|
Lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fluid to the bloodstream. Lymphedema is most frequently a complication of cancer treatment or parasitic infections, but it can also be seen in a number of genetic disorders. Though incurable and progressive, a number of treatments may improve symptoms. Tissues with lymphedema are at high risk of infection because the lymphatic system has been compromised. While there is no cure, treatment may improve outcomes. This commonly include compression therapy, good skin care, exercise, and manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), which together are known as combined decongestive therapy. Diuretics are not useful. Signs and symptoms The most common manifestation of lymphedema is soft tissue swelling, edema. As the disorder progresses, worsening edema a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphangiosarcoma
Lymphangiosarcoma is a rare cancer which occurs in long-standing cases of primary or secondary lymphedema. It involves either the upper or lower lymphedematous extremities but is most common in upper extremities. Although its name implies lymphatic origin, it is believed to arise from endothelial cells and may be more accurately referred to as angiosarcoma. Signs and symptoms Lymphangiosarcoma may present as a purple discoloration or a tender skin nodule in the extremity, typically on the anterior surface. It progresses to an ulcer with crusting to an extensive necrotic focus involving the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It metastasizes quickly. Causes It was previously a relatively common complication of the massive lymphedema of the arm which followed removal of axillary (arm pit) lymph nodes and lymphatic channels as part of the classical Halstedian radical mastectomy, as a treatment for breast cancer. The classical radical mastectomy was abandoned in most areas of the world in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart–Treves Syndrome
Stewart–Treves syndrome refers to a lymphangiosarcoma, a rare disorder marked by the presence of an angiosarcoma (a malignant tumor of blood or lymph vessels) in a person with chronic (long-term) lymphedema. Although it most commonly refers to malignancies associated with chronic lymphedema resulting from mastectomy and/or radiotherapy for breast cancer, it may also describe lymphangiosarcomas that result from congenital and other causes of chronic secondary lymphedema. Lymphangiosarcoma arising from cancer-related lymphedema has become much less common with better surgical techniques, radiation therapy, and conservative treatment. The prognosis, even with wide surgical excision and subsequent radiotherapy, is poor. Cause Common risk factors that may lead to the development of lymphangiosarcoma include lymphatic blockage, radiotherapy, mastectomy, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension. The sarcoma first appears as a bruise mark, a purplish discoloration or a tender skin nodul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a type of massage based on the hypothesis that it will encourage the natural drainage of the lymph, which carries waste products away from the tissues back toward the heart. The lymph system depends on intrinsic contractions of the smooth muscle cells in the walls of lymph vessels (peristalsis) and the movement of skeletal muscles to propel lymph through the vessels to lymph nodes and then to the lymph ducts, which return lymph to the cardiovascular system. Manual lymph drainage uses a specific amount of pressure (less than 9oz per square inch or about 4kPa), and rhythmic circular movements to stimulate lymph flow. Medical use Studies show mixed results regarding the efficacy of the method in treating lymphedema, and further studies are needed. A 2013 systematic review of manual lymphatic drainage with regard to breast cancer–related lymphedema found no clear support for the effectiveness of the intervention in either preventing limb edema in at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include Chronic venous insufficiency, venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, hypoalbuminemia, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves Hypernatremia, sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
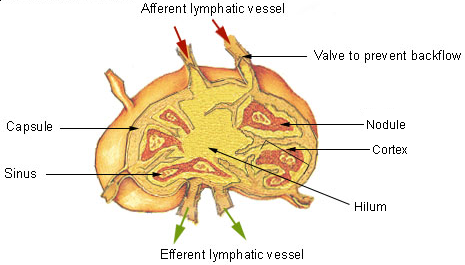
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which blood pools in the veins, straining the walls of the vein. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux which is a treatable condition. As functional venous valves are required to provide for efficient blood return from the lower extremities, this condition typically affects the legs. If the impaired vein function causes significant symptoms, such as swelling and ulcer formation, it is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is sometimes called ''chronic peripheral venous insufficiency'' and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome in which the deep veins have been damaged by previous deep vein thrombosis. Most cases of CVI can be improved with treatments to the superficial venous system or stenting the deep system. Varicose veins for example can now be treated by local anesthetic endovenous surgery. Rates of CVI are higher in women than in men. Other risk factors include genetics, smok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Medicine
Angiology (from Greek , ''angeīon'', "vessel"; and , '' -logia'') is the medical specialty dedicated to studying the circulatory system and of the lymphatic system, i.e., arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels. In the UK, this field is more often termed ''angiology'', and in the United States the term vascular medicine is more frequent. The field of vascular medicine (angiology) is the field that deals with preventing, diagnosing and treating vascular and blood vessel related diseases. Overview Arterial diseases include the aorta (aneurysms/dissection) and arteries supplying the legs, hands, kidneys, brain, intestines. It also covers arterial thrombosis and embolism; vasculitides; and vasospastic disorders. Naturally, it deals with preventing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. Venous diseases include venous thrombosis, chronic venous insufficiency, and varicose veins. Lymphatic diseases include primary and secondary forms of lymphedema. It also invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an inflammation or an infection of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. The most common cause of lymphangitis in humans is ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' (Group A strep), hemolytic streptococci, and in some cases, mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, tuberculosis, syphilis, and the fungus ''Sporothrix schenckii''. Lymphangitis is sometimes mistakenly called "blood poisoning". In reality, "blood poisoning" is synonymous with ''sepsis''. Lymphatic vessels are smaller than capillaries and tiny venules and are ubiquitous in the body. These vessels are fitted with valves to direct flow in only one direction. Fluid diffusing through the thin-walled small capillaries should be collected and the lymphatic system does just that: a fluid rich in protein, minerals, nutrients, and other substances useful for tissue growth. As well as essential nutrients, the lymphatic system can also transport or carry cancer cells, defective or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erysipelas
Erysipelas () is a relatively common bacterial infection of the superficial layer of the skin ( upper dermis), extending to the superficial lymphatic vessels within the skin, characterized by a raised, well-defined, tender, bright red rash, typically on the face or legs, but which can occur anywhere on the skin. It is a form of cellulitis and is potentially serious. Erysipelas is usually caused by the bacteria ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', also known as ''group A β-hemolytic streptococci'', which enters the body through a break in the skin, such as a scratch or an insect bite. It is more superficial than cellulitis, and is typically more raised and demarcated. The term comes from the Greek ἐρυσίπελας (''erysípelas''), meaning "red skin". In animals, erysipelas is a disease caused by infection with the bacterium ''Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae''. The disease caused in animals is called Diamond Skin Disease, which occurs especially in pigs. Heart valves and skin are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. Indications It is usually done because many types of cancer have a marked tendency to produce lymph node metastasis early in their natural history. This is particularly true of melanoma, head and neck cancer, differentiated thyroid cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Famed British surgeon Berkeley Moynihan once remarked that "the surgery of cancer is not the surgery of organs; it is the surgery of the lymphatic system". The better-known examples of lymphadenectomy are ''axillary lymph node dissection'' for breast cancer; ''radical neck dissection'' for head and neck cancer and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcer (dermatology)
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms. Signs and symptoms Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |