Portsmouth Operating Company Limited on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Portsmouth ( ) is a
 Although Portsmouth was not mentioned in the 1086
Although Portsmouth was not mentioned in the 1086 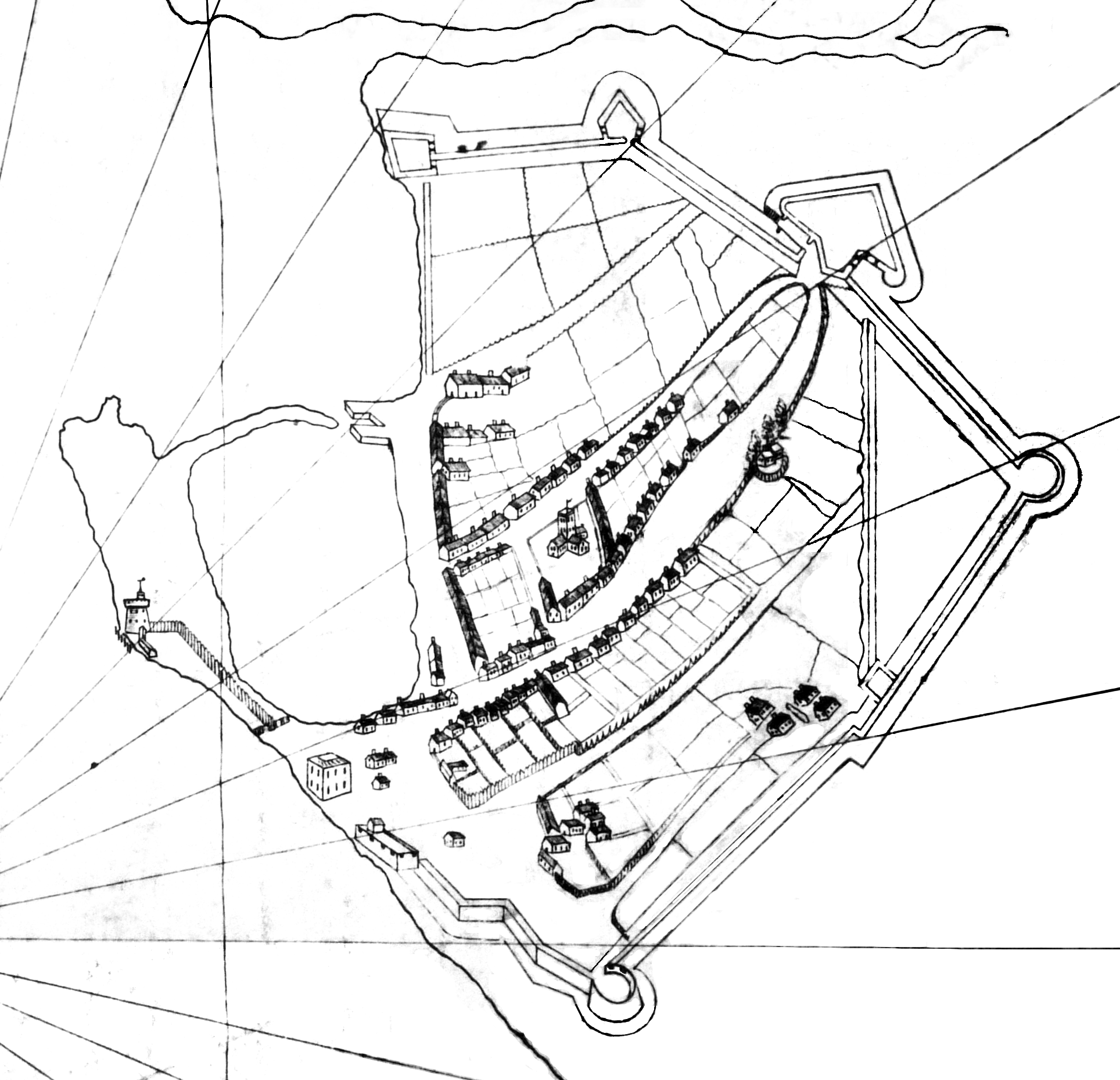
 In 1623,
In 1623,
 Marc Isambard Brunel established the world's first mass-production line at Portsmouth Block Mills, making
Marc Isambard Brunel established the world's first mass-production line at Portsmouth Block Mills, making
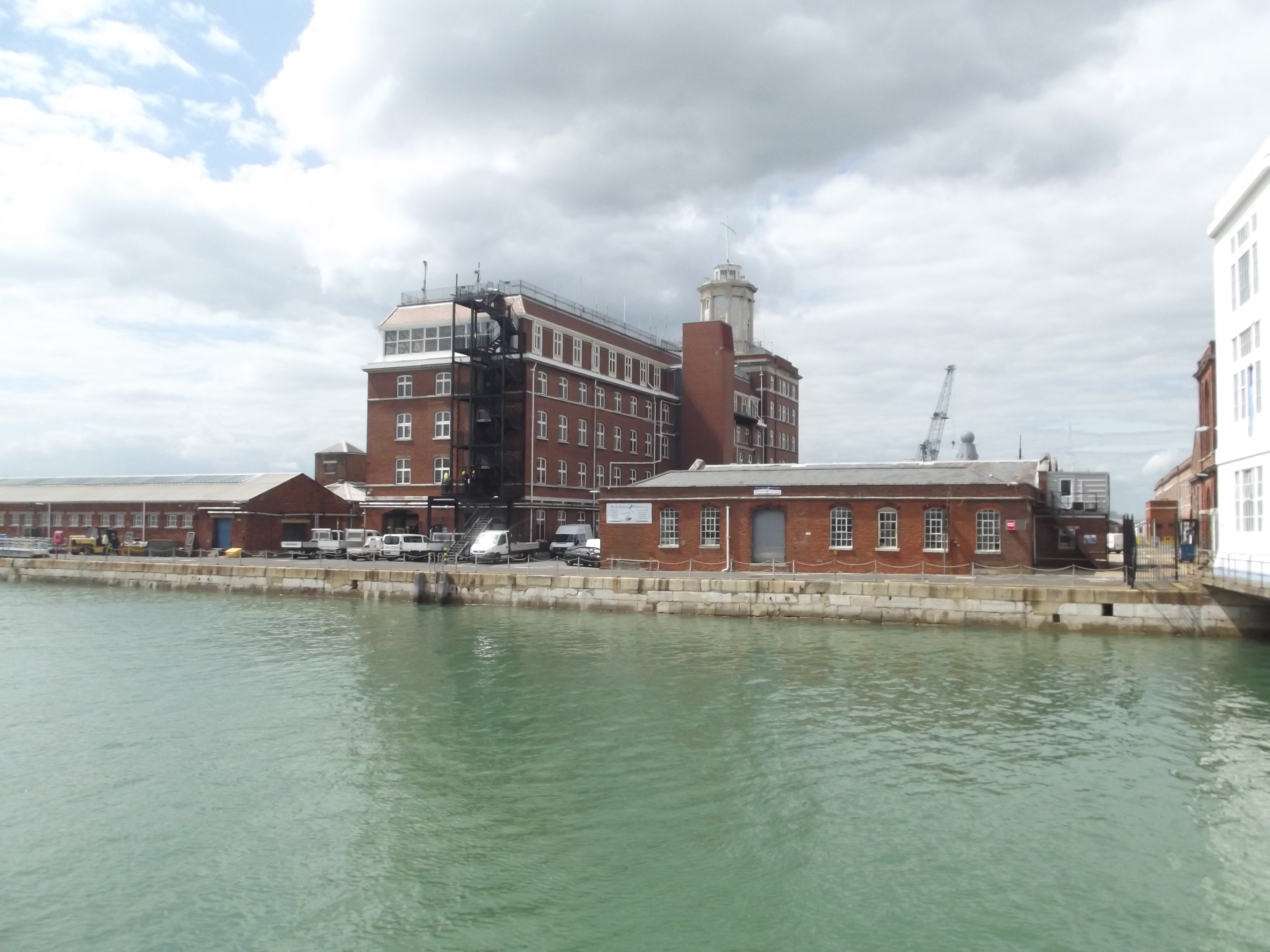 A major
A major
 On 1 October 1916, Portsmouth was bombed by a
On 1 October 1916, Portsmouth was bombed by a
 Portsmouth was affected by the decline of the British Empire in the second half of the 20th century. Shipbuilding jobs fell from 46 percent of the workforce in 1951 to 14 per cent in 1966, drastically reducing manpower in the dockyard. The city council attempted to create new work; an industrial estate was built in Fratton in 1948, and others were built at Paulsgrove and Farlington during the 1950s and 1960s. Although traditional industries such as brewing and corset manufacturing disappeared during this time, electrical engineering became a major employer. Despite the cutbacks in traditional sectors, Portsmouth remained attractive to industry. Zurich Insurance Group moved their UK headquarters to the city in 1968, and IBM relocated their European headquarters in 1979. Portsmouth's population had dropped from about 200,000 to 177,142 by the end of the 1960s. Defence Secretary
Portsmouth was affected by the decline of the British Empire in the second half of the 20th century. Shipbuilding jobs fell from 46 percent of the workforce in 1951 to 14 per cent in 1966, drastically reducing manpower in the dockyard. The city council attempted to create new work; an industrial estate was built in Fratton in 1948, and others were built at Paulsgrove and Farlington during the 1950s and 1960s. Although traditional industries such as brewing and corset manufacturing disappeared during this time, electrical engineering became a major employer. Despite the cutbacks in traditional sectors, Portsmouth remained attractive to industry. Zurich Insurance Group moved their UK headquarters to the city in 1968, and IBM relocated their European headquarters in 1979. Portsmouth's population had dropped from about 200,000 to 177,142 by the end of the 1960s. Defence Secretary
 South of Portsmouth are
South of Portsmouth are
 Portsmouth is the only city in the
Portsmouth is the only city in the


 The city is administered by Portsmouth City Council, a
The city is administered by Portsmouth City Council, a
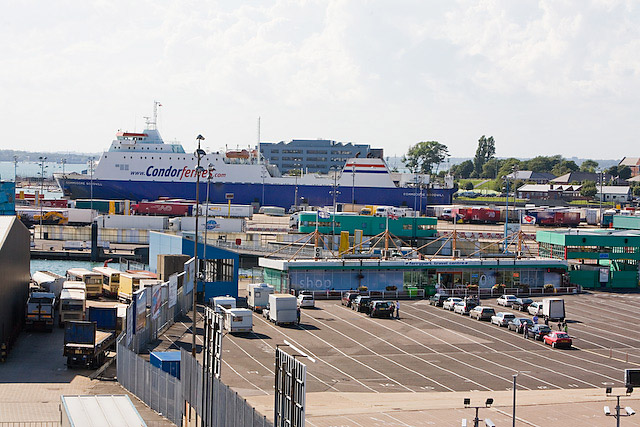 Ten per cent of Portsmouth's workforce is employed at Portsmouth Naval Dockyard, which is linked to the city's biggest industry, defence; the headquarters of BAE Systems Surface Ships is in the city. BAE's Portsmouth shipyard received construction work on the two new s. A £100 million contract was signed to develop needed facilities for the vessels. A ferry port handles passengers and cargo, and a fishing fleet of 20 to 30 boats operates out of Camber Quay, Old Portsmouth; most of the catch is sold at the quayside fish market.
The city is host to IBM's UK headquarters and Portsmouth was also the UK headquarters of Zurich Financial Services until 2007. City shopping is centred on Commercial Road and the 1980s Cascades Shopping Centre. The shopping centre has 185,000 to 230,000 visitors weekly. Redevelopment has created new shopping areas, including the Gunwharf Quays (the repurposed shore establishment, with stores, restaurants and a cinema) and the Historic Dockyard, which caters to tourists and holds an annual Victorian Christmas market. Ocean Retail Park, on the north-eastern side of Portsea Island, was built in September 1985 on the site of a former metal-box factory.
Ten per cent of Portsmouth's workforce is employed at Portsmouth Naval Dockyard, which is linked to the city's biggest industry, defence; the headquarters of BAE Systems Surface Ships is in the city. BAE's Portsmouth shipyard received construction work on the two new s. A £100 million contract was signed to develop needed facilities for the vessels. A ferry port handles passengers and cargo, and a fishing fleet of 20 to 30 boats operates out of Camber Quay, Old Portsmouth; most of the catch is sold at the quayside fish market.
The city is host to IBM's UK headquarters and Portsmouth was also the UK headquarters of Zurich Financial Services until 2007. City shopping is centred on Commercial Road and the 1980s Cascades Shopping Centre. The shopping centre has 185,000 to 230,000 visitors weekly. Redevelopment has created new shopping areas, including the Gunwharf Quays (the repurposed shore establishment, with stores, restaurants and a cinema) and the Historic Dockyard, which caters to tourists and holds an annual Victorian Christmas market. Ocean Retail Park, on the north-eastern side of Portsea Island, was built in September 1985 on the site of a former metal-box factory.
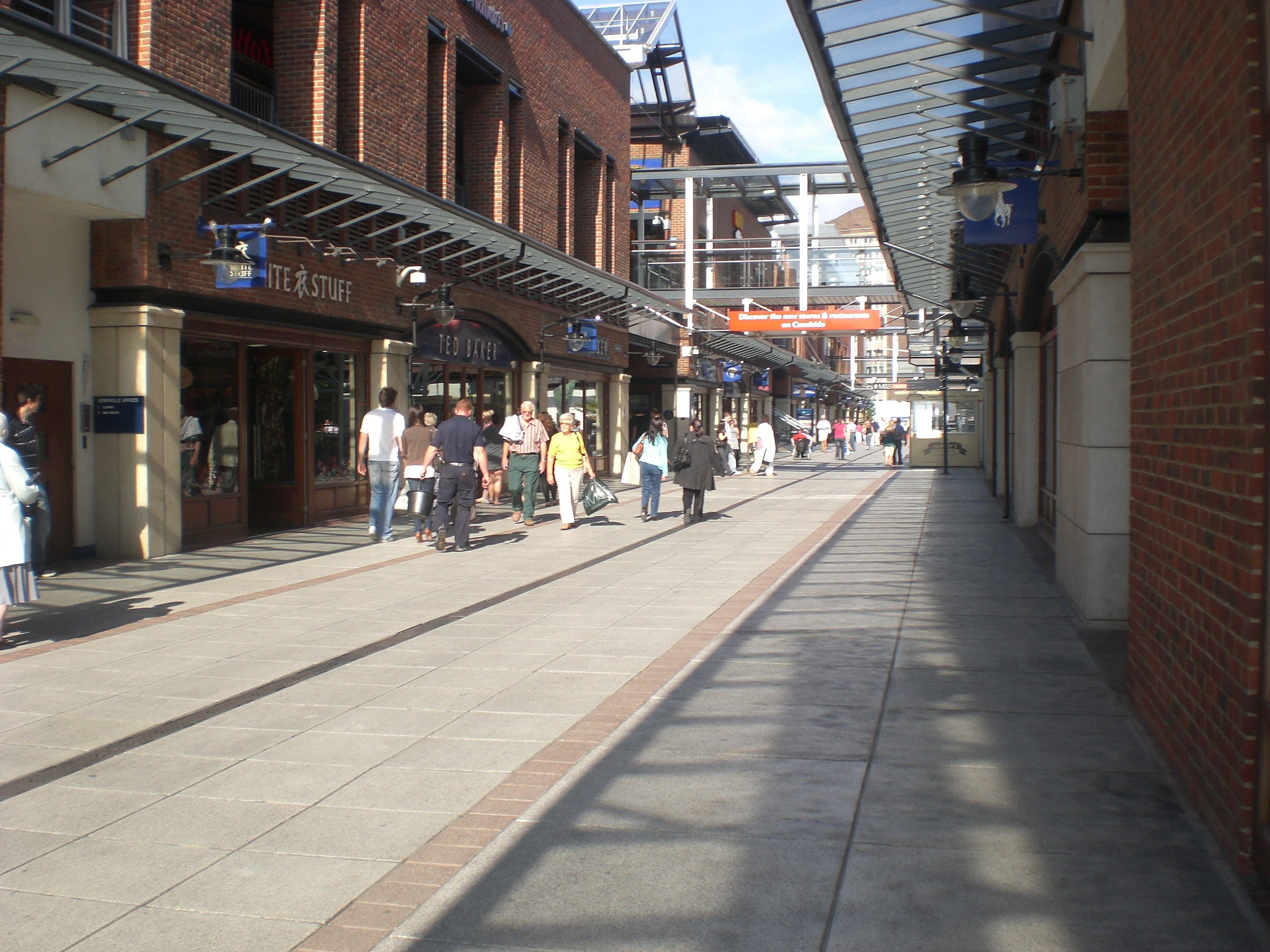 Development of Gunwharf Quays continued until 2007, when the No.1 Gunwharf Quays residential tower was completed. The development of the former Brickwoods Brewery site included the construction of the 22-storey Admiralty Quarter Tower, the tallest in a complex of primarily low-rise residential buildings. Number One Portsmouth, a proposed 25-storey tower opposite Portsmouth & Southsea station, was announced at the end of October 2008. In August 2009, internal demolition of the existing building had begun. A high-rise student dormitory, nicknamed "The Blade", has begun construction on the site of the swimming baths at the edge of Victoria Park. The tower will be Portsmouth's second-tallest structure, after the Spinnaker Tower.
In April 2007, Portsmouth F.C. announced plans to move from
Development of Gunwharf Quays continued until 2007, when the No.1 Gunwharf Quays residential tower was completed. The development of the former Brickwoods Brewery site included the construction of the 22-storey Admiralty Quarter Tower, the tallest in a complex of primarily low-rise residential buildings. Number One Portsmouth, a proposed 25-storey tower opposite Portsmouth & Southsea station, was announced at the end of October 2008. In August 2009, internal demolition of the existing building had begun. A high-rise student dormitory, nicknamed "The Blade", has begun construction on the site of the swimming baths at the edge of Victoria Park. The tower will be Portsmouth's second-tallest structure, after the Spinnaker Tower.
In April 2007, Portsmouth F.C. announced plans to move from  Portsmouth's two Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers, and , were ordered by defence secretary
Portsmouth's two Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers, and , were ordered by defence secretary
 Portsmouth is the hometown of Fanny Price, the main character of Jane Austen's novel ''Mansfield Park'', and most of its closing chapters are set there. Nicholas and Smike, the main protagonists of
Portsmouth is the hometown of Fanny Price, the main character of Jane Austen's novel ''Mansfield Park'', and most of its closing chapters are set there. Nicholas and Smike, the main protagonists of
 The
The
 Many of Portsmouth's former defences are now museums or event venues. Several Victorian-era forts on Portsdown Hill are tourist attractions;
Many of Portsmouth's former defences are now museums or event venues. Several Victorian-era forts on Portsdown Hill are tourist attractions;  Most of the city's landmarks and tourist attractions are related to its naval history. They include the D-Day Story in Southsea, which contains the Overlord Embroidery. Portsmouth is home to several well-known ships; Horatio Nelson's flagship , the world's oldest naval ship still in commission, is in the
Most of the city's landmarks and tourist attractions are related to its naval history. They include the D-Day Story in Southsea, which contains the Overlord Embroidery. Portsmouth is home to several well-known ships; Horatio Nelson's flagship , the world's oldest naval ship still in commission, is in the
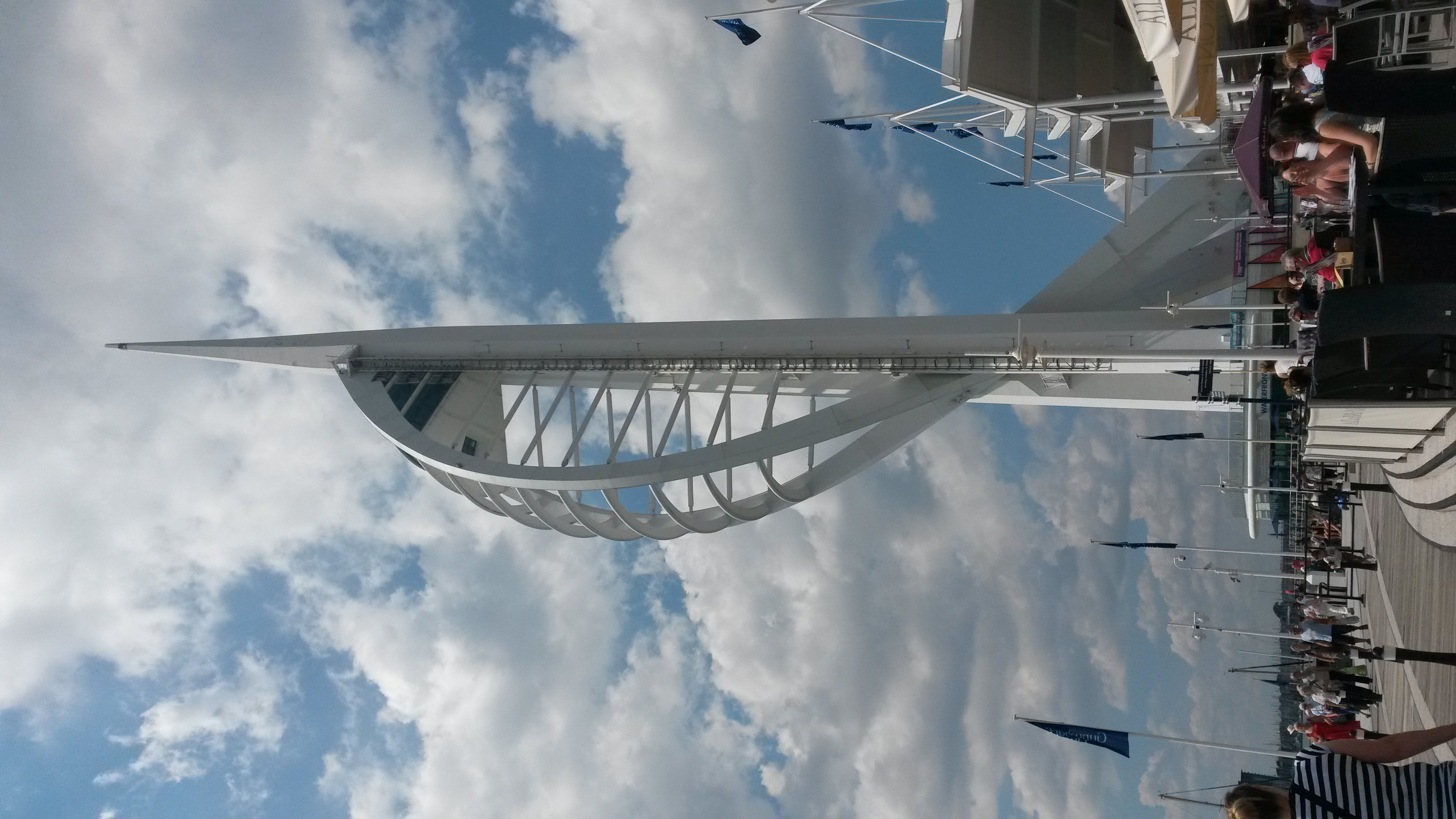 The naval shore establishment contained the Royal Navy's arsenal; weapons and ammunition which would be taken from ships at its 'Gun Wharf' as they entered the harbour, and resupplied when they headed back to sea. The 1919 ''Southsea and Portsmouth Official Guide'' described the establishment as "the finest collections of weapons outside the Tower of London, containing more than 25,000 rifles". During the early nineteenth century, the 'Gunwharf' supplied the fleet with a "grand arsenal" of cannons, mortars, bombs, and ordnance. Although gunpowder was not provided due to safety concerns, it could be obtained at Priddy's Hard (near Gosport). An armoury sold small arms to soldiers, and the stone frigate also had blacksmith and carpenter shops for armourers. It was run by three officers: a ''viz'' (storekeeper), a clerk, and a foreman. By 1817, Gunwharf reportedly employed 5,000 men and housed the world's largest naval arsenal.
HMS ''Vernon'' was closed on 1 April 1996 and was redeveloped by Portsmouth City Council as Gunwharf Quays, a mixed residential and retail site with outlet stores, restaurants, pubs, cafés and a cinema. Construction of the Spinnaker Tower began in 2001, and was completed in the summer of 2005. The project exceeded its budget and cost £36million, of which Portsmouth City Council contributed £11 million. The tower is visible at a distance of in clear weather, and its viewing platforms overlook the Solent (towards the Isle of Wight), the harbour and Southsea Castle. The tower weighs over .and has the largest glass floor in Europe.
The naval shore establishment contained the Royal Navy's arsenal; weapons and ammunition which would be taken from ships at its 'Gun Wharf' as they entered the harbour, and resupplied when they headed back to sea. The 1919 ''Southsea and Portsmouth Official Guide'' described the establishment as "the finest collections of weapons outside the Tower of London, containing more than 25,000 rifles". During the early nineteenth century, the 'Gunwharf' supplied the fleet with a "grand arsenal" of cannons, mortars, bombs, and ordnance. Although gunpowder was not provided due to safety concerns, it could be obtained at Priddy's Hard (near Gosport). An armoury sold small arms to soldiers, and the stone frigate also had blacksmith and carpenter shops for armourers. It was run by three officers: a ''viz'' (storekeeper), a clerk, and a foreman. By 1817, Gunwharf reportedly employed 5,000 men and housed the world's largest naval arsenal.
HMS ''Vernon'' was closed on 1 April 1996 and was redeveloped by Portsmouth City Council as Gunwharf Quays, a mixed residential and retail site with outlet stores, restaurants, pubs, cafés and a cinema. Construction of the Spinnaker Tower began in 2001, and was completed in the summer of 2005. The project exceeded its budget and cost £36million, of which Portsmouth City Council contributed £11 million. The tower is visible at a distance of in clear weather, and its viewing platforms overlook the Solent (towards the Isle of Wight), the harbour and Southsea Castle. The tower weighs over .and has the largest glass floor in Europe.
 Southsea is a seaside resort and residential area of Portsmouth located at the southern end of Portsea Island. Its name originates from Southsea Castle, a seafront castle built in 1544 by HenryVIII to help defend the Solent and Portsmouth Harbour. The area was developed in 1809 as Croxton Town; by the 1860s, the suburb of Southsea had expanded to provide working-class housing. Southsea developed as a seaside and bathing resort. A pump room and baths were built near the present-day
Southsea is a seaside resort and residential area of Portsmouth located at the southern end of Portsea Island. Its name originates from Southsea Castle, a seafront castle built in 1544 by HenryVIII to help defend the Solent and Portsmouth Harbour. The area was developed in 1809 as Croxton Town; by the 1860s, the suburb of Southsea had expanded to provide working-class housing. Southsea developed as a seaside and bathing resort. A pump room and baths were built near the present-day
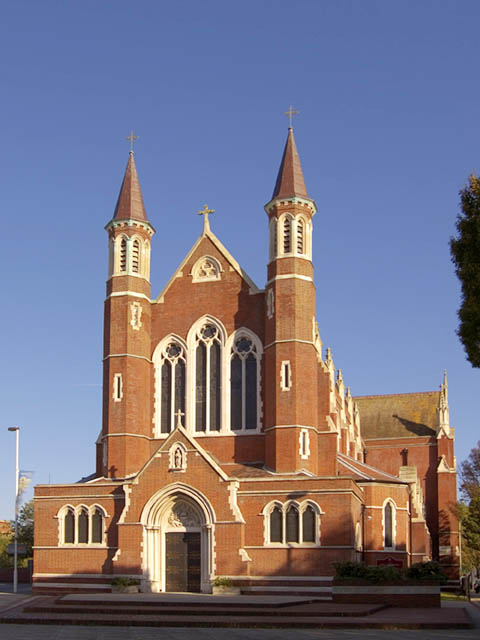 Portsmouth has two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas in Old Portsmouth and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The city is one of 34 British settlements with a
Portsmouth has two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas in Old Portsmouth and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The city is one of 34 British settlements with a

 Portsmouth Harbour railway station, Portsmouth Harbour has passenger-ferry links to
Portsmouth Harbour railway station, Portsmouth Harbour has passenger-ferry links to
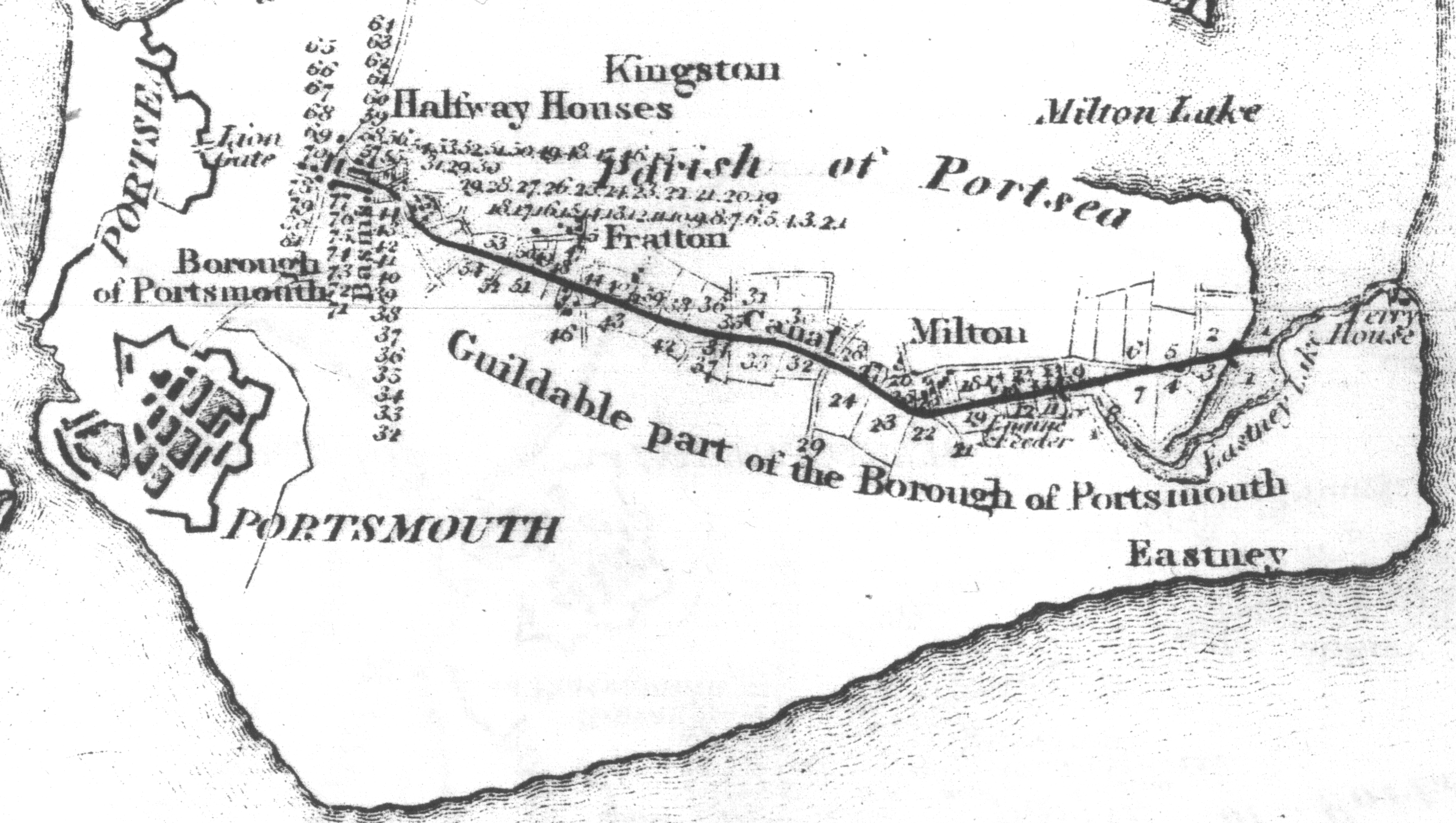 The Portsmouth and Arundel Canal ran between the towns and was built in 1823 by the Portsmouth & Arundel Navigation Company. Never financially successful, and found to be contaminating Portsea Island fresh water wells, it was abandoned in 1855 and the company was wound up in 1888. The canal was part of a larger scheme for a secure inland canal route from London to Portsmouth, allowing boats to avoid the
The Portsmouth and Arundel Canal ran between the towns and was built in 1823 by the Portsmouth & Arundel Navigation Company. Never financially successful, and found to be contaminating Portsea Island fresh water wells, it was abandoned in 1855 and the company was wound up in 1888. The canal was part of a larger scheme for a secure inland canal route from London to Portsmouth, allowing boats to avoid the
port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
and city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in the ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, with a population last recorded at 208,100. Portsmouth is located south-west of London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
and south-east of Southampton. Portsmouth is mostly located on Portsea Island
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural island in area, just off the southern coast of Hampshire in England. Portsea Island contains the majority of the city of Portsmouth.
Portsea Island has the third-largest population of all th ...
; the only English city not on the mainland of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. Portsea Island has the third highest population in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
after the islands of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. Portsmouth also forms part of the regional South Hampshire conurbation, which includes the city of Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
and the boroughs of Eastleigh
Eastleigh is a town in Hampshire, England, between Southampton and Winchester. It is the largest town and the administrative seat of the Borough of Eastleigh, with a population of 24,011 at the 2011 census.
The town lies on the River Itchen, o ...
, Fareham
Fareham ( ) is a market town at the north-west tip of Portsmouth Harbour, between the cities of Portsmouth and Southampton in south east Hampshire, England. It gives its name to the Borough of Fareham. It was historically an important manufact ...
, Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite t ...
, Havant and Waterlooville
Waterlooville is a market town in the Borough of Havant in Hampshire, England, approximately north northeast of Portsmouth. It is the largest town in the borough.
The town has a population of about 64,350 and is surrounded by Purbrook, Blendwort ...
.
Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports, its history can be traced to Roman times
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
and has been a significant Royal Navy dockyard and base for centuries. Portsmouth was first established as a town with a royal charter on 2 May 1194. Portsmouth was England's first line of defence during an attempted French invasion in 1545 at the Battle of the Solent
The naval Battle of the Solent took place on 18 and 19 July 1545 during the Italian Wars between the fleets of Francis I of France and Henry VIII of England, in the Solent, between Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. The engagement was inconclusi ...
, famously notable for the sinking of the carrack
A carrack (; ; ; ) is a three- or four- masted ocean-going sailing ship that was developed in the 14th to 15th centuries in Europe, most notably in Portugal. Evolved from the single-masted cog, the carrack was first used for European trade fr ...
''Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' (launched 1511) is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her l ...
'' and witnessed by King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
of England from Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to p ...
. Portsmouth has the world's oldest dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
, ''"The Great Stone Dock"''; originally built in 1698, rebuilt in 1769 and presently known as "No.5 Dock". The world's first mass production line
A production line is a set of sequential operations established in a factory where components are assembled to make a finished article or where materials are put through a refining process to produce an end-product that is suitable for onward c ...
was established at the naval base's Block Mills which produced pulley blocks for the Royal Navy fleet. By the early-19th century, Portsmouth was the most heavily fortified
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
city in the world, and was considered "the world's greatest naval port" at the height of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
throughout ''Pax Britannica
''Pax Britannica'' (Latin for "British Peace", modelled after ''Pax Romana'') was the period of relative peace between the great powers during which the British Empire became the global hegemonic power and adopted the role of a "global polic ...
''. By 1859, a ring of defensive land and sea forts, known as the Palmerston Forts had been built around Portsmouth in anticipation of an invasion from continental Europe.
In the 20th century, Portsmouth achieved city status on 21 April 1926. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city was a pivotal embarkation point for the D-Day landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
and was bombed extensively in the Portsmouth Blitz, which resulted in the deaths of 930 people. In 1982, a large Royal Navy task force departed from Portsmouth for the Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial de ...
. Her Majesty's Yacht ''Britannia'' was formerly based in Portsmouth and oversaw the transfer of Hong Kong in 1997, after which, Britannia was retired from royal service, decommissioned and relocated to Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by '' Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
as a museum ship.
HMNB Portsmouth
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is lo ...
is an operational Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
base and is home to two-thirds of the UK's surface fleet. The base has long been nicknamed Pompey, a nickname it shares with the wider city of Portsmouth and Portsmouth Football Club. The naval base also contains the National Museum of the Royal Navy
The National Museum of the Royal Navy was created in early 2009 to act as a single non-departmental public body for the museums of the Royal Navy. With venues across the United Kingdom, the museums detail the history of the Royal Navy operating o ...
and Portsmouth Historic Dockyard
Portsmouth Historic Dockyard is an area of HM Naval Base Portsmouth which is open to the public; it contains several historic buildings and ships. It is managed by the National Museum of the Royal Navy as an umbrella organization representing f ...
; which has a collection of historic warships, including the ''Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' (launched 1511) is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her l ...
'', Lord Nelson's flagship, (the world's oldest naval ship still in commission), and , the Royal Navy's first ironclad warship
An ironclad is a steam-propelled warship protected by iron or steel armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. T ...
.
The former shore establishment has been redeveloped into a large retail outlet destination known as Gunwharf Quays which opened in 2001. Portsmouth is among the few British cities with two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas and the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The waterfront and Portsmouth Harbour are dominated by the Spinnaker Tower, one of the United Kingdom's tallest structures at .
Southsea is Portsmouth's seaside resort
A seaside resort is a resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, suc ...
, which was named after Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to p ...
. Southsea has two piers; Clarence Pier
Clarence Pier is an amusement pier in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered b ...
amusement park and South Parade Pier
The South Parade Pier is a pier in Portsmouth, England. It is one of two piers in the city, the other being Clarence Pier. The pier once had a long hall down its centre which housed a seating area and a small restaurant. The outside of the hall ...
. The world's only regular hovercraft service operates from Southsea Hoverport
Southsea Hoverport is adjacent to Clarence Pier in the Southsea area of Portsmouth in southern England. From here frequent hovercraft services leave for Ryde on the Isle of Wight. The journey time is quicker than the conventional boats that sail ...
to Ryde
Ryde is an English seaside town and civil parish on the north-east coast of the Isle of Wight. The built-up area had a population of 23,999 according to the 2011 Census and an estimate of 24,847 in 2019. Its growth as a seaside resort came af ...
on the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
. Southsea Common
Southsea is a seaside resort and a geographic area of Portsmouth, Portsea Island in England. Southsea is located 1.8 miles (2.8 km) to the south of Portsmouth's inner city-centre. Southsea is not a separate town as all of Portsea Island's s ...
is a large open-air public recreation space which serves as a venue for a wide variety of annual events.
Portsmouth F.C.
Portsmouth Football Club is a professional football club based in Portsmouth, Hampshire, England, which compete in . They are also known as ''Pompey'', a local nickname used by both HMNB Portsmouth and the city of Portsmouth; the ''Pompey'' nick ...
is the city's professional association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
club and play their home games at Fratton Park
Fratton Park is a football ground in Portsmouth, England, which is the home of Portsmouth F.C. Fratton Park remains as the only home football ground in Portsmouth FC's entire history.
The early Fratton Park was designed by local architect A ...
. The city has several mainline railway stations that connect to London Victoria and London Waterloo
Waterloo station (), also known as London Waterloo, is a central London terminus on the National Rail network in the United Kingdom, in the Waterloo area of the London Borough of Lambeth. It is connected to a London Underground station of ...
amongst other lines in southern England. Portsmouth International Port is a commercial cruise ship and ferry port for international destinations. The port is the second busiest in the United Kingdom after Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
, handling around three million passengers a year. The city formerly had its own airport, Portsmouth Airport, until its closure in 1973. The University of Portsmouth
The University of Portsmouth is a public university in Portsmouth, England. It is one of only four universities in the South East England, South East of England rated as Gold in the Government's Teaching Excellence Framework. With approximately 28 ...
enrols 23,000 students and is ranked among the world's best modern universities.
Portsmouth is the birthplace of notable people such as author Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
, former Prime Minister James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff, ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005), commonly known as Jim Callaghan, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1976 to 1980. Callaghan is ...
, actor Peter Sellers and author-journalist Christopher Hitchens.
History
Early history
The Romans builtPortus Adurni
Portus Adurni was a Roman fort in the Roman province of Britannia situated at the north end of Portsmouth Harbour. It was part of the Saxon Shore, and is the best-preserved Roman fort north of the Alps. Around an eighth of the fort has been exca ...
, a fort, at nearby Portchester
Portchester is a locality and suburb northwest of Portsmouth, England. It is part of the borough of Fareham in Hampshire. Once a small village, Portchester is now a busy part of the expanding conurbation between Portsmouth and Southampton o ...
in the late third century. The city's Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
Anglo-Saxon name, "Portesmuða", is derived from ''port'' (a haven) and ''muða'' (the mouth of a large river or estuary). In the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'', a warrior named Port and his two sons killed a noble Briton in Portsmouth in 501. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
, in ''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples
''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples'' is a four-volume history of Britain and its former colonies and possessions throughout the world, written by Winston Churchill, covering the period from Caesar's invasions of Britain (55 BC) to the en ...
'', wrote that Port was a pirate who founded Portsmouth in 501.
England's southern coast was vulnerable to Danish Viking invasions during the eighth and ninth centuries, and was conquered by Danish pirates in 787. In 838, during the reign of Æthelwulf, King of Wessex
Æthelwulf (; Old English for "Noble Wolf"; died 13 January 858) was King of Wessex from 839 to 858. In 825 his father, King Ecgberht, defeated King Beornwulf of Mercia, ending a long Mercian dominance over Anglo-Saxon England south of the H ...
, a Danish fleet landed between Portsmouth and Southampton and plundered the region. Æthelwulf sent Wulfherd and the governor of Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
shire to confront the Danes at Portsmouth, where most of their ships were docked. Although the Danes were driven off, Wulfherd was killed. The Danes returned in 1001 and pillaged Portsmouth and the surrounding area, threatening the English with extinction. They were massacred by the English survivors the following year; rebuilding began, although the town experienced further attacks until 1066
1066 (Roman numerals, MLXVI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.
Events
Worldwide
* March 20 – Halley's Comet reaches perihelion. Its appearance is subsequently recorded in the Bayeux Tapestry.
Asia
* ''un ...
.
Norman to Tudor
 Although Portsmouth was not mentioned in the 1086
Although Portsmouth was not mentioned in the 1086 Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
, ''Bocheland'' ( Buckland), ''Copenore'' ( Copnor), and ''Frodentone'' (Fratton
Fratton is a residential and formerly industrial area of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. Victorian style terraced houses are dominant in the area, typical of most residential areas of Portsmouth. Fratton has many discount shops and "greasy spoo ...
) were. According to some sources, it was founded in 1180 by the Anglo-Norman merchant Jean de Gisors
Jean de Gisors (1133–1220) was a Norman lord of the fortress of Gisors in Normandy, where meetings were traditionally convened between English and French kings. It was here, in 1188, a squabble occurred that involved the cutting of an elm.
Ini ...
.
King Henry II died in 1189; his son, Richard I (who had spent most of his life in France), arrived in Portsmouth en route to his coronation in London. When Richard returned from captivity in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in May 1194, he summoned an army and a fleet of 100 ships to the port. Richard gave Portsmouth market-town status with a royal charter on 2 May, authorising an annual fifteen-day free-market fair, weekly markets and a local court to deal with minor matters, and exempted its inhabitants from an £18 annual tax. He granted the town the coat of arms of Isaac Komnenos of Cyprus, whom he had defeated during the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity (Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
in 1191: "a crescent of gold on a shade of azure, with a blazing star of eight points", reflecting significant involvement of local soldiers, sailors, and vessels in the holy war. The 1194 royal charter's 800th anniversary was celebrated in 1994 with ceremonies at the city museum.
King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
reaffirmed RichardI's rights and privileges, and established a permanent naval base. The first docks were begun by William of Wrotham
William of Wrotham or William de Wrotham (died ) was a medieval English royal administrator and clergyman. Although a late 13th-century source says that William held a royal office under King Henry II of England (reigned 1154–1189), the first ...
in 1212, and John summoned his earls, barons, and military advisers to plan an invasion of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
. In 1229, declaring war against France, HenryIII assembled a force described by historian Lake Allen as "one of the finest armies that had ever been raised in England". The invasion stalled, and returned from France in October 1231. HenryIII summoned troops to invade Guienne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation o ...
in 1242, and EdwardI sent supplies for his army in France in 1295. Commercial interests had grown by the following century, and its exports included wool, corn, grain, and livestock.
Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to t ...
ordered all ports on the south coast to assemble their largest vessels at Portsmouth to carry soldiers and horses to the Duchy of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine ( oc, Ducat d'Aquitània, ; french: Duché d'Aquitaine, ) was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, fluc ...
in 1324 to strengthen defences. A French fleet commanded by David II of Scotland attacked in the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, ransacked the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
and threatened the town. EdwardIII instructed all maritime towns to build vessels and raise troops to rendezvous at Portsmouth. Two years later, a French fleet led by Nicholas Béhuchet
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglicanism, Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the n ...
raided Portsmouth and destroyed most of the town; only the stone-built church and hospital survived. After the raid, EdwardIII exempted the town from national taxes to aid its reconstruction. In 1377, shortly after Edward died, the French landed in Portsmouth. Although the town was plundered and burnt, its inhabitants drove the French off to raid towns in the West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Gloucesters ...
.
Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
built Portsmouth's first permanent fortifications
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
. In 1416, a number of French ships blockaded the town (which housed ships which were set to invade Normandy); Henry gathered a fleet at Southampton, and invaded the Norman coast in August of that year. Recognising the town's growing importance, he ordered a wooden Round Tower
A fortified tower (also defensive tower or castle tower or, in context, just tower) is one of the defensive structures used in fortifications, such as castles, along with curtain walls. Castle towers can have a variety of different shapes and ful ...
to be built at the mouth of the harbour; it was completed in 1426. Henry VII rebuilt the fortifications with stone, assisted Robert Brygandine and Sir Reginald Bray in the construction of the world's first dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
, and raised the Square Tower
The Square Tower is one of the oldest parts of the fortifications of Portsmouth, England. It is a Grade I listed building.
History
A tower was built in 1494 as part of the fortifications and served as a home to the Governor of Portsmouth.
I ...
in 1494. He made Portsmouth a Royal Dockyard, England's only dockyard considered "national". Although King Alfred may have used Portsmouth to build ships as early as the ninth century, the first warship recorded as constructed in the town was the ''Sweepstake'' (built in 1497).
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
built Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to p ...
, financed by the Dissolution of the Monasteries, in 1539 in anticipation of a French invasion. He also invested heavily in the town's dockyard, expanding it to . Around this time, a Tudor defensive boom
A boom or a chain (also boom defence, harbour chain, river chain, chain boom, boom chain or variants) is an obstacle strung across a navigable stretch of water to control or block navigation.
In modern times they usually have civil uses, such as ...
stretched from the Round Tower to Fort Blockhouse in Gosport to protect Portsmouth Harbour.
From Southsea Castle, Henry witnessed his flagship ''Mary Rose'' sink in action against the French fleet in the 1545 Battle of the Solent
The naval Battle of the Solent took place on 18 and 19 July 1545 during the Italian Wars between the fleets of Francis I of France and Henry VIII of England, in the Solent, between Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. The engagement was inconclusi ...
with the loss of about 500 lives. Some historians believe that the ''Mary Rose'' turned too quickly and submerged her open gun ports; according to others, it sank due to poor design. Portsmouth's fortifications were improved by successive monarchs. The town experienced an outbreak of plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
in 1563, which killed about 300 of its 2,000 inhabitants.
Stuart to Georgian
 In 1623,
In 1623, Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
(then Prince of Wales) returned to Portsmouth from France and Spain. His unpopular military adviser, George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham
George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, 28 August 1592 – 23 August 1628), was an English courtier, statesman, and patron of the arts. He was a favourite and possibly also a lover of King James I of England. Buckingham remained at the ...
, was stabbed to death in an Old Portsmouth pub by war veteran John Felton five years later. Felton never attempted to escape, and was caught walking the streets when soldiers confronted him; he said, "I know that he is dead, for I had the force of forty men when I struck the blow". Felton was hanged, and his body chained to a gibbet on Southsea Common as a warning to others. The murder took place in the Greyhound public house on High Street, which is now Buckingham House and has a commemorative plaque.
Most residents (including the mayor) supported the parliamentarians during the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
, although military governor Colonel Goring
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel wa ...
supported the royalists. The town, a base of the parliamentarian navy, was blockaded from the sea. Parliamentarian troops were sent to besiege it, and the guns of Southsea Castle were fired at the town's royalist garrison. Parliamentarians in Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite t ...
joined the assault, damaging St Thomas's Church. On 5 September 1642, the remaining royalists in the garrison at the Square Tower were forced to surrender after Goring threatened to blow it up; he and his garrison were allowed safe passage.
Under the Commonwealth of England
The Commonwealth was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when England and Wales, later along with Ireland and Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the trial and execut ...
, Robert Blake Robert Blake may refer to:
Sportspeople
* Bob Blake (American football) (1885–1962), American football player
* Robbie Blake (born 1976), English footballer
* Bob Blake (ice hockey) (1914–2008), American ice hockey player
* Rob Blake (born 19 ...
used the harbour as his base during the First Anglo-Dutch War
The First Anglo-Dutch War, or simply the First Dutch War, ( nl, Eerste Engelse (zee-)oorlog, "First English (Sea) War"; 1652–1654) was a conflict fought entirely at sea between the navies of the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic, ...
in 1652 and the Anglo-Spanish War. He died within sight of the town, returning from Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
. After the end of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, Portsmouth was among the first towns to declare CharlesII king and began to prosper. The first ship built in over 100 years, , was launched in 1650; twelve ships were built between 1650 and 1660. After the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
, CharlesII married Catherine of Braganza at the Royal Garrison Church. During the late 17th century, Portsmouth continued to grow; a new wharf was constructed in 1663 for military use, and a mast
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mast ...
pond was dug in 1665. In 1684, a list of ships docked in Portsmouth was evidence of its increasing national importance. Between 1667 and 1685, the town's fortifications were rebuilt; new walls were constructed with bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s and two moats were dug, making Portsmouth one of the world's most heavily fortified places.
In 1759, General James Wolfe sailed to capture Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
; the expedition, although successful, cost him his life. His body was brought back to Portsmouth in November, and received high naval and military honours. Two years later, on 30 May 1775, Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
arrived on after circumnavigating the globe. The 11-ship First Fleet
The First Fleet was a fleet of 11 ships that brought the first European and African settlers to Australia. It was made up of two Royal Navy vessels, three store ships and six convict transports. On 13 May 1787 the fleet under the command ...
left on 13 May 1787 to establish the first European colony in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, the beginning of prisoner transportation; Captain William Bligh of also sailed from the harbour that year. After the 28 April 1789 mutiny on the ''Bounty'', was dispatched from Portsmouth to bring the mutineers back for trial. The court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
opened on 12 September 1792 aboard in Portsmouth Harbour; of the ten remaining men, three were sentenced to death. In 1789, a chapel was erected in Prince George's Street and was dedicated to St John by the Bishop of Winchester. Around this time, a bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Plac ...
was passed in the House of Commons on the creation of a canal to link Portsmouth to Chichester; however, the project was abandoned.
The city's nickname, Pompey, is thought to have derived from the log entry of Portsmouth Point
Portsmouth Point, or "Spice Island", is part of Old Portsmouth in Portsmouth, Hampshire, on the southern coast of England. The name Spice Island comes from the area's seedy reputation, as it was known as the "Spice of Life". Men were easily found ...
(contracted "Po'm.P." – ''Ports''m''outh ''P.''oint) as ships entered the harbour; navigational charts use the contraction. According to one historian, the name may have been brought back from a group of Portsmouth-based sailors who visited Pompey's Pillar in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
, Egypt, around 1781. Another theory is that it is named after the harbour's guardship, , a 74-gun French ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two colu ...
captured in 1793.
Portsmouth's coat of arms is attested in the early 19th century as "azure a crescent or, surmounted by an estoile of eight points of the last." Its design is apparently based on 18th-century mayoral seals. A connection of the coat of arms with the Great Seal of Richard I (which had a separate star and crescent) dates to the 20th century.
Industrial Revolution to Edwardian
pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that ...
blocks for rigging
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a sailing ship or sail boat's masts—''standing rigging'', including shrouds and stays—and which adjust the position of the vessel's sails and spars to which they are ...
on the navy's ships. The first machines were installed in January 1803, and the final set (for large blocks) in March 1805. In 1808, the mills produced 130,000 blocks. By the turn of the 19th century, Portsmouth was the largest industrial site in the world; it had a workforce of 8,000, and an annual budget of £570,000.
In 1805, Admiral Nelson left Portsmouth to command the fleet which defeated France and Spain at the Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (180 ...
. The Royal Navy's reliance on Portsmouth led to its becoming the most fortified city in the world. The Royal Navy's West Africa Squadron
The West Africa Squadron, also known as the Preventative Squadron, was a squadron of the British Royal Navy whose goal was to suppress the Atlantic slave trade by patrolling the coast of West Africa. Formed in 1808 after the British Parliame ...
, tasked with halting the slave trade, began operating out of Portsmouth in 1808. A network of forts, known as the Palmerston Forts, was built around the town as part of a programme led by Prime Minister Lord Palmerston to defend British military bases from an inland attack following an Anglo-French war scare in 1859. The forts were nicknamed "Palmerston's Follies" because their armaments were pointed inland and not out to sea.
In April 1811, the Portsea Island Company constructed the first piped-water supply to upper- and middle-class houses. It supplied water to about 4,500 of Portsmouth's 14,000 houses, generating an income of £5,000 a year. HMS ''Victory''s active career ended in 1812, when she was moored in Portsmouth Harbour and used as a depot ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing an ...
. The town of Gosport contributed £75 a year to the ship's maintenance. In 1818, John Pounds began teaching working-class children in the country's first ragged school
Ragged schools were charitable organisations dedicated to the free education of destitute children in 19th century Britain. The schools were developed in working-class districts. Ragged schools were intended for society's most destitute children ...
. The Portsea Improvement Commissioners installed gas street lighting throughout Portsmouth in 1820, followed by Old Portsmouth three years later.
During the 19th century, Portsmouth expanded across Portsea Island. Buckland was merged into the town by the 1860s, and Fratton
Fratton is a residential and formerly industrial area of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. Victorian style terraced houses are dominant in the area, typical of most residential areas of Portsmouth. Fratton has many discount shops and "greasy spoo ...
and Stamshaw
Stamshaw is a residential district of Portsmouth, located on the north western corner of Portsea Island
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural island in area, just off the southern coast of Hampshire in England. Portsea Island ...
were incorporated by the next decade. Between 1865 and 1870, the council built sewers after more than 800 people died in a cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
epidemic; according to a by-law
A by-law (bye-law, by(e)law, by(e) law), or as it is most commonly known in the United States bylaws, is a set of rules or law established by an organization or community so as to regulate itself, as allowed or provided for by some higher authorit ...
, any house within of a sewer had to be connected to it. By 1871 the population had risen to 100,000, and the national census listed Portsmouth's population as 113,569. A working-class suburb was constructed in the 1870s, when about 1,820 houses were built, and it became Somerstown. Despite public-health improvements, 514 people died in an 1872 smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
epidemic. On 21 December of that year, the ''Challenger'' expedition embarked on a circumnavigation of the globe for scientific research.
When the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
was at its height of power, covering a quarter of Earth's total land area and 458 million people at the turn of the 20th century, Portsmouth was considered "the world's greatest naval port". In 1900, Portsmouth Dockyard employed 8,000 people– a figure which increased to 23,000 during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The whole of Portsea Island came united under the control of Portsmouth borough council in 1904.
1913 terrorist attack
 A major
A major terrorist
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
incident occurred in the city in 1913, which led to the deaths of two men. During the suffragette bombing and arson campaign of 1912–1914, militant
The English word ''militant'' is both an adjective and a noun, and it is generally used to mean vigorously active, combative and/or aggressive, especially in support of a cause, as in "militant reformers". It comes from the 15th century Latin " ...
suffragettes
A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to members ...
of the Women's Social and Political Union
The Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) was a women-only political movement and leading militant organisation campaigning for women's suffrage in the United Kingdom from 1903 to 1918. Known from 1906 as the suffragettes, its membership and ...
carried out a series of politically motivated bombing and arson attacks nationwide as part of their campaign for women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
. In one of the more serious suffragette attacks, a fire was purposely started at Portsmouth dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
on 20 December 1913, in which two sailors were killed after it spread through the industrial area. The fire spread rapidly as there were many old wooden buildings in the area, including the historic semaphore tower which dated back to the eighteenth century, which was completely destroyed. The damage to the dockyard area cost the city £200,000 in damages, equivalent to £23,600,000 today. In the midst of the firestorm, a battleship, , had to be towed to safety to avoid the flames. The two victims were a pensioner and a signalman.
The attack was notable enough to be reported on in the press in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, with the ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' reporting on the disaster two days after with the headline "Big Portsmouth Fire Loss". The report also disclosed that at a previous police raid on a suffragette headquarters, "papers were discovered disclosing a plan to fire the yard".
First and Second World Wars
 On 1 October 1916, Portsmouth was bombed by a
On 1 October 1916, Portsmouth was bombed by a Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp ...
airship. Although the Oberste Heeresleitung (German Supreme Army Command) said that the town was "lavishly bombarded with good results", there were no reports of bombs dropped in the area. According to another source, the bombs were mistakenly dropped into the harbour rather than the dockyard. About 1,200 ships were refitted in the dockyard during the war, making it one of the empire's most strategic ports at the time.
Portsmouth's boundaries were extended onto the mainland of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
between 1920 and 1932 by incorporating Paulsgrove
Paulsgrove is an area of northern Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. Initially a small independent hamlet for many centuries, it was admitted to the city limits in 1920 and grew rapidly after the end of the Second World War.
History
Paulsgrove exi ...
, Wymering
Wymering is a residential area of the city of Portsmouth in the English county of Hampshire. Unlike the majority of Portsmouth, it is located on the mainland rather than Portsea Island.
Wymering was one of the estates held by Hampshire's bigges ...
, Cosham, Drayton and Farlington into Portsmouth. Portsmouth was granted city status in 1926 after a long campaign by the borough council. The application was made on the grounds that it was the "first naval port of the kingdom". In 1929, the city council added the motto
A motto (derived from the Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organisation. Mot ...
"Heaven's Light Our Guide" to the medieval coat of arms. Except for the celestial objects in the arms, the motto was that of the Star of India and referred to the troopships bound for British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
which left from the port. The crest and supporter
In heraldry, supporters, sometimes referred to as ''attendants'', are figures or objects usually placed on either side of the shield and depicted holding it up.
Early forms of supporters are found in medieval seals. However, unlike the coro ...
s are based on those of the royal arms
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varian ...
, but altered to show the city's maritime connections: the lions and unicorn have fish tails, and a naval crown and a representation of the Tudor defensive boom which stretched across Portsmouth Harbour are around the unicorn.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city (particularly the port) was bombed extensively by the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
in the Portsmouth Blitz.
Portsmouth experienced 67 air raids between July 1940 and May 1944, which destroyed 6,625 houses and severely damaged 6,549. The air raids caused 930 deaths and wounded almost 3,000 people, many in the dockyard and military establishments. On the night of the city's heaviest raid (10 January 1941), the Luftwaffe dropped 140 tonnes of high-explosive bombs which killed 171 people and left 3,000 homeless. Many of the city's houses were damaged, and areas of Landport and Old Portsmouth destroyed; the future site of Gunwharf Quays was razed to the ground. The Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
was hit by an incendiary bomb which burnt out the interior and destroyed its inner walls, although the civic plate was retrieved unharmed from the vault under the front steps. After the raid, Portsmouth mayor Denis Daley wrote for the ''Evening News'':
Portsmouth Harbour was a vital military embarkation point for the 6 June 1944 D-Day landings. Southwick House, just north of the city, was the headquarters of Supreme Allied Commander Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
. A V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buz ...
hit Newcomen Road on 15 July 1944, killing 15 people.
1945 to present
Much of the city's housing stock was damaged during the war. The wreckage was cleared in an attempt to improve housing quality after the war; before permanent accommodations could be built, Portsmouth City Council built prefabs for those who had lost their homes. More than 700 prefab houses were constructed between 1945 and 1947, some over bomb sites. The first permanent houses were built away from the city centre, in new developments such asPaulsgrove
Paulsgrove is an area of northern Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. Initially a small independent hamlet for many centuries, it was admitted to the city limits in 1920 and grew rapidly after the end of the Second World War.
History
Paulsgrove exi ...
and Leigh Park; construction of council estates in Paulsgrove was completed in 1953. The first Leigh Park housing estates were completed in 1949, although construction in the area continued until 1974. Builders still occasionally find unexploded bombs, such as on the site of the destroyed Hippodrome Theatre in 1984. Despite efforts by the city council to build new housing, a 1955 survey indicated that 7,000 houses in Portsmouth were unfit for human habitation. A controversial decision was made to replace a section of the central city, including Landport, Somerstown and Buckland, with council housing during the 1960s and early 1970s. The success of the project and the quality of its housing are debatable.
 Portsmouth was affected by the decline of the British Empire in the second half of the 20th century. Shipbuilding jobs fell from 46 percent of the workforce in 1951 to 14 per cent in 1966, drastically reducing manpower in the dockyard. The city council attempted to create new work; an industrial estate was built in Fratton in 1948, and others were built at Paulsgrove and Farlington during the 1950s and 1960s. Although traditional industries such as brewing and corset manufacturing disappeared during this time, electrical engineering became a major employer. Despite the cutbacks in traditional sectors, Portsmouth remained attractive to industry. Zurich Insurance Group moved their UK headquarters to the city in 1968, and IBM relocated their European headquarters in 1979. Portsmouth's population had dropped from about 200,000 to 177,142 by the end of the 1960s. Defence Secretary
Portsmouth was affected by the decline of the British Empire in the second half of the 20th century. Shipbuilding jobs fell from 46 percent of the workforce in 1951 to 14 per cent in 1966, drastically reducing manpower in the dockyard. The city council attempted to create new work; an industrial estate was built in Fratton in 1948, and others were built at Paulsgrove and Farlington during the 1950s and 1960s. Although traditional industries such as brewing and corset manufacturing disappeared during this time, electrical engineering became a major employer. Despite the cutbacks in traditional sectors, Portsmouth remained attractive to industry. Zurich Insurance Group moved their UK headquarters to the city in 1968, and IBM relocated their European headquarters in 1979. Portsmouth's population had dropped from about 200,000 to 177,142 by the end of the 1960s. Defence Secretary John Nott
Sir John William Frederic Nott (born 1 February 1932) is a former British Conservative Party politician. He was a senior politician of the late 1970s and early 1980s, playing a prominent role as Secretary of State for Defence during the 1982 in ...
decided in the early 1980s that of the four home dockyards, Portsmouth and Chatham
Chatham may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Chatham Islands (British Columbia)
* Chatham Sound, British Columbia
* Chatham, New Brunswick, a former town, now a neighbourhood of Miramichi
* Chatham (electoral district), New Brunswic ...
would be closed. The city council won a concession, however, and the dockyard was downgraded instead to a naval base.
On 2 April 1982, Argentine forces invaded two British territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in United Kingdom.svg
, map_caption = Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Oce ...
. The British government's response was to dispatch a naval task force, and the aircraft carriers and sailed from Portsmouth for the South Atlantic on 5 April. The successful outcome of the war reaffirmed Portsmouth's significance as a naval port and its importance to the defence of British interests. In January 1997, Her Majesty's Yacht ''Britannia'' embarked from the city on her final voyage to oversee the handover of Hong Kong; for many, this marked the end of the empire. She was decommissioned on 11 December of that year at Portsmouth Naval Base in the presence of the queen, the Duke of Edinburgh
Duke of Edinburgh, named after the city of Edinburgh in Scotland, was a substantive title that has been created three times since 1726 for members of the British royal family. It does not include any territorial landholdings and does not produc ...
, and twelve senior members of the royal family.
Redevelopment of the naval shore establishment began in 2001 as a complex of retail outlets, clubs, pubs, and a shopping centre known as Gunwharf Quays. Construction of the Spinnaker Tower, sponsored by the National Lottery, began at Gunwharf Quays in 2003. The Tricorn Centre, called "the ugliest building in the UK" by the BBC, was demolished in late 2004 after years of debate over the expense of demolition and whether it was worth preserving as an example of 1960s brutalist architecture
Brutalist architecture is an architectural style that emerged during the 1950s in the United Kingdom, among the reconstruction projects of the post-war era. Brutalist buildings are characterised by minimalist constructions that showcase the ba ...
. Designed by Owen Luder as part of a project to "revitalise" Portsmouth in the 1960s, it consisted of a shopping centre, market, nightclubs, and a multistorey car park. Portsmouth celebrated the 200th anniversary of the Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (180 ...
in 2005, with Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
present at a fleet review and a mock battle. The naval base is home to two-thirds of Britain's surface fleet.
Geography
Portsmouth is by road from central London, west ofBrighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
, and east of Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
. It is located primarily on Portsea Island
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural island in area, just off the southern coast of Hampshire in England. Portsea Island contains the majority of the city of Portsmouth.
Portsea Island has the third-largest population of all th ...
and is the United Kingdom's only island city, although the city has expanded to the mainland. Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite t ...
is a borough to the west. Portsea Island is separated from the mainland by Portsbridge Creek
Portsbridge Creek, also known as Portcreek, Portsea Creek, Canal Creek and Ports Creek, is a tidal waterway just off the southern coast of England that runs between Portsea Island and the mainland from Langstone Harbour to Tipner Lake. Through ...
, which is crossed by three road bridges (the M275 motorway, the A3 road
The A3, known as the Portsmouth Road or London Road in sections, is a major road connecting the City of London and Portsmouth passing close to Kingston upon Thames, Guildford, Haslemere and Petersfield. For much of its length, it is classified ...
, and the A2030 road
The A2030 is a road in Hampshire. The road starts off at junction 5 of the A3(M), near the village of Bedhampton. The road then runs west along the base of Portsdown Hill, following the old route of the A27 into Portsmouth until it reaches th ...
), a railway bridge, and two footbridges. Portsea Island, part of the Hampshire Basin, is low-lying; most of the island is less than above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The island's highest natural elevation is the Kingston Cross road junction, at above ordinary spring tide.
Old Portsmouth, the original town, is in the south-west part of the island and includes Portsmouth Point
Portsmouth Point, or "Spice Island", is part of Old Portsmouth in Portsmouth, Hampshire, on the southern coast of England. The name Spice Island comes from the area's seedy reputation, as it was known as the "Spice of Life". Men were easily found ...
(nicknamed Spice Island). The main channel entering Portsmouth Harbour, west of the island, passes between Old Portsmouth and Gosport. Portsmouth Harbour has a series of lakes, including Fountain Lake (near the commercial port), Portchester Lake (south central), Paulsgrove Lake (north), Brick Kiln Lake and Tipner (east), and Bombketch and Spider Lakes (west). Further northwest, around Portchester, are Wicor, Cams, and Great Cams Lakes.
The large tidal inlet of Langstone Harbour
Langstone Harbour is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Hampshire. It is an inlet of the English Channel in Hampshire, sandwiched between Portsea Island to the south and west, Hayling Island to the south and east, and Langs ...
is east of the island. The Farlington Marshes
Farlington Marshes is a Local Nature Reserve in Portsmouth in Hampshire. It is owned by Portsmouth City Council and managed by Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trust. It is part of Langstone Harbour, which is a Site of Special Scientific Int ...
, in the north off the coast of Farlington, is a 125-hectare (308-acre) grazing marsh
Grazing marsh is a British Isles term for flat, marshy grassland in polders. It consists of large grass fields separated by fresh or brackish ditches, and is often important for its wildlife.
History
Grazing marshes were created from medieval ti ...
and saline lagoon. One of the oldest local reserves in the county, built from reclaimed land in 1771, it provides a habitat for migratory wildfowl and wader
245px, A flock of Dunlins and Red knots">Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflat ...
s.
Spithead
Spithead is an area of the Solent and a roadstead off Gilkicker Point in Hampshire, England. It is protected from all winds except those from the southeast. It receives its name from the Spit, a sandbank stretching south from the Hampshire ...
, the Solent, and the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
. Its southern coast was fortified by the Round Tower
A fortified tower (also defensive tower or castle tower or, in context, just tower) is one of the defensive structures used in fortifications, such as castles, along with curtain walls. Castle towers can have a variety of different shapes and ful ...
, the Square Tower
The Square Tower is one of the oldest parts of the fortifications of Portsmouth, England. It is a Grade I listed building.
History
A tower was built in 1494 as part of the fortifications and served as a home to the Governor of Portsmouth.
I ...
, Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to p ...
, Lumps Fort
Lumps Fort is a disused fortification built on Portsea Island as part of the defences for the naval base at Portsmouth.
Early history
Lumps Fort dates from the 18th century. The earliest reference is in the records of the Board of Ordnance in 18 ...
and Fort Cumberland
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
. Four sea forts were built in the Solent by Lord Palmerston: Spitbank Fort
Spitbank Fort or Spitsand Fort or Spit Sand Fort or simply Spit Fort is a sea fort built as a result of the 1859 Royal Commission. The fort is one of four built as part of the Palmerston Forts constructions. Located in the Solent, near Portsmou ...
, St Helens Fort
St Helens Fort is a sea fort in the Solent close to the Isle of Wight, one of the Palmerston Forts near Portsmouth. It was built as a result of the Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom of 1859, in order to protect the St Helen ...
, Horse Sand Fort
Horse Sand Fort is one of the larger Royal Commission sea forts in the Solent off Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. The fort is one of four built as part of the Palmerston Forts constructions. It is across, built between 1865 and 1880, with tw ...
and No Man's Land Fort
No Man's Land Fort, also referred to as No Man's Fort, is a sea fort in the Solent, near Portsmouth, England. It is one of the Palmerston Forts built between 1867 and 1880 after the recommendations of the 1859 Royal Commission. It is 200 f ...
.
The resort of Southsea is on the central southern shoreline of Portsea Island, and Eastney
Eastney is a district in the south-east corner of Portsmouth, England, on Portsea Island. Its electoral ward is called Eastney and Craneswater. At the 2011 Census the population of this ward was 13,591.
History
Barracks and fortifications
Eas ...
is east. Eastney Lake covered nearly in 1626. North of Eastney is the residential Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
and an area of reclaimed land known as Milton Common (formerly Milton Lake), a "flat scrubby land with a series of freshwater lakes". Further north on the east coast is Baffins
Baffins is an administrative district of Portsmouth, England, located on the eastern side of Portsea Island. The district is mainly composed of 1930s housing. The population of the Baffins ward at the 2011 Census was 15,121.
Before the area beca ...
, with the Great Salterns recreation ground and golf course around Portsmouth College.
The Hilsea Lines
The Hilsea Lines are a line of 18th- and 19th-century fortifications built at Hilsea to protect the northern approach to Portsea Island, an island off the southern coast of England which forms the majority of the city of Portsmouth and its key nav ...
are a series of defunct fortifications on the island's north coast, bordering Portsbridge Creek and the mainland. Portsdown Hill dominates the skyline in the north, and contains several large Palmerston Forts such as Fort Fareham
Fort Fareham is one of the Palmerston Forts, in Fareham, England. After the Gosport Advanced Line of Fort Brockhurst, Fort Elson, Fort Rowner, Fort Grange and Fort Gomer had been approved by the Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kin ...
, Fort Wallington
Wallington is a village in Hampshire, part of the borough of Fareham. It is situated between Portsmouth and Southampton near where the River Wallington enters Portsmouth Harbour.
The name Wallington probably means 'settlement of the Welsh' (or B ...
, Fort Nelson Fort Nelson may refer to:
Canada
*Fort Nelson, British Columbia, a town
*Fort Nelson River, British Columbia
* Fort Nelson (Manitoba) (1670–1713), an early fur trading post at the mouth of the Nelson River and the first headquarters of the Hudson ...
, Fort Southwick
Fort Southwick is one of the forts found on Portsdown Hill, which overlooks the naval base of Portsmouth in the county of Hampshire, England.
History
Fort Southwick was built to defend the landward approaches to the naval base on the recommenda ...
, Fort Widley
Fort Widley is one of the forts built on top of Portsdown Hill between 1860 and 1868 on the recommendation of the Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom. It was designed, along with the other Palmerston Forts atop Portsdown, to pro ...
, and Fort Purbrook
Portsdown Hill is a long chalk ridge in Hampshire, England. The highest point of the hill lies within Fort Southwick at 131m above sea level. The ridge offers good views to the south over Portsmouth, the Solent, Hayling Island and Gosport, with ...
. Portsdown Hill is a large band of chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk ...
; the rest of Portsea Island is composed of layers of London Clay
The London Clay Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian (early Eocene Epoch, c. 56–49 million years ago) age which crops out in the southeast of England. The London Clay is well known for its fossil content. The fossils from t ...
and sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of s ...
(part of the Bagshot Formation), formed principally during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
.
Northern areas of the city include Stamshaw
Stamshaw is a residential district of Portsmouth, located on the north western corner of Portsea Island
Portsea Island is a flat and low-lying natural island in area, just off the southern coast of Hampshire in England. Portsea Island ...
, Hilsea
Hilsea is a district of the city of Portsmouth in the English county of Hampshire. Hilsea is home to one of Portsmouth's main sports and leisure facilities – the Mountbatten centre. Trafalgar School (formerly the City of Portsmouth Boys' School ...
and Copnor, Cosham, Drayton, Farlington, Paulsgrove
Paulsgrove is an area of northern Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. Initially a small independent hamlet for many centuries, it was admitted to the city limits in 1920 and grew rapidly after the end of the Second World War.
History
Paulsgrove exi ...
and Port Solent
Port Solent is the commercial business name of a housing and leisure development located in the Paulsgrove suburb of the English city of Portsmouth, Hampshire, comprising a marina, a housing estate, shopping and leisure facilities.
The Port ...
. Other districts include North End and Fratton
Fratton is a residential and formerly industrial area of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. Victorian style terraced houses are dominant in the area, typical of most residential areas of Portsmouth. Fratton has many discount shops and "greasy spoo ...
. The west of the city contains council estates
Public housing in the United Kingdom, also known as council estates, council housing, or social housing, provided the majority of rented accommodation until 2011 when the number of households in private rental housing surpassed the number in so ...
, such as Buckland, Landport, and Portsea, which replaced Victorian terraces destroyed by Second World War bombing. After the war, the Leigh Park estate was built to address the chronic housing shortage during post-war reconstruction. Although the estate has been under the jurisdiction of Havant Borough Council
Havant ( ) is a town in the south-east corner of Hampshire, England between Portsmouth and Chichester. Its borough (population: 125,000) comprises the town (45,826) and its suburbs including the resort of Hayling Island as well as Rowland's Castl ...
since the early 2000s, Portsmouth City Council remains its landlord (the borough's largest landowner).
The city's main station, Portsmouth and Southsea railway station
Portsmouth & Southsea railway station is a Grade II listed building and the main railway station in the Landport area of the city of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. It is close to the Commercial Road shopping area. British Transport Police mai ...
, is in the city centre near the Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
and the civic offices. South of the Guildhall is Guildhall Walk, with a number of pubs and clubs. The city's other railway station, Portsmouth Harbour railway station
Portsmouth Harbour railway station is a railway station in Portsmouth, England. It is situated beside Gunwharf Quays in the city's harbour, and is an important transport terminal, with a bus interchange and ferry services to Gosport and the Is ...
, is located on a pier at the harbour's edge, near Old Portsmouth. Edinburgh Road contains the city's Roman Catholic cathedral and Victoria Park Victoria Park may refer to:
Places Australia
* Victoria Park Nature Reserve, a protected area in Northern Rivers region, New South Wales
* Victoria Park, Adelaide, a park and racecourse
* Victoria Park, Brisbane, a public park and former golf ...
, a park which opened in 1878.
Climate
Portsmouth has a mildoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
, with more sunshine than most of the British Isles. Frosts are light and short-lived and snow quite rare in winter, with temperatures rarely dropping below freezing. The average maximum temperature in January is , and the average minimum is . The lowest recorded temperature is . In summer, temperatures sometimes reach . The average maximum temperature in July is , and the average minimum is . The highest recorded temperature is . The city gets about of rain annually, with a minimum of of rain reported 103 days per year.
Demographics
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
whose population density exceeds that of London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. In the 2021 census, the city had 208,100 residents. The city used to be even more densely populated, with the 1951 census showing a population of 233,545. In a reversal of that decrease, its population has been gradually increasing since the 1990s. With about 860,000 residents, South Hampshire is the fifth-largest urban area in England and the largest in South-East England outside London; it is the centre of one of the United Kingdom's most-populous metropolitan areas.
The city is predominantly white (91.8% of the population). However, Portsmouth's long association with the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
ensures some diversity. Some large, well-established non-white communities have their roots in the Royal Navy, particularly the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
community from British Hong Kong
Hong Kong was a colony and later a dependent territory of the British Empire from 1841 to 1997, apart from a period of occupation under the Japanese Empire from 1941 to 1945 during the Pacific War. The colonial period began with the Briti ...
. Portsmouth's long industrial history with the Royal Navy has drawn many people from across the British Isles (particularly Irish Catholics) to its factories and docks. According to the 2011 census, Portsmouth's population was 84% White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population wa ...
, 3.8% other White
The term Other White is a classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom and has been used in documents such as the 2011 UK Census to describe people who self-identify as white (chiefly European) persons who are not of the English, Welsh, S ...
, 1.3& Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, 1.4% Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, 0.5% mixed race, 1.8% Bangladeshi
Bangladeshis ( bn, বাংলাদেশী ) are the citizens of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centered on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the eponymous bay.
Bangladeshi citizenship was formed in 1971, when the ...
, 0.5% other
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
, 1.4% Black African, 0.5% white Irish, 1.3% other Asian
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
, 0.3% Pakistani, 0.3% Black Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the t ...
and 0.1% other Black.
Ethnicity
Government and politics
unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
which is responsible for local affairs. Portsmouth was granted its first market town charter in 1194. In 1904, its boundaries were extended to all of Portsea Island and were later expanded onto the mainland of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
between 1920 and 1932 by incorporating Paulsgrove
Paulsgrove is an area of northern Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. Initially a small independent hamlet for many centuries, it was admitted to the city limits in 1920 and grew rapidly after the end of the Second World War.
History
Paulsgrove exi ...
, Wymering
Wymering is a residential area of the city of Portsmouth in the English county of Hampshire. Unlike the majority of Portsmouth, it is located on the mainland rather than Portsea Island.
Wymering was one of the estates held by Hampshire's bigges ...
, Cosham, Drayton and Farlington into Portsmouth. Portsmouth was granted city status on 21 April 1926.
On 1 April 1974, it formed the second tier of local government (below Hampshire County Council); Portsmouth and Southampton became administratively independent of Hampshire with the creation of the unitary authority on 1 April 1997.
The city is divided into two parliamentary constituencies, Portsmouth South and Portsmouth North, represented in the House of Commons by Stephen Morgan of the Labour Party and Penny Mordaunt of the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
respectively. The two Parliamentary constituencies each contain 7 electoral wards, giving an overall total of 14 electoral wards. Portsmouth's inner city centre is located in the Portsmouth South constituency.
Portsmouth City Council has 14 electoral wards, each ward returns three councillors, making 42 in total. Each councillor serves a four-year term. After the May 2018 local elections, the Liberal Democrats formed a minority administration, they have run the city since then. The leader of the council is the Liberal Democrat, Gerald Vernon-Jackson
Gerald Vernon-Jackson CBE (born 10 January 1962) is a Liberal Democrat politician in Portsmouth, England. He has been the leader of Portsmouth City Council since 15 May 2018, having previously been leader between 2004–2014, and councillor for ...
. The lord mayor usually has a one-year term.
The council is based in the civic offices, which house the tax support, housing-benefits, resident-services, and municipal-functions departments. They are in Guildhall Square, with the Portsmouth Guildhall
Portsmouth Guildhall is a multi-use building in the centre of Portsmouth, UK, located on a pedestrian square close to the Portsmouth and Southsea railway station. Constructed in 1890, the building was known as Portsmouth Town Hall until 1926. It ...
and Portsmouth Central Library. The Guildhall, a symbol of Portsmouth, is a cultural venue. It was designed by Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
-based architect William Hill, who began it in the neo-classical style
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing style ...
in 1873 at a cost of £140,000. It was opened to the public in 1890.
Economy
 Ten per cent of Portsmouth's workforce is employed at Portsmouth Naval Dockyard, which is linked to the city's biggest industry, defence; the headquarters of BAE Systems Surface Ships is in the city. BAE's Portsmouth shipyard received construction work on the two new s. A £100 million contract was signed to develop needed facilities for the vessels. A ferry port handles passengers and cargo, and a fishing fleet of 20 to 30 boats operates out of Camber Quay, Old Portsmouth; most of the catch is sold at the quayside fish market.
The city is host to IBM's UK headquarters and Portsmouth was also the UK headquarters of Zurich Financial Services until 2007. City shopping is centred on Commercial Road and the 1980s Cascades Shopping Centre. The shopping centre has 185,000 to 230,000 visitors weekly. Redevelopment has created new shopping areas, including the Gunwharf Quays (the repurposed shore establishment, with stores, restaurants and a cinema) and the Historic Dockyard, which caters to tourists and holds an annual Victorian Christmas market. Ocean Retail Park, on the north-eastern side of Portsea Island, was built in September 1985 on the site of a former metal-box factory.
Ten per cent of Portsmouth's workforce is employed at Portsmouth Naval Dockyard, which is linked to the city's biggest industry, defence; the headquarters of BAE Systems Surface Ships is in the city. BAE's Portsmouth shipyard received construction work on the two new s. A £100 million contract was signed to develop needed facilities for the vessels. A ferry port handles passengers and cargo, and a fishing fleet of 20 to 30 boats operates out of Camber Quay, Old Portsmouth; most of the catch is sold at the quayside fish market.
The city is host to IBM's UK headquarters and Portsmouth was also the UK headquarters of Zurich Financial Services until 2007. City shopping is centred on Commercial Road and the 1980s Cascades Shopping Centre. The shopping centre has 185,000 to 230,000 visitors weekly. Redevelopment has created new shopping areas, including the Gunwharf Quays (the repurposed shore establishment, with stores, restaurants and a cinema) and the Historic Dockyard, which caters to tourists and holds an annual Victorian Christmas market. Ocean Retail Park, on the north-eastern side of Portsea Island, was built in September 1985 on the site of a former metal-box factory.
Fratton Park
Fratton Park is a football ground in Portsmouth, England, which is the home of Portsmouth F.C. Fratton Park remains as the only home football ground in Portsmouth FC's entire history.
The early Fratton Park was designed by local architect A ...
to a new stadium on reclaimed land next to the Historic Dockyard. The £600 million mixed-use development, designed by Herzog & de Meuron, would include shops, offices and 1,500 harbourside apartments. The scheme was criticised for its size and location, and some officials said that it would interfere with harbour operations. The project was rejected by the city council due to the 2008 financial crisis
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
.
 Portsmouth's two Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers, and , were ordered by defence secretary
Portsmouth's two Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers, and , were ordered by defence secretary Des Browne
Desmond Henry Browne, Baron Browne of Ladyton, (born 22 March 1952) is a Scottish politician who served in the Cabinet of the United Kingdom under Tony Blair and Gordon Brown as Secretary of State for Defence 2006 to 2008 and Secretary of St ...
on 25 July 2007. They were built in the Firth of Forth at Rosyth Dockyard and BAE Systems Surface Ships in Glasgow, Babcock International at Rosyth, and at HMNB Portsmouth. The government announced before the 2014 Scottish independence referendum
A referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom was held in Scotland on 18 September 2014. The referendum question was, "Should Scotland be an independent country?", which voters answered with "Yes" or "No". The "No" side w ...
that military shipbuilding would end in Portsmouth, with all UK surface-warship construction focused on the two older BAE facilities in Glasgow. The announcement was criticised as a political decision to aid the referendum's "No" campaign.
Culture
Portsmouth has several theatres. The New Theatre Royal in Guildhall Walk, near the city centre, specialises in professional drama. The restored Kings Theatre in Southsea features amateur musicals and national tours. The Groundlings Theatre, built in 1784, is housed at the Old Beneficial School in Portsea. New Prince's Theatre and Southsea's Kings Theatre were designed by Victorian architect Frank Matcham. The city has three musical venues: the Guildhall, the Wedgewood Rooms (which includes Edge of the Wedge, a smaller venue), andPortsmouth Pyramids Centre
The Portsmouth Pyramids Centre (also known as the Pyramids) is an indoor leisure complex in Southsea, Portsmouth, Hampshire, England.
It has a live arena, leisure gym and function rooms. The function room, located next door to the indoor leisur ...
. Portsmouth Guildhall
Portsmouth Guildhall is a multi-use building in the centre of Portsmouth, UK, located on a pedestrian square close to the Portsmouth and Southsea railway station. Constructed in 1890, the building was known as Portsmouth Town Hall until 1926. It ...
is one of the largest venues in South East England, with a seating capacity
Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available, and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile that ...
of 2,500. A concert series is presented at the Guildhall by the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra. The Portsmouth Sinfonia approached classical music from a different angle during the 1970s, recruiting players with no musical training or who played an instrument new to them. The Portsmouth Summer Show is held at King George's Fields
A King George's Field is a public open space in the United Kingdom dedicated to the memory of King George V (1865–1936).
In 1936, after the king's death, Sir Percy Vincent, the then-Lord Mayor of London, formed a committee to determine a ...
. The 2016 show held during the last weekend of April, featured cover bands such as the Silver Beatles, the Bog Rolling Stones, and Fleetingwood Mac.
A number of musical works are set in the city. ''H.M.S. Pinafore
''H.M.S. Pinafore; or, The Lass That Loved a Sailor'' is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and a libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It opened at the Opera Comique in London, on 25 May 1878 and ran for 571 performances, which ...
'' is a comic opera in two acts set in Portsmouth Harbour, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W.S. Gilbert. Portsmouth Point (Walton), ''Portsmouth Point'' is a 1925 overture for orchestra by English composer William Walton, inspired by Thomas Rowlandson's etching of Portsmouth Point in Old Portsmouth. The overture was played during a 2007 BBC The Proms, Proms concert. John Cranko's 1951 ballet ''Pineapple Poll'', which features music from Gilbert and Sullivan's operetta ''The Bumboat Woman's Story'', is also set in Portsmouth.
Portsmouth hosts yearly remembrances of the D-Day landings, attended by veterans from Allied and Commonwealth nations. The city played a major role in the 50th D-Day anniversary in 1994; visitors included US President Bill Clinton, Australian Prime Minister Paul Keating, King Harald V of Norway, French President François Mitterrand, New Zealand Prime Minister Jim Bolger, Canadian Prime Minister Jean Chrétien, Prime Minister John Major, the Queen, and the Duke of Edinburgh. The 75th Anniversary of D-Day was similarly commemorated in the city. Prime Minister Theresa May led the event, and was joined by leaders of the US, Canada, Australia, France and Germany.
The annual Portsmouth International Kite Festival, organised by the city council and the Kite Society of Great Britain, celebrated its 25th anniversary in 2016.
Portsmouth is frequently used as a filming location for television and film productions. The Historic Dockyard has featured in several productions including the Hollywood adaptation of ''Les Miserables''.
In 2005, Portsmouth featured in the first series of ITV's ''Britain's Toughest Towns''. As this documentary also indicated, Portsmouth has issues with gangs and anti-social behaviour.
Literature
 Portsmouth is the hometown of Fanny Price, the main character of Jane Austen's novel ''Mansfield Park'', and most of its closing chapters are set there. Nicholas and Smike, the main protagonists of
Portsmouth is the hometown of Fanny Price, the main character of Jane Austen's novel ''Mansfield Park'', and most of its closing chapters are set there. Nicholas and Smike, the main protagonists of Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
' novel ''The Life and Adventures of Nicholas Nickleby'', make their way to Portsmouth and become involved with a theatrical troupe. Portsmouth is most often the port from which Captain Jack Aubrey's ships sail in Patrick O'Brian's seafaring historical Aubrey-Maturin series. Portsmouth is the main setting of Jonathan Meades's 1993 novel ''Pompey''. Since the novel was published, Meades has presented a TV programme documenting Victorian architecture in Portsmouth Dockyard.
Victorian novelist and historian Sir Walter Besant documented his 1840s childhood in ''By Celia's Arbour: A Tale of Portsmouth Town'', precisely describing the town before its defensive walls were removed. Southsea (as Port Burdock) features in ''The History of Mr Polly'' by H. G. Wells, who describes it as "one of the three townships that are grouped around the Port Burdock naval dockyards". The resort is also the setting of the graphic novel ''The Tragical Comedy or Comical Tragedy of Mr. Punch'' by high fantasy author Neil Gaiman, who grew up in Portsmouth. A Southsea street was renamed The Ocean at the End of the Lane by the city council in honour of Gaiman's The Ocean at the End of the Lane, novel of the same name.
Crime novels set in Portsmouth and the surrounding area include Graham Hurley's D.I.Faraday/D.C.Winter novels and C. J. Sansom's Tudor crime novel, ''Heartstone''; the latter refers to the warship ''Mary Rose'' and describes Tudor life in the town. ''Portsmouth Fairy Tales for Grown Ups'', a collection of short stories, was published in 2014. The collection, set around Portsmouth, includes stories by crime novelists William Sutton and Diana Bretherick.
Education
 The
The University of Portsmouth
The University of Portsmouth is a public university in Portsmouth, England. It is one of only four universities in the South East England, South East of England rated as Gold in the Government's Teaching Excellence Framework. With approximately 28 ...
was founded in 1992 as a new university from Portsmouth Polytechnic; in 2016, it had 20,000 students. The university was ranked among the world's top 100 modern universities in April 2015. In 2013, it had about 23,000 students and over 2,500 staff members. Several local colleges also award Higher National Diplomas, including Highbury College (specialising in vocational education), and Portsmouth College (which offers academic courses). Admiral Lord Nelson School and Miltoncross Academy were built in the late 1990s to meet the needs of a growing school-age population.
After the cancellation of the national building programme for schools, redevelopment halted. Two schools in the city were judged "inadequate", and 29 of its 63 schools were considered "no longer good enough" by Ofsted in 2009. Before it was taken over by Ark (charity), Ark Schools and became Ark Charter Academy, StLuke's Church of England secondary school was one of England's worst schools in GCSE achievement. It was criticised by officials for its behavioural standards, with students reportedly throwing chairs at teachers. Since it became an academy in 2009, the school has improved; 69 per cent of its students achieved five GCSEs with grades of A* to C, including English and mathematics. The academy's intake policy is for a standard comprehensive school, drawing from the community rather than by religion.
Portsmouth Grammar School, the city's oldest independent school was founded in 1732. Other independent schools include Portsmouth High School, Southsea, Portsmouth High School, and Mayville High School, Southsea, Mayville High School (founded in 1897),
Landmarks
 Many of Portsmouth's former defences are now museums or event venues. Several Victorian-era forts on Portsdown Hill are tourist attractions;
Many of Portsmouth's former defences are now museums or event venues. Several Victorian-era forts on Portsdown Hill are tourist attractions; Fort Nelson Fort Nelson may refer to:
Canada
*Fort Nelson, British Columbia, a town
*Fort Nelson River, British Columbia
* Fort Nelson (Manitoba) (1670–1713), an early fur trading post at the mouth of the Nelson River and the first headquarters of the Hudson ...
