|
RASopathy
The RASopathies are developmental syndromes caused by germline mutations (or in rare cases by somatic mosaicism) in genes that alter the Ras subfamily and mitogen-activated protein kinases that control signal transduction, including: * Capillary malformation-AV malformation syndrome * Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome * Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome * Hereditary gingival fibromatosis type 1 * Neurofibromatosis type 1 * Noonan syndrome * Costello syndrome, Noonan-like * Legius syndrome, Noonan-like * Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, formerly called LEOPARD syndrome Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML) which is part of a group called Ras/MAPK pathway syndromes, is a rare autosomal dominant, multisystem disease caused by a mutation in the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 gene (''PT ..., Noonan-like * SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability References {{Medicine, state=collapsed Autosomal dominant disorders Congenital vascular defects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LEOPARD Syndrome
Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML) which is part of a group called Ras/MAPK pathway syndromes, is a rare autosomal dominant, multisystem disease caused by a mutation in the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 gene (''PTPN11''). The disease is a complex of features, mostly involving the skin, skeletal and cardiovascular systems, which may or may not be present in all patients. The nature of how the mutation causes each of the condition's symptoms is not well known; however, research is ongoing. It is a RASopathy. Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines is caused by a different missense mutation of the same gene. Noonan syndrome is fairly common (1:1,000 to 1:2,500 live births), and neurofibromatosis 1 (which was once thought to be related to NSML) is also common (1:3500); however, no epidemiological data exists for NSML. Signs and symptoms An alternative name of the condition, LEOPARD syndrome, is a mnemonic, originally coined in 1969, as the condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
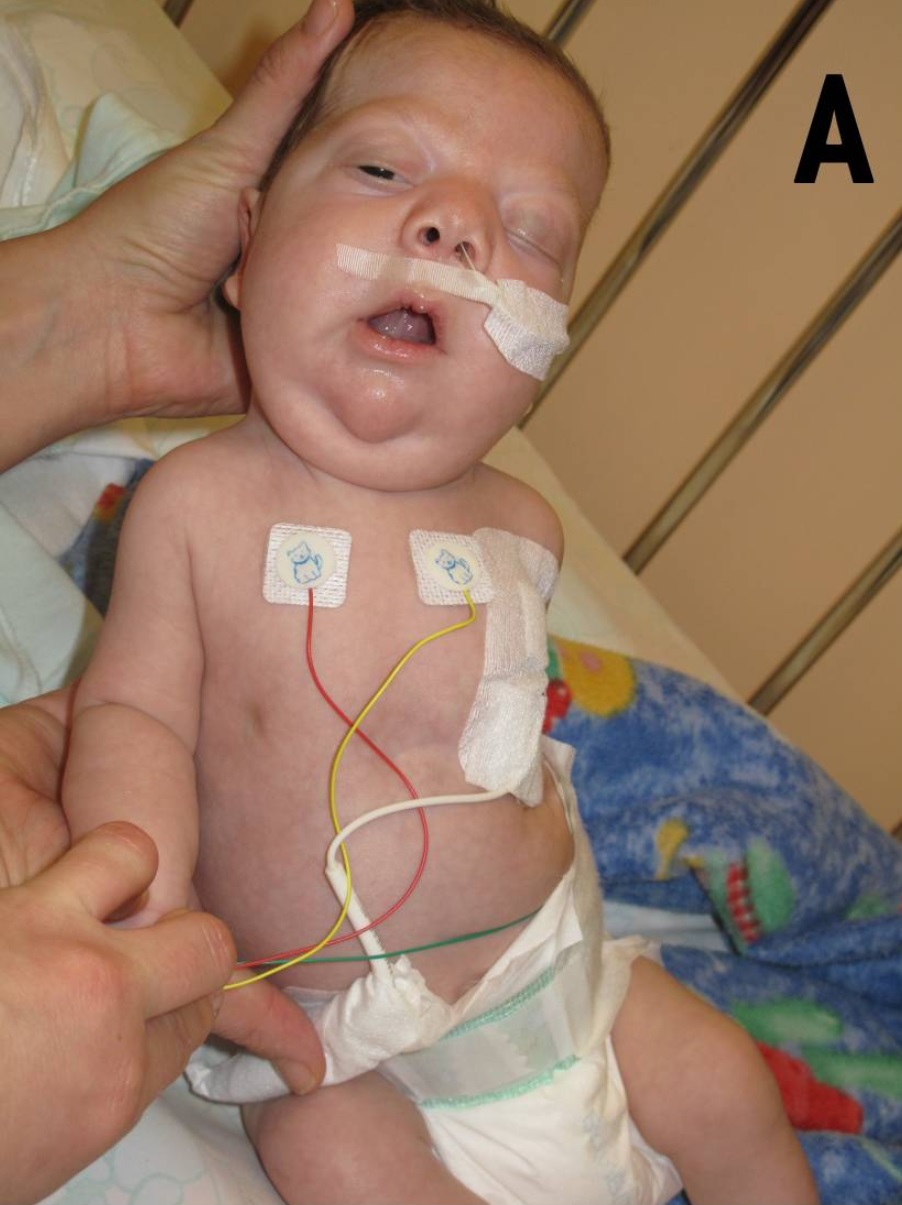
Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome
Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder, and is one of the RASopathies. It was first described in 1986. It is characterized by the following: *Distinctive facial appearance *Unusually sparse, brittle, curly scalp hair *A range of skin abnormalities from dermatitis to thick, scaly skin over the entire body (generalized ichthyosis) *Heart malformations in over 75% of patients (congenital or appearing later), especially an obstruction of the normal flow of blood from the lower right ventricle of the heart to the lungs (valvar pulmonary stenosis) *Growth delays *Feeding problems associated with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) *Foot abnormalities (extra toe or fusion of two or more toes) *Intellectual disability *Failure to thrive Presentation Head Individuals with the disorder usually have distinctive malformations of the craniofacial area including an unusually large head (macrocephaly), prominent forehead, and abnormal narrowing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legius Syndrome
Legius syndrome (LS) is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by cafe au lait spots."Legius syndrome" Genetics Home Reference, It was first described in 2007 and is often mistaken for neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1). It is caused by mutations in the '''' gene. It is also known as neurofibromatosis type 1-like syndrome (NFLS). Symptoms and signs Nearly all individuals with Legius syn ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costello Syndrome
Costello syndrome, also called faciocutaneoskeletal syndrome or FCS syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. It is characterized by delayed development and intellectual disabilities, distinctive facial features, unusually flexible joints, and loose folds of extra skin, especially on the hands and feet.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . Heart abnormalities are common, including a very fast heartbeat (tachycardia), structural heart defects, and overgrowth of the heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). Infants with Costello syndrome may be large at birth, but grow more slowly than other children and have difficulty feeding. Later in life, people with this condition have relatively short stature and many have reduced levels of growth hormones. It is a RASopathy. Beginning in early childhood, people with specific mutations on the Costello syndrome gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a group of three conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The three types are neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), and schwannomatosis. In NF1 symptoms include light brown spots on the skin, freckles in the armpit and groin, small bumps within nerves, and scoliosis. In NF2, there may be hearing loss, cataracts at a young age, balance problems, flesh colored skin flaps, and muscle wasting. In schwannomatosis there may be pain either in one location or in wide areas of the body. The tumors in NF are generally non-cancerous. The cause is a genetic mutation in certain oncogenes. These can be inherited from a person's parents, or in about half of cases spontaneously occur during early development. Different mutations result in the three types of NF. Neurofibromatosis arise from the supporting cells of the nervous system rather than the neurons themselves. In NF1, the tumors are neurofibromas (tumors of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Fibromatosis With Hypertrichosis
Gingival fibromatosis with hypertrichosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by dark terminal hairs on the peripheral face, central back, and extremities. It is a RASopathy. See also * Cantú syndrome * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ... References Genodermatoses RASopathies {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually cerebral AVM), but can appear in any location. Although many AVMs are asymptomatic, they can cause intense pain or bleeding or lead to other serious medical problems. AVMs are usually congenital and belong to the RASopathies. The genetic transmission patterns of AVMs are incomplete, but there are known genetic mutations (for instance in the epithelial line, tumor suppressor PTEN gene) which can lead to an increased occurrence throughout the body. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of AVM vary according to the location of the malformation. Roughly 88% of people with an AVM are asymptomatic; often the malformation is discovered as part of an autopsy or during treatment of an unrelated disorder (called in medicine an "incidental finding"); in rare cases, its expansion or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuro-cardio-facial-cutaneous Syndromes
Neuro-cardio-facial-cutaneous-syndromes (NCFC), (also referred to as ''neuro-craniofacial-cardiac syndromes'') is a group of developmental disorders with a genetic ground, affecting the nervous system, circulatory system, (cranio)facial and cutaneous development. These four parts are the common denominator for the syndromes, but are mostly accompanied by disturbances in other parts of the body. The two most common syndromes under this "umbrella" are: Leopard syndrome (LS) and Noonan syndrome (NS). Other members are Costello syndrome (CS), cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome (CFC) and Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1). Recently, it has been observed that NCFC syndromes result from de novo germline mutations that alter the ''Ras/Raf/Mek'' signal transduction pathway. These are called RASopathies. One percent of autistic children have either a loss or duplication in a region of Chromosome 16 that encompasses the gene for ERK 1. Mutations within the ERK signal transduction pathway appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocytic Nevi And Neoplasms
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes to induce pigmentation. Thus darker skin tones have more melanosomes present than lighter skin tones. Functionally, melanin serves as protection against UV radiation. Melanocytes also have a role in the immune system. Function Through a process called melanogenesis, melanocytes produce melanin, which is a pigment found in the skin, eyes, hair, nasal cavity, and inner ear. This melanogenesis leads to a long-lasting pigmentation, which is in contrast to the pigmentation that originates from oxidation of already-existing melanin. There are both basa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Neuroscience
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the dorsal ectoderm becomes specifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurological Disorders
A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialities of neurology and clinical neuropsychology. Interventions foneurological disordersinclude preventive measures, lifestyle changes, physiotherapy or other therapy, neurorehabilitation, pain management, medication, operations performed by neurosurgeons or a specific diet. The World Health Organization estimated in 2006 that neurological disorders and their sequelae (direct consequences) affect as many as one billion people worldwide, and identified heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |