|
Lipogenesis
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, with the latter being the process by which fatty acids are esterified to glycerol before being packaged into very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Fatty acids are produced in the cytoplasm of cells by repeatedly adding two-carbon units to acetyl-CoA. Triacylglycerol synthesis, on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue. Nevertheless, it also occurs to some extent in other tissues such as the gut and kidney. A review on lipogenes in the brain was published in 2008 by Lopez and Vidal-Puig. After being packaged into VLDL in the liver, the resulting lipoprotein is then secreted direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein 1
Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) also known as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SREBF1'' gene. This gene is located within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. The isoforms are SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c (the latter also called ADD-1). SREBP-1a is expressed in the intestine and spleen, whereas SREBP-1c is mainly expressed in liver, muscle, and fat (among other tissues). Expression The proteins encoded by this gene are transcription factors that bind to a sequence in the promoter of different genes, called sterol regulatory element-1 (SRE1). This element is a decamer (oligomer with ten subunits) flanking the LDL receptor gene and other genes involved in, for instance, sterol biosynthesis. The protein is synthesized as a precursor that is attached to the nuclear membrane and endoplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Synthesis
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine (by means of ester bonds) to form triglycerides (also known as "triacylglycerols" – to distinguish them from fatty "acids" – or simply as "fat"), the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed. Phospholipids form the bulk of the lipid bilayers that make up cell membranes and surrounds the organelles within the cells (such as the cell nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, etc.). Straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
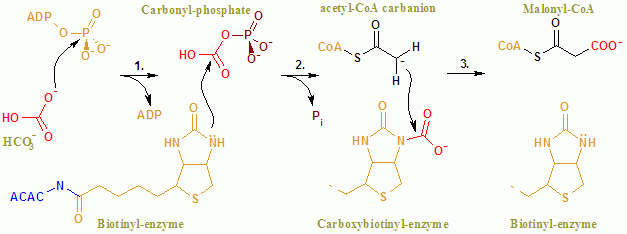
Malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Functions It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commits them to fatty acid chain synthesis. Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate,Nelson D, Cox M (2008) ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry''. 5th Ed: p. 806 requiring energy rendered from ATP. Malonyl-CoA is utilised in fatty acid biosynthesis by the enzyme malonyl coenzyme A:acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT). MCAT serves to transfer malonate from malonyl-CoA to the terminal thiol of ''holo''-acyl carrier protein (ACP). Polyketide biosynthesis MCAT is also involved in bacterial polyketide biosynthesis. The enzyme MCAT together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP), and a polyketide synthase (PKS) and chain-length f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
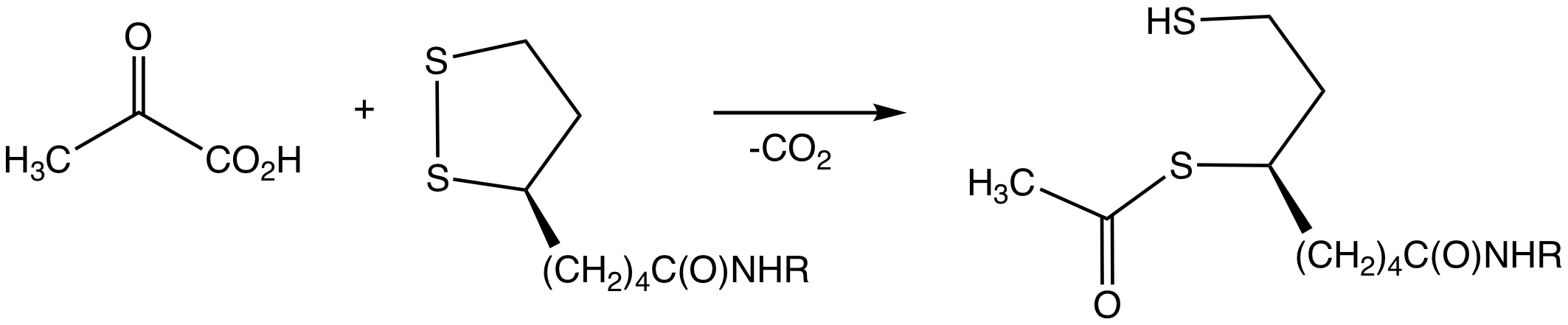
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme () that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotes. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—'' ACACA'' and ''ACACB''. Structure Prokaryotes and plants have multi-subunit ACCs composed of several polypeptides. Biotin carboxylase (BC) activity, biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP), and carboxyl transferase (CT) activity are each contained on a different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Théophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. Jöns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and named pyruvic acid because it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as E1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). PDC consists of other enzymes, referred to as E2 and E3. Collectively E1-E3 transform pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A into acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH. The conversion is crucial because acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration. To distinguish between this enzyme and the PDC, it is systematically called pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). Mechanism The thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) converts to an ylide by deprotonation. The ylide attack the ketone group of pyruvate. The resulting adduct decarboxylates. The resulting 1,3-dipole reductively acetylates lipoamide-E2. In terms of details, bioch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydration Synthesis
In chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction. Dehydration reactions in organic chemistry Esterification The classic example of a dehydration reaction is the Fischer esterification, which involves treating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to give an ester :RCO2H + R′OH RCO2R′ + H2O Often such reactions require the presence of a dehydrating agent, i.e. a substance that reacts with water. Etherification Two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, can be joined together (to form saccharose) using dehydration synthesis. The new molecule, consisting of two monosaccharides, is called a disaccharide. Nitrile formation Nitriles are often prepared by dehydration of primary amides. :RC(O)NH2 → RCN + H2O Ketene formation Ketene is produced by heating acetic acid and trapping the product: :CH3CO2H → CH2=C= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |