Metal Amido Complexes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amide
File:Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer.png, Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer
File:Tris(dimethylamino)gallium dimer.png, Tris(dimethylamino)gallium dimer
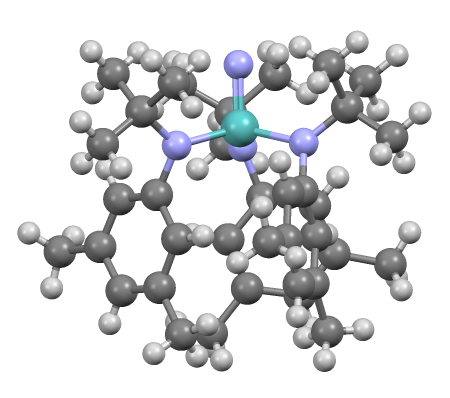
File:Ti(NMe2)4.png, Tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium
File:Ta(NMe2)5.png, Pentakis(dimethylamido)tantalum
In practice, bulky amide ligands have a lesser tendency to bridge. Amide ligands may participate in metal-ligand π-bonding giving a complex with the metal center being co-planar with the nitrogen and substituents. Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides form a significant subcategory of metal amide compounds. These compounds tend to be discrete and soluble in organic solvents.
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
s have two electron pairs available for bonding. In principle, they can be terminal or bridging. In these two examples, the dimethylamido ligands are both bridging and terminal:
Alkali metal amides
Lithium amides are the most important amides, as they are readily prepared fromn-butyllithium
''n''-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated ''n''-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly emp ...
and the appropriate amine, and they are more stable and soluble than the other alkali metal analogs. Potassium amides are prepared by transmetallation of lithium amides with potassium t-butoxide (see also Schlosser base) or by reaction of the amine with potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
, potassium hydride
Potassium hydride, KH, is the inorganic compound of potassium and hydrogen. It is an alkali metal hydride. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear gray. It is a powerful superbase that is useful in organic synthesis. It is sold c ...
, n-butylpotassium, or benzylpotassium.
The alkali metal amides, MNH2 (M = Li, Na, K) are commercially available. Sodium amide (also known as sodamide) is synthesized from sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
metal and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
with ferric nitrate catalyst. The sodium compound is white, but the presence of metallic iron turns the commercial material gray.
:2 Na + 2 NH3 → 2 NaNH2 + H2
Lithium diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature ...
is a popular non-nucleophilic base
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a sterically hindered organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical ...
used in organic synthesis. Unlike many other bases, the steric bulk prevents this base from acting as a nucleophile. It is commercially available, usually as a solution in hexane. It may be readily prepared from n-butyllithium
''n''-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated ''n''-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly emp ...
and diisopropylamine.
Transition metal complexes
Early transition metal amides may be prepared by treating anhydrous metal chloride with alkali amide reagents, or with two equivalents of amine, the second equivalent acting as a base: :MCln + n LiNR2 → M(NR2)n + n LiCl :MCln + 2n HNR2 → M(NR2)n + n HNR2·HCl Transition metal amide complexes may be prepared by: * treating a halide complex with an alkali amide * treating an alkoxide complex with an amine * deprotonation of a coordinated amine *oxidative addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxid ...
of an amine
With two organic substituents, amides derived from secondary amines can be especially bulky ligands.

Amides as intermediates
Transition metal amides are intermediates in the base-induced substitution of transition metal ammine complexes. Thus the Sn1CB mechanism for the displacement of chloride from chloropentamminecobalt chloride by hydroxide proceeds via an amido intermediate:G. L. Miessler and D. A. Tarr "Inorganic Chemistry" 3rd Ed, Pearson/Prentice Hall publisher, {{ISBN, 0-13-035471-6. : o(NH3)5Clsup>2+ + OH− → o(NH3)4(NH2)sup>2+ + H2O + Cl− : o(NH3)4NH2sup>2+ + H2O → o(NH3)5OHsup>2+See also
*Inorganic imide The inorganic imides are compounds containing an ion composed of nitrogen bonded to hydrogen with formula HN2−. Organic imides have the NH group, and two single or one double covalent bond to other atoms. The imides are related to the inorganic a ...
References