mining camp on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mining is the
Mining is the
 Ancient Egyptians mined malachite at
Ancient Egyptians mined malachite at
 Mining in Europe has a very long history. Examples include the silver mines of Laurium, which helped support the Greek city state of
Mining in Europe has a very long history. Examples include the silver mines of Laurium, which helped support the Greek city state of

 Mining as an industry underwent dramatic changes in
Mining as an industry underwent dramatic changes in
 During prehistoric times, early Americans mined large amounts of
During prehistoric times, early Americans mined large amounts of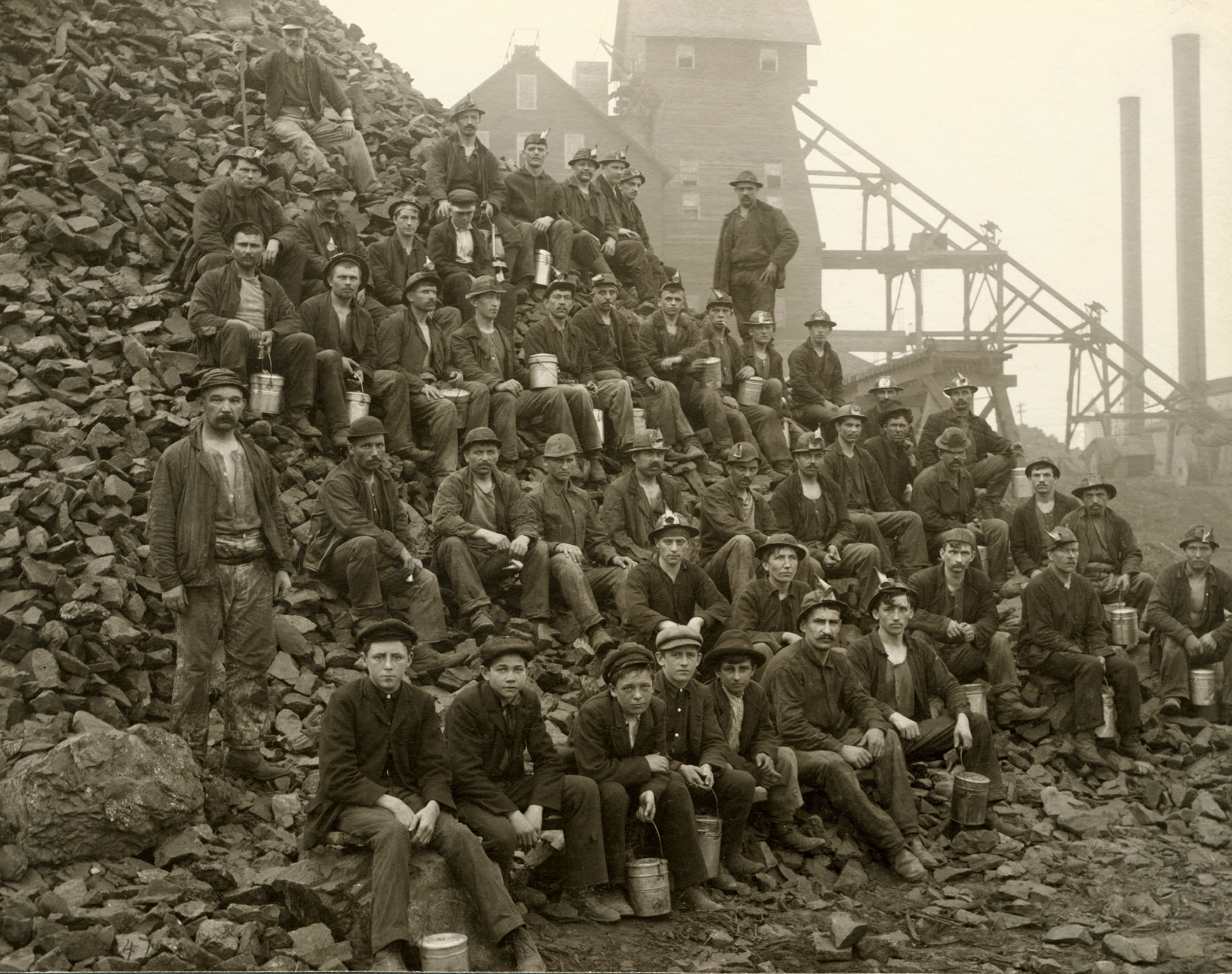  In the early colonial history of the Americas, "native gold and silver was quickly expropriated and sent back to Spain in fleets of gold- and silver-laden galleons", the gold and silver originating mostly from mines in Central and South America.
In the early colonial history of the Americas, "native gold and silver was quickly expropriated and sent back to Spain in fleets of gold- and silver-laden galleons", the gold and silver originating mostly from mines in Central and South America.
 In the early 20th century, the gold and silver rush to the western United States also stimulated mining for coal as well as
In the early 20th century, the gold and silver rush to the western United States also stimulated mining for coal as well as
p. 64
''Taylor & Francis''. Canada's mining industry grew more slowly than did the United States' due to limitations in transportation, capital, and U.S. competition; Ontario was the major producer of the early 20th century with nickel, copper, and gold. Meanwhile, Australia experienced the
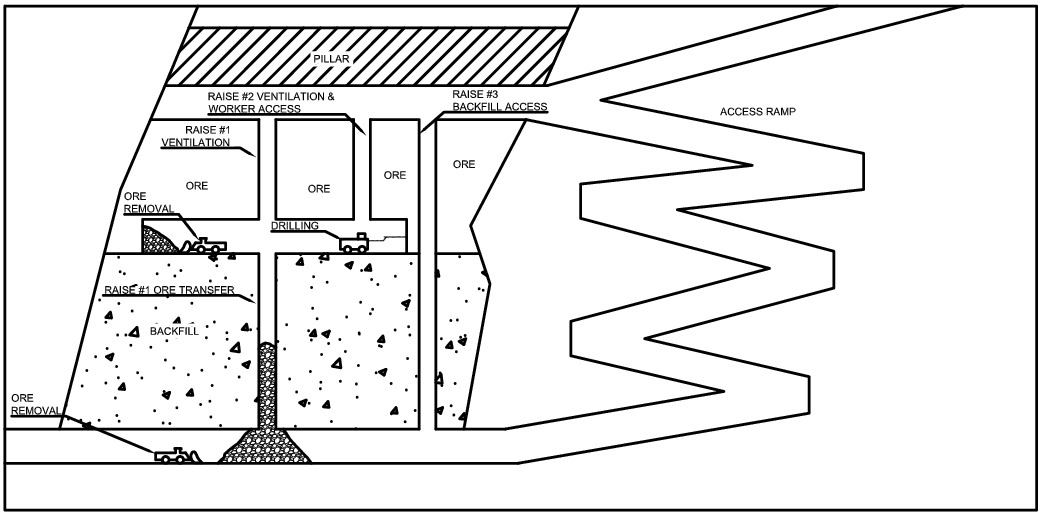 The process of mining from discovery of an ore body through extraction of minerals and finally to returning the land to its natural state consists of several distinct steps. The first is discovery of the ore body, which is carried out through
The process of mining from discovery of an ore body through extraction of minerals and finally to returning the land to its natural state consists of several distinct steps. The first is discovery of the ore body, which is carried out through
 Mining techniques can be divided into two common
Mining techniques can be divided into two common
 High wall mining, which evolved from auger mining, is another form of surface mining. In high wall mining, the remaining part of a coal seam previously exploited by other surface-mining techniques has too much overburden to be removed but can still be profitably exploited from the side of the artificial cliff made by previous mining. A typical cycle alternates sumping, which undercuts the seam, and shearing, which raises and lowers the cutter-head boom to cut the entire height of the coal seam. As the coal recovery cycle continues, the cutter-head is progressively launched further into the coal seam. High wall mining can produce thousands of tons of coal in contour-strip operations with narrow benches, previously mined areas, trench mine applications and steep-dip seams.
High wall mining, which evolved from auger mining, is another form of surface mining. In high wall mining, the remaining part of a coal seam previously exploited by other surface-mining techniques has too much overburden to be removed but can still be profitably exploited from the side of the artificial cliff made by previous mining. A typical cycle alternates sumping, which undercuts the seam, and shearing, which raises and lowers the cutter-head boom to cut the entire height of the coal seam. As the coal recovery cycle continues, the cutter-head is progressively launched further into the coal seam. High wall mining can produce thousands of tons of coal in contour-strip operations with narrow benches, previously mined areas, trench mine applications and steep-dip seams.
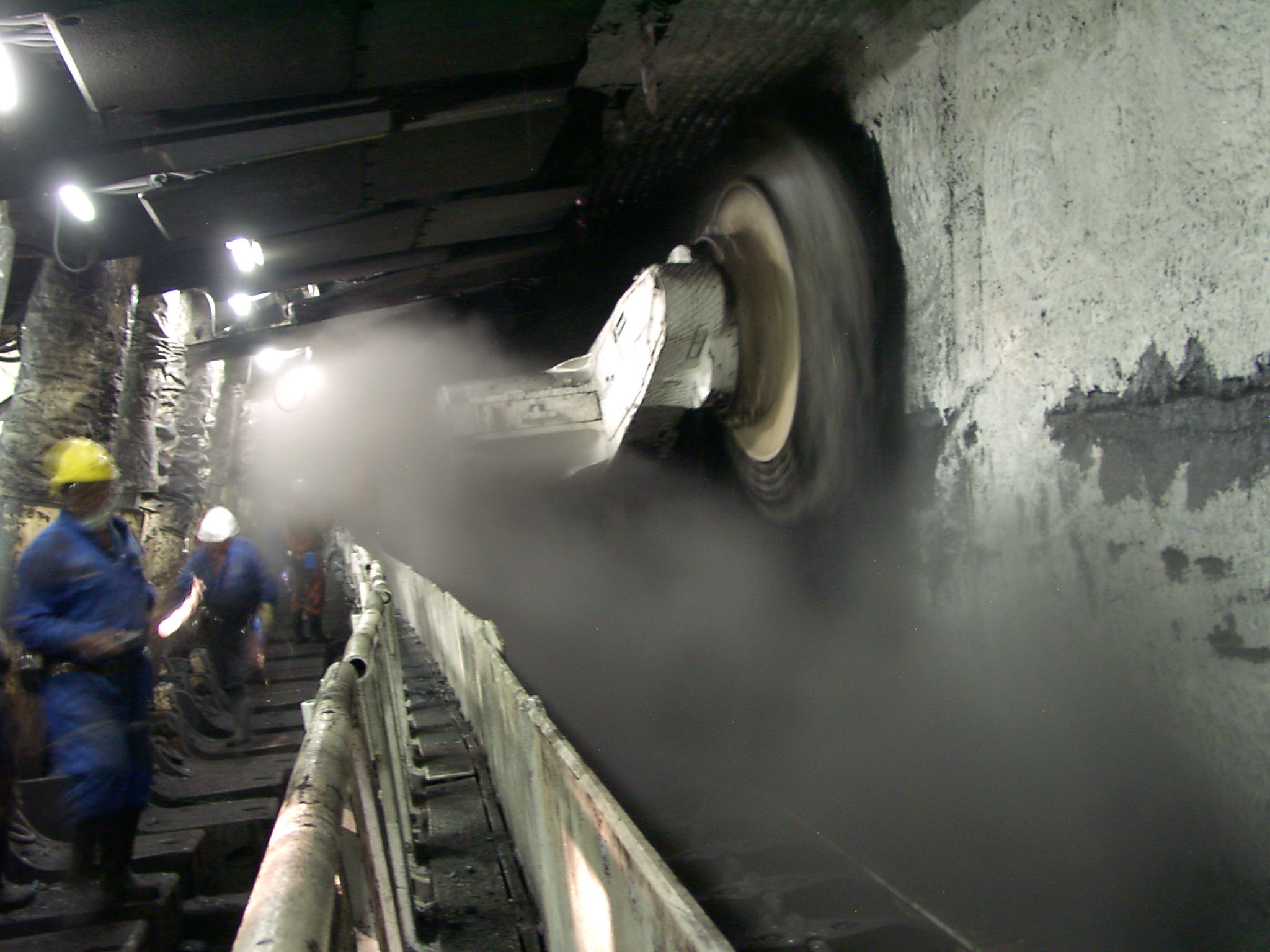
 Sub-surface mining consists of digging tunnels or shafts into the earth to reach buried ore deposits. Ore, for processing, and waste rock, for disposal, are brought to the surface through the tunnels and shafts. Sub-surface mining can be classified by the type of access shafts used, and the extraction method or the technique used to reach the mineral deposit. Drift mining uses horizontal access tunnels, slope mining uses diagonally sloping access shafts, and
Sub-surface mining consists of digging tunnels or shafts into the earth to reach buried ore deposits. Ore, for processing, and waste rock, for disposal, are brought to the surface through the tunnels and shafts. Sub-surface mining can be classified by the type of access shafts used, and the extraction method or the technique used to reach the mineral deposit. Drift mining uses horizontal access tunnels, slope mining uses diagonally sloping access shafts, and

 Heavy machinery is used in mining to explore and develop sites, to remove and stockpile overburden, to break and remove rocks of various hardness and toughness, to process the ore, and to carry out reclamation projects after the mine is closed. Bulldozers, drills, explosives and trucks are all necessary for excavating the land. In the case of
Heavy machinery is used in mining to explore and develop sites, to remove and stockpile overburden, to break and remove rocks of various hardness and toughness, to process the ore, and to carry out reclamation projects after the mine is closed. Bulldozers, drills, explosives and trucks are all necessary for excavating the land. In the case of
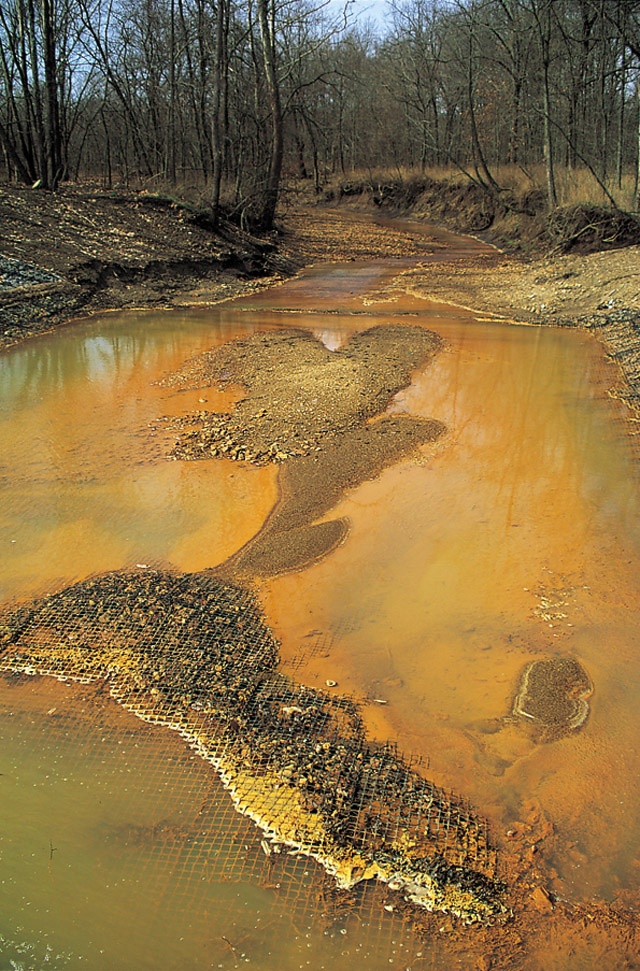 Mine operators frequently have to follow some regulatory practices to minimize environmental impact and avoid impacting human health. In better regulated economies, regulations require the common steps of
Mine operators frequently have to follow some regulatory practices to minimize environmental impact and avoid impacting human health. In better regulated economies, regulations require the common steps of
 Ore mills generate large amounts of waste, called
Ore mills generate large amounts of waste, called
Technical Report: Design and Evaluation of Tailings Dams
These ponds are secured by impoundments ( dams or
Trends in the stewardship of tailings dams
In 2015,
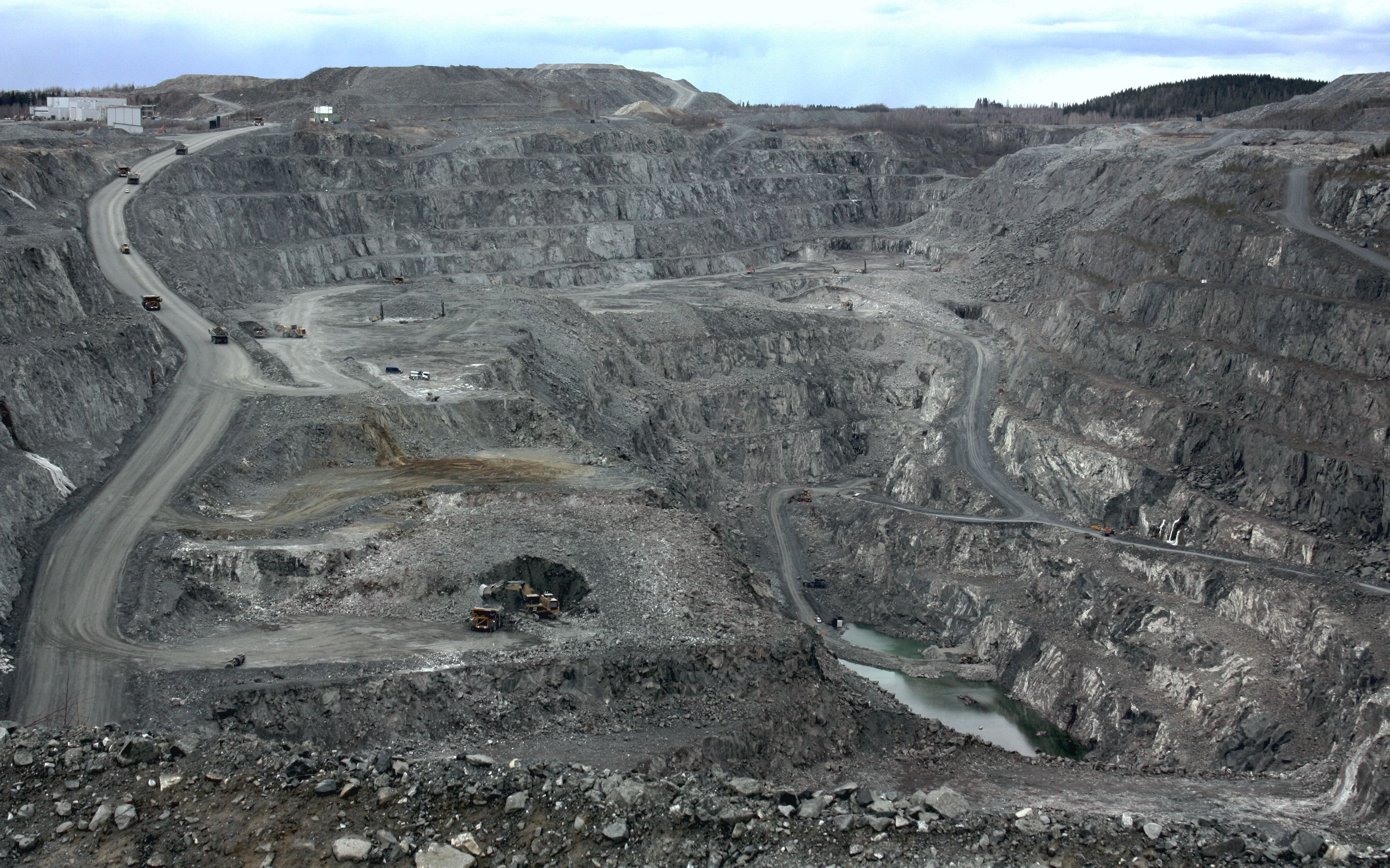 Mining exists in many countries.
Mining exists in many countries.
Industry in Transition: A Profile of the North American Mining Sector
Free full-text
The US mining industry is also large, but it is dominated by extraction of coal and other nonmetal minerals (e.g., rock and sand), and various regulations have worked to reduce the significance of mining in the United States. In 2007, the total market capitalization of mining companies was reported at US$962 billion, which compares to a total global market cap of publicly traded companies of about US$50 trillion in 2007. In 2002, Chile and Peru were reportedly the major mining countries of While exploration and mining can be conducted by individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, most modern-day mines are large enterprises requiring large amounts of capital to establish. Consequently, the mining sector of the industry is dominated by large, often multinational, companies, most of them publicly listed. It can be argued that what is referred to as the 'mining industry' is actually two sectors, one specializing in exploration for new resources and the other in mining those resources. The exploration sector is typically made up of individuals and small mineral resource companies, called "juniors", which are dependent on venture capital. The mining sector is made up of large multinational companies that are sustained by production from their mining operations. Various other industries such as equipment manufacture, environmental testing, and metallurgy analysis rely on, and support, the mining industry throughout the world. Canadian stock exchanges have a particular focus on mining companies, particularly junior exploration companies through Toronto's TSX Venture Exchange; Canadian companies raise capital on these exchanges and then invest the money in exploration globally. Some have argued that below juniors there exists a substantial sector of illegitimate companies primarily focused on manipulating stock prices.
Mining operations can be grouped into five major categories in terms of their respective resources. These are oil and gas extraction, coal mining, metal ore mining, nonmetallic mineral mining and quarrying, and mining support activities. Of all of these categories, oil and gas extraction remains one of the largest in terms of its global economic importance. Prospecting potential mining sites, a vital area of concern for the mining industry, is now done using sophisticated new technologies such as seismic prospecting and remote-sensing satellites. Mining is heavily affected by the prices of the
While exploration and mining can be conducted by individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, most modern-day mines are large enterprises requiring large amounts of capital to establish. Consequently, the mining sector of the industry is dominated by large, often multinational, companies, most of them publicly listed. It can be argued that what is referred to as the 'mining industry' is actually two sectors, one specializing in exploration for new resources and the other in mining those resources. The exploration sector is typically made up of individuals and small mineral resource companies, called "juniors", which are dependent on venture capital. The mining sector is made up of large multinational companies that are sustained by production from their mining operations. Various other industries such as equipment manufacture, environmental testing, and metallurgy analysis rely on, and support, the mining industry throughout the world. Canadian stock exchanges have a particular focus on mining companies, particularly junior exploration companies through Toronto's TSX Venture Exchange; Canadian companies raise capital on these exchanges and then invest the money in exploration globally. Some have argued that below juniors there exists a substantial sector of illegitimate companies primarily focused on manipulating stock prices.
Mining operations can be grouped into five major categories in terms of their respective resources. These are oil and gas extraction, coal mining, metal ore mining, nonmetallic mineral mining and quarrying, and mining support activities. Of all of these categories, oil and gas extraction remains one of the largest in terms of its global economic importance. Prospecting potential mining sites, a vital area of concern for the mining industry, is now done using sophisticated new technologies such as seismic prospecting and remote-sensing satellites. Mining is heavily affected by the prices of the
 New regulations and a process of legislative reforms aim to improve the harmonization and stability of the mining sector in mineral-rich countries. New legislation for mining industry in African countries still appears to be an issue, but has the potential to be solved, when a consensus is reached on the best approach.
By the beginning of the 21st century, the booming and increasingly complex mining sector in mineral-rich countries was providing only slight benefits to local communities, especially in given the sustainability issues. Increasing debate and influence by NGOs and local communities called for new approaches which would also include disadvantaged communities, and work towards sustainable development even after mine closure (including transparency and revenue management). By the early 2000s, community development issues and resettlements became mainstream concerns in World Bank mining projects. Mining-industry expansion after mineral prices increased in 2003 and also potential fiscal revenues in those countries created an omission in the other economic sectors in terms of finances and development. Furthermore, this highlighted regional and local demand for mining revenues and an inability of sub-national governments to effectively use the revenues. The Fraser Institute (a Canadian think tank) has highlighted the environmental protection laws in developing countries, as well as voluntary efforts by mining companies to improve their environmental impact.
In 2007, the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) was mainstreamed in all countries cooperating with the World Bank in mining industry reform. The EITI operates and was implemented with the support of the EITI multi-donor trust fund, managed by the World Bank. The EITI aims to increase transparency in transactions between governments and companies in extractive industries by monitoring the revenues and benefits between industries and recipient governments. The entrance process is voluntary for each country and is monitored by multiple stakeholders including governments, private companies and civil society representatives, responsible for disclosure and dissemination of the reconciliation report; however, the competitive disadvantage of company-by-company public report is for some of the businesses in Ghana at least, the main constraint. Therefore, the outcome assessment in terms of failure or success of the new EITI regulation does not only "rest on the government's shoulders" but also on civil society and companies.
However, implementation has issues; inclusion or exclusion of artisanal mining and small-scale mining (ASM) from the EITI and how to deal with "non-cash" payments made by companies to subnational governments. Furthermore, the disproportionate revenues the mining industry can bring to the comparatively small number of people that it employs, causes other problems, like a lack of investment in other less lucrative sectors, leading to swings in government revenue because of volatility in the oil markets. Artisanal mining is clearly an issue in EITI Countries such as the Central African Republic, D.R. Congo, Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone – i.e. almost half of the mining countries implementing the EITI. Among other things, limited scope of the EITI involving disparity in terms of knowledge of the industry and negotiation skills, thus far flexibility of the policy (e.g. liberty of the countries to expand beyond the minimum requirements and adapt it to their needs), creates another risk of unsuccessful implementation. Public awareness increase, where government should act as a bridge between public and initiative for a successful outcome of the policy is an important element to be considered.
New regulations and a process of legislative reforms aim to improve the harmonization and stability of the mining sector in mineral-rich countries. New legislation for mining industry in African countries still appears to be an issue, but has the potential to be solved, when a consensus is reached on the best approach.
By the beginning of the 21st century, the booming and increasingly complex mining sector in mineral-rich countries was providing only slight benefits to local communities, especially in given the sustainability issues. Increasing debate and influence by NGOs and local communities called for new approaches which would also include disadvantaged communities, and work towards sustainable development even after mine closure (including transparency and revenue management). By the early 2000s, community development issues and resettlements became mainstream concerns in World Bank mining projects. Mining-industry expansion after mineral prices increased in 2003 and also potential fiscal revenues in those countries created an omission in the other economic sectors in terms of finances and development. Furthermore, this highlighted regional and local demand for mining revenues and an inability of sub-national governments to effectively use the revenues. The Fraser Institute (a Canadian think tank) has highlighted the environmental protection laws in developing countries, as well as voluntary efforts by mining companies to improve their environmental impact.
In 2007, the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) was mainstreamed in all countries cooperating with the World Bank in mining industry reform. The EITI operates and was implemented with the support of the EITI multi-donor trust fund, managed by the World Bank. The EITI aims to increase transparency in transactions between governments and companies in extractive industries by monitoring the revenues and benefits between industries and recipient governments. The entrance process is voluntary for each country and is monitored by multiple stakeholders including governments, private companies and civil society representatives, responsible for disclosure and dissemination of the reconciliation report; however, the competitive disadvantage of company-by-company public report is for some of the businesses in Ghana at least, the main constraint. Therefore, the outcome assessment in terms of failure or success of the new EITI regulation does not only "rest on the government's shoulders" but also on civil society and companies.
However, implementation has issues; inclusion or exclusion of artisanal mining and small-scale mining (ASM) from the EITI and how to deal with "non-cash" payments made by companies to subnational governments. Furthermore, the disproportionate revenues the mining industry can bring to the comparatively small number of people that it employs, causes other problems, like a lack of investment in other less lucrative sectors, leading to swings in government revenue because of volatility in the oil markets. Artisanal mining is clearly an issue in EITI Countries such as the Central African Republic, D.R. Congo, Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone – i.e. almost half of the mining countries implementing the EITI. Among other things, limited scope of the EITI involving disparity in terms of knowledge of the industry and negotiation skills, thus far flexibility of the policy (e.g. liberty of the countries to expand beyond the minimum requirements and adapt it to their needs), creates another risk of unsuccessful implementation. Public awareness increase, where government should act as a bridge between public and initiative for a successful outcome of the policy is an important element to be considered.
 The
The
 Included within the human rights abuses that occur during mining processes are instances of
Included within the human rights abuses that occur during mining processes are instances of
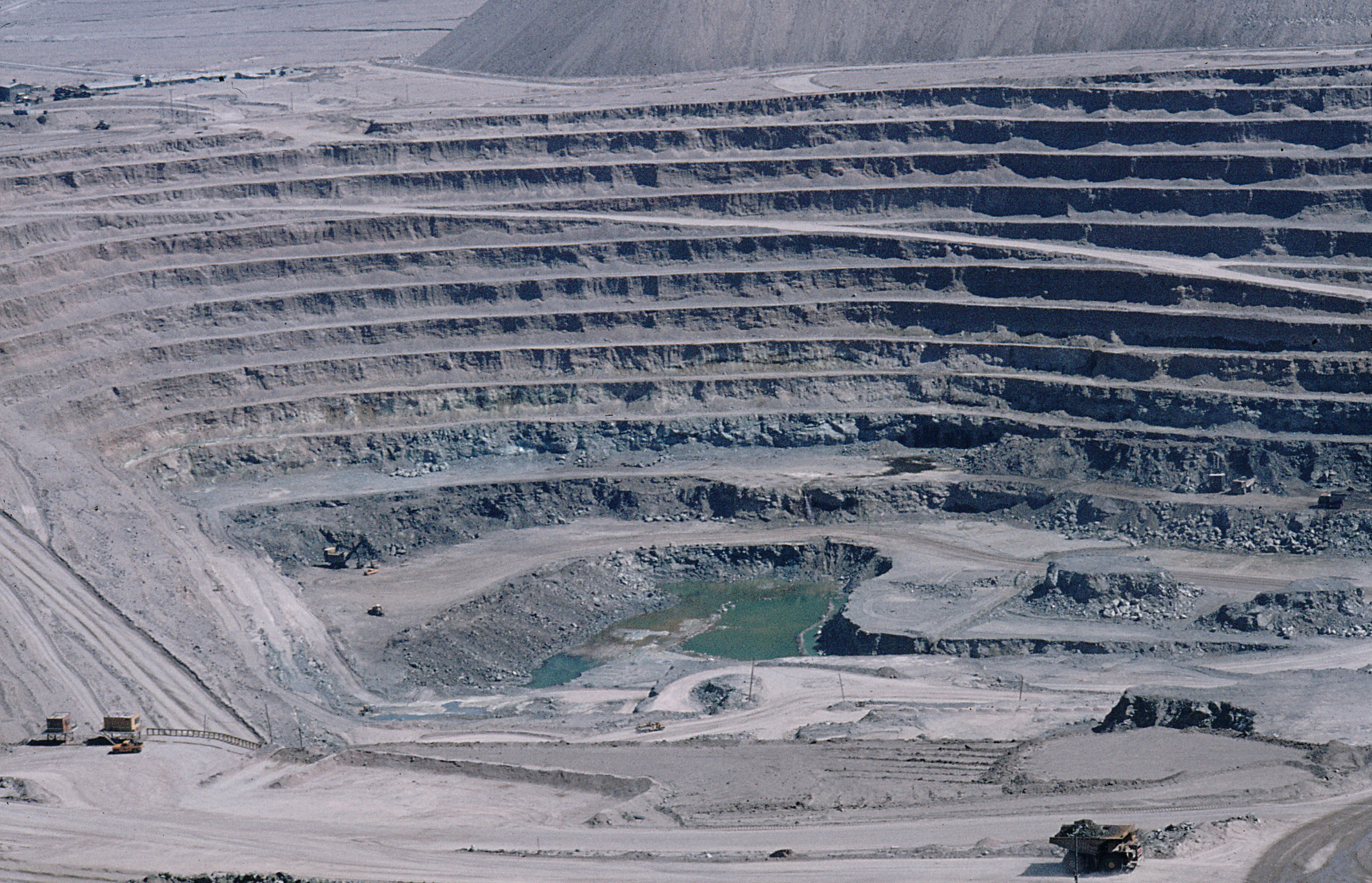 As of 2019,
As of 2019,


 During the 20th century, the variety of metals used in society grew rapidly. Today, the development of major nations such as China and India and advances in technologies are fueling an ever-greater demand. The result is that metal mining activities are expanding and more and more of the world's metal stocks are above ground in use rather than below ground as unused reserves. An example is the in-use stock of
During the 20th century, the variety of metals used in society grew rapidly. Today, the development of major nations such as China and India and advances in technologies are fueling an ever-greater demand. The result is that metal mining activities are expanding and more and more of the world's metal stocks are above ground in use rather than below ground as unused reserves. An example is the in-use stock of
2010, International Resource Panel,
Gold mines may owe their origins to bacteria
(in PDF format) * Garrett, Dennis. ''Alaska Placer Mining''. * * Morrison, Tom (1992). ''Hardrock Gold: a miner's tale''. * John Milne. ''The Miner's Handbook: A Handy Reference on the subjects of Mineral Deposits (1894) Mining operations in the 19th century.'
The Miner's Handbook: A Handy Book of Reference on the Subjects of Mineral Deposits, Mining Operations, Ore Dressing, Etc. For the Use of Students and Others Interested in Mining Matters
* Aryee, B., Ntibery, B., Atorkui, E. (2003). "Trends in the small-scale mining of precious minerals in Ghana: a perspective on its environmental impact", ''Journal of Cleaner Production'' 11: 131–40. * Temple, John (1972).
Mining: An International History
'. Ernest Benn Limited. * The Oil, gas and Mining Sustainable Community Development Fund (2009). ''Social Mine Closure Strategy, Mali'' (i
CommDev: Projects: Social Mine Closure Strategy, Mali
. * White F. (2020). ''Miner with a Heart of Gold: biography of a mineral science and engineering educator.'' Friesen Press, Victoria. ISBN 978-1-5255-7765-9 (Hardcover), 978-1-5255-7766-6 (Paperback), 978-1-5255-7767-3 (eBook).
First chapter
o
Introductory Mining Engineering
An introduction to geology and hard rock mining(archive)
* {{Authority control * Occupational safety and health Articles containing video clips
 Mining is the
Mining is the extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
of valuable mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
s or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
, seam
Seam may refer to:
Science and technology
* Seam (geology), a stratum of coal or mineral that is economically viable; a bed or a distinct layer of vein of rock in other layers of rock
* Seam (metallurgy), a metalworking process the joins the ends ...
, reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic processes—deposition (geology), deposition of ...
, or placer deposit
In geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. The name is from the Spanish language, Spanish word ''placer'', meaning "alluvium ...
. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with t ...
viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material.
Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
, oil shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitu ...
, gemstones, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
, chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Cha ...
, dimension stone
Dimension stone is natural stone or rock that has been selected and finished (e.g., trimmed, cut, drilled, ground, or other) to specific sizes or shapes. Color, texture and pattern, and surface finish of the stone are also normal requirements. ...
, rock salt, potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.
, gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classif ...
, and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physici ...
or factory
A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with t ...
. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource
A non-renewable resource (also called a finite resource) is a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption. An example is carbon-based fossil fuels. The original organic mat ...
such as petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
, or even water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
. Modern mining processes involve prospecting
Prospecting is the first stage of the geological analysis (followed by exploration) of a territory. It is the search for minerals, fossils, precious metals, or mineral specimens. It is also known as fossicking.
Traditionally prospecting rel ...
for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, and final reclamation or restoration of the land after the mine is closed.
Mining operations can create a negative environmental impact, both during the mining activity and after the mine has closed. Hence, most of the world's nations have passed regulations
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. F ...
to decrease the impact; however, the outsized role of mining in generating business for often rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are descri ...
, remote or economically depressed communities means that governments may fail to fully enforce such regulations. Work safety has long been a concern as well, and where enforcing modern practices have significantly improved safety in mines. Moreover, unregulated or poorly regulated mining, especially in developing economies, frequently contributes to local human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
violations and resource conflicts.
History
Prehistory
Since the beginning of civilization, people have usedstone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
and, later, metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
s found close to the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
's surface. These were used to make early tool
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ba ...
s and weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, ...
s; for example, high quality flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
found in northern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, southern England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
was used to create flint tools. Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
mines have been found in chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Cha ...
areas where seams of the stone were followed underground by shafts and galleries. The mines at Grimes Graves and Krzemionki are especially famous, and like most other flint mines, are Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
in origin (c. 4000–3000 BC). Other hard rocks mined or collected for axes included the greenstone of the Langdale axe industry based in the English Lake District.
The oldest-known mine on archaeological record is the Ngwenya Mine in Eswatini (Swaziland), which radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
shows to be about 43,000 years old. At this site Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
humans mined hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of ...
to make the red pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic comp ...
ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produce ...
. Mines of a similar age in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
are believed to be sites where Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While ...
s may have mined flint for weapons and tools.
Ancient Egypt
 Ancient Egyptians mined malachite at
Ancient Egyptians mined malachite at Maadi
Maadi ( ar, المعادي / transliterated: ) is a leafy suburban district south of Cairo, Egypt, on the east bank of the Nile about upriver from downtown Cairo. The Nile at Maadi is parallelled by the Corniche, a waterfront promenade ...
. At first, Egyptians used the bright green malachite stones for ornamentations and pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and po ...
. Later, between 2613 and 2494 BC, large building projects required expeditions abroad to the area of Wadi Maghareh in order to secure minerals and other resources not available in Egypt itself.Shaw, I. (2000). ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt''. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 108. Quarries for turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of y ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
were also found at Wadi Hammamat, Tura, Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ar, أسوان, ʾAswān ; cop, Ⲥⲟⲩⲁⲛ ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of ...
and various other Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin language, Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue ...
n sites on the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a ...
and at Timna.
Mining in Egypt
Mining in Egypt has had a long history that dates back to predynastic times. Active mining began in Egypt around 3000 BCE. Egypt has substantial mineral resources, including 48 million tons of tantalite (fourth largest in the world), 50 ...
occurred in the earliest dynasties. The gold mines of Nubia were among the largest and most extensive of any in Ancient Egypt. These mines are described by the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
author Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
, who mentions fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of traditional mining used most commonly from prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with liquid, causing the stone to fracture by therm ...
as one method used to break down the hard rock holding the gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
. One of the complexes is shown in one of the earliest known maps. The miners crushed the ore and ground it to a fine powder before washing the powder for the gold dust.
Ancient Greece and Rome
 Mining in Europe has a very long history. Examples include the silver mines of Laurium, which helped support the Greek city state of
Mining in Europe has a very long history. Examples include the silver mines of Laurium, which helped support the Greek city state of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
. Although they had over 20,000 slaves working them, their technology was essentially identical to their Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
predecessors. At other mines, such as on the island of Thassos, marble was quarried by the Parians after they arrived in the 7th century BC. The marble was shipped away and was later found by archaeologists to have been used in buildings including the tomb of Amphipolis. Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
, the father of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, captured the gold mines of Mount Pangeo in 357 BC to fund his military campaigns. He also captured gold mines in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
for minting coinage, eventually producing 26 tons per year.
However, it was the Romans who developed large-scale mining methods, especially the use of large volumes of water brought to the minehead by numerous aqueducts. The water was used for a variety of purposes, including removing overburden and rock debris, called hydraulic mining, as well as washing comminuted
Comminuted may refer to:
*Comminution, the process in which solid materials are reduced in size, by crushing, grinding and other processes
*Bone fracture, as in a crushed or splintered bone
*Comminuted skull fracture
A skull fracture is a break ...
, or crushed, ores and driving simple machinery.
The Romans used hydraulic mining methods on a large scale to prospect for the veins of ore, especially using a now-obsolete form of mining known as hushing
Hushing is an ancient and historic mining method using a flood or torrent of water to reveal mineral veins. The method was applied in several ways, both in prospecting for ores, and for their exploitation. Mineral veins are often hidden below ...
. They built numerous aqueducts to supply water to the minehead, where the water was stored in large reservoirs and tanks. When a full tank was opened, the flood of water sluice
Sluice ( ) is a word for a channel controlled at its head by a movable gate which is called a sluice gate. A sluice gate is traditionally a wood or metal barrier sliding in grooves that are set in the sides of the waterway and can be considered ...
d away the overburden
In mining, overburden (also called waste or spoil) is the material that lies above an area that lends itself to economical exploitation, such as the rock, soil, and ecosystem that lies above a coal seam or ore body. Overburden is distinct from t ...
to expose the bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid rock that lies under loose material ( regolith) within the crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface material. An exposed portion of be ...
underneath and any gold-bearing veins. The rock was then worked by fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of traditional mining used most commonly from prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with liquid, causing the stone to fracture by therm ...
to heat the rock, which would be quenched with a stream of water. The resulting thermal shock
Thermal shock is a type of rapidly transient mechanical load.
By definition, it is a mechanical load caused by a rapid change of temperature of a certain point.
It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient, which makes different pa ...
cracked the rock, enabling it to be removed by further streams of water from the overhead tanks. The Roman miners used similar methods to work cassiterite deposits in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlan ...
and lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
ore in the Pennines.
Sluicing methods were developed by the Romans in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
in 25 AD to exploit large alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Al ...
gold deposits, the largest site being at Las Medulas, where seven long aqueducts tapped local rivers and sluiced the deposits. The Romans also exploited the silver present in the argentiferous galena in the mines of Cartagena (''Cartago Nova''), Linares Linares may refer to:
People
*Fernando de Alencastre, 1st Duke of Linares (1641–1717), Spanish nobleman and military officer; viceroy of New Spain from 1711 to 1716
*Andreu Linares (born 1975), Spanish futsal player
* Art Linares, American polit ...
(''Castulo''), Plasenzuela and Azuaga
Azuaga () is a town located in the province of Badajoz in southern Extremadura, bordering the Andalusian provinces of Seville and Córdoba in Spain. Azuga is 140 km from Badajoz, 125 km from Córdoba, and 140 km from Seville, in ...
, among many others. Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
was one of the most important mining regions, but all regions of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
were exploited. In Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
the natives had mined minerals for millennia, but after the Roman conquest, the scale of the operations increased dramatically, as the Romans needed Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Gr ...
's resources, especially gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, tin, and lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
.
Roman techniques were not limited to surface mining. They followed the ore veins underground once opencast mining was no longer feasible. At Dolaucothi they stoped out the veins and drove adits through bare rock to drain the stopes. The same adits were also used to ventilate the workings, especially important when fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of traditional mining used most commonly from prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with liquid, causing the stone to fracture by therm ...
was used. At other parts of the site, they penetrated the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
Th ...
and dewatered the mines using several kinds of machines, especially reverse overshot water-wheels. These were used extensively in the copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
mines at Rio Tinto in Spain, where one sequence comprised 16 such wheels arranged in pairs, and lifting water about . They were worked as treadmills with miners standing on the top slats. Many examples of such devices have been found in old Roman mines and some examples are now preserved in the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
and the National Museum of Wales.
Medieval Europe

 Mining as an industry underwent dramatic changes in
Mining as an industry underwent dramatic changes in medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The mining industry in the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
was mainly focused on the extraction of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
. Other precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lu ...
s were also used, mainly for gilding or coinage. Initially, many metals were obtained through open-pit mining
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow.
This form of min ...
, and ore was primarily extracted from shallow depths, rather than through deep mine shafts. Around the 14th century, the growing use of weapons
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
, armour
Armour (British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specificall ...
, stirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ...
s, and horseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human ...
s greatly increased the demand for iron. Medieval knights
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the G ...
, for example, were often laden with up to of plate or chain link armour in addition to sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed t ...
s, lances and other weapons. The overwhelming dependency on iron for military purposes spurred iron production and extraction processes.
The silver crisis of 1465 occurred when all mines had reached depths at which the shafts could no longer be pumped dry with the available technology. Although an increased use of banknote
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable instrument, negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes w ...
s, credit and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
during this period did decrease the value of, and dependence on, precious metals, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
still remained vital to the story of medieval mining.
Due to differences in the social structure of society, the increasing extraction of mineral deposits spread from central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
to England in the mid-sixteenth century. On the continent, mineral deposits belonged to the crown, and this regalian right was stoutly maintained. But in England, royal mining rights were restricted to gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
(of which England had virtually no deposits) by a judicial decision of 1568 and a law in 1688. England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
had iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
, and tin ores. Landlords who owned the base metals and coal under their estates then had a strong inducement to extract these metals or to lease the deposits and collect royalties from mine operators. English, German, and Dutch capital combined to finance extraction and refining
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
. Hundreds of German technicians and skilled workers were brought over; in 1642 a colony of 4,000 foreigners was mining and smelting copper at Keswick in the northwestern mountains.
Use of water power in the form of water mill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the productio ...
s was extensive. The water mills were employed in crushing ore, raising ore from shafts, and ventilating galleries by powering giant bellows. Black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate ( saltpeter) ...
was first used in mining in Selmecbánya, Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephe ...
(now Banská Štiavnica, Slovakia) in 1627. Black powder allowed blasting of rock and earth to loosen and reveal ore veins. Blasting was much faster than fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of traditional mining used most commonly from prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with liquid, causing the stone to fracture by therm ...
and allowed the mining of previously impenetrable metals and ores. In 1762, the world's first mining academy was established in the same town there.
The widespread adoption of agricultural innovations such as the iron plowshare, as well as the growing use of metal as a building material, was also a driving force in the tremendous growth of the iron industry during this period. Inventions like the arrastra were often used by the Spanish to pulverize ore after being mined. This device was powered by animals and used the same principles used for grain threshing.
Much of the knowledge of medieval mining techniques comes from books such as Biringuccio
Vannoccio Biringuccio, sometimes spelled Vannocio Biringuccio (c. 1480 – c. 1539), was an Italian metallurgist. He is best known for his manual on metalworking, ''De la pirotechnia'', published posthumously in 1540.
20th Century translation by ...
's '' De la pirotechnia'' and probably most importantly from Georg Agricola's '' De re metallica'' (1556). These books detail many different mining methods used in German and Saxon mines. A prime issue in medieval mines, which Agricola explains in detail, was the removal of water from mining shafts. As miners dug deeper to access new veins, flooding became a very real obstacle. The mining industry became dramatically more efficient and prosperous with the invention of mechanically- and animal-driven pumps.
Africa
Iron metallurgy in Africa dates back over four thousand years. Gold became an important commodity for Africa during the trans-Saharan gold trade from the 7th century to the 14th century. Gold was often traded to Mediterranean economies that demanded gold and could supplysalt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quanti ...
, even though much of Africa was abundant with salt due to the mines and resources in the Sahara desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
. The trading of gold for salt was mostly used to promote trade between the different economies. Since the 19th century, gold and diamond mining in Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number ...
has had major political and economic impacts. The Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
is the largest producer of diamonds in Africa, with an estimated 12 million carats in 2019. Other types of mining reserves in Africa include cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, ...
, bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
, iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the ...
, coal, and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
.
Oceania
Gold and coal mining started in Australia and New Zealand in the 19th century.Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
has become important in the economy of New Caledonia.
In Fiji, in 1934, the Emperor Gold Mining Company Ltd. established operations at Vatukoula, followed in 1935 by the Loloma Gold Mines, N.L., and then by Fiji Mines Development Ltd. (aka Dolphin Mines Ltd.). These developments ushered in a “mining boom”, with gold production rising more than a hundred-fold, from 931.4 oz in 1934 to 107,788.5 oz in 1939, an order of magnitude then comparable to the combined output of New Zealand and Australia's eastern states.
Americas
 During prehistoric times, early Americans mined large amounts of
During prehistoric times, early Americans mined large amounts of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
along Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh w ...
's Keweenaw Peninsula and in nearby Isle Royale; metallic copper was still present near the surface in colonial times.Lankton, L. (1991). ''Cradle to Grave: Life, Work, and Death at the Lake Superior Copper Mines''. New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 5–6.West, G.A. (1970). ''Copper: its mining and use by the aborigines of the Lake Superior Region''. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press.Ricard, T. A. (1932), ''A History of American Mining'', McGraw-Hill Book Company. Indigenous peoples used Lake Superior copper from at least 5,000 years ago; copper tools, arrowheads, and other artifacts that were part of an extensive native trade-network have been discovered. In addition, obsidian, flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
, and other minerals were mined, worked, and traded. Early French explorers who encountered the sites made no use of the metals due to the difficulties of transporting them, but the copper was eventually traded throughout the continent along major river routes.  In the early colonial history of the Americas, "native gold and silver was quickly expropriated and sent back to Spain in fleets of gold- and silver-laden galleons", the gold and silver originating mostly from mines in Central and South America.
In the early colonial history of the Americas, "native gold and silver was quickly expropriated and sent back to Spain in fleets of gold- and silver-laden galleons", the gold and silver originating mostly from mines in Central and South America. Turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of y ...
dated at 700 AD was mined in pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
America; in the Cerillos Mining District in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, an estimate of "about 15,000 tons of rock had been removed from Mt. Chalchihuitl using stone tools before 1700."
In 1727 Louis Denys (Denis) (1675–1741), sieur de La Ronde – brother of Simon-Pierre Denys de Bonaventure and the son-in-law of René Chartier – took command of Fort La Pointe
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
at Chequamegon Bay; where natives informed him of an island of copper. La Ronde obtained permission from the French crown to operate mines in 1733, becoming "the first practical miner on Lake Superior"; seven years later, mining was halted by an outbreak between Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin (; Dakota language, Dakota: Help:IPA, /otʃʰeːtʰi ʃakoːwĩ/) are groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes and First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in North America. The ...
and Chippewa tribes.
Mining in the United States became widespread in the 19th century, and the United States Congress passed the General Mining Act of 1872 to encourage mining of federal lands. As with the California Gold Rush in the mid-19th century, mining for minerals and precious metals, along with ranching
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of landscape, land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are ...
, became a driving factor in the U.S. Westward Expansion
The United States of America was created on July 4, 1776, with the U.S. Declaration of Independence of thirteen British colonies in North America. In the Lee Resolution two days prior, the colonies resolved that they were free and independent ...
to the Pacific coast. With the exploration of the West, mining camps sprang up and "expressed a distinctive spirit, an enduring legacy to the new nation"; Gold Rushers would experience the same problems as the Land Rushers of the transient West that preceded them. Aided by railroads, many people traveled West for work opportunities in mining. Western cities such as Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the United ...
and Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
originated as mining towns.
When new areas were explored, it was usually the gold ( placer and then lode) and then silver that were taken into possession and extracted first. Other metals would often wait for railroads or canals, as coarse gold dust and nuggets do not require smelting and are easy to identify and transport.
Modernity
 In the early 20th century, the gold and silver rush to the western United States also stimulated mining for coal as well as
In the early 20th century, the gold and silver rush to the western United States also stimulated mining for coal as well as base metal
A base metal is a common and inexpensive metal, as opposed to a precious metal such as gold or silver. In numismatics, coins often derived their value from the precious metal content; however, base metals have also been used in coins in the past ...
s such as copper, lead, and iron. Areas in modern Montana, Utah, Arizona, and later Alaska became predominate suppliers of copper to the world, which was increasingly demanding copper for electrical and households goods.Miller C. (2013). ''Atlas of US and Canadian Environmental History''p. 64
''Taylor & Francis''. Canada's mining industry grew more slowly than did the United States' due to limitations in transportation, capital, and U.S. competition; Ontario was the major producer of the early 20th century with nickel, copper, and gold. Meanwhile, Australia experienced the
Australian gold rushes
During the Australian gold rushes, starting in 1851, significant numbers of workers moved from elsewhere in Australia and overseas to where gold had been discovered. Gold had been found several times before, but the colonial government of N ...
and by the 1850s was producing 40% of the world's gold, followed by the establishment of large mines such as the Mount Morgan Mine, which ran for nearly a hundred years, Broken Hill ore deposit (one of the largest zinc-lead ore deposits), and the iron ore mines at Iron Knob. After declines in production, another boom in mining occurred in the 1960s. Now, in the early 21st century, Australia remains a major world mineral producer.
As the 21st century begins, a globalized mining industry of large multinational corporations has arisen. Peak minerals and environmental impacts have also become a concern. Different elements, particularly rare earth mineral
A rare-earth mineral contains one or more rare-earth elements as major metal constituents. Rare-earth minerals are usually found in association with alkaline to peralkaline igneous complexes, in pegmatites associated with alkaline magmas and ...
s, have begun to increase in demand as a result of new technologies.
Mine development and life cycle
 The process of mining from discovery of an ore body through extraction of minerals and finally to returning the land to its natural state consists of several distinct steps. The first is discovery of the ore body, which is carried out through
The process of mining from discovery of an ore body through extraction of minerals and finally to returning the land to its natural state consists of several distinct steps. The first is discovery of the ore body, which is carried out through prospecting
Prospecting is the first stage of the geological analysis (followed by exploration) of a territory. It is the search for minerals, fossils, precious metals, or mineral specimens. It is also known as fossicking.
Traditionally prospecting rel ...
or exploration
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
to find and then define the extent, location and value of the ore body. This leads to a mathematical resource estimation to estimate the size and grade of the deposit.
This estimation is used to conduct a pre-feasibility study to determine the theoretical economics of the ore deposit. This identifies, early on, whether further investment in estimation and engineering studies is warranted and identifies key risks and areas for further work. The next step is to conduct a feasibility study
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a project or system. A feasibility study aims to objectively and rationally uncover the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture, opportunities and threats pr ...
to evaluate the financial viability, the technical and financial risks, and the robustness of the project.
This is when the mining company makes the decision whether to develop the mine or to walk away from the project. This includes mine planning to evaluate the economically recoverable portion of the deposit, the metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
and ore recoverability, marketability and payability of the ore concentrates, engineering concerns, milling and infrastructure costs, finance and equity requirements, and an analysis of the proposed mine from the initial excavation all the way through to reclamation. The proportion of a deposit that is economically recoverable is dependent on the enrichment factor Enrichment factor is used to describe bodies of mineral ore. It is defined as the minimum factor by which the weight percent of mineral in an orebody is greater than the average occurrence of that mineral in the Earth's crust. It can be used to com ...
of the ore in the area.
To gain access to the mineral deposit within an area it is often necessary to mine through or remove waste material
Waste comes in many different forms and may be categorized in a variety of ways. The types listed here are not necessarily exclusive and there may be considerable overlap so that one waste entity may fall into one to many types.
* Agricultural ...
which is not of immediate interest to the miner. The total movement of ore and waste constitutes the mining process. Often more waste than ore is mined during the life of a mine, depending on the nature and location of the ore body. Waste removal and placement is a major cost to the mining operator, so a detailed characterization of the waste material forms an essential part of the geological exploration program for a mining operation.
Once the analysis determines a given ore body is worth recovering, development begins to create access to the ore body. The mine buildings and processing plants are built, and any necessary equipment is obtained. The operation of the mine to recover the ore begins and continues as long as the company operating the mine finds it economical to do so. Once all the ore that the mine can produce profitably is recovered, reclamation can begin, to make the land used by the mine suitable for future use.
Technical and economic challenges notwithstanding, successful mine development must also address human factors. Working conditions are paramount to success, especially with regard to exposures to dusts, radiation, noise, explosives hazards, and vibration, as well as illumination standards. Mining today increasingly must address environmental and community impacts, including psychological and sociological dimensions. Thus, mining educator Frank T. M. White (1909–1971), broadened the focus to the “total environment of mining”, including reference to community development around mining, and how mining is portrayed to an urban society, which depends on the industry, although seemingly unaware of this dependency. He stated, “ the past, mining engineers have not been called upon to study the psychological, sociological and personal problems of their own industry – aspects that nowadays are assuming tremendous importance. The mining engineer must rapidly expand his knowledge and his influence into these newer fields.”
Techniques
 Mining techniques can be divided into two common
Mining techniques can be divided into two common excavation
Excavation may refer to:
* Excavation (archaeology)
* Excavation (medicine)
* ''Excavation'' (The Haxan Cloak album), 2013
* ''Excavation'' (Ben Monder album), 2000
* ''Excavation'' (novel), a 2000 novel by James Rollins
* '' Excavation: A Memo ...
types: surface mining and sub-surface (underground) mining. Today, surface mining is much more common, and produces, for example, 85% of minerals (excluding petroleum and natural gas) in the United States, including 98% of metallic ores.
Targets are divided into two general categories of materials: ''placer deposits'', consisting of valuable minerals contained within river gravels, beach sands, and other unconsolidated materials; and ''lode deposits'', where valuable minerals are found in veins, in layers, or in mineral grains generally distributed throughout a mass of actual rock. Both types of ore deposit, placer or lode, are mined by both surface and underground methods.
Some mining, including much of the rare earth elements and uranium mining, is done by less-common methods, such as in-situ leaching: this technique involves digging neither at the surface nor underground. The extraction of target minerals by this technique requires that they be soluble, e.g., potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.
, potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
, sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35 ...
, sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 mill ...
, which dissolve in water. Some minerals, such as copper minerals and uranium oxide, require acid or carbonate solutions to dissolve.
Artisanal
Surface
Surface mining is done by removing surface vegetation, dirt, and bedrock to reach buried ore deposits. Techniques of surface mining include:open-pit mining
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow.
This form of min ...
, which is the recovery of materials from an open pit in the ground; quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some juri ...
ing, identical to open-pit mining except that it refers to sand, stone and clay; strip mining, which consists of stripping surface layers off to reveal ore underneath; and mountaintop removal, commonly associated with coal mining, which involves taking the top of a mountain off to reach ore deposits at depth. Most placer deposits, because they are shallowly buried, are mined by surface methods. Finally, landfill mining involves sites where landfills are excavated and processed. Landfill mining has been thought of as a long-term solution to methane emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane ...
and local pollution.
High wall
 High wall mining, which evolved from auger mining, is another form of surface mining. In high wall mining, the remaining part of a coal seam previously exploited by other surface-mining techniques has too much overburden to be removed but can still be profitably exploited from the side of the artificial cliff made by previous mining. A typical cycle alternates sumping, which undercuts the seam, and shearing, which raises and lowers the cutter-head boom to cut the entire height of the coal seam. As the coal recovery cycle continues, the cutter-head is progressively launched further into the coal seam. High wall mining can produce thousands of tons of coal in contour-strip operations with narrow benches, previously mined areas, trench mine applications and steep-dip seams.
High wall mining, which evolved from auger mining, is another form of surface mining. In high wall mining, the remaining part of a coal seam previously exploited by other surface-mining techniques has too much overburden to be removed but can still be profitably exploited from the side of the artificial cliff made by previous mining. A typical cycle alternates sumping, which undercuts the seam, and shearing, which raises and lowers the cutter-head boom to cut the entire height of the coal seam. As the coal recovery cycle continues, the cutter-head is progressively launched further into the coal seam. High wall mining can produce thousands of tons of coal in contour-strip operations with narrow benches, previously mined areas, trench mine applications and steep-dip seams.
Underground mining

 Sub-surface mining consists of digging tunnels or shafts into the earth to reach buried ore deposits. Ore, for processing, and waste rock, for disposal, are brought to the surface through the tunnels and shafts. Sub-surface mining can be classified by the type of access shafts used, and the extraction method or the technique used to reach the mineral deposit. Drift mining uses horizontal access tunnels, slope mining uses diagonally sloping access shafts, and
Sub-surface mining consists of digging tunnels or shafts into the earth to reach buried ore deposits. Ore, for processing, and waste rock, for disposal, are brought to the surface through the tunnels and shafts. Sub-surface mining can be classified by the type of access shafts used, and the extraction method or the technique used to reach the mineral deposit. Drift mining uses horizontal access tunnels, slope mining uses diagonally sloping access shafts, and shaft mining
Shaft mining or shaft sinking is the action of excavating a mine shaft from the top down, where there is initially no access to the bottom. Shallow shafts, typically sunk for civil engineering projects, differ greatly in execution method from ...
uses vertical access shafts. Mining in hard and soft rock formations requires different techniques.
Other methods include shrinkage stope mining, which is mining upward, creating a sloping underground room, long wall mining, which is grinding a long ore surface underground, and room and pillar mining, which is removing ore from rooms while leaving pillars in place to support the roof of the room. Room and pillar mining often leads to retreat mining
Retreat mining is the removal of pillars in the underground mining technique known as room and pillar mining.
In the first phase of room and pillar mining, tunnels are advanced into the coal or ore body in a rectangular pattern resembling city ...
, in which supporting pillars are removed as miners retreat, allowing the room to cave in, thereby loosening more ore. Additional sub-surface mining methods include hard rock mining
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also i ...
, bore hole mining, drift and fill mining, long hole slope mining, sub level caving, and block caving.
Machines

 Heavy machinery is used in mining to explore and develop sites, to remove and stockpile overburden, to break and remove rocks of various hardness and toughness, to process the ore, and to carry out reclamation projects after the mine is closed. Bulldozers, drills, explosives and trucks are all necessary for excavating the land. In the case of
Heavy machinery is used in mining to explore and develop sites, to remove and stockpile overburden, to break and remove rocks of various hardness and toughness, to process the ore, and to carry out reclamation projects after the mine is closed. Bulldozers, drills, explosives and trucks are all necessary for excavating the land. In the case of placer mining
Placer mining () is the mining of stream bed ( alluvial) deposits for minerals. This may be done by open-pit (also called open-cast mining) or by various surface excavating equipment or tunneling equipment.
Placer mining is frequently used for ...
, unconsolidated gravel, or alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
, is fed into machinery consisting of a hopper and a shaking screen or trommel which frees the desired minerals from the waste gravel. The minerals are then concentrated using sluices or jigs.
Large drills
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to i ...
are used to sink shafts, excavate stopes, and obtain samples for analysis. Tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
s are used to transport miners, minerals and waste. Lifts carry miners into and out of mines, and move rock and ore out, and machinery in and out, of underground mines. Huge trucks, shovels and cranes are employed in surface mining to move large quantities of overburden and ore. Processing plants use large crushers, mills, reactors, roasters and other equipment to consolidate the mineral-rich material and extract the desired compounds and metals from the ore.
Processing
Once the mineral is extracted, it is often then processed. The science ofextractive metallurgy
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, wa ...
is a specialized area in the science of metallurgy that studies the extraction of valuable metals from their ores, especially through chemical or mechanical means.
Mineral processing
In the field of extractive metallurgy, mineral processing, also known as ore dressing, is the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores.
History
Before the advent of heavy machinery the raw ore was broken up using ...
(or mineral dressing) is a specialized area in the science of metallurgy that studies the mechanical means of crushing, grinding, and washing that enable the separation (extractive metallurgy) of valuable metals or minerals from their gangue (waste material). Processing of placer ore material consists of gravity-dependent methods of separation, such as sluice
Sluice ( ) is a word for a channel controlled at its head by a movable gate which is called a sluice gate. A sluice gate is traditionally a wood or metal barrier sliding in grooves that are set in the sides of the waterway and can be considered ...
boxes. Only minor shaking or washing may be necessary to disaggregate (unclump) the sands or gravels before processing. Processing of ore from a lode mine, whether it is a surface or subsurface mine, requires that the rock ore be crushed and pulverized before extraction of the valuable minerals begins. After lode ore is crushed, recovery of the valuable minerals is done by one, or a combination of several, mechanical and chemical techniques.
Since most metals are present in ores as oxides or sulfides, the metal needs to be reduced to its metallic form. This can be accomplished through chemical means such as smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a ...
or through electrolytic reduction, as in the case of aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in AmE, American and CanE, Canadian English) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately o ...
. Geometallurgy combines the geologic sciences with extractive metallurgy and mining.
In 2018, led by Chemistry and Biochemistry professor Bradley D. Smith, University of Notre Dame
The University of Notre Dame du Lac, known simply as Notre Dame ( ) or ND, is a private Catholic university, Catholic research university in Notre Dame, Indiana, outside the city of South Bend, Indiana, South Bend. French priest Edward Sorin fo ...
researchers "invented a new class of molecules whose shape and size enable them to capture and contain precious metal ions," reported in a study published by the Journal of the American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytica ...
. The new method "converts gold-containing ore into chloroauric acid and extracts it using an industrial solvent. The container molecules are able to selectively separate the gold from the solvent without the use of water stripping." The newly developed molecules can eliminate water stripping, whereas mining traditionally "relies on a 125-year-old method that treats gold-containing ore with large quantities of poisonous sodium cyanide
Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula Na C N. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its h ...
... this new process has a milder environmental impact and that, besides gold, it can be used for capturing other metals such as platinum and palladium," and could also be used in urban mining processes that remove precious metals from wastewater streams.
Environmental effects
Environmental regulation
 Mine operators frequently have to follow some regulatory practices to minimize environmental impact and avoid impacting human health. In better regulated economies, regulations require the common steps of
Mine operators frequently have to follow some regulatory practices to minimize environmental impact and avoid impacting human health. In better regulated economies, regulations require the common steps of environmental impact assessment
Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) is the assessment of the environmental consequences of a plan, policy, program, or actual projects prior to the decision to move forward with the proposed action. In this context, the term "environmental imp ...
, development of environmental management
Environmental resource management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims ...
plans, mine closure planning {{No footnotes, date=July 2009
Mine closure planning involves planning effectively for the after-mining landscape – all activities required before, during, and after the operating life of a mine that are needed to produce an acceptable landscape ...
(which must be done before the start of mining operations), and environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring describes the processes and activities that need to take place to characterize and monitor the quality of the environment. Environmental monitoring is used in the preparation of environmental impact assessments, as well a ...
during operation and after closure. However, in some areas, particularly in the developing world, government regulations may not be well enforced.
For major mining companies and any company seeking international financing, there are a number of other mechanisms to enforce environmental standards. These generally relate to financing standards such as the Equator Principles, IFC environmental standards, and criteria for Socially responsible investing
Socially responsible investing (SRI), social investment, sustainable socially conscious, "green" or ethical investing, is any investment strategy which seeks to consider both financial return and social/environmental good to bring about so ...
. Mining companies have used this oversight from the financial sector to argue for some level of industry self-regulation.Moody R. (2007). ''Rocks and Hard Places''. Zed Books. In 1992, a Draft Code of Conduct for Transnational Corporations was proposed at the Rio Earth Summit by the UN Centre for Transnational Corporations (UNCTC), but the Business Council for Sustainable Development (BCSD) together with the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) argued successfully for self-regulation instead.
This was followed by the Global Mining Initiative which was begun by nine of the largest metals and mining companies and which led to the formation of the International Council on Mining and Metals, whose purpose was to "act as a catalyst" in an effort to improve social and environmental performance in the mining and metals industry internationally. The mining industry has provided funding to various conservation groups, some of which have been working with conservation agendas that are at odds with an emerging acceptance of the rights of indigenous people – particularly the right to make land-use decisions.
Certification of mines with good practices occurs through the International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Ar ...
(ISO). For example, ISO 9000
The ISO 9000 family is a set of five quality management systems (QMS) standards that help organizations ensure they meet customer and other Stakeholder (corporate), stakeholder needs within statutory and regulatory requirements related to a pr ...
and ISO 14001
ISO 14000 is a family of standards related to environmental management that exists to help organizations (a) minimize how their operations (processes, etc.) negatively affect the environment (i.e. cause adverse changes to air, water, or land); (b) ...
, which certify an "auditable environmental management system", involve short inspections, although they have been accused of lacking rigor. Certification is also available through Ceres' Global Reporting Initiative, but these reports are voluntary and unverified. Miscellaneous other certification programs exist for various projects, typically through nonprofit groups.
The purpose of a 2012 EPS PEAKS paper was to provide evidence on policies managing ecological costs and maximize socio-economic
Socioeconomics (also known as social economics) is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how modern societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their l ...
benefits of mining using host country regulatory initiatives. It found existing literature suggesting donors encourage developing countries to:
* Make the environment-poverty link and introduce cutting-edge wealth measures and natural capital accounts.
* Reform old taxes in line with more recent financial innovation, engage directly with the companies, enact land use and impact assessments, and incorporate specialized support and standards agencies.
* Set in play transparency and community participation initiatives using the wealth accrued.
Waste
 Ore mills generate large amounts of waste, called
Ore mills generate large amounts of waste, called tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction ( gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overl ...
. For example, 99 tons of waste is generated per ton of copper, with even higher ratios in gold mining – because only 5.3 g of gold is extracted per ton of ore, a ton of gold produces 200,000 tons of tailings. (As time goes on and richer deposits are exhausted – and technology improves – this number is going down to .5 g and less.) These tailings can be toxic. Tailings, which are usually produced as a slurry, are most commonly dumped into ponds made from naturally existing valleys.US EPA. (1994)Technical Report: Design and Evaluation of Tailings Dams
These ponds are secured by impoundments ( dams or
embankment dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface and ...
s). In 2000 it was estimated that 3,500 tailings impoundments existed, and that every year, 2 to 5 major failures and 35 minor failures occurred. For example, in the Marcopper mining disaster at least 2 million tons of tailings were released into a local river.TE Martin, MP Davies. (2000)Trends in the stewardship of tailings dams
In 2015,
Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold Corporation is a mining company that produces gold and copper with 16 operating sites in 13 countries. It is headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It has mining operations in Argentina, Canada, Chile, Côte d'Ivoire, Democrati ...
Corporation spilled over 1 million liters of cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
into a total of five rivers in Argentina near their Veladero mine
The Veladero mine is a gold mine in Argentina. The mine is located in the north-western part of Argentina in San Juan Province. The mine has estimated reserves of 10 million oz of gold. It is operated by Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold Corporation ...
. Since 2007 in central Finland, the Talvivaara Terrafame polymetal mine's waste effluent and leaks of saline mine water have resulted in ecological collapse of a nearby lake. Subaqueous tailings disposal is another option. The mining industry has argued that submarine tailings disposal (STD), which disposes of tailings in the sea, is ideal because it avoids the risks of tailings ponds. The practice is illegal in the United States and Canada, but it is used in the developing world.
The waste is classified as either sterile or mineralized, with acid generating potential, and the movement and storage of this material form a major part of the mine planning process. When the mineralised package is determined by an economic cut-off, the near-grade mineralised waste is usually dumped separately with view to later treatment should market conditions change and it becomes economically viable. Civil engineering design parameters are used in the design of the waste dumps, and special conditions apply to high-rainfall areas and to seismically active areas. Waste dump designs must meet all regulatory requirements of the country in whose jurisdiction the mine is located. It is also common practice to rehabilitate dumps to an internationally acceptable standard, which in some cases means that higher standards than the local regulatory standard are applied.
Industry
 Mining exists in many countries.
Mining exists in many countries. London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
is the headquarters for large miners such as Anglo American, BHP and Rio Tinto.MacDonald A. (2002)Industry in Transition: A Profile of the North American Mining Sector
Free full-text
The US mining industry is also large, but it is dominated by extraction of coal and other nonmetal minerals (e.g., rock and sand), and various regulations have worked to reduce the significance of mining in the United States. In 2007, the total market capitalization of mining companies was reported at US$962 billion, which compares to a total global market cap of publicly traded companies of about US$50 trillion in 2007. In 2002, Chile and Peru were reportedly the major mining countries of
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
. The mineral industry of Africa includes the mining of various minerals; it produces relatively little of the industrial metals copper, lead, and zinc, but according to one estimate has as a percent of world reserves 40% of gold, 60% of cobalt, and 90% of the world's platinum group
The platinum-group metals (abbreviated as the PGMs; alternatively, the platinoids, platinides, platidises, platinum group, platinum metals, platinum family or platinum-group elements (PGEs)) are six noble, precious metallic elements clustered to ...
metals. Mining in India is a significant part of that country's economy. In the developed world, mining in Australia, with BHP founded and headquartered in the country, and mining in Canada are particularly significant. For rare earth mineral
A rare-earth mineral contains one or more rare-earth elements as major metal constituents. Rare-earth minerals are usually found in association with alkaline to peralkaline igneous complexes, in pegmatites associated with alkaline magmas and ...
s mining, China reportedly controlled 95% of production in 2013.
 While exploration and mining can be conducted by individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, most modern-day mines are large enterprises requiring large amounts of capital to establish. Consequently, the mining sector of the industry is dominated by large, often multinational, companies, most of them publicly listed. It can be argued that what is referred to as the 'mining industry' is actually two sectors, one specializing in exploration for new resources and the other in mining those resources. The exploration sector is typically made up of individuals and small mineral resource companies, called "juniors", which are dependent on venture capital. The mining sector is made up of large multinational companies that are sustained by production from their mining operations. Various other industries such as equipment manufacture, environmental testing, and metallurgy analysis rely on, and support, the mining industry throughout the world. Canadian stock exchanges have a particular focus on mining companies, particularly junior exploration companies through Toronto's TSX Venture Exchange; Canadian companies raise capital on these exchanges and then invest the money in exploration globally. Some have argued that below juniors there exists a substantial sector of illegitimate companies primarily focused on manipulating stock prices.
Mining operations can be grouped into five major categories in terms of their respective resources. These are oil and gas extraction, coal mining, metal ore mining, nonmetallic mineral mining and quarrying, and mining support activities. Of all of these categories, oil and gas extraction remains one of the largest in terms of its global economic importance. Prospecting potential mining sites, a vital area of concern for the mining industry, is now done using sophisticated new technologies such as seismic prospecting and remote-sensing satellites. Mining is heavily affected by the prices of the
While exploration and mining can be conducted by individual entrepreneurs or small businesses, most modern-day mines are large enterprises requiring large amounts of capital to establish. Consequently, the mining sector of the industry is dominated by large, often multinational, companies, most of them publicly listed. It can be argued that what is referred to as the 'mining industry' is actually two sectors, one specializing in exploration for new resources and the other in mining those resources. The exploration sector is typically made up of individuals and small mineral resource companies, called "juniors", which are dependent on venture capital. The mining sector is made up of large multinational companies that are sustained by production from their mining operations. Various other industries such as equipment manufacture, environmental testing, and metallurgy analysis rely on, and support, the mining industry throughout the world. Canadian stock exchanges have a particular focus on mining companies, particularly junior exploration companies through Toronto's TSX Venture Exchange; Canadian companies raise capital on these exchanges and then invest the money in exploration globally. Some have argued that below juniors there exists a substantial sector of illegitimate companies primarily focused on manipulating stock prices.
Mining operations can be grouped into five major categories in terms of their respective resources. These are oil and gas extraction, coal mining, metal ore mining, nonmetallic mineral mining and quarrying, and mining support activities. Of all of these categories, oil and gas extraction remains one of the largest in terms of its global economic importance. Prospecting potential mining sites, a vital area of concern for the mining industry, is now done using sophisticated new technologies such as seismic prospecting and remote-sensing satellites. Mining is heavily affected by the prices of the commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
minerals, which are often volatile. The 2000s commodities boom
The 2000s commodities boom or the commodities super cycle was the rise of many physical commodity prices (such as those of food, oil, metals, chemicals and fuels) during the early 21st century (2000–2014), following the Great Commodities Depress ...
("commodities supercycle") increased the prices of commodities, driving aggressive mining. In addition, the price of gold increased dramatically in the 2000s, which increased gold mining; for example, one study found that conversion of forest in the Amazon increased six-fold from the period 2003–2006 (292 ha/yr) to the period 2006–2009 (1,915 ha/yr), largely due to artisanal mining.
Corporate classifications
Mining companies can be classified based on their size and financial capabilities: * ''Major'' companies are considered to have an adjusted annual mining-related revenue of more than US$500 million, with the financial capability to develop a major mine on its own. * ''Intermediate'' companies have at least $50 million in annual revenue but less than $500 million. * ''Junior'' companies rely on equity financing as their principal means of funding exploration. Juniors are mainly pure exploration companies, but may also produce minimally, and do not have a revenue exceeding US$50 million. Re their valuation, and stock market characteristics, see .Regulation and governance
 New regulations and a process of legislative reforms aim to improve the harmonization and stability of the mining sector in mineral-rich countries. New legislation for mining industry in African countries still appears to be an issue, but has the potential to be solved, when a consensus is reached on the best approach.
By the beginning of the 21st century, the booming and increasingly complex mining sector in mineral-rich countries was providing only slight benefits to local communities, especially in given the sustainability issues. Increasing debate and influence by NGOs and local communities called for new approaches which would also include disadvantaged communities, and work towards sustainable development even after mine closure (including transparency and revenue management). By the early 2000s, community development issues and resettlements became mainstream concerns in World Bank mining projects. Mining-industry expansion after mineral prices increased in 2003 and also potential fiscal revenues in those countries created an omission in the other economic sectors in terms of finances and development. Furthermore, this highlighted regional and local demand for mining revenues and an inability of sub-national governments to effectively use the revenues. The Fraser Institute (a Canadian think tank) has highlighted the environmental protection laws in developing countries, as well as voluntary efforts by mining companies to improve their environmental impact.
In 2007, the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) was mainstreamed in all countries cooperating with the World Bank in mining industry reform. The EITI operates and was implemented with the support of the EITI multi-donor trust fund, managed by the World Bank. The EITI aims to increase transparency in transactions between governments and companies in extractive industries by monitoring the revenues and benefits between industries and recipient governments. The entrance process is voluntary for each country and is monitored by multiple stakeholders including governments, private companies and civil society representatives, responsible for disclosure and dissemination of the reconciliation report; however, the competitive disadvantage of company-by-company public report is for some of the businesses in Ghana at least, the main constraint. Therefore, the outcome assessment in terms of failure or success of the new EITI regulation does not only "rest on the government's shoulders" but also on civil society and companies.
However, implementation has issues; inclusion or exclusion of artisanal mining and small-scale mining (ASM) from the EITI and how to deal with "non-cash" payments made by companies to subnational governments. Furthermore, the disproportionate revenues the mining industry can bring to the comparatively small number of people that it employs, causes other problems, like a lack of investment in other less lucrative sectors, leading to swings in government revenue because of volatility in the oil markets. Artisanal mining is clearly an issue in EITI Countries such as the Central African Republic, D.R. Congo, Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone – i.e. almost half of the mining countries implementing the EITI. Among other things, limited scope of the EITI involving disparity in terms of knowledge of the industry and negotiation skills, thus far flexibility of the policy (e.g. liberty of the countries to expand beyond the minimum requirements and adapt it to their needs), creates another risk of unsuccessful implementation. Public awareness increase, where government should act as a bridge between public and initiative for a successful outcome of the policy is an important element to be considered.
New regulations and a process of legislative reforms aim to improve the harmonization and stability of the mining sector in mineral-rich countries. New legislation for mining industry in African countries still appears to be an issue, but has the potential to be solved, when a consensus is reached on the best approach.
By the beginning of the 21st century, the booming and increasingly complex mining sector in mineral-rich countries was providing only slight benefits to local communities, especially in given the sustainability issues. Increasing debate and influence by NGOs and local communities called for new approaches which would also include disadvantaged communities, and work towards sustainable development even after mine closure (including transparency and revenue management). By the early 2000s, community development issues and resettlements became mainstream concerns in World Bank mining projects. Mining-industry expansion after mineral prices increased in 2003 and also potential fiscal revenues in those countries created an omission in the other economic sectors in terms of finances and development. Furthermore, this highlighted regional and local demand for mining revenues and an inability of sub-national governments to effectively use the revenues. The Fraser Institute (a Canadian think tank) has highlighted the environmental protection laws in developing countries, as well as voluntary efforts by mining companies to improve their environmental impact.
In 2007, the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) was mainstreamed in all countries cooperating with the World Bank in mining industry reform. The EITI operates and was implemented with the support of the EITI multi-donor trust fund, managed by the World Bank. The EITI aims to increase transparency in transactions between governments and companies in extractive industries by monitoring the revenues and benefits between industries and recipient governments. The entrance process is voluntary for each country and is monitored by multiple stakeholders including governments, private companies and civil society representatives, responsible for disclosure and dissemination of the reconciliation report; however, the competitive disadvantage of company-by-company public report is for some of the businesses in Ghana at least, the main constraint. Therefore, the outcome assessment in terms of failure or success of the new EITI regulation does not only "rest on the government's shoulders" but also on civil society and companies.
However, implementation has issues; inclusion or exclusion of artisanal mining and small-scale mining (ASM) from the EITI and how to deal with "non-cash" payments made by companies to subnational governments. Furthermore, the disproportionate revenues the mining industry can bring to the comparatively small number of people that it employs, causes other problems, like a lack of investment in other less lucrative sectors, leading to swings in government revenue because of volatility in the oil markets. Artisanal mining is clearly an issue in EITI Countries such as the Central African Republic, D.R. Congo, Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone – i.e. almost half of the mining countries implementing the EITI. Among other things, limited scope of the EITI involving disparity in terms of knowledge of the industry and negotiation skills, thus far flexibility of the policy (e.g. liberty of the countries to expand beyond the minimum requirements and adapt it to their needs), creates another risk of unsuccessful implementation. Public awareness increase, where government should act as a bridge between public and initiative for a successful outcome of the policy is an important element to be considered.
World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
has been involved in mining since 1955, mainly through grants from its International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, with the Bank's Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency offering political risk insurance. Between 1955 and 1990 it provided about $2 billion to fifty mining projects, broadly categorized as reform and rehabilitation, greenfield mine construction, mineral processing, technical assistance, and engineering. These projects have been criticized, particularly the Ferro Carajas project of Brazil, begun in 1981. The World Bank established mining codes intended to increase foreign investment; in 1988, it solicited feedback from 45 mining companies on how to increase their involvement.
In 1992, the World Bank began to push for privatization of government-owned mining companies with a new set of codes, beginning with its report ''The Strategy for African Mining''. In 1997, Latin America's largest miner Companhia Vale do Rio Doce (CVRD) was privatized. These and other developments, such as the Philippines 1995 Mining Act, led the bank to publish a third report (''Assistance for Minerals Sector Development and Reform in Member Countries'') which endorsed mandatory environment impact assessments and attention to the concerns of the local population. The codes based on this report are influential in the legislation of developing nations. The new codes are intended to encourage development through tax holidays, zero custom duties, reduced income taxes, and related measures. The results of these codes were analyzed by a group from the University of Quebec, which concluded that the codes promote foreign investment but "fall very short of permitting sustainable development". The observed negative correlation between natural resources and economic development is known as the resource curse
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources (such as fossil fuels and certain minerals) having less economic growth, less democracy, or wor ...
.
Safety
Safety has long been a concern in the mining business, especially in sub-surface mining. The Courrières mine disaster, Europe's worst mining accident, involved the death of 1,099 miners in NorthernFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
on March 10, 1906. This disaster was surpassed only by the Benxihu Colliery accident in China on April 26, 1942, which killed 1,549 miners. While mining today is substantially safer than it was in previous decades, mining accidents still occur. Government figures indicate that 5,000 Chinese miners die in accidents each year, while other reports have suggested a figure as high as 20,000. Mining accidents continue worldwide, including accidents causing dozens of fatalities at a time such as the 2007 Ulyanovskaya Mine disaster in Russia, the 2009 Heilongjiang mine explosion
The 2009 Heilongjiang mine explosion () was a mining accident that occurred on November 21 2009, near Hegang in the Heilongjiang province, northeastern China, which killed 108 people. A further of 29 people were hospitalised. The explosion occurre ...
in China, and the 2010 Upper Big Branch Mine disaster
The Upper Big Branch Mine disaster occurred on April 5, 2010 roughly underground in Raleigh County, West Virginia at Massey Energy's Upper Big Branch coal mine located in Montcoal, West Virginia, Montcoal. Twenty-nine out of thirty-one miners ...
in the United States. Mining has been identified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the ...
(NIOSH) as a priority industry sector in the National Occupational Research Agenda (NORA) to identify and provide intervention strategies regarding occupational health and safety issues. The Mining Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) was established in 1978 to "work to prevent death, illness, and injury from mining and promote safe and healthful workplaces for US miners." Since its implementation in 1978, the number of miner fatalities has decreased from 242 miners in 1978 to 24 miners in 2019.
There are numerous occupational hazards associated with mining, including exposure to rockdust
Rock dust is a pulverized rock, usually limestone, sprayed on walls inside underground coal mines to prevent coal dust explosions. The dust acts as a heat sink, keeps coal dust levels down, and also prevents the incidence of black lung disease. ...
which can lead to diseases such as silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silicosi ...
, asbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart diseas ...
, and pneumoconiosis. Gases in the mine can lead to asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that ca ...
tion and could also be ignited. Mining equipment can generate considerable noise, putting workers at risk for hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
. Cave-ins, rock falls, and exposure to excess heat are also known hazards. The current NIOSH Recommended Exposure Limit (REL) of noise is 85 dBA with a 3 dBA exchange rate and the MSHA Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) is 90 dBA with a 5 dBA exchange rate as an 8-hour time-weighted average. NIOSH has found that 25% of noise-exposed workers in Mining, Quarrying, and Oil and Gas Extraction have hearing impairment. The prevalence of hearing loss increased by 1% from 1991 to 2001 within these workers.
Noise studies have been conducted in several mining environments. Stageloaders (84-102 dBA), shearers (85-99 dBA), auxiliary fans (84–120 dBA), continuous mining machines (78–109 dBA), and roof bolters (92–103 dBA) represent some of the noisiest equipment in underground coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
. Dragline
A dragline excavator is a piece of heavy equipment used in civil engineering and surface mining.
Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting cranes, and the heavy units which have to be built on-site. Mo ...
oilers, dozer operators, and welders using air arcing were occupations with the highest noise exposures among surface coal miners. Coal mines had the highest hearing loss injury likelihood.
Human rights
In addition to the environmental impacts of mining processes, a prominent criticism pertaining to this form of extractive practice and of mining companies are thehuman rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
abuses occurring within mining sites and communities close to them. Frequently, despite being protected by International Labor rights, miners are not given appropriate equipment to provide them with protection from possible mine collapse or from harmful pollutants and chemicals expelled during the mining process, work in inhumane conditions spending numerous hours working in extreme heat, darkness and 14 hour workdays with no allocated time for breaks.
Child labor
 Included within the human rights abuses that occur during mining processes are instances of
Included within the human rights abuses that occur during mining processes are instances of child labor
Child labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such ...
. These instances are a cause for widespread criticism of mines harvesting cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, ...
, a mineral essential for powering modern technologies such as laptops, smartphones
A smartphone is a Mobile device, portable computer device that combines Mobile phone, mobile telephone and Mobile computing, computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities ...
and electric vehicles. Many of these cases of child laborers are found in the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
. Reports have risen of children carrying sacks of cobalt weighing 25 kg from small mines to local traders being paid for their work only in food and accommodation. A number of companies such as Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
, Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at th ...
and Tesla have been implicated in lawsuits brought by families whose children were severely injured or killed during mining activities in Congo. In December 2019, 14 Congolese families filed a lawsuit against Glencore, a mining company which supplies the essential cobalt to these multinational corporations with allegations of negligence that led to the deaths of children or injuries such as broken spines, emotional distress and forced labor.
Indigenous peoples
There have also been instances of killings and evictions attributed to conflicts with mining companies. Almost a third of 227 murders in 2020 were of Indigenous peoples rights activists on the frontlines of climate change activism linked to logging, mining, large-scale agribusiness, hydroelectric dams, and other infrastructure, according toGlobal Witness
Global Witness is an international NGO established in 1993 that works to break the links between natural resource exploitation, conflict, poverty, corruption, and human rights abuses worldwide. The organisation has offices in London and Washi ...
.
The relationship between indigenous peoples and mining is defined by struggles over access to land. In Australia, the Aboriginal Bininj said mining posed a threat to their living culture and could damage sacred heritage sites.
In the Philippines, an anti-mining movement has raised concerns regarding "the total disregard for ndigenous communities'ancestral land rights". Ifugao peoples' opposition to mining led a governor to proclaim a ban on mining operations in Mountain Province, Philippines.
In Brazil, more than 170 tribes organized a march to oppose controversial attempts to strip back indigenous land rights and open their territories to mining operations. The United Nations Commission on Human Rights
The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006. It was a subsidiary body of ...
has called on Brazil's Supreme Court to uphold Indigenous land rights to prevent exploitation by mining groups and industrial agriculture.
Records
 As of 2019,
As of 2019, Mponeng
Mponeng is a gold mine in South Africa's Gauteng province. Previously known as Western Deep Levels #1 Shaft, the underground and surface works were commissioned in 1987. It extends over below the surface,. and is considered to be one of the most ...
is the world's deepest mine from ground level, reaching a depth of 4 km (2.5 mi) below ground level. The trip from the surface to the bottom of the mine takes over an hour. It is a gold mine Gold Mine may refer to:
* Gold Mine (board game)
*Gold Mine (Long Beach), an arena
*"Gold Mine", a song by Joyner Lucas from the 2020 album ''ADHD''
See also
* ''Gold'' (1974 film), based on the novel ''Gold Mine'' by Wilbur Smith
* Gold mining
*G ...
in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
's Gauteng
Gauteng ( ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. The name in Sotho-Tswana languages means 'place of gold'.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts for only ...
province. Previously known as Western Deep Levels #1 Shaft, the underground and surface works were commissioned in 1987. The mine is considered to be one of the most substantial gold mines in the world.
The Moab Khutsong gold mine in North West Province (South Africa)
North West is a province of South Africa. Its capital is Mahikeng. The province is located to the west of the major population centre of Gauteng and south of Botswana.
History
North West was incorporated after the end of Apartheid in 1994, a ...
has the world's longest winding steel wire rope, which is able to lower workers to in one uninterrupted four-minute journey.
The deepest mine in Europe is the 16th shaft of the uranium mines in Příbram, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
, at . Second is Bergwerk Saar in Saarland, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, at .
The deepest open-pit mine in the world is Bingham Canyon Mine in Bingham Canyon
The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest m ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, at over . The largest and second deepest open-pit copper mine in the world is Chuquicamata in northern Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
at , which annually produces 443,000 tons of copper and 20,000 tons of molybdenum.
The deepest open-pit mine with respect to sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
is Tagebau Hambach
The Tagebau Hambach is a large open-pit coal mine (german: Tagebau) in Niederzier and Elsdorf, North Rhine–Westphalia, Germany. It is operated by RWE and used for mining lignite.
The mine is on the site of the ancient Hambach Forest, wh ...
in Germany, where the base of the pit is below sea level.
The largest underground mine is Kiirunavaara Mine in Kiruna
(; se, Giron ; fi, Kiiruna ) is the northernmost city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The city was ori ...
, Sweden. With of roads, 40 million tonnes of annually produced ore, and a depth of , it is also one of the most modern underground mines. The deepest borehole in the world is Kola Superdeep Borehole at , but this is connected to scientific drilling, not mining.
Metal reserves and recycling


 During the 20th century, the variety of metals used in society grew rapidly. Today, the development of major nations such as China and India and advances in technologies are fueling an ever-greater demand. The result is that metal mining activities are expanding and more and more of the world's metal stocks are above ground in use rather than below ground as unused reserves. An example is the in-use stock of
During the 20th century, the variety of metals used in society grew rapidly. Today, the development of major nations such as China and India and advances in technologies are fueling an ever-greater demand. The result is that metal mining activities are expanding and more and more of the world's metal stocks are above ground in use rather than below ground as unused reserves. An example is the in-use stock of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
. Between 1932 and 1999, copper in use in the US rose from to per person.''The Recycling Rates of Metals: A Status Report''2010, International Resource Panel,
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
95% of the energy used to make aluminium from bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
ore is saved by using recycled material. However, levels of metals recycling are generally low. In 2010, the International Resource Panel, hosted by the United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
(UNEP), published reports on metal stocks that exist within society and their recycling rates.
The report's authors observed that the metal stocks in society can serve as huge mines above ground. However, they warned that the recycling rates of some rare metals used in applications such as mobile phones, battery packs for hybrid cars, and fuel cells are so low that unless future end-of-life recycling rates are dramatically stepped up these critical metals will become unavailable for use in modern technology.
As recycling rates are low and so much metal has already been extracted, some landfills now contain higher concentrations of metal than mines themselves. This is especially true of aluminium, used in cans, and precious metals, found in discarded electronics. Furthermore, waste after 15 years has still not broken down, so less processing would be required when compared to mining ores. A study undertaken by Cranfield University has found £360 million of metals could be mined from just four landfill sites. There is also up to 20 MJ/kg of energy in waste, potentially making the re-extraction more profitable. However, although the first landfill mine opened in Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
, Israel in 1953, little work has followed due to the abundance of accessible ores.
See also
References
Further reading
* Woytinsky, W.S., and E.S. Woytinsky (1953). ''World Population and Production Trends and Outlooks'', pp. 749–881; with many tables and maps on the worldwide mining industry in 1950, including coal, metals and minerals * Ali, Saleem H. (2003). ''Mining, the Environment and Indigenous Development Conflicts''. Tucson AZ: University of Arizona Press. * Ali, Saleem H. (2009). ''Treasures of the Earth: need, greed and a sustainable future''. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. * * Geobacter ProjectGold mines may owe their origins to bacteria
(in PDF format) * Garrett, Dennis. ''Alaska Placer Mining''. * * Morrison, Tom (1992). ''Hardrock Gold: a miner's tale''. * John Milne. ''The Miner's Handbook: A Handy Reference on the subjects of Mineral Deposits (1894) Mining operations in the 19th century.'
The Miner's Handbook: A Handy Book of Reference on the Subjects of Mineral Deposits, Mining Operations, Ore Dressing, Etc. For the Use of Students and Others Interested in Mining Matters
* Aryee, B., Ntibery, B., Atorkui, E. (2003). "Trends in the small-scale mining of precious minerals in Ghana: a perspective on its environmental impact", ''Journal of Cleaner Production'' 11: 131–40. * Temple, John (1972).
Mining: An International History
'. Ernest Benn Limited. * The Oil, gas and Mining Sustainable Community Development Fund (2009). ''Social Mine Closure Strategy, Mali'' (i
CommDev: Projects: Social Mine Closure Strategy, Mali
. * White F. (2020). ''Miner with a Heart of Gold: biography of a mineral science and engineering educator.'' Friesen Press, Victoria. ISBN 978-1-5255-7765-9 (Hardcover), 978-1-5255-7766-6 (Paperback), 978-1-5255-7767-3 (eBook).
External links
First chapter
o
Introductory Mining Engineering
An introduction to geology and hard rock mining
* {{Authority control * Occupational safety and health Articles containing video clips