|
Landfill Mining
Landfill mining and reclamation (LFMR) is a process which excavates and processes solid wastes which have previously been landfilled. The process aims to reduce the amount of landfill mass encapsulated within the closed landfill and/or temporarily remove hazardous material to allow protective measures to be taken before the landfill mass is replaced. In the process, mining recovers valuable recyclable materials, a combustible fraction, soil, and landfill space. The aeration of the landfill soil is a secondary benefit with regard to the landfill's future use. The combustible fraction is useful for power generation. The overall appearance of the landfill mining procedure is a sequence of processing machines laid out in a functional conveyor system. The operating principle is to excavate, sieve and sort the landfill material. The Hiriya landfill operated by the Dan Region Authority next to the city of Tel Aviv, Israel, introduced the concept of mining as early as 1953. Waste cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste product may become a by-product, joint product or resource through an invention that raises a waste product's value above zero. Examples include municipal solid waste (household trash/refuse), hazardous waste, wastewater (such as sewage, which contains bodily wastes ( feces and urine) and surface runoff), radioactive waste, and others. Definitions What constitutes waste depends on the eye of the beholder; one person's waste can be a resource for another person. Though waste is a physical object, its generation is a physical and psychological process. The definitions used by various agencies are as below. United Nations Environment Program According to the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
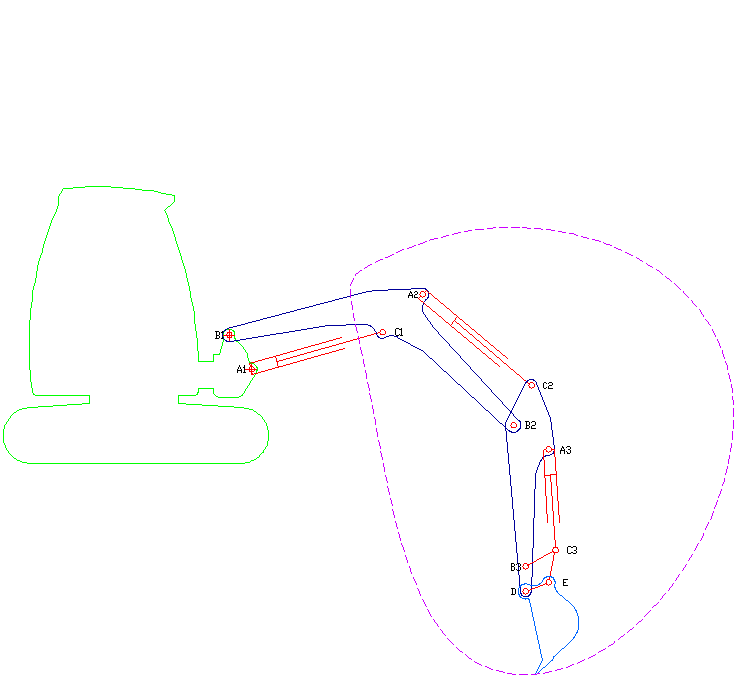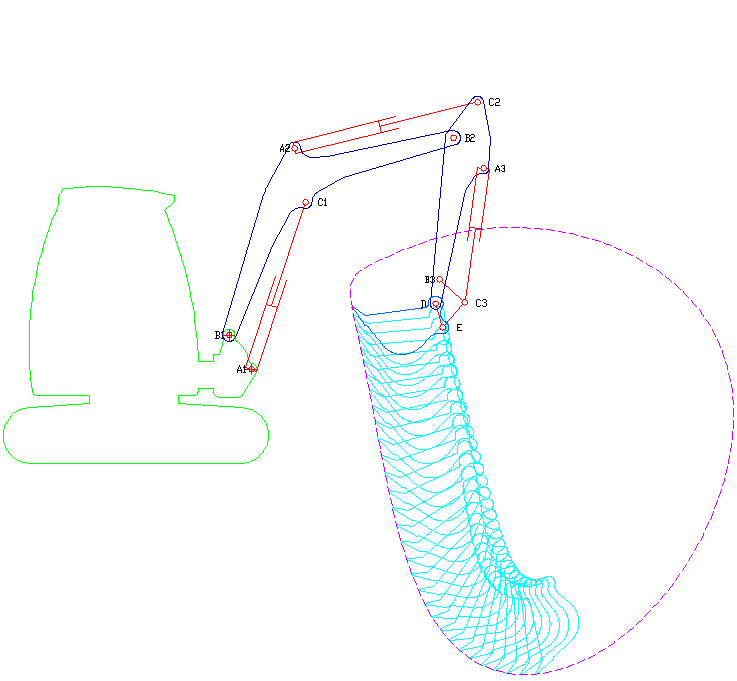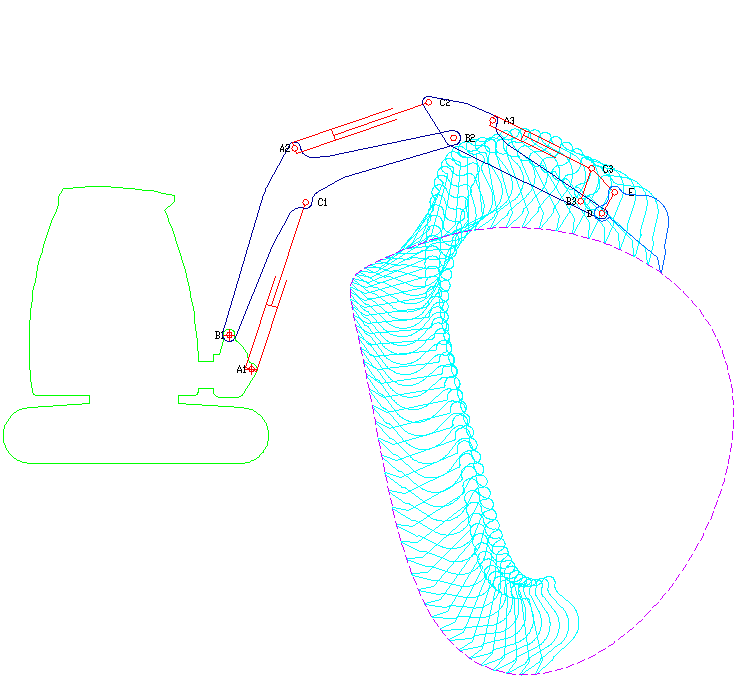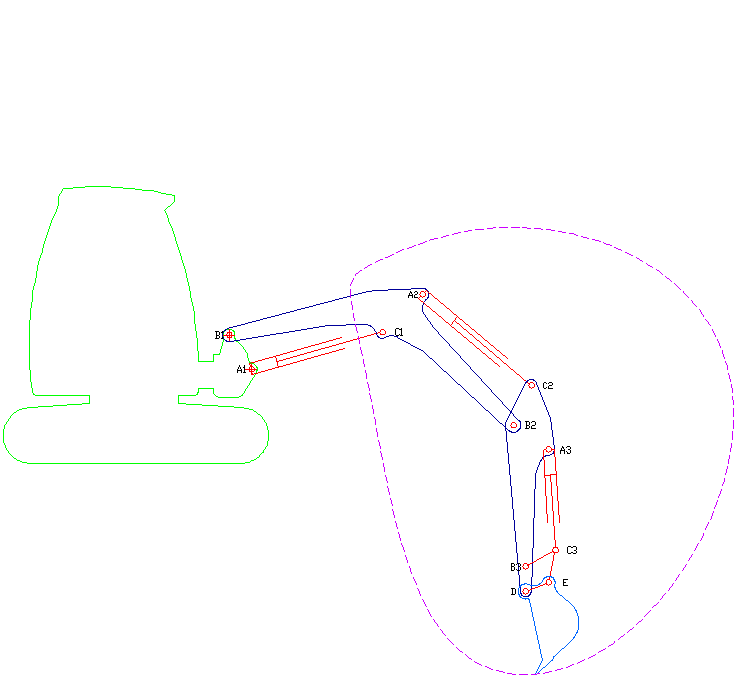
Excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression from the steam shovels and often mistakenly called power shovels. All movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors. Due to the linear actuation of hydraulic cylinders, their mode of operation is fundamentally different from cable-operated excavators which use winches and steel ropes to accomplish the movements. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, JCBs (a proprietary name, in an example of a generic trademark), mechanical shovels, or 360-degree excavators (sometimes abbreviated simply to "360"). Tracked excavators are sometimes called "trackhoes" by analogy to the backhoe. In the UK and Ireland, wheeled excavators are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytomining
Phytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless". The term is an amalgam of the Greek ''phyto'' (plant) and Latin ''remedium'' (restoring balance). Although attractive for its cost, phytoremediation has not been demonstrated to redress any significant environmental challenge to the extent that contaminated space has been reclaimed. Phytoremediation is proposed as a cost-effective plant-based approach of environmental remediation that takes advantage of the ability of plants to concentrate elements and compounds from the environment and to detoxify various compounds. The concentrating effect results from the ability of certain plants called hyperaccumulators to bioaccumulate chemicals. The remediat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
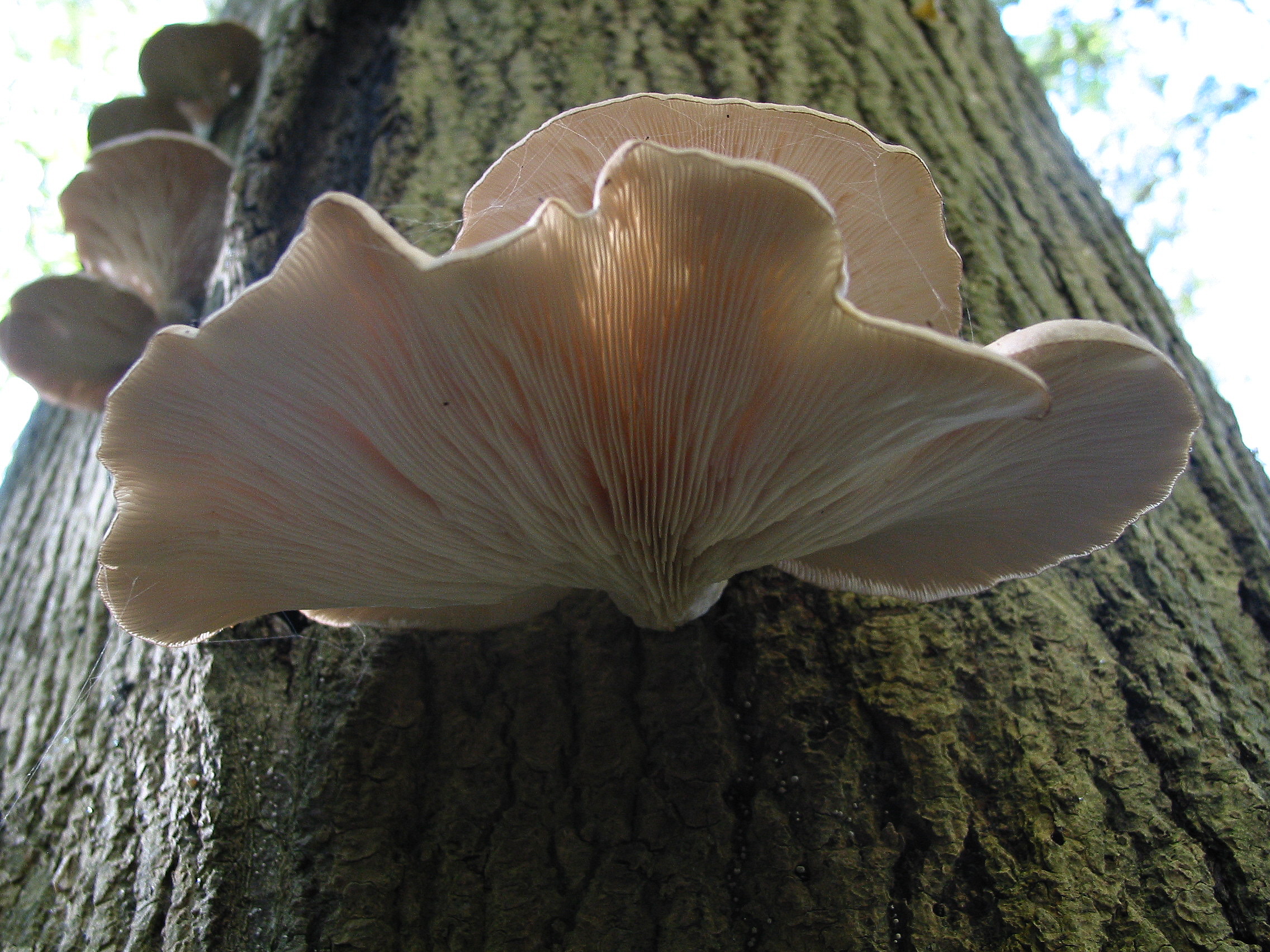
Mycoremediation
Mycoremediation (from ancient Greek ''μύκης (mukēs)'', meaning "fungus" and the suffix ''-remedium'', in Latin meaning 'restoring balance') is a form of bioremediation in which fungi-based remediation methods are used to decontaminate the environment. Fungi have been proven to be a cheap, effective and environmentally sound way for removing a wide array of contaminants from damaged environments or wastewater. These contaminants include heavy metals, organic pollutants, textile dyes, leather tanning chemicals and wastewater, petroleum fuels, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, pharmaceuticals and personal care products, pesticides and herbicides in land, fresh water, and marine environments. The byproducts of the remediation can be valuable materials themselves, such as enzymes (like laccase), edible or medicinal mushrooms, making the remediation process even more profitable. Some fungi are useful in the biodegradation of contaminants in extremely cold or radioactive environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landfill Liner
A landfill liner, or composite liner, is intended to be a low permeable barrier, which is laid down under engineered landfill sites. Until it deteriorates, the liner retards migration of leachate, and its toxic constituents, into underlying aquifers or nearby rivers, causing potentially irreversible contamination of the local waterway and its sediments. Modern landfills generally require a layer of compacted clay with a minimum required thickness and a maximum allowable hydraulic conductivity, overlaid by a high-density polyethylene geomembrane. The United States Environmental Protection Agency has stated that the barriers "will ultimately fail," while sites remain threats for "thousands of years," suggesting that modern landfill designs delay but do not prevent ground and surface water pollution. Chipped or waste tires are used to support and insulate the liner. Types There are certain levels of harmfulness in which the different types of trash have; therefore, there are d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
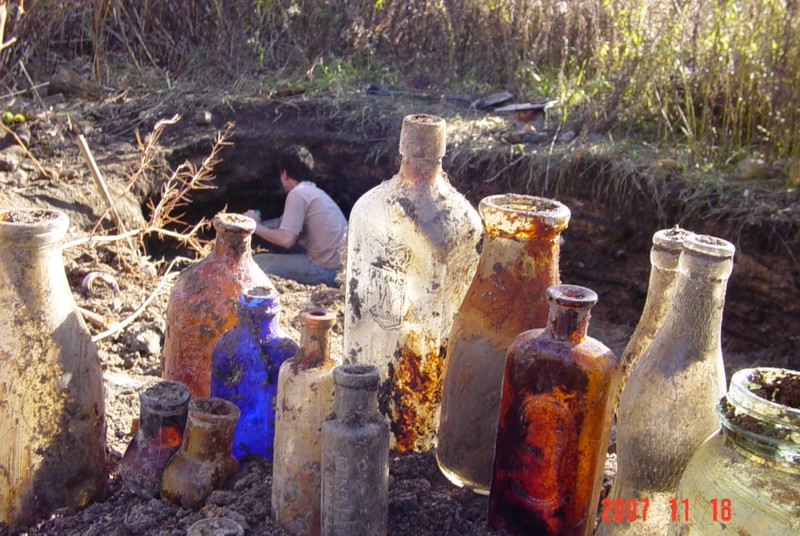
Dump Digging
Dump digging is the practice of locating and excavating old garbage dumps with the intent of discovering objects which have potential value as collectibles or antiques. These dumps are sometimes centuries old, but often date to the late 19th century or early part of the 20th century. Among other things, the practice of dump digging is directly linked to antique bottle collecting and glassmaking. It is a form of historical digging which involves long hours working with a shovel, pick and other hand tools. Finding evidence of potential antique bottle dumps or middens is done by searching areas where it is likely that older garbage was deposited. Diggers generally look for clues of pre-1920s junk piles in the woods or down embankments, places where old houses or businesses stand or once stood. Hiking along waterways and swampy areas, particularly during droughts, can also produce important clues and lead to good discoveries. Additionally, many coastal cities are surrounded by la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Cover
The daily cover on an operational landfill site is the layer of compressed soil or earth which is laid on top of a days deposition of waste. Benefits of using daily cover include: * Reduction of odor and air emissions * Control of disease vectors (birds, insects, and rodents) * Improved surface stability for landfill vehicles * Control of litter * Reduction of leachate generation (cover reduces infiltration of rainwater and runoff into the waste mass) * Fire prevention (cover reduces contact of combustible materials with air and ignition sources, and can act as a temporary firebreak) Work at the Fresno Sanitary Landfill was instrumental in establishing the need and utility of daily cover. Federal regulations in the United States require a minimum of six (6) inches of daily cover to be used at the end of each day. While soils are the traditional materials employed in daily cover, alternative daily cover (ADC) options such as "green waste", mixtures of paper sludge, tire deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a renewable energy source. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with anaerobic organisms or methanogen inside an anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor. Biogas is primarily methane () and carbon dioxide () and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide (), moisture and siloxanes. The gases methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide () can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used in fuel cells and for any heating purpose, such as cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat. Biogas can be compressed after removal of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, the same way as natural gas is compres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Mining
An urban mine is the stockpile of rare metals in the discarded waste electrical and electronic equipment Electronic waste or e-waste describes discarded electrical or electronic devices. Used electronics which are destined for refurbishment, reuse, resale, salvage recycling through material recovery, or disposal are also considered e-waste. Informa ... (WEEE) of a society. Urban mining is the process of recovering these rare metals through mechanical and chemical treatments. The name was coined in the 1980s by Professor Hideo Nanjyo of the Research Institute of Mineral Dressing and Metallurgy at Tohoku University and the idea has gained significant traction in Japan (and in other parts of Asia) in the 21st century. Research published by the Japanese government's National Institute of Materials Science in 2010 estimated that there were 6,800 tonnes of gold recoverable from used electronic equipment in Japan. References Sources * * * Further reading * Electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Classifier
An air classifier is an industrial machine which separates materials by a combination of size, shape, and density. It works by injecting the material stream to be sorted into a chamber which contains a column of rising air. Inside the separation chamber, air drag on the objects supplies an upward force which counteracts the force of gravity and lifts the material to be sorted up into the air. Due to the dependence of air drag on object size and shape, the objects in the moving air column are sorted vertically and can be separated in this manner. Air classifiers are commonly employed in industrial processes where a large volume of mixed materials with differing physical characteristics need to be separated quickly and efficiently. Air classifier is helpful for cement, air pollution control, food processing, pigments, pharmaceutical, cosmetics or chemical industries. One such example is in municipal recycling centers, where various types of metal, paper, and plastics arrive mixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |