Protorosaurus Skull Diagram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Protorosaurus'' ("first lizard") is a genus of lizard-like early
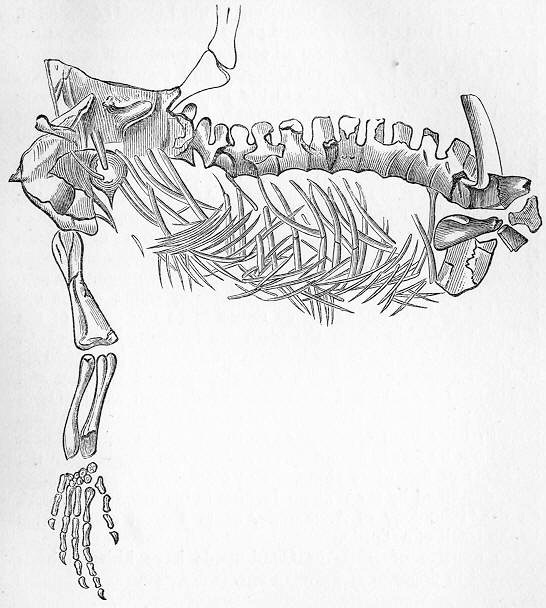 ''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in
''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in
 Stomach contents of a specimen of ''Protorosaurus'' show the presence of numerous ovules of the locally common voltzialean conifer '' Ullmannia frumentaria'', which was unexpected given its unspecialised dentiton of conical and unserrated teeth, which were assumed to represent a predatory lifestyle. Along with the coniferous ovules, several rounded pebbles were found in the body cavity, these may have functioned as
Stomach contents of a specimen of ''Protorosaurus'' show the presence of numerous ovules of the locally common voltzialean conifer '' Ullmannia frumentaria'', which was unexpected given its unspecialised dentiton of conical and unserrated teeth, which were assumed to represent a predatory lifestyle. Along with the coniferous ovules, several rounded pebbles were found in the body cavity, these may have functioned as
 The Kupferschiefer and equivalent Marl Slate is a marine unit that forms part of the
The Kupferschiefer and equivalent Marl Slate is a marine unit that forms part of the
reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s. Members of the genus lived during the late Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
period in what is now Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. Once believed to have been an ancestor to lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia alt ...
s, ''Protorosaurus'' is now known to be one of the oldest and most primitive members of Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, liza ...
, the group that would eventually lead to archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian d ...
s such as crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
s and dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s.
Description
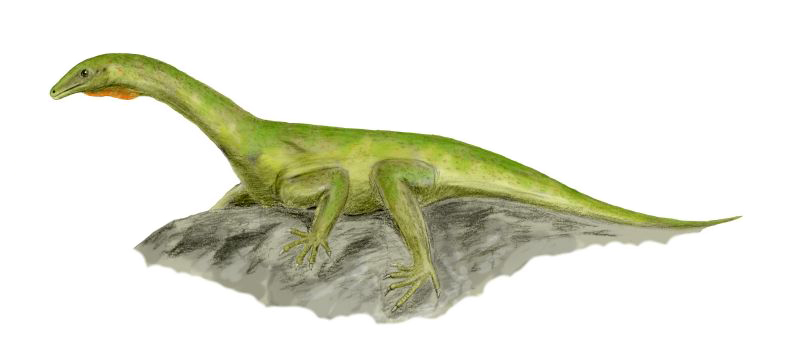
''Protorosaurus'' grew up to in length, and was a slender, lizard-like animal, vaguely resembling amonitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are recogn ...
, with long legs and a long neck.
Discovery
 ''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in
''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and larg ...
in Germany, who considered the animal to be a crocodile, and most similar to the Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern ...
(''C. niloticus''). Over a century later, in publications in 1830 and 1832 Hermann von Meyer recognised ''Protorosaurus'' as distinct extinct reptile and gave it a formal species description, dedicating an extensive monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monograph ...
to it in 1856. In 1871 Thomas Henry Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The storie ...
erected the clade Protorosauria, with ''Protorosaurus'' as the only member. The German specimens were found in the Kupferschiefer
The Kupferschiefer (German for Copper Shale, also called Copper Slate) or Kupfermergel (Copper Marl), (T1 or Z1) is an extensive and remarkable sedimentary unit in Central Europe. The relatively monotonous succession is typically and maximum th ...
a widespread unit of Late Permian (likely Wuchiapingian
In the geologic timescale, the Wuchiapingian or Wujiapingian (from in the Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province) is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the lower or earlier of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The ...
) age.
In 1914, a new ceratopsian
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
dinosaur found by Lawrence Lambe
Lawrence Morris Lambe (August 27, 1863 – March 12, 1919) was a Canadian geologist, palaeontologist, and ecologist from the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC).
His published work, describing the diverse and plentiful dinosaur discoveries from th ...
was again given the name ''Protorosaurus'' (in this sense meaning "before ''Torosaurus
''Torosaurus'' ("perforated lizard", in reference to the large openings in its frill) is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous period, between 68 and 66 million years ago, tho ...
