Lymnaea Stagnalis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Lymnaea stagnalis'', better known as the great pond snail, is a
File:Blotniarka stagnalis.jpg, Typical shell
File:Spitzschlammschnecke.jpg, Great pond snail with an adult '' Physa sp.'' snail
 ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is widely used for the study of
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is widely used for the study of 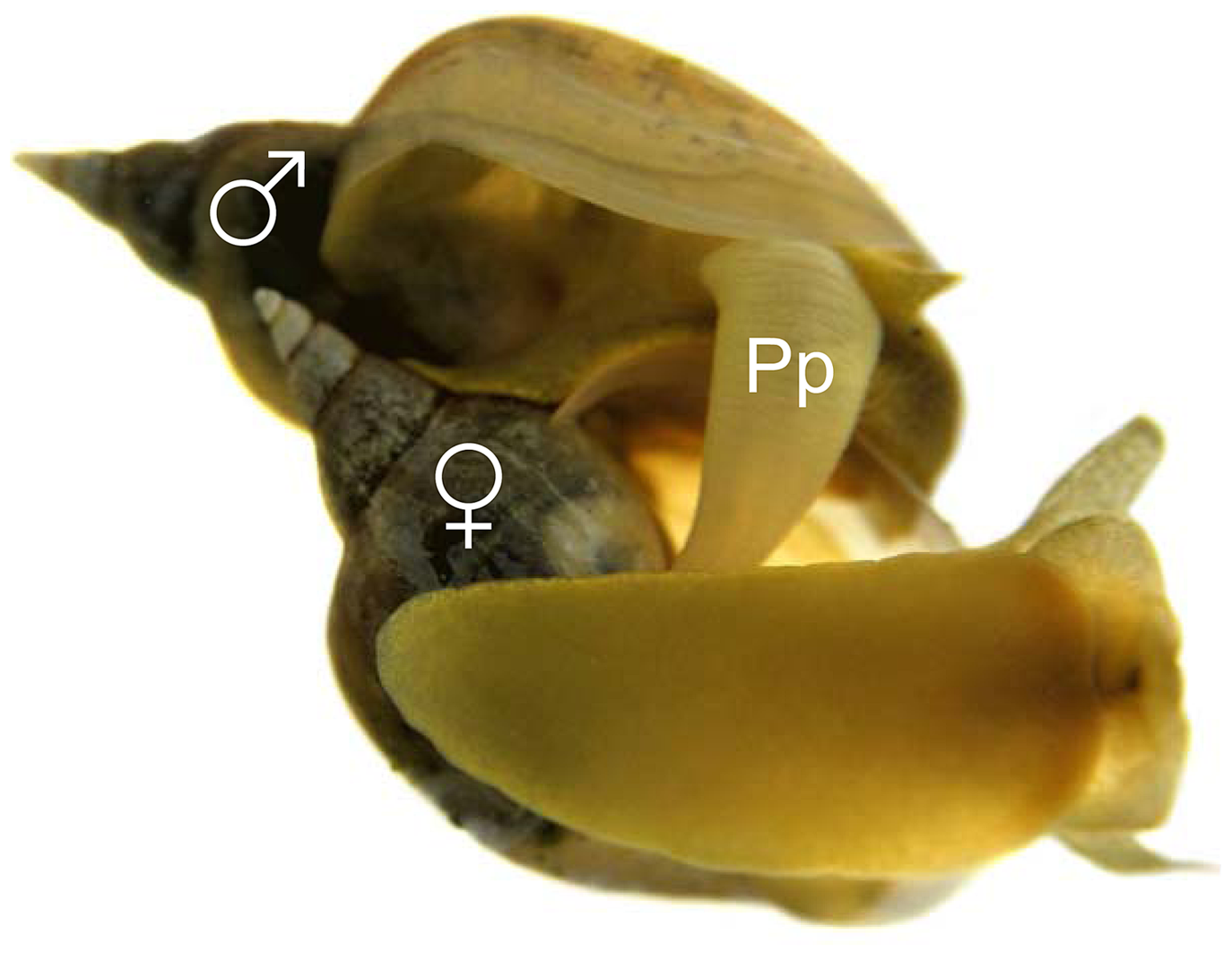
''Lymnaea stagnalis''
at
''Lymnaea''
– Scholarpedia article * https://web.archive.org/web/20090925182719/http://www.lymnaea.org/ – ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' Sequencing Consortium
Arnaud Giusti, Pierre Leprince, Gabriel Mazzucchelli, Jean-Pierre Thomé, Laurent Lagadic, Virginie Ducrot, Célia Joaquim-Justo : Proteomic Analysis of the Reproductive Organs of the Hermaphroditic Gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis Exposed to Different Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals; PLOS, ONE 19 November 2013
{{taxonbar, from=Q911251 Lymnaeidae Molluscs of Europe Gastropods described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of large air-breathing freshwater snail
Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks which live in fresh water. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs ...
