Nankangia Restoration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Nankangia'' is an
 ''Nankangia'' was first described and named by
''Nankangia'' was first described and named by 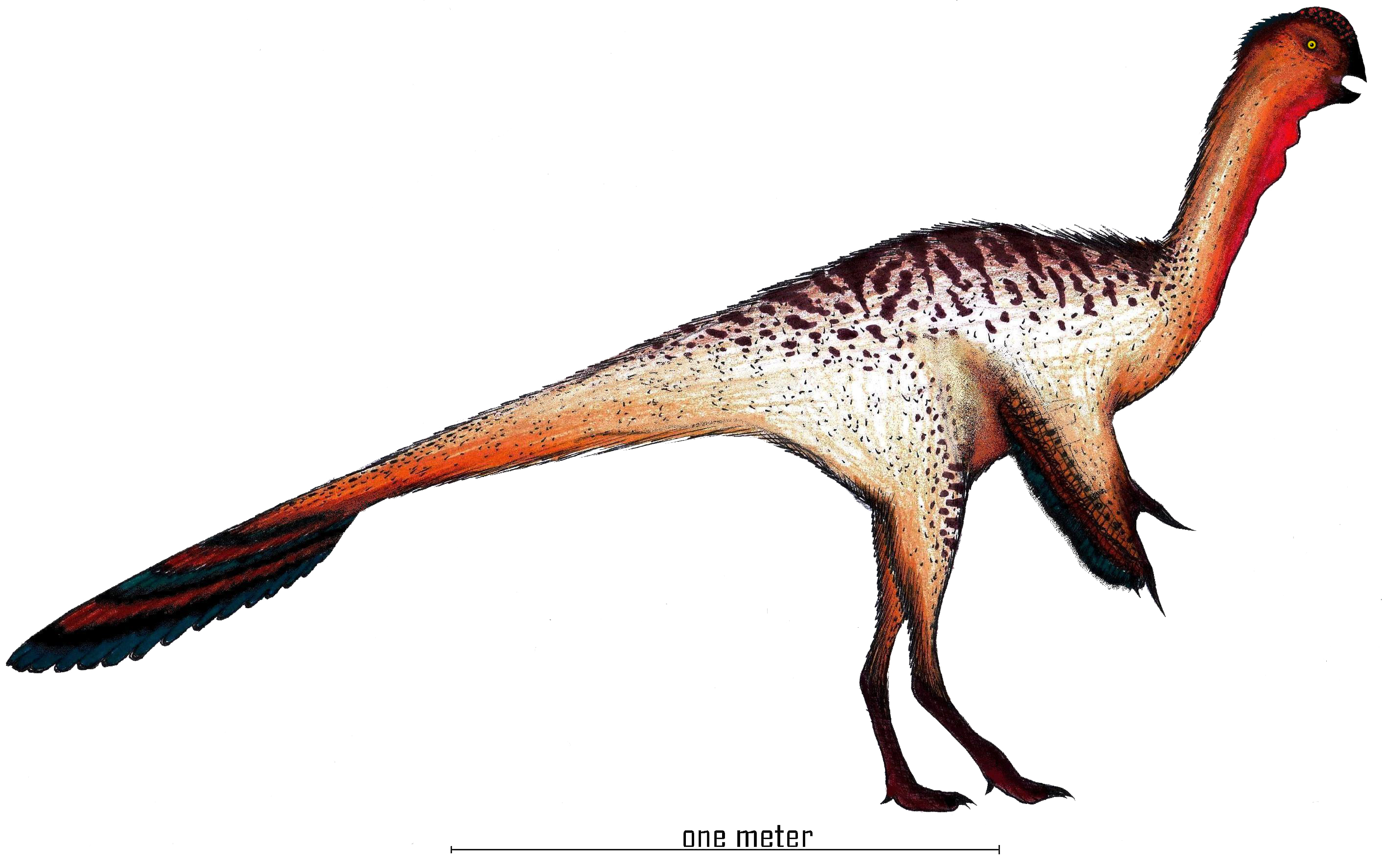 ''Nankangia'' is known solely from the
''Nankangia'' is known solely from the
 ''Nankangia'' is distinguished from all other
''Nankangia'' is distinguished from all other 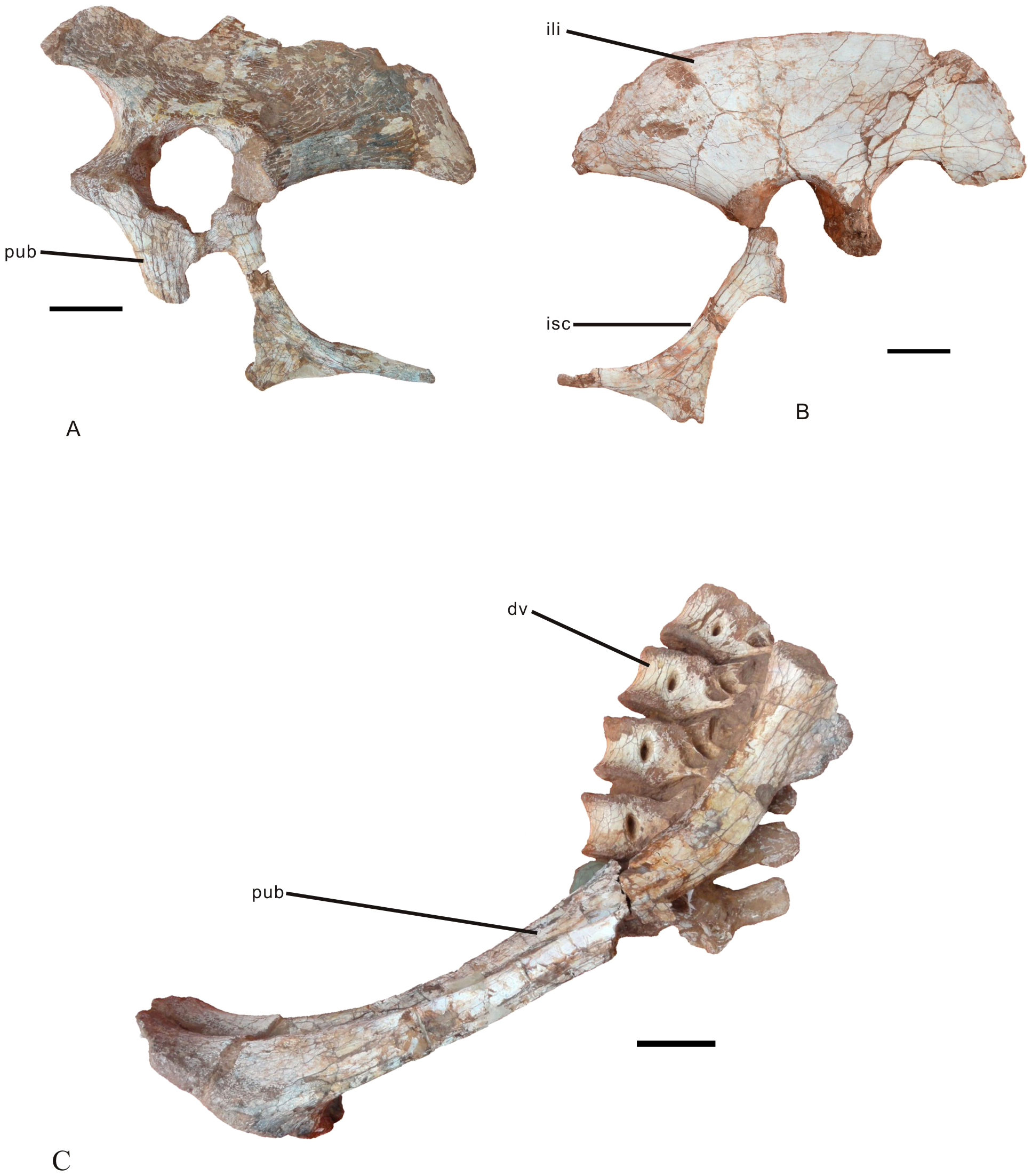 The rostral end of the mandibular symphyseal region is not downturned in ''Nankangia'', as in
The rostral end of the mandibular symphyseal region is not downturned in ''Nankangia'', as in
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of caenagnathoid
Caenagnathoidea ("recent jaw forms") is a group of advanced oviraptorosaurian dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like skulls, often wi ...
oviraptorosaur
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like s ...
ian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
known from the Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
Nanxiong Formation
The Nanxiong Formation (also known as Yuanpu Formation) is a Late Cretaceous geologic formation in Guangdong Province. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
Description
It consists of continental si ...
of Nankang County, Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
City of Jiangxi Province
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north into hi ...
, southeastern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. It contains a single species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, ''Nankangia jiangxiensis''. ''N. jiangxiensis'' coexisted with at least four other caenagnathoids, including but not limited to ''Corythoraptor
''Corythoraptor'' () is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian Nanxiong Formation of South China. It contains one species, ''C. jacobsi'', known from a single well-preserved skeleton, and named after paleontologist Louis L ...
'', '' Banji long'', '' Ganzhousaurus nankangensis'' and '' Jiangxisaurus ganzhouensis''. The relatively short dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
and non-downturned mandibular symphysis of ''Nankangia'' suggest that it may have been more herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
than carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other sof ...
. Its diet consisted of leaves and seeds.
Discovery
 ''Nankangia'' was first described and named by
''Nankangia'' was first described and named by Lü Junchang
Lü Junchang (; 1965 – 9 October 2018) was a Chinese palaeontologist and professor at the Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. An expert on Mesozoic reptiles, he described and named dozens of dinosaur and pterosaur taxa ...
, Yi Laiping, Zhong Hui and Wei Xuefang in 2013
File:2013 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: Edward Snowden becomes internationally famous for leaking classified NSA wiretapping information; Typhoon Haiyan kills over 6,000 in the Philippines and Southeast Asia; The Dhaka garment fact ...
and the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
is ''Nankangia jiangxiensis''. The generic name honors the Chinese administrative unit Nankang County in Jiangxi Province, and the specific name honors the province where the holotype site in Nankang City is located.
 ''Nankangia'' is known solely from the
''Nankangia'' is known solely from the holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
GMNH F10003, a partial lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
and partial postcrania Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated sk ...
l skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
from a single individual, housed at the Ganzhou Museum of Natural History
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
, Ganzhou City
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District.
Hist ...
of Jiangxi Province. Postcranial material includes five complete dorsal vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
, one and one-half sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
, nine complete and two partial caudal vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
, both scapulocoracoid The scapulocoracoid is the unit of the pectoral girdle that contains the coracoid and scapula.
The coracoid itself is a beak-shaped bone that is commonly found in most vertebrates with a few exceptions.
The scapula is commonly known as the ''shoulde ...
s, an incomplete furcula
The (Latin for "little fork") or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is formed by the fusion of the two pink
clavicles. In birds, its primary function is in the strengthening of the thoracic ...
, a nearly complete right humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
, the complete right and most of the left ilia, the complete right and most of the left pubic bones
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior r ...
, the complete right and a partial left ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west ...
, both femora
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with t ...
, the right tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
, and some dorsal rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
s.
The holotype was found in 2010 at the town of Longling of Nankang, Ganzhou City, by a local farmer who donated it to the Ganzhou Museum of Natural History. It was collected from the Nanxiong Formation
The Nanxiong Formation (also known as Yuanpu Formation) is a Late Cretaceous geologic formation in Guangdong Province. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
Description
It consists of continental si ...
, dating probably to the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
stage of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
.
Description
 ''Nankangia'' is distinguished from all other
''Nankangia'' is distinguished from all other oviraptorosaur
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like s ...
ians based on a combination of traits, some of which are autapomorphic
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to t ...
(i.e. unique). On the ventral surface near the base of the transverse process of the dorsal vertebrae two infradiapophyseal fossae are present. The sacral vertebrae bear slit-like pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
fossae. The neural spines of the anterior caudal vertebrae are wider transversely than anteroposteriorly, forming a large posterior fossa with a rugose central area. These vertebrae possess a large fossa on the anterior surface of the base of the transverse process (infraprezygapophyseal fossa) and as well as an infradiapophyseal fossa on the ventral surface of the transverse process.
The femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
and tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
of ''Nankangia'' are approximately the same length. Its femoral neck extends dorsomedially at about 90° to the shaft. It has relatively small ratio of height to length of ilium (0.36), which is additionally shorter than the femur as seen in ''Yulong Yulong may refer to:
* Yulong Naxi Autonomous County (), of Lijiang, Yunnan
* Yulong Snow Mountain (), or Jade Dragon Snow Mountain
* Yulong River (), in Guangxi
* Yulongsi Formation, in Yunnan
* Yulong, Xingyang (), town in Xingyang City, Henan
...
'' and ''Khaan
''Khaan'' (; from Mongol 'lord') was an oviraptorid dinosaur that was found in the Djadochta Formation of Mongolia and lived in the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian), 75-71 million years ago.
Description
''Khaan'' did not differ much from ...
''. The ilium of ''Nankangia'' is uniquely shaped, and among oviraptorosaurians, resembles the ilia of ''Chirostenotes
''Chirostenotes'' ( ; named from Greek 'narrow-handed') is a genus of oviraptorosaurian dinosaur from the late Cretaceous (about 76.5 million years ago) of Alberta, Canada. The type species is ''Chirostenotes pergracilis''.
History of discovery ...
'', ''Rinchenia
''Rinchenia'' (named after Byambyn Rinchen) is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch in what is now Mongolia, Nemegt Formation, around 70 million years ago. The type and only known species, ''Rinche ...
'', ''Heyuannia
''Heyuannia'' ("from Heyuan") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, in what is now China and Mongolia. It was the first oviraptorid found in China; most others were found in neighbouring Mongolia ...
'' and '' Shixinggia'', and clearly differs from the ilium of ''Luoyanggia
''Luoyanggia'' (meaning "from Luoyang") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur known from the Early Cretaceous Haoling Formation of the Ruyang Basin in Henan Province, central China. The type species is ''L. liudianensis''.Lü., J., Xu, L., Jiang, ...
''. Due to the lack of well-preserved corresponding elements between the specimens of ''Nankangia'' and ''Wulatelong
''Wulatelong'' is an extinct genus of basal oviraptorid dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Wulansuhai Formation (Campanian stage) of Bayan Mandahu, Linhe District of Inner Mongolia, northern China. It contains a single species, ''Wulatelong ...
'', from the Wulansuhai Formation
The Bayan Mandahu Formation (also known as Wulansuhai Formation or Wuliangsuhai Formation) is a geological unit of "redbeds" located near the village of Bayan Mandahu in Inner Mongolia, China Asia (Gobi Desert) and dates from the late Cretaceous P ...
of Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, Lü ''et al.'' (2013) could not differentiated between them.
 The rostral end of the mandibular symphyseal region is not downturned in ''Nankangia'', as in
The rostral end of the mandibular symphyseal region is not downturned in ''Nankangia'', as in caenagnathid
Caenagnathidae is a family of bird-like maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and Asia. They are a member of the Oviraptorosauria, and close relatives of the Oviraptoridae. Like other oviraptorosaurs, caenagnathids ...
s, ''Incisivosaurus
''Incisivosaurus'' ("incisor lizard") is a genus of small, probably herbivorous theropod dinosaurs from the early Cretaceous Period of what is now the People's Republic of China. The first specimen to be described (by Xu ''et al.'' in 2002), IVPP ...
'', ''Luoyanggia'' and ''Ganzhousaurus
''Ganzhousaurus'' (meaning "Ganzhou lizard") is an extinct genus of oviraptorid dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of Nankang County, Ganzhou City of Jiangxi Province, southern China. It was found in a Maastrichtian depos ...
''. Unlike the V-shaped mandibular symphysis of ''Luoyanggia'', ''Nankangia'' and other oviraptorosaurs have a U-shaped mandibular symphysis. Although ''Nankangia'' and ''Jiangxisaurus
''Jiangxisaurus'' is an extinct genus of oviraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Nanxiong Formation of southern China.
It was similar to ''Heyuannia'', but with more strongly curved anterior claws and a thinner, frailer mandible ...
'' possess similar lower jaws, the medial margin of the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
is more curved medially in ''Nankangia'' than it is in ''Jiangxisaurus''. Based on its phylogenetic position, ''Nankangia'' displays five other possible autapomorphies, including an anteriorly projecting acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acro ...
, separated anterior and greater trochanters, dorsoventral extension of the pubic peduncle that is deeper than the ischial peduncle, and the lack of a downturned symphyseal portion of the dentary. The latter trait is shared with the coeval
{{Short pages monitor