Noonan's syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a
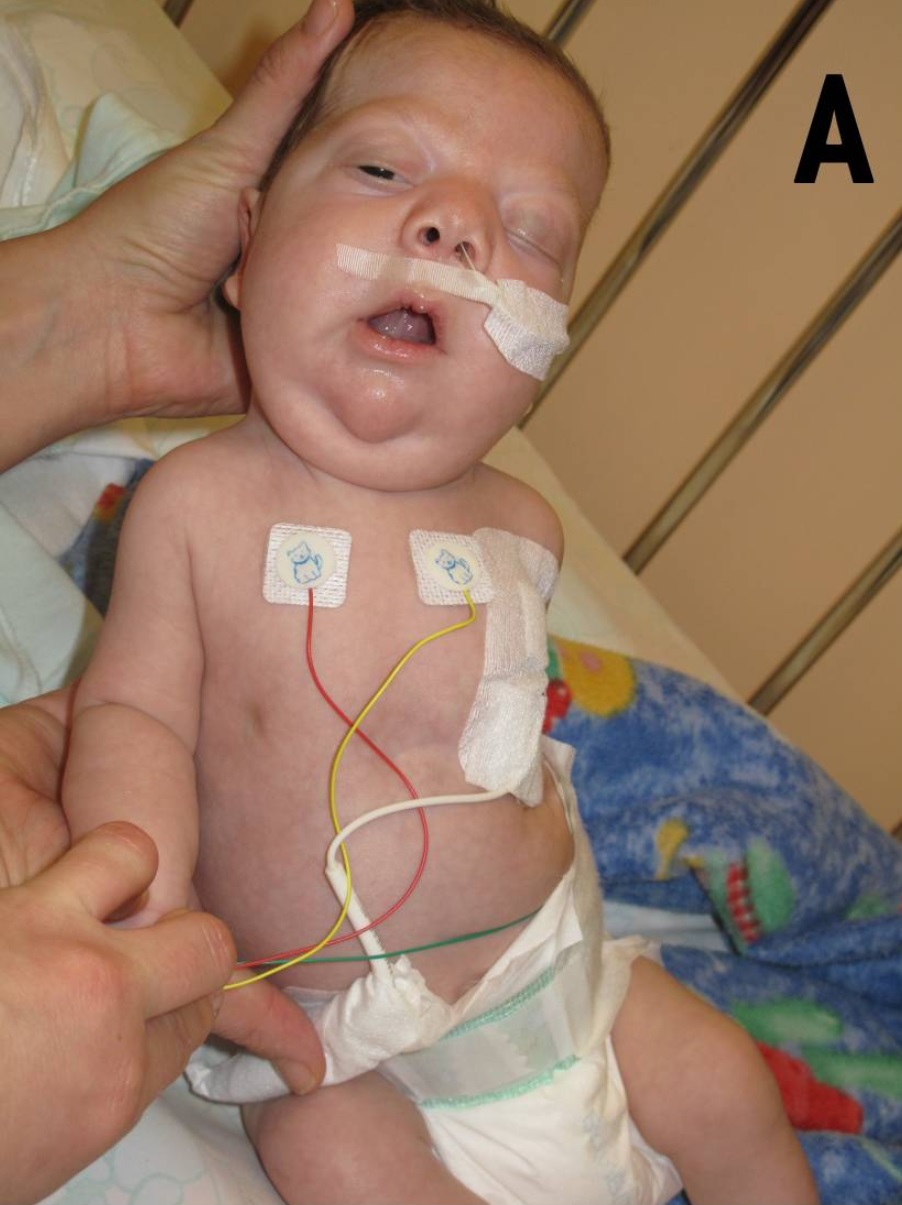
 The most common signs leading to the diagnosis of Noonan syndrome are unique facial characteristics and musculoskeletal features. The facial characteristics are most prominent in infancy, becoming less apparent with age in many people with Noonan syndrome.
The most common signs leading to the diagnosis of Noonan syndrome are unique facial characteristics and musculoskeletal features. The facial characteristics are most prominent in infancy, becoming less apparent with age in many people with Noonan syndrome.
 Jacqueline Noonan was practicing as a pediatric cardiologist at the
Jacqueline Noonan was practicing as a pediatric cardiologist at the
genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular ...
, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears
Low-set ears are a clinical feature in which the ears are positioned lower on the head than usual. They are present in many congenital conditions. Low-set ears are defined as outer ears positioned two or more standard deviations lower than the p ...
, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too n ...
. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
.
A number of genetic mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy
The RASopathies are developmental syndromes caused by germline mutations (or in rare cases by somatic mosaicism) in genes that alter the Ras subfamily and mitogen-activated protein kinases that control signal transduction, including:
* Capill ...
, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic testing.
No cure for NS is known. Treatment is based on the symptoms and underlying problems, and extra support in school may be required. Growth hormone therapy
Growth hormone therapy refers to the use of growth hormone (GH) as a prescription medication—it is one form of hormone therapy. Growth hormone is a peptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that stimulates growth and cell reproduction. I ...
during childhood can increase an affected person's final height. Long-term outcomes typically depend on the severity of heart problems.
An estimated 1 in 1000 people are mildly affected by NS, while about 1 in 2,000 have a more severe form of the condition. Males appear to be affected more often than females. The condition was first described in 1883 and was named after American pediatric
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
cardiologist
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular ...
Jacqueline Noonan, who described further cases in 1963.
Signs and symptoms

 The most common signs leading to the diagnosis of Noonan syndrome are unique facial characteristics and musculoskeletal features. The facial characteristics are most prominent in infancy, becoming less apparent with age in many people with Noonan syndrome.
The most common signs leading to the diagnosis of Noonan syndrome are unique facial characteristics and musculoskeletal features. The facial characteristics are most prominent in infancy, becoming less apparent with age in many people with Noonan syndrome.
Head
Some of the characteristic features of Noonan syndrome include a large head with excess skin on the back of the neck, low hairline at the nape of the neck, high hairline at the front of the head, triangular face shape, broad forehead, and a short, webbed neck. In the eyes,hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits (eyes), or orbital hypertelorism. In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as ...
(widely set eyes) is a defining characteristic, present in 95% of people with Noonan syndrome. This may be accompanied by epicanthal fold
An epicanthic fold or epicanthus is a skin fold of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner (medial canthus) of the eye. However, variation occurs in the nature of this feature and the possession of "partial epicanthic folds" or "slight ...
s (extra fold of skin at the inner corner of the eye), ptosis (drooping of the eyelids), proptosis
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen i ...
(bulging eyes), strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
(inward or outward turning of the eyes), nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
(jerking movement of the eyes) and refractive visual errors.
The nose may be small, wide, and upturned.
The development of the ears and auditory system may be affected in people with Noonan's syndrome. This can result in low-set ears (in over 90%), backward-rotated ears (over 90%), thick helix (outer rim) of ear (over 90%), incomplete folding of ears, chronic otitis media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
(ear infections), and hearing loss.
Development of the mouth may also be affected in Noonan syndrome. This can result in deeply grooved philtrum (top lip line) (over 90%), micrognathia
Micrognathism is a condition where the jaw is undersized. It is also sometimes called mandibular hypoplasia. It is common in infants, but is usually self-corrected during growth, due to the jaws' increasing in size. It may be a cause of abnorm ...
(undersized lower jaw), high arched palate, articulation difficulties (teeth don't line up) which can lead to dental problems. Similar to the muscular manifestations above, in the mouth, poor tongue control may be observed.
Skin
Skin signs and symptoms in Noonan syndrome includelymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fl ...
(lymph swelling of the extremities), keloid formation, excessive scar formation, hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
(overdevelopment of outer skin layer), pigmented nevi (darkly pigmented skin spots), and connective tissue disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
.
Musculoskeletal
Abnormalities in the limbs and extremities may occur in Noonan syndrome. This may manifest as bluntly ended fingers, extra padding on fingers and toes, edema of the back of hands and tops of feet, andcubitus valgus
Cubitus valgus is a medical deformity in which the forearm is angled away from the body to a greater degree than normal when fully extended. A small degree of cubitus valgus (known as the carrying angle) is acceptable and occurs in the general ...
(wide carrying angle of the elbows).
For short stature, growth hormone is sometimes combined with IGF-1 (or as an alternative, IGF-1 as a stand-alone) can be used to achieve an increased height/final height quicker. The final adult height of individuals with Noonan syndrome is about 161–167 cm in males and 150–155 cm in females, which approaches the lower limit of normal.
Spinal abnormalities may be present up to 30% of the time and this may require surgery to correct in over 60% of these cases. Other musculoskeletal manifestations in Noonan syndrome are associated with undifferentiated connective-tissue disorders which can be associated with joint contractures (tightness) or joint hypermobility (looseness). Additional factors may present in the form of winging of the scapula, scoliosis, breast bone prominence (pectus carinatum), breast bone depression (pectus excavatum). Muscle abnormalities may present as hypotonia (low muscle tone), which may lead to lordosis (increased hollow in the back) due to poor abdominal muscle tone.
Heart
Noonan syndrome is the second most common syndromic cause of congenital heart disease. This includes pulmonary valvular stenosis (50–60%), atrial septal defects (10–25%), ventricular septal defects (5–20%) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (12–35%).Lungs
Restrictive lung function has been reported in some people.Gastrointestinal
A number of diverse gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms have been associated with Noonan syndrome. These include swallowing difficulties, low gut motility,gastroparesis
Gastroparesis (gastro- from Ancient Greek γαστήρ – gaster, "stomach"; and -paresis, πάρεσις – "partial paralysis"), also called delayed gastric emptying, is a medical disorder consisting of weak muscular contractions (peristalsis) ...
(delayed gastric emptying), intestinal malrotation
Intestinal malrotation is a congenital anomaly of rotation of the midgut. It occurs during the first trimester as the fetal gut undergoes a complex series of growth and development. Malrotation can lead to a dangerous complication called volvulus ...
, and frequent or forceful vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
. These digestive issues may lead to decreased appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others ...
, failure to thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
from infancy to puberty (75%), and occasionally the need for a feeding tube.
Genitourinary system
In some males with Noonan syndrome, testicles do not descend (cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of ...
).
Circulation
Lymphatic anomalies including Posterior cervical hygroma (webbed neck) andLymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fl ...
may present in people with Noonan syndrome.
A number of bleeding disorders have been associated with Noonan syndrome, these include platelet dysfunction, Blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanis ...
disorders, partial deficiency of factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder ...
:C, partial deficiency of factor XI
Factor XI or plasma thromboplastin antecedent is the zymogen form of factor XIa, one of the enzymes of the coagulation cascade. Like many other coagulation factors, it is a serine protease. In humans, Factor XI is encoded by the ''F11'' gene.
...
:C, partial deficiency of factor XII
Coagulation factor XII, also known as Hageman factor, is a plasma protein. It is the zymogen form of factor XIIa, an enzyme () of the serine protease (or serine endopeptidase) class. In humans, factor XII is encoded by the ''F12'' gene.
Struc ...
:C, and an imbalance of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) and tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) activity. It has been associated with Von Willebrand disease
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder in humans. An acquired form can sometimes result from other medical conditions. It arises from a deficiency in the quality or quantity of von Willebrand factor ...
, Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT), also known as the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or APTT), is a blood test that characterizes coagulation of the blood. A historical name for this measure is the kaolin-cephalin clotting time ( ...
, combined coagulation defects. When present, these Noonan-syndrome accompanying disorders can be associated with a predisposition to bruise easily, or hemorrhage.
Neurological
Occasionally,Chiari malformation
Chiari malformation (CM) is a structural defect in the cerebellum, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum (the opening at the base of the skull). CMs can cause headaches, difficu ...
(type 1), may occur, which can lead to hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary inc ...
. Seizures have also been reported.
Causes
Recurrence in siblings and apparent transmission from parent to child has long suggested a genetic defect with autosomal dominant inheritance and variable expression. Mutations in theRas
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
/mitogen activated protein kinase
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen. The mechanism of action of a ...
signaling pathways are known to be responsible for about 70% of NS cases.
Persons with NS have up to a 50% chance of transmitting it to their offspring. The fact that an affected parent is not always identified for children with NS suggests several possibilities:
# Manifestations could be so subtle as to go unrecognized ( variable expressivity)
# NS is heterogeneous, comprising more than one similar condition of differing causes, and some of these may not be inherited.
# A high proportion of cases may represent new, sporadic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s.
Heterozygous mutations in '' NRAS'', ''HRAS
GTPase HRas, from "Harvey Rat sarcoma virus", also known as transforming protein p21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. The ''HRAS'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 at position 15.5, from base pair 522,241 ...
'', '' BRAF'', ''SHOC2 Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) protein SHOC-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SHOC2'' gene. The best-studied role of SHOC2 is in modulating signals of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 ( ERK1/2) pathway by forming a holo ...
'', ''MAP2K1
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual-specificity protein kinase family that acts as a mito ...
'', ''MAP2K2
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K2'' gene. It is more commonly known as MEK2, but has many alternative names including CFC4, MKK2, MAPKK2 and PRKMK2.
Function
The ...
'', and '' CBL'' have also been associated with a smaller percentage of NS and related phenotypes.
A condition known as " neurofibromatosis–Noonan syndrome" is associated with neurofibromin.
Diagnosis
NS can be confirmedgenetically
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working i ...
by the presence of any of the known mutations listed above. However, despite identification of 14 causative genes, the absence of a known mutation will not exclude the diagnosis, as more, as-yet-undiscovered genes can cause NS. Thus, the diagnosis of NS is still based on clinical features. In other words, it is made when a physician feels that a person has enough of the features to warrant the label. The principal values of making a genetic diagnosis are that it guides additional medical and developmental evaluations, it excludes other possible explanations for the features, and it allows more accurate recurrence risk estimates. With more genotype-phenotype correlation studies being performed, a positive genetic diagnosis will help the clinician to be aware of possible anomalies specific to that certain gene mutation. For example, an increase in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is seen in people with a mutation of ''KRAS'' and an increased risk of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia exists for a mutation of ''PTPN11''. In the future, studies may lead to a targeted management of NS symptoms that depends on what genetic mutation a person has.
Before birth
Prenatal features that might lead physicians to consider a diagnosis of Noonan syndrome include cystic hygroma, increased nuchal translucency, pleural effusion, and edema.Differential diagnosis
WhileTurner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
has similarities with renal anomalies and developmental delay, Turner syndrome is only found in females and often expresses differently. In Turner syndrome, there is a lower incidence of developmental delays, left-sided heart defects are constant and the occurrence of renal abnormalities is much lower.
Other RASopathies
* Watson syndrome
Watson syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by Lisch nodules of the ocular iris, axillary/inguinal freckling, pulmonary valvular stenosis, relative macrocephaly, short stature, and neurofibromas. Watson syndrome is allelic ...
- Watson Syndrome has a number of similar characteristics with Noonan's Syndrome such as short stature, pulmonary valve stenosis, variable intellectual development, and skin pigment changes.
* Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome - CFC syndrome is very similar to Noonan's Syndrome due to similar cardiac and lymphatic features. However, In CFC syndrome intellectual disability and gastrointestinal problems are often more severe and pronounced.
* Costello syndrome
Costello syndrome, also called faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome or FCS syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. It is characterized by delayed development and intellectual disabilities, distinctive facial features, unu ...
- Like CFC syndrome, Costello syndrome has overlapping features with Noonan's Syndrome. However, the conditions can be distinguished by their genetic cause.
* Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1)
* Williams syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS) is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed in people ...
Management
The treatment varies depending on complications but tend to be quite standard, reflecting the treatment of the general population. Management guidelines, divided by systems, including general, developmental, dental, growth and feeding, cardiovascular, audiological, haematological, renal and skeletal, that account for actions to be taken at diagnosis, after diagnosis and if symptomatic, have been published by an American consortium. Specifically, treatment of cardiovascular complications resemble that of the general population and treatment of bleeding diathesis is guided by the specific factor deficiency or platelet aggregation. * Neuropsychological testing is recommended to find strengths and challenges to tailor support needed for school and career. * Educational customization such as anindividualized education program
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legal document under United States law that is developed for each public school child in the U.S. who needs special education. It is created through a team of the child's parent(s) and district pers ...
plan is sometimes needed for school-aged children.
* Speech therapy if speech and articulation issues present
* Physical therapy and occupational therapy for gross- and fine-motor delays
* Hypotonia and motor difficulties often impact handwriting. Accommodations for lessening handwriting demands will improve performance and save long-term hand function.
* Periodic follow up and lifelong monitoring of abnormalities found in any system, especially the cardiovascular system, is recommended.
Anesthesia risk
Although a few people with Noonan syndrome have been reported to developmalignant hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a type of severe reaction that occurs in response to particular medications used during general anesthesia, among those who are susceptible. Symptoms include muscle rigidity, fever, and a fast heart rate. Complica ...
, the gene mutation of diseases known to be associated with malignant hyperthermia is different from that of Noonan syndrome.
Prognosis
The lifespan of people with Noonan's syndrome can be similar to the general population, however, Noonan syndrome can be associated with several health conditions that can contribute to mortality. The greatest contributor to mortality in individuals with Noonan syndrome is complications of cardiovascular disease. Prognosis is therefore largely dependent on the presence or absence of cardiac disease, as well as the type and severity of the disease (if disease is present). Most notably, Noonan syndrome with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is associated with increased mortality.History
University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (UI, U of I, UIowa, or simply Iowa) is a public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized into 12 col ...
when she noticed that children with a rare type of heart defect, valvular pulmonary stenosis, often had a characteristic physical appearance, with short stature
Short stature refers to a height of a human which is below typical. Whether a person is considered short depends on the context. Because of the lack of preciseness, there is often disagreement about the degree of shortness that should be called ' ...
, webbed neck
A webbed neck, or pterygium colli, is a congenital skin fold that runs along the sides of the neck down to the shoulders.
There are many variants.
Signs and symptoms
On babies, webbed neck may look like loose folds of skin on the neck. As the ch ...
, wide spaced eyes
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits (eyes), or orbital hypertelorism. In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as ...
, and low-set ears
Low-set ears are a clinical feature in which the ears are positioned lower on the head than usual. They are present in many congenital conditions. Low-set ears are defined as outer ears positioned two or more standard deviations lower than the p ...
. Both boys and girls were affected. These characteristics were sometimes seen running in families but were not associated with gross chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
abnormalities. She studied 833 people with Noonan syndrome at the congenital heart disease clinic, looking for other congenital abnormalities, and, in 1963, presented a paper: "Associated non-cardiac malformations in children with congenital heart disease". This described 9 children who in addition to congenital heart disease had characteristic facial features, chest deformities and short stature.
Dr. John Opitz, a former student of Dr. Noonan's, first began to call the condition "Noonan syndrome" when he saw children who looked like those whom Dr. Noonan had described. Dr. Noonan produced a paper titled "Hypertelorism with Turner Phenotype" in 1968 where she studied 19 patients who displayed symptoms indicative of Noonan's Syndrome. In 1971, at the Symposium of Cardiovascular defects, the name 'Noonan syndrome' became officially recognized.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Noonan Syndrome Autosomal dominant disorders Syndromes affecting the heart Genodermatoses Enzyme defects RASopathies Congenital heart defects Intellectual disability Syndromes affecting stature Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate