
The ocean (also the
sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
or the world ocean) is the body of
salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of
Earth and contains 97% of
Earth's water.
An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided.
["Ocean."](_blank)
''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean. Accessed March 14, 2021. Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean:
Pacific (the largest),
Atlantic,
Indian,
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
(Antarctic), and
Arctic (the smallest).
covers approximately of the planet. The ocean is the principal component of Earth's
hydrosphere, and therefore integral to
life on Earth. Acting as a huge
heat reservoir
A thermal reservoir, also thermal energy reservoir or thermal bath, is a thermodynamic system with a heat capacity so large that the temperature of the reservoir changes relatively little when a much more significant amount of heat is added or ex ...
, the ocean influences
climate and
weather patterns, the
carbon cycle, and the
water cycle.
Oceanographers divide the ocean into different vertical and horizontal zones based on physical and biological conditions. The
pelagic zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or wa ...
consists of the
water column from surface to ocean floor throughout the open ocean. The water column is further categorized in other zones depending on depth and on how much light is present. The
photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
includes water from the surface to a depth of 1% of the surface light (about 200 m in the open ocean), where
photosynthesis can occur. This makes the photic zone the most
biodiverse. Photosynthesis by plants and microscopic
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
(free floating
phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
) creates organic matter using light, water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. Ocean photosynthesis creates 50% of the oxygen in earth's atmosphere. This upper sunlit zone is the origin of the food supply which sustains most of the ocean
ecosystem. Light only penetrates to a depth of a few hundred meters; the remaining ocean below is cold and dark. The
continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
where the ocean approaches dry land is more shallow, with a depth of a few hundred meters or less. Human activity has a greater impact on the
continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
.
Ocean temperature
The ocean temperature varies by depth, geographical location and season. Both the temperature and salinity of ocean water differs. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters; in polar regions, the upper layers of ...
s depend on the amount of solar radiation reaching the ocean surface. In the tropics,
surface temperatures can rise to over . Near the poles where
sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
forms, the temperature in equilibrium is about . Deep ocean temperature is between and in all parts of the ocean.
Water continuously circulates in the oceans creating
ocean currents. These directed movements of seawater are generated by forces acting upon the water, including temperature differences,
atmospheric circulation (wind), the
Coriolis effect and differences in
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
.
Tidal currents originate from
tides, while surface currents are caused by wind and waves. Major ocean currents include the
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
,
Kuroshio Current,
Agulhas Current and
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise (as seen from the South Pole) from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feat ...
. Collectively, currents move enormous amounts of water and heat around the globe. This circulation significantly impacts global climate and the uptake and redistribution of pollutants such as
carbon dioxide by moving these contaminants from the surface into the deep ocean.
Ocean water contains large quantities of dissolved gases, including
oxygen,
carbon dioxide and
nitrogen. This
gas exchange takes place at the ocean surface and solubility depends on the temperature and salinity of the water.
The increasing concentration of
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere due to
fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
combustion leads to higher concentrations in ocean water, resulting in
ocean acidification.
The ocean provides society with important
environmental services
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. Th ...
, including climate regulation. It also offers a means of
trade and transport and access to food and other
resources. Known to be the
habitat of over 230,000
species, it may contain far more – perhaps over two million species.
However, the ocean is subject to numerous human-caused
environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
threats, including
marine pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural and municipal solid waste, residential waste, particle (ecology), particles, noise, excess carbon dioxid ...
,
overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
, and
effects of climate change on oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice ...
, such as
ocean warming
In oceanography and climatology, ocean heat content (OHC) is a term for the energy absorbed by the ocean, where it is stored for indefinite time periods as internal energy or enthalpy. The rise in OHC accounts for over 90% of Earth’s excess the ...
,
ocean acidification,
sea level rise and many more. The continental shelf and
coastal waters that are most influenced by human activity are especially vulnerable.
Terminology
Ocean and sea
The terms "the ocean" or "the sea" used without specification refer to the interconnected body of salt water covering the majority of the Earth's surface.
It includes the
Atlantic,
Pacific,
Indian,
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and
Arctic Oceans. As a general term, "the ocean" and "the sea" are often interchangeable, although speakers of
British English refer to "the sea" in all cases, even when the body of water is one of the oceans.
Strictly speaking, a "sea''"'' is a body of water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.
The word "sea" can also be used for many specific, much smaller bodies of seawater, such as the
North Sea or the
Red Sea. There is no sharp distinction between seas and oceans, though generally seas are smaller, and are often partly (as
marginal seas) or wholly (as
inland seas) bordered by land.
World ocean
The contemporary concept of the ''World Ocean'' was coined in the early 20th century by the
Russian oceanographer
Yuly Shokalsky to refer to the continuous ocean that covers and encircles most of Earth.
The global, interconnected body of salt water is sometimes referred to as the world ocean, ''global ocean'' or ''the great ocean''.
["] The concept of a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to
oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
.
Etymology
The word ''ocean'' comes from the figure in
classical antiquity,
Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus (; grc-gre, , Ancient Greek pronunciation: , also Ὠγενός , Ὤγενος , or Ὠγήν ) was a Titan son of Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys, and the father of the river gods a ...
(; grc-gre, ''Ōkeanós'', ), the elder of the
Titans in classical
Greek mythology. Oceanus was believed by the
ancient Greeks and
Romans to be the divine personification of an enormous
river encircling the world.
The concept of Ōkeanós has an
Indo-European connection. Greek Ōkeanós has been compared to the
Vedic epithet ā-śáyāna-, predicated of the dragon Vṛtra-, who captured the cows/rivers. Related to this notion, the Okeanos is represented with a dragon-tail on some early Greek vases.
Natural history
During
planetary formation
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbitin ...
Earth possibly had
magma oceans. Subsequently
outgassing,
volcanic activity and
meteorite impacts, according to current theories, produced an early atmosphere of
carbon dioxide,
nitrogen and
water vapor.
The gases and with them the atmosphere are thought to have accumulated over millions of years and after Earth's surface had significantly cooled the
water vapor over time would have condensed, forming Earth's first oceans.
The early oceans might have been significantly hotter than today and appeared green due to high iron content.
Geological evidence helps constrain the time frame for liquid water existing on Earth. A sample of pillow basalt (a type of rock formed during an underwater eruption) was recovered from the
Isua Greenstone Belt and provides evidence that water existed on Earth 3.8 billion years ago.
In the
Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt, Quebec, Canada, rocks dated at 3.8 billion years old by one study and 4.28 billion years old by another show evidence of the presence of water at these ages.
If oceans existed earlier than this, any geological evidence either has yet to be discovered or has since been destroyed by geological processes like
crustal recycling
Crustal recycling is a tectonic process by which surface material from the lithosphere is recycled into the mantle by subduction erosion or delamination. The subducting slabs carry volatile compounds and water into the mantle, as well as crustal ...
.
However, more recently, in August 2020, researchers reported that sufficient water to fill the oceans may have always been on the
Earth since the beginning of the planet's formation.
In this model, atmospheric
greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse ...
es kept the oceans from freezing when the newly forming Sun
had only 70% of its
current luminosity.
By ,
Earth's magnetic field was established, which helped prevent the atmosphere from being stripped away by the
solar wind.
Since its formation the ocean has taken many conditions and shapes with many
past ocean divisions and potentially at times covering the whole globe.
During colder climatic periods, more ice caps and glaciers form, and enough of the global water supply accumulates as ice to lessen the amounts in other parts of the water cycle. The reverse is true during warm periods. During the last ice age, glaciers covered almost one-third of Earth's land mass with the result being that the oceans were about 122 m (400 ft) lower than today. During the last global "warm spell," about 125,000 years ago, the seas were about 5.5 m (18 ft) higher than they are now. About three million years ago the oceans could have been up to 50 m (165 ft) higher.
Geography
The ocean covers ~70% of the Earth, sometimes called the "blue planet"

The entire ocean, containing 97% of Earth's water, spans 70.8% of
Earth's surface,
making it Earth's global ocean or ''world ocean''.
This makes Earth, along with its vibrant
hydrosphere a "water world"
or "
ocean world
An ocean world, ocean planet, panthalassic planet, maritime world, water world or aquaplanet, is a type of planet that contains a substantial amount of water in form of oceans, either beneath the surface, as subsurface oceans, or on the surfa ...
",
particularly in Earth's early history when the ocean is thought to have possibly covered Earth completely.
The ocean is shaped irregularly, dominating
Earth's surface unevenly, allowing the decernment of Earth's surface into a
water and land hemisphere, as well as the division of the ocean into particular oceans.
Oceanic divisions
The major oceanic divisions – listed below in descending order of area and volume – are so named based on nearest
continents, various
archipelagos, and other criteria.
Oceans are fringed with coastlines that run for
360,000 kilometres in total distance. They are also connected to smaller, adjoining bodies of water such as,
seas
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocean ...
,
gulfs
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodie ...
,
bay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a Gulf (geography), gulf, sea, sound (geography), sound, or bight (geogra ...
s,
bights, and
strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
s.
Seawater covers approximately and is customarily divided into five principal oceans, as below:
Ocean ridges and ocean basins

Every
ocean basin has a
mid-ocean ridge, which creates a long mountain range beneath the ocean. Together they form the global mid-oceanic ridge system that features the
longest mountain range in the world. The longest continuous mountain range is . This underwater mountain range is several times longer than the longest continental mountain range—the
Andes.
Oceanographers state that less than 20% of the oceans have been mapped.
Formation
The origin of Earth's oceans is unknown. Oceans are thought to have formed in the
Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a Eon (geology), geologic eon of History of Earth, Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the Formation of the Earth, planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the H ...
eon and may have been the cause for the
emergence of life. Scientists believe that a sizable quantity of
water would have been in the material that formed the Earth. Water molecules would have escaped Earth's gravity more easily when it was less massive during its formation. This is called
atmospheric escape
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
.
Plate tectonics,
post-glacial rebound, and
sea level rise continually change the
coastline and structure of the world ocean. A global ocean has existed in one form or another on Earth for eons.
Physical properties
Volumes
The volume of water in all the oceans together is approximately 1.335 billion cubic kilometers (1.335
sextillion
Two naming scales for large numbers have been used in English and other European languages since the early modern era: the long and short scales. Most English variants use the short scale today, but the long scale remains dominant in many non-Eng ...
liters, 320.3 million cubic miles).
Depth

The average depth of the oceans is about 4 km. More precisely the average depth is .
Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over deep.
"Deep ocean," which is anything below 200 meters (660 ft.), covers about 66% of Earth's surface.
This figure does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the
Caspian Sea.
The deepest point in the ocean is the
Mariana Trench, located in the Pacific Ocean near the
Northern Mariana Islands.
Its maximum depth has been estimated to be . The British naval vessel ''Challenger II'' surveyed the trench in 1951 and named the deepest part of the trench the "
Challenger Deep". In 1960, the
Trieste successfully reached the bottom of the trench, manned by a crew of two men.
Color

Oceanic zones
Oceanographers divide the ocean into different vertical and horizontal zones defined by physical and biological conditions. The
pelagic zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or wa ...
consists of the
water column of the open ocean, and can be divided into further regions categorized by light abundance and by depth.
Grouped by light penetration
* The
photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
includes the oceans from the surface to a depth of 200 m; it is the region where
photosynthesis can occur and is, therefore, the most
biodiverse. Photosynthesis by plants and microscopic
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
(free floating
phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
) allows the creation of organic matter from chemical precursors including water and carbon dioxide. This organic matter can then be consumed by other creatures. Much of the organic matter created in the photic zone is consumed there but some sinks into deeper waters.
* Below the photic zone is the mesopelagic or twilight zone where there is a very small amount of light. Below that is the aphotic deep ocean to which no surface sunlight at all penetrates. Life that exists deeper than the photic zone must either rely on material sinking from above (see
marine snow) or find another energy source.
Hydrothermal vents
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
are a source of energy in what is known as the
aphotic zone (depths exceeding 200 m). The pelagic part of the photic zone is known as the
epipelagic.
Grouped by depth and temperature
The pelagic part of the aphotic zone can be further divided into vertical regions according to depth and temperature:
* The
mesopelagic is the uppermost region. Its lowermost boundary is at a
thermocline of which generally lies at in the
tropics. Next is the
bathypelagic
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic ...
lying between , typically between and . Lying along the top of the
abyssal plain is the
abyssopelagic, whose lower boundary lies at about . The last and deepest zone is the
hadalpelagic
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deep sea, deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions.
T ...
which includes the
oceanic trench and lies between .
* The
benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
zones are aphotic and correspond to the three deepest zones of the
deep-sea. The
bathyal zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagi ...
covers the continental slope down to about . The abyssal zone covers the abyssal plains between 4,000 and 6,000 m. Lastly, the
hadal
The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches. The hadal zone ranges from around below sea level, and exists in long, narrow, topographic V-shaped depressions.
The cumula ...
zone corresponds to the hadalpelagic zone, which is found in oceanic trenches.
Distinct boundaries between ocean surface waters and deep waters can be drawn based on the properties of the water. These boundaries are called
thermoclines (temperature),
haloclines (salinity),
chemoclines (chemistry), and
pycnoclines (density). If a zone undergoes dramatic changes in temperature with depth, it contains a
thermocline, a distinct boundary between warmer surface water and colder deep water. The tropical thermocline is typically deeper than the thermocline at higher latitudes.
Polar waters, which receive relatively little solar energy, are not
stratified
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or st ...
by temperature and generally lack a thermocline because surface water at polar latitudes are nearly as cold as water at greater depths. Below the thermocline, water everywhere in the ocean is very cold, ranging from −1 °C to 3 °C. Because this deep and cold layer contains the bulk of ocean water, the average temperature of the world ocean is 3.9 °C. If a zone undergoes dramatic changes in salinity with depth, it contains a
halocline. If a zone undergoes a strong, vertical chemistry gradient with depth, it contains a
chemocline. Temperature and salinity control the density of ocean water, with colder and saltier water being more dense, and this density in turn regulates the global water circulation within the ocean.
The halocline often coincides with the thermocline, and the combination produces a pronounced
pycnocline, a boundary between less dense surface water and dense deep water.
Grouped by distance from land
The pelagic zone can be further subdivided into two sub regions based on distance from land: the
neritic zone and the
oceanic zone. The neritic zone encompasses the water mass directly above the
continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
and hence includes
coastal waters, whereas the oceanic zone includes all the completely open water.
The
littoral zone covers the region between low and high tide and represents the transitional area between marine and terrestrial conditions. It is also known as the
intertidal zone because it is the area where tide level affects the conditions of the region.
Temperature
Ocean temperatures depends on the amount of solar radiation falling on its surface. In the tropics, with the Sun nearly overhead, the
temperature of the surface layers can rise to over while near the poles the temperature in equilibrium with the
sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
is about . There is a continuous circulation of water in the oceans. Warm surface currents cool as they move away from the tropics, and the water becomes denser and sinks. The cold water moves back towards the equator as a deep sea current, driven by changes in the temperature and density of the water, before eventually welling up again towards the surface.
Deep ocean water has a temperature between and in all parts of the globe.
Sea ice
Seawater with a typical salinity of 35‰ has a freezing point of about −1.8 °C (28.8 °F).
Because sea ice is less
dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does
fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans.
Sea ice usually starts to freeze at the very surface, initially as a very thin ice film. As further freezing takes place, this ice film thickens and can form
ice sheets. The ice formed incorporates some
sea salt, but much less than the seawater it forms from. As the ice forms with low salinity this results in saltier residual seawater. This in turn increases density and promotes vertical sinking of the water.
Ocean currents and global climate


Types of ocean currents
An
ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including
wind, the
Coriolis effect,
temperature and
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
differences.
Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. They have different origins, such as tides for tidal currents, or wind and waves for surface currents.
Tidal currents are in phase with the
tide, hence are
quasiperiodic; associated with the influence of the moon and sun pull on the ocean water. Tidal currents may form various complex patterns in certain places, most notably around
headlands
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, Joh ...
. Non-periodic or non-tidal currents are created by the action of winds and changes in
density of water
Water () is a Chemical polarity, polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from Color of water, an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compou ...
. In
littoral zones,
breaking waves are so intense and the depth measurement so low, that maritime currents reach often 1 to 2
knots
A knot is a fastening in rope or interwoven lines.
Knot may also refer to:
Places
* Knot, Nancowry, a village in India
Archaeology
* Knot of Isis (tyet), symbol of welfare/life.
* Minoan snake goddess figurines#Sacral knot
Arts, entertainme ...
.
The
wind and
waves create surface currents (designated as "drift currents"). These currents can decompose in one quasi-permanent current (which varies within the hourly scale) and one movement of
Stokes drift under the effect of rapid waves movement (which vary on timescales of a couple of seconds). The quasi-permanent current is accelerated by the breaking of waves, and in a lesser governing effect, by the friction of the wind on the surface.
This acceleration of the current takes place in the direction of waves and dominant wind. Accordingly, when the ocean depth increases, the
rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
of the
earth changes the direction of currents in proportion with the increase of depth, while friction lowers their speed. At a certain ocean depth, the current changes direction and is seen inverted in the opposite direction with current speed becoming null: known as the
Ekman spiral
The oceanic, wind driven Ekman spiral is the result of a force balance created by a shear stress force, Coriolis force and the water drag. This force balance gives a resulting current of the water different from the winds. In the ocean, there are t ...
. The influence of these currents is mainly experienced at the mixed layer of the ocean surface, often from 400 to 800 meters of maximum depth. These currents can considerably change and are dependent on the yearly
seasons. If the mixed layer is less thick (10 to 20 meters), the quasi-permanent current at the surface can adopt quite a different direction in relation to the direction of the wind. In this case, the water column becomes virtually homogeneous above the
thermocline.
The wind blowing on the ocean surface will set the water in motion. The global pattern of winds (also called
atmospheric circulation) creates a global pattern of ocean currents. These are not only driven by the wind but also by the effect of the circulation of the earth (
coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
). Theses major ocean currents include the
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
,
Kuroshio current,
Agulhas current and
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise (as seen from the South Pole) from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feat ...
. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current encircles
Antarctica and influences the area's climate as well as connecting currents in several oceans.
Relationship of currents and climate

Collectively, currents move enormous amounts of water and heat around the globe influencing
climate. These wind driven currents are largely confined to the top hundreds of meters of the ocean. At greater depth the drivers of water motion are the
thermohaline circulation (the
Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermoholine circulation). This is driven by the cooling of surface waters at northern and southern polar latitudes creating dense water which sinks to the bottom of the ocean. This cold and dense water moves slowly away from the
poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
which is why the waters in the deepest layers of the world ocean are so cold. This deep ocean water circulation is relatively slow and water at the bottom of the ocean can be isolated from the ocean surface and atmosphere for hundreds or even a few thousand years.
This circulation has important impacts on global climate and the uptake and redistribution of pollutants such as
carbon dioxide by moving these contaminants from the surface into the deep ocean.
Ocean currents greatly affect Earth's climate by
transferring heat from the
tropics to the
polar regions and thereby also affecting air temperature and precipitation in coastal regions and further inland. Surface heat and freshwater
flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications to physics. For transport ph ...
es create global
density gradients that drive the
thermohaline circulation part of large-scale ocean circulation. It plays an important role in supplying heat to the polar regions, and thus in
sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
regulation.
Oceans moderate the climate of locations where prevailing winds blow in from the ocean. At similar latitudes, a place on Earth with more influence from the ocean will have a more moderate climate than a place with more influence from land. For example, the cities San Francisco (37.8 N) and New York (40.7 N) have different climates because San Francisco has more influence from the ocean. San Francisco, on the west coast of North America, gets
winds from the west over the
Pacific Ocean, and the influence of the ocean water yields a more moderate climate with a warmer winter and a longer, cooler summer, with the warmest temperatures happening later in the year. New York, on the east coast of North America gets
winds from the west over land, so New York has colder winters and hotter, earlier summers than San Francisco.
Warmer ocean currents yield warmer climates in the long term, even at high latitudes. At similar latitudes, a place influenced by warm ocean currents will have a warmer climate overall than a place influenced by cold ocean currents. French Riviera (43.5 N) and Rockland, Maine (44.1 N) have same latitude, but the French Riviera is influenced by warm waters transported by the
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
into the
Mediterranean Sea and has a warmer climate overall. Maine is influenced by cold waters transported south by the
Labrador Current giving it a colder climate overall.
Changes in the thermohaline circulation are thought to have significant impacts on
Earth's energy budget. Since the thermohaline circulation governs the rate at which deep waters reach the surface, it may also significantly influence
atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations. Modern observations,
climate simulations and paleoclimate reconstructions suggest that the
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) has weakened since the preindustrial era. The latest climate change projections in 2021 suggest that the AMOC is likely to weaken further over the 21st century.
[IPCC, 2019]
Summary for Policymakers
In
IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. Such a weakening could cause large changes to global climate, with the North Atlantic particularly vulnerable.
Waves and swell
The motions of the ocean surface, known as undulations or
wind wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, water wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result from the wind blowing over the water surface. The contact distance in the direction of t ...
s, are the partial and alternate rising and falling of the ocean surface. The series of
mechanical waves
In physics, a mechanical wave is a wave that is an oscillation of matter, and therefore transfers energy through a medium. While waves can move over long distances, the movement of the medium of transmission—the material—is limited. Therefor ...
that propagate along the interface between water and air is called
swell – a term used in
sailing,
surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitabl ...
and
navigation. These motions profoundly affect ships on the surface of the ocean and the well-being of people on those ships who might suffer from
sea sickness
Motion sickness occurs due to a difference between actual and expected motion. Symptoms commonly include nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, headache, dizziness, tiredness, loss of appetite, and increased salivation. Complications may rarely include de ...
.
Wind blowing over the surface of a body of water forms
waves that are perpendicular to the direction of the wind. The friction between air and water caused by a gentle breeze on a pond causes
ripples to form. A strong blow over the ocean causes larger waves as the moving air pushes against the raised ridges of water. The waves reach their maximum height when the rate at which they are travelling nearly matches the speed of the wind. In open water, when the wind blows continuously as happens in the Southern Hemisphere in the
Roaring Forties, long, organized masses of water called
swell roll across the ocean.
If the wind dies down, the wave formation is reduced, but already-formed waves continue to travel in their original direction until they meet land. The size of the waves depends on the
fetch, the distance that the wind has blown over the water and the strength and duration of that wind. When waves meet others coming from different directions, interference between the two can produce broken, irregular seas.
can cause individual (unexpected)
rogue waves much higher than normal.
[Garrison, Tom (2012)]
''Essentials of Oceanography''
6th ed. pp. 204 ff. Brooks/Cole, Belmont
Belmont may refer to:
People
* Belmont (surname)
Places
* Belmont Abbey (disambiguation)
* Belmont Historic District (disambiguation)
* Belmont Hotel (disambiguation)
* Belmont Park (disambiguation)
* Belmont Plantation (disambiguation)
* Belmon ...
. . Most waves are less than high
and it is not unusual for strong storms to double or triple that height. Rogue waves, however, have been documented at heights above .
The top of a wave is known as the crest, the lowest point between waves is the trough and the distance between the crests is the wavelength. The wave is pushed across the surface of the ocean by the wind, but this represents a transfer of energy and not a horizontal movement of water. As waves approach land and
move into shallow water, they change their behavior. If approaching at an angle, waves may bend (
refraction) or wrap around rocks and headlands (
diffraction
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a s ...
). When the wave reaches a point where its deepest oscillations of the water contact the
ocean floor, they begin to slow down. This pulls the crests closer together and increases the
waves' height, which is called
wave shoaling
In fluid dynamics, wave shoaling is the effect by which surface waves, entering shallower water, change in wave height. It is caused by the fact that the group velocity, which is also the wave-energy transport velocity, changes with water depth ...
. When the ratio of the wave's height to the water depth increases above a certain limit, it "
breaks", toppling over in a mass of foaming water.
This rushes in a sheet up the beach before retreating into the ocean under the influence of gravity.
s,
volcanic eruptions or other major geological disturbances can set off waves that can lead to
tsunamis in coastal areas which can be very dangerous.
Tides

Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by oceans in response to the
gravitational
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong ...
influences of the moon and the sun, and the effects of the Earth's rotation. During each tidal cycle, at any given place the water rises to a maximum height known as "high tide" before ebbing away again to the minimum "low tide" level. As the water recedes, it uncovers more and more of the
foreshore, also known as the intertidal zone. The difference in height between the high tide and low tide is known as the
tidal range or tidal amplitude.
In the open ocean tidal ranges are less than 1 meter, but in coastal areas these tidal ranges increase to more than 10 meters in some areas. Some of the largest tidal ranges in the world occur in the
Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is the hi ...
and
Ungava Bay
Ungava Bay (french: baie d'Ungava, ; iu, ᐅᖓᕙ ᑲᖏᖅᓗᒃ/) is a bay in northeastern Canada separating Nunavik (far northern Quebec) from Baffin Island. Although not geographically apparent, it is considered to be a marginal sea of the ...
in Canada, reaching up to 16 meters. Other locations with record high tidal ranges include the
Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
between England and Wales,
Cook Inlet in Alaska, and the
Río Gallegos
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
in Argentina.
Most places experience two high tides each day, occurring at intervals of about 12 hours and 25 minutes. This is half the 24 hours and 50 minute period that it takes for the Earth to make a complete revolution and return the moon to its previous position relative to an observer.
Tidal force or tide-raising force decreases rapidly with distance, so the moon has more than twice as great an effect on tides as the Sun.
When the sun, moon and Earth are all aligned (full moon and new moon), the combined effect results in the high "spring tides".
A
storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
can occur when high winds pile water up against the coast in a shallow area and this, coupled with a low pressure system, can raise the surface of the ocean at high tide dramatically.
Water cycle, weather and rainfall

Ocean water represents the largest body of water within the global
water cycle (oceans contain 97% of
Earth's water). Evaporation from the ocean moves water into the atmosphere to later rain back down onto land and the ocean.
Oceans have a significant effect on the
biosphere. The ocean as a whole is thought to cover approximately 90% of the Earth's
biosphere.
Oceanic
evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
, as a phase of the water cycle, is the source of most rainfall (about 90%),
causing a global
cloud cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud co ...
of 67% and a consistent oceanic cloud cover of 72%.
Ocean temperature
The ocean temperature varies by depth, geographical location and season. Both the temperature and salinity of ocean water differs. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters; in polar regions, the upper layers of ...
s affect
climate and
wind patterns that affect life on land. One of the most dramatic forms of
weather occurs over the oceans:
tropical cyclones (also called "typhoons" and "hurricanes" depending upon where the system forms).
As the world's ocean is the principal component of Earth's
hydrosphere, it is integral to
life on Earth, forms part of the
carbon cycle and
water cycle, and – as a huge
heat reservoir
A thermal reservoir, also thermal energy reservoir or thermal bath, is a thermodynamic system with a heat capacity so large that the temperature of the reservoir changes relatively little when a much more significant amount of heat is added or ex ...
– influences climate and weather patterns.
Chemical composition of seawater
Salinity

Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
is a measure of the total amounts of dissolved salts in
seawater. It was originally measured via measurement of the amount of
chloride in seawater and hence termed chlorinity. It is now routinely measured by measuring
electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allow ...
of the water sample. Salinity can be calculated using the chlorinity, which is a measure of the total mass of
halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
ions (includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine) in seawater. By international agreement, the following formula is used to determine salinity:
:Salinity (in ‰) = 1.80655 × Chlorinity (in ‰)
The average ocean water chlorinity is about 19.2‰, and, thus, the average salinity is around 34.7‰.
Salinity has a major influence on the density of seawater. A zone of rapid salinity increase with depth is called a
halocline. The temperature of maximum density of
seawater decreases as its salt content increases. Freezing temperature of water decreases with salinity, and boiling temperature of water increases with salinity. Typical seawater freezes at around −2 °C at
atmospheric pressure.
Salinity is higher in Earth's oceans where there is more
evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
and lower where there is more
precipitation. If precipitation exceeds evaporation, as is the case in
polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
and some
temperate regions, salinity will be lower. If evaporation exceeds precipitation, as is sometimes the case in
tropical regions, salinity will be higher. For example, evaporation is greater than precipitation in the
Mediterranean Sea, which has an average salinity of 38‰, more saline than the global average of 34.7‰.
Thus, oceanic waters in polar regions have lower salinity content than oceanic waters tropical regions.
However, when
sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
forms at high latitudes,
salt is excluded from the ice as it forms, which can increase the salinity in the residual seawater in polar regions such as the
Arctic Ocean.
Observations of sea surface salinity between 1950 to 2019 indicate that due to the
effects of climate change on oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice ...
regions of high salinity and evaporation have become more saline, while regions of low salinity and more precipitation have become fresher.
[Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, S.S. Drijfhout, T.L. Edwards, N.R. Golledge, M. Hemer, R.E. Kopp, G. Krinner, A. Mix, D. Notz, S. Nowicki, I.S. Nurhati, L. Ruiz, J.-B. Sallée, A.B.A. Slangen, and Y. Yu, 2021]
Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. It is very likely that the Pacific and Southern Oceans have freshened while the Atlantic has become more saline.
General characteristics of ocean surface waters
The waters in different regions of the ocean have quite different temperature and salinity characteristics. This is due to differences in the local water balance (
precipitation vs.
evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
) and the "sea to air"
temperature gradient
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of degree ...
s. These characteristics can vary widely among ocean regions. The table below provides an illustration of the sort of values usually encountered.
Dissolved gases

Ocean water contains large quantities of dissolved gases, including
oxygen,
carbon dioxide and
nitrogen. These dissolve into ocean water via
gas exchange at the ocean surface, with the solubility of these gases depending on the temperature and salinity of the water.
The four most abundant gases in earth’s atmosphere and oceans are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. In the ocean by volume, the most abundant gases dissolved in seawater are carbon dioxide (including bicarbonate and carbonate ions, 14 mL/L on average), nitrogen (9 mL/L), and oxygen (5 mL/L) at equilibrium at
All gases are more
soluble – more easily dissolved – in colder water than in warmer water. For example, when salinity and pressure are held constant, oxygen concentration in water almost doubles when the temperature drops from that of a warm summer day to freezing . Similarly, carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases are more
soluble at colder temperatures, and their solubility changes with temperature at different rates.
Oxygen, photosynthesis and carbon cycling
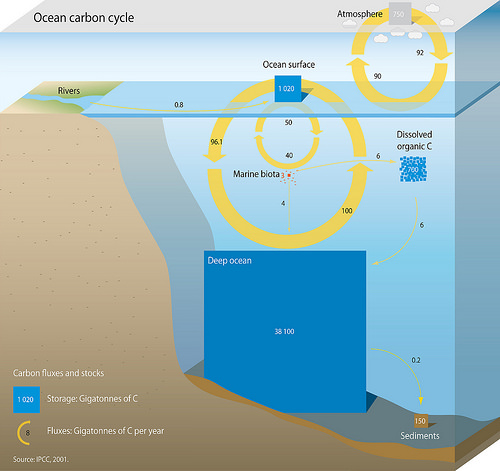
The process of
photosynthesis in the surface ocean releases oxygen and consumes carbon dioxide. This photosynthesis in the ocean is dominated by
phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
, microscopic free floating algae. After the plants grow, bacterial decomposition of the organic matter formed by photosynthesis in the ocean consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The sinking and bacterial decomposition of some organic matter in deep ocean water, at depths where the waters are out of contact with the atmosphere, leads to a reduction in oxygen concentrations and increase in carbon dioxide,
carbonate and
bicarbonate.
This
cycling of carbon dioxide in oceans is an important part of the global
carbon cycle.
The increasing
carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere due to
fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
combustion lead to higher concentrations in the ocean waters and
ocean acidification.
[IUCN (2017]
THE OCEAN AND CLIMATE CHANGE
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) Issues Brief. Dissolving atmospheric carbon dioxide reacts with bicarbonate and carbonate ions in seawater to shift the chemical balance of the water, making it more acidic. The oceans represent a major sink for carbon dioxide taken up from the atmosphere by photosynthesis and by dissolution. There is also increasing attention focused on carbon dioxide uptake in coastal
marine habitats such as
mangroves and
saltmarshes
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated ...
, a process sometimes referred to as “
Blue carbon
Blue Carbon refers to organic carbon that is captured and stored by the world's oceanic and coastal ecosystems, mostly by algae, seagrasses, macroalgae, mangroves, salt marshes and other plants in coastal wetlands. The term Blue Carbon was coined ...
”. Attention is focused on these ecosystems because they are strong carbon sinks as well as ecologically important habitats under considerable threat from human activities and
environmental degradation
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment (biophysical), environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; an ...
.
As deep ocean water circulates throughout the globe, it contains gradually less oxygen and gradually more carbon dioxide with more time away from the air at the surface. This gradual decrease in oxygen concentration happens as sinking organic matter continuously gets decomposed during the time the water is out of contact with the atmosphere.
Most of the deep waters of the ocean still contain relatively high concentrations of oxygen sufficient for most animals to survive. However, some ocean areas have very low oxygen due to long periods of isolation of the water from the atmosphere. These oxygen deficient areas, called
oxygen minimum zones or
hypoxic waters, could be made worse by the
effects of climate change on oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice ...
.
Residence times of chemical elements and ions

The ocean waters contain many
chemical elements as dissolved ions. Elements dissolved in ocean waters have a wide range of concentrations. Some elements have very high concentrations of several grams per liter, such as
sodium and
chloride, together making up the majority of ocean salts. Other elements, such as
iron, are present at tiny concentrations of just a few nanograms (10
−9 grams) per liter.
The concentration of any element depends on its rate of supply to the ocean and its rate of removal. Elements enter the ocean from rivers, the atmosphere and
hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s. Elements are removed from ocean water by sinking and becoming buried in
sediments or evaporating to the
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
in the case of water and some gases. Oceanographers consider the balance of input and removal by estimating the
residence time
The residence time of a fluid parcel is the total time that the parcel has spent inside a control volume (e.g.: a chemical reactor, a lake, a human body). The residence time of a set of parcels is quantified in terms of the frequency distribution ...
of an element. Residence time is the average time the element would spend dissolved in the ocean before it is removed. Very abundant elements in ocean water like sodium have high rates of input, reflecting high abundance in rocks and relatively rapid rock weathering, coupled to very slow removal from the ocean because sodium ions are rather unreactive and very soluble. In contrast, other elements such as iron and
aluminium are abundant in rocks but very insoluble, meaning that inputs to the ocean are low and removal is rapid. These cycles represent part of the major global cycle of elements that has gone on since the Earth first formed. The residence times of the very abundant elements in the ocean are estimated to be millions of years, while for highly reactive and insoluble elements, residence times are only hundreds of years.
Nutrients
A few elements such as
nitrogen,
phosphorus,
iron, and
potassium are essential for life, are major components of biological material, and are commonly called “
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s”. Nitrate and phosphate have ocean
residence time
The residence time of a fluid parcel is the total time that the parcel has spent inside a control volume (e.g.: a chemical reactor, a lake, a human body). The residence time of a set of parcels is quantified in terms of the frequency distribution ...
s of 10,000 and 69,000 years, respectively, while potassium is a much more abundant ion in the ocean with a residence time of 12 million years. The biological cycling of these elements means that this represents a continuous removal process from the ocean's water column as degrading organic material sinks to the ocean floor as
sediment.
Phosphate from
intensive agriculture
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ag ...
and
untreated sewage is transported via runoff to rivers and coastal zones to the ocean where it is metabolized. Eventually, it sinks to the ocean floor and is no longer available to humans as a commercial resource. Production of
rock phosphate
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxi ...
, an essential ingredient in inorganic
fertilizer is a slow geological process occurring in some of the world's ocean sediments thus making minable sedimentary
apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of OH−, F− and Cl− ions, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common e ...
(phosphate) in effect a
non-renewable resource (see
peak phosphorus). This continuous net deposition loss of non-renewable phosphate from human activities may become a resource problem in the future for fertilizer production and
food security.
Climate change
Marine life
Life within the ocean
evolved 3 billion years prior to life on land. Both the depth and the distance from shore strongly influence the
biodiversity of the plants and animals present in each region.
The diversity of life in the ocean is immense, including:
*
Animals: most animal
phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
have species that inhabit the ocean, including many that are only found in marine environments such as
sponges
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through ...
,
Cnidaria (such as
corals and
jellyfish),
comb jellies,
Brachiopods, and
Echinoderms (such as
sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) of ...
s and
sea stars). Many other familiar animal groups primarily live in the ocean, including
cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s (includes
octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
and
squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting t ...
),
crustaceans (includes
lobster
Lobsters are a family (biology), family (Nephropidae, Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs ...
s,
crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, and
shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
),
fish,
sharks,
cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
s (includes
whales,
dolphins, and
porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
s). In addition, many land animals have adapted to living a major part of their life on the oceans. For instance,
seabirds are a diverse group of birds that have adapted to a life mainly on the oceans. They feed on marine animals and spend most of their lifetime on water, many only going on land for breeding. Other birds that have adapted to oceans as their living space are
penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
s,
seagulls and
pelicans. Seven species of turtles, the
sea turtles, also spend most of their time in the oceans.
*
Plants: including
sea grasses
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
, or
mangroves
*
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
: algae is a "catch-all" term to include many
photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
,
single-celled
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s, such as
green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
,
diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s, and
dinoflagellates, but also multicellular algae, such as some
red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
(including organisms like
Pyropia, which is the source of the edible
nori seaweed), and
brown algae (including organisms like
kelp).
*
Bacteria: ubiquitous single-celled
prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
found throughout the world
*
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
:
prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
distinct from bacteria, that inhabit many environments of the ocean, as well as many
extreme environments
*
Fungi: many
marine fungi with diverse roles are found in oceanic environments
Human uses of the oceans
The ocean has been linked to human activity throughout history. These activities serve a wide variety of purposes, including
navigation and exploration,
naval warfare
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
, travel,
shipping and
trade, food production (e.g.
fishing,
whaling,
seaweed farming,
aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
), leisure (
cruising,
sailing,
recreational boat fishing,
scuba diving), power generation (see
marine energy and
offshore wind power), extractive industries (
offshore drilling and
deep sea mining),
freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
production via
desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
.
Many of the world's goods are moved by
ship between the world's
seaports. Large quantities of goods are transported across the ocean, especially across the Atlantic and around the Pacific Rim. A lot of cargo, such as manufactured goods, is usually transported within
standard sized, lockable containers, loaded on purpose-built
container ships at
dedicated terminals.
Containerization greatly increased the efficiency and decreased the cost of moving goods by sea, and was a major factor leading to the rise of
globalization and exponential increases in
international trade in the mid-to-late 20th century.
Oceans are also the major supply source for the
fishing industry. Some of the major harvests are
shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
,
fish,
crabs, and
lobster
Lobsters are a family (biology), family (Nephropidae, Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs ...
.
The biggest commercial fishery globally is for
anchovies,
Alaska pollock and
tuna.
A report by
FAO in 2020 stated that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world’s marine fisheries were classified as
overfished".
Fish and other fishery products from both
wild fisheries and aquaculture are among the most widely consumed sources of protein and other essential nutrients. Data in 2017 showed that "fish consumption accounted for 17 percent of the global population’s intake of animal proteins".
In order to fulfill this need, coastal countries have exploited marine resources in their
exclusive economic zone, although fishing vessels are increasingly venturing further afield to exploit stocks in international waters.
The ocean offers a very large supply of
energy carried by
ocean waves,
tides,
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
differences, and
ocean temperature differences which can be harnessed to
generate electricity.
Forms of
sustainable marine energy include
tidal power,
ocean thermal energy and
wave power.
is captured by
wind turbines placed out on the ocean; it has the advantage that wind speeds are higher than on land, though wind farms are more costly to construct offshore. There are large deposits of
petroleum, as oil and
natural gas, in rocks beneath the ocean floor.
Offshore platforms and
drilling rigs
extract
An extract is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures, absolutes or in powder form.
The aromatic principles of many spices, nuts, h ...
the oil or gas and store it for transport to land.
"Freedom of the seas" is a principle in
international law dating from the seventeenth century. It stresses freedom to navigate the oceans and disapproves of war fought in
international waters.
Today, this concept is enshrined in the
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
There are two major international legal organizations that are involved in
ocean governance
Ocean governance is the conduct of the policy, actions and affairs regarding the world's oceans. Within governance, it incorporates the influence of non-state actors, i.e. stakeholders, NGOs and so forth, therefore the state is not the only act ...
on a global scale, namely the
International Maritime Organization
The International Maritime Organization (IMO, French: ''Organisation maritime internationale'') is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference ...
and the
United Nations. The International Maritime Organization (IMO), which was ratified in 1958 is responsible mainly for
maritime safety, liability and compensation and they have held some conventions on marine pollution related to shipping incidents. Ocean governance is the conduct of the policy, actions and affairs regarding the world's
oceans.
Threats from human activities

Human activities affect
marine life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. M ...
and
marine habitats through many negative influences, such as
marine pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural and municipal solid waste, residential waste, particle (ecology), particles, noise, excess carbon dioxid ...
(including
marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing ...
and microplastics)
overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
,
ocean acidification and other
effects of climate change on oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice ...
.
Marine pollution
Plastic pollution
Overfishing
Protection
Protecting Earth's oceans ecosystem/s against its recognized
threats is a major component of
environmental protection and is closely related to
sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The des ...
. One of its main techniques is the creation and enforcement of
marine protected areas (MPAs). Other techniques may include
standardized product certifications, supply chain transparency requirements policies, policies to prevent marine pollution,
eco-tariff
An eco-tariff, also known as an environmental tariff or carbon tariff, is a trade barrier erected for the purpose of reducing pollution and improving the environment. These trade barriers may take the form of import or export taxes on products t ...
s,
research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
, ecosystem-assistance (e.g.
for coral reefs), support for
sustainable seafood Sustainable seafood is seafood that is caught or farmed in ways that consider the long-term vitality of harvested species and the well-being of the oceans, as well as the livelihoods of fisheries-dependent communities. It was first promoted throug ...
(e.g.
sustainable fishing practices and types of aquaculture), banning and systematically obstructing (e.g. via higher costs policies) unsustainable ocean use and associated industries (e.g.
cruise ship travel,
certain shipping practices),
monitoring, revising
waste management of plastics and
fashion industry pollutants, protection of marine resources and components whose extraction or disturbance would cause substantial harm, engagement of broader publics and impacted communities, novel
decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
mechanisms, and the development of ocean clean-up projects. Ocean protection serves to i.a. protect human health and to safeguard stable conditions of this natural ecosystem upon which humans depend.
It may be necessary to consider marine protection within a national, regional and international context. Marine protection could also have synergistic effects – for instance, according to a study, a global network of MPAs designed to improve fisheries productivity could substantially increase future catch.
In 2021, 43 expert scientists published the first scientific framework version that – via integration,
review, clarifications and
standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
– enables the evaluation of levels of protection of
marine protected areas and can serve as a guide for any subsequent efforts to improve, plan and monitor marine protection quality and extents. Examples are the efforts towards the 30%-protection-goal of the "Global Deal For Nature" and the UN's
Sustainable Development Goal 14
Sustainable Development Goal 14 (Goal 14 or SDG 14) is about "Life below water" and is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is to "Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas ...
("life below water").
Extraterrestrial oceans
Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other
elements
Element or elements may refer to:
Science
* Chemical element, a pure substance of one type of atom
* Heating element, a device that generates heat by electrical resistance
* Orbital elements, parameters required to identify a specific orbit of ...
and
compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface
liquids are the
lakes of Titan, which are made of hydrocarbons instead of water. However, there is strong evidence for subsurface water oceans' existence elsewhere in the
Solar System. The best-established candidates for subsurface water oceans in the Solar System are Jupiter's moons
Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliff ...
,
Ganymede, and
Callisto; and Saturn's moons
Enceladus and
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
.
Although Earth is the only known
planet with large stable bodies of liquid water on its surface and the only one in the
Solar System, other celestial bodies are thought to have large oceans.
In June 2020,
NASA scientists reported that it is likely that
exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s with oceans may be common in the
Milky Way galaxy, based on
mathematical modeling studies.
Supercritical fluid on gas giants
The inner structure of
gas giants remain poorly understood. Scientists suspect that, under extreme pressure,
hydrogen would act as a
supercritical fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous so ...
, hence the likelihood of oceans of liquid hydrogen deep in the interior of gas giants like
Jupiter.
Oceans of liquid
carbon have been hypothesized to exist on
ice giants, notably
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
and
Uranus.
See also
*
European Atlas of the Seas
The European Atlas of the Seas is an easy-to-use and interactive web-based atlas on the coasts and seas within and around Europe and provides information on Europe's marine environment. It is freely accessible on the internet. The latest version o ...
*
Land and water hemispheres
*
List of seas
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.
Terminology
* Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocean ...
*
Marine heatwave
*
World Ocean Atlas
The World Ocean Atlas (WOA) is a data product of the Ocean Climate Laboratory of the National Oceanographic Data Center (U.S.). The WOA consists of a climatology of fields of ''in situ'' ocean properties for the World Ocean. It was first produced ...
*
World Oceans Day
References
External links
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) Fisheries DivisionNOAA – National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (United States)United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–2030)
{{Authority control
Oceans
Coastal and oceanic landforms
Bodies of water
Articles containing video clips
 The entire ocean, containing 97% of Earth's water, spans 70.8% of Earth's surface, making it Earth's global ocean or ''world ocean''. This makes Earth, along with its vibrant hydrosphere a "water world" or "
The entire ocean, containing 97% of Earth's water, spans 70.8% of Earth's surface, making it Earth's global ocean or ''world ocean''. This makes Earth, along with its vibrant hydrosphere a "water world" or " Every ocean basin has a mid-ocean ridge, which creates a long mountain range beneath the ocean. Together they form the global mid-oceanic ridge system that features the longest mountain range in the world. The longest continuous mountain range is . This underwater mountain range is several times longer than the longest continental mountain range—the Andes.
Oceanographers state that less than 20% of the oceans have been mapped.
Every ocean basin has a mid-ocean ridge, which creates a long mountain range beneath the ocean. Together they form the global mid-oceanic ridge system that features the longest mountain range in the world. The longest continuous mountain range is . This underwater mountain range is several times longer than the longest continental mountain range—the Andes.
Oceanographers state that less than 20% of the oceans have been mapped.
 The average depth of the oceans is about 4 km. More precisely the average depth is . Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over deep. "Deep ocean," which is anything below 200 meters (660 ft.), covers about 66% of Earth's surface. This figure does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the Caspian Sea.
The deepest point in the ocean is the Mariana Trench, located in the Pacific Ocean near the Northern Mariana Islands. Its maximum depth has been estimated to be . The British naval vessel ''Challenger II'' surveyed the trench in 1951 and named the deepest part of the trench the " Challenger Deep". In 1960, the Trieste successfully reached the bottom of the trench, manned by a crew of two men.
The average depth of the oceans is about 4 km. More precisely the average depth is . Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over deep. "Deep ocean," which is anything below 200 meters (660 ft.), covers about 66% of Earth's surface. This figure does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the Caspian Sea.
The deepest point in the ocean is the Mariana Trench, located in the Pacific Ocean near the Northern Mariana Islands. Its maximum depth has been estimated to be . The British naval vessel ''Challenger II'' surveyed the trench in 1951 and named the deepest part of the trench the " Challenger Deep". In 1960, the Trieste successfully reached the bottom of the trench, manned by a crew of two men.



 Collectively, currents move enormous amounts of water and heat around the globe influencing climate. These wind driven currents are largely confined to the top hundreds of meters of the ocean. At greater depth the drivers of water motion are the thermohaline circulation (the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermoholine circulation). This is driven by the cooling of surface waters at northern and southern polar latitudes creating dense water which sinks to the bottom of the ocean. This cold and dense water moves slowly away from the
Collectively, currents move enormous amounts of water and heat around the globe influencing climate. These wind driven currents are largely confined to the top hundreds of meters of the ocean. At greater depth the drivers of water motion are the thermohaline circulation (the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermoholine circulation). This is driven by the cooling of surface waters at northern and southern polar latitudes creating dense water which sinks to the bottom of the ocean. This cold and dense water moves slowly away from the  Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by oceans in response to the
Tides are the regular rise and fall in water level experienced by oceans in response to the  Ocean water represents the largest body of water within the global water cycle (oceans contain 97% of Earth's water). Evaporation from the ocean moves water into the atmosphere to later rain back down onto land and the ocean. Oceans have a significant effect on the biosphere. The ocean as a whole is thought to cover approximately 90% of the Earth's biosphere. Oceanic
Ocean water represents the largest body of water within the global water cycle (oceans contain 97% of Earth's water). Evaporation from the ocean moves water into the atmosphere to later rain back down onto land and the ocean. Oceans have a significant effect on the biosphere. The ocean as a whole is thought to cover approximately 90% of the Earth's biosphere. Oceanic 
 Ocean water contains large quantities of dissolved gases, including oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. These dissolve into ocean water via gas exchange at the ocean surface, with the solubility of these gases depending on the temperature and salinity of the water. The four most abundant gases in earth’s atmosphere and oceans are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. In the ocean by volume, the most abundant gases dissolved in seawater are carbon dioxide (including bicarbonate and carbonate ions, 14 mL/L on average), nitrogen (9 mL/L), and oxygen (5 mL/L) at equilibrium at All gases are more soluble – more easily dissolved – in colder water than in warmer water. For example, when salinity and pressure are held constant, oxygen concentration in water almost doubles when the temperature drops from that of a warm summer day to freezing . Similarly, carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases are more soluble at colder temperatures, and their solubility changes with temperature at different rates.
Ocean water contains large quantities of dissolved gases, including oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. These dissolve into ocean water via gas exchange at the ocean surface, with the solubility of these gases depending on the temperature and salinity of the water. The four most abundant gases in earth’s atmosphere and oceans are nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. In the ocean by volume, the most abundant gases dissolved in seawater are carbon dioxide (including bicarbonate and carbonate ions, 14 mL/L on average), nitrogen (9 mL/L), and oxygen (5 mL/L) at equilibrium at All gases are more soluble – more easily dissolved – in colder water than in warmer water. For example, when salinity and pressure are held constant, oxygen concentration in water almost doubles when the temperature drops from that of a warm summer day to freezing . Similarly, carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases are more soluble at colder temperatures, and their solubility changes with temperature at different rates.
 The process of photosynthesis in the surface ocean releases oxygen and consumes carbon dioxide. This photosynthesis in the ocean is dominated by
The process of photosynthesis in the surface ocean releases oxygen and consumes carbon dioxide. This photosynthesis in the ocean is dominated by  The ocean waters contain many chemical elements as dissolved ions. Elements dissolved in ocean waters have a wide range of concentrations. Some elements have very high concentrations of several grams per liter, such as sodium and chloride, together making up the majority of ocean salts. Other elements, such as iron, are present at tiny concentrations of just a few nanograms (10−9 grams) per liter.
The concentration of any element depends on its rate of supply to the ocean and its rate of removal. Elements enter the ocean from rivers, the atmosphere and
The ocean waters contain many chemical elements as dissolved ions. Elements dissolved in ocean waters have a wide range of concentrations. Some elements have very high concentrations of several grams per liter, such as sodium and chloride, together making up the majority of ocean salts. Other elements, such as iron, are present at tiny concentrations of just a few nanograms (10−9 grams) per liter.
The concentration of any element depends on its rate of supply to the ocean and its rate of removal. Elements enter the ocean from rivers, the atmosphere and  Human activities affect
Human activities affect