|
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars produced from processed starch are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
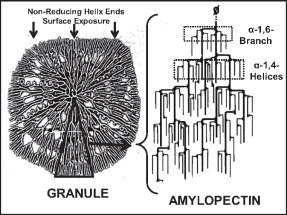
Amylopectin
Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α- glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose. Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amyloplasts. To generate energy, the plant hydrolyzes the starch, releasing the glucose subunits. Humans and other animals that eat plant foods also use amylase, an enzyme that assists in breaking down amylopectin, to initiate the hydrolyzation of starch. Starch is made of about 70–80% amylopectin by weight, though it varies depending on the source. For example, it ranges from lower percent content in long-grain rice, amylomaize, and russet potatoes to 100% in glutinous rice, waxy potato starch, and waxy corn. Amylopectin is highly branched, being formed of 2,000 to 200,000 glucose units. Its inner chains are formed of 20–24 glucose subunits. Dissolved amylopectin starch has a lower tendency of retrogradation (a partial recrystalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
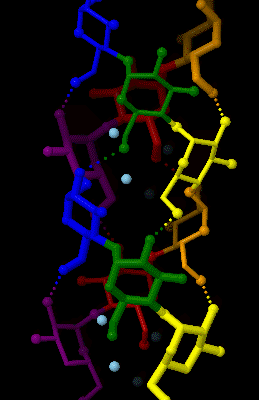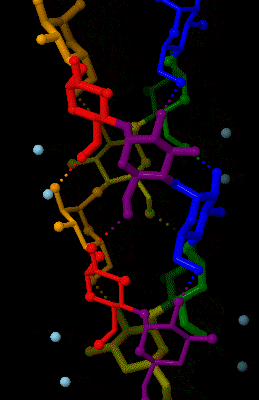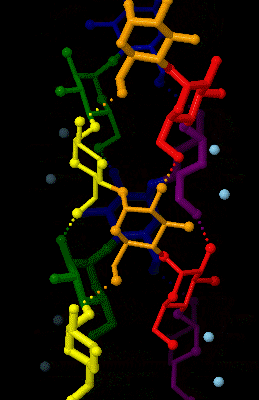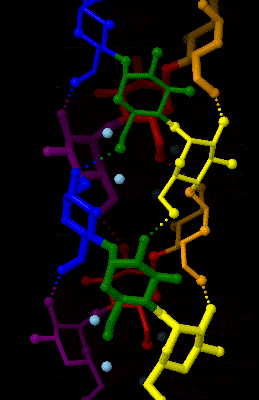
Amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation or two different helical forms. It can bind with itself in a double helix (A or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch Gelatinization
Starch gelatinization is a process of breaking down the intermolecular bonds of starch molecules in the presence of water and heat, allowing the hydrogen bonding sites (the hydroxyl hydrogen and oxygen) to engage more water. This irreversibly dissolves the starch granule in water. Water acts as a plasticizer. Three main processes happen to the starch granule: granule swelling, crystallite or double helical melting, and amylose leaching. *During heating, water is first absorbed in the amorphous space of starch, which leads to a swelling phenomenon. *Water then enters via amorphous regions into the tightly bound areas of double helical structures of amylopectin. At ambient temperatures these crystalline regions do not allow water to enter. Heat causes such regions to become diffuse, the amylose chains begin to dissolve, to separate into an amorphous form and the number and size of crystalline regions decreases. Under the microscope in polarized light starch loses its birefri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars ( monosaccharides, or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated by Native Americans independently in multiple locations,University of Wisconsin-Madison, ''Finding rewrites the evolutionary history of the origin of potatoes'' (2005/ref> but later genetic studies traced a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there approximately 7,000–10,000 years ago, from a species in the '' Solanum brevicaule'' complex. Lay summary: In the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous, some close relatives of the potato are cultivated. Potatoes were introduced to Europe from the Americas by the Spanish in the second half of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a major source of carbohydrates. Though it is often called ''yuca'' in parts of Spanish America and in the United States, it is not related to yucca, a shrub in the family Asparagaceae. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are used to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian farinha, and the related ''garri'' of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it (and roasting both in the case of farinha and garri). Cassava is the third-largest so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), biofuels are mostly used for transportation, but can also be used for heating and electricity. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricultural, domestic or industrial biowaste. The greenhouse gas mitigation potential of biofuel varies considerably, from emission levels comparable to fossil fuels in some scenarios to negative emissions in others. See the biomass article for more on this particular subject. The two most common types of biofuel are Ethanol#Fuel, bioethanol and biodiesel. The U.S. is the largest producer of bioethanol, while the EU is the largest producer of biodiesel. The energy content in the global production of bioethanol and biodiesel is 2.2 and 1.8 EJ per year, respectively. * Bioethanol is an Alcohol (chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheatpaste
Wheat paste (also known as flour and water paste, flour paste, or simply paste) is a gel or liquid adhesive made from wheat flour or starch and water. It has been used since antiquity for various arts and crafts such as book binding, découpage, collage, papier-mâché, and adhering paper posters and notices to walls. A critical difference among wheat pastes is the division between those made from flour and those made from starch. Vegetable flours contain both gluten and starch. Over time the gluten in a flour paste cross-links, making it very difficult to release the adhesive. Using only starch, a fine quality, fully reversible paste can be produced. The latter is the standard adhesive for paper conservation. Besides wheat, other vegetables also are processed into flours and starches from which pastes can be made: characteristics, such as strength and reversibility, vary with the plant species; manufacturer's processing; and the recipe of the end-user. Uses A common use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |