|
Fauna Of Jordan
The wildlife of Jordan includes its flora and fauna and their natural habitats. Although much of the country is desert, it has several geographic regions, each with a diversity of plants and animals adapted to their own particular habitats. Fossil finds show that in Palaeolithic times, the region had Syrian brown bears, Asiatic lions, zebras, Asian elephants, and rhinoceroses, but these species are all now extinct in this region. More recently, in the twentieth century, the Arabian oryx became locally extinct through hunting, and several species of deer and gazelle were reduced to remnant populations. The Royal Society for the Conservation of Nature was established in 1966 to preserve Jordan's natural resources, a number of protected areas have been set up, and conservation measures and captive breeding programs have been put in place, resulting in an increase in the numbers of these animals. In 1978, 11 Arabian Oryx were brought in to Jordan from USA. They were taken care of at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
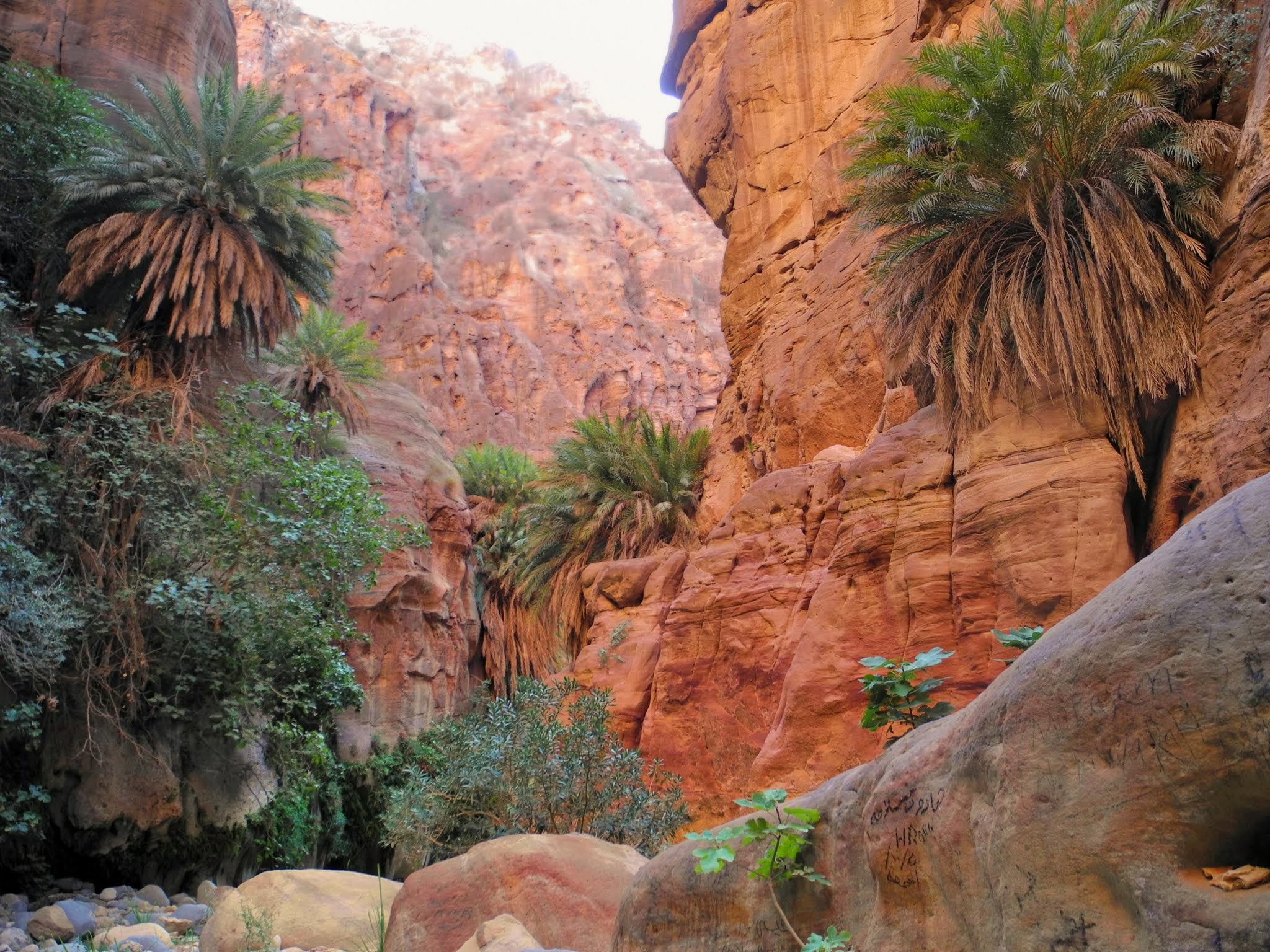
Wadi Rum In Jordan
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Etymology The term ' is very widely found in Arabic toponyms. Some Spanish toponyms are derived from Andalusian Arabic where ' was used to mean a permanent river, for example: Guadalcanal from ''wādī al-qanāl'' ( ar, وَادِي الْقَنَال, "river of refreshment stalls"), Guadalajara from ''wādī al-ḥijārah'' ( ar, وَادِي الْحِجَارَة, "river of stones"), or Guadalquivir, from ''al-wādī al-kabīr'' ( ar, اَلْوَادِي الْكَبِير, "the great river"). General morphology and processes Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portions of alluvial fans and extend to inland sabkhas or dry lakes. In basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ar, بادية الشام ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert and steppe covering of the Middle East, including parts of southern Syria, eastern Jordan, northern Saudi Arabia, and western Iraq. It accounts for 85% of the land area of Jordan and 55% of Syria. To the south it borders and merges into the Arabian Desert. The land is open, rocky or gravelly desert pavement, cut with occasional wadis. Location and name The desert is bounded by the Orontes Valley and the volcanic field of Harrat al-Shamah to the west, and by the Euphrates to the east. In the north, the desert gives way to the more fertile areas and to the south it runs into the deserts of the Arabian Peninsula. Some sources equate the Syrian Desert with the ''"Hamad Desert"'' while others limit the name ''Hamad'' to the southern central plateau. A few consider the Hamad to be the whole region and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupressus Sempervirens
