Okinawans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ryukyuan people ( ryu, 琉球民族 (るーちゅーみんずく), Ruuchuu minzuku or ryu, どぅーちゅーみんずく, Duuchuu minzuku, label=none, ja, 琉球民族/りゅうきゅうみんぞく, Ryūkyū minzoku, also Lewchewan or Loochooan) are an
 The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a
The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a
East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea a ...
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
native to the Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yonaguni ...
, which stretch between the islands of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
. Administratively, they live in either the Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city o ...
or the Kagoshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
within Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. They speak one of the Ryukyuan languages
The , also Lewchewan or Luchuan (), are the indigenous languages of the Ryukyu Islands, the southernmost part of the Japanese archipelago. Along with the Japanese language and the Hachijō language, they make up the Japonic language family.
Al ...
, considered to be one of the two branches of the Japonic language family
Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan, sometimes also Japanic, is a language family comprising Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and ...
, the other being Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
and its dialects
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
. Hachijō is sometimes considered by linguists to constitute a third branch.
Ryukyuans are not a recognized minority group
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
in Japan, as Japanese authorities consider them just a subgroup of the Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Jap ...
, akin to the Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
. Although officially unrecognized, Ryukyuans constitute the largest ethnolinguistic
Ethnolinguistics (sometimes called cultural linguistics) is an area of anthropological linguistics that studies the relationship between a language and the nonlinguistic cultural behavior of the people who speak that language.
__NOTOC__
Examples ...
minority group in Japan, with 1.4 million living in the Okinawa Prefecture alone. Ryukyuans inhabit the Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
of Kagoshima Prefecture as well, and have contributed to a considerable Ryukyuan diaspora
The Ryukyuan diaspora are the Ryukyuan emigrants from the Ryukyu Islands, especially Okinawa Island, and their descendants that reside in a foreign country. The first recorded emigration of Ryukyuans was in the 15th century when they establishe ...
. As many as 800,000 more ethnic Ryukyuans and their descendants are dispersed elsewhere in Japan and worldwide; most commonly in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and, to a lesser extent, in other territories where there is also a sizable Japanese diaspora
The Japanese diaspora and its individual members, known as Nikkei (日系) or as Nikkeijin (日系人), comprise the Japanese emigrants from Japan (and their descendants) residing in a country outside Japan. Emigration from Japan was recorded as ...
. In the majority of countries, the Ryukyuan and Japanese diaspora are not differentiated, so there are no reliable statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
for the former.
Ryukyuans have a distinct culture with some matriarchal
Matriarchy is a social system in which women hold the primary power positions in roles of authority. In a broader sense it can also extend to moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
While those definitions apply in general E ...
elements, native religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
and cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
which had a fairly late (12th century) introduction of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
. The population lived on the islands in isolation for many centuries and in the 14th century three separate Okinawan political polities merged into the Ryukyu Kingdom
The Ryukyu Kingdom, Middle Chinese: , , Classical Chinese: (), Historical English names: ''Lew Chew'', ''Lewchew'', ''Luchu'', and ''Loochoo'', Historical French name: ''Liou-tchou'', Historical Dutch name: ''Lioe-kioe'' was a kingdom in the ...
(1429–1879) which continued the maritime trade
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Princ ...
and tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
relations started in 1372 with Ming-dynasty China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. In 1609 the Satsuma Domain
The , briefly known as the , was a domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1602 to 1871.
The Satsuma Domain was based at Kagoshima Castle in Satsuma Province, the core of the modern city of Kagoshima, ...
(based in Kyushu) invaded the Ryukyu Kingdom. The Kingdom maintained a fictive independence in vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
status, in a dual subordinate status to both China and Japan, because Tokugawa Japan was prohibited to trade (directly) with China.
During the Japanese Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
the kingdom became the Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, before becoming the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islands at the Pacific edge of the East China Sea.
When the domain was created in 1872, Japan's feudal han ...
(1872–1879), after which it was politically annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
by the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
. In 1879, after the annexation, the territory was reorganized as Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city o ...
, with the last king (Shō Tai
was the last king of the Ryukyu Kingdom (8 June 1848 – 10 October 1872) and the head of the Ryukyu Domain (10 October 1872 – 27 March 1879). His reign saw greatly increased interactions with travelers from abroad, particularly from Europe a ...
) forcibly exiled to Tokyo. China renounced its claims to the islands in 1895. During this period the Meiji government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan.
Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji o ...
, which sought to assimilate the Ryukyuan people as Japanese (Yamato
was originally the area around today's Sakurai City in Nara Prefecture of Japan, which became Yamato Province and by extension a name for the whole of Japan.
Yamato is also the dynastic name of the ruling Imperial House of Japan.
Japanese his ...
), suppressed Ryukyuan ethnic identity, tradition, culture and language. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Ryūkyū Islands were occupied by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
between 1945 and 1950 and then from 1950 to 1972. During this time many violations of human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
occurred. Since the end of World War II Ryukyuans have expressed strong resentment against the Japanese government and against US military facilities stationed in Okinawa.
United Nations special rapporteur on discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
and racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
Doudou Diène
Doudou Diène (born 1941) is a Senegalese jurist. He was United Nations Special Rapporteur on contemporary forms of racism, racial discrimination, xenophobia and related intolerance from 2002–2008.
Education
Diène holds a law degree fro ...
, in his 2006 report, noted a perceptible level of discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, relig ...
and xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
against the Ryukyuans, with the most serious discrimination they endure linked to their opposition of American military installations in the archipelago.
Etymology
Their usual ethnic name derives from the Chinese name for the islands, (also spelled as Loo Choo, Lew Chew, Luchu, and more), which in theJapanese language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been ma ...
is pronounced . In the Okinawan language
The Okinawan language (, , , ) or Central Okinawan, is a Northern Ryukyuan languages, Ryukyuan language spoken primarily in the southern half of the Okinawa Island, island of Okinawa, as well as in the surrounding islands of Kerama Islands, Ker ...
, it is pronounced . These terms are rarely used, and are politicized markers of a distinct culture.
Origins
Genetic studies
According to the recent genetic studies, the Ryukyuan people share morealleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
with the southern Jōmon (16,000–3,000 years ago) hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s than the Yamato Japanese, have smaller genetic contributions from Asian continental populations, which supports the dual-structure model of K. Hanihara (1991), a widely accepted theory which suggests that the Yamato Japanese are more admixed with Asian agricultural continental people (from the Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
) than the Ainu and the Ryukyuans, with major admixture occurring in and after the Yayoi period
The started at the beginning of the Neolithic in Japan, continued through the Bronze Age, and towards its end crossed into the Iron Age.
Since the 1980s, scholars have argued that a period previously classified as a transition from the Jōmon p ...
(3,000-1,700 years ago). Within the Japanese population the Ryukyu make a separate and one of the two genome-wide clusters along the main-island Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separ ...
. The Jōmon ancestry is estimated at approximately 28%. The admixture event which formed the admixed Ryukyuans was estimated at least 1100–1075 years ago, which corresponds to the Gusuku period
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the '' Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeological ...
, and is considered to be related to the arrival of migrants from Japan.
According to archaeological evidence, there is a prehistoric cultural differentiation between the Northern Ryukyu Islands (Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
and Okinawa Islands
The Okinawa Islands ( or ) are an island group in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan and are the principal island group of the prefecture. The Okinawa Islands are part of the larger Ryukyu Islands group and are located between the Amami Islands of Kagoshi ...
) and the Southern Ryukyu Islands (Miyako Islands
The (also Miyako Jima group) are a group of islands in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, belonging to the Ryukyu Islands. They are situated between the Okinawa Island and Yaeyama Islands.
In the early 1870s, the population of the islands was estim ...
and Yaeyama Islands
The Yaeyama Islands (八重山列島 ''Yaeyama-rettō'', also 八重山諸島 ''Yaeyama-shotō'', Yaeyama: ''Yaima'', Yonaguni: ''Daama'', Okinawan: ''Yeema'', Northern Ryukyuan: ''Yapema'') are an archipelago in the southwest of Okinawa ...
). The genome-wide differentiation was pronounced, especially between Okinawa and Miyako. It is considered to have arisen due to genetic drift rather than admixture with people from neighboring regions, with the divergence dated to the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
, and without major genetic contribution of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
inhabitants to the present-day Southern Islanders. The Amami Islanders are also slightly more similar to the mainland population than the Okinawa Islanders. An autosomal DNA analysis from Okinawan samples concluded that they are most closely related to other Japanese and East Asian contemporary populations, sharing on average 80% admixture with mainland Japanese and 19% admixture with Chinese population, and that have isolate characteristics.
The female mtDNA and male Y chromosome markers are used to study human migrations. The research on the skeletal remains from the Neolithic Shell midden period (also known as Kaizuka period) in Okinawa, as well from the Gusuku Period, showed predominance of female haplogroups D4 and M7a and their genetic continuity in the contemporary female population of Okinawa. It is assumed that M7a represents "Jomon genotype" introduced by a Paleolithic ancestor from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
or the southern region of the Asian continent, around the Last Glacial Maximum with the Ryukyu Islands as one of the probable origin spots; in contrast, the frequency of the D4 haplogroup is relatively high in East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
n populations, including in Japan, indicating immigrant Yayoi people, probably by the end of the late Kaizuka period, while haplogroup B4 presumably ancient aboriginal Taiwanese
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 5 ...
ancestry. However, as in the contemporary Japanese population M7 showed a decrease, whereas the frequency of the haplogroup N9b showed an increase from the south to north direction, it indicates that the mobility pattern of females and males was different as the distribution of Y haplogroups do not show a geographical gradient in contrast to mtDNA, meaning mainly different maternal origins of the contemporary Ryukyuan and Ainu people.
 The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a
The research on the contemporary Okinawan male Y chromosome showed, in 2006; 55.6% of haplogroup D-P-M55, 22.2% O-P31, 15.6% O-M122, 4.4% C-M8, and 2.2% others. It is considered that the Y haplogroups expanded in a demic diffusion
Demic diffusion, as opposed to trans-cultural diffusion, is a demographic term referring to a migratory model, developed by Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, of population diffusion into and across an area that had been previously uninhabited by that gro ...
. The haplogroups D and C are considered of Neolithic and Paleolithic origin, with coalescence time of 19,400 YBP and expansion 12,600 YBP (14,500 YBP and 10,820 YBP respectively), and were isolated for thousands of years once land bridges between Japan and continental Asia disappeared at the end of the last glacial maximum 12,000 YBP. The haplogroup O began its expansion circa 4,000-3,810 years ago, and thus the haplogroups D-M55 and C-M8 belong to the Jomon's male lineage, and haplogroup O belongs to the Yayoi's male lineage. Haplogroup M12 is considered as mitochondrial counterpart of Y chromosome D lineage. This rare haplogroup was detected only in Yamato Japanese, Koreans, and Tibetans, with the highest frequency and diversity in Tibet.
A genetic and morphological analysis in 2021 by Watanabe et al., found that the Ryukyuans are most similar to the southern Jōmon people of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
, Shikoku
is the smallest of the four main islands of Japan. It is long and between wide. It has a population of 3.8 million (, 3.1%). It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include ''Iyo-no-futana-shima'' (), '' ...
, and Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separ ...
. Southern Jōmon samples were found to be genetically close to contemporary East Asian people
East Asian people (East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of the ...
, and quite different from Jōmon samples of Hokkaido and Tohoku. Haplogroup D-M55
Haplogroup D-M55 (M64.1/Page44.1) also known as Haplogroup D1a2a is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of Haplogroup D1a. The other is D1a1, which is found with high frequency in Tibetans and other Tibeto-Burmese populations and ...
has the highest diversity within southern Japanese and Ryukyuans, suggesting a dispersal from southwestern Japan towards the North, replacing other Jōmon period lineages through genetic drift. Haplogroup D (D1) can be linked to an East Asian source population from the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
("East Asian Highlanders"), which contributed towards the Jōmon period population of Japan, and less to ancient Southeast Asians. Southern Jōmon people were found to share most SNPs alleles with Tujia people
The Tujia ( Northern Tujia: ''Bifjixkhar'' / ''Bifzixkar'', IPA: , Southern Tujia: ''Mongrzzir'', ; ) are an ethnic group and, with a total population of over 8 million, the eighth-largest officially recognized ethnic minority in the People's ...
, Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live ...
, Miao people
The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in Southern China and Southeast Asia, who are recognized by the government of China as one of the 56 List of ethnic groups in China, official ethnic groups. The Miao live primarily in ...
, and Tripuri people
The Tripuri (also known as Tripura, Tipra, Tiprasa, Twipra) are an ethnic group originating in the Indian state of Tripura. They are the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through the ...
, rather than Ainu.
Anthropological studies
The comparative studies on the dental diversity also showed long-term gene flow from outside source (main-island Honshu and from the southern part of East Asia), long-term isolation, and genetic drift which produced the morphological diversification of the modern Ryukyuans. However, the analysis contradicts the idea of homogeneity among the Jōmon people and a closer affinity between the Ainu and the Ryukyuans. A recent craniometric study shows that the Ryukyuan people are closely related to the Yamato people and their common main ancestors, theYayoi people
The were an ancient ethnicity that migrated to the Japanese archipelago from Korea and China during the Yayoi period (300 BCE–300 CE). Although highly controversial, a single study that utilized radiometric dating techniques inconclusively ...
. The Ryukyuans differ strongly from the Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Y ...
, which, according to the authors, is a strong evidence for the heterogeneity of the Jōmon period population.
As previous morphological studies, such as Kondo et al. 2017, the genetic and morphological analysis by Watanabe et al. 2021, confirmed that the Jōmon period people were heterogeneous and differed from each other depending on the region. A North-to-South cline was detected, with the southern Jōmon of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
, Shikoku
is the smallest of the four main islands of Japan. It is long and between wide. It has a population of 3.8 million (, 3.1%). It is south of Honshu and northeast of Kyushu. Shikoku's ancient names include ''Iyo-no-futana-shima'' (), '' ...
and southwestern Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separ ...
being closer to contemporary East Asian people
East Asian people (East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of the ...
, while the northern Jōmon of Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
and Tohoku being more distant from East Asians. The study results confirmed the "dual-structure theory" regarding the origin of modern Japanese and Ryukyuans, but found that noteworthy amount of East Asian associated alleles were already present within the Jōmon period people prior to the migration of continental East Asians during the Yayoi period. The southern Jōmon, which are ancestral to the Ryukyuans, were anthropologically most similar to modern day East Asians and differed from Jōmon period samples of Hokkaido quite noteworthy.
Challenging the notion of ethnic homogeneity in Japan
The existence of the Ryukyuan challenge the notion of ethnic homogeneity in post-WWII Japan. After the demise of the multi-ethnicEmpire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
in 1945, successive governments had forged a single Japanese identity
is a genre of texts that focus on issues of Japanese national and cultural identity.
The concept became popular after World War II, with books and articles aiming to analyze, explain, or explore peculiarities of Japanese culture and mentality, u ...
by advocating monoculturalism
Monoculturalism is the policy or process of supporting, advocating, or allowing the expression of the culture of a single social or ethnic group. It generally stems from beliefs within the dominant group that their cultural practices are superior t ...
and denying the existence of ethnic minority groups. The notion of ethnic homogeneity was so ingrained in Japan that the former Deputy Prime Minister Taro Aso
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Africa ...
notably claimed in 2020 that “No other country but this one has lasted for as long as 2,000 years with one language, one ethnic group and one dynasty”. Aso's comment sparked strong criticism from Ryukyuan community.
History
Early history
The Ryukyu Islands were inhabited from at least 32,000–18,000 years ago, but their fate and relation with contemporary Ryukyuan people is uncertain. During theJōmon period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a c ...
(i.e., Kaizuka) or so-called shell midden period (6,700–1,000 YBP
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Becaus ...
) of the Northern Ryukyus, the population lived in a hunter-gatherer society, with similar mainland Jōmon pottery
The is a type of ancient earthenware pottery which was made during the Jōmon period in Japan. The term "Jōmon" () means "rope-patterned" in Japanese, describing the patterns that are pressed into the clay.
Outline
Oldest pottery in Jap ...
. In the latter part of Jōmon period, archaeological sites moved near the seashore, suggesting the engagement of people in fishery. It is considered that from the latter half of Jōmon period, the Ryukyu Islands developed their own culture. Some scholars consider that the language and cultural influence was more far-reaching than blending of race and physical types. The Yayoi culture which had a major influence on the Japanese islands, is traditionally dated from 3rd century BCE and recently from around 1000 BCE, and is notable for the introduction of Yayoi-type pottery, metal tools and cultivation of rice, however although some Yayoi pottery
Yayoi pottery (弥生土器 Yayoi doki) is earthenware pottery produced during the Yayoi period, an Iron Age era in the history of Japan, by an Island which was formerly native to Japan traditionally dated 300 BC to AD 300. The pottery allow ...
and tools were excavated on the Okinawa Islands, the rice was not widely cultivated before the 12th century CE, nor the Yayoi and the following Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(250–538 CE) culture expanded into the Ryukyus. The Southern Ryukyus culture was isolated from the Northern, and its Shimotabaru period (4,500–3,000 YBP) was characterized by a specific style of pottery, and the Aceramic period (2,500–800 YBP), during which no pottery was produced in this region. Their prehistoric Yaeyama culture showed some intermingled affinities with various Taiwanese cultures, broadly, that the Sakishima Islands
The (or 先島群島, ''Sakishima-guntō'') (Okinawan language, Okinawan: ''Sachishima'', Miyakoan language, Miyako: ''Saksїzїma'', Yaeyama language, Yaeyama: ''Sakїzїma'', Yonaguni language, Yonaguni: ''Satichima'') are an archipelago loca ...
have some traces similar to the Southeast Asian and South Pacific cultures. The Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is an archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is southwest o ...
seem to be the islands with the most mainland Japanese influence. However, both north and south Ryukyus were culturally unified in the 10th century.
The finding of ancient Chinese knife money
Knife money is the name of large, cast, bronze, knife-shaped commodity money produced by various governments and kingdoms in what is now China, approximately 2500 years ago. Knife money circulated in China between 600 and 200 B.C. during the Zh ...
near Naha
is the capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 persons per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). The total area i ...
in Okinawa indicate a probable contact with the ancient Chinese state Yan
Yan may refer to:
Chinese states
* Yan (state) (11th century – 222 BC), a major state in northern China during the Zhou dynasty
* Yan (Han dynasty kingdom), first appearing in 206 BC
* Yan (Three Kingdoms kingdom), officially claimed indepe ...
as early as the 3rd century BCE. According to the , the Yan had relations with the Wa ('dwarf', 'short') people living southeast of Korea, who could be related to both the mainland Japanese or Ryukyuan people. The futile search for the elixir of immortality by Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor ( ...
, the founder of the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), ...
(221–206 BCE), in which the emperor tried to cooperate with "happy immortals" who dwelt on the islands, could be related to both Japan and Ryukyu Islands. There is a lack of evidence that the missions by the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
(206 BCE–220 CE) reached the islands; however, as the Japanese did reach Han's capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
, notes from 57 CE do mention a general practice of tattooing among the people of "hundred kingdoms" in the eastern islands, a practice which was widespread and survived only among the Okinawan's women, Ainu in Hokkaido, and Atayal people
The Atayal (), also known as the Tayal and the Tayan, are a Taiwanese indigenous people. The Atayal people number around 90,000, approximately 15.9% of Taiwan's total indigenous population, making them the third-largest indigenous group. The pre ...
in Taiwan. Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < (220–265) and Han dynasty records show that the inhabitants of western and southern Japan and Okinawa had a lot in common regarding political-social institutions until the 2nd century CE – they were of small stature, bred
 The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from
The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from
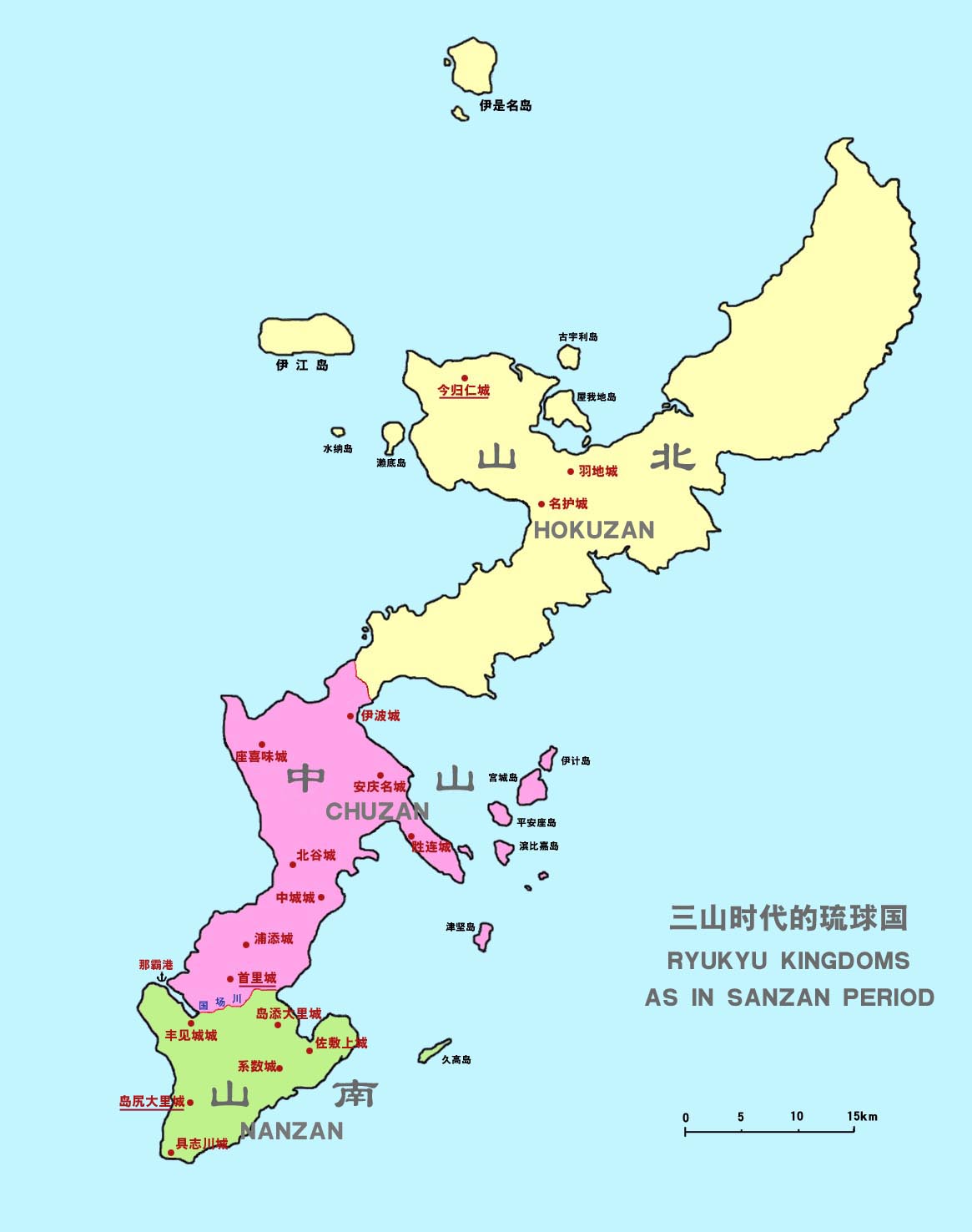 During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson,
During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson,
 Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain
Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain
 During the
During the
 Native
Native
Ryukyuans (Okinawans)
-
Okinawa Peace Network of Los Angeles
- featuring information about Ryukyuan culture worldwide {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyuan People Ethnic groups in Japan Ethnic groups in Brazil Ryukyu Islands Indigenous peoples of East Asia History of Northeast Asia
oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
and swine, and were ruled by women, with a special influence of women sorceresses, related to the Ryukyuan Noro priestesses which were closely associated with local political power until the 20th century, as well as with the Ryukyuan swine economy culture until World War II. It is suggested that the mention of a specific sorceress Pimeku, her death and successive conflict, is related to some socio-political challenges of the ancient matriarchal system.
The first certain mention of the islands and its people by the Chinese and Japanese is dated in the 7th century. Emperor Yang of Sui
Emperor Yang of Sui (隋煬帝, 569 – 11 April 618), personal name Yang Guang (), alternative name Ying (), Xianbei name Amo (), also known as Emperor Ming of Sui () during the brief reign of his grandson Yang Tong, was the second emperor of ...
, due to previous tradition, between 607–608 held expeditions in search of the "Land of Happy Immortals". As the Chinese envoy and the islanders linguistically could not understand each other, and the islanders did not want to accept the Sui rule and suzerainty, the Chinese envoy took many captives back to the court. The islands, by the Chinese named Liuqiu (Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the '' Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The ...
: ), would be pronounced by the Japanese as Ryukyu. However, when the Japanese diplomat Ono no Imoko
was a Japanese politician and diplomat in the late 6th and early 7th century, during the Asuka period.
Ono was appointed by Empress Suiko as an official envoy ( Kenzuishi) to the Sui court in 607 (Imperial embassies to China), and he delivere ...
arrived at the Chinese capital he noted that the captives probably arrived from the island of Yaku south of Kyushu. In 616 the Japanese annals for the first time mention the "Southern Islands people", and for the half-century were noted some intruders from Yaku and Tanu Tanu may refer to:
People
* Malietoa Tanumafili I (1879–1939), Samoan prince
* Tanu Nona (1902–1980), Australian pearler and politician
* Tanu Roy (born 1980), Indian actress and model
* Tanu (born 1997), a Finnish/Assyrian rapper
Places
* Ta ...
. According to the , in 698 a small force dispatched by Japanese government successfully claimed the Tane-jima, Yakushima, Amami, Tokunoshima
, also known in English as is an island in the Amami archipelago of the southern Satsunan Islands of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan.
The island, in area, has a population of approximately 27,000. The island is divided into three administrative ...
and other islands. The recorded that the Hayato people
The , which is Japanese for "falcon-people", were a people of ancient Japan who lived in the Satsuma and Ōsumi regions of southern Kyushu during the Nara period. They frequently resisted Yamato rule. After their subjugation they became subjects ...
in southern Kyushu still had female chieftains in the early 8th century. In 699 are mentioned islands Amami and Tokara
The is an archipelago in the Nansei Islands, and are part of the Satsunan Islands, which is in turn part of the Ryukyu Archipelago. The chain consists of twelve small islands located between Yakushima and Amami-Oshima. The islands have a tota ...
, in 714 Shingaki and Kume
is a List of towns in Japan, town located in Shimajiri District, Okinawa, Shimajiri District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. The town consists of the islands of Kume Island, Kume, Ōjima, Ōhajima, Kume Torishima, Torishima, and Iōtorishima. Among ...
, in 720 some 232 persons who had submitted to the Japanese capital Nara, and at last Okinawa in 753. Nevertheless the mention or authority, over the centuries the Japanese influence spread slowly among the communities.
Gusuku period
 The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from
The lack of written record resulted with later, 17th century royal tales both under Chinese and Japanese influence, which were efforts by local chieftains to explain the " divine right" of their royal authority, as well the then-political interests of Tokugawa ''shōguns'' from Minamoto clan
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were excluded from the line of succession and demoted into the ranks of the nobility from 1192 to 1333. The practice was most prevalent during the ...
who wanted to legitimize Japanese domination over Okinawa. The tradition states that the founder of the Tenson dynasty The was the first dynasty in the traditional historiography of the Ryukyu Islands. According to the Ryukyuan creation myth, the Heavenly Emperor (天帝), who lived in the Heavenly ''Gusuku'' (天城), ordered Amamikyu to create the Ryukyu Islands. ...
was a descendant of goddess Amamikyu
Amamichuu, or , is the creation goddess of the Ryukyu Islands in the Ryukyuan religion.
Name
Amamikyu's name comes from the reading of the Chinese characters 阿摩美久 or 阿摩彌姑, which were most likely written ad hoc for the Okinawan lan ...
, and the dynasty ruled 17,000 years and had 25 kings i.e. chieftains. However, the 24th throne was usurped from one of Tenson's descendants by a man named Riyu, who was defeated in revolt led by Shunten
, also known as , was a legendary ruler of Okinawa Island. Shunten is the earliest chief in Okinawa for whom a name is known. He is said to have taken power after defeating an usurper to the throne by the name of Riyū who had overthrown the 25th ...
(1187–1237), lord of Urasoe
is a city located in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. The neighboring municipalities are Naha to the south, Ginowan to the north, and Nishihara to the east. As of November 2012, the city has an estimated population of 113,718 and a population densi ...
. Shunten's parental origin is a matter of debate, according to 17th century romantic tales he was a son of a local Okinawan chief's ('' anji'') daughter and some Japanese adventurer, usually considered Minamoto no Tametomo
, also known as , was a samurai who fought in the Hōgen Rebellion of 1156. He was the son of Minamoto no Tameyoshi, and brother to Yukiie and Yoshitomo.
Tametomo is known in the epic chronicles as a powerful archer and it is said that he onc ...
, while historical and archeological-traditional evidence indicate men from the defeated Taira clan
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history – the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divided ...
who fled Minamoto's clan vengeance. The Shunten dynasty made two additional chieftains, Shunbajunki
was a legendary local ruler of Okinawa Island. Shunbajunki was the second ruler of the Shunten dynasty. He succeeded his father Shunten in 1237.Kerr,
Shunbajunki's reign is noted for the construction of Shuri Castle and the introduction of the ...
(1237-1248) and Gihon
Gihon is the name of the second river mentioned in the second chapter of the biblical Book of Genesis. The Gihon is mentioned as one of four rivers (along with the Tigris, Euphrates, and Pishon) issuing out of the Garden of Eden that branched fr ...
(1248–1259). As Gihon abdicated, his sessei
was the highest government post of the Ryūkyū Kingdom below the king; the ''sessei'' served the function of royal or national advisor. In the Ryukyuan languages, Ryukyuan language at the time, the pronunciation was closer to ''shisshii'', and ha ...
Eiso (1260–1299), who claimed Tenson's descent, founded the Eiso dynasty
The was the third dynasty in the traditional historiography of Okinawa Island. It was established by Eiso in 1259. ''Chūzan Seikan'', the first official history of the Ryūkyū Kingdom, claimed that Eiso was a descendant of the ancient Tenson ...
.
During the Gusuku period
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the '' Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeological ...
(c. 1187–1314), with recent chronology dated from c. 900-950 CE, Okinawans made significant political, social and economical growth. As the center of power moved away from the seashore to inland, the period is named after many ''gusuku
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the ''Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeologica ...
'', castle-like fortifications which were built in higher places. This period is also notable, compared to mainland Japan, for fairly late introduction of agricultural production of rice, wheat, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
and the overseas trading of these goods, as well during Shubanjunki's rule the introduction of Japanese kana
The term may refer to a number of syllabaries used to write Japanese phonological units, morae. Such syllabaries include (1) the original kana, or , which were Chinese characters (kanji) used phonetically to transcribe Japanese, the most pr ...
writing system in its older and simple phonetic form. After the years of famine and epidemic during the Gihon's rule, Eiso introduced regular taxation system (of weapons, grains and cloth) in 1264 and as the government gained strength, the control extended from Okinawa toward the islands of Kume, Kerama, Iheya, and Amami Ōshima (1266). Between 1272 and 1274, as the Mongol invasions of Japan
Major military efforts were taken by Kublai Khan of the Yuan dynasty in 1274 and 1281 to conquer the Japanese archipelago after the submission of the Korean kingdom of Goryeo to vassaldom. Ultimately a failure, the invasion attempts are of mac ...
began, Okinawa on two occasions rejected the Mongols' authority demands. To Eiso's reign period is also ascribed the introduction of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
into Okinawa.
Sanzan period
 During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson,
During the rule of Eiso's great-grandson, Tamagusuku
was a legendary local ruler of Okinawa Island.
According to Ryukyu's official history, Okinawa was split into three polities during the reign of Tamagusuku.Kerr,
He was the third son of Eiji (r. 1309-1313), he was the fourth ruler of the Eis ...
(1314–1336), Okinawa became divided into three polities
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
and began the so-called Sanzan period
The is a period in the history of the Okinawa Islands when three lines of kings, namely , and , are said to have co-existed on Okinawa Island. It is said to have started during King Tamagusuku's reign (traditional dates: 1314–1336) and, accord ...
(1314–1429). The north and largest Hokuzan
, also known as before the 18th century, located in the north of Okinawa Island, was one of three independent political entities which controlled Okinawa in the 14th century during Sanzan period. The political entity was identified as a tiny co ...
polity was the poorest due to forest and mountainous terrain (in which isolation was an advantage), with primitive farming and fishing. The central Chūzan
was one of three kingdoms which controlled Okinawa in the 14th century. Okinawa, previously controlled by a number of local chieftains or lords, loosely bound by a paramount chieftain or king of the entire island, split into these three more so ...
polity was the most advantaged due to its developed castle town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
s and harbor facilities. The south Nanzan
Nanzan (), also known as Sannan (山南) before the 18th century, located in the south of Okinawa Island, was one of three independent political entities which controlled Okinawa in the 14th century. The political entity was identified as a tiny ...
polity was the smallest, but endured because of good castle positions and sea merchants.
In this period another rapid economical, social and cultural development of Ryukyu began as the polities had developed formal trade relations with Japan, Korea and China. During the Satto
Satto (察度) (1321 – November 17, 1395) was King of Chūzan. He is the first ruler of Okinawa Island who was recorded by contemporary sources. His reign was marked by expansion and development of Chūzan's trade relations with other states, ...
's reign, Chūzan made tributary relations with China's Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
in 1374 as the Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398.
As famine, plagues and peasant revolts in ...
sent envoys in 1372 to Okinawa. In the next two decades Chūzan made nine official missions to the Chinese capital, and the formal relations between them endured until 1872 (see Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom were diplomatic missions that were intermittently sent by the Yuan, Ming and Qing emperors to Shuri, Okinawa, in the Ryukyu Islands. These diplomatic contacts were within the Sinocentric system of b ...
). Despite significant Chinese economical, cultural and political influence, the polities continued to maintain strong autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
. In 1392, all three polities began to send extensive missions to the Korean Joseon
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and re ...
kingdom. In 1403, Chūzan made formal relations with the Japanese Ashikaga shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establ ...
, and an embassy
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
was sent to Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
in 1409. The contacts with Siam continued even in 1425, and were newly made with places like Palembang
Palembang () is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River on the eastern lowland of southern Sumatra. It had a population of 1,668,848 at the 2020 Census. Palembang ...
in 1428, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
in 1430, Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
in 1463.
As in 1371, China initiated its maritime prohibition policy (Haijin
The Haijin () or sea ban was a series of related isolationist policies in China restricting private maritime trading and coastal settlement during most of the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty. Despite official proclamations the Ming policy was ...
) to Japan, Ryukyu gained a lot from its position as intermediary
An intermediary (or go-between) is a third party that offers intermediation services between two parties, which involves conveying messages between principals in a dispute, preventing direct contact and potential escalation of the issue. In law ...
in the trade between Japan and China. They shipped horses, sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
and seashells to China, from China brought ceramics, copper, and iron, from southeast Asian countries bought tin, ivory, spices (pepper), wood (sappanwood
''Biancaea sappan'' is a species of flowering tree in the legume family, Fabaceae, that is native to tropical Asia. Common names in English include sappanwood and Indian redwood. Sappanwood is related to brazilwood (''Paubrasilia echinata''), and ...
), which they sold to Japan, Korea or China, as well as transporting Chinese goods to Hakata Bay
is a bay in the northwestern part of Fukuoka city, on the Japanese island of Kyūshū. It faces the Tsushima Strait, and features beaches and a port, though parts of the bay have been reclaimed in the expansion of the city of Fukuoka. The bay ...
from where swords, silver and gold were brought.
In 1392, 36 Chinese families from Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capi ...
were invited by the chieftain of Okinawa Island's central polity (Chūzan) to settle near the port of Naha
is the capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 persons per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). The total area i ...
and to serve as diplomats, interpreters, and government officials. Some consider that many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. From the same year onward Ryukyu was allowed to send official students to China i.e. Guozijian
The Guozijian,Yuan, 194. sometimes translated as the Imperial College, Imperial Academy, Imperial University, National Academy, or National University, was the national central institution of higher learning in Chinese dynasties after the Sui ...
. The tributary relationship with China later became a basis of the 19th century Sino-Japanese disputes about the claims of Okinawa.
Ryukyu Kingdom
 Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain
Between 1416 and 1429, Chūzan chieftain Shō Hashi
was the last King of Chūzan and the first king of the Ryukyu Kingdom, uniting the three polities of Chūzan, Hokuzan, and Nanzan by conquest and ending the Sanzan period.
Family
* Father: Shishō
* mother: daughter of Miiko
* Wife: sister of I ...
successfully unified the principalities into the Ryukyuan Kingdom
The Ryukyu Kingdom, Middle Chinese: , , Classical Chinese: (), Historical English names: ''Lew Chew'', ''Lewchew'', ''Luchu'', and ''Loochoo'', Historical French name: ''Liou-tchou'', Historical Dutch name: ''Lioe-kioe'' was a kingdom in th ...
(1429–1879) with the castle town
A castle town is a settlement built adjacent to or surrounding a castle. Castle towns were common in Medieval Europe. Some examples include small towns like Alnwick and Arundel, which are still dominated by their castles. In Western Europe, ...
Shuri as royal capital, founded the First Shō dynasty
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
, and the island continued to prosper through maritime trade, especially tributary relations with the Ming dynasty. The period of Shō Shin
was a king of the Ryukyu Kingdom, the third ruler the second Shō dynasty. Shō Shin's long reign has been described as "the Great Days of Chūzan", a period of great peace and relative prosperity. He was the son of Shō En, the founder of the dyn ...
's (1477–1526) rule, descendant from the Second Shō dynasty
The was the last dynasty of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1469 to 1879, ruled by the under the title of King of Chūzan. This family took the family name from the earlier rulers of the kingdom, the first Shō family, even though the new royal famil ...
, is notable for peace and relative prosperity, peak in overseas trade, as well as expansion of the kingdom's firm control to Kikaijima
is one of the Satsunan Islands, classed with the Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa.
The island, in area, has a population of approximately 7,657 persons. Administratively the island forms the town of Kikai, Kagoshima Prefect ...
, Miyako-jima
is the largest and the most populous island among the Miyako Islands of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Miyako Island is administered as part of the City of Miyakojima, which includes not only Miyako Island, but also five other populated islands. ...
and Yaeyama Islands
The Yaeyama Islands (八重山列島 ''Yaeyama-rettō'', also 八重山諸島 ''Yaeyama-shotō'', Yaeyama: ''Yaima'', Yonaguni: ''Daama'', Okinawan: ''Yeema'', Northern Ryukyuan: ''Yapema'') are an archipelago in the southwest of Okinawa ...
(1465–1524), while during Shō Sei
was king of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1526 to 1555.Kerr, George H. (2000). He was the fifth son of King Shō Shin, who he succeeded.
Shō Sei suppressed a rebellion on Amami Ōshima in 1537 and took steps to improve defenses against '' wakō'' th ...
(1526-1555) to Amami Ōshima
, also known as Amami, is the largest island in the Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa. It is one of the Satsunan Islands.
The island, 712.35 km2 in area, has a population of approximately 73,000 people. Administratively it is d ...
(1537).
After the Kyūshū Campaign
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
(1586–1587) by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
, his assistant Kamei Korenori
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' who lived through the early Edo period. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003).html" ;"title="DF 23 of 80">"Kamei" at ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p ...
, who was interested in southern trade, wanted to be rewarded with the Ryukyu Islands. A paper fan found during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
mentioning a title "Kamei, Lord of Ryukyu", reveals that Hideyoshi at least nominally offered the post although he had no legitimate claim upon the islands. In 1591, Kamei ventured with a force to reclaim the islands, but the Shimazu clan
The were the ''daimyō'' of the Satsuma han, which spread over Satsuma, Ōsumi and Hyūga provinces in Japan.
The Shimazu were identified as one of the '' tozama'' or outsider ''daimyō'' familiesAppert, Georges ''et al.'' (1888). in contrast ...
stopped him as they guarded their special relationship with the Ryukyu kingdom. Hideyoshi was not very concerned about the quarrel because the invasion of Korea was more important in his mind. As the Ming's influence weakened due to disorder in China, Japanese established posts in Southeast Asia, and the Europeans (Spanish and Portuguese) arrived, the kingdom's overseas trade began to decline.
In the early 17th century during the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
(1603–1867), the first ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakur ...
'' Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fellow ...
intended to subject the kingdom to enable intermediary trade with China, and in 1603 ordered the Ryukyuan king to pay his respect to the shogunate. As the king did not react, with the instruction of the ''shōgun'', the Satsuma feudal domain of the Shimazu clan in Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
incorporated some of kingdom's territory during the 1609 Invasion of Ryukyu
The by forces of the Japanese feudal domain of Satsuma took place from March to May of 1609, and marked the beginning of the Ryukyu Kingdom's status as a vassal state under the Satsuma domain. The invasion force was met with stiff resistance f ...
. They nominally let a certain level of autonomy and independence to the kingdom due to Ming's prohibition of trade with the shogunate, but forbade them trade with other countries except China. The Amami Islands became part of Shimazu's territory, taxes were imposed, making them subordinate in the relations between Japan and China. Until the invasion, the Shimazu clan lords for four centuries had a vague title of the "Lords of the Twelve Southern Islands" or "Southern Islands", although initially meaning the near Kyushu islands, then covering all the Ryukyu Islands. Later in the 1870s this was used as a "justification" of Japan's sovereignty. From 1609 the Ryukyuan missions to Edo
Over the course of Japan's Edo period, the Ryūkyū Kingdom sent eighteen , the capital of Tokugawa Japan. The unique pattern of these diplomatic exchanges evolved from models established by the Chinese, but without denoting any predetermined re ...
started which lasted until 1850.
During the rule of kings Shō Shitsu
was a king of the Ryukyu Kingdom who held the throne from 1648 until his death in 1668.
The fourth son of King Shō Hō, he was named Prince of Sashiki in 1637, at the age of eight, and was granted Sashiki, Okinawa, Sashiki ''magiri'' as his doma ...
(1648–1668) and Shō Tei (1669–1709) i.e. sessei
was the highest government post of the Ryūkyū Kingdom below the king; the ''sessei'' served the function of royal or national advisor. In the Ryukyuan languages, Ryukyuan language at the time, the pronunciation was closer to ''shisshii'', and ha ...
Shō Shōken
, also known as , was a Ryukyuan scholar and served as ''sessei'', a post often translated as "prime minister," from 1666 to 1673. Shō wrote the first history of the Ryukyu Kingdom, , and enacted a number of practical political reforms aimed at i ...
(1666–1673) were recovered the internal social and economical stability with many laws about government organisation, and affairs like sugarcane production, and tax system with emphasis on agricultural production. The production was encouraged because Satsuma's annual tax deprived Ryukyu's internal resources. Although the production of sweet potatoes and sugar industry grew, the peasants were not allowed to enlarge their fields. The agricultural reforms especially continued under king Shō Kei
was king of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1713–1752. His reign, strongly guided by royal advisor Sai On, is regarded as a political and economic golden age and period of the flowering of Okinawan culture."Shō Kei." ''Okinawa rekishi jinmei jiten'' (� ...
(1713–1752) and his sanshikan
The ''Sanshikan'' (), or Council of Three, was a government body of the Ryūkyū Kingdom, which originally developed out of a council of regents.
It emerged in 1556, when the young Shō Gen, who was speech disorder, mute, ascended to the throne of ...
advisor Sai On
(1682–1762), or Cai Wen in Chinese, also known as , was a scholar-bureaucrat official of the Ryūkyū Kingdom, serving as regent, instructor, and advisor to King Shō Kei. He is renowned for the many reforms he initiated and oversaw, and is amon ...
(1728–1752) whose ''Nomucho'' (Directory of Agricultural Affairs) from 1743 became the basis of the agricultural administration until the 19th century. In the Sakishima Islands great part of the tax was paid in textiles made of ramie. The relations with the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
improved after their second mission when the first Ryukyuan official students were sent to China in 1688.
In the first half of the 19th century, French politicians like Jean-Baptiste Cécille
Jean-Baptiste Thomas Médée Cécille (16 October 1787, Rouen – 9 November 1873) was a French Admiral and politician who played an important role in the French intervention of Vietnam. He also circumnavigated the globe.
Military career
In ...
unsuccessfully tried to conclude a French trade treaty with Ryukyu, with only a promise by Shuri government about the admission of Christian missionaries. However, due to extreme measures in teaching, Bernard Jean Bettelheim's propagation of Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
between 1846–1854 was obscured by the government.
Meiji period
Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
(1868–1912) the process began, according to which the Ryukyuan Kingdom came under the jurisdiction of Kagoshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,599,779 (1 January 2020) and has a geographic area of 9,187 km2 (3,547 sq mi). Kagoshima Prefecture borders Kumamoto P ...
in 1871, encompassing the southern tip of Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
and the Ryukyuan islands to its south; this created the Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, before becoming the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islands at the Pacific edge of the East China Sea.
When the domain was created in 1872, Japan's feudal han ...
(1872–1879) of Meiji-era Japan. This method of gradual integration was designed to avoid both Ryukyuan and Chinese protests, with the ruling Shuri government unaware of the significance of these developments, including Japan's decision to grant political representation to the Ryukyuan islanders involved in the Japanese invasion of Taiwan (1874)
The Japanese punitive expedition to Taiwan in 1874, referred to in Japan as the and in Taiwan and Mainland China as the Mudan incident (), was a punitive expedition launched by the Japanese in retaliation for the murder of 54 Ryukyuan sailo ...
.
In 1875, the Ryukyuan people were forced to terminate their tributary relations with China, against their preference for a state of dual allegiance to both China and Japan, something a then-weakened China was unable to stop. A proposal by the 18th U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
for a sovereign Okinawa and the division of the other islands between China and Japan was rejected, with a last-minute decision by the Chinese government not to ratify the agreement rendering it null. On three occasions between 1875 and 1879, the last Ryukyuan King, Shō Tai
was the last king of the Ryukyu Kingdom (8 June 1848 – 10 October 1872) and the head of the Ryukyu Domain (10 October 1872 – 27 March 1879). His reign saw greatly increased interactions with travelers from abroad, particularly from Europe a ...
, refused to submit to the demands placed upon his people, and in 1879, his domain was formally abolished and established as Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city o ...
, forcing his move to Tokyo with the reduced status of Viscount.
Members of the Ryukyuan aristocratic classes such as Kōchi Chōjō
was a Ryukyuan aristocrat known for leading a movement to petition the government of Qing Dynasty China to rescue the Ryūkyū Kingdom from annexation by Imperial Japan, following the 1872 announcement by the government of Meiji Japan to do so.
...
and Rin Seikō continued to resist annexation for almost two decades; however, following the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the po ...
(1894-1895), both Chinese and Ryukyuan interest in sovereignty faded as China renounced its claims to the island. Many historians criticise Meiji-era Japan's characterisation of the process as being considered a relatively simple administrative change, rather than the creation of Japan's first colony and the beginning of its 'inner colonialism'.
During the Meiji period, as with the Ainu people
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Y ...
of Hokkaido, the Ryukyuan people had their own culture, religion, traditions and language suppressed by the Meiji government in the face of forced assimilation. From the 1880s onwards, schools forbade the display of Ryukyuan styles of dress, hairstyles and other visual aspects, considering them to be backwards and inferior, with students forced to wear Japanese clothing and to assimilate into Japanese culture. Indoctrination into a militaristic and Emperor-centred ideology for children began from the age of beginning elementary school onwards; the ultimate goal of this education was a total unification of the Ryukyuan people into the Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
, embodying the ideal of ethnic purity, with contemporary literature for the time ignoring Japan's minorities). Ryukyuans often faced prejudice, humiliation in the workplace and ethnic discrimination, with the Ryukyuan elite divided into factions either in support of or in opposition to assimilation.
Around and especially after the Japanese annexation of Taiwan in 1895, Japan's developmental focus shifted away from Okinawa, resulting in a period of famine known as ("Cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk (botany), trunk with a crown (botany), crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants o ...
hell"). Between 1920 and 1921, a fall in sugar prices, as well as the transfer of Japan's sugar production to Taiwan, led to Ryukyu being the poorest prefecture, despite having the heaviest taxation burden; the drop in sugar prices would continue into 1931, further worsening the situation. As a result of the ensuing economic crisis, many people were forced to either find work in Japan (often Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
and Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
) or abroad in Taiwan. By 1935, roughly 15% of the population had emigrated.
WW2 and modern history
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and battles like the Battle of Okinawa
The , codenamed Operation Iceberg, was a major battle of the Pacific War fought on the island of Okinawa by United States Army (USA) and United States Marine Corps (USMC) forces against the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA). The initial invasion of ...
(1945), approximately 150,000 civilians (1/3 of the population) were killed in Okinawa alone. After the war, the Ryukyu Islands were occupied by the United States Military Government of the Ryukyu Islands
The , also referred to as U.S. Ryukyu Islands, was the government in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan (centered on the Okinawa Island) from 1945 to 1950, whereupon it was replaced by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands (USCAR) ...
(1945–1950), but the U.S. maintained control even after the 1951 Treaty of San Francisco
The , also called the , re-established peaceful relations between Japan and the Allied Powers on behalf of the United Nations by ending the legal state of war and providing for redress for hostile actions up to and including World War II. It w ...
, which went into effect on April 28, 1952, as the USMMGR was replaced by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands
The was the civil administration government in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan (centered on Okinawa Island), replacing the United States Military Government of the Ryukyu Islands (itself created at the conclusion of World War II) in 1950, and functio ...
(1950–1972). During this period the U.S. military requisitioned private land for the building of their facilities, with the former owners put into refugee camps, and its personnel committed thousands of crimes against the civilians. Only twenty years later, on 15 May 1972, Okinawa and nearby islands were returned to Japan. Whereas the Japanese had enjoyed political freedom and economic prosperity in the post-war years, the facilities, used for the purposes of Japanese regional security against the communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
threat
A threat is a communication of intent to inflict harm or loss on another person. Intimidation is a tactic used between conflicting parties to make the other timid or psychologically insecure for coercion or control. The act of intimidation for co ...
, had a negative economic impact on the Islands, leading to many Ryukyuans feeling cheated, some considering the facilities a national disgrace. Since 1972 there have been extensive plans to bring Okinawa's economy up to the national level, as well continued support for the local culture and a revival of traditional arts started by the USCAR.
Okinawa comprises just 0.6% of Japan's total land mass, yet about 75 percent of all U.S. military installations stationed in Japan are assigned to bases in Okinawa. The presence of the military remains a sensitive issue in local politics. Negative feelings toward the mainland Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
, Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
(especially Hirohito
Emperor , commonly known in English-speaking countries by his personal name , was the 124th emperor of Japan, ruling from 25 December 1926 until his death in 1989. Hirohito and his wife, Empress Kōjun, had two sons and five daughters; he was ...
due to his involvement in the sacrifice of Okinawa and later military occupation), and U.S. military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
(USFJ
is a subordinate unified command of the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). It was activated at Fuchū Air Station in Tokyo, Japan, on 1 July 1957 to replace the Far East Command. USFJ is commanded by the Commander, US Forces ...
, SACO) have often caused open criticism and protests, for example by 85,000 people in 1995 after the U.S. military rape incident, and by 110,000 people in 2007 due to the Japanese Ministry of Education
An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ...
's textbook revisions (see MEXT controversy) which critics say downplays the involvement of the Japanese military in the forced mass suicide of the civilians during the Battle of Okinawa. For many years the Emperors avoided visiting Okinawa, with the first ever in history done by Akihito
is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 7 January 1989 until his abdication on 30 April 2019. He presided over the Heisei era, ''Heisei'' being an expression of achieving peace worldwide.
Bo ...
in 1993, since it was assumed that his visits would likely cause uproar, as in July 1975 when Akihito as a crown prince visited Okinawa and a firebomb was thrown at him, although these tensions have eased in recent years. Discrimination against Okinawans both past and present on the part of the mainland Japanese is the cause of their smoldering resentment against the government. There is a small post-war Ryukyu independence movement
The or the Republic of the Ryukyus (Japanese: , Kyūjitai: , Hepburn: ) is a political movement advocating for the independence of the Ryukyu Islands (commonly referred to as Okinawa after the largest island) from Japan.
The current political ...
, but there are also Okinawans who wish to be assimilated with the mainland. A poll in 2017 by the Okinawa Times, Asahi Shimbun and Ryukyusu Asahi Broadcasting Corporation (QAB) jointly conducted prefectural public opinion surveys for voters in the prefecture. 82% of Okinawa citizens chose "I'm glad that Okinawa has returned as a Japanese prefecture". It was 90% for respondents of the ages of 18 to 29, 86% for those in their 30s, 84% for those aged 40–59, 72% for respondents in their 60s, 74% for those over the age of 70.
Demography
Ryukyuans tend to see themselves as bound together by their home island and, especially among older Ryukyuans, usually consider themselves fromOkinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
first and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
second. The average annual income per resident of Okinawa in 2006 was ¥2.09 million, placing the prefecture at the bottom of the list of 47.
The Okinawans have a very low age-adjusted mortality rate at older ages and among the lowest prevalence of cardiovascular disease and other age-associated diseases in the world. Furthermore, Okinawa has long had the highest life expectancy at older ages, as well has had among the highest prevalence of centenarian
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100 years. Because life expectancies worldwide are below 100 years, the term is invariably associated with longevity. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living cente ...
s among the 47 Japanese prefectures, also the world, since records began to be kept by the Ministry of Health in the early 1960s despite the high birth rate and expanding population of Okinawa prefecture. This longevity phenotype has been in existence since records have been kept in Japan, and despite the well-known dietary and other nongenetic lifestyle advantages of the Okinawans ( Blue Zone), there may be some additional unknown genetic influence favoring this extreme phenotype. The Okinawa Centenarian Study (OCS) research team began to work in 1976, making it the world's longest ongoing population-based study of centenarians.
Culture
Language
Similarities between the Ryukyuan andJapanese language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been ma ...
s points to a common origin, possibly of immigrants from continental Asia to the archipelago. Although previously ideologically considered by Japanese scholars as a Japanese dialect and a descendant of Old Japanese
is the oldest attested stage of the Japanese language, recorded in documents from the Nara period (8th century). It became Early Middle Japanese in the succeeding Heian period, but the precise delimitation of the stages is controversial.
Old Jap ...
, modern linguists such as Thomas Pellard (2015) now classify the Ryukyuan languages as a distinct subfamily of Japonic
Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan, sometimes also Japanic, is a language family comprising Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and ...
that diverged before the Old Japanese period (c. 8th century CE); this places them in contrast to Japonic languages that are direct descendants of Old Japanese, namely Japanese and Hachijō. Early literature which records the language of the Old Japanese
is the oldest attested stage of the Japanese language, recorded in documents from the Nara period (8th century). It became Early Middle Japanese in the succeeding Heian period, but the precise delimitation of the stages is controversial.
Old Jap ...
imperial court shows archaisms which are closer to Okinawan dialects, while later periods of Japanese exhibit more significant Sinicization
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies come under the influence of Chinese culture, particularly the language, societal norms, cul ...
(such as Sino-Japanese vocabulary
Sino-Japanese vocabulary, also known as refers to Japanese vocabulary that had originated in Chinese or were created from elements borrowed from Chinese. Some grammatical structures and sentence patterns can also be identified as Sino-Japanese. Si ...
) than most Ryukyuan languages. This can be attributed to the fact that the Japanese (or Yamato people
The (or the )David Blake Willis and Stephen Murphy-Shigematsu''Transcultural Japan: At the Borderlands of Race, Gender and Identity,'' p. 272: "“Wajin,” which is written with Chinese characters that can also be read “Yamato no hito” (Ya ...
) received writing from the Sinosphere
The East Asian cultural sphere, also known as the Sinosphere, the Sinic world, the Sinitic world, the Chinese cultural sphere, the Chinese character sphere encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically ...
roughly a millennium before the Ryukyuan languages.
As the Jōmon-Yayoi transition (c. 1000 BCE) represents the formative period of the contemporary Japanese people from a genetic standpoint, it is argued that the Japonic languages are related to the Yayoi migrants as well. The estimated time of separation between Ryukyuan and mainland Japanese is a matter of debate due to methodological problems; older estimates (1959–2009) varied between 300 BCE and 700 CE, while novel (2009–2011) around 2nd century BCE to 100 CE, which has a lack of correlation with archeology and new chronology according to which Yayoi period started around 950 BCE, or the proposed spread of the Proto-Ryukyuan speakers to the islands in the 10–12th century from Kyushu. Based on linguistic differences, they separated at least before the 7th century, before or around Kofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(c. 250–538), while mainland Proto-Ryukyuan was in contact with Early Middle Japanese
is a stage of the Japanese language between 794 and 1185, which is known as the Heian Period(). The successor to Old Japanese(), it is also known as Late Old Japanese. However, the term "Early Middle Japanese" is preferred, as it is closer to L ...
until 13th century.
The Ryukyuan languages can be subdivided into two main groups, Northern Ryukyuan languages
The Northern Ryukyuan languages are a group of languages spoken in the Amami Islands, Kagoshima Prefecture and the Okinawa Islands, Okinawa Prefecture of southwestern Japan. It is one of two primary branches of the Ryukyuan languages, which are t ...
and Southern Ryukyuan languages. The Southern Ryukyuan subfamily shows north-to-south expansion, while Northern Ryukyuan does not, and several hypothetical scenarios can be proposed to explain this. It is generally considered that the likely homeland of Japonic—and thus the original expansion of Proto-Ryukyuan—was in Kyushu, though an alternate hypothesis proposes an expansion from the Ryukyu Islands to mainland Japan.
Although authors differ regarding which varieties are counted as dialects or languages, one possible classification considers there to be five Ryukyuan languages: Amami, Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
, Miyako, Yaeyama and Yonaguni
, one of the Yaeyama Islands, is the westernmost inhabited island of Japan, lying from the east coast of Taiwan, between the East China Sea and the Pacific Ocean proper. The island is administered as the Towns of Japan, town of Yonaguni, Okina ...
, while a sixth, Kunigami
is a village in Kunigami District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It occupies the north tip of Okinawa Island, with the East China Sea to the west, Pacific Ocean to the east, and villages of Higashi and Ōgimi to the south.
As of 2015, the village ...
, is sometimes differentiated from Okinawan due to its diversity. Within these languages exist dialects of local towns and specific islands, many of which have gone extinct. Although the Shuri dialect of Okinawan was historically a prestige language
Prestige refers to a good reputation or high esteem; in earlier usage, ''prestige'' meant "showiness". (19th c.)
Prestige may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Films
* ''Prestige'' (film), a 1932 American film directed by Tay Garnett ...
of the Kingdom of Ryukyu
The Ryukyu Kingdom, Middle Chinese: , , Classical Chinese: (), Historical English names: ''Lew Chew'', ''Lewchew'', ''Luchu'', and ''Loochoo'', Historical French name: ''Liou-tchou'', Historical Dutch name: ''Lioe-kioe'' was a kingdom in the ...
, there is no officially standardized Ryukyuan language. Thus, the Ryukyuan languages as a whole constitute a cluster of local dialects that can be considered unroofed abstand languages.
During the Meiji and post-Meiji period, the Ryukyuan languages were considered to be dialects of Japanese and viewed negatively. They were suppressed by the Japanese government in policies of forced assimilation and into using the standard Japanese language. From 1907, children were prohibited to speak Ryukyuan languages in school, and since the mid-1930s there existed dialect card
A was a system of punishment used in Japanese regional schools in the post-Meiji period to promote standard speech.
During the Edo period under the Tokugawa shogunate most Japanese people could not travel outside of their home domain. As a resul ...
s, a system of punishment for the students who spoke in a non-standard language. Speaking a Ryukyuan language was deemed an unpatriotic act; by 1939, Ryukyuan speakers were denied service and employment in government offices, while by the Battle of Okinawa in 1945, the Japanese military was commanded to consider Ryukyuan speakers as spies to be punished by death, with many reports that such actions were carried out. After World War II, during the United States occupation, the Ryukyuan languages and identity were distinctively promoted, also because of ideo-political reasons to separate the Ryukyus from Japan. However, resentment against the American occupation intensified Ryukyuans' rapport and unification with Japan, and since 1972 there has followed re-incursion of the standard Japanese and further diminution of the Ryukyuan languages.
It is considered that contemporary people older than 85 exclusively use Ryukyuan, between 45 and 85 use Ryukyuan and standard Japanese depending on family or working environment, younger than 45 are able to understand Ryukyuan, while younger than 30 mainly are not able to understand nor speak Ryukyuan languages. Only older people speak Ryukyuan languages, because Japanese replaced it as the daily language in nearly every context. Some younger people speak Okinawan Japanese which is a type of Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. It is not a dialect of the Okinawan language
The Okinawan language (, , , ) or Central Okinawan, is a Northern Ryukyuan languages, Ryukyuan language spoken primarily in the southern half of the Okinawa Island, island of Okinawa, as well as in the surrounding islands of Kerama Islands, Ker ...
. The six Ryukyuan languages are listed on the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger
The UNESCO ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' is an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' as a title in print after a ...
since 2009, as they could disappear by the mid-century (2050). It is unclear whether this recognition was too late, despite some positive influence by the Society of Spreading Okinawan.
Religion
 Native
Native Ryukyuan religion
The Ryukyuan religion (琉球信仰), Ryūkyū Shintō (琉球神道), Nirai Kanai Shinkō (ニライカナイ信仰), or Utaki Shinkō (御嶽信仰) is the indigenous belief system of the Ryukyu Islands. While specific legends and traditions ...
places strong emphasis upon the role of the women in the community, with women holding positions as shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritu ...
s and guardians of the home and hearth. The status of women in traditional society is higher than in China and Japan. Although the contemporary kinship system is patrilineal and patrilocal
In social anthropology, patrilocal residence or patrilocality, also known as virilocal residence or virilocality, are terms referring to the social system in which a married couple resides with or near the husband's parents. The concept of locat ...
, until the 20th century it was often bilateral and matrilocal
In social anthropology, matrilocal residence or matrilocality (also uxorilocal residence or uxorilocality) is the societal system in which a married couple resides with or near the wife's parents. Thus, the female offspring of a mother remain l ...
, with common village endogamy. Shisa
is a traditional Ryukyuan cultural artifact and decoration derived from Chinese guardian lions, often seen in similar pairs, resembling a cross between a lion and a dog, from Okinawan mythology. Shisa are wards, believed to protect from some e ...
statues can often be seen on or in front of houses—this relates to the ancient Ryukyuan belief that the male spirit is the spirit of the outside and the female spirit is the spirit of the inside. Godhood is mimicked with many attributes, and its in ease without any underlying symbolic order.
The village priestesses, Noro, until the 20th century used the white cloth and magatama
are curved, comma-shaped beads that appeared in prehistoric Japan from the Final Jōmon period through the Kofun period, approximately 1000 BCE to the 6th century CE. The beads, also described as "jewels", were made of primitive stone and eart ...
beads. The noro's duty was to preserve the generational fire in the hearth, a communal treasure, resulting with tabu system about the fire custodian in which they had to be virgins to maintain close communication with the ancestors. The office became hereditary, usually of the noro's brother's female child. The center of worship was represented by three heartstones within or near the house. The belief in the spiritual predominance of the sister was more prominent in Southern Ryukyus.
The introduction of Buddhism is ascribed to a 13th century priest from Japan (mostly funeral rites), while the 14th century trade relations resulted with Korean Buddhism
Korean Buddhism is distinguished from other forms of Buddhism by its attempt to resolve what its early practitioners saw as inconsistencies within the Mahayana Buddhist traditions that they received from foreign countries. To address this, the ...
influences (including some in architecture), as well Shinto practices from Japan. Buddhism and native religion were ideological basis until 18th century, when Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
gradually and officially became government ideology during Shō On
was king of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1795 to 1802. He made a great contribution to the education of Ryukyu during his reign.
Shō On was the eldest grandson of the former king, Shō Boku. His father Shō Tetsu died when Shō Boku was still alive, ...
(1795–1802), much to the dismay of Kumemura
was an Okinawan community of scholars, bureaucrats, and diplomats in the port city of Naha near the royal capital of Shuri, which was a center of culture and learning during the time of the Ryukyu Kingdom. The people of Kumemura, traditionally ...
. It was mostly important to the upper class families. Among the Catholic converts was not lost the former religious consciousness.
Until the 18th century, the Ryukyuan kings visited the Sefa-utaki
''Seefa-utaki'', meaning "purified place of Utaki," is a historical sacred space, overlooking Kudaka Island, that served as one of the key locations of worship in the native religion of the Ryukyuan people for millennia. Later as a part of assim ...
(historical sacred place) caves for worship. Another traditional sacred places are springs Ukinju-Hain-ju, where was placed the first rice plantation, and small island Kudaka, where the "five fruits and grains" were introduced by divine people, perhaps strangers with agricultural techniques. The foremost account, which claimed common origin between the Japanese and Ryukyuan people, was made-up by Shō Shōken
, also known as , was a Ryukyuan scholar and served as ''sessei'', a post often translated as "prime minister," from 1666 to 1673. Shō wrote the first history of the Ryukyu Kingdom, , and enacted a number of practical political reforms aimed at i ...
in the 17th century, to end up the pilgrimage of the Ryukyu king and chief priestess to the Kudaka island.
During the Meiji period the government replaced Buddhism with Shintoism as the islands' state religion, and ordered; rearrangement of statues and redesign of shrines and temples to incorporate native deities into national Shinto pantheon; Shinto worship preceded native, Buddhist, or Christian ritual; transformation of local divinities into guardian gods. In the 1920s was ordered building of Shinto shrines and remodelling of previous with Shinto architectural symbols, paid by local tax money, which was a financial burden due to the collapse of sugar prices in 1921 which devastated Okinawa's economy. In 1932 were ordered to house and support Shinto clergy from the mainland.
Most Ryukyuans of the younger generations are not serious adherents of the native religion anymore. Additionally, since being under Japanese control, Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
are also practiced and typically mixed with local beliefs and practices.
Cuisine
Okinawan food is rich invitamin
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an Nutrient#Essential nutrients, essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its ...
s and minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
and has a good balance of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
s, and carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s. Although rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
is a staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
(taco rice
is a popular example of modern Okinawan cuisine. It consists of taco-flavored ground beef served on a bed of rice, frequently served with shredded cheese, shredded lettuce, tomato and salsa.
Charlie's Tacos, serving tacos in shells made from ...
mixes it with beef), pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved; ...
('' mimigaa and chiragaa'', dishes Rafute
Rafute is a pork belly dish in the Okinawan cuisine of the island of Okinawa, Japan. Rafute is skin-on pork belly stewed in soy sauce and brown sugar. It is traditionally considered to help with longevity. Rafute was originally a form of Okinawan ...
and Soki
Soki ( ryu, ソーキ ''sooki'') is a specialty of the cuisine of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Soki are (usually boneless) stewed pork spare ribs, with the cartilage still attached. They are often served with Okinawa soba (called ''suba'').
Dishes ...
), seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
, rich miso
is a traditional Japanese seasoning. It is a thick paste produced by fermenting soybeans with salt and ''kōji'' (the fungus ''Aspergillus oryzae'') and sometimes rice, barley, seaweed, or other ingredients. It is used for sauces and spread ...
(fermented soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu an ...
) pastes and soups ( Jūshī), sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
and brown sugar
Brown sugar is unrefined or partially refined soft sugar.
Brown Sugar may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Brown Sugar'' (1922 film), a 1922 British silent film directed by Fred Paul
* ''Brown Sugar'' (1931 film), a 1931 ...
all feature prominently in native cuisine. Most famous to tourists is the ''Momordica charantia
''Momordica charantia'' (commonly called bitter melon; Goya; bitter apple; bitter gourd; bitter squash; balsam-pear; with many more names listed below) is a tropical and subtropical vine of the family Cucurbitaceae, widely grown in Asia, Afr ...
'', ''gōya'' (bitter melon), which is often mixed into a representative Okinawan stir fry
Stir frying () is a cooking technique in which ingredients are fried in a small amount of very hot oil while being stirred or tossed in a wok. The technique originated in China and in recent centuries has spread into other parts of Asia and t ...
dish known as champurū (Goya champuru
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and ...
). Kōrēgusu
''Kōrēgusu'' ( ja, コーレーグス from ryu, 高麗胡椒 こーれーぐす ''kooreegusu'', a type of hot chili pepper) also called ''kōrēgūsu'' () and ''kōrēgusū'' () is a type of Okinawan chili sauce made of chilis infused in awa ...
is a common hot sauce
Hot sauce is a type of condiment, seasoning, or salsa made from chili peppers and other ingredients. Many commercial varieties of mass-produced hot sauce exist.
History
Humans have used chili peppers and other hot spices for thousands of years ...
condiment
A condiment is a preparation that is added to food, typically after cooking, to impart a specific Flavoring, flavor, to enhance the flavor, or to complement the dish. A table condiment or table sauce is more specifically a condiment that is serv ...
used in various dishes including noodle soup
Noodle soup refers to a variety of soups with noodles and other ingredients served in a light broth. Noodle soup is a common dish across East Asia, Southeast Asia and the Himalayan states of South Asia. Various types of noodles are used, such as ...
Okinawa soba
is a type of noodle produced in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Okinawa soba is a regional collective trademark of The Okinawa Noodle Manufacturing Co-op. On Okinawa, it is sometimes simply called ''soba'' (or ''suba'' in Okinawan dialects), althou ...
. Some specifically consumed algae include Caulerpa lentillifera
''Caulerpa lentillifera'' is a species of ulvophyte green algae from coastal regions in the Asia-Pacific. This seaweed is one of the favored species of edible ''Caulerpa'' due to its soft and succulent texture. It is traditionally eaten in the c ...
. Traditional sweets include chinsuko, hirayachi
is a Japanese savory pancake dish consisting of wheat flour batter and other ingredients (mixed, or as toppings) cooked on a '' teppan'' (flat griddle). Common additions include cabbage, meat, and seafood, and toppings include ''okonomiyaki'' ...
, sata andagi
are sweet deep fried buns of dough similar to doughnuts (or the Portuguese ''malasada'', or the Dutch ''oliebollen''), native to Southern China, there named sa-yung (沙翁, Yale Romanization: sa1yung1, PinYin: ''shā wēng''), then spread to ...
, and muchi
, also known as , is a type of soft confectionery made of pounded glutinous rice and eaten in Okinawa Prefecture. Muchi means "rice cake" in the Okinawan language, sometimes called "Casa Muchi" from the fact that it is wrapped in the leaves of ...
. Local beverages include juice from ''Citrus depressa
''Citrus depressa'' (''Citrus'' × ''depressa'', formerly ''C. pectinifera'', ryu, シークヮーサー/シークァーサー, shiikwaasa, ja, ヒラミレモン, hirami remon or , , in English sometimes called shiikuwasha, shequasar, Taiwan ...
'', turmeric tea (''ukoncha''), and the alcoholic beverage awamori
''Awamori'' (, Okinawan: , āmui'') is an alcoholic beverage indigenous and unique to Okinawa, Japan. It is made from long grain indica rice, and is not a direct product of brewing (like ''sake'') but of distillation (like ''shōchū''). The ...
.
The weight-loss Okinawa diet
The Okinawa diet describes the Okinawan cuisine, eating habits of the indigenous people of the Ryukyu Islands (belonging to Japan), which is believed to contribute to their Longevity in Okinawa, exceptional longevity. It is also the name of a weig ...
derives from their cuisine and has only 30% of the sugar and 15% of the grains of the average Japanese dietary intake.
Arts
The techniques ofself-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force in ...
and using farm tools as weapons against armed opponents—called karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ) is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tii'' in Okinawan) under the ...
by today's martial artists—were created by Ryukyuans who probably incorporated some and native techniques from China into a complete system of attack and defense known simply as (literally meaning "hand"). These martial arts varied slightly from town to town, and were named for their towns of origin, examples being Naha-te
Okinawan martial arts refers to the martial arts, such as karate, tegumi and Okinawan kobudō, which originated among the indigenous people of Okinawa Island. Due to its central location, Okinawa was influenced by various cultures with a long hist ...
(currently known as Goju-Ryū), Tomari-te
Okinawan martial arts refers to the martial arts, such as karate, tegumi and Okinawan kobudō, which originated among the indigenous people of Okinawa Island. Due to its central location, Okinawa was influenced by various cultures with a long hi ...
and Shuri-te
Okinawan martial arts refers to the martial arts, such as karate, tegumi and Okinawan kobudō, which originated among the indigenous people of Okinawa Island. Due to its central location, Okinawa was influenced by various cultures with a long hist ...
.
The Kabura-ya (Japanese signal arrow)
is a type of Japanese arrow used by the samurai class of feudal Japan. Kabura-ya were arrows which whistled when shot and were used in ritual archery exchanges before formal medieval battles.
Like a Wind instrument, the sound was created by ...
still has a ceremonial use for house, village or festival celebration in Okinawa.
It is considered that the rhythms and patterns of dances, like Eisa and Angama, represent legends and prehistoric heritage. Ryūka is a genre of songs and poetry originating from the Okinawa Islands, Okinawa Prefecture of southwestern Japan. Most ryūka are featured by the 8-8-8-6 syllable structure.
Concepts and classification
The word ''ryūka'' ( u:kain archaic pronunciat ...
genre of songs and poetry originate from the Okinawa Islands. From the Chinese traditional instrument in the 16th century developed the Okinawan instrument from which the and the Japanese derive.
Women frequently wore indigo tattoos known as ''hajichi
are traditional tattoos worn on the hands of Ryukyuan (mainly Okinawan) women.
History
The custom was first recorded in the 16th century but is believed to date back much further. The tattoos could represent pride in being a woman, beauty, and ...
'' on the backs of their hands, a sign of adulthood and talisman to protect them from evil. These tattoos were banned in 1899 by the Meiji government. In remote districts their ''katakashira'' off-center topknot, similar to Yami
Yamuna is a sacred river in Hinduism and the main tributary of the Ganges River. The river is also worshipped as a Hindu goddess called Yamuna. Yamuna is known as Yami in early texts, while in later literature, she is called Kalindi. In Hindu scr ...
and Filipinos of Malay descent in Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
and elsewhere, among men and women also disappeared in the early 20th century.
The ''bashôfu'', literally meaning "banana-fibre cloth", is designated as a part of Ryukyu and Japan "important intangible cultural properties". The weaving using indigenous ramie was also widespread in the archipelago, both originated before the 14th century.
Originally living in thatching
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of ...
houses, townsmen developed architecture modeled after Japanese, Chinese and Korean structures. Other dwellings suggest a tropical origin, and some villages have high stone walls, with similar structural counterpart in Yami people at Orchid Island
Orchid Island, also known by other names, is a volcanic island off the southeastern coast of Taiwan Island. The island is part of Taiwan. It is separated from the Batanes of the Philippines by the Bashi Channel of the Luzon Strait. It is gove ...
.
For the listed categories of Cultural Properties see; archaeological materials, historical materials, crafts
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale prod ...
, paintings
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
, sculptures
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
, writings
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
, intangible
Intangibles or intangible may refer to:
* Intangible asset, an asset class used in accounting
* Intellectual capital, the difference in value between tangible assets (physical and financial) and market value
* Intellectual property, a legal concep ...
, and tangible
Tangibility is the property of being able to be perceived by touch. A commonplace understanding of "tangibility" renders it as an attribute allowing something to be perceptible to the senses.
In criminal law, one of the elements of an offense ...
.
Notable Ryukyuans
Martial arts
*Matsumura Sōkon
was one of the original karate masters of Okinawa. The years of his lifespan are reported variously as c.1809-1901 or 1798–1890 or 1809–1896 or 1800–1892. However, the dates on the plaque at Matsumura's tomb, put there by Matsumura's fam ...
* Ankō Itosu
is considered by many the father of modern karate. This title is also often given to Gichin Funakoshi because of the latter spreading karate throughout Japan, but only after Ankō sensei had introduced the art of Okinawate to the country.
Bio ...
* Ankō Asato
was a Ryūkyūan master of karate. He and Ankō Itosu were the two main karate masters who taught Gichin Funakoshi, the founder of Shotokan karate. Funakoshi appears to be the source of most of the information available on Asato. Many articles ...
* Kenwa Mabuni
was one of the first karateka to teach karate in mainland Japan and is credited as developing the style known as Shitō-ryū. Originally, he chose the name Hanko-ryu, literally "half-hard style", to imply that the style used both hard and soft ...
(Shitō-ryū
is a form of karate that was founded in 1934 by . Shitō-ryū is synthesis of the Okinawan Shuri-te and Naha-te schools of karate and today is considered one of the four main styles of the art.
History
Kenwa Mabuni (Mabuni Kenwa 摩文仁 ...
)
* Gichin Funakoshi
was a japanese martial artist who is regarded as the founder of Shotakan karate, perhaps the most widely known style of karate, and is known as a "father of modern karate". Following the teachings of Anko Itosu and Anko Asato,Funakoshi, Gichi ...
(Shotokan
is a style of karate, developed from various martial arts by Gichin Funakoshi (1868–1957) and his son Gigo (Yoshitaka) Funakoshi (1906–1945). Gichin Funakoshi was born in Okinawa and is widely credited with popularizing "karate do" throu ...
)
* Chōjun Miyagi
was an Okinawan martial artist who founded the Gōjū-ryū school of karate by blending Okinawan and Chinese influences.
Life Early life and training
Sensei Miyagi was born in Higashimachi, Naha, Okinawa on April 25, 1888. One of his parent ...
(Gōjū-ryū
, Japanese for "hard-soft style", is one of the main traditional Okinawan styles of karate, featuring a combination of hard and soft techniques. Both principles, hard and soft, come from the famous martial arts book used by Okinawan masters dur ...
)
* Chōki Motobu Chōki or Choki is a Japanese name that may refer to:
*, was a prince of the Ryukyu Kingdom
*, a martial artist
*, Japanese artist
*, aka Momokawa Chōki, a designer of ukiyo-e woodblock printing in Japan, Japanese woodblock prints
*, a prince of ...
( Motobu-ryu)
* Tatsuo Shimabuku
was an Okinawan, Japanese martial artist. He is the founder of Isshin-ryū ("One Heart Style") style of karate.)
From childhood until World War II
Family
Tatsuo Shimabukuro was born in Gushikawa village, Okinawa on September 19, 1908. He was t ...
(Isshin-ryū
is a style of Okinawan karate founded by Tatsuo Shimabuku (島袋 龍夫) in 1956. Isshin-Ryū karate is largely a synthesis of Shorin-ryū karate, Gojū-ryū karate, and kobudō. The name means, literally, "one heart method" (as in "wholeh ...
)
* Kanbun Uechi
was the founder of Uechi-Ryū, one of the primary karate styles of Okinawa.
Early life
Kanbun was born in Deikusaku section but grew up in the Takintō section of the mountain farming village of Izumi on the Motobu Peninsula of Okinawa, Ue ...
( Uechi-ryū)
* Kentsū Yabu (teacher of Shōrin-ryū
Shōrin-ryū (少林流) is one of the major modern Okinawan martial arts and is one of the oldest styles of karate. It was named by Choshin Chibana in 1933, but the system itself is much older. The characters 少林, meaning "sparse" or "scanty ...
)
Academics, journalism, and literature
*Sai On
(1682–1762), or Cai Wen in Chinese, also known as , was a scholar-bureaucrat official of the Ryūkyū Kingdom, serving as regent, instructor, and advisor to King Shō Kei. He is renowned for the many reforms he initiated and oversaw, and is amon ...
* Shō Shōken
, also known as , was a Ryukyuan scholar and served as ''sessei'', a post often translated as "prime minister," from 1666 to 1673. Shō wrote the first history of the Ryukyu Kingdom, , and enacted a number of practical political reforms aimed at i ...
* Tei Junsoku
(1663–1734), or Cheng Shunze in Chinese, was a Confucianism, Confucian scholar and government official of the Ryūkyū Kingdom. He has been described as being "in an unofficial sense... the 'minister of education'",Kerr, George H. ''Okinawa: Th ...
* Iha Fuyū
was the father of Okinawaology and a Japanese scholar who studied various aspects of Japanese and Okinawan culture, customs, linguistics, and lore. His signature was Ifa Fuyu in English, because of the Okinawan pronunciation. Iha studied lingu ...
* Higashionna Kanjun
also Higaonna Kanjun (14 October 1882–24 January 1963) was a Japanese scholar who specialized in the history of Okinawa. Alongside Iha Fuyū and Majikina Ankō, he is considered one of the pioneers of modern Okinawan studies. After reading ...
* Ōta Chōfu (journalist)
* Tatsuhiro Oshiro
Tatsuhiro (written: 龍弘, 辰寛, 達弘, 達裕, 立裕, 立禮, 竜拓 or 竜洋) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include:
*, Japanese ''daimyō''
*, Japanese judoka
*, Japanese footballer
*, Japanese writer an ...
(novelist)
* Kushi Fusako (novelist)
Music
*Namie Amuro
Namie Amuro ( ; ja, 安室奈美恵, Amuro Namie, label=none; born September 20, 1977) is a Japanese former recording artist, producer, songwriter, dancer, model, actress and entrepreneur who was active between 1992 and 2018. A leading figure of ...
* Cocco
is a female Japanese pop / folk rock singer.
Early life
Cocco went to many ballet auditions, hoping to become a professional ballerina. She went to singing auditions to earn the traveling expenses for a ballet audition in Tokyo. She did not ...
* Beni
is a Japanese R&B singer, who debuted in 2004 under the Avex Trax label. In 2008, Arashiro left Avex Trax and transferred to Universal Music Japan where she started to perform as simply Beni (stylized as BENI).
She was initially best known fo ...
* Chitose Hajime
is a Japanese singer from Amami Ōshima. She sings in the shima-uta style particular to that region, with distinctive falsetto effects.
History
Early life
Chitose Hajime began learning shamisen under her mother's encouragement from a young ag ...
* Gackt
, better known by his mononymous stage name Gackt (stylized as GACKT), is a Japanese musician, singer, songwriter, record producer and actor.
Born in Okinawa, Japan, to a Ryukyuan family, Gackt learned the piano at a young age and was raise ...
(male solo singer-songwriter and actor)
* Begin
* Orange Range
are a 5-member Japanese rock music, rock band, based in Okinawa, Japan. Formed in 2001, the band began with Spice Music and later signed with Sony Music Entertainment Japan, Sony Music Japan's gr8! records division in 2003. The band left gr8! ...
* Mongol800
is a Japanese three-piece punk rock band from Urasoe, Okinawa, Japan formed in 1998. When the members were aged 19, the band released their first album. In 2001, despite low commercial attention, they sold over two-million records from the alb ...
* Stereopony
was a Japanese pop rock band that formed in Okinawa, Japan in 2007 and disbanded in 2012. The three-girl band consisted of Aimi Haraguni (lead vocals and guitar), Nohana Kitajima (bass guitar), and Shiho Yamanoha (drums). They were signed to the ...
* High and Mighty Color
High and Mighty Color (stylized as HIGH and MIGHTY COLOR) was a Japanese rock band active from 2003 to 2010. They had two vocalists; a male and a female.
History Formation and Anti-Nobunaga
The band started in Okinawa when Sassy and Meg left a ...
* Speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quanti ...
* MAX
* Da Pump
is a Japanese boy band made up of lead vocalist, Issa Hentona and MCs Ken Okumoto, Yukinari Tamaki and Shinobu Miyara. The band formed as students at Okinawa Actors School in 1996. They made their debut on the Avex Trax subsidiary avex tune und ...
Visual arts
* Mao Ishikawa (photography) *Yuken Teruya
Yuken Teruya ( jap. 照屋 勇賢, ''Teruya Yūken;'' born 1973 in Haebaru, Okinawa) is an artist based in New York City and Berlin.
Biography
Teruya was born and raised in Okinawa. He received his BFA at Tama Art University in 1996, his Post ...
* Chikako Yamashiro
is a Japanese filmmaker and video artist. Her works in photography, video and performance create visual investigations into the history, politics and culture of her homeland Okinawa. Particularly salient are themes related to the terrible civilia ...
(film)
Entertainment
* ActressYui Aragaki
is a Ryukyuan Japanese actress, model, singer and occasional radio show host. She has been selected several times as the most desired girlfriend and the most desired female celebrity face in Oricon's yearly survey.
Early life
She was born on J ...
, notably for the television drama Nigeru wa Haji da ga Yaku ni Tatsu
is a Japanese romance ''josei'' manga series written and illustrated by Tsunami Umino. The original title is from a Hungarian proverb: "Running away is shameful, but useful" (, ). It was published by Kodansha, with serialization in ''Kiss'' ...
* Rino Nakasone
is a Japanese dancer, choreographer, artistic director and actor. Nakasone and her dance crew, Beat Freaks, participated in the third season of '' America's Best Dance Crew'', where they finished in second place. Nakasone has worked as a choreog ...
(choreographer
Choreography is the art or practice of designing sequences of movements of physical bodies (or their depictions) in which motion or form or both are specified. ''Choreography'' may also refer to the design itself. A choreographer is one who cr ...
)
Sports
*Nagisa Arakaki
is a former Japanese professional baseball player. He is currently with the Tokyo Yakult Swallows in Japan's Nippon Professional Baseball. Despite having one of the best fastballs and sliders of anyone in the league, Arakaki has battled control ...
(baseball)
* Hideki Irabu
was a Japanese professional baseball player of American and Japanese mixed ancestry. He played professionally in both Japan and the United States. Irabu played for the Lotte Orions / Chiba Lotte Marines and Hanshin Tigers of Nippon Professiona ...
(baseball)
* Yukiya Arashiro
is a Japanese road bicycle racer, who currently rides for UCI WorldTeam .
Career
Born in Ishigaki, Okinawa Prefecture, Arashiro was the Japanese Under-23 National Time Trial and Road Race Champion in 2005. He has also won the Japanese National ...
(bicycle racer)
* Kazuki Ganaha
is a Japanese football player who plays for Kamatamare Sanuki.
Club career
After graduating Ginowan High School in 1999, he joined J2 League side Kawasaki Frontale. He made his professional debut on May 2, 1999 against Vegalta Sendai. His first ...
(football)
* Yoko Gushiken
is a Japanese former professional boxer who competed from 1974 to 1981. He held the WBA light-flyweight title from 1976 to 1981, making a total of 13 successful defences. Following his retirement from boxing, he remains popular in Japan as a ' ...
(boxing)
* Akinobu Hiranaka
Akinobu Hiranaka (平仲 明信, born Nobuaki Hiranaka, on November 14, 1963) is a former world champion boxer in the Light welterweight ( Super lightweight or former Junior welterweight) division. He won the WBA Junior Welterweight championsh ...
(boxing)
* Katsuo Tokashiki
Katsuo Tokashiki (渡嘉敷 勝男, born July 27, 1960 in Okinawa, Japan) is a Japanese former WBA Light flyweight champion. He currently works as an actor and television persona, and runs own boxing gym in Tokyo, Japan.
Childhood & Early Care ...
(boxing)
* Daigo Higa
is a Japanese professional boxer who held the WBC flyweight title from 2017 to 2018.
Amateur career
Higa turned pro at the age of 18, after a brief amateur career where he accrued a 36–8 record.
Professional career
Higa's manager is Boxi ...
(boxing)
* Ai Miyazato
is a former Japanese professional golfer who competed on the U.S.-based LPGA Tour and the LPGA of Japan Tour (JLPGA). She was the top-ranked golfer in the Women's World Golf Rankings on three occasions in 2010.
Early life, family and amateur ca ...
(golf)
* Ken Gushi
is one of Japan's top competitors in the sport of Drifting (motorsport), drifting. Born in Okinawa, Japan, but raised in San Gabriel Ca, he was taught by his fatheTsukasa Gushiat the age of 13 with a Toyota AE86. Ken has become the youngest compe ...
(drifting)
In Hawaii
* Yeiki Kobashigawa (U.S. World War II soldier andMedal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor. ...
recipient)
* Yoshi Oyakawa
Yoshinobu Oyakawa (born August 9, 1933) is an American former competition swimmer, Olympic champion, and former world record-holder in the 100-meter backstroke. Oyakawa is considered to be the last of the great "straight-arm-pull" backstrokers ...
(Olympic gold medalist)
* Ethel Azama
Ethel Azama (August 28, 1934 – March 7, 1984) was an American jazz and popular singer and recording artist. She sang regularly in nightclubs and other concert venues between the mid-1950s and 1984.
Ethel was born and raised in Honolulu, H ...
(singer)
* David Ige
David Yutaka Ige (; born January 15, 1957) is an American politician and engineer who served as the eighth governor of Hawaii from 2014 to 2022. A Democrat, he served in the Hawaii State Senate from 1995 to 2014 and the Hawaii House of Represen ...
(current Governor of Hawaii)
* Jake Shimabukuro
Jake Shimabukuro (born November 3, 1976) is a Hawaiian ukulele virtuoso and composer known for his fast and complex finger work. His music combines elements of jazz, blues, funk, rock, bluegrass, classical, folk, and flamenco. Shimabukuro has writt ...
(ukulele player)
* Ryan Higa
Ryan Higa (born June 6, 1990), also known as nigahiga ( ), is an American Internet personality. Best known for his comedy videos on YouTube, Higa began making YouTube videos in 2006 and was one of the most popular creators on the platform in it ...
(Youtuber)
* Michael S. Nakamura (Nakandakari) (Former Honolulu Chief of Police)
Other parts of the United States
*Kishi Bashi
Kaoru Ishibashi (born November 4, 1975), who performs as Kishi Bashi, is an American singer, multi-instrumentalist, and songwriter currently based in Athens, Georgia. He was a founding member of Jupiter One and, for a few years, was a member of t ...
(musician)
* Yuki Chikudate
is a Japanese-American musician. She was the main vocalist and keyboardist of the dream pop band Asobi Seksu.
Musical career
In 2001, she founded the dream pop band Asobi Seksu with guitarist James Hanna, bassist Glenn Waldman and drummer Keit ...
(singer)
* Tamlyn Tomita
Tamlyn Naomi Tomita (born January 27, 1966) is a Japanese-American actress and singer. She made her screen debut as Kumiko in ''The Karate Kid Part II'' (1986) and reprised the character for the streaming series ''Cobra Kai'' (2021). She is also ...
(actor)
* Brian Tee
, known professionally as Brian Tee, is a Japanese film and television actor. He is known for playing Dr. Ethan Choi on the NBC medical drama ''Chicago Med'' and its spin-offs, and has starred in such films as '' The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo D ...
(actor)
* Natasha Allegri
Natasha Allegri (born June 18, 1986) is an American animation creator, writer, storyboard artist, storyboard revisionist, and comic book artist. She is the creator of Cartoon Hangover's and Frederator Studios ''Bee and PuppyCat'', and is also n ...
(storyboard artist)
* Dave Roberts (baseball player and coach)
Throughout the world
*Takeshi Kaneshiro
is a Japanese-Taiwanese actor and singer. Beginning his career as a pop idol, he has since moved his focus towards the film industry, where he achieved both commercial success and critical acclaim. He has worked with directors throughout East A ...
(actor in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
)
Notable fictional characters
*Mr. Miyagi
Mr. Miyagi (June 9, 1925 – November 15, 2011) is a fictional character in the original films (1984-1994) of the ''Karate Kid'' franchise. He is a karate master (portrayed by Pat Morita) who mentors Daniel LaRusso and Julie Pierce. Although he ...
(played by Pat Morita
Noriyuki "Pat" Morita (June 28, 1932 – November 24, 2005) was an American actor and comedian. He was known for his roles as Matsuo "Arnold" Takahashi on ''Happy Days'', Mr. Miyagi in ''The Karate Kid'' film series, Captain Sam Pak on the sitco ...
) from the ''Karate Kid
''The Karate Kid'' is a 1984 American martial arts drama film written by Robert Mark Kamen and directed by John G. Avildsen. It is the first installment in the '' Karate Kid'' franchise, and stars Ralph Macchio, Pat Morita, Elisabeth Shue and ...
'' trilogy
* Mugen from the anime series ''Samurai Champloo
is a 2004 Japanese historical adventure anime television series. The debut television production of studio Manglobe, the 26-episode series aired from May 2004 to March 2005. It was first partially broadcast on Fuji TV, then had a complete ai ...
''
* Mutsumi Otohime from the manga series ''Love Hina
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Ken Akamatsu. It was serialized in Kodansha's ''Weekly Shōnen Magazine'' from October 1998 to October 2001, with the chapters collected into 14 ''tankōbon'' volumes by Kodansha. The ...
''
* Maxi from the ''Soulcalibur
is a weapon-based fighting video game franchise by Bandai Namco Entertainment.
There are seven main installments of video games and various media spin-offs, including music albums and a series of manga books. The first game in the series, '' ...
'' series of video games
* The heroines-leads protagonist Yuri Miyazono from the '' Witchblade: Ao no Shōjo'' novels
* Nanjo Takeshi, Arakaki Mari, and Ryuzuka, characters in the 1973 film '' Bodigaado Kiba: Hissatsu sankaku tobi''
See also
*History of the Ryukyu Islands
This article is about the history of the Ryukyu Islands southwest of the main islands of Japan.
Etymology
The name "Ryūkyū" originates from Chinese writings. The earliest references to "Ryūkyū" write the name as 琉虬 and 流求 () in the ...
*Ryukyu independence movement
The or the Republic of the Ryukyus (Japanese: , Kyūjitai: , Hepburn: ) is a political movement advocating for the independence of the Ryukyu Islands (commonly referred to as Okinawa after the largest island) from Japan.
The current political ...
*Ryukyuan culture Ryukyuan culture (琉球の文化, ''Ryūkyū no bunka'') are the cultural elements of the indigenous Ryukyuan people, an ethnic group native to Okinawa Prefecture and parts of Kagoshima Prefecture in southwestern Japan.
The cultural elements of th ...
*Ethnic issues in Japan
Racism in Japan comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are related to each other, are held by various people and groups in Japan, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions (including violenc ...
*Okinawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city o ...
*Ryukyuan diaspora
The Ryukyuan diaspora are the Ryukyuan emigrants from the Ryukyu Islands, especially Okinawa Island, and their descendants that reside in a foreign country. The first recorded emigration of Ryukyuans was in the 15th century when they establishe ...
*Okinawans in Hawaii
The Okinawans in Hawaii ( Okinawan: ハワイ沖縄人, ''Hawai uchinānchu'') are a Ryukyuan ethnic group, numbering anywhere between 45,000-50,000 people, or 3% of Hawaii’s total population.
History
Immigration
The economy of Okinawa plu ...
*Ryukyuans in Brazil
The Ryukyuans in Brazil are Brazilian nationals of Ryukyuan descent.
History
Many people were struggling economically in the Ryukyu Islands during the late 1800s and early 1900s. As a result, many Ryukyuans emigrated elsewhere to places suc ...
*Ryukyuan Americans
Ryukyuan Americans are Americans who are fully or partially of Ryukyuan descent. The vast majority of them trace their family history to the Okinawa Islands.
History
Immigration
The first Ryukyuans to migrate to the United States were 26 Ok ...
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*Ouwehand, C. (1985). ''Hateruma: socio-religious aspects of a South-Ryukyuan island culture''. Leiden: E.J. Brill. *Pacific Science Congress, and Allan H. Smith. (1964). ''Ryukyuan culture and society: a survey''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. *Sakiyama, R. (1995). ''Ryukyuan dance = Ryūkyū buyo''̄. Naha City: Okinawa Dept. of Commerce, Industry & Labor, Tourism & Cultural Affairs Bureau. *Yamazato, Marie. (1995). ''Ryukyuan cuisine''. Naha City, Okinawa Prefecture: Okinawa Tourism & Cultural Affairs Bureau Cultural Promotion Division. *Kreiner, J. (1996). ''Sources of Ryūkyūan history and culture in European collections''. Monographien aus dem Deutschen Institut für Japanstudien der Philipp-Franz-von-Siebold-Stiftung, Bd. 13. München: Iudicium. *Ota, Masahide. (2000). ''Essays on Okinawa Problems''. Yui Shuppan Co.: Gushikawa City, Okinawa, Japan. C0036. *External links
Ryukyuans (Okinawans)
-
Minority Rights Group International
Minority Rights Group International (MRG) is an international human rights organisation founded with the objective of working to secure rights for ethnic, national, religious, linguistic minorities and indigenous peoples around the world. Their ...
Okinawa Peace Network of Los Angeles
- featuring information about Ryukyuan culture worldwide {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyuan People Ethnic groups in Japan Ethnic groups in Brazil Ryukyu Islands Indigenous peoples of East Asia History of Northeast Asia