OPGA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package.
PGAs are often mounted on
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package.
PGAs are often mounted on
 Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA.
Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA.

 A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the
A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the
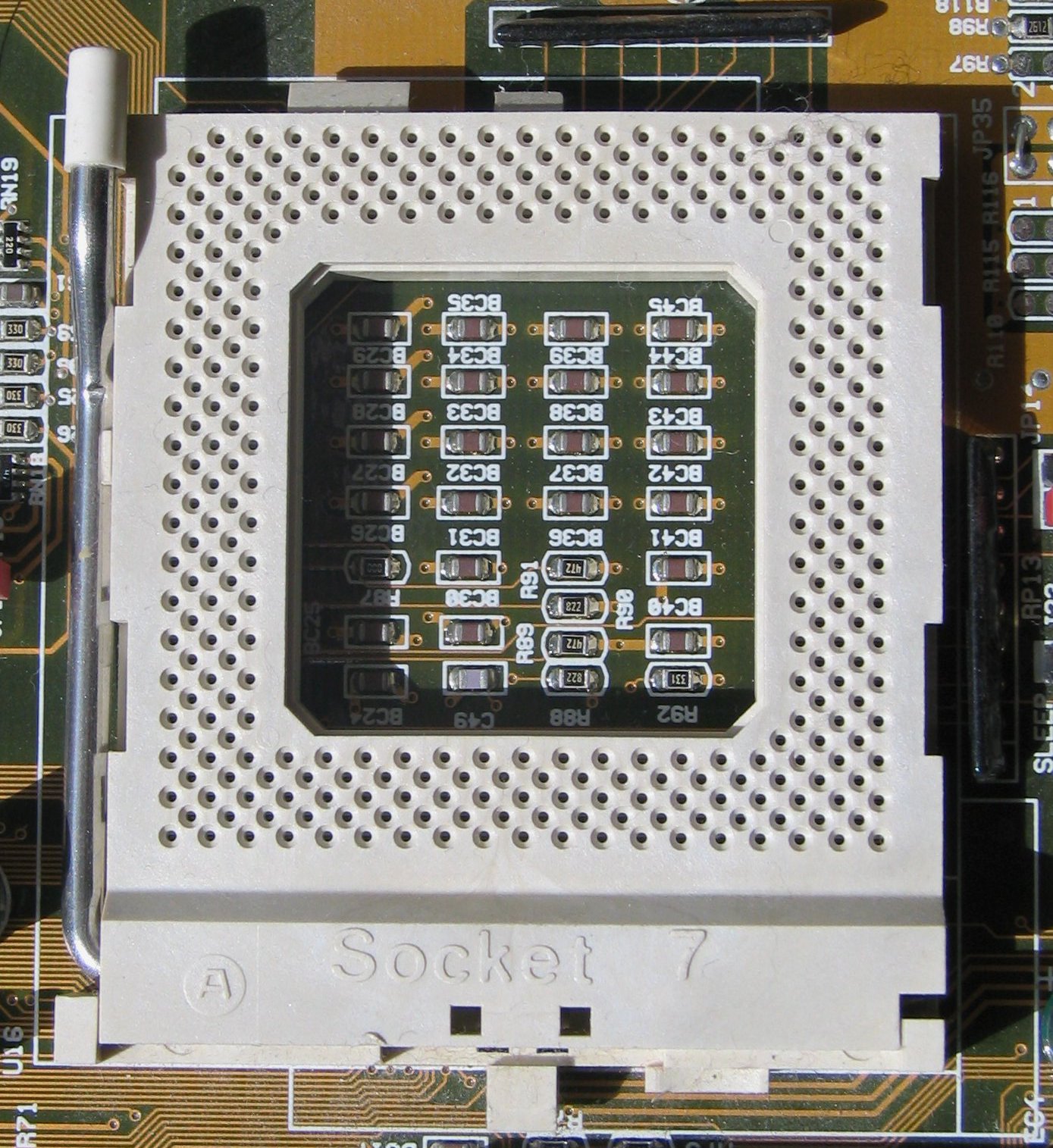
 It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square lattice. There is generally a section in the center of the package without any pins. SPGA packages are usually used by devices that require a higher pin density than what a PGA can provide, such as microprocessors.
It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square lattice. There is generally a section in the center of the package without any pins. SPGA packages are usually used by devices that require a higher pin density than what a PGA can provide, such as microprocessors.
File:VIA C3 C5XL CPGA.jpg, A 1.2 GHz VIA C3 microprocessor in a ceramic package
File:Pentium P54 Socket7 PGA.jpg, 133 MHz Pentium chip in a ceramic package
File:SL3A2down.JPG, The underside of a Celeron-400 in a PPGA
File:AMD Athlon XP 2000 - Socket A - OPGA.jpg, An OPGA CPU. Note the brown color – many OPGA parts are colored green. The die is in the center of the device, and the four gray circles are foam spacers to relieve pressure from the die, caused by the heat sink.
Intel CPU Processor Identification
Ball Grid Arrays: the High-Pincount Workhorses
John Baliga, associate editor, '' Semiconductor International'', 9/1/1999
Spot on component packaging
08/1998, '' Elektronik, Produktion & Prüftechnik''
Terminology
{{Semiconductor packages Chip carriers


printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
s using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(DIP).
PGA variants
Plastic
Flip chip
 A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the
A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This allows the die to have a more direct contact with the heatsink or other cooling mechanism.
The FC-PGA was introduced by Intel with the Coppermine core Pentium III and Celeron processors based on Socket 370, and was later used for Socket 478-based Pentium 4 and Celeron processors. FC-PGA processors fit into zero insertion force (ZIF) Socket 370 and Socket 478-based motherboard sockets; similar packages have also been used by AMD. It is still used today for mobile Intel processors.
Staggered pin
The staggered pin grid array (SPGA) is used by Intel processors based on Socket 5 and Socket 7. Socket 8 used a partial SPGA layout on half the processor.
 It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square lattice. There is generally a section in the center of the package without any pins. SPGA packages are usually used by devices that require a higher pin density than what a PGA can provide, such as microprocessors.
It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square lattice. There is generally a section in the center of the package without any pins. SPGA packages are usually used by devices that require a higher pin density than what a PGA can provide, such as microprocessors.
Ceramic
A ceramic pin grid array (CPGA) is a type of packaging used by integrated circuits. This type of packaging uses a ceramic substrate with pins arranged in a pin grid array. SomeCPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
s that use CPGA packaging are the AMD Socket A Athlons and the Duron.
A CPGA was used by AMD for Athlon and Duron processors based on Socket A, as well as some AMD processors based on Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as ...
and Socket AM2+. While similar form factors have been used by other manufacturers, they are not officially referred to as CPGA. This type of packaging uses a ceramic substrate with pins arranged in an array.
Organic
An organic pin grid array (OPGA) is a type of connection forintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s, and especially CPUs, where the silicon die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
is attached to a plate made out of an organic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
plastic which is pierced by an array of pins which make the requisite connections to the socket.
Stud
A stud grid array (SGA) is a short-pinned pin grid array chip scale package for use insurface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
. The polymer stud grid array or plastic stud grid array was developed jointly by the Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC) and Laboratory for Production Technology, Siemens AG.
rPGA
The reduced pin grid array was used by the socketed mobile variants of Intel's Core i3/5/7 processors and features a reduced pin pitch of 1mm, as opposed to the 1.27mm pin pitch used by contemporary AMD processors and older Intel processors. It is used in the G1, G2, and G3 sockets.See also
* Ball grid array (BGA) * Centered square number *Chip carrier
In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits (commonly called "chips"). Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mounti ...
- chip packaging and package types list
* Dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(DIP)
* Land grid array (LGA)
* Single in-line package (SIP)
* Zig-zag in-line package (ZIP)
References
Sources
* * *External links
Intel CPU Processor Identification
Ball Grid Arrays: the High-Pincount Workhorses
John Baliga, associate editor, '' Semiconductor International'', 9/1/1999
Spot on component packaging
08/1998, '' Elektronik, Produktion & Prüftechnik''
Terminology
{{Semiconductor packages Chip carriers