''Cupressus sempervirens'', the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress, Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, southern and coastal Bulgaria, southern coastal Croatia and Slovenia, southern Montenegro, southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, southwestern North Macedonia, southern Greece, southern Turkey, Cyprus, northern Egypt, western Syria, Lebanon, Malta, Italy, southern France, Spain, Palestine, Israel, western Jordan, South Caucasus, and also a disjunct population in Iran. Description ''Cupressus sempervirens'' is a medium-sized coniferous evergreen tree to 35 m (115 ft) tall, with a conic crown with level branches and variably loosely hanging branchlets. It is very long-lived, with some trees reported to be over 1,000 years old. The foliage grows in dense sprays, dark green in colour. The leaves are scale-like, 2–5 mm long, and produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Halepensis
''Pinus halepensis'', commonly known as the Aleppo pine, also known as the Jerusalem pine, is a pine native to the Mediterranean region. Description ''Pinus halepensis'' is a small to medium-sized tree, tall, with a trunk diameter up to , exceptionally up to . The bark is orange-red, thick, and deeply fissured at the base of the trunk, and thin and flaky in the upper crown. The leaves ('needles') are very slender, long, distinctly yellowish green, and produced in pairs (rarely a few in threes). The cones are narrow conic, long and broad at the base when closed, green at first, ripening glossy red-brown when 24 months old. They open slowly over the next few years, a process quickened if they are exposed to heat such as in forest fires. The cones open wide to allow the seeds to disperse. The seeds are long, with a wing, and are wind- dispersed.Nahal, I. (1962). Le Pin d'Alep (''Pinus halepensis'' Miller). Étude taxonomique, phytogéographique, écologique et sylvicole. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμνόσπερμος ( el, γυμνός, translit=gymnos, lit=naked, label=none and el, σπέρμα, translit=sperma, lit=seed, label=none), literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, ''Torreya'', ''Ginkgo''. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahis Ain Abu Jurban
Mahis ( ar, ماحص, Māḥis, alternatively spelled Mahas) is a town in the Balqa Governorate northwest from the governorate's capital Salt, and west of Amman. Its population was 17,754 in 2015. Most of the population of Mahis descends from the Abbadi tribe. ( ar, العبادي). The mountainous town is located at over , with views on the Jordan Valley, West Bank with Jerusalem's walls visible on the horizon. Mahis is known for its orchards and its numerous water fountains and springs, notably the Fountain of Mahis. History Mahis is believed to emerged during the Roman period, when it bordered Jewish Perea and the territory of Philadelphia - Amman of the Decapolis, and in the Byzantine period between the territory of the dioceses of Gadara and Philadelphia. The name comes from the Arabic word ( ar, محص) meaning to check out and examine due to its status as a border check point. In 1838 Mahis was noted located south of Al-Salt, and as being in ruins. The village was li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
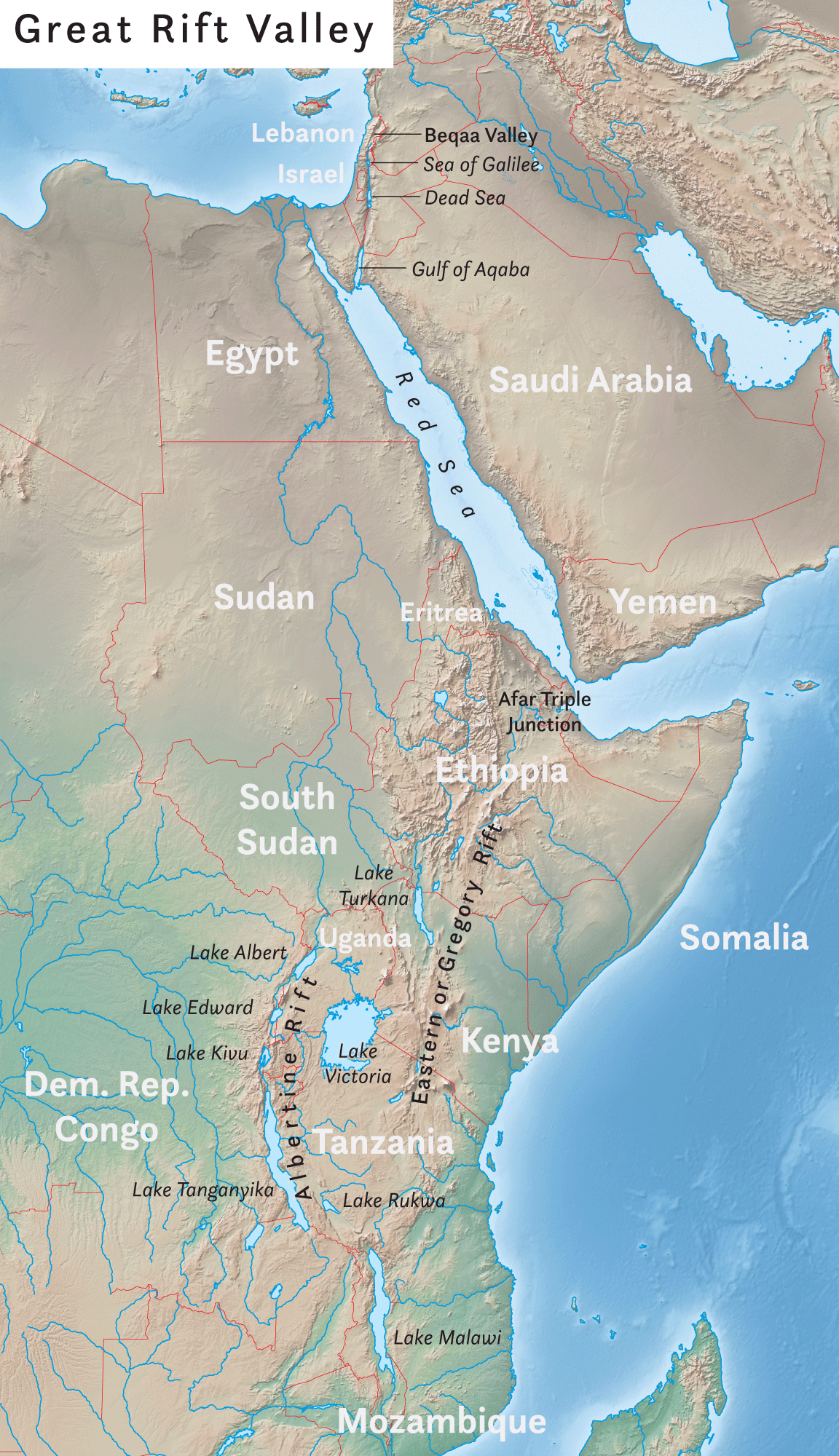
Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems. This valley extends northward for 5,950 km through the eastern part of Africa, through the Red Sea, and into Western Asia. Several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lakes, exist on the floor of this rift valley: Lakes Malawi, Rudolf and Tanganyika are examples of such lakes. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa's wildlife parks. The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the East African Rift, the divergent plate boundary which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward through eastern Africa, and is in the process of splitting the African Plate into two new and separate plates. Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escarpment''. Some sources differentiate the two terms, with ''escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has referred to the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, as "the Occupied Palestinian Territory", and this term was used as the legal definition by the ICJ in its advisory opinion of July 2004. The term occupied Palestinian territory was used by the United Nations and other international organizations between October 1999 and December 2012 to refer to areas controlled by the Palestinian National Authority, but from 2012, when Palestine was admitted as one of its non-member observer states, the United Nations started using exclusively the name State of Palestine. The European Union (EU) also adopts the term occupied Palestinian territory, with a parallel term Palestinian Authority territories also occasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank to the west. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River. As of 2019, the lake's surface is below sea level, making its shores the lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water – 9.6 times as salty as the ocean – and has a density of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point. The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around the Mediterranean Basin for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |