Modified Food Starch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Modified starch, also called starch
Modified starch, also called starch

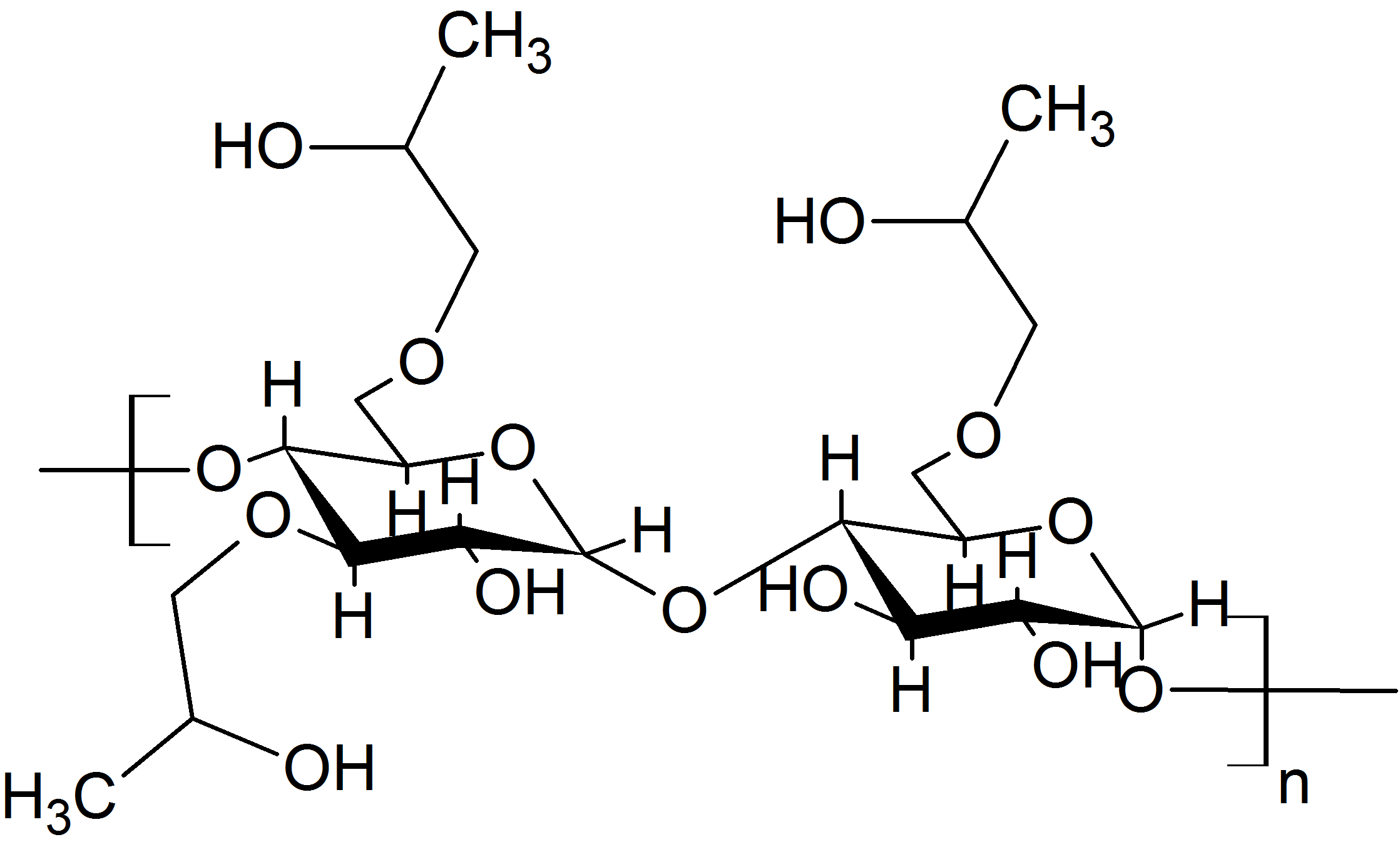
 Acid-treated starch (
Acid-treated starch (
derivatives
The derivative of a function is the rate of change of the function's output relative to its input value.
Derivative may also refer to:
In mathematics and economics
* Brzozowski derivative in the theory of formal languages
* Formal derivative, an ...
, are prepared by physically, enzymatically, or chemically treating native starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
to change its properties. Modified starches are used in practically all starch applications, such as in food products as a thickening agent
A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their t ...
, stabilizer or emulsifier
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Altho ...
; in pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
s as a disintegrant; or as binder in coated paper
Coated paper (also known as enamel paper, gloss paper, and thin paper) is paper that has been coated by a mixture of materials or a polymer to impart certain qualities to the paper, including weight, surface gloss, smoothness, or reduced ink absor ...
. They are also used in many other applications.
Starches are modified to enhance their performance in different applications. Starches may be modified to increase their stability against excessive heat, acid, shear, time, cooling, or freezing; to change their texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture ...
; to decrease or increase their viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
; to lengthen or shorten gelatinization
Starch gelatinization is a process of breaking down the intermolecular bonds of starch molecules in the presence of water and heat, allowing the hydrogen bonding sites (the hydroxyl hydrogen and oxygen) to engage more water. This irreversibly ...
time; or to increase their visco-stability.
Modification methods



 Acid-treated starch (
Acid-treated starch (INS INS or Ins or ''variant'', may refer to:
Places
* Ins, Switzerland, a municipality
* Creech Air Force Base (IATA airport code INS)
* Indonesia, ITF and UNDP code INS
Biology
*'' Ins'', a New World genus of bee flies
* INS, the gene for the insul ...
1401), also called thin boiling starch, is prepared by treating starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
or starch granules with inorganic acid
A mineral acid (or inorganic acid) is an acid derived from one or more inorganic compounds, as opposed to organic acids which are acidic, organic compounds. All mineral acids form hydrogen ions and the conjugate base when dissolved in water.
Char ...
s, e.g. hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
breaking down the starch molecule and thus reducing the viscosity.
Other treatments producing modified starch (with different INS and E-numbers
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly ...
) are:
* dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced from ...
(INS 1400), roasted starch with hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
* alkaline-modified starch (INS 1402) with sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
or potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
* bleached starch (INS 1403) with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%� ...
* oxidized starch (INS 1404, E1404) with sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite (commonly known in a dilute solution as bleach) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula NaOCl (or NaClO), comprising a sodium cation () and a hypochlorite anion (or ). It may ...
, breaking down viscosity
* enzyme-treated starch (INS 1405), maltodextrin
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food ingredient. It is produced from vegetable starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a white hygroscopic spray-dried powder. Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as r ...
, cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrins are a family of cyclic oligosaccharides, consisting of a macrocyclic ring of glucose subunits joined by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Cyclodextrins are produced from starch by enzymatic conversion. They are used in food, pharmaceutical ...
* monostarch phosphate (INS 1410, E1410) with phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid (singular)) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in th ...
or the salts sodium phosphate
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhyd ...
, potassium phosphate
Potassium phosphate is a generic term for the salt (chemistry), salts of potassium and phosphate ions including:
* Monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) (Molar mass approx: 136 g/mol)
* Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (Molar mass approx: 174 g/mol)
* ...
, or sodium triphosphate
Sodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP),
to reduce retrogradation
Retrogradation is the landward change in position of the front of a river delta with time. This occurs when the mass balance of sediment into the delta is such that the volume of incoming sediment is less than the volume of the delta that is lost ...
* distarch phosphate (INS 1412, E1412) by esterification with for example sodium trimetaphosphate
Sodium trimetaphosphate (also STMP), with formula Na3P3O9, is one of the metaphosphates of sodium. It has the formula but the hexahydrate is also well known. It is the sodium salt of trimetaphosphoric acid. It is a colourless solid that finds ...
, crosslinked
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
starch modifying the rheology
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid ( liquid or gas) state, but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an appl ...
, the texture
* acetylated starch (INS 1420, E1420) esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
with acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a col ...
* hydroxypropylated starch (INS 1440, E1440), starch ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
, with propylene oxide
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its us ...
, increasing viscosity stability
* hydroxyethyl starch
Hydroxyethyl starch (HES/HAES), sold under the brand name Voluven among others, is a nonionic starch derivative, used as a volume expander in intravenous therapy. The use of HES on critically ill patients is associated with an increased risk of ...
, with ethylene oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered Ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless a ...
* starch sodium octenyl succinate (OSA) starch (INS 1450, E1450) used as emulsifier
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Altho ...
adding hydrophobicity
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
* starch aluminium octenyl Succinate (INS 1452, E1452)
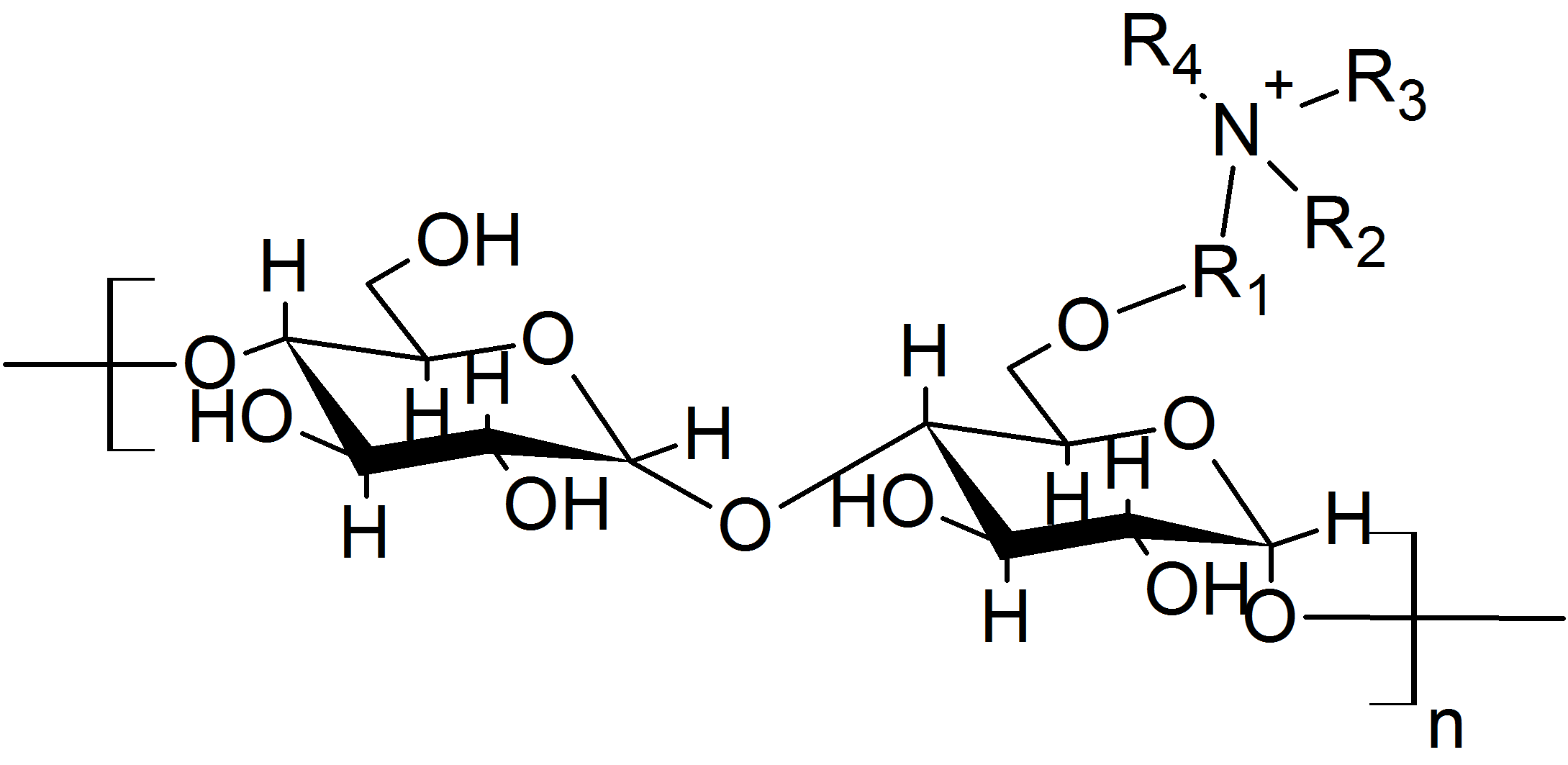
* cationic starch, adding positive electrical charge
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
to starch
* carboxymethylated starch with monochloroacetic acid
Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula ClCH2CO2H. This carboxylic acid is a useful building block in organic synthesis. It is a colorless solid. Related compounds a ...
adding negative charge
and combined modifications such as
*phosphated distarch phosphate
Phosphated distarch phosphate, is a type of chemically modified starch. It can be derived from wheat starch, tapioca starch, potato starch or many other botanical sources of starch. It is produced by replacing the hydrogen bonds between starch ...
(INS 1413, E1413)
* acetylated distarch phosphate (INS 1414, E1414)
* acetylated distarch adipate
Acetylated distarch adipate ( E1422), is a starch that is treated with acetic anhydride and adipic acid anhydride to resist high temperatures. It is used in foods as a bulking agent, stabilizer and a thickener.
No acceptable daily intake for hu ...
(INS 1422, E1422),
* hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (INS 1442, E1442),
* acetylated oxidized starch (INS 1451, E1451).
Modified starch may also be a cold-water-soluble, pregelatinized or instant starch which thickens and gels without heat, or a cook-up starch which must be cooked like regular starch. Drying methods to make starches cold-water-soluble are extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex c ...
, drum drying Drum drying is a method used for drying out liquids from raw materials with a drying drum. In the drum-drying process, pureed raw ingredients are dried at relatively low temperatures over rotating, high-capacity drums that produce sheets of drum-dr ...
, spray drying
Spray drying is a method of changing a dry powder from a liquid or slurry by rapidly drying with a hot gas. This is the preferred method of drying of many thermally-sensitive materials such as foods and pharmaceuticals, or materials which may requ ...
or dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced from ...
ization.
Other starch derivatives, the starch sugars, like glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
, high fructose syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzym ...
, glucose syrup
Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but glucos ...
s, maltodextrin
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food ingredient. It is produced from vegetable starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a white hygroscopic spray-dried powder. Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as r ...
s, starch degraded with amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
are mainly sold as liquid syrup
In cooking, a syrup (less commonly sirup; from ar, شراب; , beverage, wine and la, sirupus) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars ...
to make a sweetener
{{Wiktionary, sweetener
A sweetener is a substance added to food or drink to impart the flavor of sweetness, either because it contains a type of sugar, or because it contains a sweet-tasting sugar substitute. Many artificial sweeteners have been ...
.
Examples of use and functionality of modified starch
Pre-gelatinized starch is used to thicken instantdessert
Dessert is a course (food), course that concludes a meal. The course consists of sweet foods, such as confections, and possibly a beverage such as dessert wine and liqueur. In some parts of the world, such as much of Greece and West Africa, and ...
s, allowing the food to thicken with the addition of cold water or milk. Similarly, cheese sauce
Cheese sauce is a sauce made with cheese or processed cheese as a primary ingredient. Sometimes dried cheese or cheese powder is used. Several varieties exist and it has many various culinary uses. Mass-produced commercial cheese sauces are also ...
granules such as in Macaroni and Cheese
Macaroni and cheese (also called mac and cheese in Canada and the United States and macaroni cheese in the United Kingdom BBC, RecipesMacaroni Cheese/ref>) is a dish of cooked macaroni pasta and a cheese sauce, most commonly Cheddar sauce.
The ...
, lasagna
Lasagna (, also , also known as lasagne, ) is a type of pasta, possibly one of the oldest types, made of very wide, flat sheets. Either term can also refer to an Italian dish made of stacked layers of lasagna alternating with fillings such as ...
, or gravy
Gravy is a sauce often made from the juices of meats that run naturally during cooking and often thickened with wheat flour or corn starch for added texture. The gravy may be further coloured and flavoured with gravy salt (a simple mix of salt an ...
granules may be thickened with boiling water without the product going lumpy. Commercial pizza topping
Pizza (, ) is a dish of Italian origin consisting of a usually round, flat base of leavened wheat-based dough topped with tomatoes, cheese, and often various other ingredients (such as various types of sausage, anchovies, mushrooms, onion ...
s containing modified starch will thicken when heated in the oven, keeping them on top of the pizza, and then become runny when cooled.
A suitably modified starch is used as a fat substitute A fat substitute is a food product with the same functions, stability, physical, and chemical characteristics as regular fat, with fewer Calories per gram than fat. They are utilized in the production of low fat and low calorie foods.
Background
...
for low-fat versions of traditionally fatty foods, e.g. industrial
Industrial may refer to:
Industry
* Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry
* Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems
* Industrial city, a city dominate ...
milk-based desserts like yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in t ...
or reduced-fat hard salami
Salami ( ) is a cured sausage consisting of fermented and air-dried meat, typically pork. Historically, salami was popular among Southern, Eastern, and Central European peasants because it can be stored at room temperature for up to 45 days ...
having about 1/3 the usual fat content. For the latter type of uses, it is an alternative to the product Olestra
Olestra (also known by its brand name Olean) is a fat substitute that adds no calories to products. It has been used in the preparation of otherwise high-fat foods thereby lowering or eliminating their fat content. The Food and Drug Administrati ...
.
Modified starch is added to frozen products to prevent them from dripping when defrosted. Modified starch, bonded with phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
, allows the starch to absorb more water and keeps the ingredients together. Modified starch acts as an emulsifier for French dressing
French dressing, in consumer-facing American cuisine and store-bought products in the United States, is a creamy dressing that varies in color from pale orange to bright red. It is made of oil, vinegar, sugar, and other flavorings, with the colo ...
by enveloping oil droplets and suspending them in the water. Acid-treated starch forms the shell of jelly bean
Jelly beans are small bean shaped sugar candies with soft candy shells and thick gel interiors (see gelatin and jelly). The confection is primarily made of sugar and sold in a wide variety of colors and flavors.
History
It has been clai ...
s. Oxidized starch increases the stickiness of batter.
Carboxymethylated starches are used as a wallpaper adhesive, as textile printing
Textile printing is the process of applying color to fabric in definite patterns or designs. In properly printed fabrics the colour is bonded with the fibre, so as to resist washing and friction. Textile printing is related to dyeing but in ...
thickener, as tablet disintegrants and excipients
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication, included for the purpose of long-term stabilization, bulking up solid formulations that contain potent active ingredients in small amounts (thus often referred ...
in the pharmaceutical industry.
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
ic starch is used as wet end sizing agent in paper manufacturing
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
.
Genetically modified starch
Modified starch should not be confused withgenetically modified
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of Genetic engineering techniques, technologies used to change the gene ...
starch, which refers to starch from genetically engineered plants, such as those that have been genetically modified to produce novel fatty acids or carbohydrates which might not occur in the plant species being harvested. In Europe the term "Genetically Modified Organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with ...
" is used solely where "the genetic material has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally through fertilisation and/or natural recombination". The modification in "genetically modified" refers to the genetic engineering of the plant DNA, whereas in the term "Modified Starch" seen on mandatory
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics)
In representative democracies, a mandate (or seat) ...
ingredient
An ingredient is a substance that forms part of a mixture (in a general sense). For example, in cooking, recipes specify which ingredients are used to prepare a specific dish. Many commercial product (business), products contain secret ingredie ...
labels
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed dir ...
it refers to the later processing or treatment of the starch or starch granules.
Genetically modified starch is of interest in the manufacture of biodegradable polymer
Biodegradable polymers are a special class of polymer that breaks down after its intended purpose by bacterial decomposition process to result in natural byproducts such as gases ( CO2, N2), water, biomass, and inorganic salts. These polymers a ...
s and noncellulose feedstock in the paper industry
The pulp and paper industry comprises companies that use wood as raw material and produce pulp, paper, paperboard and other cellulose-based products.
Manufacturing process
The pulp is fed to a paper machine where it is formed as a paper web a ...
, as well as the creation of new food additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salt ...
. For example, researchers aim to alter the enzymes within living plants to create starches with desirable modified properties, and thus eliminate the need for enzymatic processing after starch is extracted from the plant.
See also
* * * *References
Suggested reading
* *''Revise for OCR GCSE Food Technology'', Alison Winson. 2003. *''Degradable Polymers, Recycling, and Plastics Waste Management''. S Huang, Ann-Christine Albertsson. 1995. *''Modified Starch'', Jenny Ridgwell, Ridgwell Press, 2001, {{ISBN, 978-1-901151-07-7 Starch Food additives Edible thickening agents