Northampton Arm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the
 Present-day Northampton is the latest in a series of settlements that began in the Bronze Age. Remains found in the Briar Hill district show evidence of a Neolithic encampment within a large circular earthwork where local farmers assembled for tribal ceremonies and seasonal events from approximately 3500 BC to 2000 BC.
During the
Present-day Northampton is the latest in a series of settlements that began in the Bronze Age. Remains found in the Briar Hill district show evidence of a Neolithic encampment within a large circular earthwork where local farmers assembled for tribal ceremonies and seasonal events from approximately 3500 BC to 2000 BC.
During the
 With the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, the town rose to national significance: its geographical location in the centre of England made Northampton a valuable strategical point for government and as a convenient meeting place for political, social, ecclesiastical and military events.
Northampton Castle is thought to have been built by
With the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, the town rose to national significance: its geographical location in the centre of England made Northampton a valuable strategical point for government and as a convenient meeting place for political, social, ecclesiastical and military events.
Northampton Castle is thought to have been built by
. British-history.ac.uk (23 September 1913). Retrieved on 17 July 2013.
 The royal connection to Northampton Castle became less significant, and by the time of the English Civil War, Northampton was decidedly pro-Parliament. Though Spencer Compton, Earl of Northampton, was a royalist ( Cavalier) and backed King Charles I, the people of Northampton supported Parliament and Oliver Cromwell's republican Roundhead army. The town had a long history of religious dissent from the Lollards and Puritanism gained a strong hold on the town. The corporation of the town, having already refused to provide troops to the King in 1632 or to pay the notorious ship money tax in 1636, petitioned Parliament in 1642 against
The royal connection to Northampton Castle became less significant, and by the time of the English Civil War, Northampton was decidedly pro-Parliament. Though Spencer Compton, Earl of Northampton, was a royalist ( Cavalier) and backed King Charles I, the people of Northampton supported Parliament and Oliver Cromwell's republican Roundhead army. The town had a long history of religious dissent from the Lollards and Puritanism gained a strong hold on the town. The corporation of the town, having already refused to provide troops to the King in 1632 or to pay the notorious ship money tax in 1636, petitioned Parliament in 1642 against  The town centre was further destroyed by the
The town centre was further destroyed by the  The devastation led to an Act of Parliament for the rebuilding the town. Local people and businesses helped to raise around £25,000 towards the rebuilding of the town centre based around the Market Square. Streets were widened and buildings made of brick and stone and tiled to prevent such devastation again. In an act of reconciliation, King Charles II donated timber from the royal forests of Salcey and Whittlebury to help with the rebuild. In 1678, the Sessions House and what is now County Hall were amongst the first buildings to be completed. A
The devastation led to an Act of Parliament for the rebuilding the town. Local people and businesses helped to raise around £25,000 towards the rebuilding of the town centre based around the Market Square. Streets were widened and buildings made of brick and stone and tiled to prevent such devastation again. In an act of reconciliation, King Charles II donated timber from the royal forests of Salcey and Whittlebury to help with the rebuild. In 1678, the Sessions House and what is now County Hall were amongst the first buildings to be completed. A 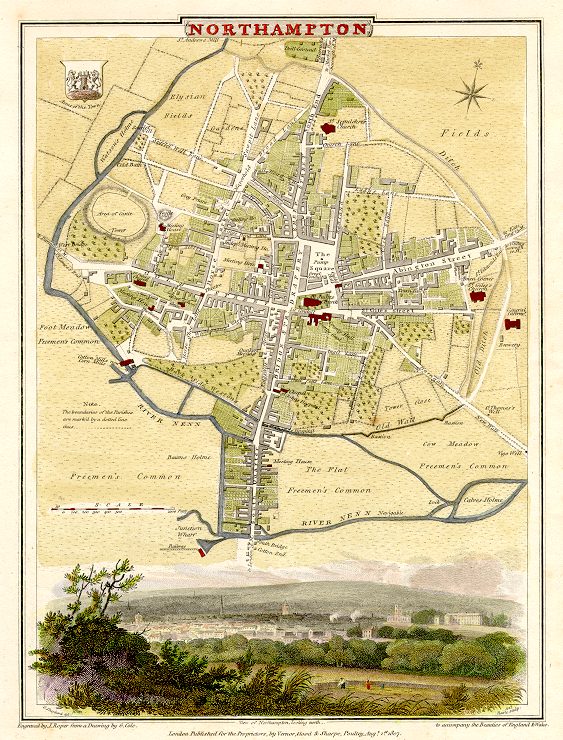 The Nene Navigation Company had previously made the River Nene navigable from King's Lynn as far up as Northampton in 1762, allowing cheap transportation of coal and other goods to the town, but in 1815, the Grand Union Canal reached the town, joining the River Nene, giving the town a direct link to the Midlands coalfields and to Birmingham, Manchester and London.
The first railway to be built into Northampton was the Northampton and Peterborough Railway, a branch from the main London and Birmingham Railway from Blisworth to Peterborough through Northampton which opened in 1845 along with the town's first railway station, Bridge Street station. This was followed by the opening of Castle station in 1859 on the site of part of the historic Northampton Castle, and later St. John's Street station in 1872. The Northampton loop of the West Coast Main Line was built in the late 1870s. Castle station was rebuilt and expanded over the site of Northampton Castle, the remains of which were purchased and demolished in 1880 to make way for the goods shed. Bridge Street Station closed in 1964 and St John's Street closed in 1939, leaving only Castle station serving the town. It is now known simply as
The Nene Navigation Company had previously made the River Nene navigable from King's Lynn as far up as Northampton in 1762, allowing cheap transportation of coal and other goods to the town, but in 1815, the Grand Union Canal reached the town, joining the River Nene, giving the town a direct link to the Midlands coalfields and to Birmingham, Manchester and London.
The first railway to be built into Northampton was the Northampton and Peterborough Railway, a branch from the main London and Birmingham Railway from Blisworth to Peterborough through Northampton which opened in 1845 along with the town's first railway station, Bridge Street station. This was followed by the opening of Castle station in 1859 on the site of part of the historic Northampton Castle, and later St. John's Street station in 1872. The Northampton loop of the West Coast Main Line was built in the late 1870s. Castle station was rebuilt and expanded over the site of Northampton Castle, the remains of which were purchased and demolished in 1880 to make way for the goods shed. Bridge Street Station closed in 1964 and St John's Street closed in 1939, leaving only Castle station serving the town. It is now known simply as
 After World War II, Northampton vastly changed. In 1959, the M1 motorway was opened to the south-west of the town; in 1968, Northampton was designated a
After World War II, Northampton vastly changed. In 1959, the M1 motorway was opened to the south-west of the town; in 1968, Northampton was designated a
Wndc.co.uk. Retrieved on 25 August 2011. In 2015, St Giles Street in the town centre was named the "Best British High Street" in a national competition run by the Department for Communities and Local Government.


 The town existed as an ancient borough in the medieval period before being one of the 178 boroughs to be reformed under the
The town existed as an ancient borough in the medieval period before being one of the 178 boroughs to be reformed under the
 Northampton is subdivided into suburbs, council wards, constituencies, ecclesiastical parishes, and other less formal areas.
Suburbs and districts of Northampton include:
Concurrent with the abolition of the borough of Northampton in 2021, the unparished area of Northampton became parished with three new parish councils being established: A new Town Council covering the majority of the urban area of Northampton was established, whilst the areas of Kingsthorpe, and Far Cotton and Delapré also gained parish councils. In addition, there are nine registered parish councils which predate the abolition of the borough of Northampton. These are Billing, Collingtree, Duston, Great Houghton, Hardingstone, Hunsbury Meadow, Upton, West Hunsbury and Wootton & East Hunsbury.
There are also settlements outside the town boundaries that are sometimes considered suburbs of Northampton, including Boughton, Cogenhoe, Ecton, Grange Park, Harpole, Little Houghton, Moulton, Overstone and Rothersthorpe.
Northampton is subdivided into suburbs, council wards, constituencies, ecclesiastical parishes, and other less formal areas.
Suburbs and districts of Northampton include:
Concurrent with the abolition of the borough of Northampton in 2021, the unparished area of Northampton became parished with three new parish councils being established: A new Town Council covering the majority of the urban area of Northampton was established, whilst the areas of Kingsthorpe, and Far Cotton and Delapré also gained parish councils. In addition, there are nine registered parish councils which predate the abolition of the borough of Northampton. These are Billing, Collingtree, Duston, Great Houghton, Hardingstone, Hunsbury Meadow, Upton, West Hunsbury and Wootton & East Hunsbury.
There are also settlements outside the town boundaries that are sometimes considered suburbs of Northampton, including Boughton, Cogenhoe, Ecton, Grange Park, Harpole, Little Houghton, Moulton, Overstone and Rothersthorpe.
 Northampton was a major centre of shoemaking and other leather industries, although only specialist shoemaking companies such as Barker Shoes, Church's, Crockett & Jones, Edward Green,
Northampton was a major centre of shoemaking and other leather industries, although only specialist shoemaking companies such as Barker Shoes, Church's, Crockett & Jones, Edward Green,
East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, Li ...
of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; it had a population of 212,100 in its previous local authority in the 2011 census (225,100 as of 2018 estimates). In its urban area, which includes Boughton and Moulton, it had a population of 215,963 as of 2011.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates to the Bronze Age, Romans and Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
s. In the Middle Ages, the town rose to national significance with the establishment of Northampton Castle, an occasional royal residence which regularly hosted the Parliament of England. Medieval Northampton had many churches, monasteries and the University of Northampton, all enclosed by the town walls. It was granted a town charter by Richard I in 1189 and a mayor was appointed by King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
in 1215. The town was also the site of two medieval battles, in 1264
Year 1264 ( MCCLXIV) was a leap year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Spring – Battle of Makryplagi: Constantine Palaiologos, half-brother of Em ...
and 1460
Year 1460 (Roman numerals, MCDLX) was a leap year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar, the 1460th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 460th year of the 2nd millennium ...
.
Northampton supported the Parliamentary Roundheads in the English Civil War, and Charles II ordered the destruction of the town walls and most of the castle. The Great Fire of Northampton
The Great Fire of Northampton occurred in September 1675 in Northampton in Northamptonshire, England. The blaze was caused by sparks from an open fire on St. Mary’s Street, near Northampton Castle. The fire devastated the town centre, destroying ...
in 1675 destroyed much of the town. It was soon rebuilt and grew rapidly with the industrial development of the 18th century. Northampton continued to grow with the arrival of the Grand Union Canal and the railways in the 19th century, becoming a centre for footwear and leather manufacture.
Growth was limited following the World Wars until it was designated a New Town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
in 1968, accelerating development which has continued into the 21st century. Northampton has unsuccessfully applied for city status three times; in 2000, 2002 and 2022.
History
Etymology
The earliest reference to Northampton in writing occurred in 914 under the name ''Ham tune'', literally meaning "home town". The prefix "North" was added later to distinguish it from other towns called Hampton, most prominently Southampton. The '' Domesday Book'' (1086) records the town as ''Northantone'', which evolved into ''Norhamptone'' by the 13th century and later ''Northampton'' by the 17th century.Ancient
 Present-day Northampton is the latest in a series of settlements that began in the Bronze Age. Remains found in the Briar Hill district show evidence of a Neolithic encampment within a large circular earthwork where local farmers assembled for tribal ceremonies and seasonal events from approximately 3500 BC to 2000 BC.
During the
Present-day Northampton is the latest in a series of settlements that began in the Bronze Age. Remains found in the Briar Hill district show evidence of a Neolithic encampment within a large circular earthwork where local farmers assembled for tribal ceremonies and seasonal events from approximately 3500 BC to 2000 BC.
During the British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ire ...
, people typically lived in protected hill forts. Present-day Hunsbury Hill is an example of this settlement; a circular ditch and a bank faced with a wall of timber and enclosing an area of which dates to around 400 BC. In the Roman period
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, a small rural settlement is thought to have existed in the present-day district of Duston; remains of Roman pottery were found there.
Following a Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
invasion, the central area of the town was turned into a stronghold called a ''burh'' probably by the Anglo-Saxons. By the time of the Peace of Wedmore
The Treaty of Wedmore is a 9th-century accord between Alfred the Great of Wessex and the Viking king Guthrum the Old. The only contemporary reference to this treaty, is that of a Welsh monk Asser in his biography of Alfred, (known as ''Vita Æl ...
in 878 the Burgh was in possession of the Danes and became the base for one of the Danish armies. A ditch was dug around the settlement and it was fortified with earth ramparts. Having conquered Mercia, the Danes turned the settlement into a centre for military and administrative purposes, which was part of the Danelaw. The Danish army of Northampton however submitted to Edward the Elder, Saxon King of Wessex (who controlled the southern and western part of the English Kingdom of Mercia) in 921
In the 9th century ''Regenhere of Northampton'' an East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
n Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
with localised veneration was buried in Northampton. By 918, Northampton had an earl and an army dependent upon it, whose territory extended to the River Welland
The River Welland is a lowland river in the east of England, some long. It drains part of the Midlands eastwards to The Wash. The river rises in the Hothorpe Hills, at Sibbertoft in Northamptonshire, then flows generally northeast to Market ...
.
Edward the Elder turned Northampton into the centre of one of the new shires, and it prospered as a river port and trading centre. In 940, it resisted the invading forces of Danish opposition in Northumbria when the Mercians successfully defended the town in a siege by King Olaf of York, but was burnt in 1010 by a Danish army, and again in 1065 by the rebellious northern earls Edwin and Morcar. Despite this, the ''Domesday Book'' records ''Northantone'' as possessing 316 houses with a population of 2000 people, ranking between Warwick and Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
in size.
Medieval
 With the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, the town rose to national significance: its geographical location in the centre of England made Northampton a valuable strategical point for government and as a convenient meeting place for political, social, ecclesiastical and military events.
Northampton Castle is thought to have been built by
With the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, the town rose to national significance: its geographical location in the centre of England made Northampton a valuable strategical point for government and as a convenient meeting place for political, social, ecclesiastical and military events.
Northampton Castle is thought to have been built by Simon de Senlis
Simon II de Senlis (or Senliz, St. Liz, etc.), 4th Earl of Huntingdon, Earl of the Honour of Huntingdon and Northampton ( 1098 – 1153) was an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman nobleman. He was the son of Simon I de Senlis, Earl of Huntingdon-Northamp ...
, who became the first Earl of Northampton, circa 1084. It was originally an earth and timber stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived ...
d construction which was later rebuilt in stone.Andrew, Martin: ''Northampton'' The Francis Frith Collection, 2002 The castle became an occasional royal residence from the reign of King Henry I in 1130 until that of King Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father died ...
. King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
regularly stayed at the castle and moved The Treasury there in 1205. Some 32 Parliaments were held there. The last Parliament at Northampton was held in 1380. Significant events in the castle's history include the trial of Thomas Becket in 1164, the publication of the Assize of Northampton in 1176, the declaration of peace with Scotland in the Treaty of Edinburgh–Northampton, the passage of the Statute of Northampton in 1328 and the imposition of poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments fr ...
in 1380. Royal tournaments and feasts were also held at the castle.The borough of Northampton – Introduction , A History of the County of Northampton: Volume 3 (pp. 1-26). British-history.ac.uk (23 September 1913). Retrieved on 17 July 2013.
Simon de Senlis
Simon II de Senlis (or Senliz, St. Liz, etc.), 4th Earl of Huntingdon, Earl of the Honour of Huntingdon and Northampton ( 1098 – 1153) was an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman nobleman. He was the son of Simon I de Senlis, Earl of Huntingdon-Northamp ...
is also thought to have built the medieval town walls, which enclosed about and had four main gates. Though demolished now, the circular pattern of the main roads surrounding the town centre marks the original position of the walls. de Senlis founded the Cluniac Priory of St Andrew's in the area of Semilong, and built The Church of the Holy Sepulchre
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in En ...
– one of four remaining round church
A round church is a church construction with a completely circular plan. There are many Nordic round churches in Sweden and Denmark (notably the island of Bornholm); round churches were popular in Scandinavia in the 11th and early 12th centuries ...
es in England – and All Hallows' Church on the current site of All Saints' Church
All Saints Church, or All Saints' Church or variations on the name may refer to:
Albania
*All Saints' Church, Himarë
Australia
*All Saints Church, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory
* All Saints Anglican Church, Henley Brook, Western Austr ...
. His son, Simon II de Senlis, built St Peter's Church on a site between a former Anglo-Saxon palace and Northampton Castle. Simon II de Senlis also founded Delapré Abbey – another Cluniac priory – which still stands today. Other priories in medieval Northampton include St James' Abbey, Graye Friers, Blackfriars and Whitefriars. St. John's, a medieval hospital, was situated east of Bridge Street. A network of medieval tunnels remains under the centre of Northampton around All Saints' Church and the Market Square but their purpose, extent and significance have been disputed.
The town was originally controlled by officials acting for the King who collected taxes and upheld the law. This changed on 18 November 1189 when King Richard I granted the town its first charter in exchange for money to fund his crusades. The charter allowed the townspeople certain rights and independence in legal and administrative matters. In 1215, King John authorised the appointment of William Tilly as the town's first Mayor and ordered that "twelve of the better and more discreet esidentsof your town" join him as a council to assist him. The importance of Northampton at this time is underlined by the fact that only London, York and King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, no ...
had mayors by this date. The mayor later ruled with 24 councillors and 48 freemen in a closed body until 1835.
In 1261, the medieval University of Northampton was established by royal charter from King Henry III. Had it survived, it would be the third oldest university founded in England after Oxford and Cambridge. However, after members of the university sided with supporters of Simon de Montfort (who was rebelling against the King) and advisors to The Crown said that Northampton was a threat to Oxford's scholastic hegemony, Henry III dissolved the university in 1265.
Markets and fairs were a key element in the town's economy in medieval times. The Market Square came to prominence in 1235 when Henry III ordered that the selling of goods in the churchyard of All Saints should be relocated to the Market Square. Street names in the town give an indication of trades and market centres; Corn Hill, Malt Hill, Mercer Row, Gold Street, Sheep Street and Horse Market. Cloth and wool were very important but these industries declined. In the 13th century, Northampton had a large Jewish population centred on Gold Street. In 1277 – two years after Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
passed the Statute of the Jewry
The Statute of the Jewry (''Statutum de Judaismo, 1275'') was a statute issued by Edward I of England in 1275. It placed a number of restrictions on Jews of England, most notably outlawing the practice of usury.Prestwich, Michael. Edward I p 345 ( ...
– some Jewish residents were executed while the remainder were driven out of town. Archaeological sites include a medieval Jewish cemetery and the Northampton Medieval Synagogue
The Northampton Medieval Synagogue is an archeology, archaeological site and medieval synagogue building in Sheep Street, Northampton, England.
The synagogue was discovered in 2010 by Marcus Roberts of National Anglo-Jewish Heritage Trail (JTrai ...
.
The First Barons' War caused significant destruction to Northampton. The barons besieged Northampton Castle in protest at King John's oppression of his subjects. In retaliation, royalist forces destroyed a large part of the town. When the forces of King Henry III overran the supporters of Simon de Montfort, the Second Barons' War broke out. The First Battle of Northampton took place in 1264 at the site of Northampton Castle where King Henry III and his son Prince Edward attacked with a large army, pillaged the town and took prisoners.
In 1349, the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
pandemic killed more than half the population of Northampton. In 1377, the population was 2,200. The town was rapidly losing its wealth and its importance as a national centre. In 1460, the Second Battle of Northampton took place during the War of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
in the meadows between the River Nene and Delapré Abbey. The Yorkists
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of York, t ...
defeated the Lancastrians and King Henry VI
Henry VI (6 December 1421 – 21 May 1471) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1422 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471, and disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. The only child of Henry V, he succeeded to the English throne a ...
was taken prisoner. In 1484, the Mayor declared that Northampton was "in great desolation and ruin". The Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1538 led to further destruction of what remained of the medieval town. Northampton was severely affected by Plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
between March and September 1638 when 665 people died.
Early modern
 The royal connection to Northampton Castle became less significant, and by the time of the English Civil War, Northampton was decidedly pro-Parliament. Though Spencer Compton, Earl of Northampton, was a royalist ( Cavalier) and backed King Charles I, the people of Northampton supported Parliament and Oliver Cromwell's republican Roundhead army. The town had a long history of religious dissent from the Lollards and Puritanism gained a strong hold on the town. The corporation of the town, having already refused to provide troops to the King in 1632 or to pay the notorious ship money tax in 1636, petitioned Parliament in 1642 against
The royal connection to Northampton Castle became less significant, and by the time of the English Civil War, Northampton was decidedly pro-Parliament. Though Spencer Compton, Earl of Northampton, was a royalist ( Cavalier) and backed King Charles I, the people of Northampton supported Parliament and Oliver Cromwell's republican Roundhead army. The town had a long history of religious dissent from the Lollards and Puritanism gained a strong hold on the town. The corporation of the town, having already refused to provide troops to the King in 1632 or to pay the notorious ship money tax in 1636, petitioned Parliament in 1642 against papist
The words Popery (adjective Popish) and Papism (adjective Papist, also used to refer to an individual) are mainly historical pejorative words in the English language for Roman Catholicism, once frequently used by Protestants and Eastern Orthodox ...
s and bishops.
When war broke out in 1642, the town willingly became the main Parliamentarian garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mil ...
for the south-east Midlands area with the former royal castle as its headquarters. In 1643, Prince Rupert
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist cavalr ...
attacked Northampton with approximately 2,000 men, but was beaten back at the North Gate of the town. Oliver Cromwell visited in 1645 and General Fairfax
Thomas Fairfax, 3rd Lord Fairfax of Cameron (17 January 161212 November 1671), also known as Sir Thomas Fairfax, was an English politician, general and Parliamentary commander-in-chief during the English Civil War. An adept and talented command ...
marched from the town to Naseby, where Charles I's Royalist army was decisively defeated. Over 4,000 pairs of leather shoes and 600 pairs of cavalry jack-boots for the Parliamentary armies were manufactured in Northampton during the Civil War, and a further 2,000 for Cromwell's New Model Army
The New Model Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Th ...
in 1648. Until well into the 19th century, the shoe industry boomed in and around the town with small manufacturing workshops set up in the surrounding areas.
The War ended with a Parliamentary victory, resulting in England becoming a Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
, which lasted a decade. Following the restoration of King Charles II in 1660, he took revenge on the town by ordering the destruction of its walls and partial demolition of its castle in 1662, since it did not support his father Charles I and his cavaliers. From then on, the castle was used as a court and a gaol, but its physical condition worsened. The new council of the town had to pay £200 to have its charter renewed and also required all officials to swear the oath of allegiance and some confirmed by the Crown.
Great Fire of Northampton
The Great Fire of Northampton occurred in September 1675 in Northampton in Northamptonshire, England. The blaze was caused by sparks from an open fire on St. Mary’s Street, near Northampton Castle. The fire devastated the town centre, destroying ...
in 1675, caused by sparks from an open fire in a thatched cottage by the castle. The fire spread eastwards by strong westerly winds and consumed three-quarters of the town centre in 24 hours. Matters were worsened because most buildings were chiefly made of wood and covered with thatch. An estimated 600 buildings were destroyed, amounting to £150,000 lost. Very little survived the fire, apart from buildings made of stone, like the Welsh House on Market Square, built in 1595, and Hazelrigg House in Mare Fair, built in 1662.
 The devastation led to an Act of Parliament for the rebuilding the town. Local people and businesses helped to raise around £25,000 towards the rebuilding of the town centre based around the Market Square. Streets were widened and buildings made of brick and stone and tiled to prevent such devastation again. In an act of reconciliation, King Charles II donated timber from the royal forests of Salcey and Whittlebury to help with the rebuild. In 1678, the Sessions House and what is now County Hall were amongst the first buildings to be completed. A
The devastation led to an Act of Parliament for the rebuilding the town. Local people and businesses helped to raise around £25,000 towards the rebuilding of the town centre based around the Market Square. Streets were widened and buildings made of brick and stone and tiled to prevent such devastation again. In an act of reconciliation, King Charles II donated timber from the royal forests of Salcey and Whittlebury to help with the rebuild. In 1678, the Sessions House and what is now County Hall were amongst the first buildings to be completed. A Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
town with new houses, shops and workshops eventually grew out of the old medieval town destroyed by the fire. In 1742 Edward Cave
Edward Cave (27 February 1691 – 10 January 1754) was an English printer, editor and publisher. He coined the term "magazine" for a periodical, founding ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' in 1731, and was the first publisher to successfully fashio ...
opened Marvel's Mill
Marvel's Mill (or Marvell's Mill) on the River Nene in Northampton, England, was the world's second factory for spinning cotton, the first to be operated as a water mill, and the first to be driven by an inanimate power-source. Opened by Edward ...
, the world's first cotton mill to be driven by a water wheel, on the River Nene.
A permanent military presence was established in the town with the completion of Gibraltar Barracks in 1797.
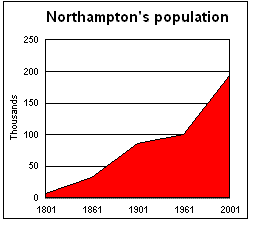
By the end of the 18th century, Northampton had become a major centre of footwear and leather manufacture. In 1801, the population was 7,020; it more than doubled to 15,351 in 1831, attributed to the fact that there was great demand for footwear caused by the Napoleonic Wars of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. A third of the adult males alone were shoemakers at the time. Northampton grew beyond the old town walls and industry grew rapidly with the mechanisation of factories by the middle of the 19th century.
 The Nene Navigation Company had previously made the River Nene navigable from King's Lynn as far up as Northampton in 1762, allowing cheap transportation of coal and other goods to the town, but in 1815, the Grand Union Canal reached the town, joining the River Nene, giving the town a direct link to the Midlands coalfields and to Birmingham, Manchester and London.
The first railway to be built into Northampton was the Northampton and Peterborough Railway, a branch from the main London and Birmingham Railway from Blisworth to Peterborough through Northampton which opened in 1845 along with the town's first railway station, Bridge Street station. This was followed by the opening of Castle station in 1859 on the site of part of the historic Northampton Castle, and later St. John's Street station in 1872. The Northampton loop of the West Coast Main Line was built in the late 1870s. Castle station was rebuilt and expanded over the site of Northampton Castle, the remains of which were purchased and demolished in 1880 to make way for the goods shed. Bridge Street Station closed in 1964 and St John's Street closed in 1939, leaving only Castle station serving the town. It is now known simply as
The Nene Navigation Company had previously made the River Nene navigable from King's Lynn as far up as Northampton in 1762, allowing cheap transportation of coal and other goods to the town, but in 1815, the Grand Union Canal reached the town, joining the River Nene, giving the town a direct link to the Midlands coalfields and to Birmingham, Manchester and London.
The first railway to be built into Northampton was the Northampton and Peterborough Railway, a branch from the main London and Birmingham Railway from Blisworth to Peterborough through Northampton which opened in 1845 along with the town's first railway station, Bridge Street station. This was followed by the opening of Castle station in 1859 on the site of part of the historic Northampton Castle, and later St. John's Street station in 1872. The Northampton loop of the West Coast Main Line was built in the late 1870s. Castle station was rebuilt and expanded over the site of Northampton Castle, the remains of which were purchased and demolished in 1880 to make way for the goods shed. Bridge Street Station closed in 1964 and St John's Street closed in 1939, leaving only Castle station serving the town. It is now known simply as Northampton railway station
Northampton railway station serves the county town of Northampton in England. It is on the Northampton Loop of the West Coast Main Line. The station is served by West Midlands Trains services southbound to London Euston and northbound to Birmi ...
.
Tram lines were also laid down in the town in 1881 and electrified in 1903. An early omnibus service ran to Wellingborough, and since 1919 motor omnibus services ran to villages around the town which brought buyers and sellers to the market.
There were iron ore quarries in the countryside around the town during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries which have left their mark on the landscape. Some of the quarries were in what is now the town area in an arc from Kingsthorpe through Duston and Hunsbury round to Hardingstone beginning in about 1860. Some have now been built over and not all lasted very long. The town area quarries that lasted the longest and closed last were at Hunsbury which began working in 1877 and closed in 1920. There are remains of some of these quarries at Hunsbury Hill. There was an iron works by the river to the west of the town next to the railway that then operated between Northampton and Blisworth. This was called the Hunsbury Ironworks and operated between about 1874 and January 1921 using ore from these quarries and elsewhere.
Contemporary
Following World War I, the shoe industry was increasingly in decline, despite the town's factories supplying over 23 million pairs of boots to the armed forces. A total of 1,700 men from the town were lost of the 6,000 killed from the Northamptonshire Regiment. The town expanded further during the 1920s and saw the erection of Northampton Power Station, which supplied electricity to areas as far away as Wolverton, until its closure in 1975. Much council housing was also built largely to the east, north and south of the town, including Abington, Far Cotton, Kingsley, Kingsthorpe and Dallington – areas which had been incorporated within the borough's boundaries in 1901. However, the population growth slowed down as people moved beyond its boundaries. In 1901, the population had expanded to 90,923; in 1931, the population was 92,341.New Town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
. Both these events and the rail link helped Northampton's growth as a commuter town for London. The Northampton Development Corporation (NDC) was set up in 1968 to substantially redevelop the town in partnership with the local council, spending £205 million to build new housing and industrial estates, initially in Lumbertubs, Moulton Park and Round Spinney to the east, followed by Briar Hill, Camp Hill and East and West Hunsbury in the south of the town, mainly to accommodate the overflow population of new residents from the London area. In the town centre, older buildings were demolished and replaced or redeveloped for other buildings, including the former Greyfriars bus station, the Grosvenor Centre, Peacock Place (now Market Walk), shops, flats and hotels.
Although growth was slower than planned, the population grew from 105,421 in 1961 to 157,217 by 1981, with 15,655 new homes added to the town between 1970 and 1985. The borough boundaries also changed following a split of the Northampton parliamentary constituency into Northampton North and Northampton South in 1974. Northampton was reconstituted as a non-metropolitan district which also covered areas outside the former borough boundaries but inside the designated New Town. The town tried for unitary status
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
during the 1990s UK local government reform
The structure of local government in the United Kingdom underwent large changes in the 1990s. The system of two-tier local government introduced in the 1970s by the Local Government Act 1972 and the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 was abolish ...
, but failed and it remained a non-metropolitan district until its abolition in 2021. On Good Friday
Good Friday is a Christian holiday commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. It is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday (also Hol ...
1998, Northampton suffered severe flooding, particularly in the areas of Far Cotton and St James; two people were killed and thousands of homes were affected.
Since the turn of the Millennium, the town has continued to expand. Northampton applied for city status in 2000 to celebrate the new millennium, in 2002 to celebrate the Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II and most recently in 2022 to celebrate the Platinum Jubilee of Elizabeth II, but failed on all three occasions and remains a town. In 2006, Northampton became a government expansion zone with new growth promoted by West Northamptonshire Development Corporation
The West Northamptonshire Development Corporation (WNDC) was an urban Development Corporation to secure the regeneration of the Urban Development Areas of Daventry, Towcester and Northampton in Northamptonshire, England.
It was established in ...
(WNDC), an unelected quango, which has provoked a series of regeneration schemes across the town. Some have been completed, including the opening of the Radlands
Radlands was a skate park situated in Northampton, England. It was constructed in 1992 by the Ince family (Chris and his sons Dee and Stee) in a former warehouse and was the first ever indoor skate park built in Britain. The park was, before ...
Plaza Skatepark and the development of Becket's Park Marina just south of Northampton's town centre, as well as the improvement of the town's Market Square, the building of the new North Gate bus station, the rebuilding of the railway station, the designation of a Cultural Quarter, the building of a new Council headquarters, the restoration of Delapré Abbey, the expansion of Northampton Museum, the resiting and rebuilding of the university on one new campus in town centre and the renovation of both the Grosvenor Shopping Centre and Weston Favell Centre.West Northamptonshire Development Corporation websiteWndc.co.uk. Retrieved on 25 August 2011. In 2015, St Giles Street in the town centre was named the "Best British High Street" in a national competition run by the Department for Communities and Local Government.
Administration
Politics

Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
was inaugurated as a constituency in 1295; that is (for many centuries) it returned two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons. Spencer Perceval was elected as one of these in 1796 and became Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in 1809, the only Solicitor General and only Attorney General to have done so, but also the only Prime Minister to be assassinated. The murder was by a highly disgruntled business owner John Bellingham in the House of Commons lobby in 1812. By the late 19th century, Northampton had acquired a reputation for political vanguardism. In 1880, radical non-conformist Charles Bradlaugh was elected as one of the MPs. During one of his election cross-candidate hustings a riot broke out in the Market Square. Local figures of authority called military to disperse it. For some decades from the 1918 general election representation was reduced to one MP.
February 1974 general election saw the seat replaced by the new constituencies of Northampton North and Northampton South, which as all current ones do elect one MP. From the 2010 general election, new, South Northamptonshire took a southern sector of the borough.
Northampton is currently represented by three Conservative MPs:
*Andrew Lewer (Northampton South)
* Michael Ellis (Northampton North)
* Andrea Leadsom (South Northamptonshire).
Local government
Municipal Corporations Act
Municipal Corporations Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used in the United Kingdom for legislation relating to municipal corporations.
List
*The Municipal Corporations Act 1835 (5 & 6 Will 4 c 76)
*The Municipal Corporation (Bou ...
in 1835, with a democratically elected council replacing the corporation before it. Town government alternated between the Liberals and Conservatives, and the town achieved independence from Northamptonshire in 1888 when it became a county borough. It had 6 electoral wards from 1898, 9 wards from 1900 and 12 wards from 1911.
Northampton was granted modern borough status
Borough status is granted by royal charter to local government districts in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The status is purely honorary, and does not give any additional powers to the council or inhabitants of the district. In Scotland, s ...
in 1974, when it was reconstituted as a non-metropolitan district, a subdivision of its non-metropolitan county (Northamptonshire). From 1974 until 2021, the town had a two-tier structure of local government: the non-metropolitan district of Northampton was administered by both Northampton Borough Council and Northamptonshire County Council.
Propositions for the borough to become a unitary authority failed during the 1990s local government reform and again, in 2011, when the motion was voted down by the council. However, in 2016, the borough council and all seven Northamptonshire MPs called for the existing eight Northamptonshire councils be scrapped for new unitary authorities.
In March 2018, following suspension of the County Council arising from its becoming insolvent, due to financial and cultural mismanagement by the cabinet and officers, the then Secretary of State for Local Government, Sajid Javid, sent commissioner Max Caller into the council, who recommended the county council and all district and borough councils in the county be abolished, and replaced by two unitary authorities, one covering the West, and one the North of the county. These proposals were approved in April 2019. It meant that the districts of Daventry, Northampton and South Northamptonshire were merged to form a new unitary authority called West Northamptonshire, whilst the second unitary authority North Northamptonshire consists of Corby, East Northamptonshire, Kettering and Wellingborough districts. These new authorities came into being on 1 April 2021. Elections for the new authorities were due to be held on 7 May 2020, but these were delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and took place in May 2021.
A year prior to these changes, three new civil parishes were created in Northampton's urban area: a large parish covering the majority of the Northampton urban area was created, allowing Northampton to have a Town (parish) Council. Northampton Town Council is the largest parish level authority in England. In addition, two smaller parishes were created for the suburbs of Far Cotton & Delapre and Kingsthorpe.
Policing
The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and th ...
in the town remains the responsibility of Northamptonshire Police; and firefighting
Firefighting is the act of extinguishing or preventing the spread of unwanted fires from threatening human lives and destroying property and the environment. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter.
Firefighters typically ...
, the responsibility of Northamptonshire Fire and Rescue Service. The Royal Anglian Regiment serves as the county regiment for Northamptonshire, with former county regiments being the Northamptonshire Regiment and the Northamptonshire Yeomanry
The Northamptonshire Yeomanry was a Yeomanry regiment of the British Army, formed in 1794 as Volunteer Force (Great Britain), volunteer cavalry. It served in the Second Boer War, the World War I, First World War and the World War II, Second World ...
Health services
NHS Northampton guides primary care services (general practitioners, dentists, opticians and pharmacists) in the town, directly provides adult social care and services in the community such as health visiting andphysiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
and also funds hospital care and other specialist treatments. Northampton General Hospital is an NHS trust hospital which founded in 1744 and moved to its present site in 1793, and has continued to provide healthcare to the local community for more than 200 years. The East Midlands Ambulance Service
The East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust (EMAS) provides emergency medical services, urgent care and patient transport services for the 4.8million people within the East Midlands region of the UK - covering Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire (exc ...
NHS Trust is responsible for the provision of statutory emergency medical services in Northampton.
St Andrew's Hospital
St Andrews Hospital is a mental health facility in Northampton, England. It is managed by St Andrew's Healthcare.
History Formation
The facility was founded by public subscription for "private and pauper lunatics" and opened as the Northampton ...
, the flagship mental health facility of the private company St Andrew's Healthcare, is also based in Northampton. Originally opened in 1838 to serve Northampton, St Andrew's became a charity and private healthcare provider when the Berrywood Asylum (later the Northampton County Lunatic Asylum, then St Crispin Hospital in 1948, and since 2010 Berrywood Hospital) opened in 1876.
Geography
Northampton is formally in theEast Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, Li ...
region but is also referred to in Government planning as being part of the South Midlands "growth area". The town is south-southeast of Leicester, north-northwest of Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
, west of Cambridge, northeast of Oxford and the same distance southwest of Peterborough.
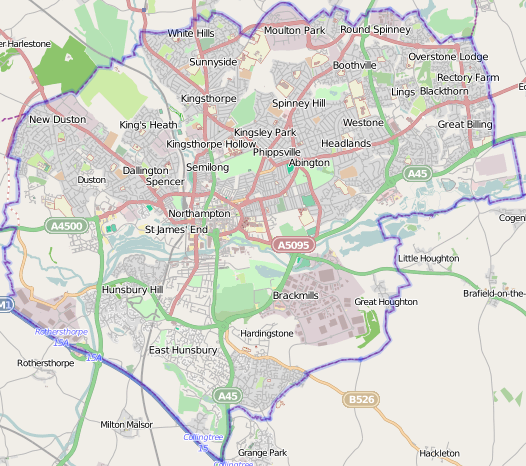
Areas and suburbs
 Northampton is subdivided into suburbs, council wards, constituencies, ecclesiastical parishes, and other less formal areas.
Suburbs and districts of Northampton include:
Concurrent with the abolition of the borough of Northampton in 2021, the unparished area of Northampton became parished with three new parish councils being established: A new Town Council covering the majority of the urban area of Northampton was established, whilst the areas of Kingsthorpe, and Far Cotton and Delapré also gained parish councils. In addition, there are nine registered parish councils which predate the abolition of the borough of Northampton. These are Billing, Collingtree, Duston, Great Houghton, Hardingstone, Hunsbury Meadow, Upton, West Hunsbury and Wootton & East Hunsbury.
There are also settlements outside the town boundaries that are sometimes considered suburbs of Northampton, including Boughton, Cogenhoe, Ecton, Grange Park, Harpole, Little Houghton, Moulton, Overstone and Rothersthorpe.
Northampton is subdivided into suburbs, council wards, constituencies, ecclesiastical parishes, and other less formal areas.
Suburbs and districts of Northampton include:
Concurrent with the abolition of the borough of Northampton in 2021, the unparished area of Northampton became parished with three new parish councils being established: A new Town Council covering the majority of the urban area of Northampton was established, whilst the areas of Kingsthorpe, and Far Cotton and Delapré also gained parish councils. In addition, there are nine registered parish councils which predate the abolition of the borough of Northampton. These are Billing, Collingtree, Duston, Great Houghton, Hardingstone, Hunsbury Meadow, Upton, West Hunsbury and Wootton & East Hunsbury.
There are also settlements outside the town boundaries that are sometimes considered suburbs of Northampton, including Boughton, Cogenhoe, Ecton, Grange Park, Harpole, Little Houghton, Moulton, Overstone and Rothersthorpe.
Compass
Northampton's nearest towns are Wellingborough, Daventry and Towcester. The nearest cities areMilton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
, Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
, Coventry and Peterborough.
Climate
As with the rest of the British Isles, Northampton experiences a maritime climate with cool summers and mild winters. The officialMet Office
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope E ...
weather station for Northampton is the Moulton Park
Moulton Park is a large industrial estate near the village of Moulton, Northamptonshire a few miles north of the town of Northampton.
Business park
Nationwide Building Society have a main office on the business park, near to the BLC Leather T ...
Weather Station at the University of Northampton. Situated at an elevation of around above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
compared to Northampton town centre at , it is one of the highest points in the town, and so may not be a perfect representation of Northampton as a whole. Its hilltop location means less pooling of cold air on calm clear nights, and lower maxima during summer. The absolute maximum recorded is on 3 August 1990. A high of was recorded on 19 July 2006, However, a maximum temperature of was recorded on 19 July 2022 at Pitsford
Pitsford is a village and civil parish in West Northamptonshire in the United Kingdom. According to 2001 census, the parish's population was 636 people, increasing to 671 at the 2011 census.
The village's name means 'Peoht's ford'.
Pitsford ...
, located from the town centre. The absolute minimum is , recorded during February 1986. It is likely the absolute maximum in the town centre is a degree or so higher owing to the lower elevation, and absolute minimum on the eastern and western edges of the urban area around the Nene valley a couple of degrees colder due to katabatic drainage of cold air allowing a frost hollow effect. Most recently, the temperature fell to on 20 December 2010.
Rainfall, at around per year is not high, though is often unpredictable, giving rise to flooding events such as 1998, but also short term droughts. Desborough Weather Station also supplies the public with a local weather service.
Demography
The town's population recorded at each census since 1801 was as follows: Since 1991, the population of the town has increased 17.41% from 180,617 to 212,069 in 2011, with a mean age in 2011 of 37.1 years, younger than the English average of 39.3 years. The population breaks down into 104,168 males, and 107,901 females, with a population density of 2,630 per km2. At the 2011 census, there were 91,484 dwellings, 88,731 of which are occupied households. Some 30.5% (27,048) of these were one person households, 61.1% (54,125) contained families, and 8.5% (7,558) fell into the other household type category. Home tenure was reported as 37.5% of 88,731 households mortgaged, 25.1% owned outright, 16.5% privately rented, 12.8% rented from council, 4.3% social rented, 1.3% private (other) rented, 1.3% shared ownership and 1.2% rent free. 75.6% of households had at least one car or van, 22.5% of residents over the age of 16 had no formal qualifications, and 15.8% have at least 5 GCSEs of grade C or above. The median income for all workers (in 2012) was £21,193, slightly below both the county average of £21,560, and the England average of £21,794. Between 2001 and 2011, the greatest nominal population increase was in the White, Other group from 3,780 to 13,825 – an increase of 10,045 – likely due to migration from Eastern Europe. The largest growth relative to their 2001 numbers was in the Black, African group, recording a 376% increase from 1,361 to 6,473. The largest nominal fall in population was in respondents reporting as White, British, there being 8,146 fewer such residents in 2011 than 10 years previous. The largest fall relative to their 2001 numbers was in the White, Irish group, their count falling 20.3% from 3,838 down to 3,060.Ethnicity
In the 2011 census, Northampton was 84.5% White, 6.5% Asian, 5.1% Black, and 3.2% Mixed/multiple.Religion
In terms of religion, 56.6% of residents described themselves as Christian, 29.4% reported no religion, 4.2% Muslim, 1.6% Hindu, 0.5% Sikh, 0.5% Other, 0.4% Buddhist and 0.1% Judaism. 6.7% failed to report any affiliation.Economy
 Northampton was a major centre of shoemaking and other leather industries, although only specialist shoemaking companies such as Barker Shoes, Church's, Crockett & Jones, Edward Green,
Northampton was a major centre of shoemaking and other leather industries, although only specialist shoemaking companies such as Barker Shoes, Church's, Crockett & Jones, Edward Green, Tricker's
R.E. Tricker Ltd, which trades as Tricker's, is a British footwear company established in 1829 by Joseph Tricker in Northampton.
Tricker's produces men's and women's shoes and boots, as well as leather accessories such as belts and wallets. It ...
, (formerly located in nearby Earls Barton), and Wildsmith, survive. A large number of old shoe factories remain, mostly now converted to offices or accommodation, some of which are surrounded by terraced houses built for factory workers.
Engineering became a major employer in Northampton during the post war years following the establishment of the British Timken tapered roller bearing factory at Duston in 1941 as a '' shadow factory'' for the main site in Birmingham during the Second World War. The factory which closed in 2002 employed over 4,000 employees at its peak and was a major engineering apprentice training employer.
Northampton's main private-sector employers are now in distribution and finance rather than manufacturing, and include Avon Products
Avon Products, Inc. or simply known as Avon, is an American-British multinational cosmetics, skin care, fragrance and personal care company, based in London. It sells directly to the public. Avon had annual sales of $9.1 billion worldwide in 2 ...
, Barclaycard, Blacks Leisure Group, Nationwide Building Society ( Anglia Building Society was formed by amalgamation of Northampton Town and County Building Society with Leicestershire Building Society in 1966 and subsequently merged with the Nationwide in 1987), Panasonic, Travis Perkins, Coca-Cola, Schweppes, Simply Business
Simply Business - the trading name of Xbridge Ltd - is an online broker of business insurance.
In March 2017 it was announced that The Travelers Companies
The Travelers Companies, Inc., commonly known as Travelers, is an American insurance ...
, National Grid, Texas Instruments and Carlsberg Carlsberg may refer to:
Places
* Carlsberg (district), a district in Copenhagen, Denmark
** Carlsberg station, its train station
* Carlsberg, Germany, a municipality in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
* Carlsberg Fjord, Greenland Other uses
* Carlsbe ...
. In 1974, Princess Benedikte of Denmark opened Northampton's Carlsberg brewery, the first outside Denmark. The University of Northampton is also a major employer, as is St Andrew's Healthcare, a national mental health charity. St Andrew's Hospital, its flagship hospital and the United Kingdom's largest psychiatric hospital, is based in Northampton. In 2014, Experian
Experian is an American–Irish multinational data analytics and consumer credit reporting company. Experian collects and aggregates information on over 1 billion people and businesses including 235 million individual U.S. consumers and more t ...
named Northampton as "the best place in the UK to start and run a business." In 2017, the town's annual economic output, as measured by gross value added, was worth £7.31 billion.
Northampton was expected to be affected by the insolvency of Northamptonshire County Council in 2018, as the council implemented significant budget cuts for two years. That was expected to include maintenance of only the "bare legal minimum of service, focused only on the most vulnerable residents".
Health inequality in Northampton is high, with the life expectancy gap between the least deprived and most deprived men reaching over a decade. Additionally, the constituency is 'considerably worse than heEngland average' in violent crime, self harm, under 18 conception and GCSE achievement.
Northampton's market square
The market square (or sometimes, the market place) is a Town square, square meant for trading, in which a market is held. It is an important feature of many towns and cities around the world.pedestrianised in 1984. Further east, part was pedestrianised in 1995 and de-pedestrianised in 2014. The east end (beyond York Road) has never been pedestrianised. There are also two indoor shopping centres in the town centre: the Grosvenor Centre, which was built in the 1970s, and Market Walk (previously Peacock Place), which was constructed in 1988. St James Retail Park is also a large shopping precinct just south of the town centre. Other out-of-town retail parks exist: Weston Favell Shopping Centre, built in the 1970s, and Riverside Retail Park in the east of the town, as well as

 The Royal & Derngate theatre complex, on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter of the town centre, is one of the main venues for arts and entertainment in Northampton.
The Royal & Derngate theatre complex, on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter of the town centre, is one of the main venues for arts and entertainment in Northampton.
 The Northamptonshire Central Library in town centre is a Grade II listed building which was erected in 1910. There are seven other public libraries that are dotted across Northampton—in Abington, Duston, Far Cotton, Hunsbury, Kingsthorpe, St James, Wootton—all run by Northamptonshire County Council.
The Northamptonshire Central Library in town centre is a Grade II listed building which was erected in 1910. There are seven other public libraries that are dotted across Northampton—in Abington, Duston, Far Cotton, Hunsbury, Kingsthorpe, St James, Wootton—all run by Northamptonshire County Council.
 Northampton Museum and Art Gallery on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter has a collection of historical footwear (one of the world's largest at 13,000), Italian art, glass and ceramics, plus visiting exhibitions and local history. There is also a smaller Grade I listed historical museum in the former Abington Park house which mainly has history on domestic life in the town and the Northamptonshire Regiment.
Northampton Museum and Art Gallery on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter has a collection of historical footwear (one of the world's largest at 13,000), Italian art, glass and ceramics, plus visiting exhibitions and local history. There is also a smaller Grade I listed historical museum in the former Abington Park house which mainly has history on domestic life in the town and the Northamptonshire Regiment.
 The town is home to Premiership rugby union team Northampton Saints, who play at Franklin's Gardens in the St James area. "The Saints" had their greatest moment when they won the
The town is home to Premiership rugby union team Northampton Saints, who play at Franklin's Gardens in the St James area. "The Saints" had their greatest moment when they won the
Nosrfc.com. Retrieved on 25 August 2011. Northampton is also home to Northampton Outlaws, its first inclusive rugby team and the 9th gay-friendly team in the United Kingdom.
was awarded a 5-year licence on 16 July 2020, and launched at 2 pm on Saturday 12 June 2021. The first song played was 'Revolution Radio' by Green Day. The transmitter is on top of National Lift Tower, Northampton Lift Tower and broadcasts on 96.1 FM. Inspiration FM was awarded a 5-year licence in July 2008 and officially launched in July 2010. The station broadcasts on FM 107.8 NNBC launched in September 2016 as a joint venture with the University of Northampton. As of 30 September 2017, the station was re-branded as NLive Radio. The station marked the re-branding with a live broadcast from Market Square on 30 September. Later that same evening, the station ran a live evening of music from a music venue in Northampton. The evening of music was headlined by Hana Brooks and broadcast live on the station under the banner 'Shoetown Sounds'. The station broadcasts on FM 106.9 A new community radio station, Embrace Radio, launched on 5 March 2022. It serves the town on FM 104.7. Regional TV news is broadcast on the BBC East service (terrestrial, satellite and cable) with a main programme, BBC Look East, and on ITV News Anglia. From 1997 to 2004, Northampton has been used as a location for television, film and theatre. Northampton Castle is featured in William Shakespeare's history play ''
 Other notable church buildings include
Other notable church buildings include
 Northampton contains several significant war memorials. The Town and County War Memorial, unveiled in 1926, commemorates casualties of the First World War from all of Northamptonshire; it replaced a temporary cenotaph which stood in Abington Square from 1919. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, it consists of two large obelisks and an altar-like stone sited in a small garden behind All Saints' Church. The Town and County memorial is a grade I listed building and part of a national collection of Lutyens' war memorials. As the Town and County memorial does not contain a list of names of the fallen, the Royal British Legion launched a campaign which resulted in the construction of a second memorial, dedicated solely to the town; this memorial, in Abington Square, takes the form of a garden of remembrance with the names of the dead inscribed on the garden walls. A bust of Edgar Mobbs was later moved into the garden; Mobbs was a rugby player for Northampton Saints who was killed while serving in the First World War.
Northampton contains several significant war memorials. The Town and County War Memorial, unveiled in 1926, commemorates casualties of the First World War from all of Northamptonshire; it replaced a temporary cenotaph which stood in Abington Square from 1919. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, it consists of two large obelisks and an altar-like stone sited in a small garden behind All Saints' Church. The Town and County memorial is a grade I listed building and part of a national collection of Lutyens' war memorials. As the Town and County memorial does not contain a list of names of the fallen, the Royal British Legion launched a campaign which resulted in the construction of a second memorial, dedicated solely to the town; this memorial, in Abington Square, takes the form of a garden of remembrance with the names of the dead inscribed on the garden walls. A bust of Edgar Mobbs was later moved into the garden; Mobbs was a rugby player for Northampton Saints who was killed while serving in the First World War.
Northamptonchron.co.uk. Retrieved 25 August 2011. For international links, the East Midlands Airport and
Northampton Town Council
West Northamptonshire Council
Northampton Chronicle & Echo
Historic OS maps of Northampton
{{Authority control Towns in Northamptonshire County towns in England Market towns in Northamptonshire New towns in England New towns started in the 1960s Towns with cathedrals in the United Kingdom Non-metropolitan districts of Northamptonshire Civil parishes in Northamptonshire Former boroughs in England Former non-metropolitan districts West Northamptonshire District
Sixfields
Sixfields is an area of Northampton, Northamptonshire, England about west of the town centre along the A4500 St James Road and Weedon Road towards M1 junction 16 about further west. It is close to the Duston, Upton and St James areas o ...
in the west. Each precinct has a range of high street shops, department stores and many smaller individual speciality shops.
Culture
Leisure

Billing Aquadrome
Billing Aquadrome is a leisure park in Great Billing, a district of eastern Northampton, England. Facilities within the park, which was built around various mature gravel pits, include a caravan site, marina and funfair. It is also frequently ...
leisure park is on the eastern outskirts. It has a caravan site, marina, funfair, bar, riverside restaurant and converted water mill with original workings. The Northampton Leisure Trust has four leisure centres across Northampton: Danes Camp, Lings Forum, Mounts Baths
Mounts Baths is a swimming pool in Northampton, England. Built in 1936, it is notable for its Art Deco style.
It is a Grade II listed building, listed on 28 January 2013. It is regarded by Historic England as "a particularly good example of a Mo ...
and Duston Sports Centre. There are also the action centres Benham Sports Arena and King's Park Tennis Centre as well as the Delapré Public Golf Course. Radlands Plaza is a new skatepark that opened in 2012.
According to the website of the (former) Northampton Borough Council, there are a total of 170 parks and open spaces around Northampton, which altogether span around . Popular parks include Abington Park, which is the town's oldest, and the Racecourse, which was used for horseracing (until 1904) and as a cricket ground (between 1844 and 1885) in addition to being the original home of Northampton Balloon Festival
The Northampton Balloon Festival was an annual hot air balloon festival held in Northampton, England.
The original festival was held in The Racecourse and managed by the (now defunct) Borough Council, and took place over a Friday, Saturday and Su ...
. Other parks include Becket's Park (which is named after Thomas Becket as are nearby Becket's Well and Thomas á Becket pub), Bradlaugh Fields (named after the Northampton MP Charles Bradlaugh), Dallington Park, Delapré Park, Eastfield Park, Hunsbury Hill (which is built around an Iron Age hillfort), Kingsthorpe Park and Victoria Park.
Popular annual events include Northampton Carnival, the Beer Festival, the Dragonboat Race, the Umbrella Fair, Diwali celebrations and St Crispins Fair. Northampton Balloon Festival used to be a major event in Northampton, but since being scaled down, it has been poorly attended. Northampton Music Festival has been celebrated every year since 2007 in the town centre. A smaller music festival A Walk in the Park has been put on since 2008 in Wootton. A new music festival, Alive at Delapré, debuted in the summer of 2013 and has since attracted artists like Alfie Boe
Alfred Giovanni Roncalli Boe (born 29 September 1973) is an English tenor and actor, notably performing in musical theatre.
He is best known for his performances as Jean Valjean in the musical ''Les Misérables'' at the Queen's Theatre in Lo ...
, Boyzone, Jessie J
Jessica Ellen Cornish (born 27 March 1988), known professionally as Jessie J, is an English singer. Born and raised in London, she began her career on stage, aged 11, with a role in the West End musical '' Whistle Down the Wind''. She studied ...
, James Morrison, McBusted, Paul Weller and The Wanted.
Entertainment
The Deco
The Deco is a restored 1930s cinema and theatre located in the heart of Northampton, England. It is now operated as a venue for corporate, social and theatrical events.
The Deco was designated a Grade II listed building in 2004. and originally f ...
, situated in Abington Square in the town centre, is a 900-seat theatre and conference centre, which shares its Art Deco building with the Northampton Jesus Centre. It was restored by the Jesus Army
The Jesus Army, also known as the Jesus Fellowship Church and the Bugbrooke Community, was a neocharismatic evangelical Christian movement based in the United Kingdom, part of the British New Church Movement. The name ''Jesus Army'' was specifi ...
as part of their Jesus Centre project. The Deco used to be a cinema in the 1960s; The Beatles appeared there twice on stage in 1963: firstly as unknowns as part of the Tommy Roe
Thomas David "Tommy" Roe (born May 9, 1942) is a retired American rock and pop singer-songwriter.
Best-remembered for his hits "Sheila" (1962) and " Dizzy" (1969), Roe was "widely perceived as one of the archetypal bubblegum artists of the late ...
/ Chris Montez tour; secondly as part of their own tour in their own right. Smaller theatres include the Northampton Playhouse and the Cripps Theatre, which is part of Northampton School for Boys.
The two commercial cinemas in Northampton are Vue
Vue or VUE may refer to:
Places
* Vue, Loire-Atlantique, a commune in France
* The Vue, a skyscraper in Charlotte, North Carolina
Arts, entertainment and media
* Vue (band), a rock and roll band from San Francisco, California
* Vue Cinemas, a cin ...
at Sol Central in the centre and Cineworld at Sixfields. There is also the subsidised Forum Cinema at Lings Forum
Lings Forum is a leisure centre located in the suburbs of Northampton, England. It is annexed to Weston Favell Shopping Centre and Northampton Academy
Northampton Academy is a mixed secondary school and sixth form in Northampton, Northampton ...
, whose film programme is widely varied and includes art-house and non-mainstream films. The Northampton Filmhouse, an independent cinema joined to the side of the Royal & Derngate theatre complex, opened in June 2013.
There are also many local entertainment venues which provide events. The Roadmender
Margaret Fairless Barber (pseudonym, Michael Fairless; 7 May 1869 – 24 August 1901), was an English Christian writer. Her book of meditations, ''The Roadmender'' (1902), became a popular classic.
Life
Barber was born in Rastrick, Brighouse, W ...
, which used to be run and funded by the council and later bought by The Purplehaus group, hosts mainstream touring bands and one off-gigs. There are other popular late-night entertainment venues, pubs, bars and clubs in the town centre, and along the Wellingborough and Kettering Roads on the way into the town centre. Northampton also has ten-pin bowling alleys and late night casinos.
Libraries, museums and galleries
 The Northamptonshire Central Library in town centre is a Grade II listed building which was erected in 1910. There are seven other public libraries that are dotted across Northampton—in Abington, Duston, Far Cotton, Hunsbury, Kingsthorpe, St James, Wootton—all run by Northamptonshire County Council.
The Northamptonshire Central Library in town centre is a Grade II listed building which was erected in 1910. There are seven other public libraries that are dotted across Northampton—in Abington, Duston, Far Cotton, Hunsbury, Kingsthorpe, St James, Wootton—all run by Northamptonshire County Council.
 Northampton Museum and Art Gallery on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter has a collection of historical footwear (one of the world's largest at 13,000), Italian art, glass and ceramics, plus visiting exhibitions and local history. There is also a smaller Grade I listed historical museum in the former Abington Park house which mainly has history on domestic life in the town and the Northamptonshire Regiment.
Northampton Museum and Art Gallery on Guildhall Road in the Cultural Quarter has a collection of historical footwear (one of the world's largest at 13,000), Italian art, glass and ceramics, plus visiting exhibitions and local history. There is also a smaller Grade I listed historical museum in the former Abington Park house which mainly has history on domestic life in the town and the Northamptonshire Regiment. 78 Derngate
78 Derngate is a Grade II* listed Georgian house in the Cultural Quarter of Northampton, England, originally built in 1815. Its interior was extensively remodelled in 1916 and 1917 by the architect Charles Rennie Mackintosh for businessman We ...
, the only house in England designed by Charles Rennie Mackintosh, includes a museum celebrating Mackintosh, an art gallery and a restaurant.
The Northampton Arts Collective is homed on a four-storey building entitled NN in the Cultural Quarter, opposite the Northampton Museum and next to the Royal & Derngate theatre complex. They relocated from the Old Fishmarket which was demolished to make way for the North Gate bus station. The Avenue Gallery, is at the Avenue campus of the University of Northampton. The university also spent £3m on its Portfolio Innovation Centre in early 2011, which houses around 60 creative freelancers, digital media developers, and designers. Other art galleries include Collective Collaborations, Artist's Sanctuary, Albus3, Gallery 177 and Primose Gallery. Northamptonshire also runs an annual county-wide Open Studios event celebrating visual arts in which artists' studios are open to the public.
Music
The composers Malcolm Arnold, William Alwyn, Trevor Hold, Edmund Rubbra and Robert Walker were born in Northampton. Northampton also boasts one of the oldest community orchestras in the U.K. - the Northampton Symphony Orchestra, which started life in 1896 as Saint Celia's Orchestral Society. Gothic rock band Bauhaus formed in Northampton, often cited as the godfathers of goth, they helped pioneer the genre during the late 1970s and throughout the 1980s. The popular UK rapperSlowthai
Tyron Kaymone Frampton (born 18 December 1994), better known by his stage name Slowthai (stylised in lowercase), is a British rapper. Raised in Northampton, he rose to popularity in 2019 for his gritty and rough instrumentals and raw, politica ...
was born in Northampton and frequently talks about his life growing up there in his music.
Sport
 The town is home to Premiership rugby union team Northampton Saints, who play at Franklin's Gardens in the St James area. "The Saints" had their greatest moment when they won the
The town is home to Premiership rugby union team Northampton Saints, who play at Franklin's Gardens in the St James area. "The Saints" had their greatest moment when they won the Heineken Cup
The European Rugby Champions Cup (known as the Heineken Champions Cup for sponsorship reasons) is an annual rugby union tournament organised by European Professional Club Rugby (EPCR). It is the top-tier competition for clubs who compete in a pre ...
in 2000 at Twickenham, beating Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the ...
9–8. There are also a number of "Junior" rugby clubs in the area, the most successful of these at producing young players is Northampton Old Scouts RFC who have produced Ben Cohen and Steve Thompson amongst others.Northampton Old Scouts RFCNosrfc.com. Retrieved on 25 August 2011. Northampton is also home to Northampton Outlaws, its first inclusive rugby team and the 9th gay-friendly team in the United Kingdom.
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
club Northampton Town, known as "The Cobblers" from the town's shoemaking background, are based at Sixfields Stadium. Established in 1897, in their centenary season of 1997 they reached Wembley through the play-offs and beat Swansea City
Swansea City Association Football Club (; cy, Clwb Pêl-droed Cymdeithas Dinas Abertawe) is a professional football club based in Swansea, Wales that plays in the Championship, the second tier of English football. Swansea have played their ho ...
1–0 with an injury time winning free kick from John Frain. It was the first club to set up a trust for supporters to work with the club as many have done. Sixfields was also briefly the home of Coventry City
Coventry City Football Club is a professional association football club based in Coventry, West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. The team currently compete in the EFL Championship, Championship, the second tier of the English footbal ...
for just over one season between August 2013 and August 2014.
There are also three non-league clubs in the United Counties Football League: Northampton Spencer; Northampton Sileby Rangers; and Northampton Old Northamptonian Chenecks.
Northamptonshire County Cricket Club
Northamptonshire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Northamptonshire. Its limited overs team is called the Northa ...
, known in limited overs cricket
Limited overs cricket, also known as one-day cricket or white ball cricket, is a version of the sport of cricket in which a match is generally completed in one day. There are a number of formats, including List A cricket (8-hour games), Twenty ...
as "The Steelbacks" (a reference to the Northamptonshire Regiment which was formed in 1881), is one of the 18 major county clubs which make up the English and Welsh domestic cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
structure. The club was promoted from Division 2 of the County Championship in 2019, and play in Group C of the Clydesdale Bank 40
The ECB40, last known as the Yorkshire Bank 40 (YB40) for sponsorship reasons, was a forty-over limited overs cricket competition for the English first-class counties. It began in the 2010 English cricket season as a replacement for the Pro40 a ...
League and the Midlands/Wales/West group of the revamped Friends Provident
Friends’ Provident Insurance was a banking institution founded in 1832 to serve the needs of the Society of Friends (Quakers). Based in Bradford, it concentrated on sickness and annuity policies until its life fund acquired Century Insurance ...
T20. They are based at the County Ground, in the Abington area.
The Silverstone Circuit
Silverstone Circuit is a motor racing circuit in England, near the Northamptonshire villages of Towcester, Silverstone and Whittlebury. It is the home of the British Grand Prix, which it first hosted as the 1948 British Grand Prix. The 1950 ...
, current home of the British Grand Prix, is a few miles south of Northampton. Rockingham Motor Speedway
Rockingham Motor Speedway is a former racing motorsport venue in Rockingham, Northamptonshire, England, United Kingdom, near the town of Corby. It hosted professional and club races, as well as testing, track days, driver training, exhibition ...
and Santa Pod Raceway
Santa Pod Raceway, located in Podington, Bedfordshire, England, is Europe's first permanent drag racing venue for 1/4 and 1/8 mile racing. It was built on a disused Second World War air base, (RAF Podington), once used by the USAAF's 92nd Bomb ...
are a few miles north and east of Northampton respectively, the latter offering a range of drag racing
Drag racing is a type of motor racing in which automobiles or motorcycles compete, usually two at a time, to be first to cross a set finish line. The race follows a short, straight course from a standing start over a measured distance, most c ...
events.
Northampton is also home to Collingtree Park Golf Club
Collingtree is a village and civil parish in the West Northamptonshire district of Northamptonshire, England. It is part of the Northampton built-up area.
Location and context
The village is about from Northampton town centre, close to the ...
, which hosted the British Masters in 1995. There are also many equestrian and country activities, and several water sports centres, such as the Nene Whitewater Centre, which provides an artificial whitewater course for canoes, kayak
A kayak is a small, narrow watercraft which is typically propelled by means of a double-bladed paddle. The word kayak originates from the Greenlandic word ''qajaq'' ().
The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each se ...
s and rafts. The Northampton Swimming Club also trained the young Olympic swimmer Caitlin McClatchey
Caitlin McClatchey (born 28 November 1985) is a British former swimmer. Representing Scotland, she won two gold medals at the 2006 Commonwealth Games, in the 200 metres freestyle and 400 metres freestyle. Representing Great Britain, she won bro ...
.
Northampton is also home to Be Military Fit
Be Military Fit, or BMF, is a private company which runs outdoor group fitness classes in 140 public parks and outdoor spaces across the United Kingdom. The classes are predominantly led by former or serving members of the British Armed Forces.
B ...
in Abington Park where members can train up to 7 times a week with serving or ex-military fitness instructors.
Northampton Greyhound Stadium hosted greyhound racing
Greyhound racing is an organized, competitive sport in which greyhounds are raced around a track. There are two forms of greyhound racing, track racing (normally around an oval track) and coursing; the latter is now banned in most countries. Tra ...
from 1928 to 1964 and speedway from 1929 to 1930.
Media
The '' Northampton Chronicle & Echo'' (established 1931) is the town's newspaper, published on Thursdays (before 2012, it was published Monday to Saturday) with jobs, property, motors and entertainment supplements. There are other free newspapers circulated within the town. These include ''The Mercury'' (on Thursdays) and ''Northants on Sunday'', both from the publishers of the ''Chronicle & Echo'', and the '' Northampton Herald & Post'' (on Thursdays). These free papers mostly consist of advertising and have limited news. ''The Mercury'' was one of the oldest newspapers still in circulation first published in 1720, founded by William Dicey, an ancestor of the public law commentator, A.V. Dicey. It was the fifth-oldest such newspaper in the United Kingdom and the tenth-oldest such in the world. Four radio stations are based in the town, one of which broadcast county-wide. BBC Radio Northampton broadcasts news, topical items and some music, switching to a regional network after 7 pm. Three community radio stations serve the town: Inspiration FM, NLive Radio (Formerly NNBC), Revolution Radio and Embrace Radio. Revolution Radiwas awarded a 5-year licence on 16 July 2020, and launched at 2 pm on Saturday 12 June 2021. The first song played was 'Revolution Radio' by Green Day. The transmitter is on top of National Lift Tower, Northampton Lift Tower and broadcasts on 96.1 FM. Inspiration FM was awarded a 5-year licence in July 2008 and officially launched in July 2010. The station broadcasts on FM 107.8 NNBC launched in September 2016 as a joint venture with the University of Northampton. As of 30 September 2017, the station was re-branded as NLive Radio. The station marked the re-branding with a live broadcast from Market Square on 30 September. Later that same evening, the station ran a live evening of music from a music venue in Northampton. The evening of music was headlined by Hana Brooks and broadcast live on the station under the banner 'Shoetown Sounds'. The station broadcasts on FM 106.9 A new community radio station, Embrace Radio, launched on 5 March 2022. It serves the town on FM 104.7. Regional TV news is broadcast on the BBC East service (terrestrial, satellite and cable) with a main programme, BBC Look East, and on ITV News Anglia. From 1997 to 2004, Northampton has been used as a location for television, film and theatre. Northampton Castle is featured in William Shakespeare's history play ''
King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
'' and in ''Becket
''Becket or The Honour of God'' (french: Becket ou l'honneur de Dieu) is a 1959 play written in French by Jean Anouilh. It is a depiction of the conflict between Thomas Becket and King Henry II of England leading to Becket's assassination in 117 ...
'', a play by Alfred, Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his ...
. The town was the location for the BBC sitcom '' Keeping Up Appearances'' from 1990 until 1995. Parts of the 2005 film '' Kinky Boots'' were also made in Northampton and featured shots of the statue outside the Grosvenor Centre in the town centre and inside RE Tricker's shoe factory in St. Michaels Road representing the original factory in Earls Barton. The film was turned into a musical '' Kinky Boots'', maintaining its Northampton backdrop, which premiered on Broadway in 2013 and won 6 Tony Awards. It transferred to the West End in London in 2015 and won 3 Olivier Awards. In addition, BBC Three shows ''Bizarre ER
''Bizarre ER'' is a BBC Three, and later E4, television show that deals with hospital mishaps.
Series guide
Every episode shows a miraculous survival story and strange facts, like the woman who fell out of a plane at 35,000 ft and survived ...
'' and ''Junior Paramedics
''Junior Paramedics'' is a British television series that was first broadcast on BBC Three from 27 February to 8 April 2014. The series follows paramedics on a six-week placement with East Midlands Ambulance Service. The nine junior paramedics a ...
'' were filmed in Northampton.
Notable buildings
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, is one of the largest and best-preserved round churches in England. It was built in 1100 on the orders of the first Earl of Northampton,Simon de Senlis
Simon II de Senlis (or Senliz, St. Liz, etc.), 4th Earl of Huntingdon, Earl of the Honour of Huntingdon and Northampton ( 1098 – 1153) was an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman nobleman. He was the son of Simon I de Senlis, Earl of Huntingdon-Northamp ...
and based on a plan of the original Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
in Jerusalem.
Simon de Senlis also built Northampton Castle c. 1084, which was for many years one of the country's most important castles. It was a royal residence, held The Parliament of England many times, and was the site of royal tournaments and feasts. Thomas Becket was imprisoned there until he escaped. The castle suffered many fates and was eventually demolished to make way for the railway station in 1879. A postern, dismantled from its original position and rebuilt into a wall by the station, and a part of the keep mound are all that remains.
The current All Saints' Church was built on the site of a great Norman church, All Hallows, which was almost completely destroyed by the Great Fire of Northampton in 1675. All that remained was the medieval tower and the fine vaulted crypt, but by 1680 All Saints' had been rebuilt, with the help of donations from all over England, including 1,000 tons of timber from King Charles II, whose statue can be seen above the portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
. Famously, the poet John Clare liked to sit beneath the portico of the church. It is home to a choral foundation.
 Other notable church buildings include
Other notable church buildings include Northampton Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of St Mary and St Thomas is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Northampton, England. It is the seat of the Bishop of Northampton and mother church of the Diocese of Northampton which covers the counties of Northamptonshire, Bedfor ...
, the mother church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Northampton
The Diocese of Northampton is one of the 22 Roman Catholic dioceses in England and Wales and a Latin Rite suffragan diocese of Westminster. Its see is in Northampton. The Cathedral of Our Lady Immaculate and St Thomas of Canterbury is the moth ...
and seat of the Bishop of Northampton; St Peter's (mostly built in Norman times); St Giles' Church; St Matthew's in Phippsville, which was built between 1891 and 1894, has a Henry Moore
Henry Spencer Moore (30 July 1898 – 31 August 1986) was an English artist. He is best known for his semi- abstract monumental bronze sculptures which are located around the world as public works of art. As well as sculpture, Moore produced ...
sculpture of the Madonna
Madonna Louise Ciccone (; ; born August 16, 1958) is an American singer-songwriter and actress. Widely dubbed the " Queen of Pop", Madonna has been noted for her continual reinvention and versatility in music production, songwriting, a ...
. St Edmund's Church (built in 1850) closed in 1978 and was demolished in 1980 (its bells are now in Saint Paul's Cathedral, Wellington).
Just south of the town centre Delapré Abbey, a former Cluniac nunnery, the County Records Office and site of the second Battle of Northampton, which was founded by Simon II de Senlis, the son of first Earl of Northampton, in 1145. At the edge of the Abbey, one of the three standing Eleanor cross
The Eleanor crosses were a series of twelve tall and lavishly decorated stone monuments topped with crosses erected in a line down part of the east of England. King Edward I had them built between 1291 and about 1295 in memory of his beloved wi ...
es still remains, in memory of Eleanor of Castile
Eleanor of Castile (1241 – 28 November 1290) was Queen of England as the first wife of Edward I, whom she married as part of a political deal to affirm English sovereignty over Gascony.
The marriage was known to be particularly close, and ...
, whose body rested here on its way to London. The original top of the monument has been knocked off and replaced several times from as early as 1460.
St Andrew's Hospital, which opened 1838, and its new building William Wake House, is one of the largest neo-classical structures in England. Northampton & County Club, which was established in 1873, was also the old county hospital before becoming a private members' club; the cellars are medieval. Northampton Guildhall, which is Grade II* listed, was constructed mostly in the 1860s in Victorian Gothic architecture designed by Edward William Godwin, and extended in 1889–92 and in the 1990s. The Clare Street drill hall was completed in 1859.
78 Derngate is a Grade II* listed Georgian Town House remodelled by Charles Rennie Mackintosh for Wenman Joseph Bassett-Lowke
Wenman Joseph Bassett-Lowke (27 December 1877 Northampton – 21 October 1953) was the son of Joseph Tom Lowke, a Northampton boilermaker and his wife, Eliza, and is noted for having founded the firm of Bassett-Lowke which specialised in producing ...
in 1916–17. It contains notable Mackintosh interiors (which have been restored) and is his only major domestic commission outside Scotland. It is open to the public. One of these Derngate buildings was previously home to Northampton High School, an independent Northampton girls' school.
The tall National Lift Tower
The National Lift Tower (previously called the Express Lift Tower) is a elevator test tower, lift-testing tower built by the Express Lift Company (a elevator, lifts division of the General Electric Company plc, General Electric Company (GEC)) o ...
is a dominant feature and visible from most of the town. A Terry Wogan radio phone-in during the 1980s came up with the name "Northampton Lighthouse" as Northampton is one of the furthest places from the sea. It is also known as the "Cobblers' Needle". It was built for testing new lifts at the Express Lifts factory, now closed. Though now redundant, it is a listed building.
The former Greyfriars bus station served the town from 1976 until 2014. In the 2000s, it was featured on Channel 4's ''Demolition
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a ...
'' programme as the ugliest transport station in the United Kingdom and worthy of demolition. Demolition work began in March 2014, following the move of bus services to North Gate bus station
North Gate bus station is the bus station which serves the town of Northampton in England. Northampton railway station is approximately 0.9 km away.
The building on Bradshaw Street opened on 2 March 2014 on the site of the town's former Fi ...
. The Greyfriars was completely destroyed on 15 March 2015 by way of a controlled explosion.
Memorials
 Northampton contains several significant war memorials. The Town and County War Memorial, unveiled in 1926, commemorates casualties of the First World War from all of Northamptonshire; it replaced a temporary cenotaph which stood in Abington Square from 1919. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, it consists of two large obelisks and an altar-like stone sited in a small garden behind All Saints' Church. The Town and County memorial is a grade I listed building and part of a national collection of Lutyens' war memorials. As the Town and County memorial does not contain a list of names of the fallen, the Royal British Legion launched a campaign which resulted in the construction of a second memorial, dedicated solely to the town; this memorial, in Abington Square, takes the form of a garden of remembrance with the names of the dead inscribed on the garden walls. A bust of Edgar Mobbs was later moved into the garden; Mobbs was a rugby player for Northampton Saints who was killed while serving in the First World War.
Northampton contains several significant war memorials. The Town and County War Memorial, unveiled in 1926, commemorates casualties of the First World War from all of Northamptonshire; it replaced a temporary cenotaph which stood in Abington Square from 1919. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, it consists of two large obelisks and an altar-like stone sited in a small garden behind All Saints' Church. The Town and County memorial is a grade I listed building and part of a national collection of Lutyens' war memorials. As the Town and County memorial does not contain a list of names of the fallen, the Royal British Legion launched a campaign which resulted in the construction of a second memorial, dedicated solely to the town; this memorial, in Abington Square, takes the form of a garden of remembrance with the names of the dead inscribed on the garden walls. A bust of Edgar Mobbs was later moved into the garden; Mobbs was a rugby player for Northampton Saints who was killed while serving in the First World War.
Transport
Northampton is served by junctions 15, 15a and 16 of the M1 motorway which connects the town with London at its most southern point and Leeds at its most northern. Both the A45 and A43 link Northampton with the other major towns in Northamptonshire and beyond, and can be accessed by a partially completedring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop, bypass or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city, or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist i ...
. The A14 is close by to the north of Northampton, providing links to East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
and a secondary route to the areas of the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Ind ...
which are situated to the north of the town.
Northampton railway station
Northampton railway station serves the county town of Northampton in England. It is on the Northampton Loop of the West Coast Main Line. The station is served by West Midlands Trains services southbound to London Euston and northbound to Birmi ...
is on the Northampton Loop of the West Coast Main Line, and has services southbound to London Euston and northbound to Birmingham and Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. The Crewe built-up area had a total population of 75,556 in 2011, which also covers parts of the adjacent civil parishes of Willaston ...
provided by West Midlands Trains. Avanti West Coast also provide two daily services to London, although these are set-down only.
Sywell Aerodrome
Sywell Aerodrome is the local aerodrome serving the towns of Northampton, Wellingborough, Kettering and Rushden, as well as wider Northamptonshire. The aerodrome is located northeast of Northampton and was originally opened in 1928 on the edg ...
is the nearest airfield which has recently been upgraded with a concrete runway, however it only caters for private flying, flight training and corporate flights.Sywell Aerodrome – new concrete runway to openNorthamptonchron.co.uk. Retrieved 25 August 2011. For international links, the East Midlands Airport and
Luton Airport
London Luton Airport is an international airport located in Luton, Bedfordshire, England, situated east of the town centre, and north of Central London. The airport is owned by London Luton Airport Ltd (LLAL), a company wholly owned by L ...
are quickly accessible by the M1; Birmingham Airport is also around to the north-west of the town via the M1 and M6 motorways and also by train.
In the town, buses are mainly operated by Stagecoach Midlands from the North Gate bus station with some services from Uno. Stagecoach serves areas within the town and also provides travel to outlying villages and towns within the county, making links to Corby, Daventry, Kettering, Rushden and Wellingborough. They also go as far afield as Bedford, Leicester, Market Harborough, Milton Keynes, Peterborough and Rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
. Uno serve the university and Kingsthorpe area as well as Rectory Farm, Abington and Sixfields. National Express also operates in Northampton, covering routes between major towns and cities in the United Kingdom. Buses used to be operated by Northampton Corporation Transport and then, since the privatization of buses in the 1980s. FirstGroup operated them until the 2010s and Arriva operate 2 services around the town (33 and 33x)
Northampton is the terminus of an arm of the Grand Union Canal, which connects to the River Nene and from that to the River Great Ouse
The River Great Ouse () is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the Wa ...
and the North Sea. No longer used for freight, the waterway is now popular with anglers and narrowboat
A narrowboat is a particular type of canal boat, built to fit the narrow locks of the United Kingdom. The UK's canal system provided a nationwide transport network during the Industrial Revolution, but with the advent of the railways, commerc ...
ers. Principal outlying villages on the canal include Gayton, Blisworth, Braunston and Stoke Bruerne.
Northampton once had a horse-drawn tramway which opened in 1881. The system was extended in stages and taken over by the council in 1897 and named Northampton Corporation Tramways
Northampton Corporation Tramways operated the tramway service in Northampton between 1901 and 1934.
History
The company was purchased from the Northampton Street Tramways Company on 21 October 1901 for the sum of £38,700 (). It continued to o ...
. It was electrified in 1904, but closed in 1934 mainly as a result of competition from motor buses which were introduced in 1929. Two of the original tram shelters are preserved: one at the Racecourse park and another in Kingsthorpe opposite the Cock Hotel.
Education
The first University of Northampton was established by royal charter by King Henry III in 1261, and started to rival the universities in Cambridge and Oxford, with their students migrating to the Northampton establishment. This university was dissolved by King Henry III in 1265, in revenge of its students siding with the rebellious barons in the Battle of Northampton (1264). Henry III was also advised by bishops and magnates that it posed a threat to Oxford, and signed a Royal Decree which banned the establishment of a university in Northampton. This was eventually repealed and the university's name was revived in 2005 when the unconnected University College Northampton, which was founded in 1924, was upgraded to full university status and renamed the University of Northampton. This is the only higher education (HE) establishment in the town and offers courses from foundation and undergraduate levels to postgraduate, professional and doctoral qualifications. The university is made of up six schools: Business, Education, Health, Science and Technology, Social Sciences and The Arts. The university was originally spread over two campuses across the town, but moved to its new £330 million waterside campus by the River Nene in the town centre in 2018. Northampton's onlyfurther education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is education in addition to that received at secondary school, that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. I ...
(FE) college is Northampton College, one of the largest FE colleges in the South Midlands, which has two campuses across the town, offering vocational courses, GCSE
The General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) is an academic qualification in a particular subject, taken in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. State schools in Scotland use the Scottish Qualifications Certificate instead. Private sc ...
s and A Levels
The A-Level (Advanced Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational aut ...
. Moulton College
Moulton College is a further education college based in Moulton, Northamptonshire, England. Although initially established as the Northamptonshire Institute of Agriculture in 1921, it now has expanded its teaching curriculum to cover a wide ...
is another FE college just north of Northampton which provides many vocational courses, specialising in land-based subjects, sports and construction. In collaboration with the University of Northampton, both colleges also offer some HE programmes.
There are 50 primary schools and 8 secondary school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' secondary education, lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) ...
s in the town. Until 2004, Northamptonshire operated a three-tier system in education of lower, middle and upper schools. In 2001, the move to a two-tier system to primary and secondary schools began, aimed at improving educational standards. Some of its successful secondary schools include Northampton School for Boys, which became the top performing comprehensive school in the country in 2007, and Northampton School for Girls, the first school in England to gain Specialist Music College status. An average of 55% of students in Northampton achieved five A*-C grades at GCSE in 2015, above the government's benchmark of 40%. There are also 5 special schools
Special education (known as special-needs education, aided education, exceptional education, alternative provision, exceptional student education, special ed., SDC, or SPED) is the practice of educating students in a way that accommodates th ...
in the town. Northampton High School is an independent school for girls.
Notable people
Twin towns
Northampton is twinned with: * Marburg, Hesse, Germany *Poitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomerat ...
, Vienne, France
Freedom of the Borough
The following people, military units, and organisations have received theFreedom of the Borough
The Freedom of the City (or Borough in some parts of the UK) is an honour bestowed by a municipality upon a valued member of the community, or upon a visiting celebrity or dignitary. Arising from the medieval practice of granting respected ...
of Northampton.
Individuals
* HRH Princess of Wales: 8 June 1989. * General Lord Horne: 1919.Military units
* Northampton UnitSea Cadet Corps
Sea cadets are members of a sea cadet corps, a formal uniformed youth organisation for young people with an interest in waterborne activities and or the national navy. The organisation may be sponsored in whole or in part by the navy or a naval s ...
: 26 March 2012.
* 9th/12th Royal Lancers
The 9th/12th Royal Lancers (Prince of Wales's) was a cavalry regiment of the British Army, formed in 1960 by the amalgamation of the 9th Queen's Royal Lancers and the 12th Royal Lancers. In the later years of its existence, the regiment served as ...
: 5 November 2012.
Organisations and groups
* NHS trust Northampton: 17 June 2020.See also
* Districts of Northampton * Flooding in Weedon Road, St James and Far Cotton around Easter 1998 * Grade I listed buildings in Northampton * Grade II* listed buildings in Northampton * HMS ''Laforey'' *Northampton Corporation Tramways
Northampton Corporation Tramways operated the tramway service in Northampton between 1901 and 1934.
History
The company was purchased from the Northampton Street Tramways Company on 21 October 1901 for the sum of £38,700 (). It continued to o ...
* Royal & Derngate
* St Peter's Church, Northampton
Notes
References
*External links
Northampton Town Council
West Northamptonshire Council
Northampton Chronicle & Echo
Historic OS maps of Northampton
{{Authority control Towns in Northamptonshire County towns in England Market towns in Northamptonshire New towns in England New towns started in the 1960s Towns with cathedrals in the United Kingdom Non-metropolitan districts of Northamptonshire Civil parishes in Northamptonshire Former boroughs in England Former non-metropolitan districts West Northamptonshire District