|
Coolidge Effect
The Coolidge effect is a biological phenomenon seen in animals, whereby males exhibit renewed sexual interest whenever a new female is introduced, even after sex with prior but still available sexual partners. To a lesser extent, the effect is also seen among females with regard to their mates. The Coolidge effect can be attributed to an increase in sexual responsiveness, and a shortening of the sexual refractory period. The evolutionary benefit to this phenomenon is that a male can fertilize multiple females. The male may be reinvigorated repeatedly for successful insemination of multiple females. This type of mating system can be referred to as polygyny, where one male has multiple female mates, but each female mates with only one or a few males. The Coolidge effect has been demonstrated to occur in humans across cultures and in both sexes. Origin of the term Behavioral endocrinologist Frank A. Beach claims in a 1974 letter to have introduced the term "Coolidge effect" in eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory Period (sex)
In human sexuality, the refractory period is usually the recovery phase after orgasm during which it is physiologically impossible for a man to have additional orgasms. This phase begins immediately after ejaculation and lasts until the excitement phase of the human sexual response cycle begins anew with low-level response. Although it is generally reported that women do not experience a refractory period and can thus experience an additional orgasm (or multiple orgasms) soon after the first one, some sources state that both men and women experience a refractory period because women may also experience a moment after orgasm in which further sexual stimulation does not produce excitement. Factors and theories Although the refractory period varies widely among individuals, ranging from minutes to days, most men cannot achieve or maintain an erection during this time, and many perceive a psychological feeling of satisfaction and are temporarily uninterested in further sexual activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
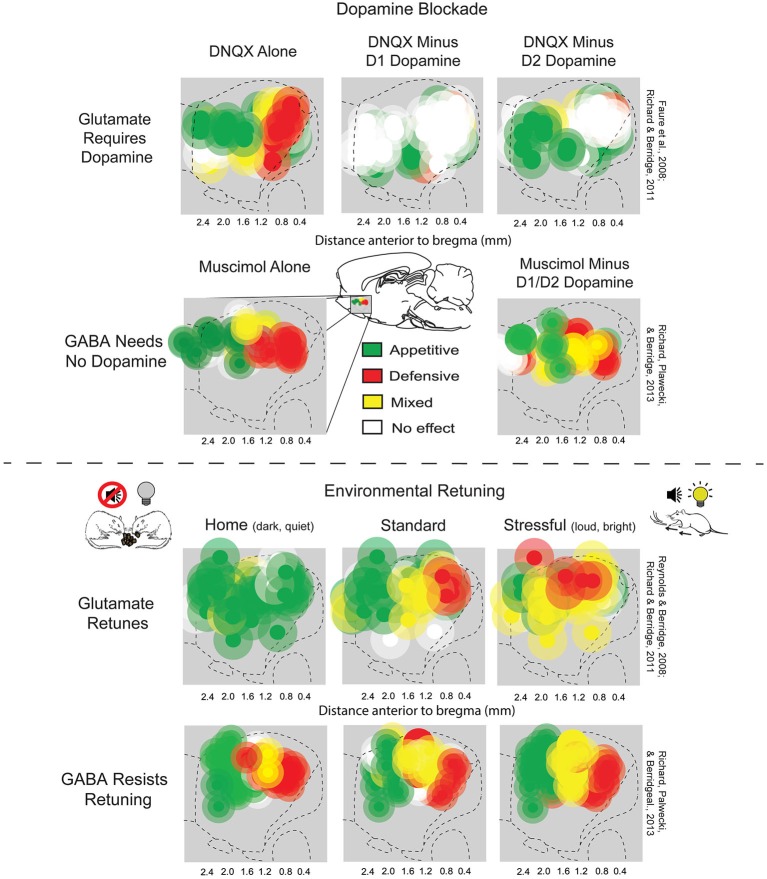
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region (D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller type—called a sperm. Sperm cells or spermatozoa are small and motile due to the flagellum, a tail-shaped structure that allows the cell to propel and move. In contrast, each egg cell or ovum is relatively large and non-motile. In short a gamete is an egg cell (female gamete) or a sperm (male gamete). In animals, ova mature in the ovaries of females and sperm develop in the testes of males. During fertilization, a spermatozoon and ovum unite to form a new diploid organism. Gametes carry half the genetic information of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating Plug
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, or sphragis (Latin, from Greek σφραγίς ''sphragis'', "a seal"), is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female genital tract, such as the vagina, and later hardens into a plug or glues the tract together. While females can expel the plugs afterwards, the male's sperm still gets a time advantage in getting to the egg, which is often the deciding factor in fertilization. The mating plug plays an important role in sperm competition and may serve as an alternative and more advantageous strategy to active mate guarding. In some species, such a passive mate-guarding strategy may reduce selection on large male size. Such a strategy may be advantageous because it would allow a male to increase reproductive success by spending more time pursuing new female mates rather than active mate guarding. Composition The mating plug of the ''Bombus terrestris'' was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Rat
A laboratory rat or lab rat is a brown rat of the subspecies '' Rattus norvegicus domestica'' which is bred and kept for scientific research. While less commonly used for research than mice (see laboratory mouse), rats have served as an important animal model for research in psychology and biomedical science. Origins In 18th century Europe, wild brown rats ran rampant and this infestation fueled the industry of rat-catching. Rat-catchers would not only make money by trapping the rodents, but also by selling them for food or, more commonly, for rat-baiting. Rat-baiting was a popular sport, which involved filling a pit with rats and timing how long it took for a terrier to kill them all. Over time, breeding the rats for these contests may have produced variations in color, notably the albino and hooded varieties. The first time one of these albino mutants was brought into a laboratory for a study was in 1828 for an experiment on fasting. Over the next 30 years, rats were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers In Zoology
''Frontiers in Zoology'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all aspects of zoology. It was established in 2004 and is published by BioMed Central on behalf of the . The editors-in-chief are Jürgen Heinze (University of Regensburg) and Ulrich Technau (University of Vienna). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.781. References External links * Zoology journals Publications established in 2004 Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals English-language journals BioMed Central academic journals {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
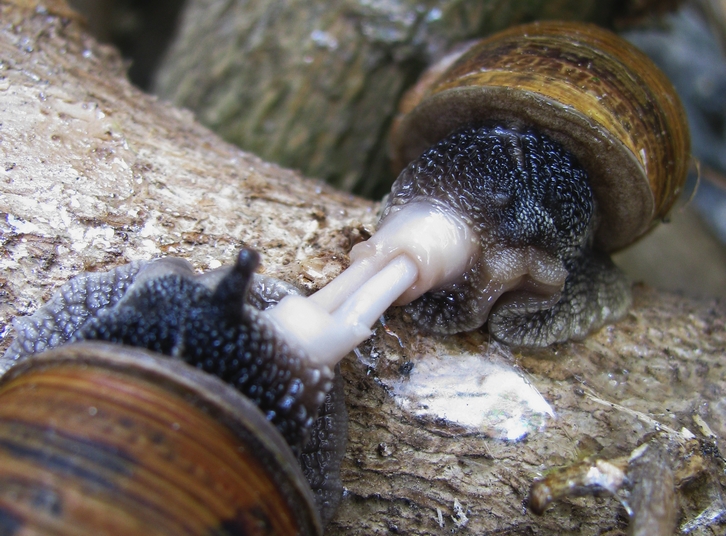
Biomphalaria Glabrata
''Biomphalaria glabrata'' is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails. ''Biomphalaria glabrata'' is an intermediate snail host for the trematode ''Schistosoma mansoni'', which is one of the main schistosomes that infect humans. This snail is a medically important pest, because of transferring the disease intestinal schistosomiasis, the most widespread of all types of schistosomiasis. The parasite ''Schistosoma mansoni'' (which these snails and other ''Biomphalaria'' snails carry) infects about 83.31 million people worldwide. ''Biomphalaria glabrata''/''Schistosoma mansoni'' provides a useful model system for investigating the intimate interactions between host and parasite. There is a great deal of information available about this snail, because it has been, and continues to be, under intensive study by many malacologists, parasitologists and other researchers, on account of its medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMC Evolutionary Biology
''BMC Ecology and Evolution'' (since January 2021), previously ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' (2001–2020), is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all fields of evolutionary biology, including phylogenetics and palaeontology. It was established in 2001 and is part of a series of BMC journals published by BioMed Central. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.260. References External links * BioMed Central academic journals Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals {{biology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymnaea Stagnalis
''Lymnaea stagnalis'', better known as the great pond snail, is a species of large air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae. The great pond snail is a model organism to study parasitology, neurology, embryonal development and genetic regulation. ''Limnaea stagnalis'' var. ''baltica'' Lindström, 1868: synonym of ''Lymnaea stagnalis'' (Linnaeus, 1758) Distribution The distribution of this species is holarctic, mainly the temperate zones of Northern America, Europe and Asia. The snail can be found in many ponds, lakes and very slow-moving rivers with a rich underwater vegetation. The northernmost populations exist in northern Norway, and in Central Europe, it inhabits even montane ecosystems at 1700 meters above sea level. In the ''Saprobiensystem'' used in Germany to judge the quality of freshwater biotopes, the species has a value of 1.9 and indicates a biotope with a water quality class II, the second-highest. Shell For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes. Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the female or male. For example, the great majority of tunicata, tunicates, pulmonate molluscs, opisthobranch, earthworms, and slugs are hermaphrodites. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species and to a lesser degree in other vertebrates. Most plants are also hermaphrodites. Animal species having different sexes, male and female, are called Gonochorism, gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphrodite. There are also species where hermaphrodites exist alongside males (called androdioecy) or alongside females (called gynodioecy), or all three exist in the same species ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical House Cricket
''Gryllodes sigillatus'', the tropical house cricket, Indian house cricket or banded cricket, is a small cricket probably native to southwestern Asia, but has spread throughout tropical regions worldwide. Like its relative the house cricket, the tropical house cricket is also raised commercially for feeding certain pets such as reptiles, birds, amphibians, and insectivorous arthropods. Description The tropical house cricket is slightly smaller than its relative the house cricket, growing about . These crickets are light yellowish tan and have two thick black bands. One of the bands runs through the bottom of the thorax while the other goes across the upper abdomen. Females are similar to males, only wingless and a long ovipositor emerging from its rear. Relationship with humans As pet food Decorated house crickets are relatively new to the pet trade and are favored by many people due to easier care requirements than the more-common house cricket or the black field cricket. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |