Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive
File:Mallory_body_high_mag_cropped_annotated.jpg, Mallory-Denk body
File:Ballooning_degeneration_high_mag_cropped_annotated.jpg,
 NAFLD is defined by evidence of
NAFLD is defined by evidence of
 A liver
A liver

 A
A
 Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD.
About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery.
A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a
Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD.
About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery.
A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a
 NAFLD incidence is rapidly rising, along with obesity and diabetes, and has become the most common cause of liver disease in developed countries, for adults, teenagers, and children. The percentage of people with NAFLD ranges from 9 to 36.9% in different parts of the world. Approximately 20% of the United States and 25% of the Asia-Pacific populations have non-alcoholic fatty liver. Similar prevalence can be found in Europe, although less data is available. NAFLD is the most common in the Middle East (32%) and South America (30%), while Africa has the lowest rates (13%). Compared to the 2000s, NAFL and NASH respectively increased 2-fold and 2.5-fold in the 2010s in the USA.
NAFLD and NASH are more prevalent in Hispanics - which can be attributed to high rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes in Hispanic populations, intermediate in Whites, and lowest in Blacks. NAFLD was observed to be twice as prevalent in men as women. For severely obese individuals, the prevalence of NAFLD rises over 90%, and for those with
NAFLD incidence is rapidly rising, along with obesity and diabetes, and has become the most common cause of liver disease in developed countries, for adults, teenagers, and children. The percentage of people with NAFLD ranges from 9 to 36.9% in different parts of the world. Approximately 20% of the United States and 25% of the Asia-Pacific populations have non-alcoholic fatty liver. Similar prevalence can be found in Europe, although less data is available. NAFLD is the most common in the Middle East (32%) and South America (30%), while Africa has the lowest rates (13%). Compared to the 2000s, NAFL and NASH respectively increased 2-fold and 2.5-fold in the 2010s in the USA.
NAFLD and NASH are more prevalent in Hispanics - which can be attributed to high rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes in Hispanic populations, intermediate in Whites, and lowest in Blacks. NAFLD was observed to be twice as prevalent in men as women. For severely obese individuals, the prevalence of NAFLD rises over 90%, and for those with
NIH
page on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Mayo Clinic
page on NAFLD {{Medical resources , DiseasesDB = 29786 , ICD10 = {{ICD10, K75.8, {{ICD10, K, 76, 0, k, 70 , ICD10CM = {{ICD10CM, K75.81, {{ICD10CM, K76.0 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 571.8 , ICDO = , OMIM = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = med , eMedicineTopic = 775 Diseases of liver Hepatitis
fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
build-up in the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with the latter also including liver inflammation. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to NASH. When NAFL does progress to NASH, it may eventually lead to complications such as cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
, liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
, liver failure, or cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
.
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
are strong risk factors for NAFLD. Other risks include being overweight
Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with mo ...
, metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndrome ...
(defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, high blood sugar
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
, high serum triglycerides, and low serum HDL cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are t ...
), a diet high in fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, and older age. NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis ...
are types of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complica ...
. Obtaining a sample of the liver after excluding other potential causes of fatty liver can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for NAFLD is weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
by dietary changes and exercise. There is tentative evidence for pioglitazone
Pioglitazone, sold under the brand name Actos among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It may be used with metformin, a sulfonylurea, or insulin. Use is recommended together with exercise and diet. It is not re ...
and vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Vitamin E deficiency, which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vi ...
; and bariatric surgery can improve or resolve severe cases. Those with NASH have a 2.6% increased risk of dying per year.
NAFLD is the most common liver disorder worldwide and is present in approximately 25% of the world's population. It is very common in developed nations, such as the United States, and affected about 75 to 100 million Americans in 2017. Over 90% of obese, 60% of diabetic
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, and up to 20% of normal-weight people develop NAFLD. NAFLD is the leading cause of chronic liver disease
Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. "Chronic liver disease" refers to disease ...
and the second most common reason for liver transplantation in the US and Europe as of 2017. NAFLD affects about 20 to 25% of people in Europe. In the United States, estimates suggest between 30 and 40% of adults have NAFLD, and about 3 to 12% of adults have NASH. The annual economic burden was approximately US$103 billion in the US in 2016.
Definition
An abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of secondary causes of fatty liver, such as significant alcohol use,viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form.
The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic v ...
, or medications that can induce fatty liver characterizes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The term NAFLD encompasses a continuum of liver abnormalities, from non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL, simple steatosis) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Steatohepatitis is a type of fatty liver disease, characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis, and together these constitute fatty liver changes.
...
(NASH). These diseases begin with fatty accumulation in the liver (hepatic steatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disea ...
). A liver can remain fatty without disturbing liver function (NAFL), but by various mechanisms and possible insults
An insult is an expression or statement (or sometimes behavior) which is disrespectful or scornful. Insults may be intentional or accidental. An insult may be factual, but at the same time pejorative, such as the word " inbred".
Jocular exc ...
to the liver, it may also progress into non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a state in which steatosis is combined with inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
and sometimes fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
(steatohepatitis). NASH can then lead to complications such as cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
and hepatocellular carcinoma.
A new name, metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease, was proposed after 70% of a panel of experts expressed support for this name.
Signs and symptoms
People with NAFLD often have no noticeable symptoms, and NAFLD is often only detected during routine blood tests or unrelated abdominal imaging orliver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy (removal of a small sample of tissue) from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.
Medica ...
. In some cases, NAFLD can cause symptoms related to liver dysfunction such as fatigue, malaise, and dull right-upper-quadrant abdominal discomfort
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more ...
. Mild yellow discoloration of the skin may occur, although this is rare. NASH can severely impair liver function, leading to cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
, liver failure, and liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
.
Comorbidities
NAFLD is strongly associated with or caused by type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome (defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein). It is also associated with hormonal disorders (panhypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is the decreased (''hypo'') secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. If there is decreased secretion of one specific pituitary hormone, the condition is know ...
, hypothyroidism, hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testes or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estrogen ...
, polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
), persistently elevated transaminases
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, transaminitis, and elevated ...
, increasing age and hypoxia caused by obstructive sleep apnea, with some of these conditions predicting disease progression.
The majority of normal-weight people affected by NAFLD ("lean NAFLD") have impaired insulin sensitivity, are sedentary, and have increased cardiovascular disease risk and increased liver lipid levels. These are the consequences of a decreased capacity for storing fat and reduced mitochondrial function in adipose tissue and increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride syn ...
. A recent systematic review has reported an increased risk of severe COVID-19 infection in NAFLD patients; however, no difference in mortality was observed between NAFLD and non-NAFLD patients.
Risk factors
Genetics
Two-thirds of families with a history of diabetes type 2 report more than one family member having NAFLD. There is a higher risk of fibrosis for family members where someone was diagnosed with NASH. Asian populations are more susceptible to metabolic syndrome and NAFLD than their western counterparts. Hispanic persons have a higher prevalence of NAFLD than white individuals, whereas the lowest prevalence is observed in black individuals. NAFLD is twice as prevalent in men as in women, which might be explained by lower levels of estrogen in men. Genetic variations in two genes are associated with NAFLD: non-synonymoussingle-nucleotide polymorphisms
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
(SNPs) in PNPLA3 and TM6SF2. Both correlate with NAFLD presence and severity, but their roles for diagnosis remain unclear. Although NAFLD has a genetic component, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) is a leading organization of scientists and health care professionals committed to preventing and curing liver disease. AASLD was founded in 1950 by a group of leading liver specialist ...
(AASLD) does not recommend screening family members as there is not enough confirmation of heritability, although there is some evidence from familial aggregation and twin studies
Twin studies are studies conducted on identical or fraternal twins. They aim to reveal the importance of environmental and genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics a ...
.
Diet
According to the Asia-Pacific Working Group (APWG) on NAFLD, overnutrition is a major factor of NAFLD and NASH, particularly for lean NAFLD. Diet composition and quantity, in particularomega-6 fatty acid
Omega-6 fatty acids (also referred to as ω-6 fatty acids or ''n''-6 fatty acids) are a family of polyunsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon-carbon double bond in the ''n''-6 position, that is, the sixth bond, counting from ...
and fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, have important roles in disease progression from NAFL to NASH and fibrosis. Choline deficiency can lead to the development of NAFLD.
Lifestyle
Habitualsnoring
Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. The sound may be soft or loud and unpleasant. Snoring during sleep may be a sign, or first alarm, of ob ...
may be a risk factor for NAFLD, even after accounting for established risk factors in individuals. Severe cases of snoring lead to airway blockage or difficulty breathing when sleeping, and usually signals the presence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSAS), a much more serious breathing condition. Blockage or narrowing of the airways, even temporarily, can cause the body to experience lowered oxygen levels in the blood, and these conditions of hypoxia are recurring in those with obstructive sleep apnea (OSAS). Constant hypoxia may cause a variety of changes within the body, such as tissue inflammation, increased insulin resistance, and liver injury. A prospective cohort study found the association between habitual snoring and NAFLD development to be significant, and the trend was noted to be most prominent in lean individuals.
Pathophysiology
The primary characteristic of NAFLD is the accumulation of lipids in the liver, largely in the form oftriglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as w ...
s. However, the mechanisms by which triglycerides accumulate and the reasons that accumulation can lead to liver dysfunction are complex and incompletely understood. NAFLD can include steatosis along with varied signs of liver injury: either lobular or portal inflammation (a form of liver injury) or ballooning degeneration
In histopathology, ballooning degeneration, formally ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes, is a form of liver parenchymal cell (i.e. hepatocyte) death.
The name is derived from the fact that the cells undergoing this form of cell death incr ...
. Similarly, NASH can include histological features such as portal inflammation, polymorphonuclear cell infiltrates, Mallory bodies, apoptotic
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
bodies, clear vacuolated nuclei, microvesicular steatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver dis ...
, megamitochondria, and perisinusoidal fibrosis. Hepatocyte death via apoptosis or necroptosis
Necroptosis is a programmed form of necrosis, or inflammatory cell death. Conventionally, necrosis is associated with unprogrammed cell death resulting from cellular damage or infiltration by pathogens, in contrast to orderly, programmed cell dea ...
is increased in NASH compared with simple steatosis, and inflammation is a hallmark of NASH.
One debated mechanism proposes that hepatic steatosis progresses to steatosis with inflammation following some further injury, or ''second hit''. Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily Detoxification, detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances ...
, hormonal imbalances, and mitochondrial abnormalities are potential causes of this "second hit" phenomenon. A further nutrigenomics
Nutritional genomics, also known as nutrigenomics, is a science studying the relationship between human genome, human nutrition and health. People in the field work toward developing an understanding of how the whole body responds to a food via s ...
model named ''multiple hit'' extends the ''second hit'' model, suggesting that multiple disease biomarkers and factors such as genes and nutrition influence NAFLD and NASH progression. This model attempts to use these factors to predict the impact of lifestyle changes and genetics for the evolution of the NAFLD pathology. Many researchers describe NAFLD as a ''multisystem'' disease, as it impacts and is influenced by organs and regulatory pathways other than the liver.
The accumulation of senescent cells
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approxi ...
in the liver is seen in persons with NAFLD. In mice, liver senescent hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s result in increased liver fat deposition. Treatment of NAFLD mice with senolytic
A senolytic (from the words ''senescence'' and ''-lytic'', "destroying") is among a class of small molecules under basic research to determine if they can selectively induce death of senescent cells and improve health in humans. A goal of this ...
agents has been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis.
Based on gene knockout studies in murine models, it has been suggested that, among many other pathogenic factors, TGF beta signals may be crucially involved in promoting the progression of NASH.
Fructose consumption
Non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease share similar histological features, which suggests that they might share common pathogenic pathways. Fructose can cause liver inflammation and addiction similarly to ethanol by using similar metabolic pathways, unlike glucose. Therefore, some researchers argue that non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver diseases are more alike than previously thought. Furthermore, high fructose consumption promotes fat accumulation in the liver by stimulating ''de novo'' lipogenesis in the liver and reducing the beta-oxidation of fat. Unlike the sugarglucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
, the enzyme fructokinase
Fructokinase (/fruc•to•ki•nase/ ki´nas, also known as D-fructokinase or D-fructose (D-mannose) kinase,adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of ...
(ATP). The decrease in ATP increases oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily Detoxification, detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances ...
and impairments in proper protein synthesis and mitochondrial function in the liver.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance contributes to the accumulation of toxic fat in the liver in several ways. First, it promotes the release offree fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s (FFAs) from adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular e ...
into the blood. Typically, adipose tissue stores lipids in the form of triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as w ...
s, slowly releasing them into the bloodstream when insulin is low. In insulin-resistant adipose tissue, such as in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes, more triglycerides are broken down into FFAs and released into the bloodstream, promoting uptake by the liver. Second, insulin promotes the production of new FFAs in the liver via ''de novo'' lipogenesis; this production of liver fats continues to be stimulated by insulin, even when other tissues are insulin-resistant. These FFAs are combined back into triglycerides in the liver, forming the major constituent of the accumulated fat in the liver. The three sources of free fatty acids that contribute to liver triglyceride accumulation include FFAs circulating in the bloodstream (59%), FFAs derived from carbohydrates such as fructose and glucose (26%), and diet (14%). Despite the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, they are not directly toxic to liver tissue. Instead, alteration of the profile of the other lipid subtypes present in the liver, such as diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as s ...
s, phospholipids, ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up ...
s, and free cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell mem ...
, have a more significant role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.
Once NAFLD progresses in severity to the point of NASH, this promotes further insulin resistance in the adipose tissue and liver, which results in a harmful cycle of insulin resistance, liver fat accumulation, and inflammation. Adipose tissue dysfunction also decreases secretion of the insulin-sensitizing adipokine
The adipokines, or adipocytokines (Greek ', fat; ', cell; and ', movement) are cytokines (cell signaling proteins) secreted by adipose tissue. Some contribute to an obesity-related low-grade state of inflammation or to the development of metabolic ...
adiponectin
Adiponectin (also referred to as GBP-28, apM1, AdipoQ and Acrp30) is a protein hormone and adipokine, which is involved in regulating glucose levels as well as fatty acid breakdown. In humans it is encoded by the ''ADIPOQ'' gene and it is produ ...
in people with NAFLD. Adiponectin has several properties that protect the liver. These properties include improved liver fat metabolism, decreased ''de novo'' lipogenesis, decreased glucose production in the liver, anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
properties, and anti-fibrotic properties. Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
insulin resistance may also play a role in NAFLD. Insulin-resistant skeletal muscle is not as efficient at taking up glucose from the bloodstream after a meal. This inefficient glucose uptake promotes the redistribution of consumed carbohydrates from glucose destined for use in glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
stores in the skeletal muscles to being used as a substrate for ''de novo'' lipogenesis in the liver.
Dysbiosis
Disruptions in the intestinal microbiota seem to influence NAFLD risk in several ways. People with NASH can have elevated levels of blood ethanol andPseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The ...
(which produce alcohol), with dysbiosis proposed as a mechanism for this elevation. Alterations in the composition of the intestinal microbiota may influence NAFLD risk in several ways. These changes appear to increase the permeability of intestinal tissue, thereby facilitating increased liver exposure to harmful substances (e.g., translocated bacteria, bacterial toxins
Microbial toxins are toxins produced by micro-organisms, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, dinoflagellates, and viruses. Many microbial toxins promote infection and disease by directly damaging host tissues and by disabling the immune system. ...
, and inflammatory chemical signals). The increased transport of these harmful substances to the liver promotes liver inflammation, enhances nutrient and calorie absorption, and alters choline Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but r ...
metabolism. Higher levels of intestinal bacteria that produce butyrate
The conjugate acids are in :Carboxylic acids.
{{Commons category, Carboxylate ions, Carboxylate anions
Carbon compounds
Oxyanions ...
may be protective.
Excessive macronutrient intake contributes to gut inflammation and perturbation of homeostasis, and micronutrients may also be involved. In addition to reducing weight and risk factors, lifestyle changes may prompt positive changes in the gut microbiota. In particular, diet diversity may play a role that was overlooked in animal studies, since they often compare a Western high-fat, low-diversity diet against a low-fat but higher-diversity chow. The health benefits after bariatric surgery may also involve changes in the gut microbiota by increasing gut permeability.
Ballooning degeneration
In histopathology, ballooning degeneration, formally ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes, is a form of liver parenchymal cell (i.e. hepatocyte) death.
The name is derived from the fact that the cells undergoing this form of cell death incr ...
File:6_Nash_8_680x512px.tif, NASH (inflammation) and fibrosis stage 1
File:2_NASH_09_680x512px.tif, NASH (inflammation) and fibrosis stage 2
File:Lobular_necro-inflammation_--_high_mag.jpg, Lobular inflammation
Diagnosis
fatty liver
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complicat ...
without another factor that could explain the liver fat accumulation, such as excessive alcohol use (>21 standard drink
A standard drink is a measure of alcohol consumption representing a hypothetical beverage which contains a fixed amount of pure alcohol. A standard drink varies in volume depending on the alcohol concentration of the beverage (for example, a st ...
s/week for men and >14 for women in the USA; >30 g daily for men and >20 g for women in UK and EU, >140 g/week for men and >70 g/week for women in Asia-Pacific and most NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
clinical studies), drug-induced steatosis, chronic hepatitis C, heredity or by deficiencies in parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the feeding of nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by pharmaceutical compounding companies. The person receives a nutritional mi ...
such as choline Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but r ...
and endocrine conditions. If any of these factors are observed, an investigation into alternative causes of fatty liver unrelated to NAFLD is recommended. A history of chronic alcohol usage is an important consideration.
NAFLD comprises two histological categories: NAFL, and the more aggressive form NASH. The presence of at least 5% fatty liver
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complicat ...
is common to both NAFL and NASH, but the features of substantial lobular inflammation and hepatocyte injuries such as ballooning or Mallory hyaline only occur in NASH. The majority of NAFL cases show minimal or no inflammation. Pericentral and perisinusoidal fibrosis occur more often in adult-onset NASH, whereas portal fibrosis is more common in children with the disorder. NASH represents a more advanced stage of NAFL and is associated with poor outcomes such as cardiovascular events, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma. ICD-11 does not use the term NAFL as it was deemed confusing with the family of disorders NAFLD. The preferred descriptions are instead: NAFLD without NASH or simple steatosis and "NASH". Also, the modifier with or without fibrosis or cirrhosis completes the diagnostic description.
Blood tests
Elevatedliver enzyme
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin tim ...
s are common. According to National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE) guidelines, it is disadvised to test enzymes levels to rule out NAFLD, as they are often within the normal range even in advanced disease.
Blood tests that are useful to confirm diagnosis or rule out others include erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of ...
, glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
, albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins ...
, and kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Functions of a healthy kidney include maintaining a person's fluid ...
. Because the liver is important for making proteins used in blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanis ...
, coagulation-related studies are often carried out, especially the INR (international normalized ratio
The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the ''extrinsic'' pathway and common pathway of coagulation. This blood test is a ...
). In people with fatty liver with associated inflammatory injury (steatohepatitis) blood tests are usually used to rule out viral hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pa ...
(hepatitis A, B, C and herpesvirus
''Herpesviridae'' is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''ἕρπειν ...
es such as Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is b ...
or cytomegalovirus), rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
, and autoimmune diseases. Low thyroid activity is more prevalent in people with NASH, which would be detected by determining the thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of ...
. Some biomarker-based blood tests have been developed and may be useful for diagnosis.
Although blood tests cannot diagnose NAFLD, circulating serum biomarkers of liver fibrosis can give moderate estimates in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. The ratio of the transaminase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α- keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Function and mechanism
An amino acid ...
liver enzyme aspartate aminotransferase
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT, SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme () that was first described by Arthur ...
(AST) to platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
s in the blood, known as the AST/platelet ratio index (APRI score), and Fibrotest are recommended as the preferred noninvasive tests for cirrhosis by the Asian-Pacific Association for Study of the Liver (APASL). Several other scores such as FIB-4 score and NAFLD fibrosis score can also reflect the burden of the fibrosis in the liver, and previous studies have confirmed that these score can predict future development of mortality and liver cancer.
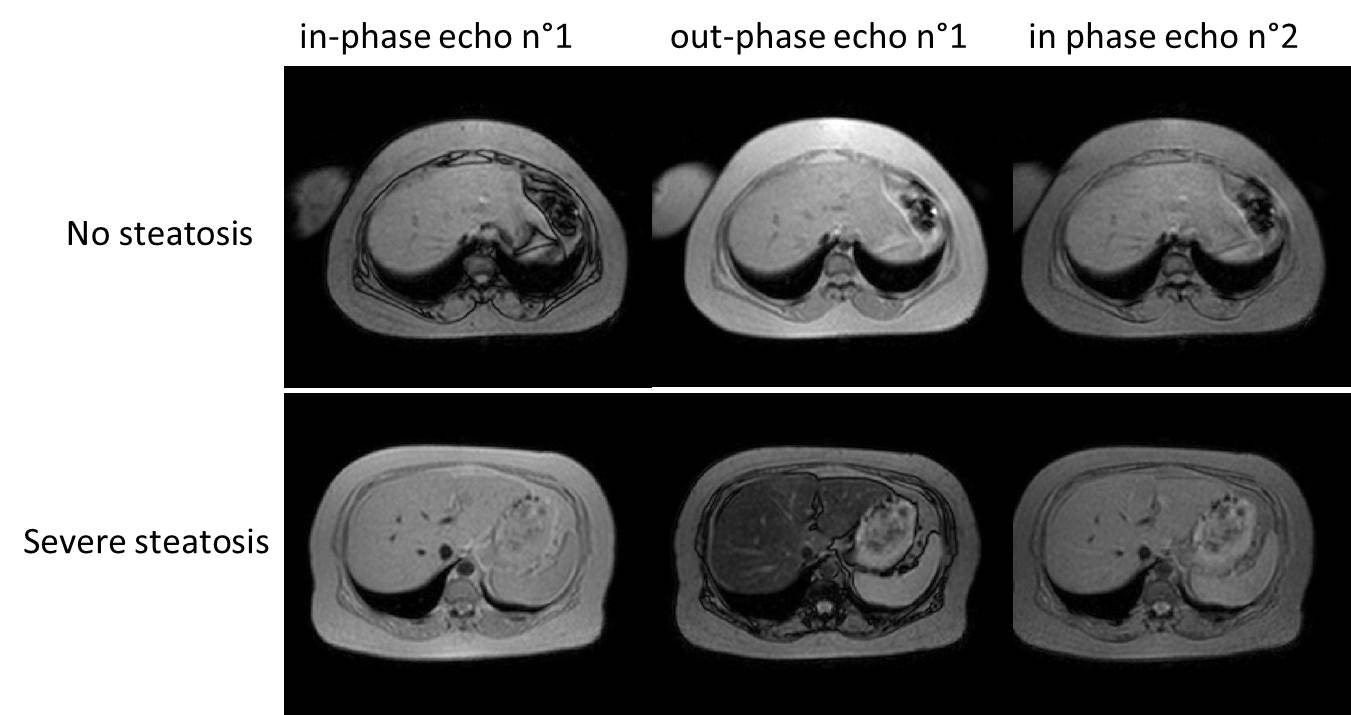
Imaging
 A liver
A liver ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
scan or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) can diagnose steatosis, but not fibrosis and confirmation of early cirrhosis detection by ultrasound by other diagnostic methods is recommended. The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) recommends screening for steatosis whenever NAFLD is suspected as this is a strong predictor of the disease evolution and predicts future type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular events, and hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
. These non-invasive methods can be used for NAFLD screening but are not accepted as a substitute for liver biopsy in NAFLD nor NASH clinical trials, as only a liver biopsy can define liver pathology.
Ultrasound presented average sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing the disease in children, while in the adult population, sensitivity and specificity were significantly higher. Proton density fat fraction magnetic resonance imaging has been increasingly used for the diagnosis of steatosis in pediatric patients. Elastography is an effective tool for staging liver fibrosis and discriminating NASH from NAFLD in children.
CT scans and MRIs are more accurate in detecting cirrhosis than conventional ultrasound. Transient elastography is recommended for the initial assessment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and helps to predict complications and prognosis, but the interpretation of results is carefully weighed in the presence of limiting factors, such as steatosis, high BMI, lower degrees of hepatic fibrosis and narrow spaces between the ribs (intercostal spaces). However, transient elastography can fail for people with pre-hepatic portal hypertension. Transient elastography is not considered to be a replacement for liver biopsy.
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is an emerging method that can accurately assess hepatic fibrosis and is recommended by the APASL. MRE possesses a good sensitivity to quantify hepatic fat and excellent accuracy to detect fibrosis in NAFLD regardless of BMI and inflammation and is suggested as a more reliable alternative to diagnose NAFLD and its progression to NASH compared to ultrasound and blood tests.
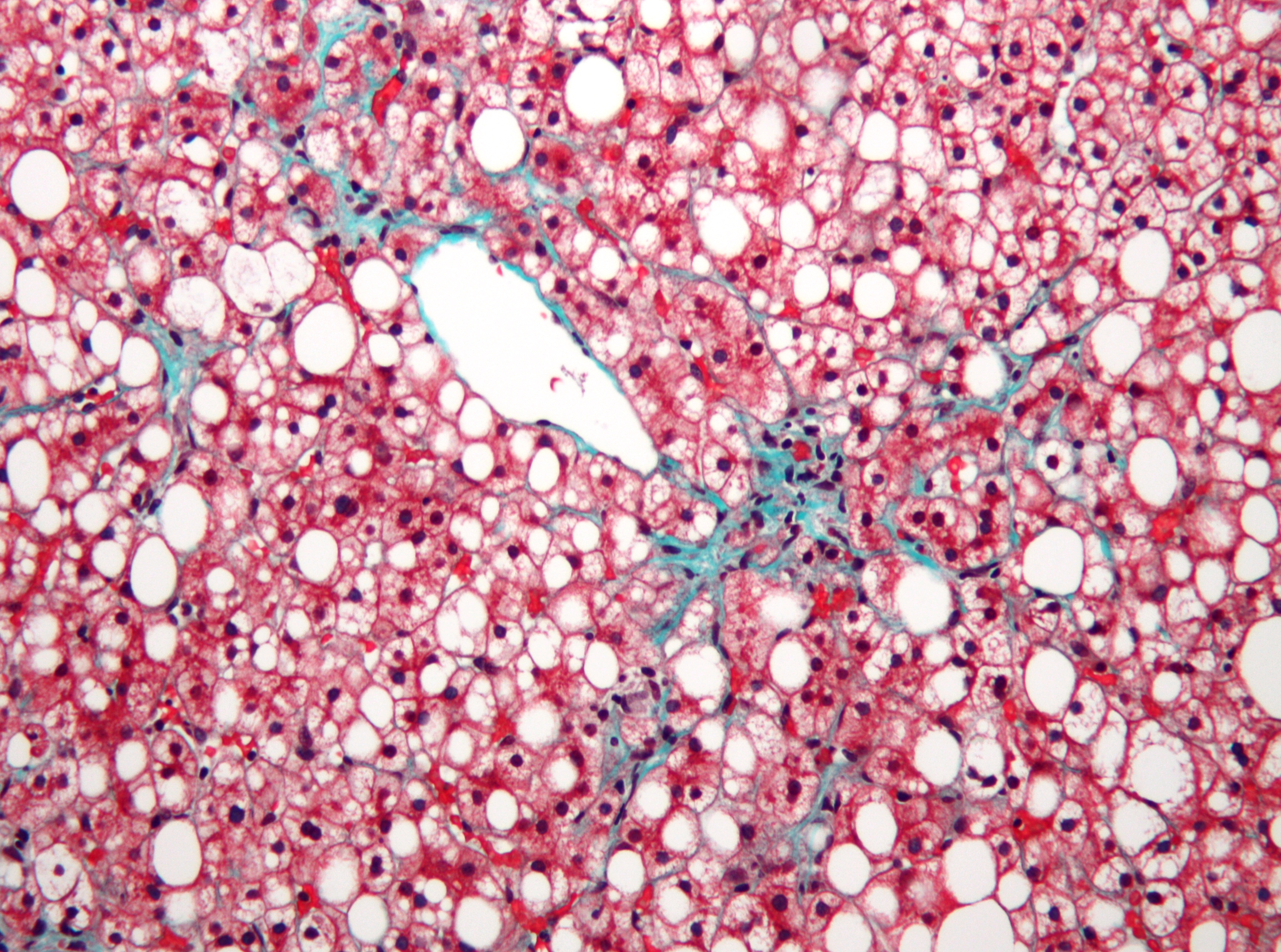
Liver biopsy

 A
A liver biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy (removal of a small sample of tissue) from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.
Medica ...
(tissue examination) is the only test widely accepted (gold standard) as definitively diagnosing and distinguishing NAFLD (including NAFL and NASH) from other forms of liver disease and can be used to assess the severity of the inflammation and resultant fibrosis. However, since most people affected by NAFLD are likely to be asymptomatic, liver biopsy presents too high a risk for routine diagnosis, so other methods are preferred, such as liver ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
or liver MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
. For young people, guidelines recommend liver ultrasonography, but biopsy remains the best evidence. Liver biopsy is also the gold standard to detect hepatic fibrosis and assess its progression. Routine liver function blood tests are not sensitive enough to detect NAFLD, and biopsy is the only procedure that can reliably differentiate NAFL from NASH.
There are several liver biopsy techniques available to obtain liver tissue. Percutaneous liver biopsy remains the most common practice. Biopsies can also be performed via the transvenous route, either during surgery or by laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medlin ...
, especially for people with contraindications to a percutaneous approach. The liver biopsy can also be image-guided, in real-time or not, which is recommended for some clinical situations such as people with known intra-hepatic lesions, previous intra-abdominal surgery who may have adhesions, a small liver that is difficult to percuss, obese people and people with evident ascites. Vital signs must be monitored frequently afterward (at least every 15 minutes in the hour following the biopsy).
According to AASLD guidelines, a liver biopsy may be considered in people with NAFLD who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis with or without advanced fibrosis, but only when all other competing chronic liver diseases are excluded (such as alcoholic liver disease). The presence of metabolic syndrome, NAFLD Fibrosis Score (FIB-4), or liver stiffness (as measured by Vibration-controlled transient elastography or MRE
A Meal, Ready-to-Eat (MRE) is a self-contained, individual field ration in lightweight packaging purchased by the United States Department of Defense for its service members for use in combat or field conditions where other food is not avail ...
) can identify the individuals who are at higher risk of steatohepatitis or advanced fibrosis.
The AASLD and ICD-11 consider that clinically useful pathology reporting distinguishes "between NAFL (steatosis), NAFL with inflammation and NASH (steatosis with lobular and portal inflammation and hepatocellular ballooning)" with the presence or absence of fibrosis being described and optionally comment on severity. The EASL recommends the Fatty Liver Inhibition of Progression (FLIP) algorithm to grade the ballooning and classify NAFLD-associated liver injury, and the use of the NAFLD Activity Score (NAS) to grade the severity of NASH rather than for its diagnosis. They also consider the steatosis, activity, and fibrosis (SAF) score to be an accurate and reproducible scoring system. The AASLD recommends the use of the NAS scoring system with or without the SAF score if deemed appropriate. The Asia-Pacific Working Group on NAFLD disadvises the use of NAS, as it is considered uninformative for NAFLD and inappropriate to diagnose NASH.
For liver fibrosis assessment, percutaneous liver biopsy, with or without image guidance, is contraindicated in uncooperative people. Transjugular liver biopsy is indicated for any person with diffuse liver disease who needs a biopsy but has a contraindication to percutaneous biopsy or needs a hemodynamic evaluation for diagnostic purposes. A transvenous liver biopsy is recommended instead of a percutaneous approach in people with clinically evident ascites, although percutaneous biopsy is an acceptable alternative approach after the removal of ascites.
Management
NAFLD warrants treatment regardless of whether the affected person is overweight or not. NAFLD is apreventable cause of death
Preventable causes of death are causes of death related to risk factors which could have been avoided. The World Health Organization has traditionally classified death according to the primary type of disease or injury. However, causes of death ...
. Guidelines are available from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) is a leading organization of scientists and health care professionals committed to preventing and curing liver disease. AASLD was founded in 1950 by a group of leading liver specialist ...
(AASLD), American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE), formerly known as the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, is a professional community of physicians specializing in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. AACE's missio ...
(AACE) National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE), the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), and the Asia-Pacific Working Party on NAFLD.
Lifestyle
Weight loss is the most effective treatment for NAFLD. A loss of 4% to 10% body weight is recommended, with 10% to 40% weight loss completely reversing NASH without cirrhosis. A structured weight loss program helps people with NAFLD lose more weight compared with advice alone. This type of program also leads to improvements in NAFLD measured using blood tests, ultrasound, imaging, or liver biopsies. Although fibrosis improves with lifestyle interventions and weight loss, there is limited evidence for cirrhosis improvement. A combination of improved diet and exercise, rather than either alone, appears to best help manage NAFLD and reduce insulin resistance. Motivational support, such as withcognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (suc ...
, is helpful, as most people with NAFLD do not perceive their condition as a disease, and thus have a low motivation to change.
Higher-intensity behavioral weight loss therapies (diet and exercise combined) may produce more weight loss than lower-intensity ones. Weight loss is associated with improvements in biomarkers, NAFLD grade, and reduced chances of NASH, but their impact on long-term health is yet unknown. A 2019 systematic review thus suggests a change of guidelines to recommend these therapies for NAFLD management.
As of 2021, there is limited evidence to indicate that lifestyle modifications and nutritional supplementation have an effect on mortality, liver cirrhosis, liver decompensation, liver transplantation, and hepatocellular carcinoma in people with nonalcohol-related fatty liver disease.
Diet
Treatment of NAFLD typically involves counseling to improve nutrition andcalorie restriction
Calorie restriction (caloric restriction or energy restriction) is a dietary regimen that reduces intake of energy from caloric foods & beverages without incurring malnutrition. "Reduce" can be defined relative to the subject's previous intake b ...
. People with NAFLD can benefit from a moderate to low-carbohydrate diet and a low-fat diet. The Mediterranean diet also showed promising results in a 6-week study with a reduction of NASH induced inflammation and fibrosis, independently from weight loss. Tentative evidence supports dietary interventions in individuals with fatty liver who are not overweight.
The EASL recommends energy restriction of 500–1000 kcal
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of o ...
per week less than the normal daily diet, a target of 7–10% weight loss for obese/overweight NAFLD, a low- to moderate-fat, and moderate- to high-carbohydrate diet, or a low-carbohydrate ketogenic or high-protein diet such as the Mediterranean diet, and avoiding all beverages and food containing fructose.
Alcohol is an aggravating factor, and the AASLD recommends that people with NAFLD or NASH avoid alcohol consumption. The EASL allows alcohol consumption below 30g/day for men and 20g/day for women. The role of coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
S ...
consumption for NAFLD treatment is unclear though some studies indicate that regular coffee consumption may have protective effects.
Herbal compounds such as silymarin
Silibinin ( INN), also known as silybin (both from ''Silybum'', the generic name of the plant from which it is extracted), is the major active constituent of silymarin, a standardized extract of the milk thistle seeds, containing a mixture of f ...
(a milk thistle
''Silybum marianum'' is a species of thistle. It has various common names including milk thistle, blessed milkthistle, Marian thistle, Mary thistle, Saint Mary's thistle, Mediterranean milk thistle, variegated thistle and Scotch thistle (thou ...
seed extract), curcumin, a turmeric extract, and green tea
Green tea is a type of tea that is made from '' Camellia sinensis'' leaves and buds that have not undergone the same withering and oxidation process which is used to make oolong teas and black teas. Green tea originated in China, and since the ...
appear to improve NAFLD biomarkers and reduce the grade of NAFLD. Studies suggest an association between microscopic organisms that inhabit the gut (microbiota) and NAFLD. Reviews reported the use of probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host i ...
s and synbiotics
Synbiotics refer to food ingredients or dietary supplements combining probiotics and prebiotics in a form of synergism, hence synbiotics. The synbiotic concept was first introduced as "mixtures of probiotics and prebiotics that beneficially affec ...
(combinations of probiotics and prebiotics
Prebiotics are compounds in food that induce the growth or activity of beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. The most common example is in the gastrointestinal tract, where prebiotics can alter the composition of organisms in the ...
) were associated with improvement in liver-specific markers of hepatic inflammation, measurements of liver stiffness, and steatosis in persons with NAFLD.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Vitamin E deficiency, which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vi ...
does not improve established liver fibrosis in those with NAFLD but seems to improve certain markers of liver function and reduces inflammation and fattiness of the liver in some people with NAFLD. The Asia-Pacific Work Group advises that Vitamin E may improve liver condition and aminotransferase levels, but only in adults without diabetes or cirrhosis who have NASH. The NICE guidelines recommend Vitamin E as an option for children and adults with NAFLD with advanced liver fibrosis, regardless of whether the person has diabetes mellitus.
Red Yeast Rice
The genum of moldAspergillus
' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide.
''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Miche ...
and/or Monascus
''Monascus'' is a genus of mold. Among the known species of this genus, the red-pigmented '' Monascus purpureus'' is among the most important because of its use in the production of certain fermented foods in East Asia, particularly China and ...
are used in the fabrication of Red yeast rice
Red yeast rice (), red rice ''koji'' (べにこうじ, lit. 'red ''koji), red fermented rice, red kojic rice, red ''koji'' rice, ''anka'', or ''angkak'', is a bright reddish purple fermented rice, which acquires its color from being cultivate ...
to stimulate the production of lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth.
...
, where lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth.
...
and other statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
s inhibit the total cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell mem ...
and LDL cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall dens ...
synthesis by blocking action of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase.
The safety of red yeast rice
Red yeast rice (), red rice ''koji'' (べにこうじ, lit. 'red ''koji), red fermented rice, red kojic rice, red ''koji'' rice, ''anka'', or ''angkak'', is a bright reddish purple fermented rice, which acquires its color from being cultivate ...
has not yet been established as studies found that some commercial supplements contain high levels of toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849– ...
citrinin.
There are reports in the literature of muscle myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. This results in muscular weakness. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease (Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meani ...
and liver damage resulting from red yeast rice usage.
Essential phospholipids
Research shows that essential phospholipids fromsoy lecithin
Lecithin (, from the Greek ''lekithos'' "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so a ...
(Latin: phospholipida sojae praeparata), polyenylphosphatidylcholine being the active component, has a well-established mode of action, therapeutic effectiveness, and lack of toxicity, which ensures clinically relevant efficacy-to-safety ratio. It influences membrane- dependent cellular functions and shows anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifibrogenic, anti apoptotic, membrane-protective, and lipid-regulating effects. Due to its positive effects on membrane composition and functions, it accelerates the improvement or normalization of subjective symptoms; pathological, clinical, and biochemical findings; hepatic imaging; and liver histology. It is justified to administer EPL together with other therapeutic measurements in the liver.
The usual dosage for adults and children older than 12 years of age (and of at least 43 kg of weight) is 600 mg three times a day.
Coffee
Allegedly seems to inverse and prevent fatty liver disease.Choline
Lowcholine Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but r ...
intake is significantly associated with the increased prevalence of NAFLD.
Physical activity
Weight loss may improve NAFLD and is recommended particularly for obese or overweight people; similar physical activities and diets are advisable for overweight people with NAFLD as for other obese and overweight people. Although physical activity is less important for weight loss than dietary adaptations (to reduce caloric intake), the NICE advises physical activity to reduce liver fat even if there is no overall bodyweight reduction. Weight loss, throughexercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
or diet, is the most effective way to reduce liver fat and help NASH and fibrosis remission. Exercise alone can prevent or reduce hepatic steatosis, but it remains unknown whether it can improve all other aspects of the liver; hence a combined approach with diet and exercise is advised. Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise (also known as endurance activities, cardio or cardio-respiratory exercise) is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, inv ...
may be more effective than resistance training, although there are contradictory results. Vigorous training is preferable to moderate training, as only the high-intensity exercise reduced the chances of NAFLD developing into NASH or advanced fibrosis. The EASL recommends between 150 and 200 min/week in 3 to 5 sessions of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or resistance training. Since both effectively reduce liver fat, a pragmatic approach to the choice of physical activity that accounts for the individual's preferences for what they can maintain in the long-term is preferred. Any engagement in physical activity or increase over previous levels is better than remaining sedentary.
Medication
Treatment with medications is primarily aimed at improving liver disease and is generally limited to those with biopsy-proven NASH and fibrosis. No medicines specifically for NAFLD or NASH had received approval, , althoughanti-diabetic medications
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists (liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thu ...
may help in liver fat loss. While many treatments appear to improve biochemical markers such as alanine transaminase
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme (). It is also called alanine aminotransferase (ALT or ALAT) and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) and was first characte ...
levels, most do not reverse histological
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
abnormalities or improve outcomes.
Insulin sensitizers (metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. ...
and thiazolidinedione
The thiazolidinediones , abbreviated as TZD, also known as glitazones after the prototypical drug ciglitazone, are a class of heterocyclic compounds consisting of a five-membered C3NS ring. The term usually refers to a family of drugs used i ...
s, such as pioglitazone
Pioglitazone, sold under the brand name Actos among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It may be used with metformin, a sulfonylurea, or insulin. Use is recommended together with exercise and diet. It is not re ...
) and liraglutide
Liraglutide, sold under the brand name Victoza among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, obesity, and chronic weight management. In diabetes it is a less preferred agent compared to metformin. Its effects on l ...
are not specifically recommended for NAFLD as they do not directly improve the liver condition. They can be indicated for diabetic individuals, after a careful assessment of risks, to reduce insulin resistance and risks of complications. Indeed, the side effects associated with thiazolidinedione medications, which include osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteop ...
, increased fracture risk, fluid retention, congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become mali ...
, and long-term weight gain, have limited their adoption. Due to these side effects, the AASLD recommends the use of pioglitazone only for individuals with biopsy-proven NASH, and the Asia-Pacific Work Group recommends them only for individuals with NAFLD with known diabetic issues. However, the AASLD advises against the use of metformin as studies were inconclusive about the improvement of the liver's histological condition. Although there was an improvement in insulin resistance and serum aminotransferases, this did not translate into NASH improvements. The NICE provides similar guidelines to the AASLD regarding pioglitazone and recommends it be administered in secondary care to adults with advanced liver fibrosis irrespective of whether or not they have diabetes.
Statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low ...
medications appear to improve liver histology and markers of liver biochemistry in people with NAFLD. Since people with NAFLD are at a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, statin treatment is indicated. People with NAFLD are not at higher risk for serious liver injury from statins, according to AASLD and EASL. However, even if statins are safe to use in people with NASH cirrhosis, the AASLD suggests avoiding them in people with decompensated cirrhosis. Guidelines recommend statins to treat dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia is an abnormal amount of lipids (e.g. triglycerides, cholesterol and/or fat phospholipids) in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease ( ASCVD). ASCVD includes coronary ar ...
for people with NAFLD. According to NICE guidelines, statins can continue unless liver enzyme levels double within three months of starting statins. Treatment with pentoxifylline is not recommended.
As of 2018, neither the AASLD nor the Asia-Pacific Working Group recommends obeticholic acid
Obeticholic acid (OCA), sold under the brand name Ocaliva, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a medication used to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Intercept ...
or elafibranor due to inconsistent results for NASH treatment and concerns about safety.
Omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chem ...
s may reduce liver fat and improve blood lipid profile but do not seem to improve liver histology (fibrosis, cirrhosis, cancer). The NICE does not recommend omega-3 fatty acid supplementation since randomized trials were inconclusive. Previous systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
s found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in those with NAFLD/NASH using doses of one gram daily or more (median dose four grams/day with median treatment duration six months) has been associated with improvements in liver fat. According to AASLD guidelines, "omega-3 fatty acids should not be used as a specific treatment of NAFLD or NASH, but they may be considered to treat hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and h ...
for patients with NAFLD".
Surgery
 Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD.
About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery.
A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a
Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD.
About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery.
A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a very-low-calorie diet
A very-low-calorie diet (VLCD), also known as semistarvation diet and crash diet, is a type of diet with very or extremely low daily food energy consumption. Often described as a fad diet, it is defined as a diet of per day or less. Modern medica ...
is usually recommended to reduce liver volume by 16–20%. Preoperative weight loss is the only factor associated with postoperative weight loss. Preoperative weight loss can reduce operative time and hospital stay, although there is insufficient evidence whether preoperative weight loss reduces long-term morbidity or complications. Weight loss and decreases in liver size may be independent of the amount of calorie restriction.
The APWG on NAFLD recommends bariatric surgery as a treatment option for those with class II obesity ( BMI >32.5 kg/m2 for Asians, 35 kg/m2 for Caucasians). They consider its effects on improving liver-related complications as unproven yet, but it effectively increases longevity by improving cardiovascular factors.
Surgery carries more risks for individuals with NASH cirrhosis, with a review estimating overall morbidity to be 21%. For people with NAFLD who have undifferentiated cirrhosis, the APWG recommends an investigation to determine the cause of the cirrhosis as well as the person's liver function and whether they have portal hypertension.
Screening
Cardiovascular system screening is considered mandatory by the EASL, as NAFLD outcomes often result in cardiovascular complications, which can manifest as subclinicalatherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usu ...
, the cause of the majority of NAFLD-related deaths. People with NAFLD are at high risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and "aggressive modification of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
risk factors is warranted in all patients with NAFLD," according to AASLD.
The AASLD further recommends for people with a cirrhotic NASH to be systematically screened for gastric
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and esophageal varices
Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop ...
and liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
. They do not recommend routine liver biopsies and screening for liver cancer for non-cirrhotic people with NASH, but such screening sometimes occurs on a case-by-case basis.
Also, people with NAFLD may be considered for screening for hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) and gastroesophageal varices. The NICE advises regular screening of NAFLD for advanced liver fibrosis every three years to adults and every two years for children using the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) blood test. Follow-up is recommended for people with obesity and insulin resistance using the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). People with NASH with fibrosis and hypertension merit closer monitoring as there is a higher risk of disease progression.
Transplantation
NAFLD is the second most common indication for liver transplantation in the US and Europe as of 2017. NAFLD/NASH is expected to become the leading cause of liver transplantation by 2020. For people with NASH and end-stage liver disease, liver failure, or liver cancer, liver transplantation is an accepted procedure according to the EASL. People with NASH cirrhosis NASH who are being considered for a liver transplant warrant systematic evaluation for cardiovascular diseases (whether the symptoms are apparent or not). The overall survival is comparable to transplantation following other diseases. People with NASH cirrhosis who undergo liver transplantation are more likely to die post-transplant because of cardiovascular disease or chronic kidney disease. These people with NASH are often older and are thus more prone to these complications. For these reasons and others, individuals with morbid obesity ( BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2) and NASH with cirrhosis may be considered unfit for liver transplantation until they follow lifestyle modifications to reduce bodyweight. Diabetic people with poor glycemic control are at similar risks, and optimal glycemic control is essential before attempting transplantation. The Asia Pacific Working Group guidelines recommend healthcare providers discuss lifestyle modifications before and after transplantation to reduce potential surgery risks and to assist with NAFLD management after the transplant. Simultaneous bariatric surgery and liver transplantation were performed in exceptional circumstances. After transplantation, liver biopsy is the best method to monitor the evolution of post-transplant fibrosis, with significant fibrosis or portal hypertension one year after transplantation predicting rapid progression and graft loss and indicating the need for urgent intervention.Related complications
There is no special treatment for liver cancer associated with NAFLD/NASH and are treated according to general guidelines on liver cancers.Prognosis
The average progression rate from one stage of liver fibrosis to the next in humans with NASH is estimated to be seven years, compared to 14 years with NAFLD. The course of progression varies with different clinical manifestations among individuals. Fibrosis in humans with NASH progressed more rapidly than in humans with NAFLD. Obesity predicts a worse long-term outcome than for lean individuals. In the Asia-Pacific region, about 25% of NAFLD cases progress to NASH under three years, but only a low proportion (3.7%) develop advanced liver fibrosis. An international study showed that people with NAFLD had a 10-year survival rate of 81.5%. NAFLD is a risk factor for fibrosis, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, ischemicstroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
, and death from cardiovascular causes based on very-low to low-quality evidence from observational studies. Although NAFLD can cause cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
and liver failure and liver cancer, most deaths among people with NAFLD are attributable to cardiovascular disease. According to a meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
of 34,000 people with NAFLD over seven years, these individuals have a 65% increased risk of developing fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular events when compared to those without NAFLD.
NAFLD and NASH increase the risk of liver cancer. Cirrhosis and liver cancer induced by NAFLD were the second cause of liver transplantation in the US in 2017. Liver cancer develops in NASH in the absence of cirrhosis in 45% in the cases, and people with NASH cirrhosis have an increased risk of liver cancer. The rate of liver cancer associated with NASH increased fourfold between 2002 and 2012 in the US, which is more than any other cause of liver cancer. NAFLD constitutes the third most common risk factor for liver cancer. NAFLD and NASH were found to worsen with cirrhosis in respectively 2–3% and 15–20% of the people over a 10–20 year period. Cirrhosis is found in only about 50% of people with NAFLD and with liver cancer, so that liver cancer and cirrhosis are not always linked.
NAFLD may be a precursor of metabolic syndrome, although a bidirectional influence is possible. The presence and stage of fibrosis are the strongest prognostic factors for liver-related events and mortality, in particular for NAFLD.
Epidemiology
diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, over 60%, and up to 20% for normal-weight people. NAFLD is present in 65% to 90% of people that had bariatric surgery, and up to 75% of them have NASH. Ultrasonography and proton NMR spectroscopy studies suggest about 25% of the population seems to be affected by NAFLD or NASH.
Although the disease is commonly associated with obesity, a significant proportion of those affected are normal weight or lean. Lean NAFLD affects between 10 and 20% of Americans and Europeans, and approximately 25% of the Asians, although some countries have a higher incidence (e.g., India has a very high proportion of lean NAFLD and almost no obese NAFLD). PNPLA3 may be relevant for the progression of NAFLD in lean people. Thus, people with NAFLD deserve consideration for treatment regardless of the presence or absence of obesity.
In children ages 1 to 19, the prevalence was found to be approximately 8% in the general population up to 34% in studies with data from child obesity clinics.
The majority of cryptogenic cirrhosis is believed to be due to NASH. NAFLD prevalence is expected to increase steadily, from 25% in 2018 to a projected 33.5% of people with NAFLD globally in 2030, and from 20% to a projected 27% of those with NAFLD will progress to NASH.
History
The first acknowledged case of obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver was observed in 1952 by Samuel Zelman. Zelman started investigating after observing a fatty liver in a hospital employee who drank more than twenty bottles of Coca-Cola a day. He then went on to design a trial for a year and a half on 20 obese people who were not alcoholic, finding that about half of them had substantially fatty livers. Fatty liver was, however, linked to diabetes since at least 1784 — an observation picked up again in the 1930s. Studies in experimental animals implicatedcholine Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but r ...
inadequacy in the 1920s and excess sugar consumption in 1949.
The name "non-alcoholic steatohepatitis" (NASH) was later defined in 1980 by Jurgen Ludwig and his colleagues from the Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, ...
to raise awareness of the existence of this pathology, as similar reports previously were dismissed as "patients' lies". This paper was mostly ignored at the time but eventually came to be seen as a landmark paper, and starting in the mid-1990s, the condition began to be intensively studied, with a series of international meetings being held on the topic since 1998. The broader NAFLD term started to be used around 2002. Diagnostic criteria began to be worked out, and in 2005 the Pathology Committee of the NIH NASH Clinical Research Network proposed the NAS scoring system.
Society and culture
Political recommendations
EASL recommends Europe's public health authorities to "restrict advertising and marketing of sugar-sweetened beverages and industrially processed foods high in saturated fat, sugar, and salt", as well as "fiscal measures to discourage the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and legislation to ensure that the food industry improves labeling and the composition of processed foods", as well as "public awareness campaigns on liver disease, highlighting that it is not only linked to excessive consumption of alcohol".Lobbying
In France, the French syndicate of non-alcoholic beverages "Boissons Rafraîchissantes de France" (that includedsoft drink
A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a drink that usually contains water (often carbonated), a sweetener, and a natural and/or artificial flavoring. The sweetener may be a sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice, a su ...
producers such as Coca-Cola France, Orangina, PepsiCo France) was denounced by the French journal '' :fr:Canard Enchainé'' for misleading consumers using a communication on their website titled "Better understanding the NASH pathology", explaining that "NASH pathology is sometimes called the soda illness by language abuse or an unfortunate semantic shortcut, as it is not directly linked to the consumption of non-alcoholic beverages". This page and others on the same website, such as one titled "Say no to disinformation," were since then removed.
Children
Pediatric NAFLD was first reported in 1983. It is the most common chronic liver disease among children and adolescents since at least 2007, affecting 10 to 20% of them in the US in 2016. NAFLD is associated withmetabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndrome ...
, which is a cluster of risk factors that contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Studies have demonstrated that abdominal obesity and insulin resistance, in particular, are significant contributors to the development of NAFLD. Coexisting liver diseases, such as hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
and cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, are also associated with an increased risk of NAFLD. Some children were diagnosed as early as two years old, with a mean age of diagnosis between 11 and 13 years old. The mean age is usually above 10 years, as children can also report non-specific symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
and are thus difficult to diagnose for NAFLD.
Boys are more likely to be diagnosed with NAFLD than girls. Overweight, or even weight gain, in childhood and adolescence, is associated with an increased risk of NAFLD later in life, with adult NAFLD predicted in a 31-year follow-up study by risk factors during childhood including BMI, plasma insulin levels, male sex, genetic background (PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 variants) and low birth weight, an emerging risk factor for adulthood NAFLD. In a study, simple steatosis was present in up to 45% in children with a clinical suspicion of NAFLD. Children with simple steatosis have a worse prognosis than adults, with significantly more of them progressing from NAFLD to NASH compared to adults. Indeed, 17-25% of children with NAFLD develop a NASH in general, and up to 83% for children with severe obesity (versus 29% for adults), further suggesting that hepatic fibrosis seems to follow a more aggressive clinical course in children compared to adults.
Early diagnosis of NAFLD in children may help prevent the development of liver disease during adulthood. This is challenging as most children with NAFLD are asymptomatic, with only 42-59% showing abdominal pain. Other symptoms might be present, such as right upper quadrant pain or acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a medical sign characterised by brown-to-black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is usually found in body folds, such as the posterior and lateral folds of the neck, the armpits, groin, navel, fore ...
, the latter of which is often present in children with NASH. An enlarged liver occurs in 30–40% of children with NAFLD.
The AASLD recommends a diagnostic liver biopsy in children when the diagnosis is unclear or before starting a potentially hepatotoxic medical therapy. The EASL suggests using fibrosis tests such as elastography
Elastography is any of a class of medical imaging modalities that map the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue.Sarvazyan A, Hall TJ, Urban MW, Fatemi M, Aglyamov SR, Garra BSOverview of elastography–an emerging branch of medical im ...
, acoustic radiation force impulse imaging
Elastography is any of a class of medical imaging modalities that map the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue.Sarvazyan A, Hall TJ, Urban MW, Fatemi M, Aglyamov SR, Garra BSOverview of elastography–an emerging branch of medical ...
, and serum biomarkers to reduce the number of biopsies. In follow up, NICE guidelines recommend that healthcare providers offer children regular NAFLD screening for advanced liver fibrosis every two years using the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) blood test. Several studies also suggest magnetic resonance elastography as an alternative to the less reliable ultrasonography.
Intensive lifestyle modifications, including physical activity and dietary changes, are the first line of treatment according to AASLD and EASL as it improves the liver histology and aminotransferase levels. In terms of pharmacological treatment, the AASLD and EASL do not recommend metformin, but vitamin E may improve liver health for some children. The NICE advises the use of vitamin E for children with advanced liver fibrosis, whether they have diabetes or not. The only treatment shown to be effective in childhood NAFLD is weight loss.
Some evidence indicates that maternal undernutrition or overnutrition increases a child's susceptibility to NASH and hastens its progression.
Research
Diagnosis and biomarkers
Since a NAFLD diagnosis based on a liver biopsy is invasive and makes it difficult to estimate epidemiology, it is a high research priority to find accurate, inexpensive, and noninvasive methods of diagnosing and monitoring NAFLD disease and its progression. The search for thesebiomarkers
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pa ...
of NAFLD, NAFL, and NASH involves lipidomics
Lipidomics is the large-scale study of pathways and networks of cellular lipids in biological systems The word " lipidome" is used to describe the complete lipid profile within a cell, tissue, organism, or ecosystem and is a subset of the "metabol ...
, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
, proteomics, blood tests, and scoring systems.
According to a review, proton density fat fraction estimation by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI-PDFF) may be considered the most accurate and even gold standard test to quantify hepatic steatosis. They recommend ultrasound-based transient elastography to accurately diagnose both fibrosis and cirrhosis in a routine clinical setting, with more objectivity than ultrasonography but with lower accuracy than magnetic resonance elastography; and plasma cytokeratin 18 (CK18) fragment levels to be a moderately accurate biomarker of steatohepatitis. However, transient elastography can fail for people with pre-hepatic portal hypertension.
Medication development
Medication development for NASH is very active and advancing rapidly. New medications are being designed to target various intrahepatic sites, from regulating lipids and glucose homeostasis to oxidant stress and mitochondrial targets in hepatocytes, inflammatory signals on hepatocytes, and intracellular targets related tohepatic stellate cell
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between th ...
activation and fibrogenesis. , pivotal trial A pivotal trial is typically a Phase III clinical trial in the multi-year process of clinical research intended to demonstrate and confirm the safety and efficacy of a treatment – such as a drug candidate, medical device or clinical diagnosti ...
s are underway for obeticholic acid
Obeticholic acid (OCA), sold under the brand name Ocaliva, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a medication used to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Intercept ...
( FXR agonist), Resmetirom ( THRβ agonist), belapectin (Galectin-3
Galectin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LGALS3'' gene. Galectin-3 is a member of the lectin family, of which 14 mammalian galectins have been identified.
Galectin-3 is approximately 30 kDa and, like all galectins, contains a ca ...
inhibitor), and Aramchol ( SCD1 inhibitor).
See also
*Foie gras
Foie gras (, ; ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a duck or goose. According to French law, foie gras is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by gavage (force feeding).
Foie gras is a popular and well-known delica ...
, fatty liver induced in poultry, with pathophysiology homologous to that of NAFLD in humans
References
External links
NIH
page on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Mayo Clinic
page on NAFLD {{Medical resources , DiseasesDB = 29786 , ICD10 = {{ICD10, K75.8, {{ICD10, K, 76, 0, k, 70 , ICD10CM = {{ICD10CM, K75.81, {{ICD10CM, K76.0 , ICD9 = {{ICD9, 571.8 , ICDO = , OMIM = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = med , eMedicineTopic = 775 Diseases of liver Hepatitis