Constitutional provisions
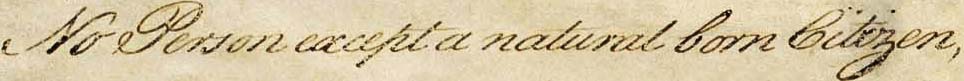 Section 1 of Article Two of the
Section 1 of Article Two of the History
Antecedents in Britain
The use of the term "natural born" was not without precedent. An early recorded example was in ''Commentaries on the Laws of England
Vol. 1, p. 363 (Oxford, The Clarendon Press 1765) by the
for the explaining the said recited Clause in the said Act . . . at all Children born out of the Ligeance of the Crown of England, or of Great Britain, or which shall hereafter be born out of such Ligeance, whose Fathers were or shall be natural-born Subjects of the Crown of England, or of Great Britain, at the Time of the Birth of such Children respectively ... are hereby declared to be natural-born Subjects of the Crown of Great Britain, to all Intents, Constructions and Purposes whatsoever.Another use is in the
"The Natural Born Citizen Clause as Originally Understood"
''
Commentaries on the Laws of England
', Vol. 1, p. 354 (Oxford, The Clarendon Press 1765). Blackstone added that offspring who are not inhabitants may also be natural born subjects: In 1775, however, Blackstone reversed his opinion and explained that the children "are now deemed to be natural-born subjects" rather than "are now natural-born subjects." Similarly, Francis Plowden initially explained that an early English statute made foreign-born children of English parents "in fact and law . . . true native subjects" and that the eighteenth-century British statutes made persons natural-born subjects by statute law just as others were natural-born subjects by the common law. However, after further consideration he also reversed his opinion and concluded in 1785 that the statutes did not make the children natural born subjects—rather, there remained a "relict of alienage in them." Prior to Blackstone,
Between 1776 and 1789
From theConstitutional Convention
The Constitution does not explain the meaning of "natural born". On June 18, 1787,Permit me to hint, whether it would not be wise and seasonable to provide a strong check to the admission of Foreigners into the administration of our national Government, and to declare expressly that the Command in chief of the American army shall not be given to, nor devolve on, any but a natural Citizen.While the
Constitutionality of the natural-born-citizen clause
In 2012, Abdul Karim Hassan filed several unsuccessful lawsuits that claimed the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment had superseded the natural-born-citizen clause; he had argued natural-born citizenship was a form of discrimination based on national origin.Proposed constitutional amendments
More than two dozen proposed constitutional amendments have been introduced in Congress to relax the restriction. Two of the more well known were introduced by RepresentativeRationale
St. George Tucker, an early federal judge, wrote in his 1803 edition of William Blackstone's ''Interpretations of the clause
Naturalization Acts of 1790 and 1795
Because of the large number ofInterpretations by the courts
1800s
Although eligibility for the Presidency was not an issue in any 19th-century litigation, there have been a few cases that shed light on the definitions of ''natural born'' and ''native born'' citizen. The leading case, ''Lynch v. Clarke'' of 1844, indicated that citizens born "within the dominions and allegiance of the United States" are citizens regardless of parental citizenship. This case dealt with a New York law (similar to laws of other states at that time) that only a U.S. citizen could inherit real estate. The plaintiff, Julia Lynch, had been born in New York while her parents, both British, were briefly visiting the U.S., and shortly thereafter all three left for Britain and never returned to the U.S. The New York Chancery Court determined that, under common law and prevailing statutes, she was a U.S. citizen by birth and nothing had deprived her of that citizenship, notwithstanding that both her parents were not U.S. citizens or that British law might also claim her through her parents'Suppose a person should be elected president who was native born, but of alien parents; could there be any reasonable doubt that he was eligible under the Constitution? I think not. The position would be decisive in his favor, that by the rule of the common law, in force when the Constitution was adopted, he is a citizen.And further:
Upon principle, therefore, I can entertain no doubt, but that by the law of the United States, every person born within the dominions and allegiance of the United States, whatever the situation of his parents, is a natural born citizen. It is surprising that there has been no judicial decision upon this question.The decision in ''Lynch'' was cited as persuasive or authoritative precedent in numerous subsequent cases, and reinforced the interpretation that "natural born citizen" meant born "within the dominions and allegiance of the United States" regardless of parental citizenship. For example, in an 1884 case, ''In re Look Tin Singg'', the federal court held, that despite laws preventing naturalization of Chinese visitors, Chinese persons born in the United States were citizens by birth, and remained such despite any long stay in China. Citing ''Lynch'', Justice
After an exhaustive examination of the law, the Vice-Chancellor said that he entertained no doubt that every person born within the dominions and allegiance of the United States, whatever the situation of his parents, was a natural-born citizen, and added that this was the general understanding of the legal profession, and the universal impression of the public mind.Supreme Court Justice Peter Vivian Daniel in a concurring opinion in the 1857 case ''
"The Constitution does not, in words, say who shall be natural-born citizens. Resort must be had elsewhere to ascertain that. At common-law, with the nomenclature of which the framers of the Constitution were familiar, it was never doubted that all children born in a country of parents who were its citizens became themselves, upon their birth, citizens also. These were natives, or natural-born citizens, as distinguished from aliens or foreigners. Some authorities go further and include as citizens children born within the jurisdiction without reference to the citizenship of their parents. As to this class there have been doubts, but never as to the first."The U.S. Supreme Court decision in ''
1900s
Consistent with the earlier decisions, in 1939, the U.S. Supreme Court stated in its decision in '' Perkins v. Elg'' that a person born in the United States and raised in another country was a natural born citizen, and specifically stated that they could "become President of the United States". The case was regarding a young woman, born in New York a year after her father became a naturalized U.S. citizen. However, when she was about four her parents returned to Sweden taking her with them, and they stayed in Sweden. At age 20, she contacted the US-American embassy in Sweden and, shortly after her 21st birthday, returned to the United States on a U.S. passport and was admitted as a U.S. citizen. Years later, while she was still in the United States, her father in Sweden relinquished his United States citizenship, and, because of that, the Department of Labor (then the location of the2000s
More recent cases, particularly '' Nguyen v. INS'' and ''Robinson v. Bowen'', suggested that the Fourteenth Amendment merely establishes a "floor" for birthright citizenship, and this category may be expanded by Congress. In 2009 in ''Ankeny v. Governor'', the Indiana Court of Appeals reaffirmed that persons born within the borders of the United States are "natural born Citizens", regardless of the citizenship of their parents. The court referred to the case of Wong Kim Ark, and provides a compilation of the arguments pertaining to this topic. A clarification to this interpretation was made in 2010, where aGovernment officials' interpretations
1800s
John Armor Bingham, the American lawyer and politician who framed the 14th Amendment, held to the belief that natural born should be interpreted as born in the United States. In 1862, during theThe Constitution leaves no room for doubt upon this subject. The words "natural born citizen of the United States" appear in it, and the other provision appears in it that, "Congress shall have power to pass a uniform system of naturalization." To naturalize a person is to admit him to citizenship. Who are ''natural born citizens'' but those born within the Republic? Those born within the Republic, whether black or white, are citizens by birth—natural born citizens.He expanded his statement four years later on 9 March 1866, emphasizing twice that this required a man born to "parents not owing allegiance to any foreign sovereignty" so he would be "not owing a foreign allegiance".
I find no fault with the introductory clause, which is simply declaratory of what is written in the Constitution, that every human being born within the jurisdiction of the United States of parents not owing allegiance to any foreign sovereignty is, in the language of your Constitution itself, a natural-born citizen; but, sir, I may be allowed to say further that I deny that the Congress of the United States ever had the power, or color of power to say that any man born within the jurisdiction of the United States, not owing a foreign allegiance, is not and shall not be a citizen of the United States. Citizenship is his birthright and neither the Congress nor the States can justly or lawfully take it from him.After the passage of the amendment on 9 July 1868, Bingham made reference to his previous statements again in the 42nd United States Congress of 1872, during a House debate.
I conclude that the ''free man of color'', mentioned in your letter, if born in the ''United States'', is a citizen of the United States. talics in original/blockquote> In the course of that opinion, Bates commented at some length on the nature ofcitizenship Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection". Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ..., and wrote,... our constitution, in speaking of ''natural born citizens'', uses no affirmative language to make them such, but only recognizes and reaffirms the universal principle, common to all nations, and as old as political society, that the people born in a country do constitute the nation, and, as individuals, are ''natural'' members of the body politic. talics in original/blockquote> In another opinion, dated September 1, 1862, Bates dealt with a question from the Secretary of State, of whether a person born in the U.S. to two non-citizens, who is taken with them back to their country, could, years later, re-enter the United States as of right, as a U.S. citizen. Bates wrote:I am quite clear in the opinion that children born in the United States of alien parents, who have never been naturalized, are native-born citizens of the United States, and, of course, do not require the formality of naturalization to entitle them to the rights and privileges of such citizenship. I might sustain this opinion by a reference to the well-settled principle of the common law of England on this subject; to the writings of many of the earlier and later commentators on our Constitution and laws; ... and lastly to the dicta and decisions of many of our national and state tribunals. But all this has been well done by Assistant Vice Chancellor Sandford, in the case of ''Lynch vs. Clarke'', and I forbear. I refer to his opinion for a full and clear statement of the principle, and of the reasons and authorities for its support.Unlike Edward Bates, U.S. Secretary of State William Learned Marcy was equivocal about whether those born in the country of alien parents and who reside elsewhere are still considered citizens. In 1854 Marcy wrote John Y. Mason, the U.S. Minister to France:In reply to the inquiry ... whether "the children of foreign parents ''born in the United States'', but brought to the country of which the father is a subject, and continuing to reside within the jurisdiction of their father's country, are entitled to protection as citizens of the United States", I have to observe that it is presumed that, according to the common law, any person born in the United States, unless he be born in one of the foreign legations therein, may be considered a citizen thereof until he formally renounces his citizenship. There is not, however any United States statute containing a provision upon this subject, nor, so far as I am aware, has there been any judicial decision in regard to it.U.S. Attorney GeneralEdwards Pierrepont Edwards Pierrepont (March 4, 1817 – March 6, 1892) was an American attorney, reformer, jurist, traveler, New York U.S. Attorney, U.S. Attorney General, U.S. Minister to England, and orator.''West's Encyclopedia of American Law'' (2005), "Pierre ..., however, shared Edward Bates' opinion that those born in the country of alien parents and who reside elsewhere are still considered citizens, and he added that they should be entitled to be president of the United States, if elected. In 1875 Pierrepont was presented with a query from the Secretary of State,Hamilton Fish Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American politician who served as the 16th Governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States Senator from New York from 1851 to 1857 and the 26th United States Secretary of State .... A young man, named Arthur Steinkauler, had been born in Missouri in 1855, a year after his father was naturalized a U.S. citizen. When he was four years old, his father returned to Germany with him and both had stayed there ever since. The father had relinquished his U.S. citizenship and the young man was now 20 years old and about to be drafted into the Imperial German army. The question was asked "What was this young man's situation as a native-born American citizen?" After studying the relevant legal authorities, Pierrepont wrote:Under the treaty f 1868 with Germany and in harmony with American doctrine, it is clear that Steinkauler the father abandoned his naturalization in America and became a German subject (his son being yet a minor), and that by virtue of German laws the son acquired German nationality. It is equally clear that the son, by birth, has American nationality, and hence he has two nationalities, one natural, the other acquired ... Young Steinkauler is a native-born American citizen. There is no law of the United States under which his father or any other person can deprive him of his birthright. He can return to America at the age of 21, and in due time, if the people elect, he can become President of the United States. ... I am of opinion that when he reaches the age of 21 years he can then elect whether he will return and take the nationality of his birth, with its duties and privileges, or retain the nationality acquired by the act of his father.
1900s
Frederick van Dyne, the Assistant Solicitor of the U.S. Department of State (1900–1907) indicated that children of citizens born outside the United States are also considered citizens. In 1904, he published a textbook, ''Citizenship of the United States'', in which he wrote:There is no uniform rule of international law covering the subject of citizenship. Every nation determines for itself who shall, and who shall not, be its citizens. ... By the law of the United States, citizenship depends, generally, on the place of birth; nevertheless the children of citizens, born out of the jurisdiction of the United States, are also citizens. ... The Constitution of the United States, while it recognized citizenship of the United States in prescribing the qualifications of the President, Senators, and Representatives, contained no definition of citizenship until the adoption of the 14th Amendment, in 1868; nor did Congress attempt to define it until the passage of the civil rights act, in 1866. ... Prior to this time the subject of citizenship by birth was generally held to be regulated by the common law, by which all persons born within the limits and allegiance of the United States were deemed natural-born citizens. It appears to have been assumed by the Supreme Court of the United States in the case of ''Murray v. The Charming Betsy'' (1804) 2 Cranch (6 U.S.) 64, 119, 2 L.Ed. 208, 226, that all persons born in the United States were citizens thereof. ... In ''M'Creery v. Somerville'' (1824) 9 Wheat. (22 U.S.) 354, 6 L.Ed. 109, which concerned the title to land in the state of Maryland, it was assumed that children born in that state to an alien were native-born citizens of the United States. ... The Federal courts have almost uniformly held that birth in the United States, of itself, confers citizenship.
Academic interpretations
1800s
William Rawle William Rawle (April 28, 1759 – April 12, 1836) was an American lawyer in Philadelphia, who in 1791 was appointed as United States district attorney in Pennsylvania. He was a founder and first president of the Historical Society of Pennsylvani ..., formerly the U.S. Attorney for Pennsylvania (1791–1799) defined ''natural born citizen'' as every person born within the United States, regardless of the citizenship of their parents. In an 1825 treatise, ''A View of the Constitution of the United States of America'', he wrote:The citizens of each state constituted the citizens of the United States when the Constitution was adopted. ... ewho was subsequently born the citizen of a State, became at the moment of his birth a citizen of the United States. Therefore every person born within the United States, its territories or districts, whether the parents are citizens or aliens, is a natural born citizen in the sense of the Constitution, and entitled to all the rights and privileges appertaining to that capacity. ... Under our Constitution the question is settled by its express language, and when we are informed ... no person is eligible to the office of President unless he is a natural born citizen, the principle that the place of birth creates the relative quality is established as to us.James F. Wilson agreed with Rawle's opinion, but added the exclusion of visiting foreign diplomats. During an 1866 House debate, he quoted Rawle's opinion, and also referred to the "general law relating to subjects and citizens recognized by all nations", saying:... and that must lead us to the conclusion that every person born in the United States is a natural-born citizen of such States, except it may be that children born on our soil to temporary sojourners or representatives of foreign Governments, are native-born citizens of the United States.Joseph Story Joseph Story (September 18, 1779 – September 10, 1845) was an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, serving from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin v. Hunter's Lessee'' and ''United States ..., an Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court 1812-1845, said that the term ''native citizen'' is synonymous with natural born citizen, though he does not define either term. Twice (1834 in "Constitutional Class Book" then 1840 in "Familiar Exposion of the Constitution") he wrote:
1900s
Alexander Porter Morse, the lawyer who represented Louisiana in ''Plessy v. Ferguson ''Plessy v. Ferguson'', 163 U.S. 537 (1896), was a landmark U.S. Supreme Court decision in which the Court ruled that racial segregation laws did not violate the U.S. Constitution as long as the facilities for each race were equal in qualit ...'', considered this connection between ''native born'' and ''natural born'' to signify that only a child of citizens should be allowed to run for president. In the ''Albany Law Journal'', he wrote:If it was intended that anybody who was a citizen by birth should be eligible, it would only have been necessary to say, "no person, except a native-born citizen"; but the framers thought it wise, in view of the probable influx of European immigration, to provide that the president should at least be the child of citizens owing allegiance to the United States at the time of his birth. It may be observed in passing that the current phrase "native-born citizen" is well understood; but it isThe 2nd Edition of ''pleonasm Pleonasm (; , ) is redundancy in linguistic expression, such as "black darkness" or "burning fire". It is a manifestation of tautology by traditional rhetorical criteria and might be considered a fault of style. Pleonasm may also be used for em ...and should be discarded; and the correct designation, "native citizen" should be substituted in all constitutional and statutory enactments, in judicial decisions and in legal discussions where accuracy and precise language are essential to intelligent discussion.Black Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...'sLaw Dictionary A law dictionary (also known as legal dictionary) is a dictionary that is designed and compiled to give information about terms used in the field of law. Types Distinctions are made among various types of law dictionaries. Differentiating facto ...'' in 1910 defined "native" as a "natural-born subject or citizen ; a denizen by birth ; one who owes his domicile or citizenship to the fact of his birth within the country referred to. The term may also include one born abroad, if his parents were then citizens of the country, and not permanently residing in foreign parts."
2000s
The 9th Edition of Black's Law Dictionary, published in 2009, defined "Natural Born Citizen" as "A person born within the jurisdiction of a national government".
=Foreign soil and territories
= In 2000, theCongressional Research Service The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a c ...(CRS), in one of its reports, wrote that most constitutional scholars interpret the natural-born-citizen clause to include citizens born outside the United States to parents who are U.S. citizens. This same CRS report also asserts that citizens born in theDistrict of Columbia ) , image_skyline = , image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...,Guam Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...,Puerto Rico Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ..., and the U.S. Virgin Islands, are legally defined as "natural born" citizens and are, therefore, also eligible to be elected president. This opinion was reaffirmed in a 2009 CRS report, which stated:Considering the history of the constitutional qualifications provision, the common use and meaning of the phrase "natural-born subject" in England and in the Colonies in the 1700s, the clause's apparent intent, the subsequent action of the first Congress in enacting theThe interpretation of natural born being the equivalent of a citizen at birth was repeated in a 2011 CRS report and a 2016 CRS report. The 2011 report stated:Naturalization Act of 1790 The Naturalization Act of 1790 (, enacted March 26, 1790) was a law of the United States Congress that set the first uniform rules for the granting of United States citizenship by naturalization. The law limited naturalization to "free White ...(expressly defining the term "natural born citizen" to include a person born abroad to parents who are United States citizens), as well as subsequent Supreme Court dicta, it appears that the most logical inferences would indicate that the phrase "natural born Citizen" would mean a person who is entitled to U.S. citizenship "at birth" or "by birth".The weight of legal and historical authority indicates that the term "natural born" citizen would mean a person who is entitled to U.S. citizenship "by birth" or "at birth," either by being born "in" the United States and under its jurisdiction, even those born to alien parents; by being born abroad to U.S. citizen-parents; or by being born in other situations meeting legal requirements for U.S. citizenship "at birth". Such term, however, would not include a person who was not a U.S. citizen by birth or at birth, and who was thus born an "alien" required to go through the legal process of "naturalization" to become a U.S. citizen.The 2016 report similarly stated:Although the eligibility of U.S. born citizens has been settled law for more than a century, there have been legitimate legal issues raised concerning those born ''outside'' of the country to U.S. citizens. From historical material and case law, it appears that the common understanding of the term "natural born" in England and in the American colonies in the 1700s included both the strict common law meaning as born in the territory (''jus soli''), as well as the ''statutory'' laws adopted in England since at least 1350, which included children born abroad to British fathers (''jus sanguinis'', the law of descent). Legal scholars in the field of citizenship have asserted that this common understanding and legal meaning in England and in the American colonies was incorporated into the usage and intent of the term in the U.S. Constitution to include those who are citizens at birth.Gabriel J. Chin Gabriel Jack Chin is an author, legal scholar, and Professor at the University of California, Davis School of Law. He teaches a variety of courses, including Criminal Law, Immigration, Criminal Appellate Advocacy, and Race and Law. In the news ..., Professor of Law atUC Davis School of Law The University of California, Davis School of Law (Martin Luther King Jr. Hall), referred to as UC Davis School of Law and commonly known as King Hall, is the professional graduate law school of the University of California, Davis. The school rec ..., held the opinion that the term "natural born" is ambiguous and citizenship-granting authority has changed over the years. He notes that persons born outside the United States to U.S.-citizen parents have not always been born citizens. For example, foreign-born children of persons who became citizens between April 14, 1802 and 1854 were aliens. He also believed that children born in the Panama Canal Zone to at least one U.S. then-citizen before August 4, 1937, when Congress granted citizenship to all such persons, were born without American citizenship. In 2009, G. Edward "Ted" White, Professor of Law at theUniversity of Virginia The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United S ..., stated the term refers to anyone born on U.S. soil ''or'' anyone born on foreign soil to American citizen parents. Unlike Chin and White, Mary McManamon, Professor of Law atWidener University School of Law Widener University Delaware Law School (Delaware Law School and formerly Widener University School of Law) is a private law school in Wilmington, Delaware. It is one of two separate ABA-accredited law schools of Widener University. Widener Un ..., has argued in the ''Catholic University Law Review'' that, aside from children born to foreign ambassadors or to hostile soldiers on U.S. territory, both of whom owe allegiance to a different sovereign, a natural born citizen must be born in the United States. She claims thatcommon law In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...provides an exception for the children of U.S. ambassadors born abroad and the children of American soldiers while engaged in hostilities. Thus, with these two limited exceptions, she equates "natural born" with "native born".McManamon, Mary (2015)
"The Natural Born Citizens Clause as Originally Understood"
64 Catholic University Law Review 317 Professor Einer Elhauge ofHarvard Law School Harvard Law School (Harvard Law or HLS) is the law school of Harvard University, a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest continuously operating law school in the United States. Each class ...agrees with Professor McManamon that "natural born" means "native born" and therefore the wording of the Constitution "does not permit his candidacy," referring to a candidate who was born inCanada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...to one U.S. citizen parent. Professor Robert Clinton at theSandra Day O'Connor College of Law The Sandra Day O'Connor College of Law (ASU Law) is one of the professional graduate schools at Arizona State University in Phoenix, Arizona. The school is located in the Beus Center for Law and Society on ASU's downtown Phoenix campus. The law ...atArizona State University Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public research university in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, ASU is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the ...is also of the opinion that "natural born citizen" means "born in the United States."University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...ProfessorEric Posner Eric Andrew Posner (; born December 5, 1965) is an American lawyer and legal scholar who has served as a counsel for the Department of Justice Antitrust Division since 2022. As a law professor at the University of Chicago Law School, Posner has ...also concludes that "natural born citizen" means a "person born in the (United States)". Former Chief Justice of the New York Court of Appeals, Sol Wachtler, concludes the same. Their conclusion is consistent with the position that the eighteenth century legal usage of the term "shall be considered as natural born" in theNaturalization Act of 1790 The Naturalization Act of 1790 (, enacted March 26, 1790) was a law of the United States Congress that set the first uniform rules for the granting of United States citizenship by naturalization. The law limited naturalization to "free White ...merely naturalized persons or granted them limited rights of the natural born. Joseph Dellapenna, retired Professor of Law atVillanova University Villanova University is a Private university, private Catholic church, Roman Catholic research university in Villanova, Pennsylvania. It was founded by the Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinians in 1842 and named after Thomas of Villanova, Sa ..., also considers "natural born" to encompass only persons born in the United States; argues that foreign-born children of U.S. citizens are naturalized at birth, but not natural born; and on this basis rejects the presidential eligibility of both Ted Cruz and John McCain. Citing ''Rogers v. Bellei ''Rogers v. Bellei'', 401 U.S. 815 (1971), was a decision by the United States Supreme Court, which held that an individual who received an automatic congressional grant of citizenship at birth, but who was born outside the United States, may lose ...'' in support of this interpretation, Dellapenna asserts that "Without addressing this judicial holding, any conclusion that 'natural born citizen' includes any person who becomes a citizen at birth is insupportable."Dellapenna, Joseph W
"Constitutional Citizenship under Attack"
61 Villanova Law Review 477, 506 (2016).
=American soil
= There is consensus among academics that those born on American soil, except children born to foreign ambassadors or to hostile soldiers on U.S. territory, both of whom owe allegiance to a different sovereign, are natural born citizens, or ''jus soli ''Jus soli'' ( , , ; meaning "right of soil"), commonly referred to as birthright citizenship, is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship. ''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contras ...'', regardless of parental citizenship status. In a 2008 article published by the ''Michigan Law Review'', Lawrence Solum, Professor of Law at the University of Illinois, stated that "there is general agreement on the core of hemeaningf the Presidential Eligibility Clause F, or f, is the sixth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Let ...Anyone born on American soil whose parents are citizens of the United States is a 'natural born citizen. In April 2010, Solum republished the same article as an online draft, in which he clarified his original statement so that it would not be misunderstood as excluding the children of one citizen parent. In a footnote he explained, "based on my reading of the historical sources, there is no credible case that a person born on American soil with one American parent was clearly not a 'natural born citizen'." He further extended natural born citizenship to all cases of ''jus soli ''Jus soli'' ( , , ; meaning "right of soil"), commonly referred to as birthright citizenship, is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship. ''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contras ...'' as the "conventional view". Although Solum stated elsewhere that the two-citizen-parents arguments were not "crazy", he believes "the much stronger argument suggests that if you were born on American soil that you would be considered a natural born citizen".Ronald Rotunda Ronald D. Rotunda (February 14, 1945 – March 14, 2018) was an American legal scholar and professor of law at Chapman University School of Law. Rotunda's first area of primary expertise is United States Constitutional law, and is the author of a ..., Professor of Law at Chapman University, has remarked "There's 'sic''some people who say that both parents need to be citizens. That's never been the law." Polly Price, Professor of Law at Emory University, has commented "It's a little confusing, but most scholars think it's a pretty unusual position for anyone to think the natural born citizen clause would exclude someone born in the U.S." Chin concurred with that assessment, stating, "there is agreement that 'natural born citizens' include those made citizens by birth under the 14th Amendment." Similarly,Eugene Volokh Eugene Volokh (; born February 29, 1968 as Yevhen Volodymyrovych Volokh ( uk, Євге́н Володимирович Волох)) is an American legal scholar known for his scholarship in American constitutional law and libertarianism as well as ..., Professor of Law at UCLA, found "quite persuasive" the reasoning employed by theIndiana Court of Appeals The Indiana Court of Appeals is the intermediate-level appellate court for the state of Indiana. It is the successor to the Indiana Appellate Court. History The Indiana Appellate Court was created by the Indiana General Assembly by statute in 1 ..., which had concluded "that persons born within the borders of the United States are 'natural born Citizens' for Article II, Section 1 purposes, regardless of the citizenship of their parents". Daniel Tokaji, Professor of Law at Ohio State University, agrees the citizenship status of a U.S.-born candidate's parents is irrelevant.
=Implied repeal of the natural-born citizen clause
= In a 2006 John Marshall Law Review article, Paul A. Clark argues that the Fifth Amendment should be read as implicitly repealing the requirement that the U.S. President needs to be a natural-born U.S. citizen. Clark points out that, starting from the 1954 caseBolling v. Sharpe ''Bolling v. Sharpe'', 347 U.S. 497 (1954), is a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court Legal case, case in which the Court held that the Constitution proh ..., courts have held that the Fifth Amendment contains an implicit equal protection clause whose scope is identical to the Fourteenth Amendment's equal protection clause and that federal discrimination against naturalized U.S. citizens (or, more specifically, federal discrimination based on national origin) would be struck down by the courts as being in violation of the Fifth Amendment. Since the requirement that the U.S. President needs to be a natural-born U.S. citizen is a form of discrimination based onnational origin National origin is the nation where a person was born, or where that person's ancestors came from. It also includes the diaspora of multi-ethnic states and societies that have a shared sense of common identity identical to that of a nation while ..., Clark argues that thecourts A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance ...should strike down this requirement. So far, Clark's argument in regards to this has not attracted wide support among the U.S. legal academy (though ProfessorJosh Blackman Joshua Michael Blackman is an American lawyer who is employed as an associate professor of law at the South Texas College of Law where he focuses on constitutional law and the intersection of law and technology. He has authored one book and co-au ...asked a question about a similar topic in 2015—specifically about the Fourteenth Amendment nullifying the natural-born citizen clause).United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...law professor A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyses and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal qualification in law and often a legal practitioner. In the Uni ...Laurence Tribe Laurence Henry Tribe (born October 10, 1941) is an American legal scholar who is a University Professor Emeritus at Harvard University. He previously served as the Carl M. Loeb University Professor at Harvard Law School. A constitutional law sc ...has made a similar argument in a September 2016 article of his, but using the 14th Amendment instead of the Fifth Amendment. Specifically, Tribe argues that theU.S. Congress The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...should use the 14th Amendment's Enforcement Clause to pass astatute A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by le ...that would allow naturalized U.S. citizens to run for and to become U.S. President. Tribe argues that while theconstitutionality Constitutionality is said to be the condition of acting in accordance with an applicable constitution; "Webster On Line" the status of a law, a procedure, or an act's accordance with the laws or set forth in the applicable constitution. When l ...of such a Congressional statute would not be ''easy'' to defend, such a statute would at least be consistent with the spirit of theReconstruction Amendments The , or the , are the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth amendments to the United States Constitution, adopted between 1865 and 1870. The amendments were a part of the implementation of the Reconstruction of the American South which occ ...to the United States Constitution. Tribe also points out that, in some 1960s cases (such as Katzenbach v. Morgan andJones v. Mayer ''Jones v. Alfred H. Mayer Co.'', 392 U.S. 409 (1968), is a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark United States Supreme Court case, which held that Congress could regulate the sale of private property to prevent racial di ...), theU.S. Supreme Court The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...ruled that the U.S. Congress has the authority to interpret the 14th Amendment (through enforcement legislation) more broadly than the U.S. Supreme Court itself has interpreted this amendment. Tribe points out that a similar logic could be used by a future U.S. Supreme Court to uphold a hypothetical Congressional statute that allows naturalized U.S. citizens to run for and to become U.S. President.
Eligibility challenges
Several courts have ruled that private citizens do not havestanding Standing, also referred to as orthostasis, is a position in which the body is held in an ''erect'' ("orthostatic") position and supported only by the feet. Although seemingly static, the body rocks slightly back and forth from the ankle in the s ...to challenge the eligibility of candidates to appear on a presidential electionballot A ballot is a device used to cast votes in an election and may be found as a piece of paper or a small ball used in secret voting. It was originally a small ball (see blackballing) used to record decisions made by voters in Italy around the 16t ....E.g. see ''Robinson v. Bowen'', 567F. Supp. 2d The ''Federal Supplement'' ( is a case law reporter published by West Publishing in the United States that includes select opinions of the United States district courts since 1932, and is part of the National Reporter System. Although the ''F ...1144 (N.D. Cal. The United States District Court for the Northern District of California (in case citations, N.D. Cal.) is the federal United States district court whose jurisdiction comprises the following counties of California: Alameda, Contra Costa, Del ...2008); ''Hollander v. McCain'', 2008 WL2853250 ( D.N.H. 2008);
Berg v. Obama
', 08-04083 ( E.D. Pa. 2008). Alternatively, there is a statutory method by which the eligibility of thepresident-elect of the United States The president-elect of the United States is the candidate who has presumptively won the United States presidential election and is awaiting inauguration to become the president. There is no explicit indication in the U.S. Constitution as to when ...to take office may be challenged in Congress. Some legal scholars assert that, even if eligibility challenges are nonjusticiable in federal courts, and are not undertaken in Congress, there are other avenues for adjudication, such as an action in state court in regard to ballot access. Every president to date was either a citizen at the adoption of the Constitution in 1789 or born in the United States; of the former group, all except one had two parents with citizenship in what would become the U.S. (Andrew Jackson Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...). Of those in the latter group, every president except two (Chester A. Arthur Chester Alan Arthur (October 5, 1829 – November 18, 1886) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 21st president of the United States from 1881 to 1885. He previously served as the 20th vice president under President James ...andBarack Obama Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...) had two U.S.-citizen parents. Further, four additional U.S. Presidents had one or both of his U.S.-citizen parents not born on U.S. soil (James Buchanan James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861. He previously served as secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and repr ...,Woodrow Wilson Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...,Herbert Hoover Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gr ..., andDonald Trump Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021. Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ...). Some presidential candidates were not born in aU.S. state In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...or did not have two U.S.-citizen parents. In addition, one U.S. vice president (Al Gore Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic Part ...) was born inWashington, D.C. ) , image_skyline = , image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...and another (Charles Curtis Charles Curtis (January 25, 1860 – February 8, 1936) was an American attorney and Republican politician from Kansas who served as the 31st vice president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 under Herbert Hoover. He had served as the Sena ...) was born in theKansas Territory The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...; Vice PresidentKamala Harris Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who is the 49th vice president of the United States. She is the first female vice president and the highest-ranking female official in U.S. history, as well ...' parents were not U.S. citizens at the time of her birth. This does not necessarily mean that these officeholders or candidates were ineligible, only that there was some controversy about their eligibility, which may have been resolved in favor of eligibility.
1800s
Chester A. Arthur
Chester A. Arthur Chester Alan Arthur (October 5, 1829 – November 18, 1886) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 21st president of the United States from 1881 to 1885. He previously served as the 20th vice president under President James ..., who was sworn in as president whenJames A. Garfield James Abram Garfield (November 19, 1831 – September 19, 1881) was the 20th president of the United States, serving from March 4, 1881 until his death six months latertwo months after he was shot by an assassin. A lawyer and Civil War gene ...died after being shot, was rumored to have been born inCanada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...."Who Can Be President?"
Voice of America News (July 29, 2008). Arthur was born inVermont Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...on October 5, 1829 to a Vermont-born mother and a father fromIreland Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...(who later became a U.S. citizen, 14 years after Arthur was born). His mother, Malvina Stone Arthur, was a native ofBerkshire Berkshire ( ; in the 17th century sometimes spelt phonetically as Barkeshire; abbreviated Berks.) is a historic county in South East England. One of the home counties, Berkshire was recognised by Queen Elizabeth II as the Royal County of Berk ..., Vermont, who moved with her family toQuebec Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ..., where she met and married the future president's father, William Arthur, on April 12, 1821. After the family had settled in Fairfield, Vermont, somewhere between 1822 and 1824, William Arthur traveled with his eldest daughter to East Stanbridge, Canada, in October 1830 and commuted to Fairfield on Sundays to preach. "It appears that he traveled regularly between the two villages, both of which were close to the Canada–US border, for about eighteen months, holding two jobs", which may well explain the confusion about Chester A. Arthur's place of birth, as perhaps did the fact that he was born in Franklin County, and thus within a day's walk of the Vermont–Quebec border. Moreover, Chester A. Arthur himself added a bit of confusion into the record by sometimes reporting his birth year as 1830. No evidence of his having been born in Canada was ever demonstrated by his Democratic opponents, although Arthur Hinman, an attorney who had investigated Arthur's family history, raised the allegation as an objection during his vice-presidential campaign and, after the end of his presidency, published a book on the subject.
Fictional character Christopher Schürmann
In "The Presidential Campaign of 1896," a work of satire by George Lynd Catlin describing an imaginary presidential election and published in 1888, a fictional Christopher Schürmann (born inNew York City New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...) was the candidate of the fictional Labor Party during the 1896 presidential election, defeated by candidate Charles Francis Adams of the fictional National Party. Some people have mistaken this fictional Schürmann, whose eligibility was questioned in the book, for a real person.
1900s
Charles Evans Hughes
The eligibility ofCharles Evans Hughes Charles Evans Hughes Sr. (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American statesman, politician and jurist who served as the 11th Chief Justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party, he previously was the ...was questioned in an article written byBreckinridge Long Samuel Miller Breckinridge Long (May 16, 1881 – September 26, 1958) was an American diplomat and politician. He served in the administrations of Woodrow Wilson and Franklin Delano Roosevelt. He is infamous among Holocaust historians for makin ..., one of Woodrow Wilson's campaign workers, and published on December 7, 1916 in the ''Chicago Legal News'' — a full month ''after'' the U.S. presidential election of 1916, in which Hughes was narrowly defeated byWoodrow Wilson Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of .... Long claimed that Hughes was ineligible because his father was not yet naturalized at the time of his birth and was still a British citizen. Observing that Hughes, although born in the United States, was also (according to British law) a British subject and therefore "enjoy da dual nationality and owe a double allegiance", Long argued that a ''native born'' citizen was not ''natural born'' without a unity of U.S. citizenship and allegiance and stated: "Now if, by any possible construction, a person at the instant of birth, and for any period of time thereafter, owes, or may owe, allegiance to any sovereign but the United States, he is not a 'natural-born' citizen of the United States."
Barry Goldwater
Barry Goldwater was born inPhoenix Phoenix most often refers to: * Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore * Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States Phoenix may also refer to: Mythology Greek mythological figures * Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ..., in what was then the incorporatedArizona Territory The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of ...of the United States. During his presidential campaign in 1964, there was a minor controversy over Goldwater's having been born in Arizona three years before it became a state. AttorneyMelvin Belli Melvin Mouron Belli (July 29, 1907 – July 9, 1996) was a prominent United States lawyer, writer, and actor known as "The King of Torts" and by insurance companies as "Melvin Bellicose". He had many celebrity clients, including Zsa Zsa Gab ...unsuccessfully sought to have to Goldwater removed from the California ballot.
George Romney
George W. Romney George Wilcken Romney (July 8, 1907 – July 26, 1995) was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as chairman and president of American Motors Corporation from 1954 to 1962, the 43rd gover ..., who ran for the Republican party presidential nomination in 1968, was born inMexico Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...to American parents.Lipsky, Seth (2009)
''The Citizen's Constitution: An Annotated Guide''
(Basic Books). p. 126.Heard, Alexander and Nelson, Michael (1987)
''Presidential Selection''
(Duke University Press) p. 127. Romney's grandfather, a member ofthe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ..., had emigrated to Mexico in 1886 with his three wives and their children, after the U.S. federal government outlawedpolygamy Crimes Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married .... However Romney's parents (monogamous under new church doctrine) retained their U.S. citizenship and returned to the United States with him and his siblings in 1912. Romney's eligibility for president becamemoot Moot may refer to: * Mootness, in American law: a point where further proceedings have lost practical significance; whereas in British law: the issue remains debatable * Moot court, an activity in many law schools where participants take part in s ...whenRichard Nixon Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...was nominated as the Republican presidential candidate.
Lowell Weicker
Lowell P. Weicker Lowell Palmer Weicker Jr. (; born May 16, 1931) is an American politician who served as a U.S. Representative, U.S. Senator, and the 85th Governor of Connecticut. He unsuccessfully sought the Republican nomination for president in 1980. He wa ...entered the race for the Republican party nomination of 1980 but dropped out before voting in the primaries began; he was also suggested as a possible vice-presidential nominee in 1976, to replace retiring Vice PresidentNelson Rockefeller Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...under the Republican ticket of incumbent PresidentGerald Ford Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected .... However Senator Bob Dole from Kansas was later chosen as the nominee. Weicker was born inParis Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...,France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ..., to parents who were U.S. citizens. His father was an executive for E. R. Squibb & Sons and his mother was born in India, the daughter of a British general.
2000s
John McCain
John McCain John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...was born in 1936 atCoco Solo Coco Solo was a United States Navy submarine base and naval air station, active from 1918 to the 1960s. History The submarine base at Coco Solo was established May 6, 1918. The site corresponds with modern-day Cativá in Panama. It was on th ..., Naval Air Station in thePanama Canal Zone The Panama Canal Zone ( es, Zona del Canal de Panamá), also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the terr .... McCain's eligibility for the presidency was not challenged during his 2000 campaign, but it was challenged during his 2008 campaign. McCain never released his birth certificate to the press or independent fact-checking organizations, but in 2008 one was shown to ''Washington Post'' reporterMichael Dobbs Michael John Dobbs, Baron Dobbs (born 14 November 1948) is a British Conservative politician and author, best known for his ''House of Cards'' trilogy. Early life and education Michael Dobbs was born on 14 November 1948 in Cheshunt, Hertfordsh ..., who wrote, " senior official of the McCain campaign showed me a copy of cCain'sbirth certificate issued by the 'family hospital' in the Coco Solo submarine base." A lawsuit filed by Fred Hollander in 2008 alleged McCain was actually born in a civilian hospital inColón, Panama Colón () is a city and seaport in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was l .... Dobbs wrote that in his autobiography, ''Faith of My Fathers'', McCain wrote that he was born "in the Canal Zone" at the U.S. Naval Air Station in Coco Solo, which was under the command of his grandfather, John S. McCain Sr. "The senator's father, John S. McCain Jr., was an executive officer on a submarine, also based in Coco Solo. His mother, Roberta McCain, has said that she has vivid memories of lying in bed listening to raucous celebrations of her son's birth from the nearby officers' club. The birth was announced days later in the English-language Panamanian American newspaper." The former unincorporated territory of the Panama Canal Zone and its related military facilities were not regarded as United States territory at the time, but , which became law in 1937, retroactively conferred citizenship on individuals born within the Canal Zone on or after February 26, 1904, and on individuals born in the Republic of Panama on or after that date who had at least one U.S. citizen parent employed by the U.S. government or the Panama Railway Company; was cited in JudgeWilliam Alsup William Haskell Alsup (born June 27, 1945) is a Senior United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. Early life and career Born in Jackson, Mississippi, Alsup received a Bachelor of ...'s 2008 ruling, described below. A March 2008 paper by former Solicitor General of the United States, Solicitor General Theodore Olson, Ted Olson and Harvard Law Professor Laurence H. Tribe opined that McCain was eligible for the Presidency. In April 2008, the U.S. Senate approved a non-binding resolution recognizing McCain's status as a natural-born citizen. In September 2008, U.S. District Judge William Alsup stated ''obiter'' in his ruling that it is "highly probable" that McCain is a natural-born citizen from birth by virtue of , although he acknowledged the alternative possibility that McCain became a natural-born citizen retroactively, by way of . These views have been criticized by Chin, who argues that McCain was at birth a citizen of Panama and was only retroactively declared a born citizen under , because at the time of his birth and with regard to the Canal Zone the Supreme Court's Insular Cases overruled theNaturalization Act of 1795 The United States Naturalization Act of 1795 (, enacted January 29, 1795) repealed and replaced the Naturalization Act of 1790. The main change made by the 1795 Act from the 1790 Act was the increase in the period of required residence in the Uni ..., which would otherwise have declared McCain a U.S. citizen immediately at birth. The U.S. United States Department of State, State Department's U.S. Department of State Foreign Affairs Manual, ''Foreign Affairs Manual'' states that children born in the Panama Canal Zone at certain times became US national, U.S. nationals without citizenship. In ''Rogers v. Bellei ''Rogers v. Bellei'', 401 U.S. 815 (1971), was a decision by the United States Supreme Court, which held that an individual who received an automatic congressional grant of citizenship at birth, but who was born outside the United States, may lose ...'', the Supreme Court ruled that children "born abroad of American parents" are not citizens within the citizenship clause of the 14th Amendment but did not elaborate on their ''natural-born'' status. Similarly, legal scholar Lawrence Solum concluded in an article on the ''natural born citizen'' clause that the question of McCain's eligibility could not be answered with certainty, and that it would depend on the particular approach of "constitutional construction".
Barack Obama
Barack Obama Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...was born in 1961 in Honolulu, Hawaii (which had become a U.S. state in 1959). Ann Dunham, His mother was a U.S. citizen and Barack Obama Sr., his father was a British subject from British Kenya. Before and after the 2008 United States presidential election, 2008 presidential election, claims were made that Obama was not a natural-born citizen. On June 12, 2008, the Obama presidential campaign launched a website to counter what it described as a smear campaign by his opponents, including Barack Obama citizenship conspiracy theories, conspiracy theories challenging his eligibility. The most prominent issue raised against Obama was the claim made in Barack Obama presidential eligibility litigation, several lawsuits that he was not actually born in Hawaii. The Supreme Court declined without comment to hear two lawsuits in which the plaintiffs argued it was irrelevant whether Obama was born in Hawaii. Most of the cases were dismissed because of the plaintiff's lack of standing; however, several courts have given guidance on the question. In ''Ankeny v. Governor'', a three-member Indiana Court of Appeals stated,Based upon the language of Article II, Section 1, Clause 4 and the guidance provided by ''Wong Kim Ark'', we conclude that persons born within the borders of the United States are 'natural born Citizens' for Article II, Section 1 purposes, regardless of the citizenship of their parents.Administrative law, Administrative Law Judge Michael Malihi in Georgia decided a group of eligibility challenge cases by saying, "The Indiana Court rejected the argument that Mr. Obama was ineligible, stating that the children born within the United States are natural born citizens, regardless of the citizenship of their parents. ... This Court finds the decision and analysis of ''Ankeny'' persuasive." Federal District Judge John A. Gibney, Jr. wrote in his decision in the case of ''Tisdale v. Obama'':The eligibility requirements to be President of the United States are such that the individual must be a "natural born citizen" of the United States ... It is well settled that those born in the United States are considered natural born citizens. See, e.g. ''United States v. Ark'' [sic] ...On October 31, 2008, Hawaii Health Director Chiyome Fukino issued a statement saying,I ... have personally seen and verified that the Hawai'i State Department of Health has Sen. Obama's original birth certificate on record in accordance with state policies and procedures.On July 27, 2009, Fukino issued an additional statement:I ... have seen the original vital records maintained on file by the Hawaii State Department of Health verifying Barack Hussein Obama was born in Hawaii and is a natural-born American citizen.Attempts to prevent Obama from participating in the Democratic Party (United States) presidential candidates, 2012, 2012 Democratic primary election in several states failed.
Marco Rubio and Bobby Jindal
Marco Rubio and Bobby Jindal both announced in 2015 that they were running for the Republican Party's nomination for president in the 2016 election. Orly Taitz and Mario Apuzzo, who both had filed multiple lawsuits challenging Obama's eligibility, claimed neither Rubio nor Jindal is eligible because both were born (albeit in the United States) to parents who were not U.S. citizens at the time of their respective births. A lawsuit filed in December 2015 in Vermont and a ballot challenge filed in February 2016 in New York challenged Jindal's eligibility. A November 2015 ballot challenge in New Hampshire alleging that Rubio was not a natural-born citizen was unsuccessful. In December, a similar lawsuit was filed in Vermont, and an unsuccessful lawsuit was filed in Florida. In January 2016, a similar unsuccessful ballot challenge was filed in Illinois. In February, a similar unsuccessful lawsuit was filed in Arkansas; a similar ballot challenge was filed in New York; and an unsuccessful ballot challenge was filed in Indiana.
Ted Cruz
Ted Cruz announced on March 22, 2015, that he was running for the Republican Party's nomination for president in the 2016 election. Cruz was born in Calgary, Alberta,Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...."Cruz, Rafael Edward (Ted), (1970– )"
''Biographical Directory of the United States Congress''. Cruz's mother was a U.S. citizen.Chin, Gabriel (August 13, 2013)
CNN. This gave Cruz dual citizenship, dual Canadian-American citizenship, as he was granted U.S. citizenship at the time of his birth by the virtue of his mother's citizenship, and Canada grants Jus soli, birthright citizenship to every person born in Canada. Ted's father was born in Cuba and eventually became a naturalized U.S. citizen in 2005. Cruz applied to formally renounce his Canadian citizenship and ceased being a citizen of Canada on May 14, 2014. Former Solicitor General Paul Clement, former Acting Solicitor General Neal Katyal, University of California, Irvine School of Law Dean Erwin Chemerinsky, Professor Chin (see #chin opinion, above), Temple University Law School Professor Peter Spiro, Professor Akhil Amar, Georgetown University Law Center Professor Randy Barnett, Yale Law School Professor Jack Balkin, and University of San Diego Professor Michael Ramsey believe Cruz meets the constitutional requirements to be eligible for the presidency. Similarly, Bryan A. Garner, Bryan Garner, the editor of Black's Law Dictionary, believes the U.S. Supreme Court would find Cruz to be eligible, and Case Western Reserve University School of Law professor Jonathan H. Adler agrees that no court will rule against Cruz's eligibility.Laurence Tribe Laurence Henry Tribe (born October 10, 1941) is an American legal scholar who is a University Professor Emeritus at Harvard University. He previously served as the Carl M. Loeb University Professor at Harvard Law School. A constitutional law sc ...of Harvard, however, described Cruz's eligibility as "murky and unsettled". Harvard Law Professor Cass Sunstein believes that Cruz is eligible, but agrees with Ramsey that Cruz's eligibility is not "an easy question". Sunstein believes concerns over Standing (law), standing and the political-question doctrine make it unlikely that courts would rule against Cruz. Mary McManamon (see #mcmanamon opinion, above) writing in the ''Catholic University Law Review'' believes that Cruz is not eligible because he was not born in the United States. Professor Einer Elhauge of Harvard, Professor Robert Clinton of Arizona State University, University of Chicago ProfessorEric Posner Eric Andrew Posner (; born December 5, 1965) is an American lawyer and legal scholar who has served as a counsel for the Department of Justice Antitrust Division since 2022. As a law professor at the University of Chicago Law School, Posner has ..., former Chief Justice of the New York Court of Appeals Sol Wachtler, retired Professor Joseph Dellapenna of Villanova University, and Professor Victor Williams of Columbus School of Law, Catholic University of America's law school agree that Cruz is not eligible. Alan Grayson, a former Democratic Congressman from Florida, does not believe Cruz is a natural-born citizen, and stated he would have filed a lawsuit if Cruz had become the Republican nominee. Larry Klayman, Taitz, and Apuzzo, who each filed multiple lawsuits challenging Obama's eligibility, have also asserted that Cruz is not eligible. Cruz's eligibility was questioned by some of his primary opponents, includingDonald Trump Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021. Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ..., Mike Huckabee, Rick Santorum, Carly Fiorina and Rand Paul. Marco Rubio, however, believes Cruz is eligible. Two November 2015 ballot challenges in New Hampshire alleging that Cruz was not a natural-born citizen were unsuccessful. In December, a similar lawsuit was filed in Vermont, and an unsuccessful lawsuit was filed in Florida. In January 2016, similar lawsuits were unsuccessfully filed in Texas and Utah, and two similar unsuccessful ballot challenges were filed in Illinois. In February, two similar unsuccessful lawsuits were filed in Pennsylvania and one was filed in Arkansas; a similar lawsuit was filed in Alabama; similar unsuccessful ballot challenges were filed in Indiana; and similar ballot challenges and an unsuccessful similar lawsuit were also filed in New York. In March, a similar lawsuit was filed in New York. In April, a similar ballot challenge was unsuccessfully filed in New Jersey. No lawsuit or challenge has been successful, and in February 2016, the Illinois Board of Elections ruled in Cruz's favor, stating, "The candidate is a natural born citizen by virtue of being born in Canada to his mother who was a U.S. citizen at the time of his birth."
Tulsi Gabbard
Tulsi Gabbard announced in 2019 that she was running for the Democratic Party's nomination for the 2020 United States presidential election. Gabbard was born in American Samoa; unlike some other U.S. territories, those born in American Samoa do not automatically acquire U.S. citizenship at birth. Gabbard's parents, however, were both U.S. citizens at the time of her birth: her mother was born in Indiana; her father was born in American Samoa to a father who was a U.S. citizen. The circumstances of Gabbard's birth have been compared to McCain and Cruz, neither of whom were born in the United States.
Kamala Harris
Kamala Harris Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who is the 49th vice president of the United States. She is the first female vice president and the highest-ranking female official in U.S. history, as well ...was born in Oakland, California, making her a natural-born citizen. In 2019, Harris unsuccessfully sought the Democratic Party's nomination for the 2020 United States presidential election. On August 11, 2020, Democratic Party presidential nominee Joe Biden selected Harris as his running mate, and they were both elected in November that year. In 2019, Donald Trump Jr. retweeted the statement "Kamala Harris is *not* an American Black. She is half Indian and half Jamaican." and then replied "Is this true? Wow." The tweets were interpreted to say that Harris was neither an American nor truly a African Americans, Black woman. Then, after 2020 Democratic Party vice presidential candidate selection, Harris was selected as Joe Biden's running mate PresidentDonald Trump Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021. Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pe ...said "I just heard it today that she doesn't meet the requirements and by the way the lawyer that wrote that piece is a very highly qualified, very talented lawyer." Trump also claimed PresidentBarack Obama Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...was born in Kenya and not Hawaii, a claim that has been Barack Obama citizenship conspiracy theories, proven false. The vice-president must be a natural-born citizen, in the same manner as the president. UCLA professorEugene Volokh Eugene Volokh (; born February 29, 1968 as Yevhen Volodymyrovych Volokh ( uk, Євге́н Володимирович Волох)) is an American legal scholar known for his scholarship in American constitutional law and libertarianism as well as ...said Harris is a natural-born citizen because she was born in the United States. In a ''Newsweek'' op-ed, Chapman University professor John C. Eastman asked if Harris's parents were U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents at the time of her birth or if they were temporary visitors, perhaps on student visas. He then stated that if they were temporary visitors, then "under the 14th Amendment as originally understood", she would not be considered a U.S. citizen at all—much less a natural-born citizen—and might not even be eligible for her then-current position in the Senate. Responding to criticism it received, ''Newsweeks editors wrote that Eastman's "essay has no connection whatsoever to so-called 'birther-ism. The response went on and stated, "the meaning of 'natural born Citizen', and the relation of that Article II textual requirement to the 14th Amendment's Citizenship Clause, are issues of legal interpretation about which scholars and commentators can, and will, robustly disagree." ''Newsweek'' also published Volokh's rebuttal to Eastman's essay. Colin Kalmbacher in ''Law & Crime'' responded to Eastman by saying that Eastman misstated "the state of the law – as well as the opinions of the legal community and the precedents of the courts – based on an incorrect reading of the" Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court case ''United States v. Wong Kim Ark ''United States v. Wong Kim Ark'', 169 U.S. 649 (1898), was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court which held that "a child born in the United States, of parents of Chinese descent, who, at the time of his birth, are subjects of the Empe ...'' from 1898. ''Newsweek'' later apologized after receiving a strong negative reaction to the publication, saying they had "entirely failed to anticipate the ways in which the essay would be interpreted, distorted and weaponized" and that their publication of it "was intended to explore a minority legal argument about the definition of who is a 'natural-born citizen' in the United States. But to many readers, the essay inevitably conveyed the ugly message that Senator Kamala Harris, a woman of color and the child of immigrants, was somehow not truly American."
Polling
A 2016 CBS News poll, found that only 21% of Americans would favor changing the Constitution to allow people who aren't natural born U.S. citizens to become President, while 75% would oppose such a change.
See also
*''Jus sanguinis'' *United States nationality law *United States presidential eligibility legislation *Natural-born-citizen clause
Notes
References
External links
*John Yinger
Essay
on the Presidential Eligibility clause and on the origins and interpretation of ''natural born citizen''. *Jill A. Pryor
"The Natural Born Citizen Clause and the Presidential Eligibility Clause; Resolving Two Hundred Years of Uncertainty"
''Yale Law Journal'', Vol. 97, 1988, pp. 881–899. *Sarah P. Herlihy
"Amending the Natural Born Citizen Requirement: Globalization as the Impetus and the Obstacle"
''Chicago-Kent Law Review'', Vol. 81, 2006, pp. 275–300. *Lawrence Friedman
"An Idea Whose Time has Come - The Curious History, Uncertain Effect, and Need for Amendment of the 'Natural Born Citizen' Requirement for the Presidency"
''St. Louis Univ. Law Journal'', Vol. 52, 2007, pp. 137–150. *U.S. Constitution Online
{{DEFAULTSORT:Natural Born Citizen Of The United States Clauses of the United States Constitution Citizenship of the United States