|
Peak Minerals
Peak minerals marks the point in time when the largest production of a mineral will occur in an area, with production declining in subsequent years. While most mineral resources will not be exhausted in the near future, global extraction and production has become more challenging. Miners have found ways over time to extract deeper and lower grade ores with lower production costs. More than anything else, declining average ore grades are indicative of ongoing technological shifts that have enabled inclusion of more 'complex' processing – in social and environmental terms ''as well as'' economic – and structural changes in the minerals exploration industry and these have been accompanied by significant increases in identified Mineral Reserves. Definition The concept of peak minerals offers a useful model for representing the changing impacts associated with processing declining resource qualities in the lead up to, and following, peak mineral production in a particular region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Curse
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources (such as fossil fuels and certain minerals) having less economic growth, less democracy, or worse economic development, development outcomes than countries with fewer natural resources. There are many theories and much academic debate about the reasons for, and exceptions to, these adverse outcomes. Most experts believe the resource curse is not universal or inevitable, but affects certain types of countries or regions under certain conditions. Thesis As far back as 1711 ''The Spectator (1711), The Spectator'' wrote "It is generally observed, that in countries of the greatest plenty there is the poorest living". The idea that resources might be more of an economic curse than a blessing emerged in debates in the 1950s and 1960s about the economic problems of low and middle-income countries. In 1993 Richard Auty first used the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Mining
Automated mining involves the removal of human labor from the mining process. The mining industry is in the transition towards automation. It can still require a large amount of human capital, particularly in the developing world where labor costs are low so there is less incentive for increasing efficiency. There are two types of automated mining- process and software automation, and the application of robotic technology to mining vehicles and equipment. Mine automation software In order to gain more control over their operations, mining companies may implement mining automation software or processes. Reports generated by mine automation software allow administrators to identify productivity bottlenecks, increase accountability, and better understand return on investment. Mining equipment automation Addressing concerns about how to improve productivity and safety in the mine site, some mine companies are turning to equipment automation consisting of robotic hardware and software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Impact Of Mining
Environmental effects of mining can occur at local, regional, and global scales through direct and indirect mining practices. The effects can result in erosion, sinkholes, loss of biodiversity, or the contamination of soil, groundwater, and surface water by the chemicals emitted from mining processes. These processes also affect the atmosphere from the emissions of carbon which have an effect on the quality of human health and biodiversity. Some mining methods (lithium mining, phosphate mining, coal mining, mountaintop removal mining, and sand mining) may have such significant environmental and public health effects that mining companies in some countries are required to follow strict environmental and rehabilitation codes to ensure that the mined area returns to its original state. Erosion Erosion of exposed hillsides, mine dumps, tailings dams and resultant siltation of drainages, creeks and rivers can significantly affect the surrounding areas, a prime example being the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. On Earth, it includes sunlight, atmosphere, water, land, all minerals along with all vegetation, and wildlife. Natural resources is a part of humanity's natural heritage or protected in nature reserves. Particular areas (such as the rainforest in Fatu-Hiva) often feature biodiversity and geodiversity in their ecosystems. Natural resources may be classified in different ways. Natural resources are materials and components (something that can be used) that can be found within the environment. Every man-made product is composed of natural resources (at its fundamental level). A natural resource may exist as a separate entity such as fresh water, air, as well as any living organism such as a fish, or it may be transformed by extractivist in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Mining
Asteroid mining is the hypothetical exploitation of materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. Notable asteroid mining challenges include the high cost of spaceflight, unreliable identification of asteroids which are suitable for mining, and the challenges of extracting usable material in a space environment. Asteroid sample return research missions (see completed missions ''Hayabusa'' and '' Hayabusa2'' and in-progress ''OSIRIS-REx'') illustrate the challenges of collecting ore from space using current technology. As of 2021, less than 1 gram of asteroid material has been successfully returned to Earth from space. In progress missions promise to increase this amount to approximately 60 grams (two ounces). Asteroid research missions are complex endeavors and return a tiny amount of material (less than 1 milligram ''Hayabusa'', 100 milligrams ''Hayabusa2'', 60 grams planned ''OSIRIS-REx'') relative to the size and expense of these projects ($3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Uranium
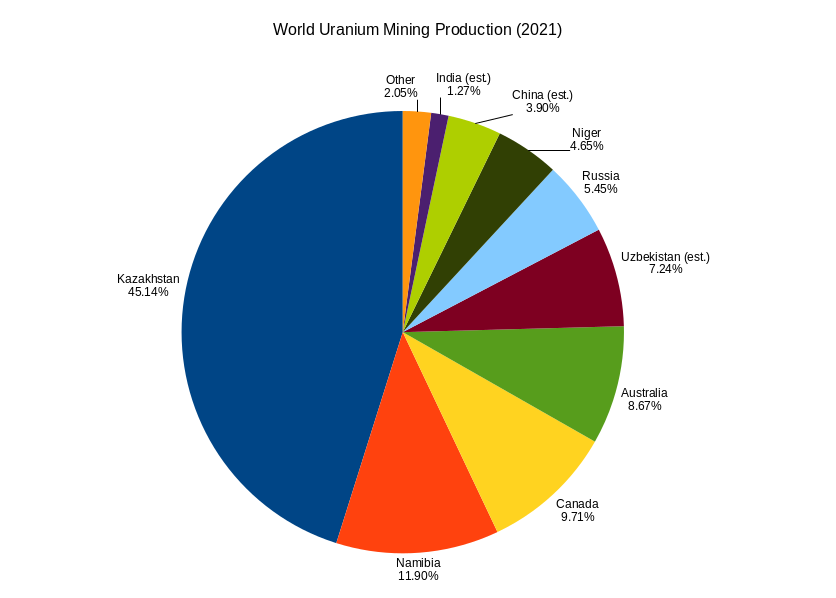
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Gas
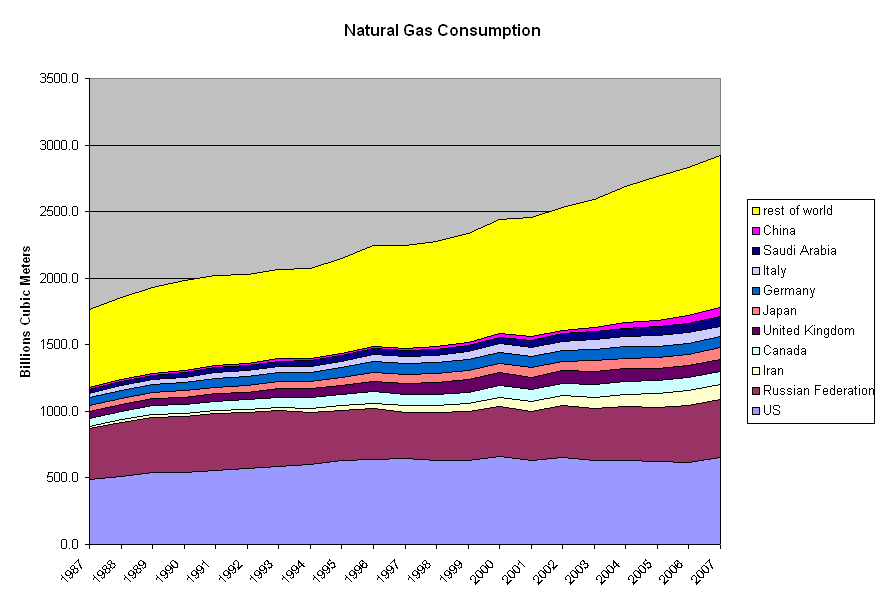
Peak gas is the year in which the maximum global natural gas (fossil gas) production rate will be reached, after which the rate of production will enter its terminal decline. Although demand is peaking in the United States and Europe, it continues to rise globally due to consumers in Asia, especially China. Natural gas is a fossil fuel formed from plant matter over the course of millions of years. Natural gas derived from fossil fuels is a non-renewable energy source; however, methane can be renewable in other forms such as biogas. Peak coal was in 2013, and peak oil is forecast to occur before peak gas. One forecast is for natural gas demand to peak in 2035. The concept of peak gas follows from Hubbert peak theory, which is most commonly associated with peak oil. Hubbert saw gas, coal and oil as natural resources, each of which would peak in production and eventually run out for a region, a country, or the world. Gas demand The world gets almost one quarter of its energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Phosphorus
Peak phosphorus is a concept to describe the point in time when humanity reaches the maximum global production rate of phosphorus as an industrial and commercial raw material. The term is used in an equivalent way to the better-known term peak oil. The issue was raised as a debate on whether phosphorus shortages might be imminent around 2010, which was largely dismissed after USGS and other organizations increased world estimates on available phosphorus resources, mostly in the form of additional resources in Morocco. However, exact reserve quantities remain uncertain, as do the possible impacts of increased phosphate use on future generations. This is important because rock phosphate is a key ingredient in many inorganic fertilizers. Hence, a shortage in rock phosphate (or just significant price increases) might negatively affect the world's food security. Phosphorus is a finite (limited) resource that is widespread in the Earth's crust and in living organisms but is relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Copper
Peak copper is the point in time at which the maximum global copper production rate is reached. Since copper is a finite resource, at some point in the future new production from mining will diminish, and at some earlier time production will reach a maximum. When this will occur is a matter of dispute. Unlike fossil fuels, copper is scrapped and reused, and it has been estimated that at least 80% of all copper ever mined is still available (having been repeatedly recycled). Copper is among the most important industrial metals, ranking third after iron and aluminium in terms of quantity used. It is valued for its heat and electrical conductivities, ductility, malleability and resistance to corrosion. Electrical uses account for about three quarters of total copper consumption, including power cables, data cables and electrical equipment. It is also used in cooling and refrigeration tubing, heat exchangers, water pipes and consumer products. Copper has been used by humans for at l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Coal
Peak coal is the peak consumption or production of coal by a human community. Global coal consumption peaked in 2013, and had dropped slightly by the end of the 2010s. The peak of coal's share in the global energy mix was in 2008, when coal accounted for 30% of global energy production. The decline in coal use is largely driven by consumption declines in the United States and Europe, as well as developed economies in Asia. In 2019, production increases in countries such as China, Indonesia, India, Russia and Australia compensated for the falls in the United States and Europe. However, coal's structural decline continued in the 2020s. Peak coal can be driven by peak demand or peak supply. Historically, it was widely believed that the supply-side would eventually drive peak coal due to the depletion of coal reserves. However, since the increasing global efforts to limit climate change, peak coal has been driven by demand, which has stayed below the 2013 peak consumption. This is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Coal Association
The Australian Coal Association (ACA) is the major Australian coal mining industry lobby group. It represents the black coal producers of New South Wales and Queensland and consists of a number of relatively small coal mining companies or subsidiaries of larger corporations in those two states. Australia is the world's largest coal exporter, and black coal is Australia's second largest commodity export, worth more than A$24 billion in the financial year ending June 2008, and $46 billion, or nearly double this amount, for the corresponding calendar year ending December. Black coal provides around 57 per cent of Australia's grid-connected electricity (brown coal around 24%) and is vital for major industries such as steel making and cement manufacture. On 23 August 2013, the Australian Coal Association released a statement that it will be subsumed into the Minerals Council of Australia. ACA and the environment The Australian Coal Association acknowledges that 34 per cent of Austra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |