Paraguayan Prisoners And Detainees on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a
 Paraguay overthrew the local Spanish administration on 14 May 1811. Paraguay's first dictator was
Paraguay overthrew the local Spanish administration on 14 May 1811. Paraguay's first dictator was
 On 12 October 1864, despite Paraguayan ultimatums,
On 12 October 1864, despite Paraguayan ultimatums,  Paraguay lost 25–33% of its territory to Argentina and Brazil, paid an enormous war debt, and sold large amounts of national properties to stabilize its internal budget. The worst consequence of the war was the catastrophic loss of population. At least 50% of the Paraguayans died during the conflict, numbers which took many decades for the country to return to. About the disaster suffered by the Paraguayans at the outcome of the war,
Paraguay lost 25–33% of its territory to Argentina and Brazil, paid an enormous war debt, and sold large amounts of national properties to stabilize its internal budget. The worst consequence of the war was the catastrophic loss of population. At least 50% of the Paraguayans died during the conflict, numbers which took many decades for the country to return to. About the disaster suffered by the Paraguayans at the outcome of the war,

 In 1904 a
In 1904 a
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
in South America. It is bordered by Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
to the south and southwest, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. It has a population of seven million, nearly three million of whom live in the capital and largest city of Asunción
Asunción (, , , Guarani: Paraguay) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay.
The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay o ...
, and its surrounding metro. Although one of only two landlocked countries in South America (Bolivia is the other), Paraguay has ports on the Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
and Paraná rivers that give exit to the Atlantic Ocean, through the Paraná-Paraguay Waterway.
Spanish conquistadores arrived in 1524, and in 1537, they established the city of Asunción
Asunción (, , , Guarani: Paraguay) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay.
The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay o ...
, the first capital of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata
The Governorate of the Río de la Plata (1549−1776) ( es, Gobernación del Río de la Plata, links=no, ) was one of the governorates of the Spanish Empire. It was created in 1549 by Spain in the area around the Río de la Plata.
It was at fir ...
. During the 17th century, Paraguay was the center of Jesuit missions, where the native Guaraní people
Guarani are a group of culturally-related indigenous peoples of South America. They are distinguished from the related Tupi by their use of the Guarani language. The traditional range of the Guarani people is in present-day Paraguay between the ...
were converted to Christianity and introduced to European culture. After the expulsion of the Jesuits
The suppression of the Jesuits was the removal of all members of the Society of Jesus from most of the countries of Western Europe and their colonies beginning in 1759, and the abolishment of the order by the Holy See in 1773. The Jesuits were ...
from Spanish territories in 1767, Paraguay increasingly became a peripheral colony, with few urban centers and settlers. Following independence from Spain in the early 19th century, Paraguay was ruled by a series of authoritarian governments characterized by nationalist, isolationist and protectionist
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. ...
policies. This period ended with the disastrous Paraguayan War
The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadlies ...
(1864–70), during which the country lost half its prewar population and around 25–33% of its territory to the Triple Alliance of Argentina, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
. In the 20th century, Paraguay faced another major international conflictthe Chaco War
The Chaco War ( es, link=no, Guerra del Chaco, gn, Cháko ÑorairõAlfredo Stroessner
Alfredo Stroessner Matiauda (; 3 November 1912 – 16 August 2006) was a Paraguayan army officer and politician who served as President of Paraguay from 15 August 1954 to 3 February 1989.
Stroessner led a coup d'état on 4 May 1954 with t ...
, which lasted until his overthrow in 1989 by an internal military coup. This marked the beginning of Paraguay's democratic era, which continues to this day.
Paraguay is a developing country, ranking 105th in the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
. It is a founding member of Mercosur
The Southern Common Market, commonly known by Spanish abbreviation Mercosur, and Portuguese Mercosul, is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full members are Arge ...
, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the Organization of American States, the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
and the Lima Group
The Lima Group (GL; Spanish and pt, links=yes, Grupo de Lima, French: Groupe de Lima) is a multilateral body that was established following the Lima Declaration on 8 August 2017 in the Peruvian capital of Lima, where representatives of 12 cou ...
. Additionally, the city of Luque
Luque () is a city in Central Department of Paraguay, part of the Gran Asunción metropolitan area. Both 1635 and 1750 have been recorded as dates of its founding.
It was temporarily the capital of Paraguay in 1868 during the Paraguayan War b ...
, in metropolitan Asuncion, is the seat of the South American Football Confederation.
The majority of Paraguay's seven million people are '' mestizo'', and Guarani culture remains widely influential; more than 90% of the population speak various dialects of the Guarani language
Guaraní (), specifically the primary variety known as Paraguayan Guarani ( "the people's language"), is a South American language that belongs to the Tupi–Guarani family of the Tupian languages. It is one of the official languages of P ...
alongside Spanish. Despite a history of poverty and political repression, in a 2017 Positive Experience Index based on global polling data, Paraguay ranked as the "world's happiest place".
Etymology
The origin of the name Paraguay is uncertain. One version postulates the name takes fromGuaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
''paraguá'' "feather crown" and ''y'' "water" thus ''paraguaí'' "feather crown of waters". Other versions affirm that the name derives from the Payaguá people
The Payaguá people, also called Evueví and Evebe, were an ethnic group of the Guaycuru peoples in the Northern Chaco of Paraguay. The Payaguá were a river tribe, living, hunting, fishing, and raiding on the Paraguay River. The name ''Pay ...
, for the Paraguay River
The Paraguay River (Río Paraguay in Spanish, Rio Paraguai in Portuguese, Ysyry Paraguái in Guarani) is a major river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Argentina. It flows about from its headwaters i ...
was called the ''Payaguá-y'', or "river of the Payaguás" by the Guaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
and hence would have come the name for the country; or that, also from the Guaraní, ''para'' would mean sea, ''gua'', originates, and ''y'', river, thus Paraguay would mean "river which gives birth to the sea".
History
Pre-Columbian era
Theindigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Guaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
had been living in eastern Paraguay for at least a millennium before the arrival of the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
. Western Paraguay, the Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato ...
, was inhabited by nomads of whom the Guaycuru peoples were the most prominent. The Paraguay River was roughly the dividing line between the agricultural Guarani people to the east and the nomadic and semi-nomadic people to the west in the Gran Chaco. The Guarcuru nomads were known for their warrior traditions and were not fully pacified until the late 19th century. These indigenous tribes belonged to five distinct language families, which were the bases of their major divisions. Differing language speaking groups were generally competitive over resources and territories. They were further divided into tribes by speaking languages in branches of these families. Today 17 separate ethnolinguistic
Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language and the nonlinguistic cultural behavior of the people who speak that language.
__NOTOC__
Example ...
groups remain.
Colonization
The first Europeans in the area were Spanish explorers in 1516.Sacks, Richard S. "Early explorers and conquistadors". In Hanratty & Meditz. The Spanish explorer Juan de Salazar de Espinosa founded the settlement ofAsunción
Asunción (, , , Guarani: Paraguay) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay.
The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay o ...
on 15 August 1537. The city eventually became the center of a Spanish colonial province of Paraguay.
An attempt to create an autonomous Christian Indian nation was undertaken by Jesuit missions and settlements in this part of South America in the eighteenth century. They developed Jesuit reduction
Reductions ( es, reducciones, also called ; , pl. ) were settlements created by Spanish rulers and Roman Catholic missionaries in Spanish America and the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America, such red ...
s to bring Guarani populations together at Spanish missions and protect them from virtual slavery by Spanish settlers and Portuguese slave raiders, the Bandeirantes, in addition to seeking their conversion to Christianity. Catholicism in Paraguay was influenced by the indigenous peoples; the syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
religion has absorbed native elements. The ''reducciones'' flourished in eastern Paraguay for about 150 years, until the expulsion of the Jesuits by the Spanish Crown in 1767. The ruins of two 18th-century Jesuit Missions of La Santísima Trinidad de Paraná and Jesús de Tavarangue have been designated as World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
.
In western Paraguay, Spanish settlement and Christianity were strongly resisted by the nomadic Guaycuru and other nomads from the 16th century onward. Most of these peoples were absorbed into the mestizo population in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Independence and rule of Francia
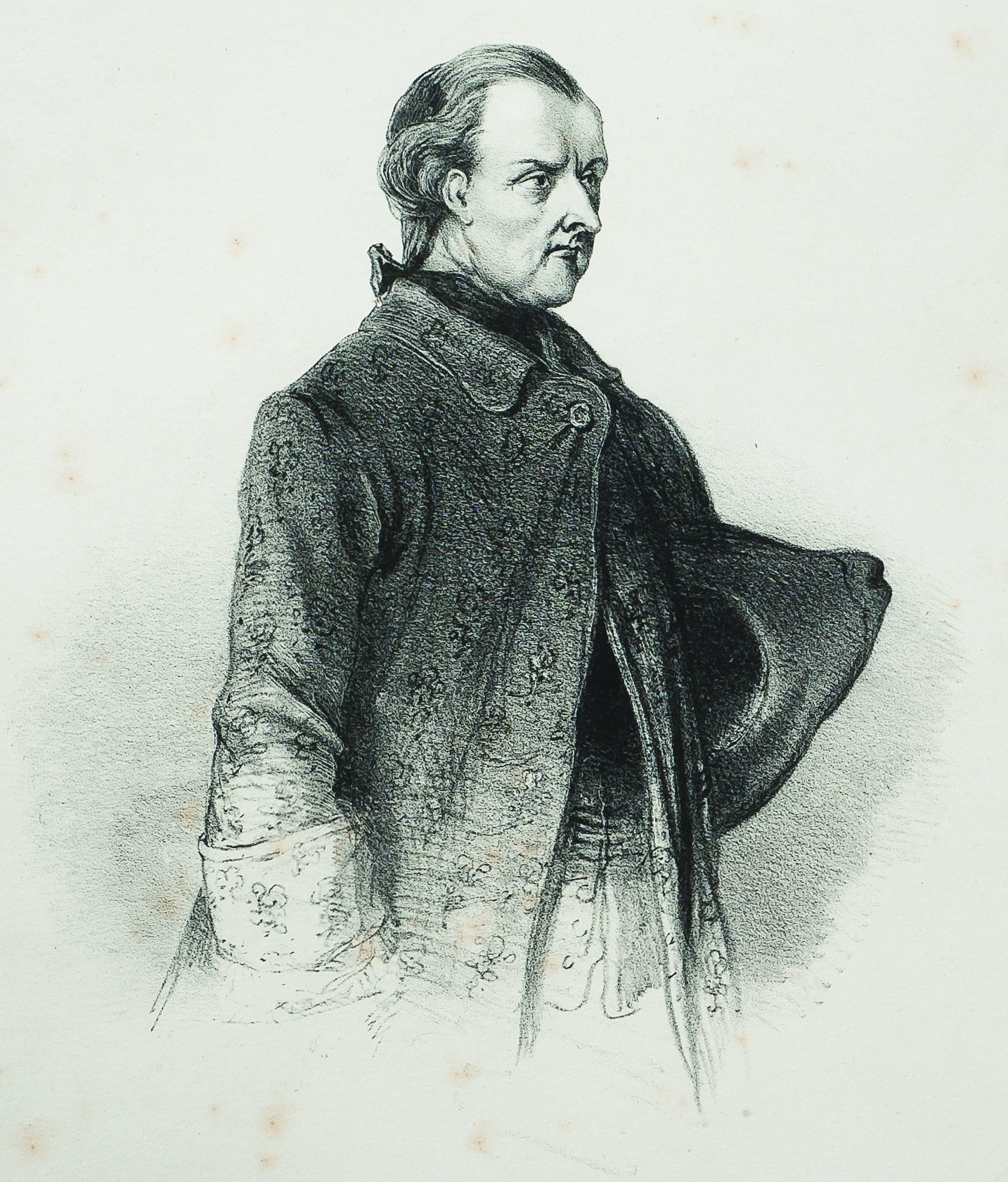
 Paraguay overthrew the local Spanish administration on 14 May 1811. Paraguay's first dictator was
Paraguay overthrew the local Spanish administration on 14 May 1811. Paraguay's first dictator was José Gaspar Rodríguez de Francia
José Gaspar Rodríguez de Francia y Velasco () (6 January 1766 – 20 September 1840) was a Paraguayan lawyer and politician, and the first dictator (1814–1840) of Paraguay following its 1811 independence from the Spanish Viceroyalty of ...
who ruled Paraguay from 1814 until his death in 1840, with very little outside contact or influence. He intended to create a utopian
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia'', describing a fictional island society ...
society based on the French theorist Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
's ''Social Contract''. Rodríguez de Francia was nicknamed ''El Supremo''.
Rodríguez de Francia established new laws that greatly reduced the powers of the Catholic church (Catholicism was then an established state religion) and the cabinet, forbade colonial citizens from marrying one another and allowed them to marry only blacks, mulattoes
(, ) is a racial classification to refer to people of mixed African and European ancestry. Its use is considered outdated and offensive in several languages, including English and Dutch, whereas in languages such as Spanish and Portuguese ...
or natives, in order to break the power of colonial-era elites and to create a mixed-race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-eth ...
or mestizo society. He cut off relations between Paraguay and the rest of South America. Because of Francia's restrictions of freedom, Fulgencio Yegros
Fulgencio Yegros y Franco de Torres (born 1780 in Quyquyhó, died 1821) was Paraguayan soldier and first head of state of independent Paraguay. The town of Yegros is named in his honor.
Life
Yegros was born to a family of military traditio ...
and several other Independence-era leaders in 1820 planned a ''coup d’état'' against Francia, who discovered the plot and had its leaders either executed or imprisoned for life.
Rule of the López family
After Francia's death in 1840, Paraguay was ruled by various military officers under a new '' junta'', untilCarlos Antonio López
Carlos Antonio López Ynsfrán (November 4, 1792 – September 10, 1862) served as leader of Paraguay from 1841 to 1862.
Early life
López was born at Manorá (Asunción) on November 4, 1792, as one of eight children. He graduated from Real C ...
(allegedly Rodríguez de Francia's nephew) came to power in 1841. López modernized Paraguay and opened it to foreign commerce. He signed a non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a tr ...
with Argentina and officially declared independence of Paraguay in 1842. After López's death in 1862, power was transferred to his eldest son, Francisco Solano López
Francisco Solano López Carrillo (24 July 1827 – 1 March 1870) was President of Paraguay from 1862 until his death in 1870. He was the eldest son of Juana Pabla Carrillo and of President Carlos Antonio López, Francisco's predecessor.
...
.
The regime of the López family was characterized by pervasive and rigid centralism in production and distribution. There was no distinction between the public and the private spheres, and the López family ruled the country as it would a large estate.
The government exerted control on all exports. The export of yerba mate
Yerba mate or yerba-maté (''Ilex paraguariensis''; from Spanish ; pt, erva-mate, or ; gn, ka'a, ) is a plant species of the holly genus '' Ilex'' native to South America. It was named by the French botanist Augustin Saint-Hilaire. The lea ...
and valuable wood products maintained the balance of trade between Paraguay and the outside world. The Paraguayan government was extremely protectionist, levying high tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and pol ...
s against imported foreign products. This protectionism
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulatio ...
made the society self-sufficient, and it also avoided the debt suffered by Argentina and Brazil. Slavery existed in Paraguay, although not in great numbers, until 1844, when it was legally abolished in the new constitution.
Francisco Solano López
Francisco Solano López Carrillo (24 July 1827 – 1 March 1870) was President of Paraguay from 1862 until his death in 1870. He was the eldest son of Juana Pabla Carrillo and of President Carlos Antonio López, Francisco's predecessor.
...
, the son of Carlos Antonio López, replaced his father as the President-Dictator in 1862, and generally continued the political policies of his father. Both wanted to give an international image of Paraguay as "democratic and republican", but in fact, the ruling family had almost total control of all public life in the country, including church and colleges.
Militarily, Carlos Antonio López modernized and expanded industry and the Paraguayan Army and greatly strengthened the strategic defenses of Paraguay by developing the Fortress of Humaitá
The Fortress of Humaitá (1854–68), known metaphorically as the Gibraltar of South America, was a Paraguayan military installation near the mouth of the River Paraguay. A strategic site without equal in the region, "a fortress the likes o ...
. The government hired more than 200 foreign technicians, who installed telegraph line
Electrical telegraphs were point-to-point text messaging systems, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems ...
s and railroads to aid the expanding steel, textile, paper and ink, naval construction, weapons and gunpowder industries. The Ybycuí foundry, completed in 1850, initially supplied all public works with iron and was used to make tools for the populace. In the 1860s, it also started to manufacture cannons, mortars and bullets of all calibers. River warships were built in the shipyards of Asunción. Fortifications were built, especially along the Apa River and in Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato ...
.Hooker, T.D., 2008, The Paraguayan War, Nottingham: Foundry Books, The work was continued by his son Francisco Solano and in terms of socio-economic development, the country was dubbed as "the most advanced Republic in South America", notably by the British judge and politician Sir Robert Phillimore.
According to George Thompson, Lieutenant Colonel of Engineers in the Paraguayan Army prior to and during the war, López's government was comparatively a good one for Paraguay:
Paraguayan War (1864–1870)
 On 12 October 1864, despite Paraguayan ultimatums,
On 12 October 1864, despite Paraguayan ultimatums, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
(allied with the Argentine Government under General Bartolomé Mitre and the rebellious Uruguayan colorados led by Gen. Venancio Flores
Venancio Flores Barrios (18 May 1808 – 19 February 1868) was a Uruguayan political leader and general. Flores was President of Uruguay from 1854 to 1855 (interim) and from 1865 to 1868.
Background and early career
In 1839, he was made politic ...
) invaded the Republic of Uruguay in order to overthrow the government of that time (which was under the rule of the Blanco Party, an ally of López), thus starting the Paraguayan War
The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadlies ...
.
The Paraguayans, led by the Marshal of the Republic Francisco Solano López
Francisco Solano López Carrillo (24 July 1827 – 1 March 1870) was President of Paraguay from 1862 until his death in 1870. He was the eldest son of Juana Pabla Carrillo and of President Carlos Antonio López, Francisco's predecessor.
...
, retaliated by attacking Mato Grosso on 15 December 1864 and later declared war against Argentina on 23 March 1865. The Blanco Government was toppled and replaced by a Colorado Government under General Venancio Flores on 22 February 1865. Afterward, the Argentine Republic
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, the Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom ...
and the Republic of Uruguay signed the Secret Treaty of the Triple Alliance against the Paraguayan Government on 1 May 1865.
The Paraguayans put up a ferocious resistance but ultimately lost in 1870 in the Battle of Cerro Corá, where Marshal Solano López refused to surrender and died in action. The real causes of this war, which remains the bloodiest international conflict in the history of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, are still highly debatable.
 Paraguay lost 25–33% of its territory to Argentina and Brazil, paid an enormous war debt, and sold large amounts of national properties to stabilize its internal budget. The worst consequence of the war was the catastrophic loss of population. At least 50% of the Paraguayans died during the conflict, numbers which took many decades for the country to return to. About the disaster suffered by the Paraguayans at the outcome of the war,
Paraguay lost 25–33% of its territory to Argentina and Brazil, paid an enormous war debt, and sold large amounts of national properties to stabilize its internal budget. The worst consequence of the war was the catastrophic loss of population. At least 50% of the Paraguayans died during the conflict, numbers which took many decades for the country to return to. About the disaster suffered by the Paraguayans at the outcome of the war, William D. Rubinstein
William D. Rubinstein (born 12 August 1946) is a historian and author. His best-known work, ''Men of Property: The Very Wealthy in Britain Since the Industrial Revolution'', charts the rise of the ' super rich', a class he sees as expanding ex ...
wrote:
"The normal estimate is that of a Paraguayan population of somewhere between 450,000 and 900,000, only 220,000 survived the war, of whom only 28,000 were adult males."
During the pillaging of Asunción in 1869, the Imperial Brazilian Army
The Imperial Brazilian Army ( Portuguese: Exército Imperial Brasileiro) was the name given to the land force of the Empire of Brazil. The Brazilian Army was formed after the independence of the country from Portugal in 1822 and reformed in 1889, ...
packed up and transported the Paraguayan National Archives to Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a ...
. Brazil's records from the war have remained classified. This has made Paraguayan history in the colonial and early national periods difficult to research and study.
Following the attacks, in 1870, The Republic of Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Cari ...
officially offered to all citizens of Paraguay, the Colombian citizenship, just by stepping on Colombian national territory.
20th century

 In 1904 a
In 1904 a revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
against the rule of the Colorados, who had been in power since the 1880s, broke out. The subsequent period, on which Paraguay was governed by the Liberals, was one of great political instability. Between 1904 and 1954 Paraguay had thirty-one presidents
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
, most of whom were removed from office by force. Conflicts between the factions of the ruling Liberal party led to the Paraguayan Civil War of 1922.
A long-lasting unresolved border conflict with Bolivia over the Chaco region erupted in the early 1930s in the Chaco War
The Chaco War ( es, link=no, Guerra del Chaco, gn, Cháko ÑorairõFebruary Revolution brought colonel
, in ''Comparative Studies in Society and History'', 1999, Vol. 41, Issue 1: 148–181. Cambridge University Press. The June 1992 constitution established a democratic system of government and dramatically improved protection of fundamental human rights. In May 1993, Colorado Party candidate
 Political instability following Lugo's election and disputes within his cabinet encouraged some renewal of popular support for the Colorado Party. Reports suggested that the businessman
Political instability following Lugo's election and disputes within his cabinet encouraged some renewal of popular support for the Colorado Party. Reports suggested that the businessman
 Paraguay is divided by the Río Paraguay into two well differentiated geographic regions. The eastern region (Región Oriental); and the western region, officially called Western Paraguay (Región Occidental) and also known as the Chaco, which is part of the
Paraguay is divided by the Río Paraguay into two well differentiated geographic regions. The eastern region (Región Oriental); and the western region, officially called Western Paraguay (Región Occidental) and also known as the Chaco, which is part of the
 The overall climate is
The overall climate is
 The
The
, '' El Clarín'', 9 September 2005 In 2019, Asuncion hosted the first meeting of the Regional Security Mechanism (RSM), which promotes cooperation between Paraguay, Argentina, Brazil, and the U.S. in addressing

 For many years, the country's image was associated with the
For many years, the country's image was associated with the  The market economy is distinguished by a large informal sector, featuring re-export of imported consumer goods to neighboring countries, as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. Nonetheless, over the last 10 years the Paraguayan economy diversified dramatically, with the energy, auto parts and clothing industries leading the way.
Paraguay's most important
The market economy is distinguished by a large informal sector, featuring re-export of imported consumer goods to neighboring countries, as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. Nonetheless, over the last 10 years the Paraguayan economy diversified dramatically, with the energy, auto parts and clothing industries leading the way.
Paraguay's most important
 Paraguay's population is distributed unevenly through the country, with the vast majority of people living in the eastern region near the capital and largest city,
Paraguay's population is distributed unevenly through the country, with the vast majority of people living in the eastern region near the capital and largest city,  There is no official data on the ethnic composition of the Paraguayan population, as the Department of Statistics, Surveys and Censuses of Paraguay does not ask about ''race'' and ''ethnicity'' in census surveys, although it does inquire about the indigenous population. According to the census of 2002, indigenous people made up 1.7% of Paraguay's total population.
Traditionally, the majority of the Paraguayan population is considered mixed (''mestizo'' in Spanish). HLA-DRB1 polymorphism studies have shown genetic distances between Paraguayans and Spanish populations were closer than between Paraguayans and Guaranis, suggesting the predominance of Spanish genetics among Paraguayans.
According to , Paraguay has a population of , of which 95% are Mestizo or white and 5% are labelled as "other", which includes members of 17 distinct ethnolinguistic indigenous groups, many of which are poorly documented.
There is no official data on the ethnic composition of the Paraguayan population, as the Department of Statistics, Surveys and Censuses of Paraguay does not ask about ''race'' and ''ethnicity'' in census surveys, although it does inquire about the indigenous population. According to the census of 2002, indigenous people made up 1.7% of Paraguay's total population.
Traditionally, the majority of the Paraguayan population is considered mixed (''mestizo'' in Spanish). HLA-DRB1 polymorphism studies have shown genetic distances between Paraguayans and Spanish populations were closer than between Paraguayans and Guaranis, suggesting the predominance of Spanish genetics among Paraguayans.
According to , Paraguay has a population of , of which 95% are Mestizo or white and 5% are labelled as "other", which includes members of 17 distinct ethnolinguistic indigenous groups, many of which are poorly documented.

, Ethnologue There are approximately 19 other indigenous languages spoken in Paraguay, many of which are threatened by extinction. Languages such as Guana, Ayoreo and Ishir (Chamacoco) are considered endangered.
 Average life expectancy in Paraguay is rather high given its poverty: , it was 75 years, equivalent to far wealthier Argentina, and the eighth highest in the Americas according to World Health Organization. Public expenditure on health is 2.6% of GDP, while private health expenditure is 5.1%. Infant mortality was 20 per 1,000 births in 2005. Maternal mortality was 150 per 100,000 live births in 2000.
The
Average life expectancy in Paraguay is rather high given its poverty: , it was 75 years, equivalent to far wealthier Argentina, and the eighth highest in the Americas according to World Health Organization. Public expenditure on health is 2.6% of GDP, while private health expenditure is 5.1%. Infant mortality was 20 per 1,000 births in 2005. Maternal mortality was 150 per 100,000 live births in 2000.
The
 This cultural fusion is expressed in arts such as embroidery (''ao po'í'') and lace making (''ñandutí''). The music of Paraguay, which consists of lilting polkas, bouncy ''galopas,'' and languid '' guaranias'' is played on the native harp. Paraguay's culinary heritage is also deeply influenced by this cultural fusion. Several popular dishes contain
This cultural fusion is expressed in arts such as embroidery (''ao po'í'') and lace making (''ñandutí''). The music of Paraguay, which consists of lilting polkas, bouncy ''galopas,'' and languid '' guaranias'' is played on the native harp. Paraguay's culinary heritage is also deeply influenced by this cultural fusion. Several popular dishes contain
Chief of State and Cabinet Members
National Department of Tourism
Ministry of Finance with economic and government information; also available in English
General information
Paraguay
from the ''
Paraguay
''
Paraguay
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Paraguay profile
from the
Key Development Forecasts for Paraguay
from
La Rueda – Weekly reviews
ABC Color
Última Hora
La Nación
Paraguay.com
Ñanduti
Paraguayan Pymes News
Trade
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Paraguay
Exchange rate of the Guaraní – Paraguayan Currency
Travel
Paraguay.com: Tradition, Culture, Maps, Tourism
*
Tourism in Paraguay, information, pictures and more. Turismo.com.py
{{Authority control Countries in South America 1811 establishments in South America States and territories established in 1811 Former Spanish colonies Landlocked countries Member states of Mercosur Member states of the United Nations Republics Spanish-speaking countries and territories Southern Cone countries
Rafael Franco
Rafael de la Cruz Franco Ojeda (October 22, 1896 – September 16, 1973) was a Paraguayan military officer and politician, served as Provisional President of Paraguay from February 17, 1936, to August 13, 1937, being also the historical leader ...
to power. Between 1940 and 1948, the country was ruled by general Higinio Morínigo
Higinio Nicolás Morínigo Martínez (January 11, 1897 – January 27, 1983) was a military officer, politician and Paraguayan dictator. He participated in the Chaco War (1932–1935) as a prominent officer of the Paraguayan Army. After the wa ...
. Dissatisfaction with his rule resulted in the Paraguayan civil war of 1947. In its aftermath Alfredo Stroessner
Alfredo Stroessner Matiauda (; 3 November 1912 – 16 August 2006) was a Paraguayan army officer and politician who served as President of Paraguay from 15 August 1954 to 3 February 1989.
Stroessner led a coup d'état on 4 May 1954 with t ...
, began involvement in a string of plots, which resulted in his military coup d'état of 4 May 1954. In the aftermath of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Paraguay had become a hideout for Nazi fugitives accused of war crimes.
Stroessner era, 1954–1989
A series of unstable governments ensued until the establishment in 1954 of the regime of the dictatorAlfredo Stroessner
Alfredo Stroessner Matiauda (; 3 November 1912 – 16 August 2006) was a Paraguayan army officer and politician who served as President of Paraguay from 15 August 1954 to 3 February 1989.
Stroessner led a coup d'état on 4 May 1954 with t ...
, who remained in office for more than three decades until 1989. Paraguay was modernized to some extent under Stroessner's regime, although his rule was marked by extensive human rights abuses.
Stroessner and the ''Colorado'' party ruled the country from 1954 to 1989. The dictator oversaw an era of economic expansion, but also had a poor human rights and environmental record (see "Political History"). Paraguay actively participated in Operation Condor
Operation Condor ( es, link=no, Operación Cóndor, also known as ''Plan Cóndor''; pt, Operação Condor) was a United States–backed campaign of political repression and state terror involving intelligence operations and assassination of op ...
. Torture and death for political opponents was routine. After his overthrow, the ''Colorado'' continued to dominate national politics until 2008.
The splits in the ''Colorado'' Party in the 1980s, and the prevailing conditions – Stroessner's advanced age, the character of the regime, the economic downturn, and international isolation – were catalysts for anti-regime demonstrations and statements by the opposition prior to the 1988 general elections.
'' PLRA'' leader Domingo Laíno
Domingo Isabelino Laíno Figueredo (born July 8, 1935 in Asunción, Paraguay) is a Paraguayan politician, economist, and activist. The first leader of the Authentic Radical Liberal Party, a Senator, and a former Member of the Chamber of Deputie ...
served as the focal point of the opposition in the second half of the 1980s. The government's effort to isolate Laíno by exiling him in 1982 had backfired. On his sixth attempt to re-enter the country in 1986, Laíno returned with three television crews from the U.S., a former United States ambassador to Paraguay, and a group of Uruguayan and Argentine congressmen. Despite the international contingent, the police violently barred Laíno's return.
The Stroessner regime relented in April 1987, and permitted Laíno to return to Asunción. Laíno took the lead in organizing demonstrations and reducing infighting among the opposition party. The opposition was unable to reach agreement on a common strategy regarding the elections, with some parties advocating abstention, and others calling for blank voting. The parties held numerous 'lightning demonstrations' (''mítines relámpagos''), especially in rural areas. Such demonstrations were gathered and quickly disbanded before the arrival of the police.
In response to the upsurge in opposition activities, Stroessner condemned the Accord for advocating "sabotage of the general elections and disrespect of the law". He used national police and civilian vigilantes
Vigilantism () is the act of preventing, investigating and punishing perceived offenses and crimes without legal authority.
A vigilante (from Spanish, Italian and Portuguese “vigilante”, which means "sentinel" or "watcher") is a person who ...
of the ''Colorado'' Party to break up demonstrations. A number of opposition leaders were imprisoned or otherwise harassed. , another key leader of the ''PLRA'', was imprisoned for four months in 1987 on charges of sedition. In early February 1988, police arrested 200 people attending a National Coordinating Committee meeting in Coronel Oviedo. Laíno and several other opposition figures were arrested before dawn on the day of the election, 14 February, and held for twelve hours. The government declared Stroessner's re-election with 89% of the vote.
The opposition attributed the results in part to the virtual Colorado monopoly on the mass media. They noted that 53% of those polled indicated that there was an "uneasiness" in Paraguayan society. Some 74% believed that the political situation required changes, including 45% who wanted a substantial or total change. Finally, 31% stated that they planned to abstain from voting in the February elections.
Stroessner's overthrow, post-1989
On 3 February 1989, Stroessner was overthrown in a military coup headed by General Andrés Rodríguez. As president, Rodríguez instituted political, legal, and economic reforms and initiated a ''rapprochement'' with the international community. Reflecting the deep hunger of the rural poor for land, hundreds immediately occupied thousands of acres of unused territories belonging to Stroessner and his associates; by mid-1990, 19,000 families occupied . At the time, 2.06 million people lived in rural areas, more than half of the 4.1 million total population, and most were landless.Nagel, Beverly Y.(1999) "'Unleashing the Fury': The Cultural Discourse of Rural Violence and Land Rights in Paraguay", in ''Comparative Studies in Society and History'', 1999, Vol. 41, Issue 1: 148–181. Cambridge University Press. The June 1992 constitution established a democratic system of government and dramatically improved protection of fundamental human rights. In May 1993, Colorado Party candidate
Juan Carlos Wasmosy
Juan Carlos Wasmosy Monti (born December 15, 1938) was the president of Paraguay from August 15, 1992 until August 15, 1998. He was a member of the Colorado Party, and the country's first freely elected president, as well as the first civilian ...
was elected as Paraguay's first civilian president in almost forty years, in what international observers deemed free and fair elections.
With support from the United States, the Organization of American States, and other countries in the region, the Paraguayan people rejected an April 1996 attempt by then Army Chief General Lino Oviedo
Lino César Oviedo Silva (23 September 1943 – 2 February 2013) was the leader of the National Union of Ethical Citizens, which split from the Colorado Party (Paraguay), Colorado Party in 2002.
Life and work
Early career
Oviedo was born in po ...
to oust President Wasmosy.
Oviedo was nominated as the Colorado candidate for president in the 1998 election. However, when the Supreme Court upheld in April his conviction on charges related to the 1996 coup attempt, he was not allowed to run and was detained in jail. His former running mate, Raúl Cubas, became the Colorado Party's candidate, and was elected in May in elections deemed by international observers to be free and fair. One of Cubas' first acts after taking office in August was to commute Oviedo's sentence and release him. In December 1998, Paraguay's Supreme Court declared these actions unconstitutional. In this tense atmosphere, the murder of Vice President and long-time Oviedo rival Luis María Argaña
Luis María del Corazón de Jesús Dionisio Argaña Ferraro (October 3, 1932 – March 23, 1999) was a prominent Paraguayan politician and Supreme Court judge. He was an influential member of the Colorado Party and rose to the Vice-Presi ...
on 23 March 1999, led the Chamber of Deputies to impeach Cubas the next day. On 26 March, eight student anti-government demonstrators were murdered, widely believed to have been carried out by Oviedo supporters. This increased opposition to Cubas, who resigned on 28 March. Senate President Luis González Macchi, a Cubas opponent, was peacefully sworn in as president the same day.
In 2003, Nicanor Duarte
Óscar Nicanor Duarte Frutos (born 11 October 1956) is a Paraguayan politician who served as President of Paraguay from 2003 to 2008. In 2013, President Horacio Cartes appointed Duarte as Ambassador to Argentina, a diplomatic posting he held fro ...
was elected as president.
Election of Fernando Lugo
For the 2008 general elections, the Colorado Party was favored in polls. Their candidate was Minister of EducationBlanca Ovelar
Blanca Margarita Ovelar de Duarte (born September 2, 1957) is a Paraguayan politician and former Minister of Education. She was the Colorado Party's nominee for president in the April 2008 presidential election, in which she was defeated.
Ovel ...
, the first woman to be nominated as a candidate for a major party in Paraguayan history. After sixty years of Colorado rule, voters chose Fernando Lugo
Fernando Armindo Lugo Méndez (; born 30 May 1951) is a Paraguayan politician and laicized Catholic bishop who was President of Paraguay from 2008 to 2012. Previously he was a Roman Catholic priest and bishop, serving as Bishop of the Diocese ...
, a former Roman Catholic Bishop and not a professional politician in civil government, and a member of the Authentic Radical Liberal Party, Paraguay's largest opposition party. Lugo was an adherent of liberation theology
Liberation theology is a Christian theological approach emphasizing the liberation of the oppressed. In certain contexts, it engages socio-economic analyses, with "social concern for the poor and political liberation for oppressed peoples". I ...
. Lugo achieved a historic victory in Paraguay's presidential election, defeating the ruling party candidate, and ending 61 years of conservative rule. Lugo won with nearly 41% of the vote, compared to almost 31% for Blanca Ovelar of the Colorado party. Outgoing President Nicanor Duarte Frutos hailed the moment as the first time in the history of the nation that a government had transferred power to opposition forces in a constitutional and peaceful fashion.
Lugo was sworn in on 15 August 2008. The Lugo administration set its two major priorities as the reduction of corruption and economic inequality.
 Political instability following Lugo's election and disputes within his cabinet encouraged some renewal of popular support for the Colorado Party. Reports suggested that the businessman
Political instability following Lugo's election and disputes within his cabinet encouraged some renewal of popular support for the Colorado Party. Reports suggested that the businessman Horacio Cartes
Horacio Manuel Cartes Jara (born 5 July 1956) is a Paraguayan businessman and politician who served as the president of Paraguay from 2013 to 2018. He is a member of the Colorado Party. Cartes owns about two dozen businesses in his Grupo Carte ...
became the new political figure amid disputes. Despite the US Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA; ) is a United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating drug trafficking and distribution within the U.S. It is the lead agency for domestic en ...
's strong accusations against Cartes related to drug trafficking, he continued to amass followers in the political arena.
On 14 January 2011, the Colorado Party convention nominated Horacio Cartes as the presidential candidate for the party. However, the party's constitution did not allow it. On 21 June 2012, impeachment proceedings against President Lugo began in the country's lower house, which was controlled by his opponents. Lugo was given less than twenty-four hours to prepare for the proceedings and only two hours in which to mount a defense. Impeachment was quickly approved and the resulting trial in Paraguay's Senate, also controlled by the opposition, ended with the removal of Lugo from office and Vice President Federico Franco assuming the duties of president. Lugo's rivals blamed him for the deaths of 17 people – eight police officers and nine farmers – in armed clashes after police were ambushed by armed peasants when enforcing an eviction order against rural trespassers.
Lugo's supporters gathered outside Congress to protest the decision as a "politically motivated coup d'état". Lugo's removal from office on 22 June 2012 is considered by UNASUR and other neighboring countries, especially those currently governed by leftist leaders, as a coup d'état. However, the Organization of American States, which sent a mission to Paraguay to gather information, concluded that the impeachment process was not a coup d'état, as it had been carried out in accordance with the Constitution of Paraguay
The Republic of Paraguay is governed under the constitution of 1992, which is the country's sixth since independence from Spain in 1811.
Independence
The recorded history of Paraguay began in 1516 with the failed expedition of Juan Díaz de Sol ...
.
Present day
From August 2013 to 15 August 2018, thePresident of Paraguay
The president of Paraguay ( es, Presidente del Paraguay), officially known as the President of the Republic of Paraguay ( es, Presidente de la República del Paraguay), is according to the Constitution of Paraguay the head of the executive bran ...
was Horacio Cartes
Horacio Manuel Cartes Jara (born 5 July 1956) is a Paraguayan businessman and politician who served as the president of Paraguay from 2013 to 2018. He is a member of the Colorado Party. Cartes owns about two dozen businesses in his Grupo Carte ...
. Since 15 August 2018, the President of Paraguay
The president of Paraguay ( es, Presidente del Paraguay), officially known as the President of the Republic of Paraguay ( es, Presidente de la República del Paraguay), is according to the Constitution of Paraguay the head of the executive bran ...
has been Mario Abdo Benítez
Mario Abdo Benítez (; born 10
November 1971) is a Paraguayan politician who has served as the president of Paraguay since 2018. He was previously a senator and President of the Senate.
Early life and education
Abdo Benítez was born in Asun ...
. They are both from the conservative Colorado Party.
Geography
 Paraguay is divided by the Río Paraguay into two well differentiated geographic regions. The eastern region (Región Oriental); and the western region, officially called Western Paraguay (Región Occidental) and also known as the Chaco, which is part of the
Paraguay is divided by the Río Paraguay into two well differentiated geographic regions. The eastern region (Región Oriental); and the western region, officially called Western Paraguay (Región Occidental) and also known as the Chaco, which is part of the Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato ...
. The country lies between latitudes 19° and 28°S, and longitudes 54° and 63°W.
The terrain consists mostly of grassy plains and wooded hills in the eastern region. To the west are mostly low, marshy plains. Paraguay contains six terrestrial ecoregions: Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, Chaco, Cerrado
The ''Cerrado'' (, ) is a vast ecoregion of tropical savanna in eastern Brazil, particularly in the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Minas Gerais, and the Federal District. The core areas of the Cerrado biome are the ...
, Humid Chaco, Pantanal
The Pantanal () is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and ...
, and Paraná flooded savanna
The Paraná flooded savanna (NT0908) is an ecoregion that borders the southern Paraná River in Argentina. It has largely been converted to agriculture or occupied by urban development, but scattered patches of the original habitat remain along the ...
. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 6.39/10, ranking it 74th globally out of 172 countries. The Guarani Aquifer is an important exorheic basin to the region.
Although Paraguay is landlocked, there are a number of noteworthy lakeside beaches.
Climate
tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
to subtropical. Like most lands in the region, Paraguay has only wet and dry periods. Winds play a major role in influencing Paraguay's weather: between October and March, warm winds blow from the Amazon Basin in the north, while the period between May and August brings cold winds from the Andes.
The absence of mountain ranges to provide a natural barrier allows winds to develop speeds as high as . This also leads to significant changes in temperature within a short span of time; between April and September, temperatures will sometimes drop below freezing. January is the hottest summer month, with an average daily temperature of 28.9 degrees Celsius (84 degrees F).
Rainfall varies dramatically across the country, with substantial rainfall in the eastern portions, and semi-arid conditions in the far west. The far eastern forest belt receives an average of of rain annually, while the western Chaco region typically averages no more than a year. The rains in the west tend to be irregular and evaporate quickly, contributing to the aridity of the area.
Fauna
Wildlife in Paraguay includemarsh deer
The marsh deer (''Blastocerus dichotomus'') is the largest deer species from South America reaching a length of and a shoulder height of . It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay. Formerly found in much of tropical ...
, monkeys, armadillos, anteaters, otters, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
s, tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South and Central America, with one species inh ...
s, jaguars, ocelots, bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s, and the coypu
The nutria (''Myocastor coypus''), also known as the coypu, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent.
Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, ''Myocastor'' is now included within Echimyidae, the family of t ...
.
Government and politics
Paraguay is a representative democratic republic, with amulti-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in ...
and separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typic ...
across three branches. Executive power is exercised solely by the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
, who is head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
. Legislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known a ...
is vested in the two chambers of the National Congress. The judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
is vested on tribunals
A tribunal, generally, is any person or institution with authority to judge, adjudicate on, or determine claims or disputes—whether or not it is called a tribunal in its title.
For example, an advocate who appears before a court with a si ...
and Courts of Civil Law and a nine-member Supreme Court of Justice, all of them independent of the executive and the legislature.
Military
military of Paraguay
The Armed forces of Paraguay ( es, Fuerzas Armadas de Paraguay) consist of the Paraguayan army, navy (including naval aviation and marine corps) and air force.
The constitution of Paraguay establishes the president of Paraguay as the commande ...
consists of an army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
, navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
(including naval aviation
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based ...
and marine corps
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refl ...
) and air force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
. Paraguay's constitution establishes the president of Paraguay
The president of Paraguay ( es, Presidente del Paraguay), officially known as the President of the Republic of Paraguay ( es, Presidente de la República del Paraguay), is according to the Constitution of Paraguay the head of the executive bran ...
as commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
Paraguay has compulsory military service
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
; all 18-year-old males, as well as 17-year-old males in the year of their 18th birthday, are liable for one year of active duty
Active duty, in contrast to reserve duty, is a full-time occupation as part of a military force. In the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth of Nations, the equivalent term is active service.
India
The Indian Armed Forces are considered to be o ...
. While the constitution allows for conscientious objection
A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on the grounds of freedom of thought, conscience, or religion. The term has also been extended to objecti ...
, no enabling legislation has yet been approved.
Paraguay has partnered with Argentina, Brazil, and the United States in regional anti-terrorism and anti-narcotics efforts. In July 2005, U.S. special forces began arriving at Paraguay's Mariscal Estigarribia
Mariscal Estigarribia () is a town in the Boquerón Department, Paraguay.
Strategic importance
Mariscal Estigarribia is home to Dr. Luis Maria Argaña International Airport (IATA code: ESG), which some media reports claim is a US military ...
air base to support joint training and humanitarian operations.US Marines put a foot in Paraguay, '' El Clarín'', 9 September 2005 In 2019, Asuncion hosted the first meeting of the Regional Security Mechanism (RSM), which promotes cooperation between Paraguay, Argentina, Brazil, and the U.S. in addressing
transnational crime Transnational crimes are crimes that have actual or potential effect across national borders and crimes that are intrastate but offend fundamental values of the international community. The term is commonly used in the law enforcement and academic c ...
and terrorism in the "triple frontier" region.
Administrative Divisions
Paraguay consists of seventeen departments and one capital district (''distrito capital''). It is also divided into two regions: The "Occidental Region" or Chaco (Boquerón, Alto Paraguay and Presidente Hayes), and the "Oriental Region" (the other departments and the capital district). These are the departments, with their capitals, population, area and the number of districts:Economy
 For many years, the country's image was associated with the
For many years, the country's image was associated with the illicit trade Illicit trade is the production or distribution of a good or service that is considered illegal by a legislature. It includes trade that is strictly illegal in different jurisdictions, as well as trade that is illegal in some jurisdictions but legal ...
in electronic products, weapons
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
and drugs. However, this scenario began to change in the 2000s, with the rise of legalized businesses such as the production of soy, maize, beef, among others. Data from the Central Bank of Paraguay (BCP) showed that, in 2006, exports related to the triangulation trade (China-Paraguay-Brazil), treated by Brazil – in most cases – as smuggling and embezzlement, represented 22% of the country's GDP. In 2016, this percentage dropped to 12%. With higher tax collections through legalized employment, the country has been able to improve its infrastructure, which was precarious. Paraguay has an economic development policy based on exports and dependence on the Brazilian market prevails. The triangulation trade has in its essence the export of products originating in China, with Brazil as its main destination. The energy exported is essentially the hydroelectric surplus generated by the Itaipu Power Plant, for which Brazil is the main buyer. And maquilas, whose main investors are Brazilians, also have a large consumer market in Brazil for their products. Therefore, in these three pillars of Paraguay's development strategy, there is the outstanding characteristic of re-exports. In the case of agricultural commodities, it is the export of products originating in Paraguay.
In the 2010s, the economy, largely directed towards soybean production, grew by an average of 4%. The economic growth did not, however, reduce poverty, which in 2018, according to official figures, reached more than 26% of the population. According to ''The New York Times'', Paraguay is "one of the Latin American countries where the gap between rich and poor has widened the most in recent years." In the countryside, 85% of agricultural land is owned by 2.6% of the owners. In addition, people of indigenous descent have been expelled to make way for soybean companies.
In 2005, the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
stated that fewer than 10% of workers in Paraguay participate in the pension system, 95% of which is administered by two institutions. Both are financed on a pay as you go system by worker contributions; the first, is for private sector employees, and the for public employees (including university professors, teachers, judicial employees, army officers and police officers) and veterans of the Chaco War (or their descendants).
 The market economy is distinguished by a large informal sector, featuring re-export of imported consumer goods to neighboring countries, as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. Nonetheless, over the last 10 years the Paraguayan economy diversified dramatically, with the energy, auto parts and clothing industries leading the way.
Paraguay's most important
The market economy is distinguished by a large informal sector, featuring re-export of imported consumer goods to neighboring countries, as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. Nonetheless, over the last 10 years the Paraguayan economy diversified dramatically, with the energy, auto parts and clothing industries leading the way.
Paraguay's most important urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
s are located along the Argentina-Paraguay border: Asunción
Asunción (, , , Guarani: Paraguay) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay.
The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay o ...
, Alberdi, Encarnación, Pilar and Ciudad del Este
Ciudad del Este (, Spanish for Eastern City; often shortered as CDE) is the second-largest city in Paraguay and capital of the Alto Paraná Department, situated on the Paraná River. It is located 327 km from Asunción, the capital, and is ...
, the latter being the third most important free commercial zone in the world, only trailing behind Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
and Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
. A large percentage of the population, especially in rural areas, derives its living from agricultural activity, often on a subsistence basis. Because of the importance of the informal sector, accurate economic measures are difficult to obtain. The economy grew rapidly between 2003 and 2013 as growing world demand for commodities combined with high prices and favorable weather to support Paraguay's commodity-based export expansion.
In 2012, Paraguay's government introduced the MERCOSUR (FOCEM) system in order to stimulate the economy and job growth through a partnership with both Brazil and Argentina.
Agriculture
Paraguay is the sixth-largestsoybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu a ...
producer in the world, the second-largest producer of stevia and the ninth-largest exporter of beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantit ...
.
In 2018, in addition to soy, the country had a large production of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
and sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
, where it positioned itself as the 21st largest producer in the world; other important cultures of the country are cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
, yerba mate
Yerba mate or yerba-maté (''Ilex paraguariensis''; from Spanish ; pt, erva-mate, or ; gn, ka'a, ) is a plant species of the holly genus '' Ilex'' native to South America. It was named by the French botanist Augustin Saint-Hilaire. The lea ...
, and sorghum. In livestock, Paraguay produced, in 2020, 481 thousand tons of beef, being the 26th largest producer in the world.
The culture of soy was brought by Brazilians to the country: in 2019, almost 70% of soy and rice producers in Paraguay were people from Brazil, or descendants of Brazilians (the so-called brasiguaios). The first Brazilian producers began to arrive in the country in the 1980s. Before that, there was a lot of undisturbed land in the country.
Industry and manufacturing
TheWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
lists the top producing countries each year, based on the total value of production. By the 2019 list, Paraguay had the 79th most valuable industry in the world ($6.9 billion). The country was the seventh largest producer of soybean oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the soybean (''Glycine max''). It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processed s ...
in the world in 2018.
The mineral industry of Paraguay produces about 25% of the country's gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is oft ...
(GDP) and employs about 31% of the labor force. Production of cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
, iron ore, and steel occurs commonly throughout Paraguay's industrial sector. The growth of the industry was further fueled by the maquila
A (), or (), is a word that refers to factories that are largely duty free and tariff-free. These factories take raw materials and assemble, manufacture, or process them and export the finished product. These factories and systems are present t ...
industry, with large industrial complexes located in the eastern part of the country. Paraguay put in place many incentives aimed to attract industries to the country. One of them is the so-called "Maquila law" by which companies can relocate to Paraguay, enjoying minimal tax rates.
In the pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
, Paraguayan companies now meet 70% of domestic consumption and have begun to export drugs. Paraguay is quickly supplanting foreign suppliers in meeting the country's drug needs. Strong growth also is evident in the production of edible oils, garments, organic sugar, meat processing, and steel.
In 2003, manufacturing comprised 13.6% of the GDP and it employed about 11% of the working population in 2000. Paraguay's primary manufacturing focus is on food and beverages. Wood products, paper products, hides and furs, and non-metallic mineral products also contribute to manufacturing totals. Steady growth in the manufacturing GDP during the 1990s (1.2% annually) laid the foundation for 2002 and 2003, when the annual growth rate rose to 2.5%. Paraguay was ranked 88th in the Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British ma ...
in 2021, up from 95th in 2019.
Infrastructure
Transport
According to official data from the M.O.P.C (Ministry of Public Works and Communications of Paraguay), in 2019, there were a total of of roads, of which were paved. One of the most important recent investments in the country's history is the construction of the Bioceanic Corridor, which will cross the north of Paraguay in a horizontal line, connecting Brazil to Argentina, reaching both the ports of northern Chile, as to Brazilian ports. The work will open a new route for exports of products to Asia, and will enable the development of an isolated region of Paraguay, the Chaco. In February 2022, Paraguay inaugurated of the road (about half of the route), connecting Carmelo Peralta (Alto Paraguay), on the border with Brazil, to Loma Plata (Boquerón), in the center of the country. Paraguay has also been implementing the country's first double highway: of the Route 2, which connects the capital Asunción to Ciudad del Este, on the border with Brazil (the highway that also connects withPort of Paranaguá
The Port of Paranaguá is one of the main ports of Brazil and Latin America. It's located in the city of Paranaguá, in the Brazilian state of Paraná. It's the second largest port of Brazil in tonnage and the third in container shipping. It's a ...
). In January 2022, there were almost duplicated.
River transport is important due to the Paraná-Paraguay system, which covers an area of of navigable network and concentrates the most intense commercial maritime traffic to the Port of Buenos Aires
The Port of Buenos Aires ( es, Puerto de Buenos Aires) is the principal maritime port in Argentina. Operated by the ''Administración General de Puertos'' (General Ports Administration), a state enterprise, it is the leading transshipment point fo ...
. Asunción is the main port of Paraguay.
Asunción airport is an important stopover for international airlines and Ciudad del Este airport, is an important international air cargo hub.
Energy
All of Paraguay's electricity is generated byhydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
, making it one of the cleanest in the world. Paraguay has an installed electrical production capacity of 8,110 MW, producing 63 billion kWh/year in 2016; with domestic consumption of just 15 billion kWh, the excess production is sold to Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, making Paraguay the world's largest exporter of electric power. This production is from two large hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
projects along its borders, including the Itaipu Dam
The Itaipu Dam ( pt, Barragem de Itaipu , es, Represa de Itaipú ) is a hydroelectric dam on the Paraná River located on the border between Brazil and Paraguay. The construction of the dam was first contested by Argentina, but the negotiations ...
, the world's second largest generating station.
Demographics
 Paraguay's population is distributed unevenly through the country, with the vast majority of people living in the eastern region near the capital and largest city,
Paraguay's population is distributed unevenly through the country, with the vast majority of people living in the eastern region near the capital and largest city, Asunción
Asunción (, , , Guarani: Paraguay) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay.
The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay o ...
, which accounts for 10% of the country's population. The Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato ...
region, which includes the Alto Paraguay
Alto Paraguay (; ''Upper Paraguay'') is the least populous as well as a sparsely populated department of Paraguay. The capital is the town of Fuerte Olimpo.
In 1992, the Chaco Department was merged with Alto Paraguay.
Nature and national park ...
, Boquerón and Presidente Hayes Department, and accounts for about 60% of the territory, is home to less than 2% of the population. About 56% of Paraguayans live in urban areas, making Paraguay one of the least urbanized nations in South America.
For most of its history, Paraguay has been a recipient of immigrants, owing to its low population density, especially after the demographic collapse caused by the Paraguayan War. Immigrants include Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Germans, Spanish, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, Russians, Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
, Chinese, Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Brazilians, Argentines
Argentines (mistakenly translated Argentineans in the past; in Spanish (masculine) or (feminine)) are people identified with the country of Argentina. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Argentines, ...
, Americans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Ame ...
, Bolivians
Bolivians ( es, Bolivianos) are people identified with the country of Bolivia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Bolivians, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
, Venezuelans
Venezuelans ( Spanish: ''venezolanos'') are the citizens identified with the country of Venezuela. This connection may be through citizenship, descent or cultural. For most Venezuelans, many or all of these connections exist and are the source of ...
, Mexicans, Chileans
Chileans ( es, Chilenos) are people identified with the country of Chile, whose connection may be residential, legal, historical, ethnic, or cultural. For most Chileans, several or all of these connections exist and are collectively the source ...
, Taiwanese and Uruguayans
Uruguayans ( es, uruguayos) are people identified with the country of Uruguay, through citizenship or descent. Uruguay is home to people of different ethnic origins. As a result, many Uruguayans do not equate their nationality with ethnicity, b ...
.
Along with German Argentines, German Paraguayans are one of the most prominent and growing German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
communities in South America, with some 25,000 German-speaking Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
s living in the Paraguayan Chaco. German settlers founded several towns, such as Hohenau, Filadelfia
Filadelfia () is the capital of Boquerón Department in the Gran Chaco of western Paraguay. It is the centre of the Fernheim Colony. It is about a 5-hour drive from the capital of Asunción. With a population of about 20,000, it is the largest ...
, Neuland, Obligado and Nueva Germania. Several websites that promote German immigration to Paraguay claim that 5–7% of the population is of German ancestry, including 150,000 people of German-Brazilian descent. Similarly, from the 1920-30s, Paraguay received waves
Waves most often refers to:
*Waves, oscillations accompanied by a transfer of energy that travel through space or mass.
*Wind waves, surface waves that occur on the free surface of bodies of water.
Waves may also refer to:
Music
*Waves (band) ...
of Slavic people who settled in Asunción and Southern Paraguay ( Itapúa, Misiones
Misiones (, ''Missions'') is one of the 23 provinces of Argentina, located in the northeastern corner of the country in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by Paraguay to the northwest, Brazil to the north, east and south, and Corrientes P ...
and Ñeembucú), especially in the towns of Fram, Coronel Bogado
Coronel Bogado District is a town and district in the Itapúa Department of Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked countr ...
, Encarnación, San Juan del Paraná, San Ignacio and Pilar Paraguay has also been a haven for communities persecuted for the religious faith, like the Bruderhof who were forced to leave England in 1941 because of their pacifist beliefs. Many of these communities have retained their languages and culture, particularly the Brazilians, who represent the largest and most prominent immigrant group, at around 400,000. Many Brazilian Paraguayans are of German, Italian and Polish descent. There are an estimated 63,000 Afro-Paraguayans
Afro-Paraguayan are Paraguayans of African descent. They can be found in Camba Cua outside Asuncion; Kamba Kokue outside Paraguari, and the city of Emboscada. Currently, the black Paraguayan population accounts for less than 1% of the total pop ...
, comprising 1% of the population.
 There is no official data on the ethnic composition of the Paraguayan population, as the Department of Statistics, Surveys and Censuses of Paraguay does not ask about ''race'' and ''ethnicity'' in census surveys, although it does inquire about the indigenous population. According to the census of 2002, indigenous people made up 1.7% of Paraguay's total population.
Traditionally, the majority of the Paraguayan population is considered mixed (''mestizo'' in Spanish). HLA-DRB1 polymorphism studies have shown genetic distances between Paraguayans and Spanish populations were closer than between Paraguayans and Guaranis, suggesting the predominance of Spanish genetics among Paraguayans.
According to , Paraguay has a population of , of which 95% are Mestizo or white and 5% are labelled as "other", which includes members of 17 distinct ethnolinguistic indigenous groups, many of which are poorly documented.
There is no official data on the ethnic composition of the Paraguayan population, as the Department of Statistics, Surveys and Censuses of Paraguay does not ask about ''race'' and ''ethnicity'' in census surveys, although it does inquire about the indigenous population. According to the census of 2002, indigenous people made up 1.7% of Paraguay's total population.
Traditionally, the majority of the Paraguayan population is considered mixed (''mestizo'' in Spanish). HLA-DRB1 polymorphism studies have shown genetic distances between Paraguayans and Spanish populations were closer than between Paraguayans and Guaranis, suggesting the predominance of Spanish genetics among Paraguayans.
According to , Paraguay has a population of , of which 95% are Mestizo or white and 5% are labelled as "other", which includes members of 17 distinct ethnolinguistic indigenous groups, many of which are poorly documented.

Religion
Christianity, particularlyCatholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, is the dominant religion in Paraguay. According to the 2002 census, 89.9% of the population was Catholic, 6.2% was Evangelical Protestant
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "born again", in which an individual exper ...
, 1.1% identified with other Christian sects, and 0.6% practiced indigenous religions. A U.S. State Department report on Religious Freedom names Catholicism, evangelical Protestantism, mainline Protestantism, Judaism (Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform), Mormonism
Mormonism is the religious tradition and theology of the Latter Day Saint movement of Restorationist Christianity started by Joseph Smith in Western New York in the 1820s and 1830s. As a label, Mormonism has been applied to various aspects of ...
, and the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the ...
as prominent religious groups. It also mentions a large Muslim community in Alto Paraná
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: ''altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In 4-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in choruses by ...
(as a result of Middle-Eastern immigration, especially from Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
) and a prominent Mennonite community in Boquerón.
Languages
Paraguay is a bilingual nation. Both Spanish/Castilian andGuaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
are official languages. The Guaraní language is a remarkable trace of the indigenous Guaraní culture that has endured in Paraguay. Guaraní claims its place as one of the last surviving and thriving of South American indigenous national languages. In 2015, Castilian was spoken by about 87% of the population, while Guaraní is spoken by more than 90%, or slightly more than 5.8 million speakers. 52% of rural Paraguayans are bilingual in Guaraní. While Guaraní is still widely spoken, Spanish is generally given a preferential treatment in government, business, media and education as one of South America's lingua francas.Paraguayan Guaraní, Ethnologue There are approximately 19 other indigenous languages spoken in Paraguay, many of which are threatened by extinction. Languages such as Guana, Ayoreo and Ishir (Chamacoco) are considered endangered.
Education
Literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
was about 93.6% and 87.7% of Paraguayans finish the fifth grade according to UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's last Educational Development Index 2008. Literacy does not differ much by gender. A more recent study reveals that attendance at primary school by children between 6 and 12 years old is about 98%. Primary education is free and mandatory and takes nine years. Secondary education takes three years.
Main universities in Paraguay include:
* National University of Asunción
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
(public and founded in 1889)
* Autonomous University of Asunción (private and founded in 1979)
* Universidad Católica Nuestra Señora de la Asunción
Universidad (Spanish for "university") may refer to:
Places
* Universidad, San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Universidad (Madrid)
Football clubs
* Universidad SC, a Guatemalan football club that represents the Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala
...
(private and run by the church).
* Universidad Americana
The Universidad Americana (Spanish for ''American University'') is a private university located in Paraguay.
Founded in 1994, the university has two teaching facilities in Asunción, one in Ciudad del Este and one in Encarnación. It has 4,000 ...
(private).
* Universidad del Pacífico (private and founded in 1991).
The net primary enrollment rate was at 88% in 2005. Public expenditure on education was about 4.3% of GDP in the early 2000s.
Health
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
has helped the Paraguayan government reduce the country's maternal and infant mortality. The ''Mother and Child Basic Health Insurance Project'' aimed to contribute to reducing mortality by increasing the use of selected life-saving services included in the country's Mother and Child Basic Health Insurance Program (MCBI) by women of child-bearing age, and children under age six in selected areas. To this end, the project also targeted improving the quality and efficiency of the health service network within certain areas, in addition to increasing the Ministry of Public Health and Social Welfare's (MSPandBS) management.
Culture
Paraguay's cultural heritage can be traced to the extensive intermarriage between the original male Spanish settlers and indigenousGuaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
women. Their culture is highly influenced by various European countries, including Spain. Therefore, the Paraguayan culture is a fusion of two cultures and traditions; one European, the other, Southern Guaraní. Although this is common throughout the country, it is more visible around the towns of Atyrá, Tobatí
Tobatí is a city in Tobatí District in the Cordillera Department, Paraguay. The population of the city is 9,688.Direccioón General de Estadística, Encuentras, y Censos. Censo Nacional de Población y Viviendas 2002.
History
Tobati was fou ...
and Altos. More than 93% of Paraguayans are ''mestizos
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
'', making Paraguay one of the most homogeneous countries in Latin America. A characteristic of this cultural fusion is the extensive bilingualism present to this day: more than 80% of Paraguayans speak both Spanish and the indigenous language, Guaraní Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to
Ethnography
* Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia)
* Guaraní language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay
* ...
. Jopara, a mixture of Guaraní and Spanish, is also widely spoken.
 This cultural fusion is expressed in arts such as embroidery (''ao po'í'') and lace making (''ñandutí''). The music of Paraguay, which consists of lilting polkas, bouncy ''galopas,'' and languid '' guaranias'' is played on the native harp. Paraguay's culinary heritage is also deeply influenced by this cultural fusion. Several popular dishes contain
This cultural fusion is expressed in arts such as embroidery (''ao po'í'') and lace making (''ñandutí''). The music of Paraguay, which consists of lilting polkas, bouncy ''galopas,'' and languid '' guaranias'' is played on the native harp. Paraguay's culinary heritage is also deeply influenced by this cultural fusion. Several popular dishes contain manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, a local staple crop similar to the yuca
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
also known as Cassava root found in the Southwestern United States and Mexico, as well as other indigenous ingredients. A popular dish is '' sopa paraguaya'', similar to a thick corn bread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are ...
. Another notable food is ''chipa
Chipa (, ) is a type of small, baked, cheese-flavored rolls, a popular snack and breakfast food in Paraguay. The recipe has existed since the 18th century and its origins lie with the Guaraní people of Asunción.
It is inexpensive and often sold ...
'', a bagel
A bagel ( yi, בײגל, translit=beygl; pl, bajgiel; also spelled beigel) is a bread roll originating in the Jewish communities of Poland. It is traditionally shaped by hand into a roughly hand-sized ring from yeasted wheat dough that is first ...
-like bread made from cornmeal, manioc, and cheese. Many other dishes consist of different kinds of cheeses, onions, bell peppers, cottage cheese, cornmeal, milk, seasonings, butter, eggs and fresh corn kernels.
The 1950s and 1960s were the time of the birth of a new generation of Paraguayan novelists and poets such as José Ricardo Mazó
José Ricardo Mazó (Pilar, 1927- Asunción, 1987), the Paraguayan poet, was born in Pilar, in the department of Ñeembucúbr> He was a member of the Literary Academy of theCollege of San Joséand of the Paraguayan Academia Universitaria. After ...
, Roque Vallejos, and Nobel Prize nominee Augusto Roa Bastos. Several Paraguayan films have been made.
Inside the family, conservative values predominate. In lower classes, godparent
In infant baptism and denominations of Christianity, a godparent (also known as a sponsor, or '' gossiprede'') is someone who bears witness to a child's christening and later is willing to help in their catechesis, as well as their lifelon ...
s have a special relationship to the family, since usually, they are chosen because of their favourable social position, in order to provide extra security for the children. Particular respect is owed them, in return for which the family can expect protection and patronage.
The most popular instruments in Paraguayan music are the harp and the guitar. The native genres are the Paraguayan polka and the guarania, characterised by a slow song that was developed by José Asunción Flores around the 1920s.
Sport
Sport in Paraguay is an important part of the country's national culture. Football is the most popular sport, the main national team is theParaguay national football team
The Paraguay national football team ( es, Selección de fútbol de Paraguay) represents Paraguay in men's international Association football, football competitions, and are controlled by the Paraguayan Football Association (Asociación Paraguaya ...
.
Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
is also very popular. Other sports such as volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Sum ...
, handball, futsal Futsal is a football-based game played on a hard court smaller than a football pitch, and mainly indoors. It has similarities to five-a-side football and indoor football.
Futsal is played between two teams of five players each, one of whom is ...
, swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
and tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
are also popular. Additional Paraguayan sports and pastimes include rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
, chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
, motorsport, golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping ...
and rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically ...
.
See also
* Bibliography of Paraguay * Index of Paraguay-related articles * Outline of ParaguayNotes
References
External links
GovernmentChief of State and Cabinet Members
National Department of Tourism
Ministry of Finance with economic and government information; also available in English
General information
Paraguay
from the ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
''
Paraguay
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Paraguay
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Paraguay profile
from the
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadca ...
*
*
Key Development Forecasts for Paraguay
from
International Futures
International Futures (IFs) is a global integrated assessment modelling, integrated assessment model designed to help with thinking strategically and systematically about key global systems (economic, demographic, education, health, environment, ...
News media
La Rueda – Weekly reviews
ABC Color
Última Hora
La Nación
Paraguay.com
Ñanduti
Paraguayan Pymes News
Trade
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Paraguay
Exchange rate of the Guaraní – Paraguayan Currency
Travel
Paraguay.com: Tradition, Culture, Maps, Tourism
*
Tourism in Paraguay, information, pictures and more. Turismo.com.py
{{Authority control Countries in South America 1811 establishments in South America States and territories established in 1811 Former Spanish colonies Landlocked countries Member states of Mercosur Member states of the United Nations Republics Spanish-speaking countries and territories Southern Cone countries