''"). When Lambe found that the name had already been used for the early archosauromorph, he renamed his ceratopsian ''Chasmosaurus
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' ...
''.
In 1870, a new species, ''Protorosaurus huxleyi'' was described from a railway cutting
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
near Middridge in County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East E ...
in northern England, in sediments belonging to the Marl Slate
The Marl Slate Formation is a geological formation in England. Despite its name, it is mostly dolomite rock. The Marl Slate Formation was formed about 273 to 259 million years ago, during the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the late Permian ...
, a unit that is equivalent to the Kupferschiefer, however it was later shown that this specimen was not ''Protorosaurus'', and it was subsequently placed in the new genus '' Adelosaurus''. In 1993, a specimen of ''Protorosaurus'' was described from Quarrington Quarry also in County Durham, in sediments of the Marl Slate. This skeleton included fragments of the skull that had not previously been known. A thorough redescription of ''Protorosaurus'' was published in 2009, including a specimen with a complete skull.
Paleobiology
 Stomach contents of a specimen of ''Protorosaurus'' show the presence of numerous ovules of the locally common voltzialean conifer '' Ullmannia frumentaria'', which was unexpected given its unspecialised dentiton of conical and unserrated teeth, which were assumed to represent a predatory lifestyle. Along with the coniferous ovules, several rounded pebbles were found in the body cavity, these may have functioned as
Stomach contents of a specimen of ''Protorosaurus'' show the presence of numerous ovules of the locally common voltzialean conifer '' Ullmannia frumentaria'', which was unexpected given its unspecialised dentiton of conical and unserrated teeth, which were assumed to represent a predatory lifestyle. Along with the coniferous ovules, several rounded pebbles were found in the body cavity, these may have functioned as gastroliths
A gastrolith, also called a stomach stone or gizzard stone, is a rock held inside a gastrointestinal tract. Gastroliths in some species are retained in the muscular gizzard and used to grind food in animals lacking suitable grinding teeth. In oth ...
.
Relationships
''Protorosaurus'' has been suggested to be closely related to ''Czatkowiella
''Czatkowiella'' is an extinct genus of long-necked archosauromorph known from Early Triassic (Olenekian age) rocks of Czatkowice 1, Poland. It was first named by Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka and Susan E. Evans in 2009 and the type species is ' ...
'' from the Early Triassic of Poland, but the remains of ''Czatkowiella'' are fragmentary and mixed in with those of other reptiles, so it is possible that the taxon is a chimaera
Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes , known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish, spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last three names are not to be confused with rattails, Opisthoproctidae, or Siganidae, respectively.
At ...
. In a comprehensive analysis of "Protorosauria" in 2021, ''Protorosaurus'' was consistently recovered as the earliest diverging member of Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, liza ...
.
The cladogram below follows an analysis by Ezcurra (2016), and highlights the position of ''Protorosaurus'' among other early archosauromorph reptiles.
Paleoenvironment
 The Kupferschiefer and equivalent Marl Slate is a marine unit that forms part of the
The Kupferschiefer and equivalent Marl Slate is a marine unit that forms part of the Zechstein
The Zechstein (German either from ''mine stone'' or ''tough stone'') is a unit of sedimentary rock layers of Middle to Late Permian (Guadalupian to Lopingian) age located in the European Permian Basin which stretches from the east coast of Englan ...
, a sequence of rocks formed on the edge of the Zechstein Sea, a large inland shallow sea that existed in Northern Europe during the Late Permian. The environment at the time of deposition is considered to have been semi-arid. The terrestrial flora of the Zechstein is dominated by conifers, with seed ferns
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm pl ...
also being common, while taeniopterids, ginkgophytes and sphenophytes are rare. Other terrestrial vertebrates found in the Kupfershiefer and lower Zechstein include the gliding weigeltisaurid
Weigeltisauridae is a family of gliding neodiapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian, between 258 and 252 million years ago. Fossils of weigeltisaurids have been found in Madagascar, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia. A possible weigelt ...
reptiles '' Weigeltisaurus'' and '' Glaurung,'' the pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, ...
''Parasaurus
''Parasaurus'' (meaning "near lizard") is a genus of pareiasaur known from fossils collected in the Kupferschiefer in Germany (Hesse, Thuringia and Lower Saxony), dating to the Late Permian (Wuchiapingian). The type species, ''Parasaurus geinit ...
,'' the cynodont
The cynodonts () (clade Cynodontia) are a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts had a wide variety ...
'' Procynosuchus,'' and indeterminate captorhinids
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea.
Description
C ...
, dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typicall ...
s, and dissorophid
Dissorophidae is an extinct family of medium-sized, temnospondyl amphibians that flourished during the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. The clade is known almost exclusively from North America.
History of study
Dissorophidae is a ...
temnospondyls.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q134702 Prehistoric reptile genera Lopingian life Prehistoric archosauromorphs Permian reptiles of Europe Permian Germany Fossils of Germany Kupferschiefer Fossil taxa described in 1830 Taxa named by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer