|
Coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek κόραξ, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In dinosaurs the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
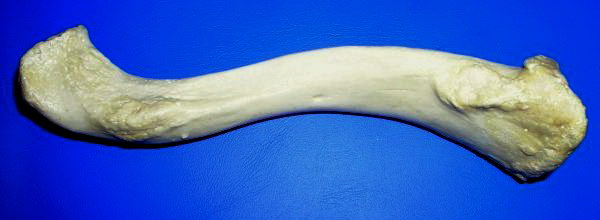
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medialward; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and lateralward. Anatomically it is divided into intervals of: base of coracoid process, angle of coracoid process, shaft and the apex of the coracoid process. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it house underneath it the subcoracoid space. The '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medialward; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and lateralward. Anatomically it is divided into intervals of: base of coracoid process, angle of coracoid process, shaft and the apex of the coracoid process. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it house underneath it the subcoracoid space. The '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species (such as the dog and the horse) have only the scapula. The pectoral girdles are to the upper limbs as the pelvic girdle is to the lower limbs; the girdles are the parts of the appendicular skeleton that anchor the appendages to the axial skeleton. In humans, the only true anatomical joints between the shoulder girdle and the axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. No anatomical joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection or physiological joint between the two permits great mobility of the shoulder girdle compared to the compact pelvic girdle; because the upper limb is not usually involved in weight bearing, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes the forearm and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out ( flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapulocoracoid
The scapulocoracoid is the unit of the pectoral girdle that contains the coracoid and scapula. The coracoid itself is a beak-shaped bone that is commonly found in most vertebrates with a few exceptions. The scapula is commonly known as the ''shoulder blade''. The humerus is linked to the body via the scapula, and the clavicle is connected to the sternum via the scapula as well. Theria Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes. ...n mammals lack a scapulocoracoid. References * Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution by Kenneth V. Kardong. Page 325. Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods ( last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals ( Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, jaws, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and other body parts, compared to the more common mammalian types. In addition, they lay eggs rather than bearing live young, but, like all mammals, the female monotremes nurse their young with milk. Monotremes have been considered members of Australosphenida, a clade that contains extinct mammals from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Madagascar, South America, and Australia, though this is disputed. The only surviving examples of monotremes are all indigenous to Australia and New Guinea, although there is evidence that they were once more widespread, as '' Monotrematum'' is known from the Paleocene of South America. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and four species of echidnas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theria
Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes. Characteristics Therian mammals give birth (''see viviparity'') to live young without a shelled egg. This is possible thanks to key proteins called syncytins which allow exchanges between the mother and its offspring through a placenta, even rudimental ones such as in marsupials. Genetic studies have suggested a viral origin of syncytins through the endogenization process. The marsupials and the placental mammals evolved from a common therian ancestor that gave live birth by suppressing the mother's immune system. While the marsupials continued to give birth to an underdeveloped fetus after a short pregnancy, the ancestors of placental mammals gradually evolved a prolonged pregnancy. Therian mammals no longer have the coracoid bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)