Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the
largest city in the
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and the
second most populous city in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
after
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, as well as one of the world's most populous
megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of
Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban a ...
. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits ,
Los Angeles is known for its
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the
Hollywood film industry
The cinema of the United States, consisting mainly of major film studios (also known as Hollywood) along with some independent film, has had a large effect on the global film industry since the early 20th century. The dominant style of Ame ...
, and its
sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in
a basin in Southern California adjacent to the
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
in the west and extending through the
Santa Monica Mountains
The Santa Monica Mountains is a coastal mountain range in Southern California, next to the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Transverse Ranges. Because of its proximity to densely populated regions, it is one of the most visited natural areas in ...
and north into the
San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the
San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about ,
and is the
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
of
Los Angeles County, which is the
most populous county in the United States with an estimated 9.86 million residents .
Home to the
Chumash Chumash may refer to:
*Chumash (Judaism), a Hebrew word for the Pentateuch, used in Judaism
*Chumash people, a Native American people of southern California
*Chumashan languages, indigenous languages of California
See also
*Chumash traditional n ...
and
Tongva
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people prefer Kizh as an endonym that, they argue, is more historically ...
indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
s, the area that became Los Angeles was claimed by
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo for
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in 1542. The city was founded on September 4, 1781, under Spanish governor
Felipe de Neve
Felipe de Neve y Padilla (1724 – 3 November 1784) was a Spanish soldier who served as the 4th Governor of the Californias, from 1775 to 1782. Neve is considered one of the founders of Los Angeles and was instrumental in the foundation of San ...
, on the village of
Yaanga
Yaanga was a large Tongva (or Kizh) village originally located near what is now downtown Los Angeles, just west of the Los Angeles River and beneath U.S. Route 101. People from the village were recorded as ''Yabit'' in missionary records althou ...
.
It became a part of
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
in 1821 following the
Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
. In 1848, at the end of the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, Los Angeles and the rest of California were purchased as part of the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
, and thus became part of the United States. Los Angeles was
incorporated as a municipality on April 4, 1850, five months before California achieved
statehood. The discovery of
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
in the 1890s brought rapid growth to the city. The city was further expanded with the completion of the
Los Angeles Aqueduct in 1913, which delivers water from
Eastern California
Eastern California is a region defined as either the strip to the east of the crest of the Sierra Nevada or as the easternmost counties of California.
Demographics
According to the 2010 census, the population of the eastern border counties of Ca ...
.
Los Angeles has a diverse economy, and hosts businesses in a broad range of professional and cultural fields. It also has the
busiest container port in the Americas. In 2018, the Los Angeles metropolitan area had a
gross metropolitan product
Gross metropolitan product (GMP) is a monetary measure of the value of all final goods and services produced within a metropolitan statistical area during a specified period (''e.g.'', a quarter, a year). GMP estimates are commonly used to compare ...
of over $1.0 trillion,
[ making it the city with the third-largest GDP in the world, after ]New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
and Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
. Los Angeles hosted the 1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort to assassinate Emperor Hiro ...
and 1984 Summer Olympics
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the sec ...
and will host the 2028 Summer Olympics
The 2028 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXXIV Olympiad, also known as Los Angeles 2028 or LA28) is an upcoming international multi-sport event scheduled to take place from July 14 to July 30, 2028, in and around Los Angeles, Cali ...
. More recently, statewide droughts in California
The historical and ongoing droughts in California result from various complex meteorological phenomena, some of which are not fully understood by scientists.
Drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended peri ...
have strained both the city’s and Los Angeles County’s water security
Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. T ...
.
Pronunciation of the name
 The local English pronunciation of the name of the city has varied over time. A 1953 article in the
The local English pronunciation of the name of the city has varied over time. A 1953 article in the journal
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to:
*Bullet journal, a method of personal organization
*Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period
*Daybook, also known as a general journal, a ...
of the American Name Society
The American Name Society (ANS) is a non-profit organization founded in 1951 to promote onomastics, the study of names and naming practices, both in the United States and abroad. The organization investigates cultural insights, settlement history, ...
asserts that the pronunciation was established following the 1850 incorporation of the city and that since the 1880s the pronunciation emerged out of a trend in California to give places Spanish, or Spanish-sounding, names and pronunciations.Charles Fletcher Lummis
Charles Fletcher Lummis (March 1, 1859, in Lynn, Massachusetts – November 25, 1928, in Los Angeles, California) was a United States journalist, and an activist for Indian rights and historic preservation. A traveler in the American Southwest, h ...
, who argued for the name's pronunciation with a hard ''g'' (), reported that there were at least 12 pronunciation variants. In the early 1900s, the ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the U ...
'' advocated for pronouncing it ''Loce AHNG-hayl-ais'' (), approximating Spanish , by printing the respelling under its masthead for several years.
History
Pre-colonial history
The Los Angeles coastal area was settled by the Tongva
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people prefer Kizh as an endonym that, they argue, is more historically ...
(''Gabrieleño'') and Chumash Chumash may refer to:
*Chumash (Judaism), a Hebrew word for the Pentateuch, used in Judaism
*Chumash people, a Native American people of southern California
*Chumashan languages, indigenous languages of California
See also
*Chumash traditional n ...
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
. Los Angeles would eventually be founded on the village of ''iyáanga’'' or Yaanga
Yaanga was a large Tongva (or Kizh) village originally located near what is now downtown Los Angeles, just west of the Los Angeles River and beneath U.S. Route 101. People from the village were recorded as ''Yabit'' in missionary records althou ...
(written "Yang-na" by the Spanish), meaning " poison oak place".Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
in 1542 while on an official military exploring expedition moving northward along the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
coast from earlier colonizing bases of New Spain in Central and South America. Gaspar de Portolà
Gaspar is a given and/or surname of French, German, Portuguese, and Spanish origin, cognate to Casper (given name) or Casper (surname).
It is a name of biblical origin, per Saint Gaspar, one of the wise men mentioned in the Bible.
Notable peo ...
and Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
missionary Juan Crespí
Joan Crespí or Juan Crespí (1 March 1721 – 1 January 1782) was a Franciscan missionary and explorer of Las Californias.
Biography
A native of Majorca, Crespí entered the Franciscan order at the age of seventeen. He came to New Spain ...
reached the present site of Los Angeles on August 2, 1769.
Spanish rule
 In 1771, Franciscan
In 1771, Franciscan friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders founded in the twelfth or thirteenth century; the term distinguishes the mendicants' itinerant apostolic character, exercised broadly under the jurisdiction of a superior general, from the ...
Junípero Serra
Junípero Serra y Ferrer (; ; ca, Juníper Serra i Ferrer; November 24, 1713August 28, 1784) was a Spanish Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Order. He is credited with establishing the Franciscan Missions in the Sierr ...
directed the building of the Mission San Gabriel Arcángel, the first mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
in the area.
Mexican rule
New Spain achieved its independence from the Spanish Empire in 1821, and the pueblo now existed within the new Mexican Republic. During Mexican rule, Governor Pío Pico made Los Angeles, Alta California's regional capital. By this time, the new republic introduced more secularization
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
acts within the Los Angeles region. In 1846, during the wider Mexican-American war, marines from the United States occupied the pueblo. This resulted in the siege of Los Angeles where 150 Mexican militias fought the occupiers which eventually surrendered.
1847 to present
Mexican rule ended during the Mexican–American War: Americans took control from the Californios
Californio (plural Californios) is a term used to designate a Hispanic Californian, especially those descended from Spanish and Mexican settlers of the 17th through 19th centuries. California's Spanish-speaking community has resided there sinc ...
after a series of battles, culminating with the signing of the Treaty of Cahuenga on January 13, 1847.
Railroads arrived with the completion of the transcontinental Southern Pacific line from to Los Angeles in 1876 and the Santa Fe Railroad
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison and Topeka, Kansas, and ...
in 1885.water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
. The completion of the Los Angeles Aqueduct in 1913, under the supervision of William Mulholland, ensured the continued growth of the city.zoning
Zoning is a method of urban planning in which a municipality or other tier of government divides land into areas called zones, each of which has a set of regulations for new development that differs from other zones. Zones may be defined for a si ...
ordinance in the United States. On September 14, 1908, the Los Angeles City Council
The Los Angeles City Council is the legislative body of the City of Los Angeles in California.
The council is composed of 15 members elected from single-member districts for four-year terms. The president of the council and the president pro tem ...
promulgated residential and industrial land use zones. The new ordinance established three residential zones of a single type, where industrial uses were prohibited. The proscriptions included barns, lumber yards, and any industrial land use employing machine-powered equipment. These laws were enforced against industrial properties after the fact. These prohibitions were in addition to existing activities that were already regulated as nuisances. These included explosives warehousing, gas works, oil drilling, slaughterhouses, and tanneries. Los Angeles City Council also designated seven industrial zones within the city. However, between 1908 and 1915, the Los Angeles City Council created various exceptions to the broad proscriptions that applied to these three residential zones, and as a consequence, some industrial uses emerged within them. There are two differences between the 1908 Residence District Ordinance and later zoning laws in the United States. First, the 1908 laws did not establish a comprehensive zoning map as the 1916 New York City Zoning Ordinance did. Second, the residential zones did not distinguish types of housing; they treated apartments, hotels, and detached-single-family housing equally.World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
Los Angeles was a major center of wartime manufacturing, such as shipbuilding and aircraft. Calship built hundreds of Liberty Ship
Liberty ships were a class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost construction. Ma ...
s and Victory Ship
The Victory ship was a class of cargo ship produced in large numbers by North American shipyards during World War II to replace losses caused by German submarines. They were a more modern design compared to the earlier Liberty ship, were sli ...
s on Terminal Island, and the Los Angeles area was the headquarters of six of the country's major aircraft manufacturers ( Douglas Aircraft Company, Hughes Aircraft
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other pro ...
, Lockheed, North American Aviation, Northrop Corporation
Northrop Corporation was an American aircraft manufacturer from its formation in 1939 until its 1994 merger with Grumman to form Northrop Grumman. The company is known for its development of the flying wing design, most successfully the B-2 Sp ...
, and Vultee). During the war, more aircraft were produced in one year than in all the pre-war years since the Wright brothers flew the first airplane in 1903, combined. Manufacturing in Los Angeles skyrocketed, and as William S. Knudsen, of the National Defense Advisory Commission put it, "We won because we smothered the enemy in an avalanche of production, the like of which he had never seen, nor dreamed possible."
After the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
Los Angeles grew more rapidly than ever, sprawling into the San Fernando Valley.Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
during the 1950s and 1960s helped propel suburban growth and signaled the demise of the city's electrified rail system, once the world's largest.
As a consequence of World War II, suburban growth, and population density, many amusement parks were built and operated in this area.Beverly Center
Beverly Center is a shopping mall in Los Angeles, California, United States. It is an eight-story structure located at the edge of Beverly Hills and West Hollywood, between La Cienega and San Vicente boulevards. Anchor tenants include Blooming ...
.ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical fou ...
transmission was sent from the University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California S ...
(UCLA) to the Stanford Research Institute
SRI International (SRI) is an American nonprofit scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California. The trustees of Stanford University established SRI in 1946 as a center of innovation to support economic ...
in Menlo Park.Symbionese Liberation Army
The United Federated Forces of the Symbionese Liberation Army (SLA) was a small, American far-left organization active between 1973 and 1975; it claimed to be a vanguard movement. The FBI and American law enforcement considered the SLA to be the ...
's South Central standoff in 1974 and the Hillside Stranglers murder cases in 1977–1978.Simi Valley
Simi Valley (; Chumash: ''Shimiyi'') is a city in the valley of the same name in the southeast region of Ventura County, California, United States. Simi Valley is from Downtown Los Angeles, making it part of the Greater Los Angeles Area. The ...
jury of four Los Angeles Police Department
The Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD), officially known as the City of Los Angeles Police Department, is the municipal police department of Los Angeles, California. With 9,974 police officers and 3,000 civilian staff, it is the third-large ...
(LAPD) officers captured on videotape beating Rodney King
Rodney Glen King (April 2, 1965June 17, 2012) was an African American man who was a victim of police brutality. On March 3, 1991, he was beaten by Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD) officers during his arrest after a pursuit for driving whi ...
, culminating in large-scale riots.Rampart scandal
The Rampart scandal involved widespread police corruption in the Community Resources Against Street Hoodlums (CRASH) anti-gang unit of the Los Angeles Police Department's Rampart Division in the late 1990s. More than 70 police officers either as ...
, one of the most extensive documented cases of police misconduct in American history.
In 2002, Mayor James Hahn
James Kenneth Hahn (born July 3, 1950) is an American lawyer and politician. A Democrat, Hahn was elected the 40th mayor of Los Angeles in 2001. He served until 2005, at which time he was defeated in his bid for re-election. Prior to his term a ...
led the campaign against secession, resulting in voters defeating efforts by the San Fernando Valley and Hollywood to secede from the city.
In 2022
File:2022 collage V1.png, Clockwise, from top left: Road junction at Yamato-Saidaiji Station several hours after the assassination of Shinzo Abe; Anti-government protest in Sri Lanka in front of the Presidential Secretariat; The global monkeypo ...
, Karen Bass
Karen Ruth Bass (; born October 3, 1953) is an American politician, social worker and former physician assistant who is serving as the 43rd mayor of Los Angeles since 2022. A member of the Democratic Party, Bass had previously served in the U.S ...
became the city's first female mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
, making Los Angeles the largest US city to have ever had a woman as mayor.
Los Angeles will host the 2028 Summer Olympics
The 2028 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXXIV Olympiad, also known as Los Angeles 2028 or LA28) is an upcoming international multi-sport event scheduled to take place from July 14 to July 30, 2028, in and around Los Angeles, Cali ...
and Paralympic Games, making Los Angeles the third city to host the Olympics three times.
Geography
Topography
 The city of Los Angeles covers a total area of , comprising of land and of water.
The city of Los Angeles covers a total area of , comprising of land and of water.Mount Lukens
Mount Lukens is a mountain peak of the San Gabriel Mountains, in Los Angeles County, Southern California.
Geography
It is in the Sunland-Tujunga community within the northeast corner of the city of Los Angeles, above the Crescenta Valley. Th ...
at , located at the northeastern end of the San Fernando Valley. The eastern end of the Santa Monica Mountains
The Santa Monica Mountains is a coastal mountain range in Southern California, next to the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Transverse Ranges. Because of its proximity to densely populated regions, it is one of the most visited natural areas in ...
stretches from Downtown to the Pacific Ocean and separates the Los Angeles Basin from the San Fernando Valley. Other hilly parts of Los Angeles include the Mt. Washington area north of Downtown, eastern parts such as Boyle Heights
Boyle is an English, Irish and Scottish surname of Gaelic, Anglo-Saxon or Norman origin. In the northwest of Ireland it is one of the most common family names. Notable people with the surname include:
Disambiguation
*Adam Boyle (disambiguation), ...
, the Crenshaw district around the Baldwin Hills, and the San Pedro district.
Surrounding the city are much higher mountains. Immediately to the north lie the San Gabriel Mountains, which is a popular recreation area for Angelenos. Its high point is Mount San Antonio
Mount San Antonio, commonly referred to as Mount Baldy or Old Baldy, is a summit in the San Gabriel Mountains on the border of Los Angeles and San Bernardino counties of California. Lying within the San Gabriel Mountains National Monument and ...
, locally known as Mount Baldy, which reaches . Further afield, the highest point in southern California is San Gorgonio Mountain, east of downtown Los Angeles, with a height of .
The Los Angeles River
, name_etymology =
, image = File:Los Angeles River from Fletcher Drive Bridge 2019.jpg
, image_caption = L.A. River from Fletcher Drive Bridge
, image_size = 300
, map = LARmap.jpg
, map_size ...
, which is largely seasonal, is the primary drainage channel. It was straightened and lined in of concrete by the Army Corps of Engineers to act as a flood control channel.Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
at the Pacific Ocean. The smaller Ballona Creek
Ballona Creek (pronunciation: “Bah-yo-nuh” or “Buy-yo-nah”
) is an channelized stream in southwestern Los Angeles County, California, United States, that was once a “year-round river lined with sycamores and willows.” Ballona Creek ...
flows into the Santa Monica Bay
Santa Monica Bay is a bight of the Pacific Ocean in Southern California, United States. Its boundaries are slightly ambiguous, but it is generally considered to be the part of the Pacific within an imaginary line drawn between Point Dume, in ...
at Playa del Rey
Playa del Rey (Spanish for "Beach of the King") is a seaside community in the Santa Monica Bay and the Westside region of Los Angeles, California. It has a ZIP code of 90293 and area codes of 310 and 424. As of 2018, the community had a populat ...
.
Vegetation
 Los Angeles is rich in native plant species partly because of its diversity of habitats, including beaches,
Los Angeles is rich in native plant species partly because of its diversity of habitats, including beaches, wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
s, and mountains. The most prevalent plant communities are coastal sage scrub, chaparral shrubland, and riparian woodland.California poppy
''Eschscholzia californica'', the California poppy, golden poppy, California sunlight or cup of gold, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae, native to the United States and Mexico. It is cultivated as an ornamental pla ...
, matilija poppy, toyon
''Heteromeles arbutifolia'' (; more commonly by Californian botanists), commonly known as toyon, is a common perennial shrub native to extreme southwest Oregon, California, and the Baja California Peninsula. It is the sole species in the genus ...
, Ceanothus, Chamise
''Adenostoma fasciculatum'', commonly known as chamise or greasewood, is a flowering plant native to California and Baja California. This shrub is one of the most widespread plants of the California chaparral ecoregion. Chamise produces a specia ...
, Coast Live Oak
''Quercus agrifolia'', the California live oak, or coast live oak, is a highly variable, often evergreen oak tree, a type of live oak, native to the California Floristic Province. It may be shrubby, depending on age and growing location, but is ...
, sycamore
Sycamore is a name which has been applied to several types of trees, but with somewhat similar leaf forms. The name derives from the ancient Greek ' (''sūkomoros'') meaning "fig-mulberry".
Species of trees known as sycamore:
* ''Acer pseudoplata ...
, willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
and Giant Wildrye. Many of these native species, such as the Los Angeles sunflower, have become so rare as to be considered endangered. Although it is not native to the area, the official tree of Los Angeles is the Coral Tree ('' Erythrina caffra'')
Geology
Los Angeles is subject to earthquakes because of its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring o ...
. The geologic instability has produced numerous faults, which cause approximately 10,000 earthquakes annually in Southern California, though most of them are too small to be felt.San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizonta ...
system, which sits at the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
, passes through the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The segment of the fault passing through Southern California experiences a major earthquake roughly every 110 to 140 years, and seismologists have warned about the next "big one", as the last major earthquake was the 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake
The 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake occurred at about 8:20 a.m. (Pacific time) on January 9 in central and Southern California. One of the largest recorded earthquakes in the United States, with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9, it ruptured ...
. The Los Angeles basin and metropolitan area are also at risk from blind thrust earthquakes. Major earthquakes that have hit the Los Angeles area include the 1933 Long Beach, 1971 San Fernando, 1987 Whittier Narrows, and the 1994 Northridge events. All but a few are of low intensity and are not felt. The USGS has released the UCERF California earthquake forecast, which models earthquake occurrence in California. Parts of the city are also vulnerable to tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
s; harbor areas were damaged by waves from Aleutian Islands earthquake in 1946, Valdivia earthquake in 1960, Alaska earthquake in 1964, Chile earthquake __NOTOC__
Chile lay in a region which is adjacent to the fast-moving Nazca Plate, and has high tectonic activity. The records for earlier centuries are apparently incomplete.
Of the world's 46 known earthquakes with M ≥ 8.5 since the year 15 ...
in 2010 and Japan earthquake in 2011.
Cityscape
The city is divided into many different districts and neighborhoods, some of which were incorporated cities that have merged with Los Angeles.
Overview
The city's street patterns generally follow a grid plan, with uniform block lengths and occasional roads that cut across blocks. However, this is complicated by rugged terrain, which has necessitated having different grids for each of the valleys that Los Angeles covers. Major streets are designed to move large volumes of traffic through many parts of the city, many of which are extremely long; Sepulveda Boulevard
Sepulveda Boulevard is a major street and transportation corridor in the City of Los Angeles and several other cities in western Los Angeles County, California. The street parallels Interstate 405 for much of its route. Portions of Sepulveda Bou ...
is long, while Foothill Boulevard is over long, reaching as far east as San Bernardino. Drivers in Los Angeles suffer from one of the worst rush hour periods in the world, according to an annual traffic index by navigation system maker, TomTom
TomTom N.V. is a Dutch multinational developer and creator of location technology and consumer electronics. Founded in 1991 and headquartered in Amsterdam, TomTom released its first generation of satellite navigation devices to market in 2004. ...
. LA drivers spend an additional 92 hours in traffic each year. During the peak rush hour, there is 80% congestion, according to the index.
Los Angeles is often characterized by the presence of low-rise
A low-rise is a building that is only a few stories tall or any building that is shorter than a high-rise, though others include the classification of mid-rise.
Definition
Emporis defines a low-rise as "an enclosed structure below 35 metres 15 ...
buildings, in contrast to New York City. Outside of a few centers such as Downtown, Warner Center
Warner Center is a master-planned neighborhood and business district development in the Canoga Park and Woodland Hills neighborhoods of the San Fernando Valley in Los Angeles, California.Station 84(Woodland Hills) an(Canoga Park) serve Warner Ce ...
, Century City, Koreatown
A Koreatown ( Korean: 코리아타운), also known as a Little Korea or Little Seoul, is a Korean-dominated ethnic enclave within a city or metropolitan area outside the Korean Peninsula.
History
Koreatowns as an East Asian ethnic enclave have ...
, Miracle Mile, Hollywood, and Westwood, skyscrapers and high-rise buildings are not common in Los Angeles. The few skyscrapers built outside of those areas often stand out above the rest of the surrounding landscape. Most construction is done in separate units, rather than wall-to-wall. That being said Downtown Los Angeles itself has many buildings over 30 stories, with fourteen over 50 stories, and two over 70 stories, the tallest of which is the Wilshire Grand Center
Wilshire Grand Center is a skyscraper in the financial district of downtown Los Angeles, California, occupying the entire city block between Wilshire Boulevard and 7th, Figueroa, and Francisco streets. Completed in 2017, it is the tallest b ...
. Also Los Angeles is increasingly becoming a city of apartments rather than single-family dwellings, especially in the dense inner city and Westside neighborhoods.
Climate
Los Angeles has a two-season Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
of dry summer and very mild winter (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Csb'' on the coast and most of downtown, ''Csa'' near the metropolitan region to the west), and receives just enough annual precipitation to avoid being classified as a semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of sem ...
(''BSh)''. The Los Angeles area is also subject to phenomena typical of a
The Los Angeles area is also subject to phenomena typical of a microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
, causing extreme variations in temperature in close physical proximity to each other. For example, the average July maximum temperature at the Santa Monica Pier is whereas it is in Canoga Park, away.droughts in California
The historical and ongoing droughts in California result from various complex meteorological phenomena, some of which are not fully understood by scientists.
Drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended peri ...
have further strained the city's water security
Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. T ...
. Downtown Los Angeles averages of precipitation annually, mainly occurring between November and March,El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date ...
conditions in the Pacific, dry years with cooler water La Niña
La Niña (; ) is an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. The name ''La Niña'' originates from Spanish for "the girl", by an ...
episodes. A series of rainy days can bring floods to the lowlands and mudslides to the hills, especially after wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identi ...
s have denuded the slopes.
Both freezing temperatures and snowfall are extremely rare in the city basin and along the coast, with the last occurrence of a reading at the downtown station being January 29, 1979;Santa Ana winds
The Santa Ana winds (sometimes devil winds) "Scholars who have looked into the name's origins generally agree that it derives from Santa Ana Canyon, the portal where the Santa Ana River -- as well as a congested Riverside (CA-91) Freeway -- leav ...
sometimes bring much warmer and drier conditions to Los Angeles, and raise wildfire risk.
Environmental issues
 A Gabrielino settlement in the area was called ''iyáangẚ'' (written ''Yang-na'' by the Spanish), which has been translated as "poison oak place".
A Gabrielino settlement in the area was called ''iyáangẚ'' (written ''Yang-na'' by the Spanish), which has been translated as "poison oak place".Los Angeles Basin
The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary Structural basin, basin located in Southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an wikt:anomalous, anomalous group of east-west trending chains of mountai ...
and the San Fernando Valley are susceptible to atmospheric inversion
In meteorology, an inversion is a deviation from the normal change of an atmospheric property with altitude. It almost always refers to an inversion of the air temperature lapse rate, in which case it is called a temperature inversion. N ...
, which holds in the exhausts from road vehicles, airplanes, locomotives, shipping, manufacturing, and other sources. The percentage of small particle pollution (the kind that penetrates into the lungs) coming from vehicles in the city can get as high as 55 percent.
The smog season lasts from approximately May to October.low-emission vehicle
A low-emission vehicle is a motor vehicle that emits relatively low levels of motor vehicle emissions. The term may be used in a general sense, but in some countries it is defined in air quality statutes.
Different groups of people ("go greens" ...
s. Smog is expected to continue to drop in the coming years because of aggressive steps to reduce it, which include electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
and hybrid cars, improvements in mass transit, and other measures.
The number of Stage 1 smog alerts in Los Angeles has declined from over 100 per year in the 1970s to almost zero in the new millennium. Despite improvement, the 2006 and 2007 annual reports of the American Lung Association
The American Lung Association is a voluntary health organization whose mission is to save lives by improving lung health and preventing lung disease through education, advocacy and research.
History
The organization was founded in 1904 to figh ...
ranked the city as the most polluted in the country with short-term particle pollution and year-round particle pollution.population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of bobcats
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUC ...
(''Lynx rufus'').Mange
Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infectio ...
is a common problem in this population.selection
Selection may refer to:
Science
* Selection (biology), also called natural selection, selection in evolution
** Sex selection, in genetics
** Mate selection, in mating
** Sexual selection in humans, in human sexuality
** Human mating strateg ...
of immune genetics at several loci they do not demonstrate that this produces a real difference which helps the bobcats to survive future mange outbreaks.
Demographics
The 2010 U.S. census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators serving ...
reported Los Angeles had a population of 3,792,621. According to the 2010 United States Census, Los Angeles had a median household income of $49,497, with 22.0% of the population living below the federal poverty line.
According to the 2010 United States Census, Los Angeles had a median household income of $49,497, with 22.0% of the population living below the federal poverty line.
Race and ethnicity
 According to the 2010 census, the racial makeup of Los Angeles included: 1,888,158
According to the 2010 census, the racial makeup of Los Angeles included: 1,888,158 Whites
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
(49.8%), 365,118 African Americans (9.6%), 28,215 Native Americans (0.7%), 426,959 Asians (11.3%), 5,577 Pacific Islanders
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oce ...
(0.1%), 902,959 from other races
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
(23.8%), and 175,635 (4.6%) from two or more races.Ethnic enclave
In sociology, an ethnic enclave is a geographic area with high ethnic concentration, characteristic cultural identity, and economic activity. The term is usually used to refer to either a residential area or a workspace with a high concentration ...
s like Chinatown, Historic Filipinotown, Koreatown
A Koreatown ( Korean: 코리아타운), also known as a Little Korea or Little Seoul, is a Korean-dominated ethnic enclave within a city or metropolitan area outside the Korean Peninsula.
History
Koreatowns as an East Asian ethnic enclave have ...
, Little Armenia, Little Ethiopia, Tehrangeles, Little Tokyo, Little Bangladesh, and Thai Town provide examples of the polyglot
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all Eu ...
character of Los Angeles.
Non-Hispanic Whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Ame ...
were 28.7% of the population in 2010,Los Feliz
LOS, or Los, or LoS may refer to:
Science and technology
* Length of stay, the duration of a single episode of hospitalisation
* Level of service, a measure used by traffic engineers
* Level of significance, a measure of statistical significanc ...
.
Mexican ancestry make up the largest ethnic group of Hispanics at 31.9% of the city's population, followed by those of Salvadoran (6.0%) and Guatemalan (3.6%) heritage. The Hispanic population has a long established Mexican-American and Central American community and is spread well-nigh throughout the entire city of Los Angeles and its metropolitan area. It is most heavily concentrated in regions around Downtown as East Los Angeles, Northeast Los Angeles
Northeast Los Angeles (abbreviated NELA) is a region of Los Angeles County, comprising seven neighborhoods within the City of Los Angeles. The area is home to Occidental College located in Eagle Rock.
History
The bulk of the area closer to Pu ...
and Westlake. Furthermore, a vast majority of residents in neighborhoods in eastern South Los Angeles
South Los Angeles, also known as South Central Los Angeles or simply South Central, is a region in southwestern Los Angeles County, lying mostly within the city limits of Los Angeles, south of downtown.
It is "defined on Los Angeles city maps as a ...
towards Downey are of Hispanic origin.
The largest Asian ethnic groups are Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
(3.2%) and Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
(2.9%), which have their own established ethnic enclaves—Koreatown
A Koreatown ( Korean: 코리아타운), also known as a Little Korea or Little Seoul, is a Korean-dominated ethnic enclave within a city or metropolitan area outside the Korean Peninsula.
History
Koreatowns as an East Asian ethnic enclave have ...
in the Wilshire Center and Historic Filipinotown. Chinese people, which make up 1.8% of Los Angeles's population, reside mostly outside of Los Angeles city limits and rather in the San Gabriel Valley of eastern Los Angeles County, but make a sizable presence in the city, notably in Chinatown. Chinatown and Thaitown are also home to many Thais and Cambodians
The Khmer people ( km, ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, ) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million. , which make up 0.3% and 0.1% of Los Angeles's population, respectively. The Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
comprise 0.9% of LA's population and have an established Little Tokyo in the city's downtown, and another significant community of Japanese Americans is in the Sawtelle district of West Los Angeles. Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
make up 0.5% of Los Angeles's population. Indians make up 0.9% of the city's population. The city is also home to Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Assyrians, and Iranians, many of whom live in enclaves like Little Armenia and Tehrangeles.
African Americans have been the predominant ethnic group in South Los Angeles
South Los Angeles, also known as South Central Los Angeles or simply South Central, is a region in southwestern Los Angeles County, lying mostly within the city limits of Los Angeles, south of downtown.
It is "defined on Los Angeles city maps as a ...
, which has emerged as the largest African American community in the western United States since the 1960s. The neighborhoods of South Los Angeles with highest concentration of African Americans include Crenshaw, Baldwin Hills, Leimert Park, Hyde Park, Gramercy Park, Manchester Square
Manchester Square is an 18th-century garden square in Marylebone, London. Centred north of Oxford Street it measures internally north-to-south, and across. It is a small Georgian predominantly 1770s-designed instance in central London; co ...
and Watts.Mid-Wilshire
Mid-Wilshire is a neighborhood in the central region of Los Angeles, California. It is known for the Los Angeles County Museum of Art, the Petersen Automotive Museum, and the Miracle Mile shopping district.
Geography
City of Los Angeles bound ...
have a moderate concentration of African Americans as well.
Los Angeles has the second largest Mexican, Armenian, Salvadoran, Filipino and Guatemalan population by city in the world, the third largest Canadian population in the world, and has the largest Japanese, Iranian/Persian, Cambodian and Romani (Gypsy) population in the country.
There is an Italian community in Los Angeles. Italians are concentrated in San Pedro.
Religion
 According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, Christianity is the most prevalently practiced religion in Los Angeles (65%).
According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, Christianity is the most prevalently practiced religion in Los Angeles (65%).[Major U.S. metropolitan areas differ in their religious profiles](_blank)
Pew Research CenterRoman Catholic Archdiocese of Los Angeles
The Archdiocese of Los Angeles ( la, Archidiœcesis Angelorum in California, es, Arquidiócesis de Los Ángeles) is an ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church ( particularly the Roman Catholic or Latin Church) located in th ...
is the largest archdiocese in the country. Cardinal Roger Mahony, as the archbishop, oversaw construction of the Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels
The Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels ( es, Catedral de Nuestra Señora de los Ángeles), informally known as COLA or the Los Angeles Cathedral, is a cathedral of the Roman Catholic Church in Los Angeles, California, United States. It opened in 2 ...
, which opened in September 2002 in Downtown Los Angeles.
In 2011, the once common, but ultimately lapsed, custom of conducting a procession and Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
in honor of Nuestra Señora de los Ángeles, in commemoration of the founding of the City of Los Angeles in 1781, was revived by the Queen of Angels Foundation and its founder Mark Albert, with the support of the Archdiocese of Los Angeles as well as several civic leaders. The recently revived custom is a continuation of the original processions and Masses that commenced on the first anniversary of the founding of Los Angeles in 1782 and continued for nearly a century thereafter.
With 621,000 Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
in the metropolitan area, the region has the second-largest population of Jews in the United States, after New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.Boyle Heights
Boyle is an English, Irish and Scottish surname of Gaelic, Anglo-Saxon or Norman origin. In the northwest of Ireland it is one of the most common family names. Notable people with the surname include:
Disambiguation
*Adam Boyle (disambiguation), ...
once had a large Jewish population prior to World War II due to restrictive housing covenants. Major Orthodox Jewish neighborhoods include Hancock Park
Hancock Park is a city park in the Miracle Mile section of the Mid-Wilshire neighborhood in Los Angeles, California.
The park's destinations include the La Brea Tar Pits; the adjacent George C. Page Museum of La Brea Discoveries, which displ ...
, Pico-Robertson Pico-Robertson is a relatively densely-populated neighborhood in the Westside of Los Angeles, California, flanked on the north, northeast, and west by Beverly Hills, on the east by Carthay and Mid-City, on the south by Mid-City, Beverlywood and ...
, and Valley Village
Valley Village is a neighborhood in the city of Los Angeles, located within the San Fernando Valley.
History
Founding
According to Elke Garman, co-president of the Valley Village Homeowners Association in 1991, the history of Valley Village wen ...
, while Jewish Israelis are well represented in the Encino and Tarzana neighborhoods, and Persian Jews
Persian Jews or Iranian Jews ( fa, یهودیان ایرانی, ''yahudiān-e-Irāni''; he, יהודים פרסים ''Yəhūdīm Parsīm'') are the descendants of Jews who were historically associated with the Persian Empire, whose successor ...
in Beverly Hills
Beverly Hills is a city located in Los Angeles County, California. A notable and historic suburb of Greater Los Angeles, it is in a wealthy area immediately southwest of the Hollywood Hills, approximately northwest of downtown Los Angeles. ...
. Many varieties of Judaism are represented in the greater Los Angeles area, including Reform
Reform ( lat, reformo) means the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The use of the word in this way emerges in the late 18th century and is believed to originate from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement ...
, Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
, Orthodox, and Reconstructionist. The Breed Street Shul
Breed Street Shul, also known as Congregation Talmud Torah of Los Angeles or Breed Street Synagogue, is an Orthodox Jewish synagogue in the Boyle Heights section of Los Angeles, California. It was the largest Orthodox synagogue west of Chicago fr ...
in East Los Angeles, built in 1923, was the largest synagogue west of Chicago in its early decades; it is no longer in daily use as a synagogue and is being converted to a museum and community center. The Kabbalah Centre
The Kabbalah Centre International is a non-profit organizationworldwide
located in Los Angeles, California that provides courses on the Zohar and Kabbalistic teachings online as well as through its regional and city-based centers and study groups ...
also has a presence in the city.
The International Church of the Foursquare Gospel
The Foursquare Church is an Evangelical Pentecostal Christian denomination founded in 1923 by preacher Aimee Semple McPherson. The headquarters are in Los Angeles, California, United States.
History
The church has its origins in a vision of ...
was founded in Los Angeles by Aimee Semple McPherson in 1923 and remains headquartered there to this day. For many years, the church convened at Angelus Temple
Angelus Temple is a Pentecostal megachurch of the International Church of the Foursquare Gospel in the Echo Park district of Los Angeles, California, United States. The senior pastor is Matthew Barnett. The maximum capacity is 8,975 persons. ...
, which, at its construction, was one of the largest churches in the country.
Los Angeles has had a rich and influential Protestant tradition. The first Protestant service in Los Angeles was a Methodist meeting held in a private home in 1850 and the oldest Protestant church still operating, First Congregational Church, was founded in 1867.Christian Fundamentalist
Christian fundamentalism, also known as fundamental Christianity or fundamentalist Christianity, is a religious movement emphasizing biblical literalism. In its modern form, it began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries among British and ...
movement and the Azusa Street Revival
The Azusa Street Revival was a historic series of revival meetings that took place in Los Angeles, California. It was led by William J. Seymour, an African-American preacher. The revival began on April 9, 1906, and continued until roughly 1915. ...
launched Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement .First Presbyterian Church of Hollywood
The First Presbyterian Church of Hollywood has had a significant impact on both the Presbyterian Church and evangelical Christianity around the world.
The church was founded in 1903. A large brick gothic sanctuary was built in 1923, and seats 1,8 ...
, Bel Air Presbyterian Church, First African Methodist Episcopal Church of Los Angeles, West Angeles Church of God in Christ, Second Baptist Church, Crenshaw Christian Center
The Crenshaw Christian Center is a non-denominational megachurch based in Los Angeles, California. It has around 28,000 members.
History
The church was founded in 1973 by Frederick K. C. Price in Inglewood, California.
In 1981, the church b ...
, McCarty Memorial Christian Church, and First Congregational Church.
The Los Angeles California Temple
The Los Angeles California Temple (formerly the Los Angeles Temple), the tenth operating and the second-largest temple operated by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), is on Santa Monica Boulevard in the Westwood dist ...
, the second-largest temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
operated by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
, is on Santa Monica Boulevard
Santa Monica Boulevard is a major west–east thoroughfare in Los Angeles County. It runs from Ocean Avenue in Santa Monica near the Pacific Ocean to Sunset Boulevard at Sunset Junction in Los Angeles. It passes through Beverly Hills and West Ho ...
in the Westwood neighborhood of Los Angeles. Dedicated in 1956, it was the first temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
built in California and it was the largest in the world when completed.
The Hollywood region of Los Angeles also has several significant headquarters, churches, and the Celebrity Center
Church of Scientology Celebrity Centres are Churches of Scientology that are open to the general public but are intended for "artists, politicians, leaders of industry, and sports figures".
The Celebrity Centre International was established in ...
of Scientology
Scientology is a set of beliefs and practices invented by American author L. Ron Hubbard, and an associated movement. It has been variously defined as a cult, a Scientology as a business, business, or a new religious movement. The most recent ...
.
Because of Los Angeles's large multi-ethnic population, a wide variety of faiths are practiced, including Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Islam, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
, Baháʼí, various Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
es, Sufism, Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
ism, Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a ...
, Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be filled ...
and countless others. Immigrants from Asia for example, have formed a number of significant Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
congregations making the city home to the greatest variety of Buddhists in the world. The first Buddhist joss house
Chinese temple architecture refer to a type of structures used as place of worship of Chinese Buddhism, Taoism or Chinese folk religion, where people revere ethnic Chinese gods and ancestors. They can be classified as:
* '' miào'' () or '' ...
was founded in the city in 1875.Unchurched Belt
The Unchurched Belt is a region in the far Northwestern United States that has low rates of religious participation. The term derives from ''Bible Belt'' and the notion of the unchurched.
The term was first applied to the West Coast of the Unit ...
.
Homelessness
 As of January 2020, there are 41,290
As of January 2020, there are 41,290 homeless people
Homelessness or houselessness – also known as a state of being unhoused or unsheltered – is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and adequate housing. People can be categorized as homeless if they are:
* living on the streets, also kn ...
in the City of Los Angeles, comprising roughly 62% of the homeless population of LA County. This is an increase of 14.2% over the previous year (with a 12.7% increase in the overall homeless population of LA County).Skid Row
A skid row or skid road is an impoverished area, typically urban, in English-speaking North America whose inhabitants are mostly poor people " on the skids". This specifically refers to poor or homeless, considered disreputable, downtrodden or fo ...
neighborhood, which contains 8,000 homeless people, one of the largest stable populations of homeless people in the United States.
Crime
 In 1992, the city of Los Angeles recorded 1,092 murders. Los Angeles experienced a significant decline in crime in the 1990s and late 2000s and reached a 50-year low in 2009 with 314 homicides. This is a rate of 7.85 per 100,000 population—a major decrease from 1980 when a homicide rate of 34.2 per 100,000 was reported. This included 15 officer-involved shootings. One shooting led to the death of a SWAT team member, Randal Simmons, the first in LAPD's history.
In 1992, the city of Los Angeles recorded 1,092 murders. Los Angeles experienced a significant decline in crime in the 1990s and late 2000s and reached a 50-year low in 2009 with 314 homicides. This is a rate of 7.85 per 100,000 population—a major decrease from 1980 when a homicide rate of 34.2 per 100,000 was reported. This included 15 officer-involved shootings. One shooting led to the death of a SWAT team member, Randal Simmons, the first in LAPD's history.Cohen crime family
Meyer Harris "Mickey" Cohen (September 4, 1913 – July 29, 1976) was an American gangster, boxer and entrepreneur based in Los Angeles during the mid-20th century.
Early life
Mickey Cohen was born on September 4, 1913, in New York City to J ...
dominated organized crime in the city during the Prohibition era
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic be ...
Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties forme ...
gangs in the late 1960s and early 1970s.Los Angeles Police Department
The Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD), officially known as the City of Los Angeles Police Department, is the municipal police department of Los Angeles, California. With 9,974 police officers and 3,000 civilian staff, it is the third-large ...
, the city is home to 45,000 gang members, organized into 450 gangs. Among them are the Crips
The Crips is an alliance of street gangs that is based in the coastal regions of Southern California. Founded in Los Angeles, California, in 1969, mainly by Raymond Washington and Stanley Williams, the Crips were initially a single alliance ...
and Bloods
The Bloods are a primarily African-American street gang founded in Los Angeles, California. The gang is widely known for its rivalry with the Crips. It is identified by the red color worn by its members and by particular gang symbols, includ ...
, which are both African American street gangs that originated in the South Los Angeles
South Los Angeles, also known as South Central Los Angeles or simply South Central, is a region in southwestern Los Angeles County, lying mostly within the city limits of Los Angeles, south of downtown.
It is "defined on Los Angeles city maps as a ...
region. Latino street gangs such as the Sureños
Sureños (; Spanish: ''Southerners''), Southern United Raza, Sur 13 or Sureños X3 are groups of loosely affiliated gangs that pay tribute to the Mexican Mafia while in U.S. state and federal correctional facilities. Many Sureño gangs have ...
, a Mexican American street gang, and Mara Salvatrucha
Mara Salvatrucha, commonly known as MS-13, is an international criminal gang that originated in Los Angeles, California, in the 1970s and 1980s. Originally, the gang was set up to protect Salvadoran immigrants from other gangs in the Los Ange ...
, which has mainly members of Salvadoran descent, all originated in Los Angeles. This has led to the city being referred to as the "Gang Capital of America".
Economy

 The economy of Los Angeles is driven by international trade, entertainment (television, motion pictures, video games, music recording, and production), aerospace, technology, petroleum, fashion, apparel, and tourism. Other significant industries include finance, telecommunications, law, healthcare, and transportation. In the 2017
The economy of Los Angeles is driven by international trade, entertainment (television, motion pictures, video games, music recording, and production), aerospace, technology, petroleum, fashion, apparel, and tourism. Other significant industries include finance, telecommunications, law, healthcare, and transportation. In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index
The Global Financial Centres Index (GFCI) is a ranking of the competitiveness of financial centres based on over 29,000 financial centre assessments from an online questionnaire together with over 100 indices from organisations such as the World ...
, Los Angeles was ranked as having the 19th most competitive financial center in the world, and sixth most competitive in the United States (after New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, and Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
).
One of the five major film studios, Paramount Pictures, is within the city limits, its location being part of the so-called "Thirty-Mile Zone
The studio zone, also known as the thirty-mile zone (TMZ), is an area defined by a radius of "Hollywood" used by the American entertainment industry to determine employee benefits for filmwork done within it. Its center has traditionally been ...
" of entertainment headquarters in Southern California.
Los Angeles is the largest manufacturing center in the United States.Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
together comprise the busiest port in the United States by some measures and the fifth-busiest port in the world, vital to trade within the Pacific Rim.Los Angeles metropolitan area
Greater Los Angeles is the second-largest metropolitan region in the United States with a population of 18.5 million in 2021, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Bernardino C ...
has a gross metropolitan product
Gross metropolitan product (GMP) is a monetary measure of the value of all final goods and services produced within a metropolitan statistical area during a specified period (''e.g.'', a quarter, a year). GMP estimates are commonly used to compare ...
of over $1.0 trillion (),Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
and New York.cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
in 2016. , more than 300 existing cannabis businesses (both retailers and their suppliers) have been granted approval to operate in what is considered the nation's largest market.
, Los Angeles is home to three Fortune 500 companies: AECOM
AECOM (, ; formerly AECOM Technology Corporation) is an American multinational infrastructure consulting firm.
AECOM has approximately 51,000 employees, and is number 157 on the 2019 Fortune 500 list.
The company's official name from 1990 t ...
, CBRE Group
CBRE Group, Inc. is an American commercial real estate services and investment firm. The abbreviation CBRE stands for Coldwell Banker Richard Ellis. It is the world's largest commercial real estate services and investment firm (based on 2021 reven ...
, and Reliance Steel & Aluminum Co.The Aerospace Corporation
The Aerospace Corporation is an American nonprofit corporation that operates a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in El Segundo, California. The corporation provides technical guidance and advice on all aspects of space mi ...
, California Pizza Kitchen
California Pizza Kitchen (CPK) is an American casual dining restaurant chain that specializes in California-style pizza. The restaurant was started in 1985 by attorneys Rick Rosenfield and Larry Flax in Beverly Hills, California, United States ...
, Capital Group Companies
Capital Group is an American financial services company. It ranks among the world's oldest and largest investment management organizations, with over $2.6 trillion in assets under management. Founded in Los Angeles, California in 1931, it is ...
, Deluxe Entertainment Services Group
Deluxe Media Inc., also known simply as Deluxe and formerly Deluxe Entertainment Services Group, Inc., is an American multinational multimedia and entertainment service provisions company owned by Platinum Equity, founded in 1915 by Hungarian-b ...
, Dine Brands Global, DreamWorks Animation, Dollar Shave Club, Fandango Media
Fandango Media, LLC is an American ticketing company that sells movie tickets via their website as well as through their mobile app, as well as a provider of television and streaming media information through its subsidiary Rotten Tomatoes.
...
, Farmers Insurance Group
Farmers Insurance Group (informally Farmers) is an American insurer group of vehicles, homes and small businesses and also provides other insurance and financial services products. Farmers Insurance has more than 48,000 exclusive and independen ...
, Forever 21, Hulu, Panda Express
Panda Express is an American fast food restaurant chain that serves American Chinese cuisine. With over 2,200 locations, it is the largest Asian-segment restaurant chain in the United States, where it was founded, and is mainly located in North ...
, SpaceX, Ubisoft Film & Television, The Walt Disney Company
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment industry, entertainment conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios (Burbank), Walt Disney Stud ...
, Universal Pictures
Universal Pictures (legally Universal City Studios LLC, also known as Universal Studios, or simply Universal; common metonym: Uni, and formerly named Universal Film Manufacturing Company and Universal-International Pictures Inc.) is an Ameri ...
, Warner Bros.
Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. (commonly known as Warner Bros. or abbreviated as WB) is an American film and entertainment studio headquartered at the Warner Bros. Studios complex in Burbank, California, and a subsidiary of Warner Bros. D ...
, Warner Music Group
Warner Music Group Corp. ( d.b.a. Warner Music Group, commonly abbreviated as WMG) is an American multinational entertainment and record label conglomerate headquartered in New York City. It is one of the " big three" recording companies and t ...
, and Trader Joe's
Trader Joe's is an American chain of grocery stores headquartered in Monrovia, California. The chain has over 569 stores across the United States.
The first Trader Joe's store was opened in 1967 by founder Joe Coulombe in Pasadena, Californi ...
.
Arts and culture
 Los Angeles is often billed as the "Creative Capital of the World" because one in every six of its residents works in a creative industry and there are more artists, writers, filmmakers, actors, dancers and musicians living and working in Los Angeles than any other city at any other time.
Los Angeles is often billed as the "Creative Capital of the World" because one in every six of its residents works in a creative industry and there are more artists, writers, filmmakers, actors, dancers and musicians living and working in Los Angeles than any other city at any other time.
Movies and the performing arts
The city's Hollywood neighborhood has been recognized as the center of the motion picture industry
The film industry or motion picture industry comprises the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking, i.e., film production companies, film studios, cinematography, animation, film production, screenwriting, pre-production, post pr ...
, having held this distinction since the early 20th century, and the Los Angeles area is also associated with being the center of the television industry
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
. The city is home to major film studios as well as major record labels. Los Angeles plays host to the annual Academy Awards
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
, the Primetime Emmy Awards, the Grammy Awards as well as many other entertainment industry awards shows. Los Angeles is the site of the USC School of Cinematic Arts
The University of Southern California School of Cinematic Arts (SCA) houses seven academic divisions: Film & Television Production; Cinema & Media Studies; John C. Hench Division of Animation + Digital Arts; John Wells Division of Writing for Sc ...
which is the oldest film school in the United States.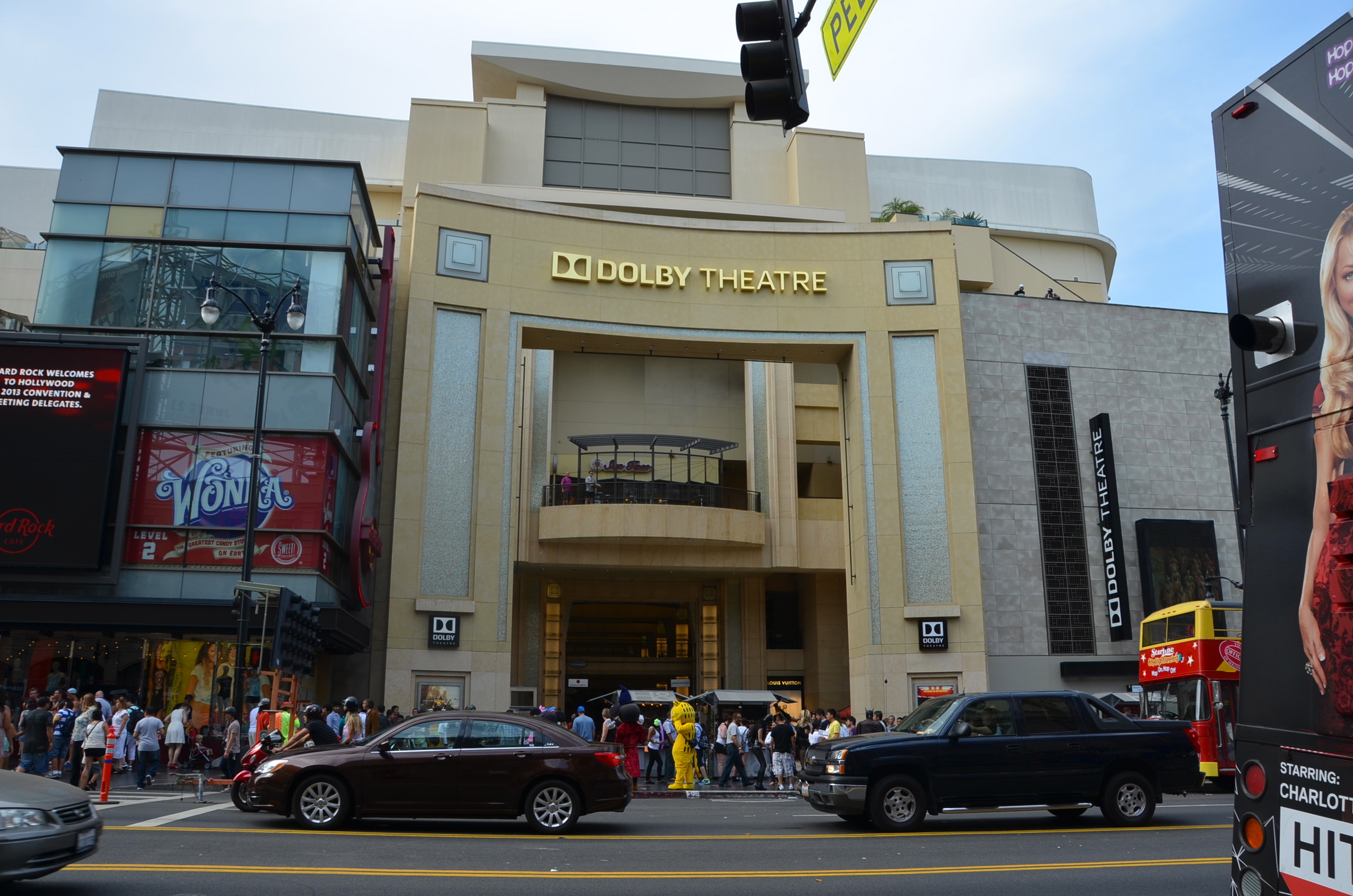  The performing arts play a major role in Los Angeles's cultural identity. According to the USC Stevens Institute for Innovation, "there are more than 1,100 annual theatrical productions and 21 openings every week."
The performing arts play a major role in Los Angeles's cultural identity. According to the USC Stevens Institute for Innovation, "there are more than 1,100 annual theatrical productions and 21 openings every week."Center Theatre Group
Center Theatre Group is a non-profit arts organization located in Los Angeles, California. It is one of the largest theatre companies in the nation, programming subscription seasons year-round at the Mark Taper Forum, the Ahmanson Theatre and the ...
, the Los Angeles Master Chorale
The Los Angeles Master Chorale is a professional chorus in Los Angeles, California, and one of the resident companies of both The Music Center and Walt Disney Concert Hall in Los Angeles. It was founded in 1964 by Roger Wagner to be one of the t ...
, and the Los Angeles Opera are also resident companies of the Music Center. Talent is locally cultivated at premier institutions such as the Colburn School and the USC Thornton School of Music
The USC Thornton School of Music is a private music school in Los Angeles, California. Founded in 1884 only four years after the University of Southern California, the Thornton School is the oldest continually operating arts institution in Los An ...
.
Museums and galleries
There are 841 museums and art galleries in Los Angeles County,Los Angeles County Museum of Art
The Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) is an art museum located on Wilshire Boulevard in the Miracle Mile vicinity of Los Angeles. LACMA is on Museum Row, adjacent to the La Brea Tar Pits (George C. Page Museum).
LACMA was founded in 19 ...
(the largest art museum in the Western United States), the Getty Center (part of the J. Paul Getty Trust, the world's wealthiest art institution), the Petersen Automotive Museum, the Huntington Library
The Huntington Library, Art Museum and Botanical Gardens, known as The Huntington, is a collections-based educational and research institution established by Henry E. Huntington (1850–1927) and Arabella Huntington (c.1851–1924) in San Ma ...
, the Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more. ...
, the Battleship Iowa, and the Museum of Contemporary Art. A significant number of art galleries are on Gallery Row
Gallery Row is a neighborhood in Downtown Los Angeles designated by the City Council in 2003 to promote the concentration of art galleries along Main Street and Spring Street.
Geography
Gallery Row spans north–south along Main and Spring Stre ...
, and tens of thousands attend the monthly Downtown Art Walk there.
Libraries
The Los Angeles Public Library
The Los Angeles Public Library system (LAPL) is a public library system in Los Angeles, California. The system holds more than six million volumes, and with around 19 million residents in the Los Angeles Metropolitan area, it serves the large ...
system operates 72 public libraries in the city. Enclaves of unincorporated areas are served by branches of the County of Los Angeles Public Library
LA County Library is one of the largest public library systems in the United States which serves residents living in 49 of the 88 incorporated cities of Los Angeles County, California. United States, and those living in unincorporated areas r ...
, many of which are within walking distance to residents.
Landmarks
Important landmarks in Los Angeles include the Hollywood Sign, Walt Disney Concert Hall, Capitol Records Building, the Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels
The Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels ( es, Catedral de Nuestra Señora de los Ángeles), informally known as COLA or the Los Angeles Cathedral, is a cathedral of the Roman Catholic Church in Los Angeles, California, United States. It opened in 2 ...
, Angels Flight
Angels Flight is a landmark and historic narrow gauge funicular railway in the Bunker Hill district of Downtown Los Angeles, California. It has two funicular cars, named ''Olivet'' and ''Sinai'', that run in opposite directions on a shared ...
, Grauman's Chinese Theatre, Dolby Theatre, Griffith Observatory, Getty Center, Getty Villa
The Getty Villa is at the easterly end of the Malibu coast in the Pacific Palisades neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. One of two campuses of the J. Paul Getty Museum, the Getty Villa is an educational center and museum dedi ...
, Stahl House, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, L.A. Live, the Los Angeles County Museum of Art
The Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) is an art museum located on Wilshire Boulevard in the Miracle Mile vicinity of Los Angeles. LACMA is on Museum Row, adjacent to the La Brea Tar Pits (George C. Page Museum).
LACMA was founded in 19 ...
, the Venice Canal Historic District
The Venice Canal Historic District is embedded in the residential Venice suburb of Los Angeles, California. The historic district is noteworthy for possessing man-made wetland canals, built in 1905 by developer Abbot Kinney as part of his Ven ...
and boardwalk, Theme Building
The Theme Building is a structure at Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), considered an architectural example of the Space Age design style. Influenced by " Populuxe" architecture, it is an example of the Mid-century modern design movement ...
, Bradbury Building, U.S. Bank Tower, Wilshire Grand Center
Wilshire Grand Center is a skyscraper in the financial district of downtown Los Angeles, California, occupying the entire city block between Wilshire Boulevard and 7th, Figueroa, and Francisco streets. Completed in 2017, it is the tallest b ...
, Hollywood Boulevard
Hollywood Boulevard is a major east–west street in Los Angeles, California. It begins in the east at Sunset Boulevard in the Los Feliz district and proceeds to the west as a major thoroughfare through Little Armenia and Thai Town, Hollywoo ...
, Los Angeles City Hall
Los Angeles City Hall, completed in 1928, is the center of the government of the city of Los Angeles, California, and houses the mayor's office and the meeting chambers and offices of the Los Angeles City Council. It is located in the Civic Cente ...
, Hollywood Bowl, battleship , Watts Towers
The Watts Towers, Towers of Simon Rodia, or ''Nuestro Pueblo'' ("our town" in Spanish) are a collection of 17 interconnected sculptural towers, architectural structures, and individual sculptural features and mosaics within the site of the artis ...
, Staples Center, Dodger Stadium
Dodger Stadium is a baseball stadium in the Elysian Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California. It is the home stadium of Major League Baseball's Los Angeles Dodgers. Opened in 1962, it was constructed in less than three years at a cost of ...
, and Olvera Street.
Cuisine
 Los Angeles's food culture is a fusion of global cuisine brought on by the city's rich immigrant history and population. Latin American immigrants, particularly Mexican immigrants, brought
Los Angeles's food culture is a fusion of global cuisine brought on by the city's rich immigrant history and population. Latin American immigrants, particularly Mexican immigrants, brought taco
A taco (, , ) is a traditional Mexican food consisting of a small hand-sized corn- or wheat-based tortilla topped with a filling. The tortilla is then folded around the filling and eaten by hand. A taco can be made with a variety of fillin ...
s, burrito
A burrito (, ) is a dish in Mexican and Tex-Mex cuisine that took form in Ciudad Juárez, consisting of a flour tortilla wrapped into a sealed cylindrical shape around various ingredients. The tortilla is sometimes lightly grilled or stea ...
s, quesadillas, torta
Torta is a culinary term that can, depending on the cuisine, refer to cakes, pies, flatbreads, sandwiches, or omelettes.
Usually, it refers to:
* cake or pie in South America, much of Europe, and southern Philippines
* flatbread in Spain
* a ...
s, tamale
A tamale, in Spanish tamal, is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of masa, a dough made from nixtamalized corn, which is steamed in a corn husk or banana leaf. The wrapping can either be discarded prior to eating or used as a plate. Tam ...
s, and enchilada
An enchilada (, ) is a Mexican dish consisting of a corn tortilla rolled around a filling and covered with a savory sauce. Enchiladas can be filled with various ingredients, including meats, cheese, beans, potatoes, vegetables, or combinations. ...
s served from food trucks and stands, taquerias, and café
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non ...
s. Asian restaurants, many immigrant-owned, exist throughout the city with hotspots in Chinatown, Koreatown
A Koreatown ( Korean: 코리아타운), also known as a Little Korea or Little Seoul, is a Korean-dominated ethnic enclave within a city or metropolitan area outside the Korean Peninsula.
History
Koreatowns as an East Asian ethnic enclave have ...
, and Little Tokyo. Los Angeles also carries an outsized offering of vegan, vegetarian, and plant-based options. As of 2022, the Michelin Guide recognized 10 restaurants granting 2 restaurants two stars and eight restaurants one star.
Sports
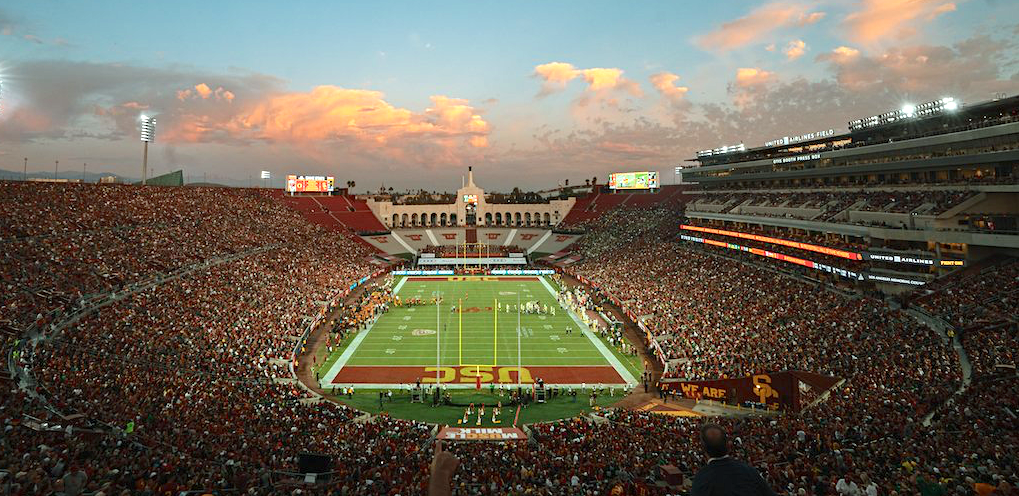 The city of Los Angeles and its metropolitan area are the home of eleven top-level professional sports teams, several of which play in neighboring communities but use Los Angeles in their name. These teams include the
The city of Los Angeles and its metropolitan area are the home of eleven top-level professional sports teams, several of which play in neighboring communities but use Los Angeles in their name. These teams include the Los Angeles Dodgers
The Los Angeles Dodgers are an American professional baseball team based in Los Angeles. The Dodgers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) West division. Established in 1883 in the city of Brooklyn ...
and Los Angeles Angels
The Los Angeles Angels are an American professional baseball team based in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Angels compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) West division. Since 1966, the team h ...
of Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
(MLB), the Los Angeles Rams and Los Angeles Chargers
The Los Angeles Chargers are a professional American football team based in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Chargers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) West division, and ...
of the National Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a professional American football league that consists of 32 teams, divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National Football Conference (NFC). The NFL is one of the ...
(NFL), the Los Angeles Lakers and Los Angeles Clippers
The Los Angeles Clippers are an American professional basketball team based in Los Angeles. The Clippers compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Pacific Division in the league's Western Conference. The Clipper ...
of the National Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America. The league is composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada) and is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United St ...
(NBA), the Los Angeles Kings
The Los Angeles Kings are a professional ice hockey team based in Los Angeles. The team competes in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Pacific Division in the Western Conference and was founded on June 5, 1967, after Jack Kent ...
and Anaheim Ducks of the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
(NHL), the Los Angeles Galaxy
LA Galaxy, also known as the Los Angeles Galaxy, are an American professional soccer club based in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Galaxy competes in Major League Soccer (MLS), as a member of the Western Conference. The club began pla ...
and Los Angeles FC of Major League Soccer (MLS), and the Los Angeles Sparks of the Women's National Basketball Association
The Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA) is an American professional basketball league. It is composed of twelve teams, all based in the United States. The league was founded on April 22, 1996, as the women's counterpart to the Natio ...
(WNBA).
Other notable sports teams include the UCLA Bruins
The UCLA Bruins are the athletic teams that represent the University of California, Los Angeles. The Bruin men's and women's teams participate in NCAA Division I as part of the Pac-12 Conference and the Mountain Pacific Sports Federation (MPSF) ...
and the USC Trojans
The USC Trojans are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent the University of Southern California (USC), located in Los Angeles, California. While the men's teams are nicknamed the ''Trojans'', the women's athletic teams are referred ...
in the National Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges ...
(NCAA), both of which are Division I teams in the Pac-12 Conference, but will soon be moved to the Big Ten Conference
The Big Ten Conference (stylized B1G, formerly the Western Conference and the Big Nine Conference) is the oldest Division I collegiate athletic conference in the United States. Founded as the Intercollegiate Conference of Faculty Representati ...
.
 Los Angeles is the second-largest city in the United States but hosted no NFL team between 1995 and 2015. At one time, the Los Angeles area hosted two NFL teams: the Rams and the Raiders. Both left the city in 1995, with the Rams moving to
Los Angeles is the second-largest city in the United States but hosted no NFL team between 1995 and 2015. At one time, the Los Angeles area hosted two NFL teams: the Rams and the Raiders. Both left the city in 1995, with the Rams moving to St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, and the Raiders moving back to their original home of Oakland. After 21 seasons in St. Louis, on January 12, 2016, the NFL announced the Rams would be moving back to Los Angeles for the 2016 NFL season
The 2016 NFL season was the 97th season in the history of the National Football League (NFL) and the 51st of the Super Bowl era. The season began on September 8, 2016, with defending Super Bowl 50 champion Denver defeating Carolina in the NF ...
with its home games played at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum for four seasons. Prior to 1995, the Rams played their home games in the Coliseum from 1946 to 1979 which made them the first professional sports team to play in Los Angeles, and then moved to Anaheim Stadium
Angel Stadium of Anaheim is a baseball stadium located in Anaheim, California. Since its opening in 1966, it has served as the home ballpark of the Los Angeles Angels of Major League Baseball (MLB), and was also the home stadium to the Los Angel ...
from 1980 until 1994. The San Diego Chargers announced on January 12, 2017, that they would also relocate back to Los Angeles (the first since its inaugural season in 1960) and become the Los Angeles Chargers
The Los Angeles Chargers are a professional American football team based in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Chargers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) West division, and ...
beginning in the 2017 NFL season
The 2017 NFL season was the 98th season in the history of the National Football League (NFL) and the 52nd of the Super Bowl era. The season began on September 7, 2017, with Kansas City defeating defending Super Bowl LI champion New England i ...
and played at Dignity Health Sports Park
Dignity Health Sports Park is a multi-use sports complex located on the campus of California State University, Dominguez Hills in Carson, California. The complex consists of the 27,000-seat Dignity Health Sports Park soccer stadium, the Dignity ...
in Carson, California for three seasons. The Rams and the Chargers would soon move to the newly built SoFi Stadium
SoFi Stadium () is a 70,240-seat sports and entertainment indoor stadium in the Los Angeles suburb of Inglewood, California, United States. SoFi occupies the former site of the Hollywood Park Racetrack, from Los Angeles International Airport an ...
, located in nearby Inglewood during the 2020 season.  Los Angeles boasts a number of sports venues, including
Los Angeles boasts a number of sports venues, including Dodger Stadium
Dodger Stadium is a baseball stadium in the Elysian Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California. It is the home stadium of Major League Baseball's Los Angeles Dodgers. Opened in 1962, it was constructed in less than three years at a cost of ...
, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, Banc of California Stadium and the Crypto.com Arena
Crypto.com Arena is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Downtown Los Angeles. Adjacent to the L.A. Live development, it is located next to the Los Angeles Convention Center complex along Figueroa Street. The arena opened on October 17, 1999; it w ...
. The Forum, SoFi Stadium
SoFi Stadium () is a 70,240-seat sports and entertainment indoor stadium in the Los Angeles suburb of Inglewood, California, United States. SoFi occupies the former site of the Hollywood Park Racetrack, from Los Angeles International Airport an ...
, Dignity Health Sports Park
Dignity Health Sports Park is a multi-use sports complex located on the campus of California State University, Dominguez Hills in Carson, California. The complex consists of the 27,000-seat Dignity Health Sports Park soccer stadium, the Dignity ...
, the Rose Bowl, Angel Stadium
Angel Stadium of Anaheim is a baseball stadium located in Anaheim, California. Since its opening in 1966, it has served as the home ballpark of the Los Angeles Angels of Major League Baseball (MLB), and was also the home stadium to the Los An ...
, and the Honda Center
The Honda Center (formerly known as the Arrowhead Pond of Anaheim) is an indoor arena located in Anaheim, California. The arena is home to the Anaheim Ducks of the National Hockey League.
Originally named the Anaheim Arena during construction ...
are also in adjacent cities and cities in Los Angeles's metropolitan area.
Los Angeles has twice hosted the Summer Olympic Games: in 1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort to assassinate Emperor Hiro ...
and in 1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
, and will host the games for a third time in 2028
Predicted and scheduled events
* January 1 – Books, films, and other works published in 1932 will enter the public domain in the United States.
* January 12 – Partial lunar eclipse.
* January 26 – Small annular solar ecli ...
. Los Angeles will be the third city after London ( 1908, 1948 and 2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gat ...
) and Paris (1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2 ...
, 1924
Events
January
* January 12 – Gopinath Saha shoots Ernest Day, whom he has mistaken for Sir Charles Tegart, the police commissioner of Calcutta, and is arrested soon after.
* January 20– 30 – Kuomintang in China holds ...
and 2024
Predicted and scheduled events
* January 1
** In the United States, books, films, and other works published in 1928 will enter the public domain, assuming there are no changes made to copyright law.
***''Steamboat Willie'', Walt Disney's f ...
) to host the Olympic Games three times. When the tenth Olympic Games were hosted in 1932, the former 10th Street was renamed Olympic Blvd. Los Angeles also hosted the Deaflympics in 1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a ...
and Special Olympics World Summer Games in 2015.
8 NFL Super Bowls were also held in the city and its surrounding areas- 2 at the Memorial Coliseum ( the first Super Bowl, I and VII), 5 at the Rose Bowl in suburban Pasadena ( XI, XIV, XVII, XXI, and XXVII), and 1 at the suburban Inglewood ( LVI) . The Rose Bowl also hosts an annual and highly prestigious NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
college football game called the Rose Bowl, which happens every New Year's Day.
Los Angeles also hosted 8 FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
soccer games at the Rose Bowl in 1994, including the final
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to:
* Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which decides a winner for an event
** Another term for playoffs, describing a sequence of con ...
, where Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
won. The Rose Bowl also hosted 4 matches in the 1999 FIFA Women's World Cup
The 1999 FIFA Women's World Cup was the third edition of the FIFA Women's World Cup, the world championship for women's national soccer teams. It was hosted as well as won by the United States and took place from June 19 to July 10, 1999, at ...
, including the final
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to:
* Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which decides a winner for an event
** Another term for playoffs, describing a sequence of con ...
, where the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
won against China on penalty kicks. This was the game where Brandi Chastain took her shirt off after she scored the tournament-winning penalty kick, creating an iconic image. Los Angeles will be one of eleven US host cities for the 2026 FIFA World Cup
The 2026 FIFA World Cup will be the 23rd FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international men's soccer championship contested by the national teams of the member associations of FIFA. The tournament will be jointly hosted by 16 cities in three ...
with matches set to be held at SoFi Stadium
SoFi Stadium () is a 70,240-seat sports and entertainment indoor stadium in the Los Angeles suburb of Inglewood, California, United States. SoFi occupies the former site of the Hollywood Park Racetrack, from Los Angeles International Airport an ...
.
Los Angeles is one of six North American cities to have won championships in all five of its major leagues (MLB, NFL, NHL, NBA and MLS), having completed the feat with the Kings' 2012 Stanley Cup title.
Government
 Los Angeles is a
Los Angeles is a charter city
In the United States, a charter city is a city in which the governing system is defined by the city's own charter document rather than solely by general law. In states where city charters are allowed by law, a city can adopt or modify its orga ...
as opposed to a general law city. The current charter was adopted on June 8, 1999, and has been amended many times. The elected government consists of the Los Angeles City Council
The Los Angeles City Council is the legislative body of the City of Los Angeles in California.
The council is composed of 15 members elected from single-member districts for four-year terms. The president of the council and the president pro tem ...
and the mayor of Los Angeles, which operate under a mayor–council government
The mayor–council government system is a system of local government that has a mayor who is directly elected by the voters serve as chief executive, and a separately elected legislative city council. It is one of the two most common forms of ...
, as well as the city attorney
A city attorney is a position in city and municipal government in the United States. The city attorney is the attorney representing the municipality.
Unlike a district attorney or public defender, who usually handles criminal cases, a city att ...
(not to be confused with the district attorney, a county office) and controller. The mayor is Karen Bass
Karen Ruth Bass (; born October 3, 1953) is an American politician, social worker and former physician assistant who is serving as the 43rd mayor of Los Angeles since 2022. A member of the Democratic Party, Bass had previously served in the U.S ...
. There are 15 city council districts.
The city has many departments and appointed officers, including the Los Angeles Police Department
The Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD), officially known as the City of Los Angeles Police Department, is the municipal police department of Los Angeles, California. With 9,974 police officers and 3,000 civilian staff, it is the third-large ...
(LAPD), the Los Angeles Board of Police Commissioners, the Los Angeles Fire Department
The Los Angeles Fire Department (LAFD or LA City Fire) provides emergency medical services, Fire investigation, fire cause determination, fire prevention, Firefighting, fire suppression, Dangerous goods, hazardous materials mitigation, and Resc ...
(LAFD), the Housing Authority of the City of Los Angeles
The Housing Authority of the City of Los Angeles (HACLA) is a state-chartered public agency. Established in 1938, HACLA provides the largest stock of affordable housing in the city Los Angeles, California and is one of the nation's oldest public ...
(HACLA), the Los Angeles Department of Transportation
The Los Angeles Department of Transportation, commonly referred to as LADOT, is a municipal agency that oversees transportation planning, design, construction, maintenance and operations within the city of Los Angeles. LADOT was created by city or ...
(LADOT), and the Los Angeles Public Library
The Los Angeles Public Library system (LAPL) is a public library system in Los Angeles, California. The system holds more than six million volumes, and with around 19 million residents in the Los Angeles Metropolitan area, it serves the large ...
(LAPL).
The charter of the City of Los Angeles ratified by voters in 1999 created a system of advisory neighborhood councils that would represent the diversity of stakeholders, defined as those who live, work or own property in the neighborhood. The neighborhood councils are relatively autonomous and spontaneous in that they identify their own boundaries, establish their own bylaws, and elect their own officers. There are about 90 neighborhood councils.
Residents of Los Angeles elect supervisors for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th supervisorial districts.
Federal and state representation
In the California State Assembly, Los Angeles is split between fourteen districts. In the California State Senate, the city is split between eight districts. In the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
, it is split among ten congressional districts.
Education
Colleges and universities
 There are three public universities within the city limits:
There are three public universities within the city limits: California State University, Los Angeles
California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State LA) is a public university in Los Angeles, California. It is part of the 23-campus California State University (CSU) system. Cal State LA offers 142 bachelor's degrees, 122 master's degrees, ...
(CSULA), California State University, Northridge (CSUN) and University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California S ...
(UCLA).
Private colleges in the city include:
* American Film Institute Conservatory
* Alliant International University
* American Academy of Dramatic Arts (Los Angeles Campus)
* American Jewish University
American Jewish University (AJU), formerly the separate institutions University of Judaism and Brandeis-Bardin Institute, is a Jewish institution in Los Angeles, California.
Its largest component is its Whizin Center for Continuing Education in ...
* Abraham Lincoln University Abraham Lincoln University (ALU) is a private, for-profit online university based in Glendale, California.
History
ALU was founded in 1996 by Hyung J. Park, a tax attorney and graduate of Loyola Law School. Classes initially were held in a confere ...
* The American Musical and Dramatic Academy – Los Angeles campus
* Antioch University
Antioch University is a private university with multiple campuses in the United States and online programs. Founded in 1852 as Antioch College, its first president was politician, abolitionist, and education reformer Horace Mann. It changed its ...
's Los Angeles campus
* Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science
* Colburn School
* Columbia College Hollywood
Columbia College Hollywood (CCH) is a private college in Los Angeles, California. It is one of only 20 film institutions in the United States that have been awarded full membership by the International Association of Film and Television Schools ...
* Emerson College (Los Angeles Campus)
* Emperor's College
* Fashion Institute of Design & Merchandising
The Fashion Institute of Design & Merchandising (FIDM) is a private college in downtown Los Angeles. It offers degree programs in majors including fashion, entertainment, beauty, interior design, and graphic design. The college was founded in 19 ...
's Los Angeles campus (FIDM)
* Los Angeles Film School
The Los Angeles Film School (informally LA Film School) is a for-profit college in Los Angeles, California offering associate and bachelor's degrees in majors relating to the entertainment industry. The school encompasses the Los Angeles Recordin ...
* Loyola Marymount University
Loyola Marymount University (LMU) is a private Jesuit and Marymount research university in Los Angeles, California. It is located on the west side of the city near Playa Vista. LMU is the parent school to Loyola Law School, which is located ...
(LMU is also the parent university of Loyola Law School
Loyola Law School is the law school of Loyola Marymount University, a private Catholic university in Los Angeles, California. Loyola was established in 1920.
Academics
Degrees offered include the Juris Doctor (JD); Master of Science in Legal ...
in Los Angeles)
* Mount St. Mary's College
Mount Saint Mary's University, Los Angeles (known as Mount St. Mary's College until January 2015) is a private, Catholic university primarily for women, in Los Angeles, California. Women make up ninety percent of the student body.
It was found ...
* National University of California
* Occidental College ("Oxy")
* Otis College of Art and Design
Otis College of Art and Design is a private art and design school in Los Angeles, California. Established in 1918, it was the city's first independent professional school of art. The main campus is located in the former IBM Aerospace headquarte ...
(Otis)
* Southern California Institute of Architecture (SCI-Arc)
* Southwestern Law School
Southwestern Law School is a Private university, private Law school in the United States, law school in Mid-Wilshire, Los Angeles. It is accredited by the American Bar Association and enrolls nearly 1,000 students. Its campus includes the Bulloc ...
* University of Southern California
, mottoeng = "Let whoever earns the palm bear it"
, religious_affiliation = Nonsectarian—historically Methodist
, established =
, accreditation = WSCUC
, type = Private research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $8.1 ...
(USC)
* Woodbury University
Woodbury University is a private university in Burbank, California, with a satellite campus in San Diego.
History
The school was founded in 1884 as Woodbury's Business College by its namesake, F. C. Woodbury, formerly a partner in Heald's Busi ...
The community college system consists of nine campuses governed by the trustees of the Los Angeles Community College District:
* East Los Angeles College (ELAC)
* Los Angeles City College
Los Angeles City College (LACC) is a public community college in East Hollywood, Los Angeles, California. A part of the Los Angeles Community College District, it is located on Vermont Avenue south of Santa Monica Boulevard on the former campu ...
(LACC)
* Los Angeles Harbor College
Los Angeles Harbor College (LAHC) is a public community college in Wilmington, California. It is one of two community colleges serving the South Bay region of Los Angeles. LAHC serves mainly students from Harbor City, Carson, San Pedro, Ga ...
* Los Angeles Mission College
* Los Angeles Pierce College
Los Angeles Pierce College (Pierce College or Pierce) is a public community college in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, California. It is part of the Los Angeles Community College District and is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and C ...
* Los Angeles Valley College
Los Angeles Valley College (LAVC) is a public community college in Los Angeles, California. It is part of the Los Angeles Community College District.
The college is adjacent to Grant High School in the neighborhood of Valley Glen. Often call ...
(LAVC)
* Los Angeles Southwest College
Los Angeles Southwest College (LASC) is a public community college in the unincorporated area of West Athens, California in Los Angeles County, California. It is part of the Los Angeles Community College District and its service area includes In ...
* Los Angeles Trade-Technical College
* West Los Angeles College
West Los Angeles College (West L.A. College or WLAC) is a public community college in Ladera Heights, Los Angeles County, California. It is part of the California Community Colleges System and the Los Angeles Community College District. It is ac ...
There are numerous additional colleges and universities outside the city limits in the Greater Los Angeles area, including the Claremont Colleges
The Claremont Colleges (known colloquially as the 7Cs) are a consortium of seven private institutions of higher education located in Claremont, California, United States. They comprise five undergraduate colleges (the 5Cs)— Pomona College, Sc ...
consortium, which includes the most selective liberal arts colleges in the U.S., and the California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
(Caltech), one of the top STEM-focused research institutions in the world.
Schools
Los Angeles Unified School District serves almost all of the city of Los Angeles, as well as several surrounding communities, with a student population around 800,000. After Proposition 13
Proposition 13 (officially named the People's Initiative to Limit Property Taxation) is an amendment of the Constitution of California enacted during 1978, by means of the initiative process. The initiative was approved by California voters on J ...
was approved in 1978, urban school districts had considerable trouble with funding. LAUSD has become known for its underfunded, overcrowded and poorly maintained campuses, although its 162 Magnet schools help compete with local private schools.
Several small sections of Los Angeles are in the Inglewood Unified School District
Inglewood Unified School District abbreviated (IUSD) is a public school system district headquartered in Inglewood, California ( USA)
IUSD serves most of the city of Inglewood and much of the unincorporated Los Angeles County community of Lad ...
, and the Las Virgenes Unified School District
Las Virgenes Unified School District (LVUSD) is a K–12 school district headquartered in Calabasas, California, United States. The district, serving the western section of the San Fernando Valley and the eastern Conejo Valley in Los Angeles Cou ...
. The Los Angeles County Office of Education operates the Los Angeles County High School for the Arts
Los Angeles County High School for the Arts (LACHSA, ) is a visual and performing arts high school located on the campus of California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State LA) in Los Angeles, California, United States.
History
The school was ...
.
Media
 The Los Angeles metro area is the second-largest broadcast
The Los Angeles metro area is the second-largest broadcast designated market area
A media market, broadcast market, media region, designated market area (DMA), television market area, or simply market is a region where the population can receive the same (or similar) television and radio station offerings, and may also incl ...
in the U.S. (after New York) with 5,431,140 homes (4.956% of the U.S.), which is served by a wide variety of local AM and FM radio and television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
stations. Los Angeles and New York City are the only two media markets to have seven VHF allocations assigned to them.
 As part of the region's aforementioned creative industry, the Big Four major broadcast television networks, ABC,
As part of the region's aforementioned creative industry, the Big Four major broadcast television networks, ABC, CBS
CBS Broadcasting Inc., commonly shortened to CBS, the abbreviation of its former legal name Columbia Broadcasting System, is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the CBS Entertainm ...
, FOX, and NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters are l ...
, all have production facilities and offices throughout various areas of Los Angeles. All four major broadcast television networks, plus major Spanish-language networks Telemundo
Telemundo (; formerly NetSpan) is an American Spanish-language terrestrial television network owned by NBCUniversal Telemundo Enterprises, a division of NBCUniversal, which in turn is owned by Comcast. It provides content nationally with pr ...
and Univision
Univision () is an American Spanish-language free-to-air television network owned by TelevisaUnivision. It is the United States' largest provider of Spanish-language content. The network's programming is aimed at the Latino public and includes ...
, also own and operate stations that both serve the Los Angeles market and serve as each network's West Coast flagship station: ABC's KABC-TV
KABC-TV (channel 7) is a television station in Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the West Coast of the United States, West Coast Flagship (broadcasting), flagship of the American Broadcasting Company, ABC network. ...
(Channel 7), CBS's KCBS-TV (Channel 2), Fox's KTTV
KTTV (channel 11) is a television station in Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the West Coast flagship of the Fox network. It is owned and operated by the network's Fox Television Stations division alongside MyNetworkTV ou ...
-TV (Channel 11), NBC's KNBC-TV (Channel 4), MyNetworkTV's KCOP-TV (Channel 13), Telemundo's KVEA
KVEA (channel 52) is a television station licensed to Corona, California, United States, serving the Los Angeles area with programming from the Spanish-language Telemundo network. It is owned and operated by NBCUniversal's Telemundo Station ...
-TV (Channel 52), and Univision's KMEX-TV
KMEX-DT (channel 34) is a television station in Los Angeles, California, United States, serving as the western flagship station of the Spanish-language Univision network. It is owned and operated by TelevisaUnivision alongside Ontario, Califor ...
(Channel 34). The region also has four PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educat ...
stations, with KCET, re-joining the network as secondary affiliate in August 2019, after spending the previous eight years as the nation's largest independent public television station. KTBN (Channel 40) is the flagship station of the religious Trinity Broadcasting Network
The Trinity Broadcasting Network (TBN) is an international Christian-based broadcast television network and the world's largest religious television network. TBN was headquartered in Costa Mesa, California, until March 3, 2017, when it sold its ...
, based out of Santa Ana. A variety of independent television stations, such as KCAL-TV (Channel 9) and KTLA-TV (Channel 5), also operate in the area.
The major daily English-language newspaper in the area is the ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the U ...
''. ''La Opinión
''La Opinión'' is a Spanish-language daily newspaper and website based in Los Angeles, California. It is the largest Spanish-language newspaper in the United States and the second-most read newspaper in Los Angeles (after ''The Los Angeles Time ...
'' is the city's major daily Spanish-language paper. ''The Korea Times
''The Korea Times'' is the oldest of three English-language newspapers published daily in South Korea. It is a sister paper of the '' Hankook Ilbo'', a major Korean language daily; both are owned by Dongwha Enterprise, a wood-based manufacture ...
'' is the city's major daily Korean-language paper while '' The World Journal'' is the city and county's major Chinese newspaper. The ''Los Angeles Sentinel
The ''Los Angeles Sentinel'' is a weekly African-American owned newspaper published in Los Angeles, California. The paper boasts of reaching 125,000 readers , making it one of the oldest, largest and most influential African-American newspapers ...
'' is the city's major African-American weekly paper, boasting the largest African-American readership in the Western United States. ''Investor's Business Daily
''Investor's Business Daily'' (''IBD'') is an American newspaper and website covering the stock market, international business, finance and economics. Founded in 1984 by William O'Neil as a print news publication, it is owned by News Corp and is ...
'' is distributed from its LA corporate offices, which are headquartered in Playa del Rey.
There are also a number of smaller regional newspapers, alternative weeklies and magazines, including the '' Los Angeles Register'', Los Angeles Community News, (which focuses on coverage of the greater Los Angeles area), '' Los Angeles Daily News'' (which focuses coverage on the San Fernando Valley), '' LA Weekly'', '' L.A. Record'' (which focuses coverage on the music scene in the Greater Los Angeles Area
Greater Los Angeles is the second-largest metropolitan region in the United States with a population of 18.5 million in 2021, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Bernardino Coun ...
), ''Los Angeles Magazine'', the ''Los Angeles Business Journal
The ''Los Angeles Business Journal'', established in 1979, is a weekly newspaper and online news source in Los Angeles, California, which provides coverage of local business news. According to the ''Journals website, it has a weekly print circul ...
'', the ''Los Angeles Daily Journal'' (legal industry paper), ''The Hollywood Reporter
''The Hollywood Reporter'' (''THR'') is an American digital and print magazine which focuses on the Hollywood film, television, and entertainment industries. It was founded in 1930 as a daily trade paper, and in 2010 switched to a weekly larg ...
'', ''Variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
'' (both entertainment industry papers), and ''Los Angeles Downtown News
The ''Los Angeles Downtown News'' is a free weekly newspaper in Los Angeles, California, serving the Downtown Los Angeles area.
The newspaper focuses on general news with an emphasis on real estate and business along with coverage of the arts sc ...
''. In addition to the major papers, numerous local periodicals serve immigrant communities in their native languages, including Armenian, English, Korean, Persian, Russian, Chinese, Japanese, Hebrew, and Arabic. Many cities adjacent to Los Angeles also have their own daily newspapers whose coverage and availability overlaps with certain Los Angeles neighborhoods. Examples include ''The Daily Breeze
The ''Daily Breeze'' is a 57,000-circulation daily newspaper published in Hermosa Beach, California, United States. It serves the South Bay cities of Los Angeles County. Its slogan is "LAX to LA Harbor".
Early history
The paper was founded ...
'' (serving the South Bay), and ''The Long Beach Press-Telegram
The ''Press-Telegram'' is a paid daily newspaper published in Long Beach, California. Coverage area for the ''Press-Telegram'' includes Long Beach, Lakewood, Signal Hill, Artesia, Bellflower, Cerritos, Compton, Downey, Hawaiian Gardens, Ly ...
''.
Los Angeles arts, culture and nightlife news is also covered by a number of local and national online guides, including ''Time Out Los Angeles'', ''Thrillist
Thrillist is an online media website covering food, drink, travel and entertainment. The company was founded in 2004 and is based in New York City, United States. In October 2016, Thrillist merged with internet brands '' The Dodo'', NowThis Ne ...
'', ''Kristin's List'', ''DailyCandy'', ''Diversity News Magazine'', ''LAist'', and ''Flavorpill''.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Freeways
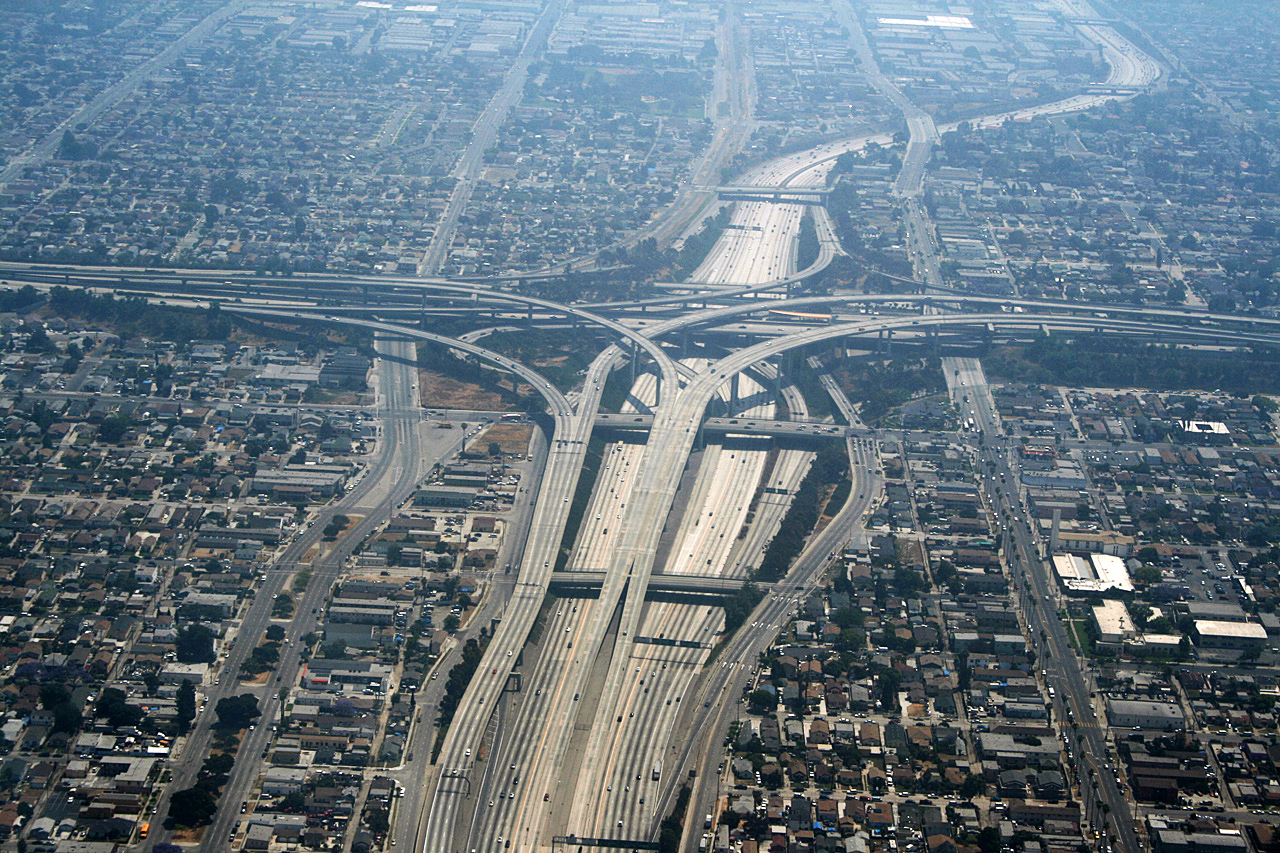 The city and the rest of the
The city and the rest of the Los Angeles metropolitan area
Greater Los Angeles is the second-largest metropolitan region in the United States with a population of 18.5 million in 2021, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Bernardino C ...
are served by an extensive network of freeways and highways. Texas Transportation Institute
The Texas A&M Transportation Institute (TTI) in Bryan/College Station, Texas is a transportation research agency in the United States. The institute was created in 1950, primarily in response to the needs of the Texas Highway Department (now th ...
's annual Urban Mobility Report ranked Los Angeles area roads the most congested in the United States in 2019 as measured by annual delay per traveler, area residents experiencing a cumulative average of 119 hours waiting in traffic that year. Los Angeles was followed by San Francisco/ Oakland, Washington, D.C., and Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
. Despite the congestion in the city, the mean daily travel time for commuters in Los Angeles is shorter than other major cities, including New York City, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
and Chicago. Los Angeles's mean travel time for work commutes in 2006 was 29.2 minutes, similar to those of San Francisco and Washington, D.C.[https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/acs/]
The major highways that connect LA to the rest of the nation include Interstate 5
Interstate 5 (I-5) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States, running largely parallel to the Pacific coast of the contiguous U.S. from Mexico to Canada. It travels through the states of Californi ...
, which runs south through San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United State ...
to Tijuana
Tijuana ( ,["Tijuana"](_blank)
(US) and [< ...]
in Mexico and north through Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
, Portland, and Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
to the Canada–US border; Interstate 10, the southernmost east–west, coast-to-coast Interstate Highway in the United States, going to Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
; and U.S. Route 101, which heads to the California Central Coast
The Central Coast is an area of California, roughly spanning the coastal region between Point Mugu and Monterey Bay. It lies northwest of Los Angeles County and south of San Mateo and Santa Clara counties, and includes the rugged, undeveloped ...
, San Francisco, the Redwood Empire
The North Coast of California (also called the Redwood Empire or the Redwood Coast in reference to the dense Sequoia sempervirens, redwood forests throughout the region) is a region in Northern California that lies on the Pacific coast between Sa ...
, and the Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
coasts.
Transit systems
 The LA County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LA County Metro) and other agencies operate an extensive system of bus lines, as well as subway and light rail lines across Los Angeles County, with a combined monthly ridership (measured in individual boardings) of 38.8 million . The majority of this (30.5 million) is taken up by the city's bus system,
The LA County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LA County Metro) and other agencies operate an extensive system of bus lines, as well as subway and light rail lines across Los Angeles County, with a combined monthly ridership (measured in individual boardings) of 38.8 million . The majority of this (30.5 million) is taken up by the city's bus system,Santa Monica
Santa Monica (; Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 U.S. Census population was 93,076. Santa Monica is a popular resort town, owing to i ...
. The Metro G and J lines are bus rapid transit lines with stops and frequency similar to those of light rail. , the total number of light rail stations is 99. The city is also central to the commuter rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Downtown, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter r ...
system Metrolink, which links Los Angeles to all neighboring counties as well as many suburbs.
Besides the rail service provided by Metrolink and the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority, Los Angeles is served by inter-city passenger trains from Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
. The main rail station in the city is Union Station
A union station (also known as a union terminal, a joint station in Europe, and a joint-use station in Japan) is a railway station at which the tracks and facilities are shared by two or more separate railway companies, allowing passengers to ...
just north of Downtown.
In addition, the city directly contracts for local and commuter bus service through the Los Angeles Department of Transportation
The Los Angeles Department of Transportation, commonly referred to as LADOT, is a municipal agency that oversees transportation planning, design, construction, maintenance and operations within the city of Los Angeles. LADOT was created by city or ...
, or LADOT.
Airports
The main international and domestic airport serving Los Angeles is Los Angeles International Airport , commonly referred to by its airport code, LAX.
Other major nearby commercial airports include:
* Ontario International Airport
Ontario International Airport is an international airport two miles east of downtown Ontario, in San Bernardino County, California, United States, about east of downtown Los Angeles and west of downtown San Bernardino. It is owned and operat ...
, owned by the city of Ontario, CA; serves the Inland Empire.
* Hollywood Burbank Airport
Hollywood Burbank Airport, legally and formerly marketed as Bob Hope Airport after entertainer Bob Hope , is a public airport northwest of downtown Burbank, in Los Angeles County, California, United States.. Federal Aviation Administration. ef ...
, jointly owned by the cities of Burbank, Glendale, and Pasadena. Formerly known as Bob Hope Airport and Burbank Airport, the closest airport to Downtown Los Angeles serves the San Fernando, San Gabriel, and Antelope Valleys.
* Long Beach Airport
Long Beach Airport is a public airport three miles northeast of downtown Long Beach, in Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is also called Daugherty Field, named after local aviator Earl Daugherty. The airport was an operating base ...
, serves the Long Beach/Harbor area.
* John Wayne Airport of Orange County.
One of the world's busiest general-aviation airports is also in Los Angeles: Van Nuys Airport
: ''For the United States Air Force use of the airport (1942–1990), see Van Nuys Air National Guard Base''
Van Nuys Airport is a public airport in the Van Nuys neighborhood of the City of Los Angeles. The airport is operated by Los Angeles ...
.
Seaports

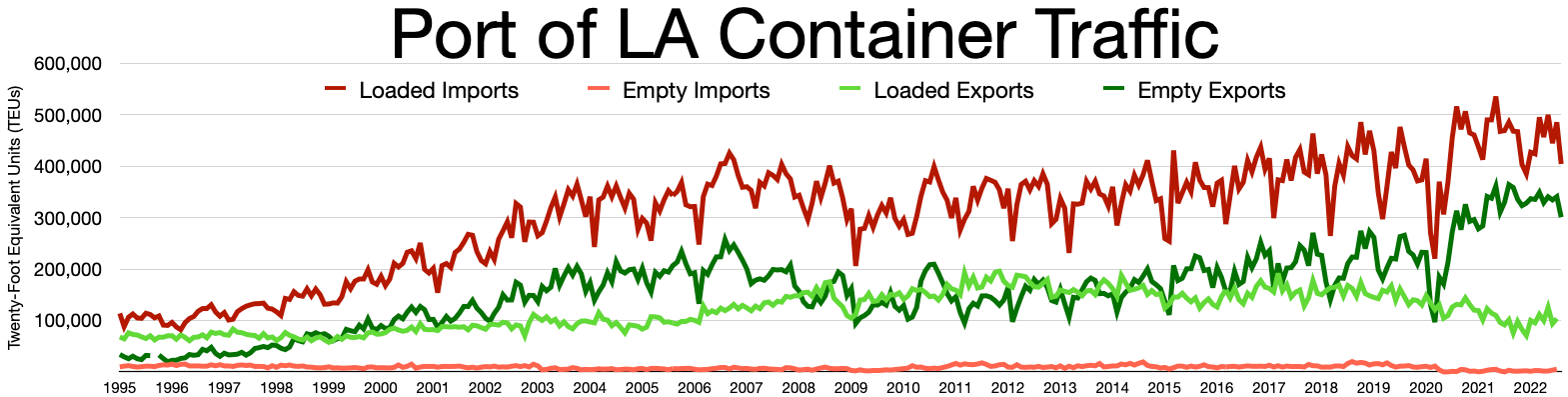 The Port of Los Angeles is in San Pedro Bay in the San Pedro neighborhood, approximately south of Downtown. Also called Los Angeles Harbor and WORLDPORT LA, the port complex occupies of land and water along of waterfront. It adjoins the separate
The Port of Los Angeles is in San Pedro Bay in the San Pedro neighborhood, approximately south of Downtown. Also called Los Angeles Harbor and WORLDPORT LA, the port complex occupies of land and water along of waterfront. It adjoins the separate Port of Long Beach
The Port of Long Beach, also known as the Harbor Department of the City of Long Beach, is a container port in the United States, which adjoins Port of Los Angeles. Acting as a major gateway for US–Asian trade, the port occupies of land with ...
.
The sea ports of the Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach
The Port of Long Beach, also known as the Harbor Department of the City of Long Beach, is a container port in the United States, which adjoins Port of Los Angeles. Acting as a major gateway for US–Asian trade, the port occupies of land with ...
together make up the ''Los Angeles/Long Beach Harbor''. Together, both ports are the fifth busiest container
A container is any receptacle or enclosure for holding a product used in storage, packaging, and transportation, including shipping.
Things kept inside of a container are protected on several sides by being inside of its structure. The term ...
port in the world, with a trade volume of over 14.2 million TEU's in 2008. Singly, the Port of Los Angeles is the busiest container port in the United States and the largest cruise ship center on the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
– The Port of Los Angeles's World Cruise Center served about 590,000 passengers in 2014.
There are also smaller, non-industrial harbors along Los Angeles's coastline. The port includes four bridges: the Vincent Thomas Bridge
The Vincent Thomas Bridge is a suspension bridge, crossing Los Angeles Harbor in Los Angeles, California, linking San Pedro with Terminal Island. It is the only suspension bridge in the Greater Los Angeles area. The bridge is part of State R ...
, Henry Ford Bridge
The Henry Ford Bridge, also known as the Badger Avenue Bridge, is a bridge located in Los Angeles County, Southern California. It carries the Pacific Harbor Line railroad across the Cerritos Channel to Terminal Island from San Pedro, to serve t ...
, Gerald Desmond Bridge
The 1968 Gerald Desmond Bridge was a through arch bridge that carried five lanes of Ocean Boulevard from Interstate 710 in Long Beach, California, west across the Back Channel to Terminal Island. The bridge was named after Gerald Desmond, a pro ...
, and Commodore Schuyler F. Heim Bridge
The Commodore Schuyler F. Heim Bridge was a vertical-lift bridge in the Port of Los Angeles. Dedicated on January 10, 1948, the bridge allowed State Route 47 (the Terminal Island Freeway) to cross over the Cerritos Channel. Named after Schuyler ...
. Passenger ferry service from San Pedro to the city of Avalon
Avalon (; la, Insula Avallonis; cy, Ynys Afallon, Ynys Afallach; kw, Enys Avalow; literally meaning "the isle of fruit r appletrees"; also written ''Avallon'' or ''Avilion'' among various other spellings) is a mythical island featured in the ...
on Santa Catalina Island is provided by Catalina Express.
Notable people
Sister cities
 Los Angeles has 25
Los Angeles has 25 sister cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
,Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most po ...
, Japan (1959)
* Salvador, Brazil (1962)
* Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefect ...
, France (1964)Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
, Germany (1967)Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, Mexico (1969)
* Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about ...
, New Zealand (1971)
* Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea, ...
, South Korea (1971)
* Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, India (1972)
* Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
, Iran (1972)
* Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the ...
, Taiwan (1979)
* Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, China (1981)Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Greece (1984)
* Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Russia (1984)
* Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, Canada (1986)Makati
Makati ( ), officially the City of Makati ( fil, Lungsod ng Makati), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines.
Makati is the financial center of the Philippines; it has the highest concentration ...
, Philippines (1992)
* Split, Croatia
)''
, settlement_type = City
, anthem = ''Marjane, Marjane''
, image_skyline =
, imagesize = 267px
, image_caption = Top: Nighttime view of Split from Mosor; 2nd row: Cathedra ...
(1993)Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
, Lebanon (2006)
* Ischia, Campania
Ischia is a town and ''comune'' on Ischia island in the Tyrrhenian Sea.
Administratively it is part of the Metropolitan city of Naples, in the Campania region in southern Italy.
It is famed for its thermal baths due to the volcanic nature of t ...
, Italy (2006)
* Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and i ...
, Armenia (2007)Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of cant ...
, Poland
* City of Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, Australia
* Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
, United KingdomTel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the ...
, Israel
See also
* Largest cities in Southern California
This is a list of the 100 largest cities in the U.S. state of California ranked by population, based on estimates for July 1, 2021, by the United States Census Bureau.
Note: The population figures are for the incorporated areas of the listed cit ...
* Largest cities in the Americas
This is a list of the 50 largest cities in the Americas by population residing within city limits as of 2015, the most recent year for which official population census results, estimates or short-term projections are available for most of these ci ...
* List of hotels in Los Angeles
This is a list of hotels in Los Angeles (including the Greater Los Angeles Area).
Hotels in Los Angeles
* Alan Hotel
* Ambassador Hotel
* Andaz West Hollywood
* The Beverly Hills Hotel
* The Beverly Hilton
* Beverly Wilshire Hotel
* Bo ...
* List of largest houses in the Los Angeles Metropolitan Area
* List of museums in Los Angeles
* List of museums in Los Angeles County, California
* List of music venues in Los Angeles
A list of music venues
A music venue is any location used for a concert or musical performance. Music venues range in size and location, from a small coffeehouse for folk music shows, an outdoor bandshell or bandstand or a concert hall to an ...
* List of people from Los Angeles
* List of tallest buildings in Los Angeles
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Los Angeles, California
Notes
References
Further reading
General
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Architecture and urban theory
*
*
*
*
*
*
Race relations
*
*
*
*
*
LGBT
*
*
Environment
*
*
Social movements
*
Art and literature
*
*
External links
*
{{authority control
Cities in Los Angeles County, California
County seats in California
Incorporated cities and towns in California
Populated coastal places in California
Port cities in California
Railway towns in California
Populated places established in 1781
1781 establishments in New Spain
1850 establishments in California
 The local English pronunciation of the name of the city has varied over time. A 1953 article in the
The local English pronunciation of the name of the city has varied over time. A 1953 article in the  In 1771, Franciscan
In 1771, Franciscan  The city of Los Angeles covers a total area of , comprising of land and of water. The city extends for north-south and for east-west. The perimeter of the city is .
Los Angeles is both flat and hilly. The highest point in the city proper is
The city of Los Angeles covers a total area of , comprising of land and of water. The city extends for north-south and for east-west. The perimeter of the city is .
Los Angeles is both flat and hilly. The highest point in the city proper is  Los Angeles is rich in native plant species partly because of its diversity of habitats, including beaches,
Los Angeles is rich in native plant species partly because of its diversity of habitats, including beaches,  The Los Angeles area is also subject to phenomena typical of a
The Los Angeles area is also subject to phenomena typical of a  A Gabrielino settlement in the area was called ''iyáangẚ'' (written ''Yang-na'' by the Spanish), which has been translated as "poison oak place". ''Yang-na'' has also been translated as "the valley of smoke". Owing to geography, heavy reliance on automobiles, and the Los Angeles/Long Beach port complex, Los Angeles suffers from air pollution in the form of smog. The
A Gabrielino settlement in the area was called ''iyáangẚ'' (written ''Yang-na'' by the Spanish), which has been translated as "poison oak place". ''Yang-na'' has also been translated as "the valley of smoke". Owing to geography, heavy reliance on automobiles, and the Los Angeles/Long Beach port complex, Los Angeles suffers from air pollution in the form of smog. The  According to the 2010 United States Census, Los Angeles had a median household income of $49,497, with 22.0% of the population living below the federal poverty line.
According to the 2010 United States Census, Los Angeles had a median household income of $49,497, with 22.0% of the population living below the federal poverty line.
 According to the 2010 census, the racial makeup of Los Angeles included: 1,888,158
According to the 2010 census, the racial makeup of Los Angeles included: 1,888,158  According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, Christianity is the most prevalently practiced religion in Los Angeles (65%).Major U.S. metropolitan areas differ in their religious profiles
According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, Christianity is the most prevalently practiced religion in Los Angeles (65%).Major U.S. metropolitan areas differ in their religious profiles As of January 2020, there are 41,290
As of January 2020, there are 41,290  In 1992, the city of Los Angeles recorded 1,092 murders. Los Angeles experienced a significant decline in crime in the 1990s and late 2000s and reached a 50-year low in 2009 with 314 homicides. This is a rate of 7.85 per 100,000 population—a major decrease from 1980 when a homicide rate of 34.2 per 100,000 was reported. This included 15 officer-involved shootings. One shooting led to the death of a SWAT team member, Randal Simmons, the first in LAPD's history. Los Angeles in the year of 2013 totaled 251 murders, a decrease of 16 percent from the previous year. Police speculate the drop resulted from a number of factors, including young people spending more time online. In 2021, murders rose to the highest level since 2008 and there were 348.
In 2015, it was revealed that the LAPD had been under-reporting crime for eight years, making the crime rate in the city appear much lower than it really is.
The Dragna crime family and the
In 1992, the city of Los Angeles recorded 1,092 murders. Los Angeles experienced a significant decline in crime in the 1990s and late 2000s and reached a 50-year low in 2009 with 314 homicides. This is a rate of 7.85 per 100,000 population—a major decrease from 1980 when a homicide rate of 34.2 per 100,000 was reported. This included 15 officer-involved shootings. One shooting led to the death of a SWAT team member, Randal Simmons, the first in LAPD's history. Los Angeles in the year of 2013 totaled 251 murders, a decrease of 16 percent from the previous year. Police speculate the drop resulted from a number of factors, including young people spending more time online. In 2021, murders rose to the highest level since 2008 and there were 348.
In 2015, it was revealed that the LAPD had been under-reporting crime for eight years, making the crime rate in the city appear much lower than it really is.
The Dragna crime family and the 
 The economy of Los Angeles is driven by international trade, entertainment (television, motion pictures, video games, music recording, and production), aerospace, technology, petroleum, fashion, apparel, and tourism. Other significant industries include finance, telecommunications, law, healthcare, and transportation. In the 2017
The economy of Los Angeles is driven by international trade, entertainment (television, motion pictures, video games, music recording, and production), aerospace, technology, petroleum, fashion, apparel, and tourism. Other significant industries include finance, telecommunications, law, healthcare, and transportation. In the 2017  Los Angeles is often billed as the "Creative Capital of the World" because one in every six of its residents works in a creative industry and there are more artists, writers, filmmakers, actors, dancers and musicians living and working in Los Angeles than any other city at any other time.
Los Angeles is often billed as the "Creative Capital of the World" because one in every six of its residents works in a creative industry and there are more artists, writers, filmmakers, actors, dancers and musicians living and working in Los Angeles than any other city at any other time.
 The performing arts play a major role in Los Angeles's cultural identity. According to the USC Stevens Institute for Innovation, "there are more than 1,100 annual theatrical productions and 21 openings every week." The Los Angeles Music Center is "one of the three largest performing arts centers in the nation", with more than 1.3 million visitors per year. The Walt Disney Concert Hall, centerpiece of the Music Center, is home to the prestigious Los Angeles Philharmonic. Notable organizations such as
The performing arts play a major role in Los Angeles's cultural identity. According to the USC Stevens Institute for Innovation, "there are more than 1,100 annual theatrical productions and 21 openings every week." The Los Angeles Music Center is "one of the three largest performing arts centers in the nation", with more than 1.3 million visitors per year. The Walt Disney Concert Hall, centerpiece of the Music Center, is home to the prestigious Los Angeles Philharmonic. Notable organizations such as  Los Angeles's food culture is a fusion of global cuisine brought on by the city's rich immigrant history and population. Latin American immigrants, particularly Mexican immigrants, brought
Los Angeles's food culture is a fusion of global cuisine brought on by the city's rich immigrant history and population. Latin American immigrants, particularly Mexican immigrants, brought  The city of Los Angeles and its metropolitan area are the home of eleven top-level professional sports teams, several of which play in neighboring communities but use Los Angeles in their name. These teams include the
The city of Los Angeles and its metropolitan area are the home of eleven top-level professional sports teams, several of which play in neighboring communities but use Los Angeles in their name. These teams include the  Los Angeles is the second-largest city in the United States but hosted no NFL team between 1995 and 2015. At one time, the Los Angeles area hosted two NFL teams: the Rams and the Raiders. Both left the city in 1995, with the Rams moving to
Los Angeles is the second-largest city in the United States but hosted no NFL team between 1995 and 2015. At one time, the Los Angeles area hosted two NFL teams: the Rams and the Raiders. Both left the city in 1995, with the Rams moving to  Los Angeles boasts a number of sports venues, including
Los Angeles boasts a number of sports venues, including  Los Angeles is a
Los Angeles is a  There are three public universities within the city limits:
There are three public universities within the city limits: 
 The Los Angeles metro area is the second-largest broadcast
The Los Angeles metro area is the second-largest broadcast  As part of the region's aforementioned creative industry, the Big Four major broadcast television networks, ABC,
As part of the region's aforementioned creative industry, the Big Four major broadcast television networks, ABC,  The LA County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LA County Metro) and other agencies operate an extensive system of bus lines, as well as subway and light rail lines across Los Angeles County, with a combined monthly ridership (measured in individual boardings) of 38.8 million . The majority of this (30.5 million) is taken up by the city's bus system, the second busiest in the country. The subway and light rail combined average the remaining roughly 8.2 million boardings per month. LA County Metro recorded over 397 million boardings for the 2017 calendar year, including about 285 million bus riders and about 113 million riding on rail transit. For the first quarter of 2018, there were just under 95 million system-wide boardings, down from about 98 million in 2017, and about 105 million in 2016. In 2005, 10.2% of Los Angeles commuters rode some form of public transportation. According to the 2016 American Community Survey, 9.2% of working Los Angeles (city) residents made the journey to work via public transportation.
The city's subway system is the ninth busiest in the United States and its light rail system is the country's busiest. The rail system includes the B and D subway lines, as well as the A, C, E, and L light rail lines. In 2016, the E Line was extended to the Pacific Ocean at
The LA County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LA County Metro) and other agencies operate an extensive system of bus lines, as well as subway and light rail lines across Los Angeles County, with a combined monthly ridership (measured in individual boardings) of 38.8 million . The majority of this (30.5 million) is taken up by the city's bus system, the second busiest in the country. The subway and light rail combined average the remaining roughly 8.2 million boardings per month. LA County Metro recorded over 397 million boardings for the 2017 calendar year, including about 285 million bus riders and about 113 million riding on rail transit. For the first quarter of 2018, there were just under 95 million system-wide boardings, down from about 98 million in 2017, and about 105 million in 2016. In 2005, 10.2% of Los Angeles commuters rode some form of public transportation. According to the 2016 American Community Survey, 9.2% of working Los Angeles (city) residents made the journey to work via public transportation.
The city's subway system is the ninth busiest in the United States and its light rail system is the country's busiest. The rail system includes the B and D subway lines, as well as the A, C, E, and L light rail lines. In 2016, the E Line was extended to the Pacific Ocean at  The Port of Los Angeles is in San Pedro Bay in the San Pedro neighborhood, approximately south of Downtown. Also called Los Angeles Harbor and WORLDPORT LA, the port complex occupies of land and water along of waterfront. It adjoins the separate
The Port of Los Angeles is in San Pedro Bay in the San Pedro neighborhood, approximately south of Downtown. Also called Los Angeles Harbor and WORLDPORT LA, the port complex occupies of land and water along of waterfront. It adjoins the separate  Los Angeles has 25
Los Angeles has 25