|
Chasmosaurus
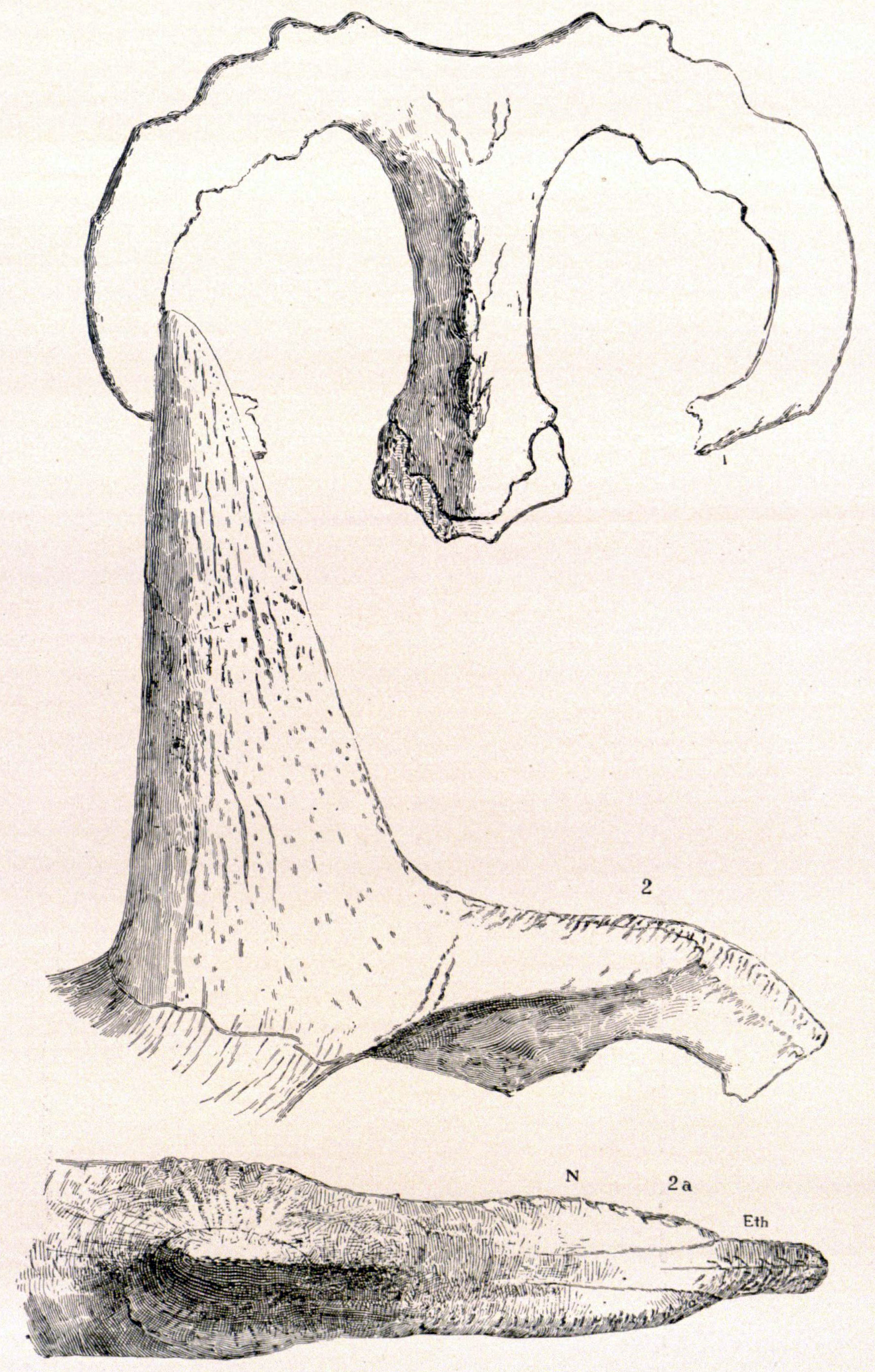
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' or 'gulf' and ''sauros'' meaning 'lizard'). With a length of and a weight of , ''Chasmosaurus'' was a ceratopsian of average size. Like all ceratopsians, it was purely herbivorous. It was initially to be called ''Protorosaurus'', but this name had been previously published for another animal. All specimens of ''Chasmosaurus'' were collected from the Dinosaur Park Formation of the Dinosaur Provincial Park of Alberta, Canada. Referred specimens of ''C. russelli'' come from the lower beds of the formation while ''C. belli'' comes from middle and upper beds. Discovery and species In 1898, at ''Berry Creek'', Alberta, Lawrence Morris Lambe of the Geological Survey of Canada made the first discovery of ''Chasmosaurus'' remains; holotype NMC 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagaceratops
''Vagaceratops'' (meaning "wandering (''vagus'', Latin) horned face", in reference to its close relationship with ''Kosmoceratops'' from Utah) is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a chasmosaurine ceratopsian which lived during the Late Cretaceous period (late Campanian) in what is now Alberta. Its fossils have been recovered from the Upper Dinosaur Park Formation. It is sometimes included in the genus ''Chasmosaurus'' as ''Chasmosaurus irvinensis'' instead of being recognized as its own genus. Description ''Vagaceratops'' was a medium-sized ceratopsian, reaching in length and weighing . It is known primarily from three fossil skulls. Although the general structure was typical of ceratopsids (i.e. a parrot-like beak, large neck frill, and nasal horn) it has some peculiarities. The skulls are characterized by a reduced supraorbital horn, brow horns that are reduced to low bosses and a larger snout compared to related animals. ''Vagaceratops'' had smaller parieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant remains, are also abundant. The formation has been named after Dinosaur Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914 In Paleontology
References * Trexler, D., 2001, Two Medicine Formation, Montana: geology and fauna: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, pp. 298–309. 1910s in paleontology 1914, Paleontology 1914 in science, Paleontology 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Provincial Park
Dinosaur Provincial Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site situated a two hour drive east of Calgary, Alberta, Canada; or , about a half-hour drive northeast of Brooks. The park is situated in the Red Deer River valley, which is noted for its striking badland topography, and abundance of dinosaur fossils. The park is well known for being one of the richest dinosaur fossil locales in the world. Fifty-eight dinosaur species have been discovered at the park and more than 500 specimens have been removed and exhibited in museums around the globe. The renowned fossil assemblage of nearly 500 species of life, from microscopic fern spores to large carnivorous dinosaurs, justified its becoming a World Heritage Site in 1979. Dinosaur Provincial Park Visitor Centre The Dinosaur Provincial Park Visitor Centre features exhibits about dinosaurs, fossils, and the geology and natural history of the park. There is a video theatre, fossil prep lab area, and a gift shop. Public programs are offered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonius
''Monoclonius'' (meaning "single sprout") is a dubious genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous layers of the Judith River Formation in Montana, United States, and the uppermost rock layers of the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta, Canada dated to between 75 and 74.6 million years ago. ''Monoclonius'' was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1876. Later, much taxonomic confusion was caused by the discovery of ''Centrosaurus'', a very similar genus of ceratopsian that is known from much better remains. Today, typical ''Monoclonius'' specimens are usually believed to be juveniles or subadults, in many cases of other genera such as ''Centrosaurus''. Those specimens that remain under the name ''Monoclonius'' are mostly too incomplete or immature to be confidently matched with adult specimens from the same time and place. This is especially true of the type species, ''Monoclonius crassus''. Therefore, ''Monoclonius'' is now usually considered a '' nomen dubiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Lambe
Lawrence Morris Lambe (August 27, 1863 – March 12, 1919) was a Canadian geologist, palaeontologist, and ecologist from the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC). His published work, describing the diverse and plentiful dinosaur discoveries from the fossil beds in Alberta, did much to bring dinosaurs into the public eye and helped usher in the ''Golden Age of Dinosaurs'' in the province. During this period, between the 1880s and World War I, dinosaur hunters from all over the world converged on Alberta. ''Lambeosaurus'', a well-known hadrosaur, was named after him as a tribute, in 1923. In addition to paleontology, Lambe discovered a number of invertebrate species ranging from Canada to the Pacific Northwest. Lambe's contemporary discoveries were published in works such as ''Sponges From the Atlantic Coast of Canada'' and ''Catalogue of the recent marine sponges of Canada and Alaska''. Early life and education Lambe was born in Montreal on August 27, 1863. Lambe studied at the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 ''Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herba' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Survey Of Canada
The Geological Survey of Canada (GSC; french: Commission géologique du Canada (CGC)) is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country, developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the environment. A branch of the Earth Sciences Sector of Natural Resources Canada, the GSC is the country's oldest scientific agency and was one of its first government organizations. History In September 1841, the Province of Canada legislature passed a resolution that authorized the sum of £1,500 sterling be granted to the government for the estimated expense of performing a geological survey of the province. In 1842, the Geological Survey of Canada was formed to fulfill this request.Christy Vodden (1992)No Stone Unturned: The First 150 years of the Geological Survey of Canada Geological Survey of Canada Web site William Edmond Logan was in Montreal at the time and made it known that he was interested in participating in this survey. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunting Dinosaurs In The Bad Lands Of The Red Deer River, Alberta, Canada; A Sequel To The Life Of A Fossil Hunter (1917) (20765045131)
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, etc.), for recreation/taxidermy (see trophy hunting), to remove predators dangerous to humans or domestic animals (e.g. wolf hunting), to eliminate pests and nuisance animals that damage crops/livestock/poultry or spread diseases (see varminting), for trade/tourism (see safari), or for ecological conservation against overpopulation and invasive species. Recreationally hunted species are generally referred to as the ''game'', and are usually mammals and birds. A person participating in a hunt is a hunter or (less commonly) huntsman; a natural area used for hunting is called a game reserve; an experienced hunter who helps organize a hunt and/or manage the game reserve is known as a gamekeeper. Many non-human animals also hunt (see predat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_NPS_img1.jpg)


_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)

