|
Aquatic Animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether invertebrate or vertebrate, that lives in water for most or all of its lifetime. Many insects such as mosquitoes, mayflies, dragonflies and caddisflies have aquatic larvae, with winged adults. Aquatic animals may breathe air or extract oxygen from water through specialised organs called gills, or directly through the skin. Natural environments and the animals that live in them can be categorized as aquatic (water) or terrestrial (land). This designation is polyphyletic. Description The term aquatic can be applied to animals that live in either fresh water or salt water. However, the adjective marine is most commonly used for animals that live in saltwater, i.e. in oceans, seas, etc. Aquatic animals (especially freshwater animals) are often of special concern to conservationists because of the fragility of their environments. Aquatic animals are subject to pressure from overfishing, destructive fishing, marine pollution, hunting, and cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
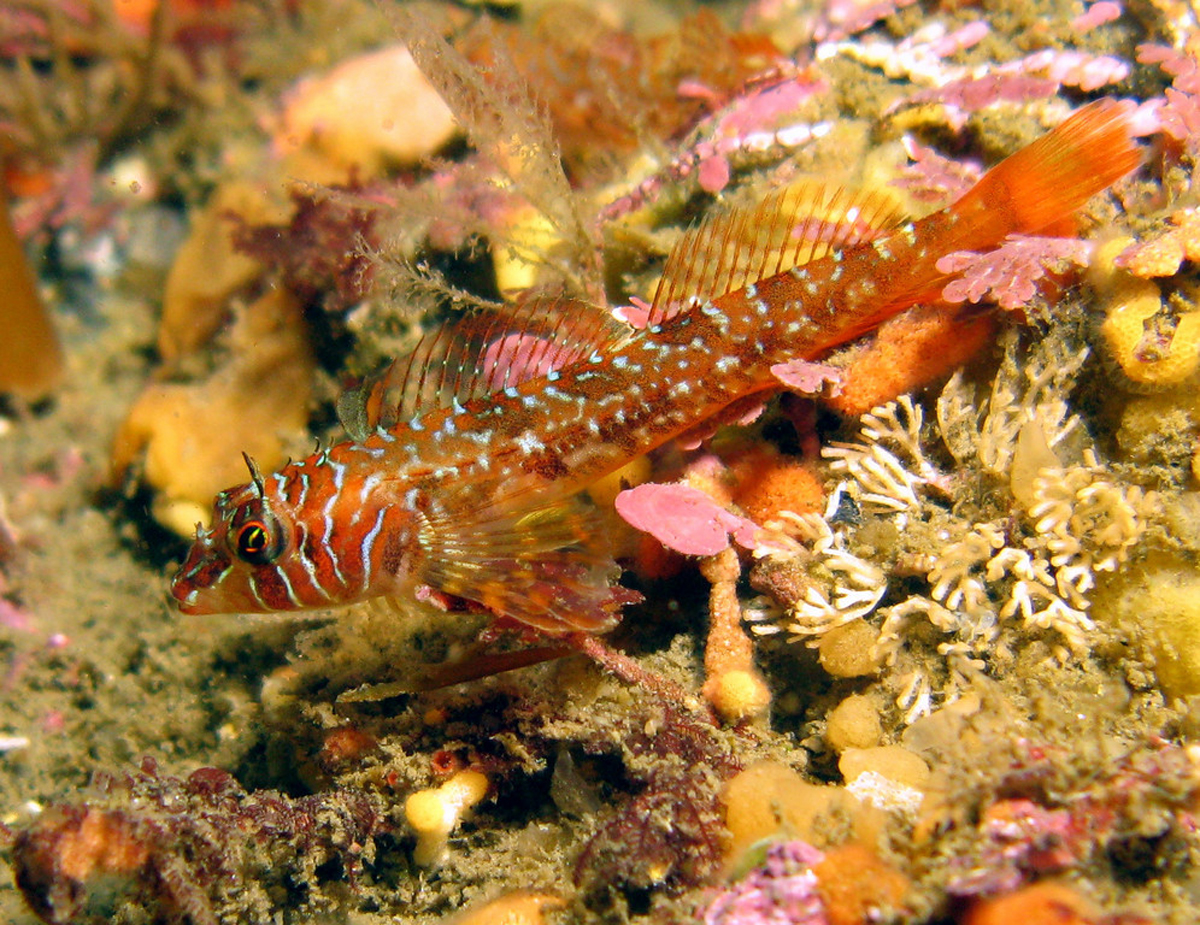
Jordania Zonope
The longfin sculpin (''Jordania zonope'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Jordaniidae, a small family of sculpins. This species is found in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. This species is the only known member of its genus, ''Jordania''. Taxonomy The longfin sculpin was first formally described in 1895 by the American ichthyologist Edwin Chapin Starks with its type locality given as Point Orchard in Puget Sound near Seattle, Washington. Starks classified this new species in the new monospecific genus ''Jordania''. This genus is one of two monospecific genera classified within the family Jordaniidae. Etymology The longfin sculpin's genus name, ''Jordania'', honours David Starr Jordan who Starks said was his "teacher in ichthyology". Starks did not exp;lain his choice of specific name but in 1898 Jordan and Barton Warren Evermann suggested that it was a compound of ''zona'', "zone" or "band", and ''opi'', meaning "window" or "hole", an allusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided."Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
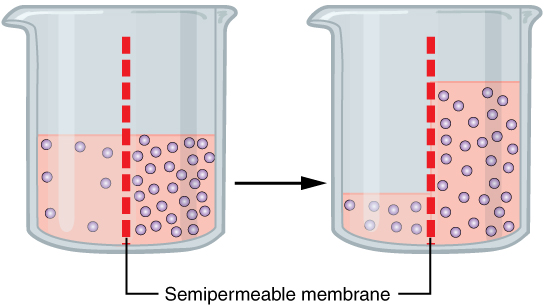
Osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semiperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Fish
Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine conditions in many ways, especially the difference in levels of salinity. To survive fresh water, the fish need a range of physiology, physiological adaptations. 41.24% of all known species of fish are found in fresh water. This is primarily due to the rapid speciation that the scattered habitats make possible. When dealing with ponds and lakes, one might use the same basic models of speciation as when studying island biogeography. Physiology Freshwater fish differ physiologically from salt water fish in several respects. Their gills must be able to diffuse dissolved gases while keeping the salts in the body fluids inside. Their scales reduce water diffusion through the skin: freshwater fish that have lost too many scales will die. They also have well developed kidneys to reclaim salts from body flui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractile Vacuole
A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists and in unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole. Overview The contractile vacuole is a specialized type of vacuole that regulates the quantity of water inside a cell. In freshwater environments, the concentration of solutes is hypotonic, lesser outside than inside the cell. Under these conditions, osmosis causes water to accumulate in the cell from the external environment. The contractile vacuole acts as part of a protective mechanism that prevents the cell from absorbing too much water and possibly lysing (rupturing) through excessive internal pressure. The contractile vacuole, as its name suggests, expels water out of the cell by contracting. The growth (water gathering) and contraction (water expulsion) of the contractile vacuole are periodical. One cycle takes several seconds, depending on the species and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
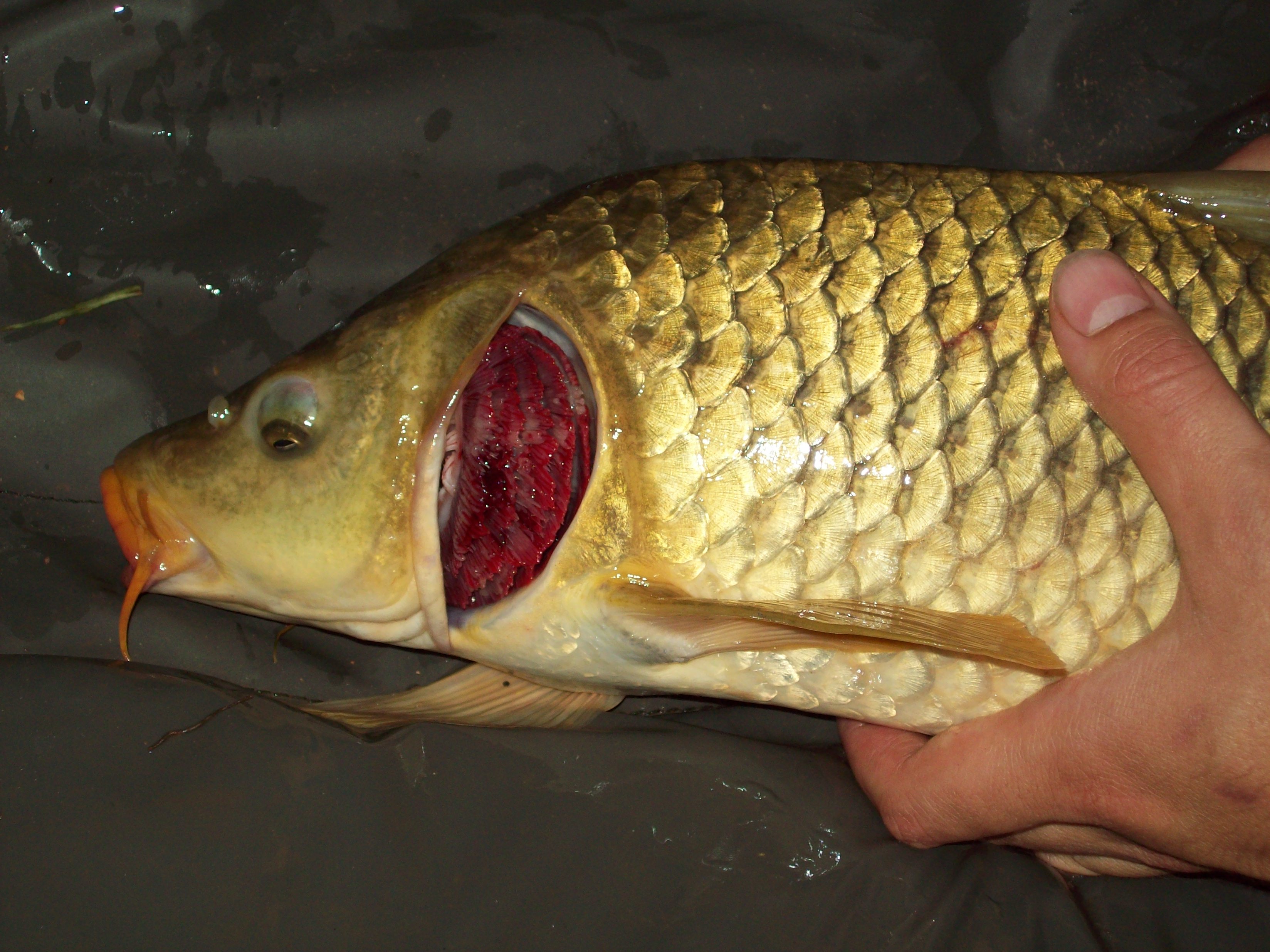
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonicity
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane-impermeable solutes across a cell membrane which determine the direction and extent of osmotic flux. It is commonly used when describing the swelling-versus-shrinking response of cells immersed in an external solution. Unlike osmotic pressure, tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the membrane, as only these exert an effective osmotic pressure. Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect tonicity because they will always equilibrate with equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane without net solvent movement. It is also a factor affecting imbibition. There are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another: ''hypertonic'', ''hypotonic'', and ''isotonic''.A hypotonic sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisheries And Climate Change
Climate change and fisheries affect one another because rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation are radically altering marine aquatic ecosystems, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distribution and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant especially for those countries which depend the most on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions. The impacts of climate change on ocean systems has impacts on the sustainability of fisheries and aquaculture, on the livelihoods of the communities that depend on fisheries, and on the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, bone/tusks, horn (anatomy), horn/antler, etc.), for recreation/taxidermy (see trophy hunting), to remove predators dangerous to humans or domestic animals (e.g. wolf hunting), to pest control, eliminate pest (organism), pests and nuisance animals that damage crops/livestock/poultry or zoonosis, spread diseases (see varmint hunting, varminting), for trade/tourism (see safari), or for conservation biology, ecological conservation against overpopulation and invasive species. Recreationally hunted species are generally referred to as the ''game (food), game'', and are usually mammals and birds. A person participating in a hunt is a hunter or (less commonly) huntsman; a natural area used for hunting is called a game reserve; an experienced hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural and municipal solid waste, residential waste, particle (ecology), particles, noise, excess carbon dioxide or invasive organisms enter the ocean and cause harmful effects there. The majority of this waste (80%) comes from land-based activity, although Marine Transportation, marine transportation significantly contributes as well. Since most inputs come from land, either via the rivers, sewage or the atmosphere, it means that Continental shelf, continental shelves are more vulnerable to pollution. Air pollution is also a contributing factor by carrying off iron, carbonic acid, nitrogen, silicon, sulfur, pesticides or dust particles into the ocean. The pollution often comes from nonpoint source pollution, nonpoint sources such as agricultural surface runoff, runoff, wind-blown debris, and dust. These nonpoint sources are largely due to runoff th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |