|
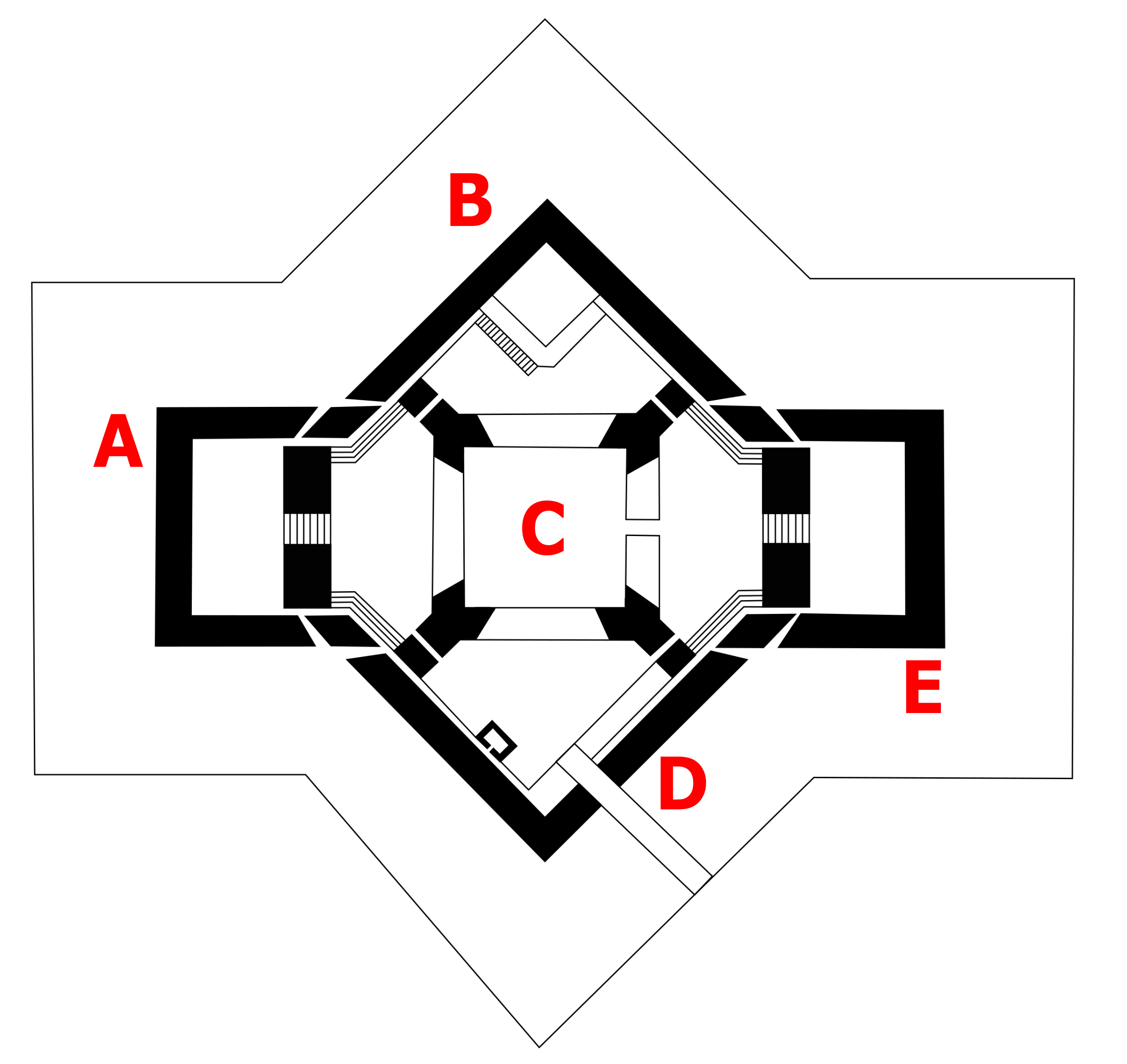
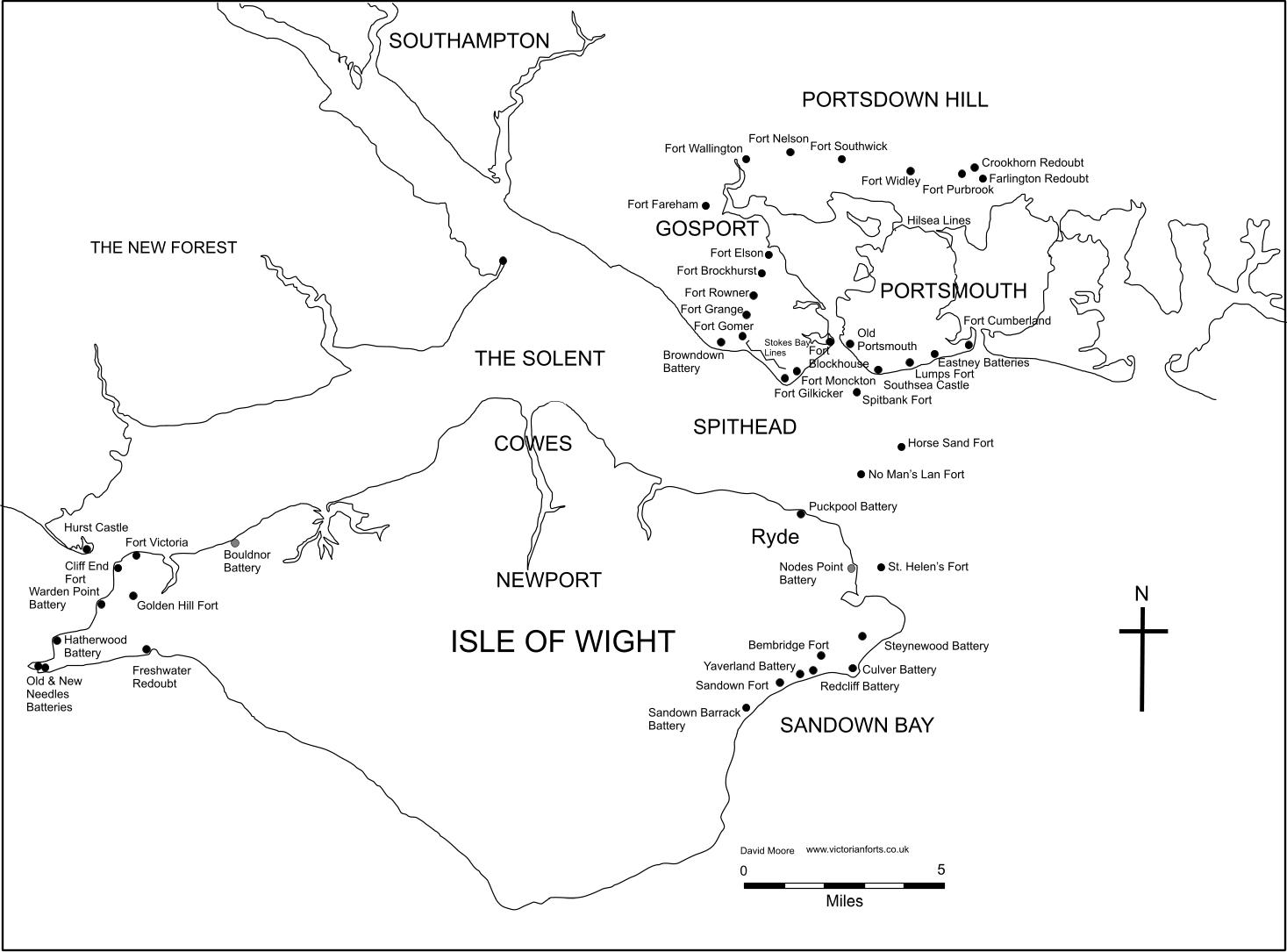
Palmerston Forts, Portsmouth
The Palmerston Forts that encircle Portsmouth were built in response to the 1859 Royal Commission dealing with the perceived threat of a French invasion. The forts were intended to defend the Dockyard in Portsmouth. Construction was carried out by the Royal Engineers and civilian contractors (under Royal Engineer supervision). In addition to the newly constructed forts, extensive work was carried out on existing fortifications. The Portsmouth defences can be split into four distinct groups of forts, comprising four sea forts built in the Solent, a group of forts on Portsea Island, a group of forts along Portsdown Hill overlooking Portsmouth, and a group of forts on the Gosport peninsula. As well as these forts surrounding Portsmouth, further protection for Portsmouth was provided by additional Palmerston forts on the Isle of Wight. Solent forts These man-made island forts were originally built to protect the eastern approaches to Portsmouth Harbour from attack by enemy forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Forts Plan
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council. Portsmouth is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom, with a population last recorded at 208,100. Portsmouth is located south-west of London and south-east of Southampton. Portsmouth is mostly located on Portsea Island; the only English city not on the mainland of Great Britain. Portsea Island has the third highest population in the British Isles after the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. Portsmouth also forms part of the regional South Hampshire conurbation, which includes the city of Southampton and the boroughs of Eastleigh, Fareham, Gosport, Havant and Waterlooville. Portsmouth is one of the world's best known ports, its history can be traced to Roman times and has been a significant Royal Navy dockyard and base for centuries. Portsmouth was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Man's Land Fort
No Man's Land Fort, also referred to as No Man's Fort, is a sea fort in the Solent, near Portsmouth, England. It is one of the Palmerston Forts built between 1867 and 1880 after the recommendations of the 1859 Royal Commission. It is 200 feet in diameter, and lies off the coast of the Isle of Wight. History The fort was designed by Captain E. H. Stewart, overseen by Assistant Inspector General of Fortifications, Colonel W. F. D. Jervois. Construction work began in 1865, and the fort was completed in 1880, long after the threat of a seaborne invasion from France had passed, at a cost of £462,500. A 2020 report stated that during the Second World War, "the forts were used to defend the Portsmouth dockyards. Life on site was grim; those serving were deliberately chosen for their inability to swim, to avoid any attempt to escape". No Man's Land Fort is almost identical to Horse Sand Fort. It has been used as a luxury home/hospitality centre for high-paying guests – due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crookhorn Redoubt
Portsdown Hill is a long chalk ridge in Hampshire, England. The highest point of the hill lies within Fort Southwick at 131m above sea level. The ridge offers good views to the south over Portsmouth, the Solent, Hayling Island and Gosport, with the Isle of Wight beyond. The hill is on the mainland, just to the north of Ports Creek, which separates the mainland from Portsea Island, on which lies the main part of the city of Portsmouth, one of the United Kingdom's main naval bases. To the north lies the Forest of Bere, with the South Downs visible in the distance. Butser Hill can be seen on a clear day. The hill is formed from an inlier of chalk which has been brought to the surface by an east–west upfold of the local strata known as the Portsdown Anticline. Southwick House is close by the north side of the hill, the HQ for U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower during the D-Day invasions; the generals prayed together before D-Day at Christ Church Portsdown, on the hill, which has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Purbrook
Portsdown Hill is a long chalk ridge in Hampshire, England. The highest point of the hill lies within Fort Southwick at 131m above sea level. The ridge offers good views to the south over Portsmouth, the Solent, Hayling Island and Gosport, with the Isle of Wight beyond. The hill is on the mainland, just to the north of Ports Creek, which separates the mainland from Portsea Island, on which lies the main part of the city of Portsmouth, one of the United Kingdom's main naval bases. To the north lies the Forest of Bere, with the South Downs visible in the distance. Butser Hill can be seen on a clear day. The hill is formed from an Inliers and outliers (geology), inlier of chalk which has been brought to the surface by an east–west anticline, upfold of the local stratum, strata known as the Portsdown Anticline. Southwick House is close by the north side of the hill, the HQ for U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower during the D-Day invasions; the generals prayed together before D-Day a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
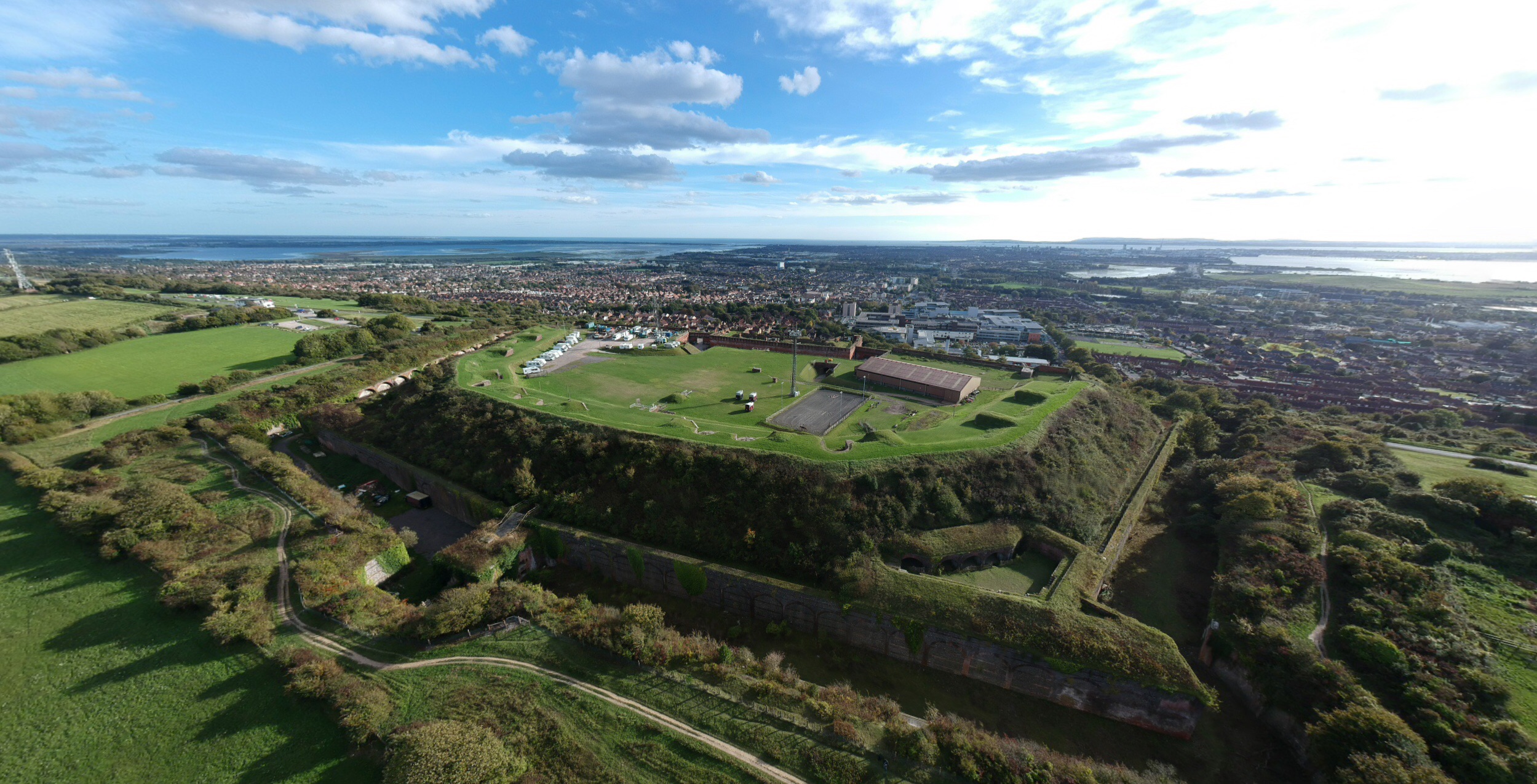
Fort Widley
Fort Widley is one of the forts built on top of Portsdown Hill between 1860 and 1868 on the recommendation of the Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom. It was designed, along with the other Palmerston Forts atop Portsdown, to protect Portsmouth from attack from the rear. Design and construction Fort Widley was a polygonal Fort designed by William Crossman, an officer of the Royal Engineers, who was part of the staff of the Inspector General of Fortifications at the War Office. The fort was built up from chalk, with red brick and local flint being used for buildings and revetment to the large dry ditch which was also dug at the same time. Armament was fitted into three different categories - the main armament which was mounted on a semi-circular rampart, high angle armament provided by 13-inch mortars, mounted in two protected mortar batteries and close range armament, mounted in one full and two demi-caponiers. Barracks accommodation was also provided for both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Southwick
Fort Southwick is one of the forts found on Portsdown Hill, which overlooks the naval base of Portsmouth in the county of Hampshire, England. History Fort Southwick was built to defend the landward approaches to the naval base on the recommendation of the Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom which reported in 1860. It is the highest fort on the hill, and holds the water storage tanks for the other forts, supplying them via a brick lined aqueduct. Construction was started in 1861 and completed by 1870. It was designed to house a large complement of men (about 220) in a crescent-shaped barrack block. Its north projection has one full caponier to defend the dry ditch, and has two smaller demi-caponiers at the corners. A small musketry gallery crosses the ditch at the south-west angle to cover a minor branch of the ditch. Mortar batteries of five mortars each can be found set into the rampart behind the demi-caponiers. In 1893 the fort was armed with a total of 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Nelson, Portsmouth
Fort Nelson, in the civil parish of Boarhunt in the English county of Hampshire, is one of five defensive forts built on the summit of Portsdown Hill in the 1860s, overlooking the important naval base of Portsmouth. It is now part of the Royal Armouries, housing their collection of artillery, and a Grade I Listed Building. Description Fort Nelson is a typical Polygonal or Palmerston Fort. It is six-sided with a deep ditch protected by three caponiers. Above each caponier is a well-protected emplacement for 13-inch mortars. It was originally entered by two Guthrie rolling bridges and has a barrack block for 172 officers and other ranks, protected by a V-shaped redan. A large open parade ground gives access to the magazines 40 feet underneath it. There are open emplacements on the ramparts for 64 pounder rifled muzzle-loading guns and RML 6.6-inch howitzers. There are also three Haxo casemates for 7 inch rifled breech-loaders. The Nelson Monument, which gave the fort its nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Wallington
Wallington is a village in Hampshire, part of the borough of Fareham. It is situated between Portsmouth and Southampton near where the River Wallington enters Portsmouth Harbour. The name Wallington probably means 'settlement of the Welsh' (or Britons) – ''Weala-tun'' / ''Walintone'' (Old English) and not 'walled town' as might be inferred. Industry The village is now an affluent residential suburb of Fareham, but was once a separate entity with a brewery and tannery as its main industries. Wallington was also important in brickmaking and pottery. The bricks known as " Fareham reds" were made locally – the most famous use of which is the Royal Albert Hall. Wallington also boasts the largest collection of ''Fareham pots'' – chimney pots. Fort Wallington In the 1860s the Royal Commission on the Defences of the United Kingdom recommended that a line of forts be built along Portsdown Hill. The western end of this line was Fort Wallington. Building of the fort was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell (projectile)
A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. Modern usage sometimes includes large solid kinetic projectiles that is properly termed shot. Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used. All explosive- and incendiary-filled projectiles, particularly for mortars, were originally called ''grenades'', derived from the French word for pomegranate, so called because of the similarity of shape and that the multi-seeded fruit resembles the powder-filled, fragmentizing bomb. Words cognate with ''grenade'' are still used for an artillery or mortar projectile in some European languages. Shells are usually large-caliber projectiles fired by artillery, armored fighting vehicles (e.g. tanks, assault guns, and mortar carriers), warships, and autocannons. The shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilsea Lines
The Hilsea Lines are a line of 18th- and 19th-century fortifications built at Hilsea to protect the northern approach to Portsea Island, an island off the southern coast of England which forms the majority of the city of Portsmouth and its key naval base. They are now used as a greenspace and leisure area, also known locally as ''Foxes Forest''. Natural defences The island is separated from the mainland by a narrow stretch of water called Portsbridge Creek. The first means of crossing the creek was by stepping stones, followed by a single track bridge, built to allow the passage of pedestrians and horse-drawn carts to have access to Portsea Island. Early defences Early defences were focused on the 'Portsbridge' that crossed the creek. A fortification is thought to have been built at the mainland end of the bridge during the reign of King Henry VIII. In 1642 the fort was captured by parliamentary forces as part of the English Civil War. It was rebuilt in 1688 and again in 1746. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Battery
Point Battery (which is also known by its earlier name, Eighteen Gun Battery) is a former gun emplacement on Portsmouth Point in Hampshire. Part of the fortifications of Portsmouth, it was built alongside an earlier defensive structure (the 15th-century Round Tower) to help defend Portsmouth Harbour in the event of an attack. Fort Blockhouse on the other side of the harbour entrance was rebuilt at around the same time as part of the same scheme. In the mid-19th century the battery was enlarged and Point Barracks were built alongside, to house the artillery troops responsible for manning the defences. Point Battery, along with the barracks and other associated structures, is a Grade I listed building. History The gun battery was created as part of Bernard de Gomme's rebuilding of the fortifications around Portsmouth in the late seventeenth century. It is a casemated structure which originally consisted of a long row of twelve gun emplacements facing out to sea, joined at the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southsea Castle
Southsea Castle, historically also known as Chaderton Castle, South Castle and Portsea Castle, is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII on Portsea Island, Hampshire, in 1544. It formed part of the King's Device programme to protect against invasion from France and the Holy Roman Empire, and defended the Solent and the eastern approach to Portsmouth. The castle had a square central keep, two rectangular gun platforms to the east and west, and two angled bastions to the front and rear, and was an early English example of the ''trace italienne''-style of fortification popular on the Continent. The Cowdray engraving of the Battle of the Solent in 1545 depicted Henry VIII visiting the castle. Despite several serious fires, it remained in service and saw brief action at the start of the English Civil War in 1642 when it was stormed by Parliamentary forces. The castle was expanded in the 1680s by Sir Bernard de Gomme and, after a period of neglect in the 18th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009.jpg)