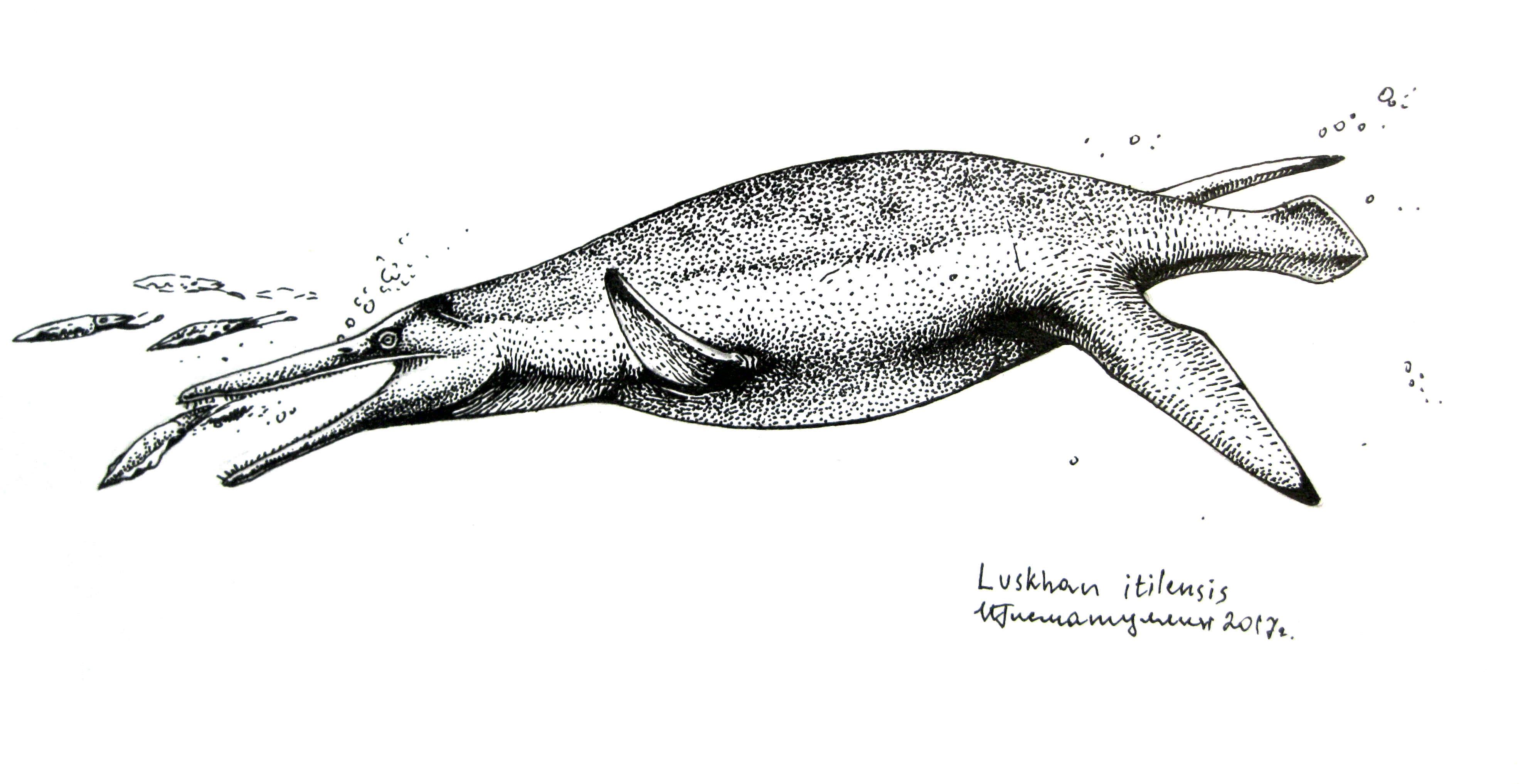
Luskhan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Luskhan'' (meaning "water spirit chief") is an
 A nearly complete fossil skeleton of a
A nearly complete fossil skeleton of a
 The holotype of ''Luskhan'' measures long. At the end of a relatively short neck, the long skull tapers to an elongate snout, which is longer than the region of the skull behind the eyes, as in other members of the Brachaucheninae. It has a lower jaw long. Additional characteristics typical of brachauchenines include the
The holotype of ''Luskhan'' measures long. At the end of a relatively short neck, the long skull tapers to an elongate snout, which is longer than the region of the skull behind the eyes, as in other members of the Brachaucheninae. It has a lower jaw long. Additional characteristics typical of brachauchenines include the
 A number of unique characters, or
A number of unique characters, or
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of brachauchenine pliosaur
Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of plesiosaurs, known from the earliest Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous. They are best known for the subclade Thalassophonea, which contained crocodile-like short-necked forms with large heads and massive toot ...
from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The type and only species is ''Luskhan itilensis'', named by Valentin Fischer and colleagues in 2017 from a well-preserved and nearly complete skeleton. As an early-diverging brachauchenine, ''Luskhan'' consequently exhibits an intermediate combination of traits seen in more basal (less specialized) and more derived (more specialized) pliosaurs. However, ''Luskhan'' departs significantly from other pliosaurs in that it exhibits a lack of adaptations in its skull to feeding on large prey; its slender snout, small teeth, and short tooth rows instead indicate a skull adapted for feeding on small, soft prey. With these features, it is the pliosaur that approaches closest to the distantly-related piscivorous
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
polycotylids
Polycotylidae is a family of plesiosaurs from the Cretaceous, a sister group to Leptocleididae. Polycotylids first appeared during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous, before becoming abundant and widespread during the early Late Cretaceous ...
, having convergently evolved
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
these traits more than 10 million years apart.
Discovery and naming
 A nearly complete fossil skeleton of a
A nearly complete fossil skeleton of a pliosaur
Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of plesiosaurs, known from the earliest Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous. They are best known for the subclade Thalassophonea, which contained crocodile-like short-necked forms with large heads and massive toot ...
, preserved in three dimensions, was found by Gleb N. Uspensky in 2002 on the eastern bank of the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
, north of the village of Slantsevy Rudnik in the Ulyanovsk
Ulyanovsk, known until 1924 as Simbirsk, is a city and the administrative center of Ulyanovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Volga River east of Moscow. Population:
The city, founded as Simbirsk (), was the birthplace of Vladimir Lenin (born ...
region of western Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. Deposits in the region consist of dark grey and slightly sandy shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
layers and siltite layers, in which carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
nodules are embedded. The skeleton was found in the g-5 horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
(layer). After its discovery, the specimen was stored in the I.A. Goncharov Ulyanovsk Regional Museum of Local Lore (YKM), under the specimen number YKM 68344/1_262.
Uspensky co-authored a research paper describing YKM 68344/1_262 that was published in the journal ''Current Biology
''Current Biology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers all areas of biology, especially molecular biology, cell biology, genetics, neurobiology, ecology, and evolutionary biology. The journal includes research articles, var ...
'' on June 5, 2017. Other authors were Valentin Fischer, Roger Benson, Nikolay Zverkov, Laura Soul, Maxim Arkhangelsky, Olivier Lambert, Ilya Stenshin, and Patrick Druckenmiller. They named the specimen as a new genus and species, ''Luskhan itilensis''. The genus name, ''Luskhan'', is derived from ''luuses'', spirits and masters of water in Mongolian and Turkic mythology
Turkic mythology refers to myths and legends told by the Turkic people. It features Tengrist and Shamanist strata of belief along with many other social and cultural constructs related to the nomadic and warrior way of life of Turkic and Mongol ...
, plus the suffix ''khan'', meaning "chief". ''Itil'' is the ancient Turkic name for the Volga River, hence the species epithet ''itilensis'' means "of the Volga River".
Description
parietal bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the Human skull, skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the Human skull, cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, an ...
extending forward to the position of the nostrils; the snout being unconstricted, but bearing an expansion on the bottom surface like ''Megacephalosaurus
''Megacephalosaurus'' (; "great-headed lizard") is an extinct genus of short-necked pliosaur that inhabited the Western Interior Seaway of North America about 94 to 93 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, containin ...
''; the retroarticular process at the back of the lower jaw being inturned; the teeth in the upper jaw being equally-sized; the facets
A facet is a flat surface of a geometric shape, e.g., of a cut gemstone.
Facet may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Facets'' (album), an album by Jim Croce
* ''Facets'', a 1980 album by jazz pianist Monty Alexander and his tri ...
that articulate with the cervical rib
A cervical rib in humans is an extra rib which arises from the seventh cervical vertebra. Their presence is a congenital abnormality located above the normal first rib. A cervical rib is estimated to occur in 0.2% to 0.5% (1 in 200 to 500) of th ...
s on the cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
being placed relatively high, similar to ''Kronosaurus
''Kronosaurus'' ( ; meaning "lizard of Kronos") is a potentially dubious genus of extinct short-necked pliosaur. With an estimated length of , it was among the largest pliosaurs, and is named after the leader of the Greek Titans, Kronos. It ...
'' and ''Brachauchenius
''Brachauchenius'' (meaning 'short neck') is an extinct genus of pliosaurid that lived in North America (United States) and Morocco during the Late Cretaceous.
History
The type species, ''Brachauchenius lucasi'', lived in the Western Inland S ...
'' but unlike Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
pliosaurs and other plesiosaurs; the transverse processes
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic i ...
attaching to the dorsal vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
above the level of the neural canals; and the long coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek κόραξ, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is prese ...
measuring 2.3 times the length of the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
(2.5 in ''Kronosaurus'').
''Luskhan'' also exhibits some more "primitive" traits which resemble non-brachauchenine thalassophonea
Thalassophonea is an extinct clade of pliosaurids from the Middle Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous (Callovian to Turonian) of Australia, Europe, North America and South America. ''Thalassophonea'' was erected by Roger Benson and Patrick D ...
ns, consistent with it being among the earliest brachauchenines. Like ''Pliosaurus
''Pliosaurus'' (meaning 'more lizard') is an extinct genus of thalassophonean pliosaurid known from the Kimmeridgian and Tithonian stages (Late Jurassic) of Europe and South America. Their diet would have included fish, cephalopods, and marine re ...
'', the squamosal bone The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral c ...
s overlap the rear processes of the jugal bone
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anato ...
s; it also excludes them, as in most plesiosaurs, from the border of the temporal fenestrae
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
. There is also a bulb on each squamosal, as well as a ridge extending upwards from the rear surface. As in ''Pliosaurus westburyensis'', the processes of the pterygoid bone
The pterygoid is a paired bone forming part of the palate of many vertebrates, behind the palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the th ...
s that articulate with the quadrate bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, birds), and early synapsids.
In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms upper ...
are thick, and there is a U-shaped notch on the bottom of the supraoccipital bone. The flanges on the bottom of the pterygoids come into contact with each other at the midline of the skull. On the bottom of the cervicals, there are large foramina, or pits. The number of cervical vertebrae in ''Luskhan'' (14) can be seen as intermediate between ''Pliosaurus'' (18) and ''Brachauchenius'' (12).
Unusually, ''Luskhan'' also lacks many of the adaptations for hunting large prey seen in other brachauchenines: the snout is very thin; there is no keel on the bottom of the fused symphysis
A symphysis (, pl. symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint.
# A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint.
# A growing together ...
of the lower jaw; there is no diastema
A diastema (plural diastemata, from Greek διάστημα, space) is a space or gap between two teeth. Many species of mammals have diastemata as a normal feature, most commonly between the incisors and molars. More colloquially, the condition ...
(or gap in the tooth row); the bones of the upper jaw (the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
and maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
) are expanded outwards; and there are no caniniform
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened howeve ...
("canine-like") teeth. The length of the symphysis as a proportion of the overall length of the lower jaw (34%) is also longer than brachauchenines and thalassophoneans, but instead is within the range of the symphyses of the distantly-related Polycotylidae
Polycotylidae is a family of plesiosaurs from the Cretaceous, a sister group to Leptocleididae. Polycotylids first appeared during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous, before becoming abundant and widespread during the early Late Cretaceous. ...
. Also like polycotylids, the teeth are more widely spaced and terminate further forward on the jaw, below the midpoint of the eye socket. As in ''Dolichorhynchops
''Dolichorhynchops'' is an extinct genus of polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous (early Turonian to late Campanian stage) of North America, containing three species, ''D. osborni'', ''D. bonneri'' and ''D. tropicensis'', as well as a ...
'', the arch of the squamosal is angled further forwards than thalassophoneans.
Autapomorphies
 A number of unique characters, or
A number of unique characters, or autapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to t ...
, set ''Luskhan'' apart from all other plesiosaurs. Among thalassophoneans, ''Luskhan'' is unique for having seven teeth in the premaxilla. The first of these is procumbent (angled forwards) such that it is nearly horizontal, and the space between it and the subsequent tooth is also widened. A roughened, hook-like projection develops on the squamosal from its suture with the quadrate. At the back of the skull, the exoccipital bones enclose the bottom of the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum ( la, great hole) is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblon ...
, thereby excluding the basioccipital bone
The basilar part of the occipital bone (also basioccipital) extends forward and upward from the foramen magnum, and presents in front an area more or less quadrilateral in outline.
In the young skull this area is rough and uneven, and is joined ...
. The plate-like lamellae of the pterygoids bear deep grooves on their outer surfaces. On the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geographic ...
(the first cervical), the intercentrum is swollen and has a ridge underneath; meanwhile, the bottom of the axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
(the second cervical) is covered by a tongue-like projection from the third cervical.
In the shoulder girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of t ...
, the projection at the front of the coracoid that points forwards in other plesiosaurs is instead pointed downwards in ''Luskhan'', such that it is perpendicular to the rest of the bone. Unlike other thalassophoneans, but like the Elasmosauridae
Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of p ...
, the blade of the scapula is relatively short, being only as tall vertically as the longitudinal distance from its base to the articulation with the coracoid. On the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
, the humeral tuberosity is located above the expansion of the capitulum
capitulum (plural capitula) may refer to:
*the Latin word for chapter
** an index or list of chapters at the head of a gospel manuscript
** a short reading in the Liturgy of the Hours
*** derived from which, it is the Latin for the assembly known ...
at the bottom end. The ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
and radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
of the front flippers are very small, being only about the same size as the tarsus of the hind flippers; the former of these is longer. Unlike all other pliosaurids, there is no opening (epipodial foramen) where the two bones meet. The fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
is much longer than the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
; the intermedium of the tarsus contacts only the fibula, and lacks an articulation for the tibia unlike other thalassophoneans and ''Marmornectes
''Marmornectes'' is a genus of pliosaurid known from the Middle Jurassic of Bedfordshire, United Kingdom.
Description
''Marmornectes'' is known from the holotype BEDFM 1999.201, an articulated partial skeleton which includes the skull. I ...
''.
Classification
The followingcladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ...
follows an analysis by Fischer and colleagues in 2017, based on a dataset published by Benson and Druckenmiller in 2014 that was previously modified for the description of ''Makhaira
The makhaira is a type of Ancient Greek bladed weapon, generally a large knife or sword with a single cutting edge.
Terminology
The Greek word μάχαιρα (''mákhaira'', plural ''mákhairai''), also transliterated ''machaira'' or ''mac ...
'' in 2015. Due to the completeness of ''Luskhan'', its position is based on scorings for 74% of the characteristics listed in the dataset. In the strict consensus of the 20,000 most parsimonious
Occam's razor, Ockham's razor, or Ocham's razor ( la, novacula Occami), also known as the principle of parsimony or the law of parsimony ( la, lex parsimoniae), is the problem-solving principle that "entities should not be multiplied beyond neces ...
phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
s recovered, ''Makhaira'' forms a polytomy
An internal node of a phylogenetic tree is described as a polytomy or multifurcation if (i) it is in a rooted tree and is linked to three or more child subtrees or (ii) it is in an unrooted tree and is attached to four or more branches. A tr ...
with ''Pliosaurus'' species, instead of forming a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
with other brachauchenines; however, in the consensus of the 24 most parsimonious trees, it is the most basal brachauchenine, with ''Luskhan'' being the next most basal brachauchenine.
Evolutionary context
Along with ''Makhaira'' and ''Stenorhynchosaurus
''Stenorhynchosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pliosaurid plesiosaurs which lived in the Early Cretaceous of South America. The type species and only known is ''Stenorhynchosaurus munozi''. It was a medium-sized pliosaur, reaching an adult body l ...
'', ''Luskhan'' forms an evolutionary grade
A grade is a taxon united by a level of morphological or physiological complexity. The term was coined by British biologist Julian Huxley, to contrast with clade, a strictly phylogenetic unit.
Definition
An evolutionary grade is a group of ...
that fills a critical gap of 40 million years - from the Berriasian
In the geological timescale, the Berriasian is an age/stage of the Early/Lower Cretaceous. It is the oldest subdivision in the entire Cretaceous. It has been taken to span the time between 145.0 ± 4.0 Ma and 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma (million years ago) ...
to the Barremian
The Barremian is an age in the geologic timescale (or a chronostratigraphic stage) between 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago) and 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma). It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous Epoch (or Lower Cretaceous Series). It is preceded ...
epochs of the Early Cretaceous - in the evolution of brachauchenines. While María Páramo-Fonseca and colleagues, the describers of ''Stenorhynchosaurus'', indicated that including it in the Brachaucheninae would necessitate a re-definition of the clade, Fischer and colleagues did not see this as necessary.
Paleobiology
Most thalassophoneanpliosaurids
Pliosauridae is a family of plesiosaurian marine reptiles from the Latest Triassic to the early Late Cretaceous (Rhaetian to Turonian stages) of Australia, Europe, North America and South America. The family is more inclusive than the archetypal ...
, with their robust skulls and short necks, were well-adapted to apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
niches. Although serrated teeth, spatula-shaped snouts, and strongly-developed crests on the skull roof were lost in brachauchenines, their large size and teeth still indicate predatory lifestyles. Meanwhile, with their slimmer body proportions, polycotylids were likely fast-swimming piscivore
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
s. Principal component
Principal may refer to:
Title or rank
* Principal (academia), the chief executive of a university
** Principal (education), the office holder/ or boss in any school
* Principal (civil service) or principal officer, the senior management level ...
and ecomorphological Ecomorphology or ecological morphology is the study of the relationship between the ecological role of an individual and its morphological adaptations. The term "morphological" here is in the anatomical context. Both the morphology and ecology ex ...
analyses place ''Luskhan'' as being significantly closer to polycotylids than other thalassophoneans in terms of skull traits, but not in terms of the rest of the body; thus, ''Luskhan'' is the most polycotylid-like pliosaurid. The early thalassophonean ''Peloneustes
''Peloneustes'' (meaning "mud swimmer") is a genus of pliosaurid plesiosaur from the Middle Jurassic of England. Its remains are known from the Peterborough Member of the Oxford Clay Formation, which is Callovian in age. It was originally descri ...
'' is also polycotylid-like, but less so than ''Luskhan''.
Ecologically speaking, ''Luskhan'' probably preyed on small, soft animals. This is suggested by the slender snout, the long symphysis, and the relatively short tooth row compared to other thalassophoneans. A few traits in ''Luskhan'' are shared with typical thalassophoneans, such as the presence of serrations in the rearmost teeth and the presence of weakly trihedral (triangular in cross-section) teeth; however, these are probably vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
traits retained from ''Pliosaurus''-like ancestors. Thus, ''Luskhan'' departed from the typical apex predator niche of thalassophoneans in order to colonize a lower trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it i ...
, having done so independently 10 million years after polycotylids. ''Makhaira'', by contrast, retained a bauplan that is better-suited to being an apex predator; for instance, its teeth are larger than ''Luskhan''.
Paleoecology
Based on the presence of theammonite
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
'' Speetoniceras versicolor'' several meters north of the site where ''Luskhan'' was discovered, the g-5 horizon can be correlated
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics ...
with the ''S. versicolor'' zone
Zone or The Zone may refer to:
Places Climate and altitude zones
* Death zone (originally the lethal zone), altitudes above a certain point where the amount of oxygen is insufficient to sustain human life for an extended time span
* Frigid zone, ...
. Magnetostratigraphy
Magnetostratigraphy is a geophysical correlation technique used to date sedimentary and volcanic sequences. The method works by collecting oriented samples at measured intervals throughout the section. The samples are analyzed to determine their '' ...
indicates that this zone dates to the Hauterivian
The Hauterivian is, in the geologic timescale, an age in the Early Cretaceous Epoch or a stage in the Lower Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 132.9 ± 2 Ma and 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago). The Hauterivian is preceded by the Va ...
epoch of the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period, approximately 128 million years ago. ''Makhaira'' originates from the ''S. versicolor'' zone, and it was found nearby ''Luskhan'' as well - north of Slantsevy Rudnik. Also from the ''S. versicolor'' zone is the cryptoclidid plesiosaurid '' Abyssosaurus'', which was found within the region of Chuvashia
Chuvashia (russian: Чувашия; cv, Чӑваш Ен), officially the Chuvash Republic — Chuvasia,; cv, Чӑваш Республики — Чӑваш Ен is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuv ...
near a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
of the Sura River
The Sura (russian: Сура́, cv, Сăр, ''Săr'') is a river in Russia, a north-flowing right tributary of the Volga. Its mouth on the Volga is about half way between Nizhny Novgorod and Kazan. It flows through Penza Oblast, Mordovia, Ulyano ...
(itself a tributary of the Volga). Additionally, vertebrae from a brachiosaurid
The Brachiosauridae ("arm lizards", from Greek ''brachion'' (βραχίων) = "arm" and ''sauros'' = "lizard") are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the le ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
have been found.
In terms of invertebrates, the ''S. versicolor'' zone is additionally characterized by the ammonites ''S. coronatiforme'', ''S. pavlovae'', ''S. intermedium'', and ''S. polivnense''; the bivalves
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
'' Inoceramus aucella'', '' Prochinnites substuderi'', '' Astarte porrecta'', and '' Thracia creditica''; and the belemnite
Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most ...
s '' Acroteuthis pseudopanderi'', '' Praeoxyteuthis jasikofiana'', '' Aulacoteuthis absolutiformis'', and ''A. speetonensis''. The gastropods
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. Ther ...
'' Ampullina sp.'', '' Avellana hauteriviensis'', '' Claviscala antiqua'', '' Cretadmete neglecta'', '' Eucyclus sp.'', '' Hudlestonella pusilla'', '' Khetella glasunovae'', '' Sulcoactaeon sp.'', '' Tornatellaea kabanovi'', '' Trilemma russiense'', and '' Turbinopsis multicostulata'' have also been found within the ''S. versicolor'' zone around Ulyanovsk.
See also
*List of plesiosaur genera
This list of plesiosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Plesiosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered inv ...
* Timeline of plesiosaur research
This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished duri ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q30088293 Sauropterygian genera Pliosaurids Early Cretaceous plesiosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2017