One-humped Camel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'' or ;), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel, or one-humped camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus '' Camelus'', with one hump on its back.
It is the tallest of the three species of
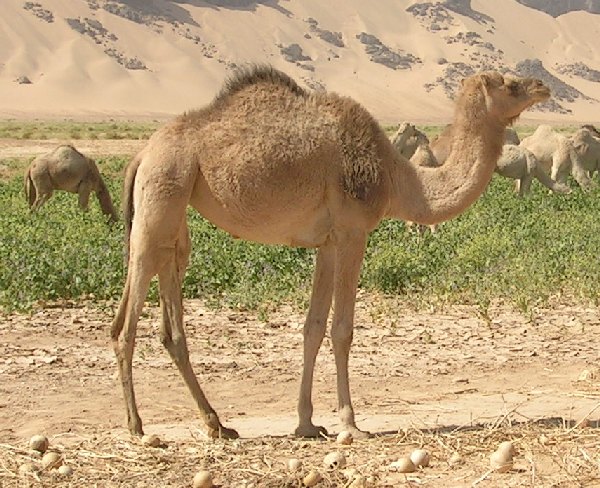
 The dromedary is the tallest of the three camel species. Adult males range in height between at the shoulder; Guinness World Records
The dromedary is the tallest of the three camel species. Adult males range in height between at the shoulder; Guinness World Records
Largest species of camel
/ref> females range between . Males typically weigh between ; females range between . The distinctive features are its long, curved neck, narrow chest and single hump (the Bactrian camel has two), thick, double-layered eyelashes and bushy eyebrows. They have sharp vision and a good sense of smell. The male has a soft palate ( in Arabic) nearly long, which he inflates to produce a deep pink sac. The palate, which is often mistaken for the tongue, dangles from one side of the mouth and is used to attract females during the mating season. The
 The
The 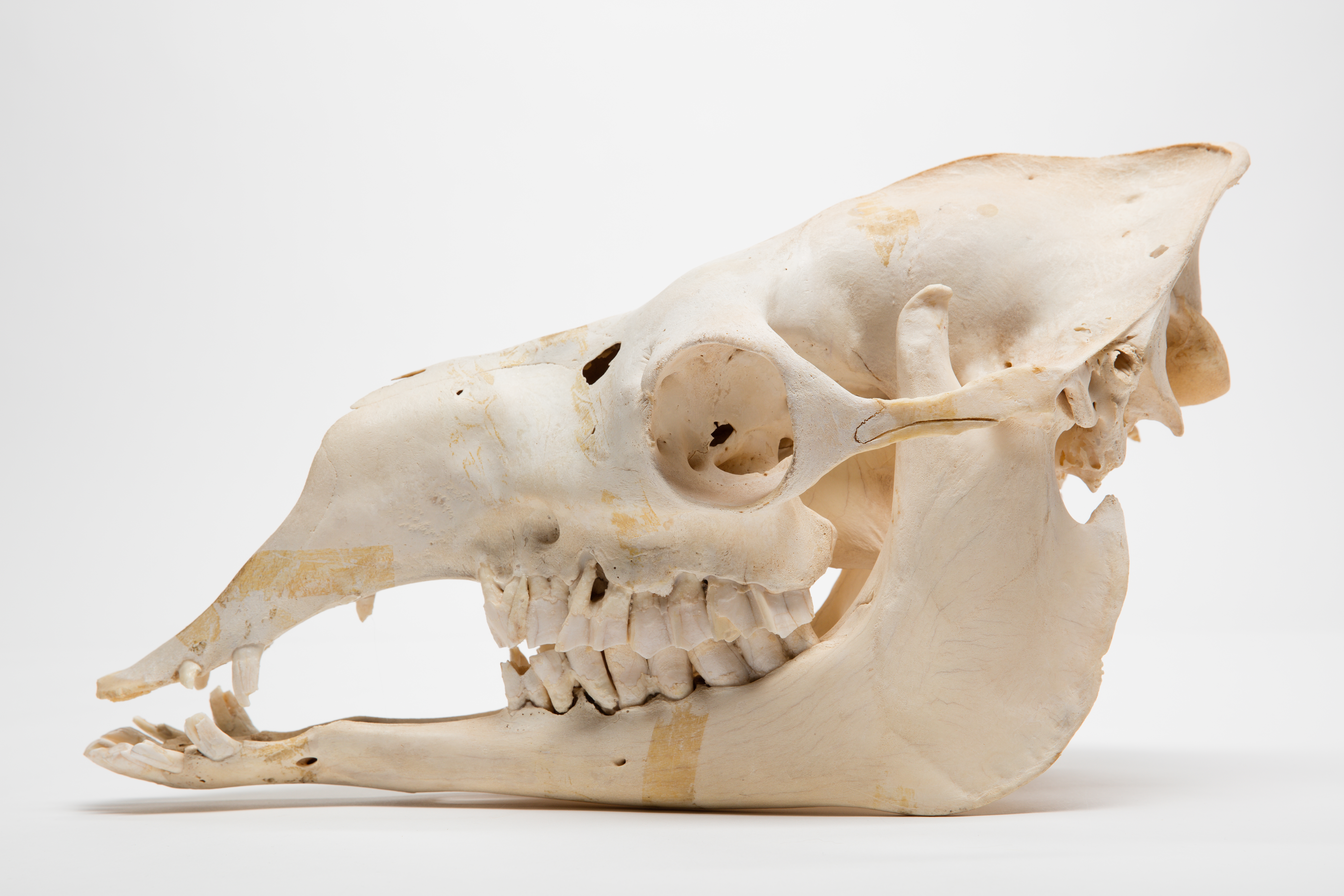 The dromedary has 22
The dromedary has 22  The heart weighs around ; it has two ventricles with the tip curving to the left. The
The heart weighs around ; it has two ventricles with the tip curving to the left. The
camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. C ...
; adult males stand at the shoulder, while females are tall. Males typically weigh between , and females weigh between .
The species' distinctive features include its long, curved neck, narrow chest, a single hump (compared with two on the Bactrian camel and wild Bactrian camel), and long hairs on the throat, shoulders and hump. The coat is generally a shade of brown. The hump, tall or more, is made of fat bound together by fibrous tissue.
Dromedaries are mainly active during daylight hours. They form herds of about 20 individuals, which are led by a dominant male. They feed on foliage and desert vegetation; several adaptations, such as the ability to tolerate losing more than 30% of its total water content, allow it to thrive in its desert habitat. Mating occurs annually and peaks in the rainy season; females bear a single calf after a gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
of 15 months.
The dromedary has not occurred naturally in the wild for nearly 2,000 years. It was probably first domesticated in the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
about 4,000 years ago, or in Somalia where there are paintings in Laas Geel that figure it from 5,000 to 9,000 years ago. In the wild, the dromedary inhabited arid regions, including the Sahara Desert. The domesticated dromedary is generally found in the semi-arid to arid regions of the Old World, mainly in Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, and a significant feral population occurs in Australia. Products of the dromedary, including its meat and milk, support several North African tribes; it is also commonly used for riding and as a pack animal.
Etymology
The common name "dromedary" comes from the Old French ''dromedaire'' or the Late Latin ''dromedarius''. These originated from the Greek word ''dromas'', δρομάς (ο, η) ( GEN (γενική) ''dromados'', δρομάδος), meaning "running" or "runner",. used in Greek in the combination (''dromas kamelos''), literally "running camel", to refer to the dromedary. The first recorded use in English of the name "dromedary" occurred in the 14th century. The dromedary possibly originated in Arabia or Somalia and is therefore sometimes referred to as the Arabian or East African camel. The word "camel" generally refers either to the dromedary or the congeneric Bactrian; the word came into English via Old Norman, from the Latin word ''camēlus'', from Ancient Greek (''kámēlos''), ultimately from aSemitic
Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.
Semitic may also refer to:
Religions
* Abrahamic religions
** ...
source akin to Hebrew (''gamál'') and Arabic (''jamal'').
Taxonomy and classification
The dromedary shares the genus '' Camelus'' with the Bactrian camel (''C. bactrianus'') and the wild Bactrian camel (''C. ferus''). The dromedary belongs to the familyCamelidae
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, ...
. The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle (4th century BC) was the first to describe
Shneur Hasofer is a Hasidic musician known as DeScribe. Hasofer's musical style has been characterized as "Hasidic hip-hop," "Hasidic rap" and "Hasidic R&B".
Background
Hasofer was born to a Chabad Hasidic family in Melbourne, Australia. Hasof ...
the species of ''Camelus''. He named two species in his '' History of Animals''; the one-humped Arabian camel and the two-humped Bactrian camel. The dromedary was given its current binomial name ''Camelus dromedarius'' by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 publication ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''. In 1927, British veterinarian Arnold Leese
Arnold Spencer Leese (16 November 1878 – 18 January 1956) was a British fascist politician. Leese was initially prominent as a veterinary expert on camels. A virulent anti-Semite, he led his own fascist movement, the Imperial Fascist League, a ...
classified dromedaries by their basic habitats; the hill camels are small, muscular animals and efficient beasts of burden; the larger plains camels could be further divided into the desert type that can bear light burdens and are apt for riding, and the riverine type – slow animals that can bear heavy burdens; and those intermediate between these two types.
In 2007, Peng Cui of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and colleagues carried out a phylogenetic study of the evolutionary relationships between the two tribes of Camelidae; Camelini – consisting of the three ''Camelus'' species (the study considered the wild Bactrian camel as a subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of the Bactrian camel) – and Lamini
Lamini (members are called ''laminoids'') is a tribe of the subfamily Camelinae. It contains one extant genus with four species, all exclusively from South America: llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. The former two are domesticated specie ...
, which consists of the alpaca (''Vicugna pacos''), the guanaco (''Lama guanicoe''), the llama (''L. glama'') and the vicuña (''V. vicugna''). The study showed the two tribes had diverged 25 million years ago (early Miocene), earlier than previously estimated from North American fossils.
The dromedary and the Bactrian camel often interbreed to produce fertile offspring. Where the ranges of the species overlap, such as in northern Punjab, Persia, and Afghanistan, the phenotypic differences between them tend to decrease as a result of extensive crossbreeding. The fertility of their hybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two dif ...
has given rise to speculation that the dromedary and the Bactrian camel should be merged into a single species with two varieties. However, a 1994 analysis of the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
l cytochrome b gene showed the species display 10.3% divergence in their sequences.
Genetics and hybrids
The dromedary has 74diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively ...
chromosomes, the same as other camelids. The autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in au ...
s consist of five pairs of small to medium-sized metacentrics and submetacentrics. The X chromosome is the largest in the metacentric and submetacentric group. There are 31 pairs of acrocentrics. The dromedary's karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
is similar to that of the Bactrian camel.
Camel hybridization began in the first millennium BC. For about a thousand years, Bactrian camels and dromedaries have been successfully bred in regions where they are sympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species sh ...
to form hybrids with either a long, slightly lopsided hump or two humps – one small and one large. These hybrids are larger and stronger than their parents – they can bear greater loads. A cross between a first generation female hybrid and a male Bactrian camel can also produce a hybrid. Hybrids from other combinations tend to be bad-tempered or runts.
Evolution
The extinct ''Protylopus
''Protylopus'' is an extinct genus of camel that lived during middle to late Eocene some 50-40 million years ago in North America.
Along with being the oldest camel known, it was also the smallest, reaching a length of , and probably weighing a ...
'', which occurred in North America during the upper Eocene, is the oldest and the smallest-known camel. During the transition from Pliocene to Pleistocene, several mammals faced extinction. This period marked the successful radiation of the ''Camelus'' species, which migrated over the Bering Strait and dispersed widely into Asia, eastern Europe and Africa. By the Pleistocene, ancestors of the dromedary occurred in the Middle East and northern Africa.
The modern dromedary probably evolved in the hotter, arid regions of western Asia from the Bactrian camel, which in turn was closely related to the earliest Old World camels. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that the dromedary foetus has two humps, while in the adult male an anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
vestigial hump is present. A jawbone of a dromedary that dated
Date or dates may refer to:
*Date (fruit), the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'')
Social activity
*Dating, a form of courtship involving social activity, with the aim of assessing a potential partner
**Group dating
*Play date, an ...
from 8,200 BC was found in Saudi Arabia on the southern coast of the Red Sea.
In 1975, Richard Bulliet of Columbia University wrote that the dromedary exists in large numbers in areas from which the Bactrian camel has disappeared; the converse is also true to a great extent. He said this substitution could have taken place because of the heavy dependence on the milk, meat and wool of the dromedary by Syrian and Arabian nomads, while the Asiatic people domesticated the Bactrian camel but did not have to depend upon its products.
Characteristics

 The dromedary is the tallest of the three camel species. Adult males range in height between at the shoulder; Guinness World Records
The dromedary is the tallest of the three camel species. Adult males range in height between at the shoulder; Guinness World RecordsLargest species of camel
/ref> females range between . Males typically weigh between ; females range between . The distinctive features are its long, curved neck, narrow chest and single hump (the Bactrian camel has two), thick, double-layered eyelashes and bushy eyebrows. They have sharp vision and a good sense of smell. The male has a soft palate ( in Arabic) nearly long, which he inflates to produce a deep pink sac. The palate, which is often mistaken for the tongue, dangles from one side of the mouth and is used to attract females during the mating season. The
coat
A coat typically is an outer garment for the upper body as worn by either gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, a ...
is generally brown but can range from black to nearly white. Leese reported piebald dromedaries in Kordofan and Darfur
Darfur ( ; ar, دار فور, Dār Fūr, lit=Realm of the Fur) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju ( ar, دار داجو, Dār Dājū, links=no) while ruled by the Daju, ...
in Sudan. Piebald coloration in some camels is thought to be caused by the ''KITW1'' allele of the KIT gene, though there is likely at least one other mutation that also causes white spotting. The hair is long and concentrated on the throat, shoulders and the hump. The large eyes are protected by prominent supraorbital ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin.
Structure
The brow ridge is a nodule or crest ...
s; the ears are small and rounded. The hump is at least high. The dromedary has long, powerful legs with two toes on each foot. The feet resemble flat, leathery pads. Like the giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...
, dromedaries moves both legs on one side of the body at the same time.
Compared with the Bactrian camel, the dromedary has a lighter build, longer limbs, shorter hairs, a harder palate and an insignificant or absent ethmoidal
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The cells are variable in both size and number in the lateral mass of each of the ethmoid bones and cannot be palpated during an extraoral e ...
fissure. Unlike the camelids of the genus ''Lama'', the dromedary has a hump, and in comparison has a longer tail, smaller ears, squarer feet, and a greater height at the shoulder. The dromedary has four teats instead of the two in the ''Lama'' species.
Anatomy
 The
The cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
of the dromedary consists of a postorbital bar The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most streps ...
, a tympanic bulla
The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.
It originates as a separate bone (tympanic ...
filled with spongiosa, a well-defined sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptiona ...
, a long facial part and an indented nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.
Eac ...
. Typically, there are eight sternal
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
and four non-sternal pairs of rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s. The spinal cord is nearly long; it terminates in the second and third sacral vertebra
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
. The fibula is reduced to a malleolar bone. The dromedary is a digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
animal; it walks on its toes, which are known as digits. It lacks the second and fifth digits. The front feet are wide and long; they are larger than the hind feet, which measure wide and long.
 The dromedary has 22
The dromedary has 22 milk teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in the ...
, which are eventually replaced by 34 permanent teeth. The dental formula for permanent dentition is , and for milk dentition. In the juvenile, the lower first molars develop by 12 to 15 months and the permanent lower incisors appear at 4.5 to 6.5 years of age. All teeth are in use by 8 years. The lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
of the eyes contain crystallin, which constitutes 8 to 13% of the protein present there.
The skin is black; the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
is thick and the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
is thick. The hump is composed of fat bound together by fibrous tissue. There are no glands on the face; males have glands that appear to be modified apocrine sweat gland
An apocrine sweat gland (; from Greek ''apo'' 'away' and ''krinein'' 'to separate') is composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the ...
s that secrete pungent, coffee-coloured fluid during the rut, located on either side of the neck midline. The glands generally grow heavier during the rut, and range from . Each cover hair is associated with an arrector pilli
The arrector pili muscles, also known as hair erector muscles, are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
Structure
...
muscle, a hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
, a ring of sebaceous glands and a sweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial sur ...
. Females have cone-shaped, four-chambered mammary glands that are long with a base diameter of . These glands can produce milk with up to 90% water content even if the mother is at risk of dehydration.
 The heart weighs around ; it has two ventricles with the tip curving to the left. The
The heart weighs around ; it has two ventricles with the tip curving to the left. The pulse rate
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
is 50 beats per minute. The dromedary is the only mammal with oval red blood corpuscles
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
, which facilitates blood flow during dehydration. The pH of the blood varies from 7.1 to 7.6 (slightly alkaline). The individual's state of hydration and sex and the time of year can influence blood values
Reference ranges (reference intervals) for blood tests are sets of values used by a health professional to interpret a set of medical test results from blood samples. Reference ranges for blood tests are studied within the field of clinical chem ...
. The lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s lack lobes. A dehydrated camel has a lower breathing rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is mea ...
. Each kidney has a capacity of , and can produce urine with high chloride concentrations. Like the horse, the dromedary has no gall bladder. The grayish violet, crescent-like spleen weighs less than . The triangular, four-chambered liver weighs ; its dimensions are .
Reproductive system
The ovaries are reddish, circular and flattened. They are enclosed in a conicalbursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
and have the dimensions during anestrus. The oviducts are long. The uterus is bicornuate
A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus (from the Latin ''cornū'', meaning "horn"), is a type of mullerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.
Pathophysiology
A bicornuate uterus ...
. The vagina is long and has well-developed Bartholin's gland
The Bartholin's glands (named after Caspar Bartholin the Younger; also called Bartholin glands or greater vestibular glands) are two pea sized compound alveolar glandsManual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . located slightly poster ...
s. The vulva is deep and has a small clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the ope ...
. The placenta is diffuse and epitheliochorial
Placentation refers to the formation, type and structure, or arrangement of the placenta. The function of placentation is to transfer nutrients, respiratory gases, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in some instances to remov ...
, with a crescent-like chorion.
The penis is covered by a triangular penile sheath that opens backwards; it is about long. The scrotum is located high in the perineum with the testicles in separate sacs. Testicles are long, deep and wide. The right testicle is often smaller than the left. The typical mass of either testicle is less than ; during the rut the mass increases from . The Cowper's gland
The bulbourethral glands or Cowper's glands (named for English anatomist William Cowper) are two small exocrine glands in the reproductive system of many male mammals (of all domesticated animals, they are absent only in dogs). They are homologo ...
is white, almond-shaped and lacks seminal vesicles; the prostate gland is dark yellow, disc-shaped and divided into two lobes.
The camel epididymis interstitium revealed several blood vessels harboring special regulatory devices such as the spiral arteries, spiral veins, and throttle arterioles.
Health and diseases
The dromedary generally suffers from fewer diseases than other domestic livestock such as goats and cattle. Temperature fluctuations occur throughout the day in a healthy dromedary – the temperature falls to its minimum at dawn, rises until sunset and falls during the night. Nervous camels may vomit if they are carelessly handled; this does not always indicate a disorder. Rutting males may develop nausea. The dromedary is prone to trypanosomiasis, a disease caused by a parasite transmitted by thetsetse fly
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies), are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glo ...
. The main symptoms are recurring fever, anaemia and weakness; the disease is typically fatal for the camel. Brucellosis is another prominent malady. In an observational study, the seroprevalence of this disease was generally low (2 to 5%) in nomadic or moderately free dromedaries, but it was higher (8 to 15%) in denser populations. Brucellosis is caused by different biotype
{{Short pages monitor