Metre Gauge Railways In Norway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The metre (

 As a result of the Lumières and during the French Revolution, the
As a result of the Lumières and during the French Revolution, the
British spelling
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American ...
) or meter (American spelling
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American ...
; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Interna ...
in the International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(SI), though its prefixed forms are also used relatively frequently.
The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
to the North Pole along a great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geomet ...
, so the Earth's circumference
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the Equator, it is . Measured around the poles, the circumference is .
Measurement of Earth's circumference has been important to navigation since ancient times. The first know ...
is approximately km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar (the actual bar used was changed in 1889). In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in of a second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
. After the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units
In 2019, four of the seven SI base units specified in the International System of Quantities were redefined in terms of natural physical constants, rather than human artifacts such as the standard kilogram.
Effective 20 May 2019, the 144t ...
, this definition was rephrased to include the definition of a second in terms of the caesium frequency .
Spelling
''Metre'' is the standard spelling of the metric unit for length in nearly all English-speaking nations except the United States and the Philippines, which use ''meter.'' Other West Germanic languages, such as German and Dutch, and North Germanic languages, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish, likewise spell the word ''Meter'' or ''meter''. Measuring devices (such as ammeter,speedometer
A speedometer or speed meter is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the early 20th century, and as standard equipment f ...
) are spelled "-meter" in all variants of English. The suffix "-meter" has the same Greek origin as the unit of length.
Etymology
The etymological roots of ''metre'' can be traced to the Greek verb () (to measure, count or compare) and noun () (a measure), which were used for physical measurement, for poetic metre and by extension for moderation or avoiding extremism (as in "be measured in your response"). This range of uses is also found in Latin (), French (), English and other languages. The Greek word is derived from the Proto-Indo-European root '' *meh₁-'' 'to measure'. The motto () in the seal of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), which was a saying of the Greek statesman and philosopherPittacus of Mytilene
Pittacus (; grc-gre, Πιττακός; 640 – 568 BC) was an ancient Mytilenean military general and one of the Seven Sages of Greece.
Biography
Pittacus was a native of Mytilene and son of Hyrradius. He became a Mytilenaean general who, with ...
and may be translated as "Use measure!", thus calls for both measurement and moderation. The use of the word ''metre'' (for the French unit ) in English began at least as early as 1797. Oxford English Dictionary, Clarendon Press 2nd ed.1989, vol.IX p.697 col.3.
History of definition

Pendulum or meridian
In 1671,Jean Picard
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, base ...
measured the length of a " seconds pendulum" and proposed a unit of measurement twice that length to be called the universal toise (French: ''Toise universelle''). In 1675, Tito Livio Burattini
Tito Livio Burattini ( pl, Tytus Liwiusz Burattini, 8 March 1617 – 17 November 1681) was an inventor, architect, Egyptologist, scientist, instrument-maker, traveller, engineer, and nobleman, who spent his working life in Poland and Lithuania. ...
suggested the term metre for a unit of length based on a pendulum length, but then it was discovered that the length of a seconds pendulum varies from place to place.
Since Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
, geographers had used meridian arc
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to de ...
s to assess the size of the Earth, which in 1669, Jean Picard
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, base ...
determined to have a radius of toises, treated as a simple sphere. In the 18th century, geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
grew in importance as a means of empirically demonstrating the theory of gravity, which Émilie du Châtelet
Gabrielle Émilie Le Tonnelier de Breteuil, Marquise du Châtelet (; 17 December 1706 – 10 September 1749) was a French natural philosopher and mathematician from the early 1730s until her death due to complications during childbirth in 1749. ...
promoted in France in combination with Leibniz mathematical work, and because the radius of the Earth
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or R_E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid, the radius ranges from a maximum of nearly (equatorial radius, deno ...
was the unit to which all celestial distances were to be referred.
Meridional definition
 As a result of the Lumières and during the French Revolution, the
As a result of the Lumières and during the French Revolution, the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
charged a commission with determining a single scale for all measures. On 7 October 1790 that commission advised the adoption of a decimal system, and on 19 March 1791 advised the adoption of the term ''mètre'' ("measure"), a basic unit of length, which they defined as equal to one ten-millionth of the quarter meridian
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to d ...
, the distance between the North Pole and the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
along the meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
through Paris. On 26 March 1791, the French National Constituent Assembly adopted the proposal.
The French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
commissioned an expedition led by Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre and Pierre Méchain, lasting from 1792 to 1799, which attempted to accurately measure the distance between a belfry in Dunkerque
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Montjuïc castle in Barcelona at the longitude of the Paris Panthéon (see
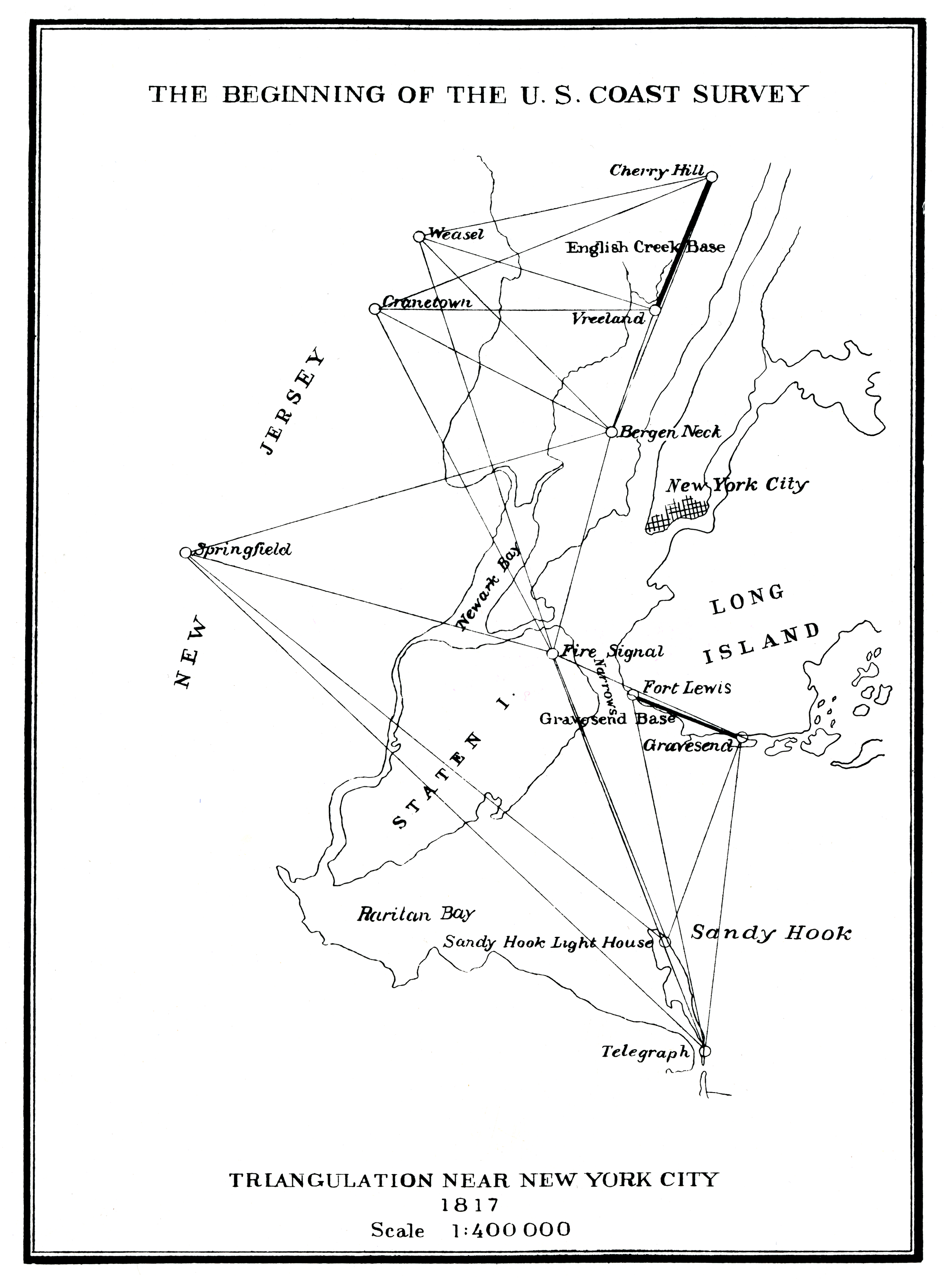 In 1816,
In 1816,  In 1866, at the meeting of the Permanent Commission of the association in
In 1866, at the meeting of the Permanent Commission of the association in
meridian arc of Delambre and Méchain
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
). The expedition was fictionalised in Denis Guedj, ''Le Mètre du Monde''. Ken Alder wrote factually about the expedition in ''The Measure of All Things: the seven year odyssey and hidden error that transformed the world''. This portion of the Paris meridian
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.02500″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian of the world. The "Paris merid ...
was to serve as the basis for the length of the half meridian connecting the North Pole with the Equator. From 1801 to 1812 France adopted this definition of the metre as its official unit of length based on results from this expedition combined with those of the Geodesic Mission to Peru. The latter was related by Larrie D. Ferreiro in ''Measure of the Earth: The Enlightenment Expedition that Reshaped Our World''.
In the 19th century, geodesy underwent a revolution through advances in mathematics as well as improvements in the instruments and methods of observation, for instance accounting for individual bias in terms of the personal equation. The application of the least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems (sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns) by minimizing the sum of the squares of the res ...
method to meridian arc
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to de ...
measurements demonstrated the importance of the scientific method in geodesy. On the other hand, the invention of the telegraph made it possible to measure parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster of IBM ...
arcs, and the improvement of the reversible pendulum gave rise to the study of the Earth's gravitational field
In physics, a gravitational field is a model used to explain the influences that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body. Thus, a gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenome ...
. A more accurate determination of the Figure of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-k ...
would soon result from the measurement of the Struve Geodetic Arc
The Struve Geodetic Arc is a chain of survey triangulations stretching from Hammerfest in Norway to the Black Sea, through ten countries and over , which yielded the first accurate measurement of a meridian arc.
The chain was established ...
(1816–1855) and would have given another value for the definition of this standard of length. This did not invalidate the metre but highlighted that progress in science would allow better measurement of Earth's size and shape.
In 1832, Carl Friedrich Gauss studied the Earth's magnetic field and proposed adding the second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
to the basic units of the metre and the kilogram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially ...
in the form of the CGS system ( centimetre, gram, second). In 1836, he founded the ''Magnetischer Verein'', the first international scientific association, in collaboration with Alexander von Humboldt and Wilhelm Edouard Weber. The coordination of the observation of geophysical phenomena such as the Earth's magnetic field, lightning and gravity in different points of the globe stimulated the creation of the first international scientific associations. The foundation of the ''Magnetischer Verein'' would be followed by that of the Central European Arc Measurement (German: ''Mitteleuropaïsche Gradmessung'') on the initiative of Johann Jacob Baeyer
Johann Jacob Baeyer (born 5 November 1794 in Berlin, died 10 September 1885 in Berlin) was a German geodesist and a lieutenant-general in the Royal Prussian Army. He was the first director of the Royal Prussian Geodetic Institute and is regarded ...
in 1863, and by that of the International Meteorological Organisation whose second president, the Swiss meteorologist and physicist, Heinrich von Wild would represent Russia at the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM).
International prototype metre bar
 In 1816,
In 1816, Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler
Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler (October 6, 1770 – November 20, 1843) was a Swiss-American surveyor who is considered the forefather of both the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Institute of Standards and Techno ...
was appointed first Superintendent of the Survey of the Coast
The United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (abbreviated USC&GS), known from 1807 to 1836 as the Survey of the Coast and from 1836 until 1878 as the United States Coast Survey, was the first scientific agency of the United States Government. It ...
. Trained in geodesy in Switzerland, France and Germany, Hassler had brought a standard metre made in Paris to the United States in 1805. He designed a baseline apparatus which instead of bringing different bars in actual contact during measurements, used only one bar calibrated on the metre and optical contact. Thus the metre became the unit of length for geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
in the United States.
Since 1830, Hassler was also head of the Bureau of Weights and Measures which became a part of the Coast Survey. He compared various units of length used in the United States at that time and measured coefficients of expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ...
to assess temperature effects on the measurements.
In 1841, Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, taking into account errors which had been recognized by Louis Puissant
Louis Puissant (22 September 1769, in Le Châtelet-en-Brie – 10 January 1843, in Paris) was a French topographical engineer, geodesist, and mathematician.
He was appointed an officer in the corps of topographical engineers (''ingénieurs géo ...
in the French meridian arc comprising the arc measurement of Delambre and Méchain
The arc measurement of Delambre and Méchain was a geodetic survey carried out by Jean-Baptiste Delambre and Pierre Méchain in 1792–1798 to measure an arc section of the Paris meridian between Dunkirk and Barcelona. This arc measurement serv ...
which had been extended southward by François Arago
Dominique François Jean Arago ( ca, Domènec Francesc Joan Aragó), known simply as François Arago (; Catalan: ''Francesc Aragó'', ; 26 February 17862 October 1853), was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of t ...
and Jean-Baptiste Biot, recalculated the flattening of the Earth ellipsoid making use of nine more arc measurements, namely Peruan, Prussian, first East-Indian, second East-Indian, English, Hannover, Danish, Russian and Swedish covering almost 50 degrees of latitude, and stated that the Earth quadrant used for determining the length of the metre was nothing more than a rather imprecise conversion factor
Conversion of units is the conversion between different units of measurement for the same quantity, typically through multiplicative conversion factors which change the measured quantity value without changing its effects.
Overview
The process ...
between the toise and the metre.
Regarding the precision of the conversion from the toise to the metre, both units of measurement were then defined by primary standards, and unique artifacts made of different alloys with distinct coefficients of expansion
Expansion may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''L'Expansion'', a French monthly business magazine
* ''Expansion'' (album), by American jazz pianist Dave Burrell, released in 2004
* ''Expansions'' (McCoy Tyner album), 1970
* ''Expansio ...
were the legal basis of units of length. A wrought iron ruler, the Toise of Peru, also called ''Toise de l'Académie'', was the French primary standard of the toise, and the metre was officially defined by the ''Mètre des Archives'' made of platinum. Besides the latter, another platinum and twelve iron standards of the metre were made in 1799. One of them became known as the ''Committee Meter'' in the United States and served as standard of length in the Coast Survey until 1890. According to geodesists, these standards were secondary standards deduced from the Toise of Peru. In Europe, surveyors continued to use measuring instruments calibrated on the Toise of Peru. Among these, the toise of Bessel and the apparatus of Borda were respectively the main references for geodesy in Prussia and in France. A French scientific instrument maker, Jean Nicolas Fortin Jean Nicolas Fortin (1750–1831) was a French maker of scientific instruments, born on 9 August 1750 in Mouchy-la-Ville in Picardy. Among his customers were such noted scientists as Lavoisier, for whom he made a precision balance, Gay-Lussac, Fr ...
, had made two direct copies of the Toise of Peru, the first for Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve in 1821 and a second for Friedrich Bessel in 1823.
On the subject of the theoretical definition of the metre, it had been inaccessible and misleading at the time of Delambre and Mechain arc measurement, as the geoid is a ball, which on the whole can be assimilated to an oblate spheroid, but which in detail differs from it so as to prohibit any generalization and any extrapolation. As early as 1861, after Friedrich von Schubert showed that the different meridians were not of equal length, Elie Ritter, a mathematician from Geneva, deduced from a computation based on eleven meridian arcs covering 86 degrees that the meridian equation differed from that of the ellipse: the meridian was swelled about the 45th degree of latitude by a layer whose thickness was difficult to estimate because of the uncertainty of the latitude of some stations, in particular that of Montjuïc in the French meridian arc. By measuring the latitude of two stations in Barcelona, Méchain had found that the difference between these latitudes was greater than predicted by direct measurement of distance by triangulation. We know now that, in addition to other errors in the survey of Delambre and Méchain, an unfavourable vertical deflection gave an inaccurate determination of Barcelona's latitude, a metre "too short" compared to a more general definition taken from the average of a large number of arcs.
Nevertheless Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler
Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler (October 6, 1770 – November 20, 1843) was a Swiss-American surveyor who is considered the forefather of both the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Institute of Standards and Techno ...
's use of the metre in coastal survey contributed to the introduction of the Metric Act of 1866 allowing the use of the metre in the United States, and also played an important role in the choice of the metre as international scientific unit of length and the proposal by the European Arc Measurement (German: ''Europäische Gradmessung'') to “establish a European international bureau for weights and measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry ...
”. However, in 1866, the most important concern was that the Toise of Peru, the standard of the toise constructed in 1735 for the French Geodesic Mission to the Equator, might be so much damaged that comparison with it would be worthless, while Bessel had questioned the accuracy of copies of this standard belonging to Altona and Koenigsberg Observatories, which he had compared to each other about 1840. Indeed when the primary Imperial yard standard was partially destroyed in 1834, a new standard of reference had been constructed using copies of the "Standard Yard, 1760" instead of the pendulum's length as provided for in the Weights and Measures Act of 1824.
In 1864, Urbain Le Verrier refused to join the first general conference of the Central European Arc Measurement because the French geodetic works had to be verified.
 In 1866, at the meeting of the Permanent Commission of the association in
In 1866, at the meeting of the Permanent Commission of the association in Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), ...
, Antoine Yvon Villarceau announced that he had checked eight points of the French arc. He confirmed that the metre was too short. It then became urgent to undertake a complete revision of the meridian arc. Moreover, while the extension of the French meridian arc to the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
(1803–1807) had seemed to confirm the length of the metre, this survey had not been secured by any baseline in Spain. For that reason, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
's announcement, at this conference, of his 1858 measurement of a baseline in Madridejos was of particular importance. Indeed surveyors determined the size of triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
networks by measuring baselines which concordance granted the accuracy of the whole survey.
In 1867 at the second general conference of the International Association of Geodesy held in Berlin, the question of an international standard unit of length was discussed in order to combine the measurements made in different countries to determine the size and shape of the Earth. The conference recommended the adoption of the metre in replacement of the toise and the creation of an international metre commission, according to the proposal of Johann Jacob Baeyer
Johann Jacob Baeyer (born 5 November 1794 in Berlin, died 10 September 1885 in Berlin) was a German geodesist and a lieutenant-general in the Royal Prussian Army. He was the first director of the Royal Prussian Geodetic Institute and is regarded ...
, Adolphe Hirsch
Adolphe Hirsch (21 May 1830 - 16 April 1901) was a German born, Swiss astronomer and geodesist.
Bibliography
Adolph Hirsch was born in Halberstadt. He studied astronomy at the universities of Heidelberg and Vienna. He founded and directed the ...
and Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
who had devised two geodetic standards calibrated on the metre for the map of Spain.
Ibáñez adopted the system which Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler
Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler (October 6, 1770 – November 20, 1843) was a Swiss-American surveyor who is considered the forefather of both the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Institute of Standards and Techno ...
used for the United States Survey of the Coast
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication; mapping and charting; and a large number of applications ...
, consisting of a single standard with lines marked on the bar and microscopic measurements. Regarding the two methods by which the effect of temperature was taken into account, Ibáñez used both the bimetallic rulers, in platinum and brass, which he first employed for the central baseline of Spain, and the simple iron ruler with inlaid mercury thermometers which was utilized in Switzerland. These devices, the first of which is referred to as either Brunner apparatus or Spanish Standard, were constructed in France by Jean Brunner
Jean Brunner or Johann Josef Brunner (1804 in Balsthal – 1862 in Paris), was a Swiss-born, French measuring instrument maker and mechanic.Eveline Hänggi: ''Die fünf Turmuhren von Balsthal und der vergessene Balsthaler Künstler Johann Josef Bru ...
, then his sons. Measurement traceability between the toise and the metre was ensured by comparison of the Spanish Standard with the standard devised by Borda Borda may refer to:
*Qaṣīda al-Burda, a famous Sufi poem.
* Borda (building) or borde, traditional cattle farmers' buildings in the Pyrenees, a barn, sheepfold, or stable
* Places in India
** Borda, Goa, a town and suburb of the city of Margao ...
and Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
CNRS (
meridian arc
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to de ...
connecting Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Barcelona.
Hassler's metrological and geodetic work also had a favourable response in Russia. In 1869, the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences sent to the  In the 1870s and in light of modern precision, a series of international conferences was held to devise new metric standards. When a conflict broke out regarding the presence of impurities in the metre-alloy of 1874, a member of the Preparatory Committee since 1870 and Spanish representative at the Paris Conference in 1875,
In the 1870s and in light of modern precision, a series of international conferences was held to devise new metric standards. When a conflict broke out regarding the presence of impurities in the metre-alloy of 1874, a member of the Preparatory Committee since 1870 and Spanish representative at the Paris Conference in 1875,  The comparison of the new prototypes of the metre with each other and with the Committee metre (French: '' Mètre des Archives'') involved the development of special measuring equipment and the definition of a reproducible temperature scale. The BIPM's thermometry work led to the discovery of special alloys of iron-nickel, in particular invar, for which its director, the Swiss physicist Charles-Edouard Guillaume, was granted the Nobel Prize for physics in 1920.
The comparison of the new prototypes of the metre with each other and with the Committee metre (French: '' Mètre des Archives'') involved the development of special measuring equipment and the definition of a reproducible temperature scale. The BIPM's thermometry work led to the discovery of special alloys of iron-nickel, in particular invar, for which its director, the Swiss physicist Charles-Edouard Guillaume, was granted the Nobel Prize for physics in 1920.
 As
As  Efforts to supplement the various national
Efforts to supplement the various national
modified Edlén equation
or th
Ciddor equation
The documentation provide
a discussion of how to choose
between the two possibilities. As described by NIST, in air, the uncertainties in characterising the medium are dominated by errors in measuring temperature and pressure. Errors in the theoretical formulas used are secondary. By implementing a refractive index correction such as this, an approximate realisation of the metre can be implemented in air, for example, using the formulation of the metre as wavelengths of helium–neon laser light in a vacuum, and converting the wavelengths in a vacuum to wavelengths in air. Air is only one possible medium to use in a realisation of the metre, and any
''Refinement of values for the yard and the pound''
Washington DC: National Bureau of Standards, republished on National Geodetic Survey web site and the Federal Register (Doc. 59-5442, Filed, 30 June 1959) * * * * * *
Retrieved 26 May 2010. * National Institute of Standards and Technology. (27 June 2011).
NIST-F1 Cesium Fountain Atomic Clock
'. Author. * National Physical Laboratory. (25 March 2010).
Iodine-Stabilised Lasers
'. Author. * * Republic of the Philippines. (2 December 1978).
'. Author. * Republic of the Philippines. (10 October 1991). '' ttps://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/1991/10oct/19911010-RA-7160-CCA.pdf Republic Act No. 7160: The Local Government Code of the Philippines'. Author. * Supreme Court of the Philippines (Second Division). (20 January 2010).
G.R. No. 185240
'. Author. * Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (Eds.). (2008a)
''The International System of Units (SI)''
United States version of the English text of the eighth edition (2006) of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures publication ''Le Système International d’ Unités (SI)'' (Special Publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 18 August 2008. * Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (2008b)
''Guide for the Use of the International System of Units''
(Special Publication 811). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 23 August 2008. * Turner, J. (Deputy Director of the National Institute of Standards and Technology). (16 May 2008
"Interpretation of the International System of Units (the Metric System of Measurement) for the United States"
''Federal Register'' Vol. 73, No. 96, p.28432-3. * Zagar, B.G. (1999)
Laser interferometer displacement sensors
in J.G. Webster (ed.). ''The Measurement, Instrumentation, and Sensors Handbook.'' CRC Press. . {{Authority control SI base units
French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
a report drafted by Otto Wilhelm von Struve, Heinrich von Wild and Moritz von Jacobi inviting his French counterpart to undertake joint action to ensure the universal use of the metric system in all scientific work.
 In the 1870s and in light of modern precision, a series of international conferences was held to devise new metric standards. When a conflict broke out regarding the presence of impurities in the metre-alloy of 1874, a member of the Preparatory Committee since 1870 and Spanish representative at the Paris Conference in 1875,
In the 1870s and in light of modern precision, a series of international conferences was held to devise new metric standards. When a conflict broke out regarding the presence of impurities in the metre-alloy of 1874, a member of the Preparatory Committee since 1870 and Spanish representative at the Paris Conference in 1875, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
intervened with the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
to rally France to the project to create an International Bureau of Weights and Measures equipped with the scientific means necessary to redefine the units of the metric system according to the progress of sciences.
The Metre Convention (''Convention du Mètre'') of 1875 mandated the establishment of a permanent International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM: ') to be located in Sèvres, France. This new organisation was to construct and preserve a prototype metre bar, distribute national metric prototypes, and maintain comparisons between them and non-metric measurement standards. The organisation distributed such bars in 1889 at the first General Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established i ...
(CGPM: '), establishing the '' International Prototype Metre'' as the distance between two lines on a standard bar composed of an alloy of 90% platinum and 10% iridium, measured at the melting point of ice. National Institute of Standards and Technology 2003; Historical context of the SI: Unit of length (meter)
 As
As Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
stated, the progress of metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
combined with those of gravimetry through improvement of Kater's pendulum led to a new era of geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
. If precision metrology had needed the help of geodesy, the latter could not continue to prosper without the help of metrology. It was then necessary to define a single unit to express all the measurements of terrestrial arcs and all determinations of the force of gravity by the mean of pendulum. Metrology had to create a common unit, adopted and respected by all civilized nations.
Moreover, at that time, statistician
A statistician is a person who works with theoretical or applied statistics. The profession exists in both the private and public sectors.
It is common to combine statistical knowledge with expertise in other subjects, and statisticians may wor ...
s knew that scientific observations are marred by two distinct types of errors, constant errors on the one hand, and fortuitous errors, on the other hand. The effects of the latters can be mitigated by the least-squares method. Constant or regular errors on the contrary must be carefully avoided, because they arise from one or more causes that constantly act in the same way and have the effect of always altering the result of the experiment in the same direction. They therefore deprive of any value the observations that they impinge. However, the distinction between systematic and random errors is far from being as sharp as one might think at first assessment. In reality, there are no or very few random errors. As science progresses, the causes of certain errors are sought out, studied, their laws discovered. These errors pass from the class of random errors into that of systematic errors. The ability of the observer consists in discovering the greatest possible number of systematic errors in order to be able, once he has become acquainted with their laws, to free his results from them using a method or appropriate corrections.
For metrology the matter of expansibility was fundamental; as a matter of fact the temperature measuring error related to the length measurement in proportion to the expansibility of the standard and the constantly renewed efforts of metrologists to protect their measuring instruments against the interfering influence of temperature revealed clearly the importance they attached to the expansion-induced errors. It was thus crucial to compare at controlled temperatures with great precision and to the same unit all the standards for measuring geodetic baselines and all the pendulum rods. Only when this series of metrological comparisons would be finished with a probable error of a thousandth of a millimetre would geodesy be able to link the works of the different nations with one another, and then proclaim the result of the measurement of the Globe.
As the figure of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-k ...
could be inferred from variations of the seconds pendulum length with latitude, the United States Coast Survey instructed Charles Sanders Peirce in the spring of 1875 to proceed to Europe for the purpose of making pendulum experiments to chief initial stations for operations of this sort, in order to bring the determinations of the forces of gravity in America into communication with those of other parts of the world; and also for the purpose of making a careful study of the methods of pursuing these researches in the different countries of Europe. In 1886 the association of geodesy changed name for the International Geodetic Association )
, merged =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, founding_location =
, extinction =
, merger =
, type = scholarly society
, tax_id ...
, which Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
presided up to his death in 1891. During this period the International Geodetic Association )
, merged =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, founding_location =
, extinction =
, merger =
, type = scholarly society
, tax_id ...
(German: ''Internationale Erdmessung'') gained worldwide importance with the joining of United States, Mexico, Chile, Argentina and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
.
 Efforts to supplement the various national
Efforts to supplement the various national surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
systems, which began in the 19th century with the foundation of the '' Mitteleuropäische Gradmessung'', resulted in a series of global ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the ...
s of the Earth (e.g., Helmert 1906, Hayford 1910 and 1924) which would later lead to develop the World Geodetic System. Nowadays the practical realisation of the metre is possible everywhere thanks to the atomic clocks embedded in GPS satellites.
Wavelength definition
In 1873, James Clerk Maxwell suggested that light emitted by an element be used as the standard both for the metre and for the second. These two quantities could then be used to define the unit of mass. In 1893, the standard metre was first measured with aninterferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber op ...
by Albert A. Michelson, the inventor of the device and an advocate of using some particular wavelength of light as a standard of length. By 1925, interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
was in regular use at the BIPM. However, the International Prototype Metre remained the standard until 1960, when the eleventh CGPM defined the metre in the new International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
(SI) as equal to wavelengths of the orange- red emission line in the electromagnetic spectrum of the krypton-86 atom in a vacuum.
Speed of light definition
To further reduce uncertainty, the 17th CGPM in 1983 replaced the definition of the metre with its current definition, thus fixing the length of the metre in terms of thesecond
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
and the speed of light:
::The metre is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second.
This definition fixed the speed of light in vacuum at exactly metres per second (≈ or ≈1.079 billion km/hour). An intended by-product of the 17th CGPM's definition was that it enabled scientists to compare lasers accurately using frequency, resulting in wavelengths with one-fifth the uncertainty involved in the direct comparison of wavelengths, because interferometer errors were eliminated. To further facilitate reproducibility from lab to lab, the 17th CGPM also made the iodine-stabilised helium–neon laser "a recommended radiation" for realising the metre. For the purpose of delineating the metre, the BIPM currently considers the HeNe laser wavelength, , to be with an estimated relative standard uncertainty (''U'') of .The term "relative standard uncertainty" is explained by NIST on their web site: This uncertainty is currently one limiting factor in laboratory realisations of the metre, and it is several orders of magnitude poorer than that of the second, based upon the caesium fountain atomic clock (). Consequently, a realisation of the metre is usually delineated (not defined) today in labs as wavelengths of helium-neon laser light in a vacuum, the error stated being only that of frequency determination. This bracket notation expressing the error is explained in the article on measurement uncertainty
In metrology, measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a measured quantity. All measurements are subject to uncertainty and a measurement result is complete only when it is accompanied by ...
.
Practical realisation of the metre is subject to uncertainties in characterising the medium, to various uncertainties of interferometry, and to uncertainties in measuring the frequency of the source. A commonly used medium is air, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has set up an online calculator to convert wavelengths in vacuum to wavelengths in air.The formulas used in the calculator and the documentation behind them are found at The choice is offered to use either thmodified Edlén equation
or th
Ciddor equation
The documentation provide
a discussion of how to choose
between the two possibilities. As described by NIST, in air, the uncertainties in characterising the medium are dominated by errors in measuring temperature and pressure. Errors in the theoretical formulas used are secondary. By implementing a refractive index correction such as this, an approximate realisation of the metre can be implemented in air, for example, using the formulation of the metre as wavelengths of helium–neon laser light in a vacuum, and converting the wavelengths in a vacuum to wavelengths in air. Air is only one possible medium to use in a realisation of the metre, and any
partial vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
can be used, or some inert atmosphere like helium gas, provided the appropriate corrections for refractive index are implemented.
The metre is ''defined'' as the path length travelled by light in a given time, and practical laboratory length measurements in metres are determined by counting the number of wavelengths of laser light of one of the standard types that fit into the length, and converting the selected unit of wavelength to metres. Three major factors limit the accuracy attainable with laser interferometers for a length measurement:
A more detailed listing of errors can be found in
Zagar, 1999, pp. 6–65''ff''.
* uncertainty in vacuum wavelength of the source,
* uncertainty in the refractive index of the medium,
* least count {{Short description, Smallest value a measuring instrument can measure
In the science of measurement, the least count of a measuring instrument is the smallest value in the measured quantity that can be resolved on the instrument's scale. William ...
resolution of the interferometer.
Of these, the last is peculiar to the interferometer itself. The conversion of a length in wavelengths to a length in metres is based upon the relation
:
which converts the unit of wavelength ''λ'' to metres using ''c'', the speed of light in vacuum in m/s. Here ''n'' is the refractive index of the medium in which the measurement is made, and ''f'' is the measured frequency of the source. Although conversion from wavelengths to metres introduces an additional error in the overall length due to measurement error in determining the refractive index and the frequency, the measurement of frequency is one of the most accurate measurements available.
The CIPM issued a clarification in 2002:
Timeline
Early adoptions of the metre internationally
In France, the metre was adopted as an exclusive measure in 1801 under the Consulate. This continued under the First French Empire until 1812, whenNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
decreed the introduction of the non-decimal ''mesures usuelles Mesures usuelles (, ''customary measurements'') were a French system of measurement introduced by Napoleon I in 1812 to act as compromise between the metric system and traditional measurements. The system was restricted to use in the retail indust ...
'', which remained in use in France up to 1840 in the reign of Louis Philippe. Meanwhile, the metre was adopted by the Republic of Geneva. After the joining of the canton of Geneva to Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
in 1815, Guillaume Henri Dufour
Guillaume Henri Dufour (15 September 178714 July 1875) was a Swiss military officer, structural engineer and topographer. He served under Napoleon I and held the Swiss office of General four times in his career, firstly in 1847 when he led the ...
published the first official Swiss map, for which the metre was adopted as the unit of length. Louis Napoléon Bonaparte
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
, a Swiss–French binational officer, was present when a baseline was measured near Zürich for the Dufour map, which would win the gold medal for a national map at the Exposition Universelle of 1855. Among the scientific instruments calibrated on the metre that were displayed at the Exposition Universelle, was Brunner Brunner may refer to:
Places
* Brunner, New Zealand
* Lake Brunner, New Zealand
* Brunner Mine, New Zealand
* Brunner, Houston, United States
* Brunner (crater), lunar crater
Other uses
* Brunner (surname)
* Brunner the Bounty Hunter, a character ...
's apparatus, a geodetic instrument devised for measuring the central baseline of Spain, whose designer, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero
Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero, 1st Marquis of Mulhacén, (14 April 1825 – 28 or 29 January 1891) was a Spanish divisional general and geodesist. He represented Spain at the 1875 Conference of the Metre Convention and was the first presid ...
would represent Spain at the International Statistical Institute
The International Statistical Institute (ISI) is a professional association of statisticians. It was founded in 1885, although there had been international statistical congresses since 1853. The institute has about 4,000 elected members from gov ...
. In 1885, in addition to the Exposition Universelle and the second Statistical Congress held in Paris, an International Association for Obtaining a Uniform Decimal System of Measures, Weights, and Coins was created there. Copies of the Spanish standard were made for Egypt, France and Germany. These standards were compared to each other and with the Borda apparatus, which was the main reference for measuring all geodetic bases in France. In 1869, Napoleon III convened the International Metre Commission, which was to meet in Paris in 1870. The Franco-Prussian War broke out, the Second French Empire collapsed, but the metre survived.
Metre adoption dates by country
* France: 1801 - 1812, then 1840, *Republic of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva (french: link=no, République et canton de Genève; frp, Rèpublica et canton de Geneva; german: Republik und Kanton Genf; it, Repubblica e Cantone di Ginevra; rm, Republica e ...
, Switzerland: 1813,
* Kingdom of the Netherlands: 1820,
* Kingdom of Belgium: 1830,
* Chile: 1848,
* Kingdom of Sardinia, Italy: 1850,
* Spain: 1852,
* Portugal: 1852,
* Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
: 1853,
* Ecuador: 1856,
* Mexico: 1857,
* Brazil: 1862,
* Argentina: 1863,
* Italy: 1863,
* German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
, Germany: 1872,
* Austria, 1875,
* Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
: 1877.
SI prefixed forms of metre
SI prefix
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
es can be used to denote decimal multiples and submultiples of the metre, as shown in the table below. Long distances are usually expressed in km, astronomical units (149.6 Gm), light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s (10 Pm), or parsecs (31 Pm), rather than in Mm, Gm, Tm, Pm, Em, Zm or Ym; "30 cm", "30 m", and "300 m" are more common than "3 dm", "3 dam", and "3 hm", respectively.
The terms ''micron'' and ''millimicron'' can be used instead of ''micrometre'' (μm) and ''nanometre'' (nm), but this practice may be discouraged.
Equivalents in other units
Within this table, "inch" and "yard" mean "international inch" and "international yard" respectively, though approximate conversions in the left column hold for both international and survey units. : "≈" means "is approximately equal to"; : "=" means "is exactly equal to". One metre is exactly equivalent to inches and to yards. A simple mnemonic aid exists to assist with conversion, as three "3"s: : 1 metre is nearly equivalent to 3 feet inches. This gives an overestimate of 0.125mm; however, the practice of memorising such conversion formulas has been discouraged in favour of practice and visualisation of metric units. The ancient Egyptian cubit was about 0.5m (surviving rods are 523–529mm). Scottish and English definitions of theell
An ell (from Proto-Germanic *''alinō'', cognate with Latin ''ulna'') is a northwestern European unit of measurement, originally understood as a cubit (the combined length of the forearm and extended hand). The word literally means "arm", and ...
(two cubits) were 941mm (0.941m) and 1143mm (1.143m) respectively. The ancient Parisian ''toise'' (fathom) was slightly shorter than 2m and was standardised at exactly 2m in the mesures usuelles Mesures usuelles (, ''customary measurements'') were a French system of measurement introduced by Napoleon I in 1812 to act as compromise between the metric system and traditional measurements. The system was restricted to use in the retail indust ...
system, such that 1m was exactly toise. The Russian verst was 1.0668km. The Swedish mil
A Scandinavian mile (Norwegian and sv, mil, [], like "meal") is a unit of length common in Norway and Sweden, but not Denmark. Today, it is standardised as 1 being , but it had different values in the past.
The word is derived from the same ...
was 10.688km, but was changed to 10km when Sweden converted to metric units.
See also
* Conversion of units for comparisons with other units *International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
* ISO 1
ISO 1 is an international standard set by the International Organization for Standardization that specifies the standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification. The temperature is fixed at 20 °C, which is ...
standard reference temperature for length measurements
* Length measurement
* Metre Convention
* Metric system
* Metric prefix
* Metrication
* Orders of magnitude (length)
* SI prefix
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
* Speed of light
* Vertical metre
Vertical position or vertical location, also known as vertical level or simply level, is a position along a vertical direction above or below a given vertical datum (reference level).
Vertical distance or vertical separation is the distance betwe ...
Notes
References
* * Astin, A. V. & Karo, H. Arnold, (1959)''Refinement of values for the yard and the pound''
Washington DC: National Bureau of Standards, republished on National Geodetic Survey web site and the Federal Register (Doc. 59-5442, Filed, 30 June 1959) * * * * * *
Retrieved 26 May 2010. * National Institute of Standards and Technology. (27 June 2011).
NIST-F1 Cesium Fountain Atomic Clock
'. Author. * National Physical Laboratory. (25 March 2010).
Iodine-Stabilised Lasers
'. Author. * * Republic of the Philippines. (2 December 1978).
'. Author. * Republic of the Philippines. (10 October 1991). '' ttps://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/1991/10oct/19911010-RA-7160-CCA.pdf Republic Act No. 7160: The Local Government Code of the Philippines'. Author. * Supreme Court of the Philippines (Second Division). (20 January 2010).
G.R. No. 185240
'. Author. * Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (Eds.). (2008a)
''The International System of Units (SI)''
United States version of the English text of the eighth edition (2006) of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures publication ''Le Système International d’ Unités (SI)'' (Special Publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 18 August 2008. * Taylor, B.N. and Thompson, A. (2008b)
''Guide for the Use of the International System of Units''
(Special Publication 811). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 23 August 2008. * Turner, J. (Deputy Director of the National Institute of Standards and Technology). (16 May 2008
"Interpretation of the International System of Units (the Metric System of Measurement) for the United States"
''Federal Register'' Vol. 73, No. 96, p.28432-3. * Zagar, B.G. (1999)
Laser interferometer displacement sensors
in J.G. Webster (ed.). ''The Measurement, Instrumentation, and Sensors Handbook.'' CRC Press. . {{Authority control SI base units