|
Socket G2
Socket G2, also known as rPGA 988B is Intel's CPU socket used with their line of mobile Core i7, the successor to the Core 2 line, and also with several mobile Core i5 and Core i3 processors. It is based on Intel's Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge architecture. Like its predecessor, socket G1 systems, it can only run in dual-channel memory mode, but with data rates up to 1600 MHz (as opposed to the triple-channel mode which is unique to the LGA-1366 platform and subsequent Xeon sockets). Socket G2 CPUs are also known as FCPGA988 socket processors, which should be pin compatible with PPGA988. Although nearly all motherboards using this socket are intended for mobile products like laptops, a few desktop boards using this do exist. Supermicro, for example, produced a number of mini ITX motherboards using the QM77 chipset. Technical specifications * Pins arranged in a 35×36 grid array (it is incompatible with G1 socket due to different placing of one pin) * 18×15 size grid remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin Grid Array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). PGA variants Plastic Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA. Flip chip A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)
Ivy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 22 nm microarchitecture used in the third generation of the Intel Core processors ( Core i7, i5, i3). Ivy Bridge is a die shrink to 22 nm process based on FinFET ("3D") Tri-Gate transistors, from the former generation's 32 nm Sandy Bridge microarchitecture—also known as tick–tock model. The name is also applied more broadly to the Xeon and Core i7 Ivy Bridge-E series of processors released in 2013. Ivy Bridge processors are backward compatible with the Sandy Bridge platform, but such systems might require a firmware update (vendor specific). In 2011, Intel released the 7-series Panther Point chipsets with integrated USB 3.0 and SATA 3.0 to complement Ivy Bridge. Volume production of Ivy Bridge chips began in the third quarter of 2011. Quad-core and dual-core-mobile models launched on April 29, 2012 and May 31, 2012 respectively. Core i3 desktop processors, as well as the first 22 nm Pentium, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
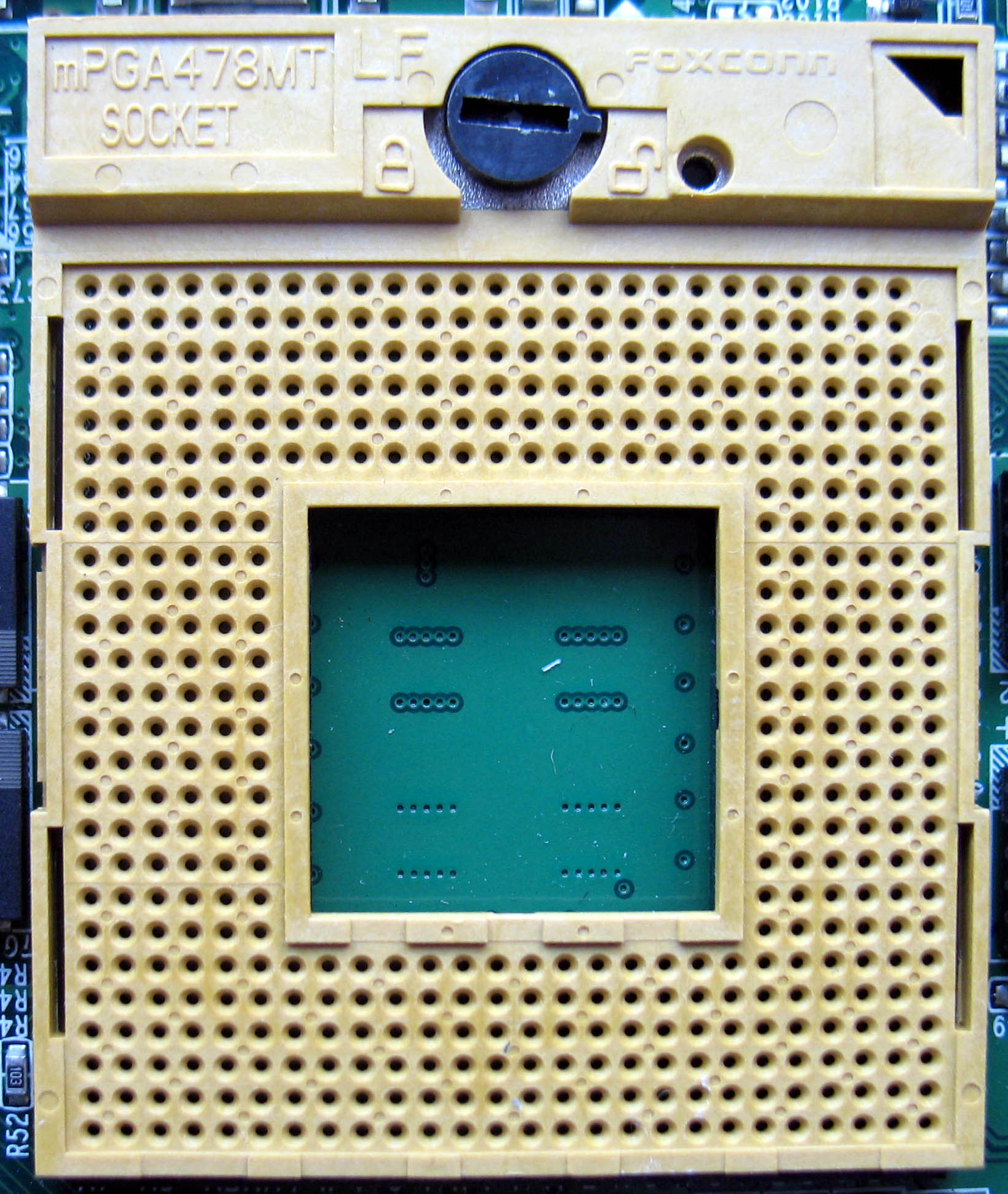
Socket P
The Intel Socket P (mPGA478MN) is the mobile processor socket replacement for Core microarchitecture chips such as Core 2 Duo. It launched on May 9, 2007, as part of the Santa Rosa platform with the Merom and Penryn processors. Technical specifications The front-side bus (FSB) of CPUs that install in Socket P can run at 400, 533, 667, 800, or 1066 MT/s. By adapting the multiplier the frequency of the CPU can throttle up or down to save power, given that all Socket P CPUs support EIST, except for Celeron that do not support EIST. Socket P has 478 pins, but is not electrically pin-compatible with Socket M or Socket 478 Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A .... Socket P is also known as a 478-pin Micro FCPGA or μFCPGA-478. On the plastic grid is printed mPGA478M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro-FCPGA
Socket M (mPGA478MT) is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors. Technical specifications Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman. It was also used in the first generation of the mobile version of Intel's Core 2 Duo, specifically, the T5x00 and T7x00 Merom lines (referred to as Napa Refresh), though that line switched to Socket P (Santa Rosa) in 2007. It typically uses the Intel 945PM/945GM chipsets which support up to 667 MHz FSB and the Intel PM965/GM965 which allows 800 MHz FSB support, though the Socket M, PM965/GM965 combination is less common. The "Sossaman" Xeons use the E7520 chipset. Relation to other sockets Socket M is pin-compatible with desktop socket mPGA478A but it is not electrically compatible. Socket M is not pin-compatible with the older desktop Socket 478 (mPGA478B) or the newer mobile Socket P (mPGA478MN) by location of one pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Microprocessors
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Raptor Lake") 12th generation Core Desktop (codenamed " Alder Lake") Mobile (codenamed " Alder Lake") 11th generation Core Desktop (codenamed " Rocket Lake") Mobile (codenamed " Tiger Lake") 10th generation Core Desktop (codenamed " Comet Lake") Mobile (codenamed " Comet Lake", " Ice Lake", and " Amber Lake") 9th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Coffee Lake Refresh") 8th generation Core Desktop (codenamed " Coffee Lake") Mobile (codenamed " Coffee Lake", " Amber Lake" and "Whiskey Lake") 7th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and " Skylake-X") Mobile (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and "Apollo Lake") All processors All processors are listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SO-DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations, printers, and servers. They are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini ITX
Mini-ITX is a motherboard form-factor, developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, they were a niche product, designed for fan-less cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience. The four mounting holes in a Mini-ITX board line up with four of the holes in ATX-specification motherboards, and the locations of the backplate and expansion slot are the same (though one of the holes used was optional in earlier versions of the ATX spec). Mini-ITX boards can therefore often be used in cases designed for ATX, micro-ATX and other ATX variants if desired. The design provides one expansion slot. Earlier motherboards conventionally have a standard 33 MHz 5V 32-bit PCI slot. Many older case designs use riser cards and some even have two-slot riser cards, although the two-slot riser cards are not compat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermicro
Super Micro Computer, Inc., dba Supermicro, is an information technology company based in San Jose, California. It has manufacturing operations in the Silicon Valley, the Netherlands and at its Science and Technology Park in Taiwan. Founded on November 1, 1993, Supermicro is a provider of high-performance and high-efficiency servers, server management softwares, and storage systems for various markets, including enterprise data centers, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, 5G and edge computing. Supermicro’s stock trades under the ticker symbol SMCI on the Nasdaq exchange. Supermicro fiscal year 2022 revenues were $5.2 billion and Supermicro has 4,607 employees globally. History Formation and initial public offering In 1993, Supermicro began as a 5 person operation run by Charles Liang alongside his wife and company treasurer, Chiu-Chu Liu, known as Sara. In 1996, the company opened a manufacturing subsidiary in Taiwan, Ablecom, which is run by Charles’s broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xeon
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture. They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus. Overview The ''Xeon'' brand has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-channel Architecture
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically, this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs two channels. The technique goes back as far as the 1960s having been used in IBM System/360 Model 91 and in CDC 6600. Modern high-end desktop and workstation processors such as the AMD Ryzen Threadripper series and the Intel Core i9 Extreme Edition lineup support quad-channel memory. Server processors from the AMD Epyc series and the Intel Xeon platforms give support to memory bandwidth starting from quad-channel module layout to up to octa-channel layout. In March 2010, AMD released Socket G34 and Magny-Cours Opteron 6100 series processors with support for quad-channel memory. In 2006, Intel released chipsets t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-channel Architecture
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically, this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs two channels. The technique goes back as far as the 1960s having been used in IBM System/360 Model 91 and in CDC 6600. Modern high-end desktop and workstation processors such as the AMD Ryzen Threadripper series and the Intel Core i9 Extreme Edition lineup support quad-channel memory. Server processors from the AMD Epyc series and the Intel Xeon platforms give support to memory bandwidth starting from quad-channel module layout to up to octa-channel layout. In March 2010, AMD released Socket G34 and Magny-Cours Opteron 6100 series processors with support for quad-channel memory. In 2006, Intel released chipsets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket G1
Socket G1, also known as rPGA 988A, is a CPU socket introduced by Intel in 2009 for the mobile variants of the first-generation Intel Core processors. It is the successor to Socket P, and the mobile counterpart to LGA 1156 and LGA 1366. History The first CPUs for the Socket G1 platform were released on September 23, 2009, in the form of the i7-720QM, 820QM, and 920XM. These CPUs use the Clarksfield core, which maintained the same 45 nm manufacturing process as the desktop Nehalem architecture. On January 4, 2010, the range was expanded with Core i3, i5, and i7 processors using the 32 nm Arrandale core and based on the Westmere architecture. On March 28, 2010, low-end Arrandale-based CPUs were released as the Pentium P6x00 series and Celeron P4x00 series. Further Clarksfield-based processors were released as the i7-740QM, 840QM, and 940XM on June 21, 2010. All Socket G1 processors have the Intel HD Graphics Ironlake core packaged onto the CPU substrate. Supported processors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_CPU-pins_PNr°0295.jpg)