, an aquatic pulmonate
Pulmonata or pulmonates, is an informal group (previously an order, and before that a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group includ ...
gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. T ...
mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is e ...
in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Lymnaeidae
Lymnaeidae, common name the pond snails, is a taxonomic family of small to large air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks, that belong to the clade Hygrophila.
Lymnaeidae is the only family within the superfamily ...
. The great pond snail is a model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
to study parasitology, neurology, embryonal development and genetic regulation.
''Limnaea stagnalis'' var. ''baltica'' Lindström, 1868: synonym of ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' (Linnaeus, 1758)
Distribution
The distribution of this species isholarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical reg ...
, mainly the temperate zones of Northern America, Europe and Asia. The snail can be found in many ponds, lakes and very slow-moving rivers with a rich underwater vegetation. The northernmost populations exist in northern Norway, and in Central Europe, it inhabits even montane ecosystems
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial f ...
at 1700 meters above sea level. In the ''Saprobiensystem'' used in Germany to judge the quality of freshwater biotopes, the species has a value of 1.9 and indicates a biotope with a water quality class II, the second-highest.
Shell
For the terms used in this section, seegastropod shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of a Gastropoda, gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium s ...
. The shells vary from light brown to dark brown, and the height of an adult shell ranges from 45 to 60 millimeters. Rarely, snails with a 70 mm shell can be found. The width of an adult shell ranges from 20 to 30 mm.
The shell has 4.5 to 6 weakly convex whorls. The upper whorls are pointed, while the last whorl is suddenly inflated. Young great pond snails can be confused with those of the genus ''Physa
''Physa'' is a genus of small, left-handed or sinistral, air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Physinae of the family Physidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Physa Draparnaud, 1801. Ac ...
'', and rarely, in cases of irregularly grown shells, great pond snails can be mixed up with ''Radix peregra
''Peregriana peregra'' is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.
Distribution and habitat
This small pond snail is found in Europe, Newfoundland and northern A ...
'' — though adults of the latter species are a lot smaller, with shell heights of only 12 to 20 millimeters.
Nervous system
 ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is widely used for the study of
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is widely used for the study of learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machine learning, machines ...
, memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
and neurobiology.
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' has a relatively simple central nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
(CNS) consisting of a total of ~20,000 neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s, many of them individually identifiable, organized in a ring of interconnected ganglia. Most neurons of the ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' central nervous system are large in size (diameter: up to ~100 μm), thus allowing electrophysiological dissection of neuronal networks that has yielded profound insights in the working mechanisms of neuronal networks controlling relatively simple behaviors such as feeding, respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
, locomotion, and reproduction. Studies using the central nervous system of ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' as a model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
have also identified novel cellular and molecular mechanisms in neuronal regeneration, synapse formation, synaptic plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuit ...
, learning and memory formation
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
, the neurobiology of development and aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
, the modulatory role of neuropeptide
Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the ...
s, and adaptive responses to hypoxic
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the t ...
stress.

Life cycle
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is a simultaneously hermaphroditic species and can mate in the male and female role, but within one copulation only one sexual role is performed at a time. ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' perform more inseminations in larger groups and prefer to inseminate novel over familiar partners. Such higher motivation to copulate when a new partner is encountered is known as theCoolidge effect
The Coolidge effect is a biological phenomenon seen in animals, whereby males exhibit renewed sexual interest whenever a new female is introduced, even after sex with prior but still available sexual partners. To a lesser extent, the effect is also ...
and has been demonstrated in hermaphrodites firstly in 2007.
Parasites
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' is anintermediate host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include a ...
for:
* '' Moliniella anceps'' ( Molin, 1859) Hubner, 1939
Other parasites of ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' include:
* '' Echinoparyphium aconiatum''
* '' Echinoparyphium recurvatum''Soldanova M., Selbach C., Sures B., Kostadinova A. & Perez-del-Olmo A. (2010). "Larval trematode communities in ''Radix auricularia'' and ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' in a reservoir system of the Ruhr River". ''Parasites & Vectors
''Parasites & Vectors'' is a peer-reviewed open-access medical journal published by BioMed Central. The journal publishes articles on the biology of parasites, parasitic diseases, intermediate hosts, vectors and vector-borne pathogens. ''Paras ...
'' 2010, 3: 56. .
* '' Opisthioglyphe ranae''
* ''Plagiorchis elegans
''Plagiorchis elegans'' is a species of parasitic trematodes (flukes) in the genus ''Plagiorchis
''Plagiorchis'' is a genus of parasitic trematodes (flukes) in the family Plagiorchiidae
Plagiorchiidae is a family of parasitic trematodes (fl ...
''
* '' Diplostomum pseudospathaceum''
* ''Echinostoma revolutum
''Echinostoma revolutum'' is a trematode parasites, of which the adults can infect birds and mammals, including humans. In humans, it causes echinostomiasis..
Distribution
''Echinostoma revolutum'' is the most widely distributed species of the ...
''
* '' Trichobilharzia szidati''
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' has been experimentally infected with ''Elaphostrongylus rangiferi
''Elaphostrongylus'' is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the family Protostrongylidae.
Species
* ''Elaphostrongylus cervi'' Cameron, 1931
* '' Elaphostrongylus panticola'' Lubinov, 1945
* '' Elaphostrongylus rangiferi'' Mitskevich, 1958
* '' ...
''.Skorping A. (1985). "''Lymnea stagnalis'' as experimental intermediate host for ''Elaphostrongylus rangiferi''". '' Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde'' 71: 265–270.
As aquarium pets
''Lymnaea stagnalis'' snails can be easily be kept in a freshwater aquarium at room temperature, and fed with various sorts of vegetables, salad, cabbage anddandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
leaves. Fish food will also be eaten, as well as aquarium pests like algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, the ''Hydra viridissima
''Hydra viridissima'' is a species of cnidarian which is commonly found in still or slow-moving freshwater in the Northern temperate zone. ''Hydra viridissima'' is commonly called green hydra due to its coloration, which is due to the symbiotic ...
'' polyp, and the eggs of other water snails.
Due to the development of toxic nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
s, leftover food must be removed in time, and the water exchanged often. Using a water conditioner
Water conditioners are formulations designed to be added to tap water before its use in an aquarium. If the tap water is chlorinated then a simple conditioner containing a dechlorinator may be used. These products contain sodium thiosulfate which ...
is also recommended. Depending on water hardness
Hard water is water that has high mineral content (in contrast with "soft water"). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone, chalk or gypsum, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates, bicarbo ...
, a piece of cuttlebone
Cuttlebone, also known as cuttlefish bone, is a hard, brittle internal structure (an internal shell) found in all members of the family Sepiidae, commonly known as cuttlefish, within the cephalopods. In other cephalopod families it is calle ...
must be offered to cover the snails' calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
needs.
References
This article incorporates CC-BY-2.0 text from referencesFeng Z-P., Zhang Z., Kesteren R. E. van, Straub V. A., Nierop P. van, Jin K., Nejatbakhsh N., Goldberg J. I., Spencer G. E., Yeoman M. S., Wildering W., Coorssen J. R., Croll R. P., Buck L. T., Syed N. I. & Smit A. B. (23 September 2009) "Transcriptome analysis of the central nervous system of the mollusc ''Lymnaea stagnalis''". ''BMC Genomics'' 10: 451. Koene J. M. & Maat A. T. (6 November 2007) "Coolidge effect
The Coolidge effect is a biological phenomenon seen in animals, whereby males exhibit renewed sexual interest whenever a new female is introduced, even after sex with prior but still available sexual partners. To a lesser extent, the effect is also ...
in pond snails: male motivation in a simultaneous hermaphrodite". ''BMC Evolutionary Biology
''BMC Ecology and Evolution'' (since January 2021), previously ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' (2001–2020), is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all fields of evolutionary biology, including phylogenetics and palaeontology. It ...
'' 7: 212. and CC-BY-2.5 text from the referenceKoene J. M., Sloot W., Montagne-Wajer K., Cummins S. F., Degnan B. M., Smith J. S., Nagle G. T. & Maat A. ter (2010). "Male Accessory Gland Protein Reduces Egg Laying in a Simultaneous Hermaphrodite". '' PLoS ONE'' 5(4): e10117. .
External links
''Lymnaea stagnalis''
at
Animalbase AnimalBase is a project brought to life in 2004 and is maintained by the University of Göttingen, Germany. The goal of the AnimalBase project is to digitize early zoological literature, provide copyright-free open access to zoological works, and pr ...
taxonomy,short description, distribution, biology,status (threats), images
* Hoffer J. N. A., Ellers J. & Koene J. M. (2010). "Costs of receipt and donation of ejaculates in a simultaneous hermaphrodite". ''BMC Evolutionary Biology
''BMC Ecology and Evolution'' (since January 2021), previously ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' (2001–2020), is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all fields of evolutionary biology, including phylogenetics and palaeontology. It ...
'' 10: 393. .
''Lymnaea''
– Scholarpedia article * https://web.archive.org/web/20090925182719/http://www.lymnaea.org/ – ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' Sequencing Consortium
Arnaud Giusti, Pierre Leprince, Gabriel Mazzucchelli, Jean-Pierre Thomé, Laurent Lagadic, Virginie Ducrot, Célia Joaquim-Justo : Proteomic Analysis of the Reproductive Organs of the Hermaphroditic Gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis Exposed to Different Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals; PLOS, ONE 19 November 2013
{{taxonbar, from=Q911251 Lymnaeidae Molluscs of Europe Gastropods described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus