pin grid array on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of
 Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core
Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core 
 A
A
 It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square
It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square
File:VIA C3 C5XL CPGA.jpg, A 1.2 GHz
File:SL3A2down.JPG, The underside of a
Intel CPU Processor Identification
Ball Grid Arrays: the High-Pincount Workhorses
John Baliga, associate editor, ''
Spot on component packaging
08/1998, '' Elektronik, Produktion & Prüftechnik''
Terminology
{{Semiconductor packages Chip carriers


integrated circuit packaging
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. ...
. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package.
PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
s using the through hole
A hole is an opening in or through a particular medium, usually a solid body. Holes occur through natural and artificial processes, and may be useful for various purposes, or may represent a problem needing to be addressed in many fields of en ...
method or inserted into a socket
Socket may refer to:
Mechanics
* Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts
* Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexag ...
. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(DIP).
PGA variants
Plastic
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32
IA-32 (short for "Intel Architecture, 32-bit", commonly called ...
processors based on Socket 370
Socket 370 (also known as the PGA370 socket) is a CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to first complement and later replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of ...
. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA.
Flip chip
 A
A flip-chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to exter ...
pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This allows the die to have a more direct contact with the heatsink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, the ...
or other cooling mechanism.
The FC-PGA was introduced by Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
with the Coppermine core Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial p ...
and Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32
IA-32 (short for "Intel Architecture, 32-bit", commonly called ...
processors based on Socket 370, and was later used for Socket 478
Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.
Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and th ...
-based Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 ...
and Celeron processors. FC-PGA processors fit into zero insertion force
Zero insertion force (ZIF) is a type of IC socket or electrical connector that requires very little (but not literally zero) force for insertion. With a ZIF socket, before the IC is inserted, a lever or slider on the side of the socket is mo ...
(ZIF) Socket 370 and Socket 478-based motherboard sockets; similar packages have also been used by AMD. It is still used today for mobile Intel processors.
Staggered pin
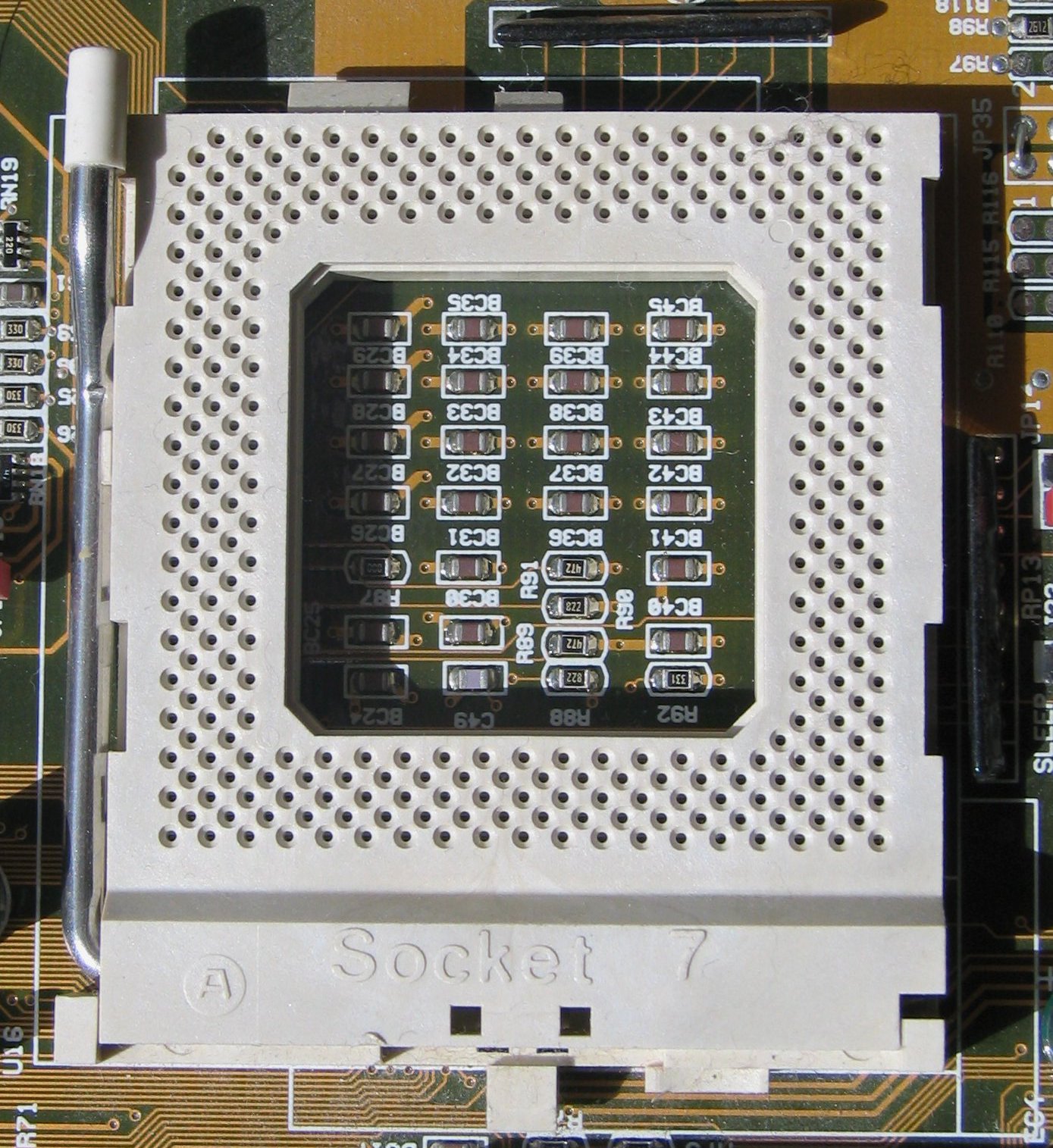
The staggered pin grid array (SPGA) is used by Intel processors based onSocket 5
Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 133 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. It superseded the earlier Sock ...
and Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by ...
. Socket 8
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II and Slot 2 with the release of ...
used a partial SPGA layout on half the processor.

 It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square
It consists of two square arrays of pins, offset in both directions by half the minimum distance between pins in one of the arrays. Put differently: within a square boundary the pins form a diagonal square lattice
Lattice may refer to:
Arts and design
* Latticework, an ornamental criss-crossed framework, an arrangement of crossing laths or other thin strips of material
* Lattice (music), an organized grid model of pitch ratios
* Lattice (pastry), an orna ...
. There is generally a section in the center of the package without any pins. SPGA packages are usually used by devices that require a higher pin density than what a PGA can provide, such as microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
s.
Ceramic
A ceramic pin grid array (CPGA) is a type of packaging used byintegrated circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
. This type of packaging uses a ceramic substrate with pins arranged in a pin grid array. Some CPUs that use CPGA packaging are the AMD Socket A
Socket A (also known as Socket 462) is a zero insertion force pin grid array (PGA) CPU socket used for AMD processors ranging from the Athlon Thunderbird to the Athlon XP/MP 3200+, and AMD budget processors including the Duron and Sempron. Soc ...
Athlon
Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). The original Athlon (now called Athlon Classic) was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the fi ...
s and the Duron
Duron is a line of budget x86-compatible microprocessors manufactured by AMD. Released on June 19, 2000 as a lower-cost offering to complement AMD's then mainstream performance Athlon processor line, it also competed with rival chipmaker Inte ...
.
A CPGA was used by AMD for Athlon and Duron processors based on Socket A, as well as some AMD processors based on Socket AM2 and Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboa ...
. While similar form factors have been used by other manufacturers, they are not officially referred to as CPGA. This type of packaging uses a ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
substrate with pins arranged in an array.
VIA C3
The VIA C3 is a family of x86 central processing units for personal computers designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies. The different CPU cores are built following the design methodology of Centaur Technology.
In addition to ...
microprocessor in a ceramic package
File:Pentium P54 Socket7 PGA.jpg, 133 MHz Pentium chip in a ceramic package
Organic
An organic pin grid array (OPGA) is a type of connection forintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s, and especially CPUs
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
, where the silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
die
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life.
Die may also refer to:
Games
* Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers
Manufacturing
* Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semicondu ...
is attached to a plate made out of an organic plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
which is pierced by an array of pin
A pin is a device used for fastening objects or material together.
Pin or PIN may also refer to:
Computers and technology
* Personal identification number (PIN), to access a secured system
** PIN pad, a PIN entry device
* PIN, a former Dutch ...
s which make the requisite connections to the socket
Socket may refer to:
Mechanics
* Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts
* Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexag ...
.
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32
IA-32 (short for "Intel Architecture, 32-bit", commonly called ...
-400 in a PPGA
File:AMD Athlon XP 2000 - Socket A - OPGA.jpg, An OPGA CPU. Note the brown color – many OPGA parts are colored green. The die is in the center of the device, and the four gray circles are foam spacers to relieve pressure from the die, caused by the heat sink.
Stud
A stud grid array (SGA) is a short-pinned pin grid array chip scale package for use insurface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
. The polymer stud grid array or plastic stud grid array was developed jointly by the Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre
Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC) is an international research & development organization, active in the fields of nanoelectronics and digital technologies, with headquarters in Belgium. Luc Van den hove has served as President and ...
(IMEC) and Laboratory for Production Technology
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physici ...
, Siemens AG
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
.
rPGA
The reduced pin grid array was used by the socketed mobile variants of Intel's Core i3/5/7 processors and features a reduced pin pitch of 1mm, as opposed to the 1.27mm pin pitch used by contemporary AMD processors and older Intel processors. It is used in the G1, G2, and G3 sockets.See also
*Ball grid array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be p ...
(BGA)
* Centered square number
In elementary number theory, a centered square number is a centered figurate number that gives the number of dots in a square with a dot in the center and all other dots surrounding the center dot in successive square layers. That is, each cen ...
* Chip carrier
In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits (commonly called "chips"). Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mounti ...
- chip packaging and package types list
* Dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(DIP)
* Land grid array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a ...
(LGA)
* Single in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
(SIP)
* Zig-zag in-line package
The zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging (DIL or DIP). A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 16, 20, 28 or 4 ...
(ZIP)
References
Sources
* * *External links
Intel CPU Processor Identification
Ball Grid Arrays: the High-Pincount Workhorses
John Baliga, associate editor, ''
Semiconductor International
''Semiconductor International'' () was a trade publication and web site owned by Reed Business Information serving the information needs of manufacturers of semiconductors and integrated circuits.
The editor-in-chief was Pete Singer.
Established ...
'', 9/1/1999
Spot on component packaging
08/1998, '' Elektronik, Produktion & Prüftechnik''
Terminology
{{Semiconductor packages Chip carriers