, a its summit, is home to the Royal Armouries museum. Tudor-era Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to p ...
has a small museum, and much of the seafront defences leading to the Round Tower
A fortified tower (also defensive tower or castle tower or, in context, just tower) is one of the defensive structures used in fortifications, such as castles, along with curtain walls. Castle towers can have a variety of different shapes and ful ...
are open to the public. The castle was withdrawn from active service in 1960, and was purchased by Portsmouth City Council. The southern part of the Royal Marines' Eastney Barracks is now the Royal Marines Museum, and was opened to the public under the National Heritage Act 1983. The museum received a £14 million grant from the National Lottery Fund, and was scheduled to relocate to Portsmouth Historic Dockyard in 2019. The birthplace of Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, at Mile End Terrace, is the Charles Dickens' Birthplace Museum; the four-storey red brick building became a GradeI listed building in 1953. Other tourist attractions include the Blue Reef Aquarium (with an "underwater safari" of British aquatic life) and the Cumberland House Natural History Museum, housing a variety of local wildlife.
 Most of the city's landmarks and tourist attractions are related to its naval history. They include the D-Day Story in Southsea, which contains the Overlord Embroidery. Portsmouth is home to several well-known ships; Horatio Nelson's flagship , the world's oldest naval ship still in commission, is in the
Most of the city's landmarks and tourist attractions are related to its naval history. They include the D-Day Story in Southsea, which contains the Overlord Embroidery. Portsmouth is home to several well-known ships; Horatio Nelson's flagship , the world's oldest naval ship still in commission, is in the dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
of Portsmouth Historic Dockyard
Portsmouth Historic Dockyard is an area of HM Naval Base Portsmouth which is open to the public; it contains several historic buildings and ships. It is managed by the National Museum of the Royal Navy as an umbrella organization representing f ...
. The ''Victory'' was placed in a permanent dry dock in 1922 when the Society for Nautical Research led a national appeal to restore her, and 22million people have visited the ship. The remains of Henry VIII's flagship, ''Mary Rose'', was rediscovered on the seabed in 1971. She was raised and brought to a purpose-built structure in Portsmouth Historic Dockyard in 1982. Britain's first iron-hulled warship, , was restored and moved to Portsmouth in June 1987 after serving as an oil fuel pier at Pembroke Dock in Pembrokeshire for fifty years. The National Museum of the Royal Navy
The National Museum of the Royal Navy was created in early 2009 to act as a single non-departmental public body for the museums of the Royal Navy. With venues across the United Kingdom, the museums detail the history of the Royal Navy operating o ...
, in the dockyard, is sponsored by an charity which promotes research of the Royal Dockyard's history and archaeology. The dockyard hosts the Victorian Festival of Christmas, featuring Father Christmas in a traditional green robe, each November.
Portsmouth's long association with the armed forces is demonstrated by a large number of war memorials, including several at the Royal Marines Museum and a large collection of memorials related to the Royal Navy in Victoria Park Victoria Park may refer to:
Places Australia
* Victoria Park Nature Reserve, a protected area in Northern Rivers region, New South Wales
* Victoria Park, Adelaide, a park and racecourse
* Victoria Park, Brisbane, a public park and former golf ...
. The Portsmouth Naval Memorial, in Southsea Common, commemorates the 24,591 British sailors who died during both World Wars and have no known grave. Designed by Sir Robert Lorimer, it was unveiled by George VI on 15 October 1924. In the city centre, the Guildhall Square Cenotaph contains the names of the fallen and is guarded by stone sculptures of machine gunners by Charles Sargeant Jagger. The west face of the memorial reads:
The city has three cemeteries: Kingston, Milton Road, and Highland Road. Kingston Cemetery, opened in 1856, is in east Fratton
Fratton is a residential and formerly industrial area of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. Victorian style terraced houses are dominant in the area, typical of most residential areas of Portsmouth. Fratton has many discount shops and "greasy spoo ...
. At , it is Portsmouth's largest cemetery and has about 400 burials a year. In February 2014, a ceremony celebrating the 180th anniversary of Portsmouth's Polish community was held at the cemetery. The approximately Milton Road Cemetery, founded on 8 April 1912, has about 200 burials per year. There is a crematorium in Portchester
Portchester is a locality and suburb northwest of Portsmouth, England. It is part of the borough of Fareham in Hampshire. Once a small village, Portchester is now a busy part of the expanding conurbation between Portsmouth and Southampton o ...
.
Gunwharf Quays
 The naval shore establishment contained the Royal Navy's arsenal; weapons and ammunition which would be taken from ships at its 'Gun Wharf' as they entered the harbour, and resupplied when they headed back to sea. The 1919 ''Southsea and Portsmouth Official Guide'' described the establishment as "the finest collections of weapons outside the Tower of London, containing more than 25,000 rifles". During the early nineteenth century, the 'Gunwharf' supplied the fleet with a "grand arsenal" of cannons, mortars, bombs, and ordnance. Although gunpowder was not provided due to safety concerns, it could be obtained at Priddy's Hard (near Gosport). An armoury sold small arms to soldiers, and the stone frigate also had blacksmith and carpenter shops for armourers. It was run by three officers: a ''viz'' (storekeeper), a clerk, and a foreman. By 1817, Gunwharf reportedly employed 5,000 men and housed the world's largest naval arsenal.
HMS ''Vernon'' was closed on 1 April 1996 and was redeveloped by Portsmouth City Council as Gunwharf Quays, a mixed residential and retail site with outlet stores, restaurants, pubs, cafés and a cinema. Construction of the Spinnaker Tower began in 2001, and was completed in the summer of 2005. The project exceeded its budget and cost £36million, of which Portsmouth City Council contributed £11 million. The tower is visible at a distance of in clear weather, and its viewing platforms overlook the Solent (towards the Isle of Wight), the harbour and Southsea Castle. The tower weighs over .and has the largest glass floor in Europe.
The naval shore establishment contained the Royal Navy's arsenal; weapons and ammunition which would be taken from ships at its 'Gun Wharf' as they entered the harbour, and resupplied when they headed back to sea. The 1919 ''Southsea and Portsmouth Official Guide'' described the establishment as "the finest collections of weapons outside the Tower of London, containing more than 25,000 rifles". During the early nineteenth century, the 'Gunwharf' supplied the fleet with a "grand arsenal" of cannons, mortars, bombs, and ordnance. Although gunpowder was not provided due to safety concerns, it could be obtained at Priddy's Hard (near Gosport). An armoury sold small arms to soldiers, and the stone frigate also had blacksmith and carpenter shops for armourers. It was run by three officers: a ''viz'' (storekeeper), a clerk, and a foreman. By 1817, Gunwharf reportedly employed 5,000 men and housed the world's largest naval arsenal.
HMS ''Vernon'' was closed on 1 April 1996 and was redeveloped by Portsmouth City Council as Gunwharf Quays, a mixed residential and retail site with outlet stores, restaurants, pubs, cafés and a cinema. Construction of the Spinnaker Tower began in 2001, and was completed in the summer of 2005. The project exceeded its budget and cost £36million, of which Portsmouth City Council contributed £11 million. The tower is visible at a distance of in clear weather, and its viewing platforms overlook the Solent (towards the Isle of Wight), the harbour and Southsea Castle. The tower weighs over .and has the largest glass floor in Europe.
Southsea
 Southsea is a seaside resort and residential area of Portsmouth located at the southern end of Portsea Island. Its name originates from Southsea Castle, a seafront castle built in 1544 by HenryVIII to help defend the Solent and Portsmouth Harbour. The area was developed in 1809 as Croxton Town; by the 1860s, the suburb of Southsea had expanded to provide working-class housing. Southsea developed as a seaside and bathing resort. A pump room and baths were built near the present-day
Southsea is a seaside resort and residential area of Portsmouth located at the southern end of Portsea Island. Its name originates from Southsea Castle, a seafront castle built in 1544 by HenryVIII to help defend the Solent and Portsmouth Harbour. The area was developed in 1809 as Croxton Town; by the 1860s, the suburb of Southsea had expanded to provide working-class housing. Southsea developed as a seaside and bathing resort. A pump room and baths were built near the present-day Clarence Pier
Clarence Pier is an amusement pier in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered b ...
, and a complex was developed which included vapour baths, showers, and card-playing and assembly rooms for holiday-goers.
Clarence Pier, opened in 1861 by the Prince and Princess of Wales, was named after Portsmouth military governor Lord Frederick FitzClarence and was described as "one of the largest amusement parks on the south coast". South Parade Pier
The South Parade Pier is a pier in Portsmouth, England. It is one of two piers in the city, the other being Clarence Pier. The pier once had a long hall down its centre which housed a seating area and a small restaurant. The outside of the hall ...
was built in 1878, and is among the United Kingdom's 55 remaining private piers. Originally a terminal for ferries travelling to the Isle of Wight, it was soon redeveloped as an entertainment centre. The pier was rebuilt after fires in 1904, 1967 and 1974 (during the filming of ''Tommy (1975 film), Tommy''). Plans were announced in 2015 for a Solent Eye at the pier: a £750,000, 24-gondola Ferris wheel similar to the London Eye.
Southsea is dominated by Southsea Common, a grassland created by draining the marshland next to the vapour baths in 1820. The common met the demands of the early-19th-century military for a clear Shooting range, firing range, and parallels the shore from Clarence Pier to Southsea Castle. A popular recreation area, it hosts a number of annual events which include carnivals, Christmas markets, and Victorian festivals. The common has a large collection of mature elm trees, believed to be the oldest and largest surviving in Hampshire and which have escaped Dutch elm disease due to their isolation. Other plants include the Canary Island date palms (''Phoenix canariensis''), some of Britain's largest, which have recently produced viable seed.
Southsea is often mistaken as a town separate from Portsmouth, mainly due to the confusing Portsmouth & Southsea railway station name. The resort of Southsea previously had its own dedicated light railway line; the Southsea Railway and its own terminus, East Southsea railway station. The Southsea Railway and station were closed in 1914, with the station's name merged into that of Portsmouth's main railway station name in 1925.
Religion
 Portsmouth has two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas in Old Portsmouth and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The city is one of 34 British settlements with a
Portsmouth has two cathedrals: the Anglican Cathedral of St Thomas in Old Portsmouth and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St John the Evangelist. The city is one of 34 British settlements with a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
cathedral. Portsmouth's first chapel, dedicated to Thomas Becket, was built by Jean deGisors in the second half of the 12th century. It was rebuilt and developed into a parish church and an Anglican cathedral. Damaged during the 1642 Siege of Portsmouth, its tower and nave were rebuilt after the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
. Significant changes were made when the Diocese of Portsmouth was founded in 1927. It became a cathedral in 1932 and was enlarged, although construction was halted during the Second World War. The cathedral was re-consecrated before Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother in 1991.
The Royal Garrison Church was founded in 1212 by Peter des Roches, Bishop of Winchester. After centuries of decay, it became an ammunition store in 1540. The 1662 marriage of CharlesII and Catherine of Braganza was celebrated in the church, and large receptions were held there after the defeat of Napoleon at the 1814 Battle of Leipzig. In 1941, a firebomb fell on its roof and destroyed the nave. Although the church's chancel was saved by servicemen shortly after the raid, replacing the roof was deemed impossible due to the large amounts of salt solution absorbed by the stonework.
The Cathedral of St John the Evangelist was built in 1882 to accommodate Portsmouth's increasing Roman Catholic population, and replaced a chapel built in 1796 to the west. Before 1791, Roman Catholic chapels in towns with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status were prohibited. The chapel opened after the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791 was passed, and was replaced by the cathedral. It was constructed in phases; the nave was completed in 1882; the Crossing (architecture), crossing in 1886, and the chancel by 1893. During the blitz, the cathedral was badly damaged when Luftwaffe bombing destroyed Bishop's House next door; it was restored in 1970, 1982, and 2001. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Portsmouth was founded in 1882 by Pope Leo XIII. Smaller places of worship in the city include StJude's Church in Southsea, St Mary's Church, Portsea, StMary's Church in Portsea, St Ann's Church, HMNB Portsmouth, StAnn's Chapel in the naval base and the Portsmouth and Southsea Synagogue, one of Britain's oldest. Other places of worship include the Immanuel Baptist Church, Southsea; Trinity Methodist Church, Highland Road; Buckland United Reformed Church; The Oasis Centre Elim Penteostal Church; Jubilee Pentecostal Church, Somers Road; Kings Church Assemblies of God (St Peter's Somers Road); Family Church; Christ Central Church, John Pounds Centre; The Jami Mosque, Bradford Junction; The Sikh Gurudwara, Margate Road.
Sport

Portsmouth F.C.
Portsmouth Football Club is a professional football club based in Portsmouth, Hampshire, England, which compete in . They are also known as ''Pompey'', a local nickname used by both HMNB Portsmouth and the city of Portsmouth; the ''Pompey'' nick ...
play their home games at Fratton Park
Fratton Park is a football ground in Portsmouth, England, which is the home of Portsmouth F.C. Fratton Park remains as the only home football ground in Portsmouth FC's entire history.
The early Fratton Park was designed by local architect A ...
. They have won two Football League titles (1949 and 1950), and won the FA Cup in 1939 and 2008. The club returned to the Premier League in 2003. They were relegated to the Football League Championship, Championship in 2010 and, experiencing serious financial difficulties in February 2012, were relegated again to Football League One, League One. The club was relegated the following year to League Two, the fourth tier of Football in England#League system, English football. PortsmouthF.C. was purchased in April 2013 by the Pompey Supporters Trust, becoming the largest fan-owned club in English Football history. In May 2017, as League Two champions, they were promoted to League One for the 2017–18 season.
Moneyfields F.C. have played in the Wessex Football League Premier Division since 1998. United Services Portsmouth F.C. (formerly known as Portsmouth Royal Navy) and Baffins Milton Rovers F.C. compete in Wessex League Division One; United Services was founded in 1962, and Baffins Milton Rovers in 2011. The rugby union, rugby teams United Services Portsmouth Rugby Football Club, United Services Portsmouth RFC and Royal Navy Rugby Union play their home matches at the United Services Recreation Ground. Royal Navy Rugby Union play in the annual Army Navy Match at Twickenham.
Portsmouth began hosting first-class cricket at the United Services Recreation Ground in 1882, and Hampshire County Cricket Club matches were played there from 1895 to 2000. In 2000, Hampshire moved their home matches to the new Rose Bowl (cricket ground), Rose Bowl cricket ground in West End, Hampshire, West End. Portsmouth is home to four Field hockey, hockey clubs: City of Portsmouth Hockey Club, based at the university's Langstone Campus; Portsmouth & Southsea Hockey Club and Portsmouth Sharks Hockey Club, based at the Admiral Lord Nelson School; and United Services Portsmouth Hockey Club, based on Burnaby Road. Great Salterns Golf Club, established in 1926, is an 18-hole parkland course with two holes played across a lake; there are coastal courses at Hayling Golf Club, Hayling and the Gosport and Stokes Bay Golf Club. Boxing was a popular sport between 1910 and 1960, and a monument commemorating the city's boxing heritage was built in 2017.
Transport
Ferries
 Portsmouth Harbour railway station, Portsmouth Harbour has passenger-ferry links to
Portsmouth Harbour railway station, Portsmouth Harbour has passenger-ferry links to Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite t ...
and the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
, with car-ferry service to the Isle of Wight nearby. Hovertravel, Britain's longest-standing commercial hovercraft service, begun in the 1960s, runs from near Clarence Pier in Southsea to Ryde
Ryde is an English seaside town and civil parish on the north-east coast of the Isle of Wight. The built-up area had a population of 23,999 according to the 2011 Census and an estimate of 24,847 in 2019. Its growth as a seaside resort came af ...
, Isle of Wight. Portsmouth International Port has links to Caen, Cherbourg-Octeville, St Malo and Le Havre in France, Santander, Cantabria, Santander and Bilbao in Spain, and the Channel Islands. Ferry services from the port are operated by Brittany Ferries and Condor Ferries.
On 18 May 2006, Trasmediterranea began service to Bilbao in competition with P&O Ferries, P&O's service. Its ferry, ''Fortuny'', was detained in Portsmouth by the Maritime and Coastguard Agency for a number of safety violations. They were quickly corrected and the service was cleared for passengers on 23 May of that year. Trasmediterránea discontinued its Bilbao service in March 2007, citing a need to deploy the ''Fortuny'' elsewhere. P&O Ferries ended their service to Bilbao on 27 September 2010 due to "unsustainable losses". The second-busiest ferry port in the UK (after Dover), Portsmouth handles about three million passengers per year.
Buses
Local bus services are provided by Stagecoach South and First Hampshire & Dorset to the city and its surrounding towns. Hovertravel and Stagecoach operate a Hoverbus service from the city centre to Southsea Hovercraft Terminal and the Hard Interchange, near the seafront. National Express Coaches, National Express service from Portsmouth operates primarily from the Hard Interchange to Victoria Coach Station, Cornwall, Bradford Interchange, Bradford, Birkenhead and Bristol bus station, Bristol.Railways
Portsmouth has four railway stations on Portsea Island: , , and , with a fifth station at in the northern mainland suburb of Cosham, Cosham, Portsmouth. Portsmouth previously had additional stations at East Southsea railway station, Southsea, Farlington Halt railway station, Farlington and Paulsgrove Halt railway station, Paulsgrove, but these were closed during at various periods of the twentieth century. The city of Portsmouth is on two direct South Western Railway (train operating company), South Western Railway routes to , via and via . There is a South Western Railway stopping service to and Great Western Railway (train operating company), Great Western Railway service to via Southampton, , and Bristol Temple Meads railway station, Bristol. Southern (train operating company), Southern has service to , , East Croydon railway station, Croydon and .Closed stations
Southsea once had its own branch line, the Southsea Railway, which opened in 1885 between East Southsea railway station, Southsea railway station and Fratton; it was closed in 1914 due to competition from tram services. Farlington Halt railway station was built to serve Portsmouth Park Horseracing in the United Kingdom, racecourse, opening as Farlington Race Course on 26 June 1891. The racecourse was closed during World War I, World War One, but the station was retained to serve the ammunition dump put in its place. The station closed in 1917. Re-opened in 1922 until 1927. Under the Southern Railway (UK), Southern Railway, it re-opened as a general public railway halt, halt in 1928 named ''Farlington Halt''; however, this was short-lived as the station closed due to insufficient customers on 4 July 1937. Paulsgrove Halt railway station was a railway station opened in 1928 to serve the adjacent Portsmouth Racecourse, a pony racing stronghold. The station was formerly located between Cosham and Portchester stations. Paulsgrove Halt was closed along with the racecourse when the land was acquired by the military in 1939, at the outbreak of World War II.Air
Portsmouth Airport, with a grass runway, was in operation from 1932 to 1973. After it closed, housing (Anchorage Park) and industry were built on the site. The nearest airport is Southampton Airport in the Borough of Eastleigh, away. It has a South Western Railway (train operating company), South Western Railway rail connection, requiring a change at Southampton Central railway station, Southampton Central or Eastleigh railway station, Eastleigh. Heathrow Airport, Heathrow and Gatwick Airport, Gatwick are and away, respectively. Gatwick is linked by Southern train service to London Victoria station and Heathrow is linked by coach to Woking, which is on both rail lines to London Waterloo and the London Underground. Heathrow is linked to Portsmouth by National Express coaches.Former canal
 The Portsmouth and Arundel Canal ran between the towns and was built in 1823 by the Portsmouth & Arundel Navigation Company. Never financially successful, and found to be contaminating Portsea Island fresh water wells, it was abandoned in 1855 and the company was wound up in 1888. The canal was part of a larger scheme for a secure inland canal route from London to Portsmouth, allowing boats to avoid the
The Portsmouth and Arundel Canal ran between the towns and was built in 1823 by the Portsmouth & Arundel Navigation Company. Never financially successful, and found to be contaminating Portsea Island fresh water wells, it was abandoned in 1855 and the company was wound up in 1888. The canal was part of a larger scheme for a secure inland canal route from London to Portsmouth, allowing boats to avoid the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
. It had three sections: a pair of ship canals (one on Portsea Island and one to Chichester) and a barge canal from Ford, West Sussex, Ford on the River Arun to Hunston, West Sussex, Hunston, where it joined the canal's Chichester section.
The route through Portsea Island began from a basin formerly located on Arundel Street and cut through Landport, Fratton
Fratton is a residential and formerly industrial area of Portsmouth in Hampshire, England. Victorian style terraced houses are dominant in the area, typical of most residential areas of Portsmouth. Fratton has many discount shops and "greasy spoo ...
and Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
, ending at the eastern end of Locksway Road in Milton (where a set of lock gates accessed Langstone Harbour, Langstone and Chichester Harbours. After the island route was closed, the drained canal-bed sections through Landport and Fratton were reused for the Portsmouth Direct line, or filled-in to surface level to form a new main road route to Milton, named Goldsmith Avenue.
The brick-lined canal walls are clearly visible between the Fratton and Portsmouth & Southsea railway stations. The canal lock entrance at Locksway Road in Milton is east of the Thatched House pub.
Future plans
A new public transport structure was once under discussion, including monorails and light rail. Although a light-rail link to Gosport was authorised in 2002 (with completion expected to be in 2005), the project was in jeopardy as the Department for Transport refused to fund it in November 2005. In April 2011, ''The News (Portsmouth), The News'' reported a scheme to replace conventional rail lines to Southampton via Fareham, Bursledon and Sholing with light rail.Media
Portsmouth, Southampton and their adjacent towns are served primarily by programming from the Rowridge transmitting station, Rowridge and Chillerton Down transmitting station, Chillerton Down transmitters on theIsle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
, although the transmitter at Midhurst transmitting station, Midhurst can substitute for Rowridge. Portsmouth was one of the first cities in the UK to have a local TV station (MyTV), although the Isle of Wight began local television broadcasting in 1998. In November 2014, That's Solent was introduced as part of a nationwide roll-out of local Freeview (UK), Freeview channels in south-central England. The stations broadcast from Rowridge.
According to RAJAR, popular radio stations include regional Wave 105 and Global Radio's Heart South and Capital South. Greatest Hits Radio South West broadcasts from Southampton to the city on 107.4 MHz, and the non-profit community station, Express FM, broadcasts on 93.7. Patients at Queen Alexandra Hospital (Portsmouth's primary hospital) receive local programming from Portsmouth Hospital Broadcasting, which began in 1951. When the first local commercial radio stations were licensed during the 1970s by the Independent Broadcasting Authority (IBA), Radio Victory received the first licence and began broadcasting in 1975. In 1986, the IBA increased the Portsmouth licence to include Southampton and the Isle of Wight. The new licence went to Ocean Sound (later known as Ocean FM), with studios in Fareham
Fareham ( ) is a market town at the north-west tip of Portsmouth Harbour, between the cities of Portsmouth and Southampton in south east Hampshire, England. It gives its name to the Borough of Fareham. It was historically an important manufact ...
; Ocean FM became Heart Hampshire. For the city's 800th birthday in 1994, VictoryFM broadcast for three 28-day periods over 18 months. It was purchased by TLRC, who relaunched the station in 2001 as the Quay; Portsmouth Football Club became a stakeholder in 2007, selling it in 2009.
Portsmouth's daily newspaper is ''The News (Portsmouth), The News'', founded in 1873 and previously known as the ''Portsmouth Evening News''. ''The Journal'', a free weekly newspaper, is published by ''News'' publisher Johnston Press.
Notable residents
Portsmouth has been home to a number of famed authors;Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, whose works include ''A Christmas Carol'', ''Great Expectations'', ''Oliver Twist'' and ''A Tale of Two Cities'', was born there. Arthur Conan Doyle, author of the Sherlock Holmes stories, practised medicine in the city and played in goal for the amateur Portsmouth Association Football Club. Rudyard Kipling (poet and author of ''The Jungle Book'') and H. G. Wells, author of ''The War of the Worlds'' and ''The Time Machine'', lived in Portsmouth during the 1880s. Novelist and historian Walter Besant, author of ''By Celia's Arbour, A Tale of Portsmouth Town'', was born in Portsmouth. Historian Frances Yates, known for her work on Renaissance Western esotericism, esotericism, was born in the city. Francis Austen, brother of Jane Austen, briefly lived in the area after graduating from Portsmouth Naval Academy. Contemporary literary figures include social critic, journalist and author Christopher Hitchens, who was born in Portsmouth. Nevil Shute moved to the city in 1934 when he relocated his aircraft company, and his former home is in Southsea. Fantasy author Neil Gaiman grew up in Purbrook and Southsea.
Industrial Revolution engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
was born in Portsmouth. His father, Marc Isambard Brunel, worked for the Royal Navy and developed the world's first production line
A production line is a set of sequential operations established in a factory where components are assembled to make a finished article or where materials are put through a refining process to produce an end-product that is suitable for onward c ...
to mass-produce Block (sailing), pulley blocks for ship rigging. James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff, ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005), commonly known as Jim Callaghan, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1976 to 1980. Callaghan is ...
, British prime minister from 1976 to 1979, was born and raised in Portsmouth. Son of a Protestant Northern Irish petty officer in the Royal Navy, Callaghan was the only person to hold all four Great Offices of State: foreign secretary, home secretary, chancellor and prime minister. John Pounds, the founder of ragged school
Ragged schools were charitable organisations dedicated to the free education of destitute children in 19th century Britain. The schools were developed in working-class districts. Ragged schools were intended for society's most destitute children ...
s (which provided free education to working-class children), lived in Portsmouth and founded England's first ragged school there.
Comedian and actor Peter Sellers was born in Southsea, and Arnold Schwarzenegger briefly lived and trained in Portsmouth. Other actors who were born or lived in the city include ''EastEnders'' actresses Emma Barton and Lorraine Stanley, and Bollywood actress Geeta Basra. Cryptozoologist Jonathan Downes was born in Portsmouth, and lived there for a time. Ant Middleton, former SBS, current television presenter and author was born in Portsmouth.
Helen Duncan, the last person to be imprisoned under the 1735 Witchcraft Act, was arrested in Portsmouth.
Notable sportspeople include Commonwealth Games gold medalist Michael East (athlete), Michael East, Olympic medallist in cycling Rob Hayles, former British light-heavyweight boxing champion Tony Oakey, Olympic medallist Alan Pascoe as well as professional footballer Mason Mount. Single-handed yachtsman Alec Rose, 2003 World Aquatics Championships gold medallist Katy Sexton, and Olympic medallist Roger Black were also born in the city. Jamshid bin Abdullah of Zanzibar, the last constitutional monarch of the island state, lives in exile in Portsmouth with his wife and six children.
International relations
Twin towns - sister cities
* Caen, Normandy, France * Duisburg, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany * Haifa, Haifa District, Israel * Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada * Lakewood, Colorado, Lakewood, Jefferson County, Colorado, Jefferson County, Colorado,United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
* Maizuru, Kyoto Prefecture, Japan
* Portsmouth, Virginia, Portsmouth, Virginia, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
* Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
* Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
* Sylhet, Bangladesh
* Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
Freedom of the City
According to the Portsmouth City Council website, the following individuals and military units have received the Freedom of the City in Portsmouth.Individuals
* Edward Macnaghten, Baron Macnaghten, Baron Macnaghten, (1895) * Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Frederick Roberts, 1st Earl Roberts, Lord Roberts of Kandahar, (1898) * Alderman John Baker (Portsmouth MP), Sir John Baker, (1901) * Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant General Frederick Fitzwygram, Sir Frederick Fitzwygram, (1901) * Alderman Sir William Pink, JP (1905) * Alderman Sir T. Scott Foster, JP (1906) * Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (1921) * Alderman F. G. Foster, JP (1924) * David Lloyd George, (1924) * Edward VIII, Prince of Wales (1926) * Major-general (United Kingdom), Major General J. E. B. Seely, 1st Baron Mottistone, J. E. B. Seely, (1927) * William Joynson-Hicks, 1st Viscount Brentford, Sir William Joynson-Hicks, (1927) * Councillor Frank J. Privett, JP (1928) * Alderman Sir Harold R. Pink, JP (1928) * Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral William James (Royal Navy admiral), Sir William James, (1942) * Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery, Lord Montgomery of Alamein, (1946) * Winston Churchill, Sir Winston Churchill, (1950) * Alderman List of mayors of Portsmouth, Albert Johnson (1966) * Alderman J. P. D. Lacey, (1966) * Alec Rose, Sir Alec Rose (1968) * Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet Louis Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma, Lord Mountbatten of Burma, (1976) * Charles III, Prince of Wales (1979) * James Callaghan, Lord Callaghan of Cardiff, (1991) * Diana, Princess of Wales, Princess of Wales (1992) * Frank Judd, Baron Judd, Lord Judd of Portsea (1995) * Lady Margaret Daley, (1996) * Herr Josef Krings, (1997) * Ian G. Gibson, OBE (2002) * Milan Mandarić (2003) * Alfred Blake, Sir Alfred Blake, (2003) * Brian Kidd (2003), former Head of Parks and Gardens in Portsmouth.) * Harry Redknapp (2008) * Syd Rapson (2016)Military units
* Royal Hampshire Regiment (1950) * Royal Marines (1959) * Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth, Portsmouth Command of theRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
(1965)
* Princess of Wales's Royal Regiment (1992)
* , Royal Naval Reserve, RNR (2003)
* , Royal Navy, RN (2007)
Organisations and groups
* Key worker, Essential Workers of Portsmouth: 16 March 2021. (service will be held in May 2021). * Royal Navy, Royal Naval Association: 8 December 2021. * Royal Marines Association (Portsmouth Branch): 8 December 2021. * Women's Royal Naval Service, Association of Wrens and Women of the Royal Naval Services: 8 December 2021. * Portsmouth F.C., Pompey in the Community: 29 March 2022.See also
* List of tallest buildings and structures in Portsmouth * List of twin towns and sister cities in the United Kingdom * Portsmouth power stationNotes
References
Citations
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *General references
*External links
* * {{Authority control Portsmouth, 1180 establishments in England Local government districts of South East England Local government in Hampshire Populated coastal places in Hampshire Port cities and towns in South East England Ports and harbours of Hampshire Ports and harbours of the English Channel Towns in Hampshire Unitary authority districts of England Unparished areas in Hampshire Boroughs in England