodation in the UK is also provided by housing associations, with specialist projects for people with mental health issues or learning disabilities, with substance misuse pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Poor Law Commission
The Poor Law Commission was a body established to administer poor relief after the passing of the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834. The commission was made up of three commissioners who became known as "The Bashaws of Somerset House", their secretary and nine clerks or assistant commissioners. The commission lasted until 1847 when it was replaced by a Poor Law Boardthe Andover workhouse scandal being one of the reasons for this change. Edwin Chadwick, one of the writers of the 1832 Royal Commission hoped to become Commissioner but instead only got the post of Secretary. This caused clashes with the Poor Law Commissioners. This was one reason the Poor Law Commission was eventually abolishedthere was too much infighting within the organisation. Powers The Poor Law Commission was independent of Parliament. This made it vulnerable to criticism from those inside Parliament. In the parishes the commissioners were almost universally hated.Poverty and Public Health 1815-1948 by Rosemary Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
James Phillips Kay
Sir James Phillips Kay-Shuttleworth, 1st Baronet (20 July 1804 – 26 May 1877, born James Kay) of Gawthorpe Hall, Lancashire, was a British politician and educationist. He founded a further-education college that would eventually become Plymouth Marjon University. Early life He was born James Kay at Rochdale, Lancashire, the son of Robert Kay and the brother of Joseph Kay and Sir Edward Ebenezer Kay. Career At first engaged in a Rochdale bank, he became in 1824 a medical student at the University of Edinburgh. He settled in Manchester about 1827 and was instrumental in setting up the Manchester Statistical Society. He worked for the Ardwick and Ancoats Dispensary. While still known simply as Dr James Kay, he wrote ''The Moral and Physical Condition of the Working Class Employed in the Cotton Manufacture in Manchester'' (1832), which Friedrich Engels cited in ''The Condition of the Working Class in England''. The experience he gained of the conditions of the poor in Lancashir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Neil Arnott
Dr Neil Arnott FRS LLD (15 May 1788March 1874) was a Scottish physician and inventor. He was the inventor of one of the first forms of the waterbed, the Arnott waterbed, and was awarded the Rumford Medal in 1852 for the construction of the smokeless fire grate, as well as other improvements to ventilation and heating. Life He was born in Arbroath, the son of Alexander Arnott and his wife, Ann MacLean of Borreray. He came from a line of master bakers. Neil Arnott was a distinguished graduate of Marischal College, University of Aberdeen (AM, 1805; MD 1814) and subsequently studied in London under Sir Everard Home (1756–1832), through whom he obtained, when only eighteen, the appointment of full surgeon to an East Indiaman. After making two voyages to China acting as a surgeon in the service of the British East India Company (1807-9 and 1810–11), he settled in London where he practised from 1811–1854, and quickly acquired a high reputation. He gave lectures at the Philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Diseases Of Poverty
Diseases of poverty (also known as poverty-related diseases) are diseases that are more prevalent in low-income populations. They include infectious diseases, as well as diseases related to malnutrition and poor health behaviour. Poverty is one of the major social determinants of health. The World Health Report (2002) states that diseases of poverty account for 45% of the disease burden in the countries with high poverty rate which are preventable or treatable with existing interventions. Diseases of poverty are often co-morbid and ubiquitous with malnutrition. Poverty increases the chances of having these diseases as the deprivation of shelter, safe drinking water, nutritious food, sanitation, and access to health services contributes towards poor health behaviour. At the same time, these diseases act as a barrier for economic growth to affected people and families caring for them which in turn results into increased poverty in the community. These diseases produced in part by po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |