, house =
Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
, father =
Louis XIII
, mother =
Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place =
Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (Nati ...
,
Saint-Germain-en-Laye,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, death_date =
, death_place =
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
,
Versailles, France
, burial_date = 9 September 1715
, burial_place =
Basilica of Saint-Denis
, religion =
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(
Gallican Rite)
, signature = Louis XIV Signature.svg
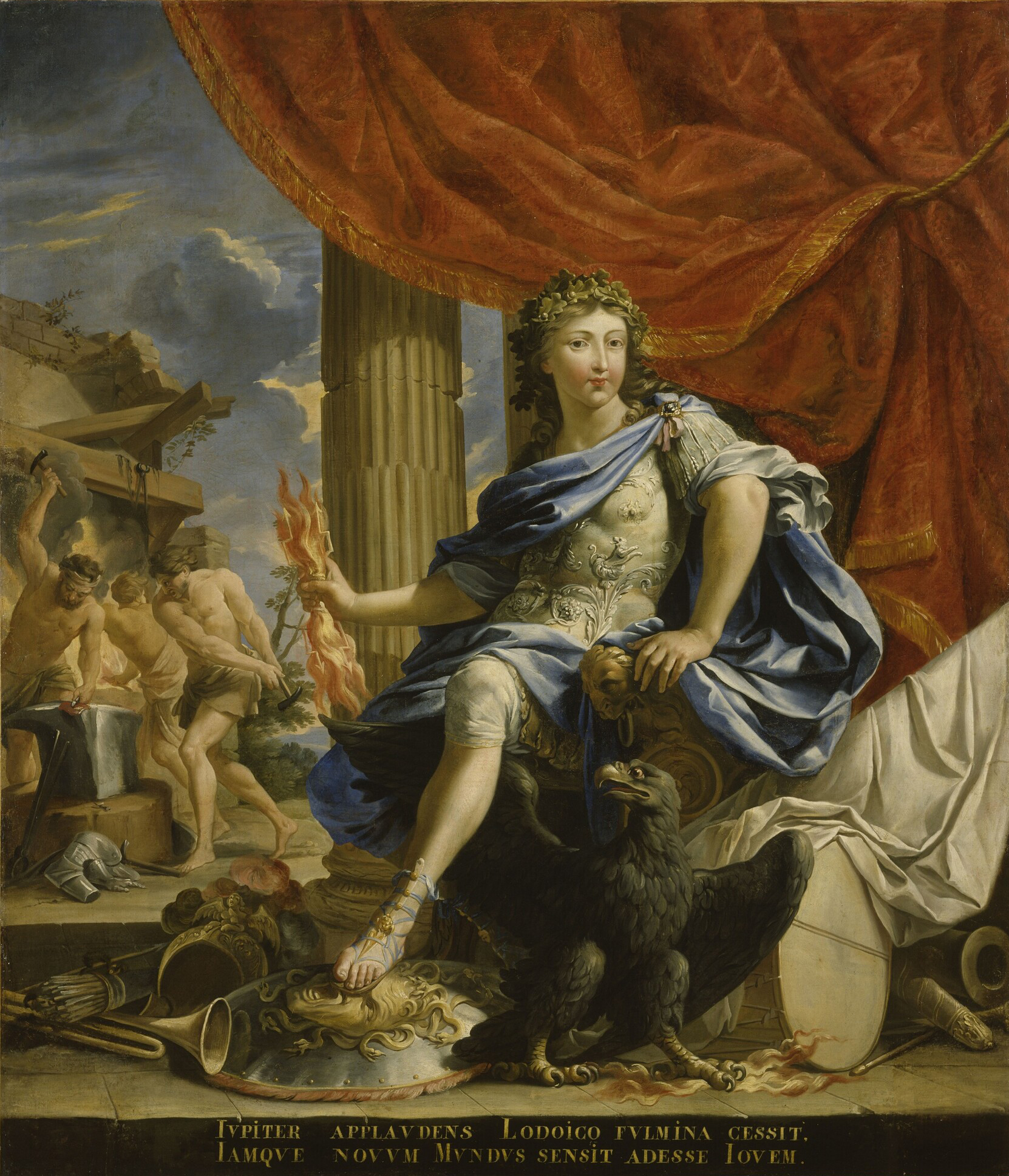
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was
King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the first ...
from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the
longest of any sovereign in history whose date is verifiable. Although Louis XIV's France was emblematic of the
age of absolutism in Europe, the King surrounded himself with a variety of significant political, military, and cultural figures, such as
Bossuet Bossuet is a French surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Jacques-Bénigne Bossuet (1627–1704), French bishop and theologian, uncle of Louis
* Louis Bossuet (1663–1742), French parliamentarian, nephew of Jacques-Bénigne
See als ...
,
Colbert,
Le Brun,
Le Nôtre,
Lully,
Mazarin,
Molière,
Racine,
Turenne, and
Vauban.
Louis began his personal rule of France in 1661, after the death of his chief minister, the
Cardinal Mazarin.
An adherent of the concept of the
divine right of kings
In European Christianity, the divine right of kings, divine right, or God's mandation is a political and religious doctrine of political legitimacy of a monarchy. It stems from a specific metaphysical framework in which a monarch is, before b ...
, Louis continued his predecessors' work of creating a
centralised state
Centralisation or centralization (see spelling differences) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning and decision-making, framing strategy and policies become concentrated within a partic ...
governed from the capital. He sought to eliminate the remnants of
feudalism persisting in parts of France; by compelling many members of the
nobility to inhabit his lavish
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
, he succeeded in pacifying the aristocracy, many members of which had participated in
the Fronde during his minority. By these means he became one of the most powerful French monarchs and consolidated a system of
absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constituti ...
in France that endured until the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
. Louis also enforced uniformity of religion under the
Gallican Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. His
revocation of the
Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aim ...
abolished the rights of the
Huguenot Protestant minority and subjected them to a wave of
dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant households ...
, effectively forcing Huguenots to emigrate or convert, as well as virtually destroying the French Protestant community.
During Louis's long reign, France emerged as the leading European power and regularly asserted its military strength. A
conflict with Spain marked his entire childhood, while during his reign, the kingdom took part in three major continental conflicts, each against powerful foreign alliances: the
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
, the
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
, and the
War of the Spanish Succession. In addition, France also contested shorter wars, such as the
War of Devolution and the
War of the Reunions. Warfare defined Louis's foreign policy and his personality shaped his approach. Impelled by "a mix of commerce, revenge, and pique", he sensed that war was the ideal way to enhance his glory. In peacetime, he concentrated on preparing for the next war. He taught his diplomats that their job was to create tactical and strategic advantages for the French military. Upon his death in 1715, Louis XIV left his great-grandson and successor,
Louis XV, a powerful kingdom, albeit in major debt after the thirteen-year-long War of the Spanish Succession.
Significant achievements during his reign which would go on to have a wide influence on the
early modern period well into the
Industrial Revolution and until today, include the construction of the
Canal du Midi
The Canal du Midi (; ) is a long canal in Southern France (french: le Midi). Originally named the ''Canal royal en Languedoc'' (Royal Canal in Languedoc) and renamed by French revolutionaries to ''Canal du Midi'' in 1789, the canal is considere ...
, the patronage of
artists, and the founding of the
French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
.
Early years


Louis XIV was born on 5 September 1638 in the
Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (Nati ...
, to
Louis XIII and
Anne of Austria. He was named Louis Dieudonné (Louis the God-given) and bore the traditional title of French
heirs apparent: ''
Dauphin''. At the time of his birth, his parents had been married for 23 years. His mother had experienced four
stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term ...
s between 1619 and 1631. Leading contemporaries thus regarded him as a divine gift and his birth a miracle of God.
Louis's relationship with his mother was uncommonly affectionate for the time. Contemporaries and eyewitnesses claimed that the Queen would spend all her time with Louis. Both were greatly interested in food and theatre, and it is highly likely that Louis developed these interests through his close relationship with his mother. This long-lasting and loving relationship can be evidenced by excerpts in Louis' journal entries, such as:
"Nature was responsible for the first knots which tied me to my mother. But attachments formed later by shared qualities of the spirit are far more difficult to break than those formed merely by blood."
It was his mother who gave Louis his belief in the absolute and divine power of his monarchical rule.
During his childhood, he was taken care of by the governesses
Françoise de Lansac and
Marie-Catherine de Senecey. In 1646,
Nicolas V de Villeroy became the young king's tutor. Louis XIV became friends with Villeroy's young children, particularly
François de Villeroy, and divided his time between the
Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal ...
and the nearby Hotel de Villeroy.
Minority and the ''Fronde''
Accession

Sensing imminent death, Louis XIII decided to put his affairs in order in the spring of 1643, when Louis XIV was four years old. In defiance of custom, which would have made Queen Anne the sole
regent of France, the king decreed that a regency council would rule on his son's behalf. His lack of faith in Queen Anne's political abilities was his primary rationale. He did, however, make the concession of appointing her head of the council.
Louis XIII died on 14 May 1643, and on 18 May, Queen Anne had her husband's will annulled by the ''
Parlement de Paris'' (a judicial body comprising mostly nobles and high clergymen). This action abolished the regency council and made Anne the sole Regent of France. Anne exiled some of her husband's ministers (Chavigny, Bouthilier), and she nominated Brienne as her minister of foreign affairs.
Anne kept the direction of religious policy strongly in her hand until 1661; her most important political decisions were to nominate
Cardinal Mazarin as her chief minister and the continuation of her late husband's and
Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the ...
's policy, despite their persecution of her, for the sake of her son. Anne wanted to give her son absolute authority and a victorious kingdom. Her rationales for choosing Mazarin were mainly his ability and his total dependence on her, at least until 1653 when she was no longer regent. Anne protected Mazarin by arresting and exiling her followers who conspired against him in 1643: the
Duke of Beaufort
Duke of Beaufort (), a title in the Peerage of England, was created by Charles II in 1682 for Henry Somerset, 3rd Marquess of Worcester, a descendant of Charles Somerset, 1st Earl of Worcester, legitimised son of Henry Beaufort, 3rd Duke of So ...
and
Marie de Rohan. She left the direction of the daily administration of policy to Cardinal Mazarin.
The best example of Anne's statesmanship and the partial change in her heart towards her native Spain is seen in her keeping of one of Richelieu's men, the Chancellor of France
Pierre Séguier, in his post. Séguier was the person who had interrogated Anne in 1637, treating her like a "common criminal" as she described her treatment following the discovery that she was giving military secrets and information to Spain. Anne was virtually under house arrest for a number of years during her husband's rule. By keeping him in his post, Anne was giving a sign that the interests of France and her son Louis were the guiding spirit of all her political and legal actions. Though not necessarily opposed to Spain, she sought to end the war with a French victory, in order to establish a lasting peace between the Catholic nations.
The Queen also gave a partial Catholic orientation to French foreign policy. This was felt by the Netherlands, France's Protestant ally, which negotiated a separate peace with Spain in 1648.
In 1648, Anne and Mazarin successfully negotiated the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
, which ended the
Thirty Years' War. Its terms ensured
Dutch independence
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
from
Spain, awarded some autonomy to the various German princes of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and granted Sweden seats on the
Imperial Diet and territories to control the mouths of the
Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows thr ...
,
Elbe, and
Weser rivers. France, however, profited most from the settlement. Austria, ruled by the
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
Emperor
Ferdinand III, ceded all Habsburg lands and claims in
Alsace to France and acknowledged her ''de facto'' sovereignty over the
Three Bishoprics of
Metz,
Verdun, and
Toul. Moreover, eager to emancipate themselves from Habsburg domination, petty German states sought French protection. This anticipated the formation of the 1658
League of the Rhine, leading to the further diminution of Imperial power.
Early acts
As the Thirty Years' War came to an end, a civil war known as
the Fronde (after the slings used to smash windows) erupted in France. It effectively checked France's ability to exploit the Peace of Westphalia. Anne and Mazarin had largely pursued the policies of
Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the ...
, augmenting the Crown's power at the expense of the nobility and the '. Anne interfered much more in internal policy than foreign affairs; she was a very proud queen who insisted on the divine rights of the King of France.

All this led her to advocate a forceful policy in all matters relating to the King's authority, in a manner that was much more radical than the one proposed by Mazarin. The Cardinal depended totally on Anne's support and had to use all his influence on the Queen to temper some of her radical actions. Anne imprisoned any aristocrat or member of parliament who challenged her will; her main aim was to transfer to her son an absolute authority in the matters of finance and justice. One of the leaders of the Parlement of Paris, whom she had jailed, died in prison.
The ', political heirs of the disaffected feudal aristocracy, sought to protect their traditional feudal privileges from the increasingly centralized royal government. Furthermore, they believed their traditional influence and authority was being usurped by the recently ennobled bureaucrats (the ', or "nobility of the robe"), who administered the kingdom and on whom the monarchy increasingly began to rely. This belief intensified the nobles' resentment.
In 1648, Anne and Mazarin attempted to tax members of the '. The members refused to comply and ordered all of the king's earlier financial edicts burned. Buoyed by the victory of (later known as ') at the
Battle of Lens, Mazarin, on Queen Anne's insistence, arrested certain members in a show of force. The most important arrest, from Anne's point of view, concerned
Pierre Broussel, one of the most important leaders in the '.

People in France were complaining about the expansion of royal authority, the high rate of taxation, and the reduction of the authority of the Parlement de Paris and other regional representative entities. Paris erupted in rioting as a result, and Anne was forced, under intense pressure, to free Broussel. Moreover, on the night of 9–10 February 1651, when Louis was twelve, a mob of angry Parisians broke into the royal palace and demanded to see their king. Led into the royal bed-chamber, they gazed upon Louis, who was feigning sleep, were appeased, and then quietly departed. The threat to the royal family prompted Anne to flee Paris with the king and his courtiers.
Shortly thereafter, the conclusion of the
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
allowed Condé's army to return to aid Louis and his court. Condé's family was close to Anne at that time, and he agreed to help her attempt to restore the king's authority. The queen's army, headed by Condé, attacked the rebels in Paris; the rebels were under the political control of Anne's old friend
Marie de Rohan. Beaufort, who had escaped from the prison where Anne had incarcerated him five years before, was the military leader in Paris, under the nominal control of Conti. After a few battles, a political compromise was reached; the
Peace of Rueil was signed, and the court returned to Paris.
Unfortunately for Anne, her partial victory depended on Condé, who wanted to control the queen and destroy Mazarin's influence. It was Condé's sister who pushed him to turn against the queen. After striking a deal with her old friend Marie de Rohan, who was able to impose the nomination of as minister of justice, Anne arrested Condé, his brother
Armand de Bourbon, Prince of Conti, and the husband of their sister Anne Genevieve de Bourbon,
duchess of Longueville
Countess of Longueville
House of Orléans-Longueville, 1443–1505
Duchess of Longueville
House of Orléans-Longueville, 1505–1694
{, width=95% class="wikitable"
!width = "8%" , Picture
!width = "10%" , Name
!width = "9%" , Fat ...
. This situation did not last long, and Mazarin's unpopularity led to the creation of a coalition headed mainly by Marie de Rohan and the duchess of Longueville. This aristocratic coalition was strong enough to liberate the princes, exile Mazarin, and impose a condition of virtual house arrest on Queen Anne.
All these events were witnessed by Louis and largely explained his later distrust of Paris and the higher aristocracy. "In one sense, Louis' childhood came to an end with the outbreak of the Fronde. It was not only that life became insecure and unpleasant – a fate meted out to many children in all ages – but that Louis had to be taken into the confidence of his mother and Mazarin on political and military matters of which he could have no deep understanding". "The family home became at times a near-prison when Paris had to be abandoned, not in carefree outings to other chateaux but in humiliating flights". The royal family was driven out of Paris twice in this manner, and at one point Louis XIV and Anne were held under virtual arrest in the royal palace in Paris. The Fronde years planted in Louis a hatred of Paris and a consequent determination to move out of the ancient capital as soon as possible, never to return.
Just as the first ' (the ' of 1648–1649) ended, a second one (the ' of 1650–1653) began. Unlike that which preceded it, tales of sordid intrigue and half-hearted warfare characterized this second phase of upper-class insurrection. To the aristocracy, this rebellion represented a protest for the reversal of their political demotion from
vassals to
courtiers. It was headed by the highest-ranking French nobles, among them Louis' uncle
Gaston, Duke of Orléans
'' Monsieur'' Gaston, Duke of Orléans (Gaston Jean Baptiste; 24 April 1608 – 2 February 1660), was the third son of King Henry IV of France and his second wife, Marie de' Medici. As a son of the king, he was born a '' Fils de France''. He lat ...
and first cousin
Anne Marie Louise d'Orléans, Duchess of Montpensier, known as ';
Princes of the Blood such as Condé, his brother
Armand de Bourbon, Prince of Conti, and their sister the
Duchess of Longueville
Countess of Longueville
House of Orléans-Longueville, 1443–1505
Duchess of Longueville
House of Orléans-Longueville, 1505–1694
{, width=95% class="wikitable"
!width = "8%" , Picture
!width = "10%" , Name
!width = "9%" , Fat ...
; dukes of
legitimised royal descent, such as
Henri, Duke of Longueville, and
François, Duke of Beaufort; so-called "
foreign princes" such as
Frédéric Maurice, Duke of Bouillon, his brother
Marshal
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
Turenne, and
Marie de Rohan, Duchess of Chevreuse; and
scions of France's oldest families, such as
François de La Rochefoucauld François de La Rochefoucauld may refer to:
* François III de La Rochefoucauld (1521–1572), French courtier and soldier
* François de La Rochefoucauld (writer) (1613–1680), French author
* François de La Rochefoucauld (cardinal) (1558–164 ...
.
Queen Anne played the most important role in defeating the Fronde because she wanted to transfer absolute authority to her son. In addition, most of the princes refused to deal with Mazarin, who went into exile for a number of years. The ' claimed to act on Louis' behalf, and in his real interest, against his mother and Mazarin.
Queen Anne had a very close relationship with the Cardinal, and many observers believed that Mazarin became Louis XIV's stepfather by a secret marriage to Queen Anne. However, Louis' coming-of-age and subsequent
coronation deprived them of the ' pretext for revolt. The ' thus gradually lost steam and ended in 1653, when Mazarin returned triumphantly from exile. From that time until his death, Mazarin was in charge of foreign and financial policy without the daily supervision of Anne, who was no longer regent.
During this period, Louis fell in love with Mazarin's niece
Marie Mancini, but Anne and Mazarin ended the king's infatuation by sending Mancini away from court to be married in Italy. While Mazarin might have been tempted for a short period of time to marry his niece to the King of France, Queen Anne was absolutely against this; she wanted to marry her son to the daughter of her brother,
Philip IV of Spain, for both dynastic and political reasons. Mazarin soon supported the Queen's position because he knew that her support for his power and his foreign policy depended on making peace with Spain from a strong position and on the Spanish marriage. Additionally, Mazarin's relations with Marie Mancini were not good, and he did not trust her to support his position. All of Louis' tears and his supplications to his mother did not make her change her mind. The Spanish marriage would be very important both for its role in ending the war between France and Spain, because many of the claims and objectives of Louis' foreign policy for the next 50 years would be based upon this marriage, and because it was through this marriage that the Spanish throne would ultimately be delivered to the House of Bourbon (which holds it to this day).
Personal reign and reforms
Coming of age and early reforms

Louis XIV was declared to have reached the age of majority on 7 September 1651. On the death of Mazarin, in March 1661, Louis assumed personal control of the reins of government and astonished his court by declaring that he would rule without a chief minister: "Up to this moment I have been pleased to entrust the government of my affairs to the late Cardinal. It is now time that I govern them myself. You
e was talking to the secretaries and ministers of state
E, or e, is the fifth letter and the second vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''e'' (pronounced ); plura ...
will assist me with your counsels when I ask for them. I request and order you to seal no orders except by my command . . . I order you not to sign anything, not even a passport . . . without my command; to render account to me personally each day and to favor no one". Louis was able to capitalize on the widespread public yearning for law and order, that resulted from prolonged foreign wars and domestic civil strife, to further consolidate central political authority and reform at the expense of the feudal aristocracy. Praising his ability to choose and encourage men of talent, the historian
Chateaubriand noted: "it is the voice of genius of all kinds which sounds from the tomb of Louis".
Louis began his personal reign with administrative and fiscal reforms. In 1661, the treasury verged on bankruptcy. To rectify the situation, Louis chose
Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the countr ...
as
Controller-General of Finances in 1665. However, Louis first had to neutralize
Nicolas Fouquet, the
Superintendent of Finances
The Superintendent of Finances (french: Surintendant des finances) was the name of the minister in charge of finances in France from 1561 to 1661. The position was abolished in 1661 with the downfall of Nicolas Fouquet, and a new position was cr ...
, in order to give Colbert a free hand. Although Fouquet's financial indiscretions were not very different from Mazarin's before him or Colbert's after him, his ambition was worrying to Louis. He had, for example, built an opulent château at
Vaux-le-Vicomte where he entertained Louis and his court ostentatiously, as if he were wealthier than the king himself. The court was left with the impression that the vast sums of money needed to support his lifestyle could only have been obtained through
embezzlement
Embezzlement is a crime that consists of withholding assets for the purpose of conversion of such assets, by one or more persons to whom the assets were entrusted, either to be held or to be used for specific purposes. Embezzlement is a type ...
of government funds.
Fouquet appeared eager to succeed Mazarin and Richelieu in assuming power, and he indiscreetly purchased and privately fortified the remote island of
Belle Île. These acts sealed his doom. Fouquet was charged with embezzlement. The ''Parlement'' found him guilty and sentenced him to exile. However, Louis altered the sentence to life imprisonment and abolished Fouquet's post.
With Fouquet dismissed, Colbert reduced the national debt through more efficient taxation. The principal taxes included the ''aides'' and ''douanes'' (both
customs duties
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
), the ''
gabelle'' (a tax on salt), and the ''
taille
The ''taille'' () was a direct land tax on the French peasantry and non-nobles in ''Ancien Régime'' France. The tax was imposed on each household and was based on how much land it held, and was directly paid to the state.
History
Originally ...
'' (a tax on land). The ''taille'' was reduced at first; financial officials were forced to keep regular accounts, auctioning certain taxes instead of selling them privately to a favoured few, revising inventories and removing unauthorized exemptions (for example, in 1661 only 10 per cent from the royal domain reached the King). Reform proved difficult because the ''taille'' was levied by officers of the Crown who had purchased their post at a high price: punishment of abuses necessarily lowered the value of the post. Nevertheless, excellent results were achieved: the deficit of 1661 turned into a surplus in 1666. The interest on the debt was reduced from 52 million to 24 million livres. The ''taille'' was reduced to 42 million in 1661 and 35 million in 1665; finally the revenue from indirect taxation progressed from 26 million to 55 million. The revenues of the royal domain were raised from 80,000 livres in 1661 to 5.5 million livres in 1671. In 1661, the receipts were equivalent to 26 million British pounds, of which 10 million reached the treasury. The expenditure was around 18 million pounds, leaving a deficit of 8 million. In 1667, the net receipts had risen to 20 million
pounds sterling, while expenditure had fallen to 11 million, leaving a surplus of 9 million pounds.
To support the reorganized and enlarged army, the panoply of Versailles, and the growing civil administration, the king needed a good deal of money. Finance had always been the weak spot in the French monarchy: methods of collecting taxes were costly and inefficient; direct taxes passed through the hands of many intermediate officials; and indirect taxes were collected by private concessionaries, called tax farmers, who made a substantial profit. Consequently, the state always received far less than what the taxpayers actually paid.
The main weakness arose from an old bargain between the French crown and nobility: the king might raise taxes without consent if only he refrained from taxing the nobles. Only the "unprivileged" classes paid direct taxes, and this term came to mean the peasants only, since many bourgeois, in one way or another, obtained exemptions.
The system was outrageously unjust in throwing a heavy tax burden on the poor and helpless. Later, after 1700, the French ministers who were supported by Louis' secret wife Madame De Maintenon, were able to convince the king to change his fiscal policy. Louis was willing enough to tax the nobles but was unwilling to fall under their control, and only towards the close of his reign, under extreme stress of war, was he able, for the first time in French history, to impose direct taxes on the aristocratic elements of the population. This was a step toward equality before the law and toward sound public finance, but so many concessions and exemptions were won by nobles and bourgeois that the reform lost much of its value.
Louis and Colbert also had wide-ranging plans to bolster French commerce and trade. Colbert's
mercantilist administration established new industries and encouraged manufacturers and inventors, such as the
Lyon silk manufacturers and the
Gobelins manufactory
The Gobelins Manufactory () is a historic tapestry factory in Paris, France. It is located at 42 avenue des Gobelins, near Les Gobelins métro station in the 13th arrondissement of Paris. It was originally established on the site as a medieval ...
, a producer of tapestries. He invited manufacturers and artisans from all over Europe to France, such as
Murano
Murano is a series of islands linked by bridges in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy. It lies about north of Venice and measures about across with a population of just over 5,000 (2004 figures). It is famous for its glass making. It was on ...
glassmakers, Swedish ironworkers, and Dutch shipbuilders. In this way, he aimed to decrease foreign imports while increasing French exports, hence reducing the net outflow of precious metals from France.
Louis instituted reforms in military administration through
Michel le Tellier and the latter's son
François-Michel le Tellier, Marquis de Louvois. They helped to curb the independent spirit of the nobility, imposing order on them at court and in the army. Gone were the days when generals protracted war at the frontiers while bickering over precedence and ignoring orders from the capital and the larger politico-diplomatic picture. The old military aristocracy (the ''Noblesse d'épée'', or "nobility of the sword") ceased to have a monopoly over senior military positions and rank. Louvois, in particular, pledged to modernize the army and re-organize it into a professional, disciplined, well-trained force. He was devoted to the soldiers' material well-being and morale, and even tried to direct campaigns.
Relations with the major colonies

Legal matters did not escape Louis' attention, as is reflected in the numerous "
Great Ordinances" he enacted. Pre-revolutionary France was a patchwork of legal systems, with as many legal customs as there were provinces, and two co-existing legal traditions—
customary law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior that can be objectively verified within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law".
Customary law (also, consuetudina ...
in the north and
Roman civil law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Just ...
in the south. The ''Grande Ordonnance de Procédure Civile'' of 1667, also known as the ''Code Louis'', was a comprehensive legal code attempting a uniform regulation of
civil procedure throughout legally irregular France. Among other things, it prescribed baptismal, marriage and death records in the state's registers, not the church's, and it strictly regulated the right of the ''Parlements'' to remonstrate. The ''Code Louis'' played an important part in French legal history as the basis for the
Napoleonic code, from which many modern legal codes are, in turn, derived.
One of Louis' more infamous decrees was the ''Grande Ordonnance sur les Colonies'' of 1685, also known as the ''
Code Noir'' ("black code"). Although it sanctioned slavery, it attempted to humanise the practice by prohibiting the separation of families. Additionally, in the colonies, only Roman Catholics could own slaves, and these had to be baptised.
Louis ruled through a number of councils:
* Conseil d'en haut ("High Council", concerning the most important matters of state)—composed of the king, the crown prince, the controller-general of finances, and the secretaries of state in charge of various departments. The members of that council were called ministers of state.
* Conseil des dépêches ("Council of Messages", concerning notices and administrative reports from the provinces).
* Conseil de Conscience ("Council of Conscience", concerning religious affairs and episcopal appointments).
* Conseil royal des finances ("Royal Council of Finances") who was headed by the "chef du conseil des finances" (an honorary post in most cases)—this was one of the few posts in the council that was opened to the high aristocracy.
Early wars in the Low Countries
Spain


The death of his maternal uncle King
Philip IV of Spain, in 1665, precipitated the
War of Devolution. In 1660, Louis had married Philip IV's eldest daughter,
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). ...
, as one of the provisions of the 1659
Treaty of the Pyrenees. The marriage treaty specified that Maria Theresa was to renounce all claims to Spanish territory for herself and all her descendants. Mazarin and
Lionne, however, made the renunciation conditional on the full payment of a Spanish dowry of 500,000
écus. The dowry was never paid and would later play a part persuading his maternal first cousin
Charles II of Spain to leave his empire to Philip, Duke of Anjou (later
Philip V of Spain), the grandson of Louis XIV and Maria Theresa.
The War of Devolution did not focus on the payment of the dowry; rather, the lack of payment was what Louis XIV used as a pretext for nullifying Maria Theresa's renunciation of her claims, allowing the land to "devolve" to him. In
Brabant (the location of the land in dispute), children of first marriages traditionally were not disadvantaged by their parents' remarriages and still inherited property. Louis' wife was Philip IV's daughter by his first marriage, while the new king of Spain, Charles II, was his son by a subsequent marriage. Thus, Brabant allegedly "devolved" to Maria Theresa, giving France a justification to attack the
Spanish Netherlands.
Relations with the Dutch
During the
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
with
Spain, France supported the
Dutch Republic as part of a general policy of opposing Habsburg power.
Johan de Witt, Dutch
Grand Pensionary from 1653 to 1672, viewed them as crucial for Dutch security and against his domestic
Orangist opponents. Louis provided support in the 1665-1667
Second Anglo-Dutch War but used the opportunity to launch the
War of Devolution in 1667. This captured
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; frp, Franche-Comtât; also german: Freigrafschaft; es, Franco Condado; all ) is a cultural and historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of Doubs, ...
and much of the
Spanish Netherlands; French expansion in this area was a direct threat to Dutch economic interests.
The Dutch opened talks with
Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest surviving child of ...
on a common diplomatic front against France, leading to the
Triple Alliance Triple Alliance may refer to:
* Aztec Triple Alliance (1428–1521), Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan and in central Mexico
* Triple Alliance (1596), England, France, and the Dutch Republic to counter Spain
* Triple Alliance (1668), England, the ...
, between England, the Dutch and
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. The threat of an escalation and a secret treaty to divide Spanish possessions with
Emperor Leopold
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria An ...
, the other major claimant to the throne of Spain, led Louis to relinquish many of his gains in the 1668
Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle.
Louis placed little reliance on his agreement with
Leopold and as it was now clear French and Dutch aims were in direct conflict, he decided to first defeat the
Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
, then seize the Spanish Netherlands. This required breaking up the Triple Alliance; he paid Sweden to remain neutral and signed the 1670
Secret Treaty of Dover with Charles, an Anglo-French alliance against the Dutch Republic. In May 1672, France invaded the
Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
, supported by
Münster and the
Electorate of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (german: Kurfürstentum Köln), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (german: Kurköln, links=no), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. ...
.
Rapid French advance led to a coup that toppled
De Witt and brought
William III William III or William the Third may refer to:
Kings
* William III of Sicily (c. 1186–c. 1198)
* William III of England and Ireland or William III of Orange or William II of Scotland (1650–1702)
* William III of the Netherlands and Luxembourg ...
to power.
Leopold viewed French expansion into the Rhineland as an increasing threat, especially after their seizure of the strategic
Duchy of Lorraine in 1670. The prospect of Dutch defeat led Leopold to an alliance with
Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenz ...
on 23 June, followed by another with the Republic on 25th. Although Brandenburg was forced out of the war by the June 1673
Treaty of Vossem, in August an anti-French alliance was formed by the Dutch,
Spain, Emperor Leopold and the
Duke of Lorraine.
The French alliance was deeply unpopular in England, who made peace with the Dutch in the February 1674
Treaty of Westminster. However, French armies held significant advantages over their opponents; an undivided command, talented generals like
Turenne,
Condé and
Luxembourg and vastly superior logistics. Reforms introduced by
Louvois, the
Secretary of War, helped maintain large field armies that could be mobilised much more quickly, allowing them to mount offensives in early spring before their opponents were ready.
The French were forced to retreat from the Dutch Republic but these advantages allowed them to hold their ground in Alsace and the Spanish Netherlands while retaking Franche-Comté. By 1678, mutual exhaustion led to the
Treaty of Nijmegen, which was generally settled in France's favour and allowed Louis to intervene in the
Scanian War
The Scanian War ( da, Skånske Krig, , sv, Skånska kriget, german: Schonischer Krieg) was a part of the Northern Wars involving the union of Denmark–Norway, Brandenburg and Sweden. It was fought from 1675 to 1679 mainly on Scanian soil, ...
. Despite military defeat, his ally Sweden regained much of what they had lost under the 1679 treaties of
Saint-Germain-en-Laye,
Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissement ...
and
Lund
Lund (, , ) is a city in the southern Swedish provinces of Sweden, province of Scania, across the Øresund, Öresund strait from Copenhagen. The town had 91,940 inhabitants out of a municipal total of 121,510 . It is the seat of Lund Municipali ...
imposed on
Denmark-Norway and Brandenburg.
Louis was at the height of his power, but at the cost of uniting his opponents; this increased as he continued his expansion. In 1679, he dismissed his foreign minister
Simon Arnauld, marquis de Pomponne, because he was seen as having compromised too much with the allies. Louis maintained the strength of his army, but in his next series of territorial claims avoided using military force alone. Rather, he combined it with legal pretexts in his efforts to augment the boundaries of his kingdom. Contemporary treaties were intentionally phrased ambiguously. Louis established the
Chambers of Reunion to determine the full extent of his rights and obligations under those treaties.
Cities and territories, such as
Luxembourg and
Casale, were prized for their strategic positions on the frontier and access to important waterways. Louis also sought
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
, an important strategic crossing on the left bank of the Rhine and theretofore a Free Imperial City of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, annexing it and other territories in 1681. Although a part of Alsace, Strasbourg was not part of Habsburg-ruled Alsace and was thus not ceded to France in the Peace of Westphalia.
Following these annexations, Spain declared war, precipitating the
War of the Reunions. However, the Spanish were rapidly defeated because the Emperor (distracted by the
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War (german: Großer Türkenkrieg), also called the Wars of the Holy League ( tr, Kutsal İttifak Savaşları), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Pola ...
) abandoned them, and the Dutch only supported them minimally. By the
Truce of Ratisbon, in 1684, Spain was forced to acquiesce in the French occupation of most of the conquered territories, for 20 years.
Louis' policy of the ''Réunions'' may have raised France to its greatest size and power during his reign, but it alienated much of Europe. This poor public opinion was compounded by French actions off the Barbary Coast and at Genoa. First, Louis had
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
and
Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
*Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in t ...
, two Barbary pirate strongholds, bombarded to obtain a favourable treaty and the liberation of Christian slaves. Next, in 1684, a
punitive mission was launched against
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of t ...
in retaliation for its support for Spain in previous wars. Although the Genoese submitted, and the
Doge led an official mission of apology to Versailles, France gained a reputation for brutality and arrogance. European apprehension at growing French might and the realisation of the extent of the
dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant households ...
' effect (discussed below) led many states to abandon their alliances with France. Accordingly, by the late 1680s, France became increasingly isolated in Europe.
Non-European relations and the colonies
 French colonies
French colonies multiplied in Africa, the Americas, and Asia during Louis' reign, and French explorers made important discoveries in North America. In 1673,
Louis Jolliet and
Jacques Marquette discovered the
Mississippi River. In 1682,
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, the Mississippi River, ...
, followed the
Mississippi to the
Gulf of Mexico and claimed the vast Mississippi basin in Louis' name, calling it ''
Louisiane
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is border ...
''. French trading posts were also established in India, at
Chandernagore and
Pondicherry, and in the Indian Ocean at
Île Bourbon. Throughout these regions Louis and Colbert embarked on an extensive program of architecture and urbanism meant to reflect the styles of Versailles and Paris and the 'gloire' of the realm.

Meanwhile, diplomatic relations were initiated with distant countries. In 1669,
Suleiman Aga
Müteferrika Süleyman Ağa, known as Suleiman Aga and Soleiman Agha in France, was an Ottoman Empire ambassador to the French king Louis XIV in 1669. Suleiman visited Versailles, but only wore a simple wool coat and refused to bow to Louis XIV, ...
led an
Ottoman embassy to revive the old
Franco-Ottoman alliance. Then, in 1682, after the reception of the Moroccan embassy of
Mohammed Tenim in France,
Moulay Ismail, Sultan of Morocco, allowed French consular and commercial establishments in his country. In 1699, Louis once again received a Moroccan ambassador,
Abdallah bin Aisha, and in 1715, he received a
Persian embassy led by
Mohammad Reza Beg
Mohammad Reza Beg (Persian: محمدرضا بیگ, in French-language sources; ''Méhémet Riza Beg''), was the Safavid mayor (''kalantar'') of Erivan (Iravan), and the ambassador to France during the reign of king Sultan Husayn (1694-1722). He l ...
.
From farther afield, Siam dispatched an embassy in 1684, reciprocated by the French magnificently the next year under
Alexandre, Chevalier de Chaumont. This, in turn, was succeeded by another Siamese embassy under
Kosa Pan, superbly received at Versailles in 1686. Louis then sent another embassy in 1687, under
Simon de la Loubère, and French influence grew at the Siamese court, which granted
Mergui as a naval base to France. However, the death of
Narai, King of Ayutthaya, the execution of his pro-French minister
Constantine Phaulkon, and the
Siege of Bangkok in 1688 ended this era of French influence.
France also attempted to participate actively in
Jesuit missions to China. To break the Portuguese dominance there, Louis sent Jesuit missionaries to the court of the
Kangxi Emperor in 1685:
Jean de Fontaney,
Joachim Bouvet,
Jean-François Gerbillon,
Louis Le Comte, and
Claude de Visdelou
Claude de Visdelou (12 August 1656 – 11 November 1737) was a French Jesuit missionary.
Life
De Visdelou was born at the Château de Bienassis, Erquy, Brittany. He entered the Society of Jesus on 5 September 1673, and was one of the missionari ...
. Louis also received a Chinese Jesuit,
Michael Shen Fu-Tsung, at Versailles in 1684. Furthermore, Louis' librarian and translator
Arcadio Huang was Chinese.
Height of power
Centralisation of power
By the early 1680s, Louis had greatly augmented French influence in the world. Domestically, he successfully increased the influence of the crown and its authority over the church and aristocracy, thus consolidating absolute monarchy in France.
Louis initially supported traditional
Gallicanism, which limited
papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
authority in France, and convened an
Assembly of the French clergy in November 1681. Before its dissolution eight months later, the Assembly had accepted the
Declaration of the Clergy of France, which increased royal authority at the expense of papal power. Without royal approval, bishops could not leave France, and appeals could not be made to the pope. Additionally, government officials could not be excommunicated for acts committed in pursuance of their duties. Although the king could not make ecclesiastical law, all papal regulations without royal assent were invalid in France. Unsurprisingly, the Pope repudiated the Declaration.
[
] By attaching nobles to his court at Versailles, Louis achieved increased control over the French aristocracy. According to historian Philip Mansel, the king turned the palace into:
:an irresistible combination of marriage market, employment agency and entertainment capital of aristocratic Europe, boasting the best theatre, opera, music, gambling, sex and (most important) hunting.
Apartments were built to house those willing to pay court to the king.
By attaching nobles to his court at Versailles, Louis achieved increased control over the French aristocracy. According to historian Philip Mansel, the king turned the palace into:
:an irresistible combination of marriage market, employment agency and entertainment capital of aristocratic Europe, boasting the best theatre, opera, music, gambling, sex and (most important) hunting.
Apartments were built to house those willing to pay court to the king.[ For this purpose, an elaborate court ritual was created wherein the king became the centre of attention and was observed throughout the day by the public. With his excellent memory, Louis could then see who attended him at court and who was absent, facilitating the subsequent distribution of favours and positions. Another tool Louis used to control his nobility was censorship, which often involved the opening of letters to discern their author's opinion of the government and king.][ Moreover, by entertaining, impressing, and domesticating them with extravagant luxury and other distractions, Louis not only cultivated public opinion of him, but he also ensured the aristocracy remained under his scrutiny.
Louis's extravagance at Versailles extended far beyond the scope of elaborate court rituals. He took delivery of an African elephant as a gift from the king of Portugal. He encouraged leading nobles to live at Versailles. This, along with the prohibition of private armies, prevented them from passing time on their own estates and in their regional power bases, from which they historically waged local wars and plotted resistance to royal authority. Louis thus compelled and seduced the old military aristocracy (the "nobility of the sword") into becoming his ceremonial courtiers, further weakening their power. In their place, he raised commoners or the more recently ennobled bureaucratic aristocracy (the "nobility of the robe"). He judged that royal authority thrived more surely by filling high executive and administrative positions with these men because they could be more easily dismissed than nobles of ancient lineage and entrenched influence. It is believed that Louis's policies were rooted in his experiences during the ''Fronde'', when men of high birth readily took up the rebel cause against their king, who was actually the kinsman of some. This victory over the nobility may thus have ensured the end of major civil wars in France until the French Revolution about a century later.
]
France as the pivot of warfare
Under Louis, France was the leading European power, and most wars pivoted around its aggressiveness. No European state exceeded it in population, and no one could match its wealth, central location, and very strong professional army. It had largely avoided the devastation of the Thirty Years' War. Its weaknesses included an inefficient financial system that was hard-pressed to pay for its military adventures, and the tendency of most other powers to gang up against it.
During Louis's reign, France fought three major wars: the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
, the War of the League of Augsburg
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
, and the War of the Spanish Succession. There were also two lesser conflicts: the War of Devolution and the War of the Reunions. The wars were very expensive but defined Louis XIV's foreign policy, and his personality shaped his approach. Impelled "by a mix of commerce, revenge, and pique," Louis sensed that war was the ideal way to enhance his glory. In peacetime he concentrated on preparing for the next war. He taught his diplomats that their job was to create tactical and strategic advantages for the French military. By 1695, France retained much of its dominance but had lost control of the seas to England and Holland, and most countries, both Protestant and Catholic, were in alliance against it. Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban
Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Seigneur de Vauban, later Marquis de Vauban (baptised 15 May 163330 March 1707), commonly referred to as ''Vauban'' (), was a French military engineer who worked under Louis XIV. He is generally considered the ...
, France's leading military strategist, warned Louis in 1689 that a hostile "Alliance" was too powerful at sea. He recommended that France fight back by licensing French merchants ships to privateer and seize enemy merchant ships while avoiding its navies:
:France has its declared enemies Germany and all the states that it embraces; Spain with all its dependencies in Europe, Asia, Africa and America; the Duke of Savoy n Italy
N, or n, is the fourteenth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet# ...
England, Scotland, Ireland, and all their colonies in the East and West Indies; and Holland with all its possessions in the four corners of the world where it has great establishments. France has ... undeclared enemies, indirectly hostile, hostile, and envious of its greatness, Denmark, Sweden, Poland, Portugal, Venice, Genoa, and part of the Swiss Confederation, all of which states secretly aid France's enemies by the troops that they hire to them, the money they lend them and by protecting and covering their trade.
Vauban was pessimistic about France's so-called friends and allies:
:For lukewarm, useless, or impotent friends, France has the Pope, who is indifferent; the King of England ames II
Ames may refer to:
Places United States
* Ames, Arkansas, a place in Arkansas
* Ames, Colorado
* Ames, Illinois
* Ames, Indiana
* Ames, Iowa, the most populous city bearing this name
* Ames, Kansas
* Ames, Nebraska
* Ames, New York
* Ames, Oklah ...
expelled from his country; the Grand Duke of Tuscany; the Dukes of Mantua, Modena, and Parma ll in Italy
Ll/ll is a digraph that occurs in several languages
English
In English, often represents the same sound as single : . The doubling is used to indicate that the preceding vowel is (historically) short, or that the "l" sound is to be extended ...
and the other faction of the Swiss. Some of these are sunk in the softness that comes of years of peace, the others are cool in their affections....The English and Dutch are the main pillars of the Alliance; they support it by making war against us in concert with the other powers, and they keep it going by means of the money that they pay every year to... Allies.... We must therefore fall back on privateering as the method of conducting war which is most feasible, simple, cheap, and safe, and which will cost least to the state, the more so since any losses will not be felt by the King, who risks virtually nothing....It will enrich the country, train many good officers for the King, and in a short time force his enemies to sue for peace.
Edict of Fontainebleau
 Louis decided to persecute Protestants and revoke the 1598
Louis decided to persecute Protestants and revoke the 1598 Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aim ...
, which awarded Huguenots political and religious freedom. He saw the persistence of Protestantism as a disgraceful reminder of royal powerlessness. After all, the Edict was the pragmatic concession of his grandfather Henry IV to end the longstanding French Wars of Religion. An additional factor in Louis' thinking was the prevailing contemporary European principle to assure socio-political stability, '' cuius regio, eius religio'' ("whose realm, his religion"), the idea that the religion of the ruler should be the religion of the realm (as originally confirmed in central Europe in the Peace of Augsburg of 1555).
Responding to petitions, Louis initially excluded Protestants from office, constrained the meeting of synods
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word mea ...
, closed churches outside of Edict-stipulated areas, banned Protestant outdoor preachers, and prohibited domestic Protestant migration. He also disallowed Protestant-Catholic intermarriages to which third parties objected, encouraged missions to the Protestants, and rewarded converts to Catholicism. This discrimination did not encounter much Protestant resistance, and a steady conversion of Protestants occurred, especially among the noble elites.
In 1681, Louis dramatically increased his persecution of Protestants. The principle of ''cuius regio, eius religio'' generally had also meant that subjects who refused to convert could emigrate, but Louis banned emigration and effectively insisted that all Protestants must be converted. Secondly, following the proposal of René de Marillac and the Marquis of Louvois, he began quartering dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat w ...
s in Protestant homes. Although this was within his legal rights, the ''dragonnades'' inflicted severe financial strain on Protestants and atrocious abuse. Between 300,000 and 400,000 Huguenots converted, as this entailed financial rewards and exemption from the ''dragonnades
The ''Dragonnades'' were a French government policy instituted by King Louis XIV in 1681 to intimidate Huguenot (Protestant) families into converting to Catholicism. This involved the billeting of ill-disciplined dragoons in Protestant households ...
''.
 On 15 October 1685, Louis issued the
On 15 October 1685, Louis issued the Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion witho ...
, which cited the redundancy of privileges for Protestants given their scarcity after the extensive conversions. The Edict of Fontainebleau revoked the Edict of Nantes and repealed all the privileges that arose therefrom.[ By his edict, Louis no longer tolerated the existence of Protestant groups, pastors, or churches in France. No further churches were to be constructed, and those already existing were to be demolished. Pastors could choose either exile or secular life. Those Protestants who had resisted conversion were now to be baptised forcibly into the established church.
Historians have debated Louis' reasons for issuing the Edict of Fontainebleau. He may have been seeking to placate ]Pope Innocent XI
Pope Innocent XI ( la, Innocentius XI; it, Innocenzo XI; 16 May 1611 – 12 August 1689), born Benedetto Odescalchi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 September 1676 to his death on August 12, 1689.
Poli ...
, with whom relations were tense and whose aid was necessary to determine the outcome of a succession crisis in the Electorate of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (german: Kurfürstentum Köln), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (german: Kurköln, links=no), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. ...
. He may also have acted to upstage Emperor Leopold I and regain international prestige after the latter defeated the Turks without Louis' help. Otherwise, he may simply have desired to end the remaining divisions in French society dating to the Wars of Religion by fulfilling his coronation oath to eradicate heresy.
Many historians have condemned the Edict of Fontainebleau as gravely harmful to France.Camisard
Camisards were Huguenots (French Protestants) of the rugged and isolated Cévennes region and the neighbouring Vaunage in southern France. In the early 1700s, they raised a resistance against the persecutions which followed Louis XIV's Revocation ...
s of south-central France at the end of his reign, Louis may have helped ensure that his successor would experience fewer instances of the religion-based disturbances that had plagued his forebears. French society would sufficiently change by the time of his descendant, Louis XVI, to welcome tolerance in the form of the 1787 Edict of Versailles
The Edict of Versailles, also known as the Edict of Tolerance, was an official act that gave non-Catholics in France the access to civil rights formerly denied to them, which included the right to contract marriages without having to convert to t ...
, also known as the Edict of Tolerance
An edict of toleration is a declaration, made by a government or ruler, and states that members of a given religion will not be persecuted for engaging in their religious practices and traditions. The edict implies tacit acceptance of the religio ...
. This restored to non-Catholics their civil rights and the freedom to worship openly. With the advent of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
in 1789, Protestants were granted equal rights with their Roman Catholic counterparts.
Nine Years' War
Causes and conduct of the war
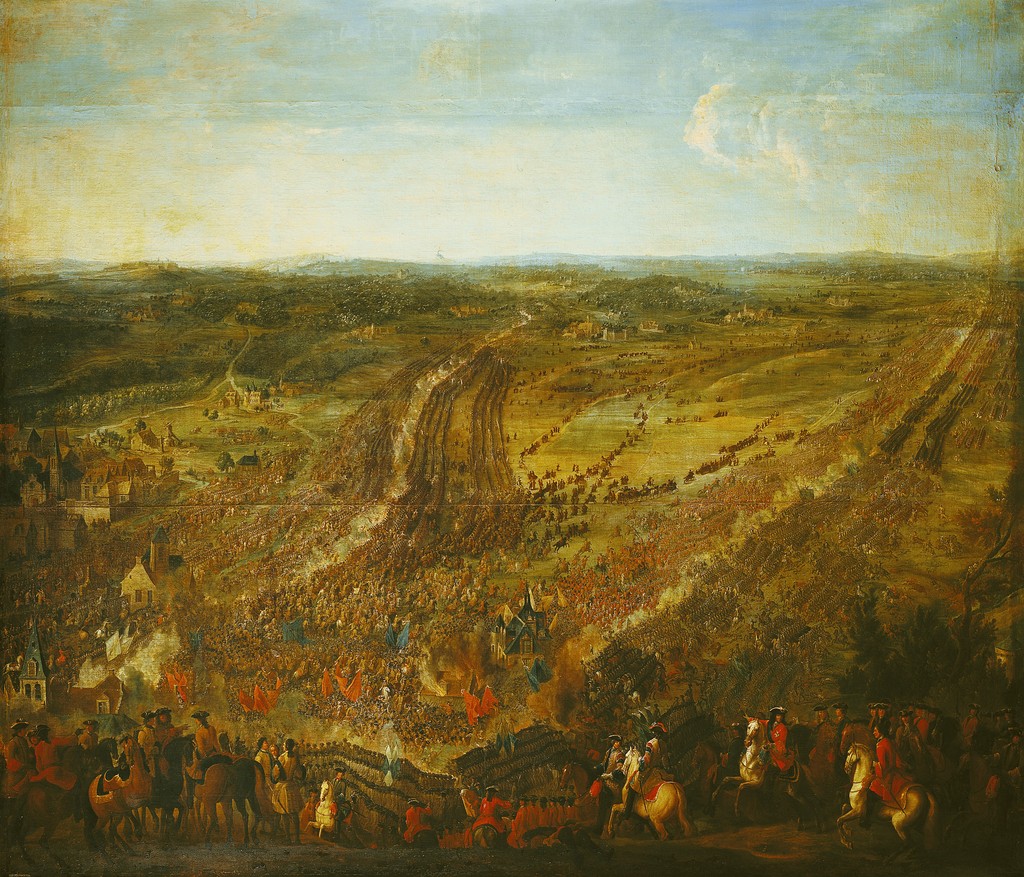 The
The Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
, which lasted from 1688 to 1697, initiated a period of decline in Louis's political and diplomatic fortunes. It arose from two events in the Rhineland. First, in 1685, the Elector Palatine Charles II died. All that remained of his immediate family was Louis's sister-in-law, Elizabeth Charlotte. German law ostensibly barred her from succeeding to her brother's lands and electoral dignity, but it was unclear enough for arguments in favour of Elizabeth Charlotte to have a chance of success. Conversely, the princess was clearly entitled to a division of the family's personal property. Louis pressed her claims to land and chattels, hoping the latter, at least, would be given to her. Then, in 1688, Maximilian Henry of Bavaria, Archbishop of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne is an archbishop governing the Archdiocese of Cologne of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and is also a historical state in the Rhine holding the birthplace of Beethoven and northern Rhineland-Palati ...
, an ally of France, died. The archbishopric had traditionally been held by the Wittelsbachs of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, but the Bavarian claimant to replace Maximilian Henry, Prince Joseph Clemens of Bavaria, was at that time not more than 17 years old and not even ordained. Louis sought instead to install his own candidate, Wilhelm Egon von Fürstenberg, to ensure the key Rhenish state remained an ally.
In light of his foreign and domestic policies during the early 1680s, which were perceived as aggressive, Louis's actions, fostered by the succession crises of the late 1680s, created concern and alarm in much of Europe. This led to the formation of the 1686 League of Augsburg by the Holy Roman Emperor, Spain, Sweden, Saxony, and Bavaria. Their stated intention was to return France to at least the borders agreed to in the Treaty of Nijmegen. Emperor Leopold I's persistent refusal to convert the Truce of Ratisbon into a permanent treaty fed Louis's fears that the Emperor would turn on France and attack the Reunions after settling his affairs in the Balkans.
Another event Louis found threatening was England's Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
of 1688. Although King James II James II may refer to:
* James II of Avesnes (died c. 1205), knight of the Fourth Crusade
* James II of Majorca (died 1311), Lord of Montpellier
* James II of Aragon (1267–1327), King of Sicily
* James II, Count of La Marche (1370–1438), King C ...
was Catholic, his two Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
daughters, Mary and Anne, ensured the English people a Protestant succession. But when James II's son James Francis Edward Stuart was born, he took precedence in succession over his sisters. This seemed to herald an era of Catholic monarchs in England. Protestant lords called on the Dutch Prince William III of Orange, grandson of Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after ...
, to come to their aid. He sailed for England with troops despite Louis's warning that France would regard it as a provocation. Witnessing numerous desertions and defections, even among those closest to him, James II fled England. Parliament declared the throne vacant, and offered it to James's daughter Mary II and his son-in-law and nephew William. Vehemently anti-French, William (now William III of England) pushed his new kingdoms into war, thus transforming the League of Augsburg into the Grand Alliance. Before this happened, Louis expected William's expedition to England to absorb his energies and those of his allies, so he dispatched troops to the Rhineland after the expiry of his ultimatum to the German princes requiring confirmation of the Truce of Ratisbon and acceptance of his demands about the succession crises. This military manoeuvre was also intended to protect his eastern provinces from Imperial invasion by depriving the enemy army of sustenance, thus explaining the preemptive scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, communi ...
policy pursued in much of southwestern Germany (the "Devastation of the Palatinate").
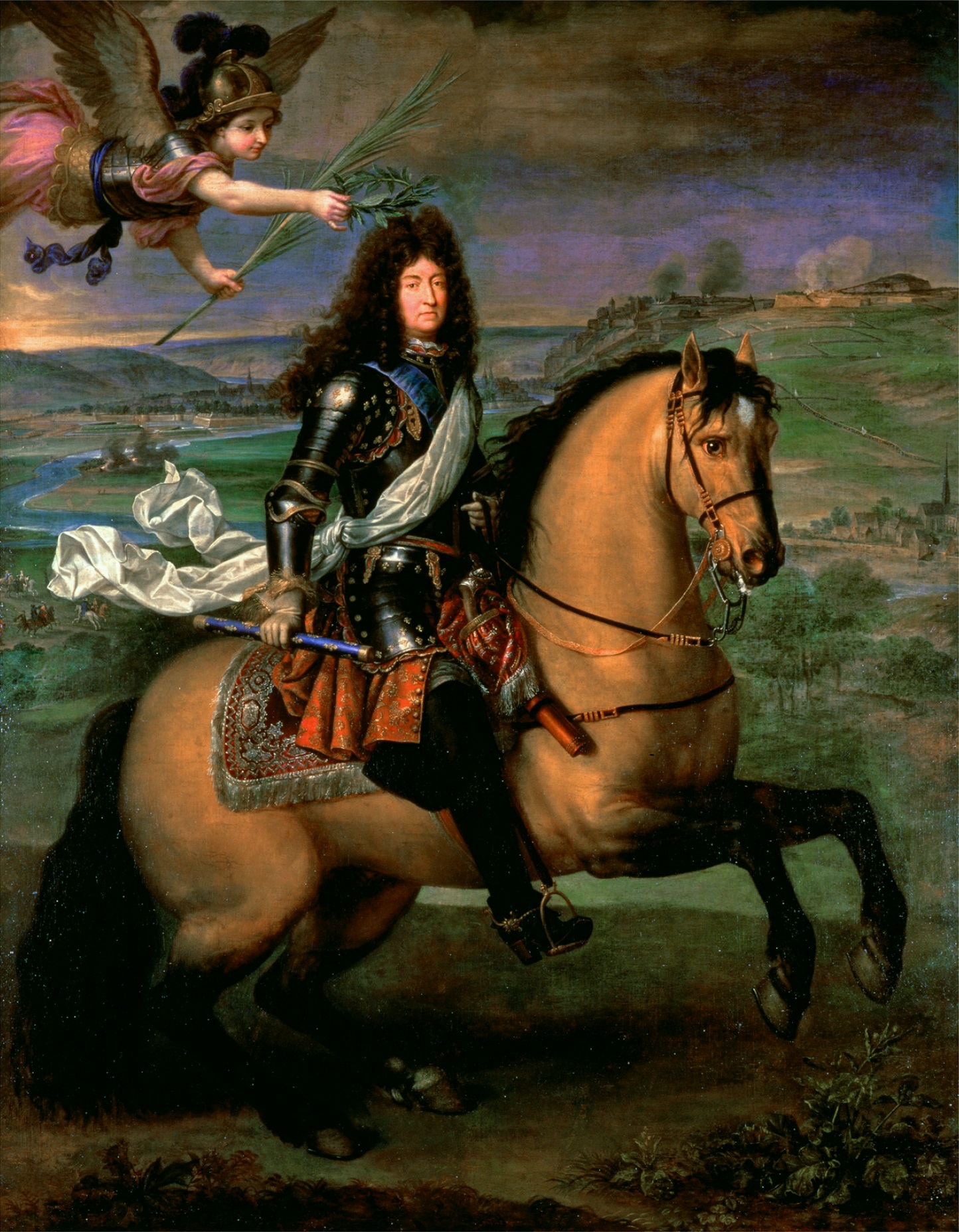 French armies were generally victorious throughout the war because of Imperial commitments in the Balkans, French logistical superiority, and the quality of French generals such as Condé's famous pupil, François Henri de Montmorency-Bouteville, duc de Luxembourg. His triumphs at the Battles of Fleurus in 1690,
French armies were generally victorious throughout the war because of Imperial commitments in the Balkans, French logistical superiority, and the quality of French generals such as Condé's famous pupil, François Henri de Montmorency-Bouteville, duc de Luxembourg. His triumphs at the Battles of Fleurus in 1690, Steenkerque
Steenkerque (French; nl, Steenkerke; in older English references also ''Steenkerke'', ''Steenkirk'', ''Steinkerque'', ''Steinkerke'' or ''Steinkirk''; wa, Stinkerke) is a village of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of Braine-le-Comte ...
in 1692, and Landen in 1693 preserved northern France from invasion.
 Although an attempt to restore James II failed at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690, France accumulated a string of victories from Flanders in the north, Germany in the east, and Italy and Spain in the south, to the high seas and the colonies. Louis personally supervised the captures of
Although an attempt to restore James II failed at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690, France accumulated a string of victories from Flanders in the north, Germany in the east, and Italy and Spain in the south, to the high seas and the colonies. Louis personally supervised the captures of Mons
Mons (; German and nl, Bergen, ; Walloon and pcd, Mont) is a city and municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the province of Hainaut, Belgium.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. T ...
in 1691 and Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Namu ...
in 1692. Luxembourg gave France the defensive line of the Sambre
The Sambre (; nl, Samber, ) is a river in northern France and in Wallonia, Belgium. It is a left-bank tributary of the Meuse, which it joins in the Wallonian capital Namur.
The source of the Sambre is near Le Nouvion-en-Thiérache, in the Aisne ...
by capturing Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593. in 1693. France also overran most of the Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The duc ...
after the battles of Marsaglia
Marsaglia is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Cuneo in the Italian region Piedmont, located about southeast of Turin and about east of Cuneo.
References
External links
Official website
Cities and towns in Piedmont
C ...
and Staffarde in 1693. While naval stalemate ensued after the French victory at the Battle of Beachy Head in 1690 and the Allied victory at Barfleur-La Hougue in 1692, the Battle of Torroella in 1694 exposed Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
to French invasion, culminating in the capture of Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ...
. The Dutch captured Pondichéry in 1693, but a 1697 French raid on the Spanish treasure port of Cartagena, Spain, yielded a fortune of 10,000,000 livres.
In July 1695, the city of Namur
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration.
Namu ...
, occupied for three years by the French, was besieged by an allied army led by William III. Louis XIV ordered the surprise destruction of a Flemish city to divert the attention of these troops. This led to the bombardment of Brussels, in which more than 4,000 buildings were destroyed, including the entire city centre. The strategy failed, as Namur fell three weeks later, but harmed Louis XIV's reputation: a century later, Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
deemed the bombardment "as barbarous as it was useless."
Peace was broached by Sweden in 1690. By 1692, both sides evidently wanted peace, and secret bilateral talks began, but to no avail. Louis tried to break up the alliance against him by dealing with individual opponents but did not achieve his aim until 1696 when the Savoyards agreed to the Treaty of Turin and switched sides. Thereafter, members of the League of Augsburg rushed to the peace table, and negotiations for a general peace began in earnest, culminating in the Peace of Ryswick of 1697.
Peace of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick ended the War of the League of Augsburg and disbanded the Grand Alliance. By manipulating their rivalries and suspicions, Louis divided his enemies and broke their power.
The treaty yielded many benefits for France. Louis secured permanent French sovereignty over all of Alsace, including Strasbourg, and established the Rhine as the Franco-German border (as it is to this day). Pondichéry and Acadia were returned to France, and Louis's ''de facto'' possession of Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
was recognised as lawful. However, he returned Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
and most of the Reunions.
French military superiority might have allowed him to press for more advantageous terms. Thus, his generosity to Spain with regard to Catalonia has been read as a concession to foster pro-French sentiment and may ultimately have induced King Charles II to name Louis's grandson Philip, Duke of Anjou
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724, and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign of 45 years is the longest in the history of the Spanish mon ...
, heir to the Spanish throne. In exchange for financial compensation, France renounced its interests in the Electorate of Cologne and the Palatinate. Lorraine, which had been occupied by the French since 1670, was returned to its rightful Duke Leopold, albeit with a right of way to the French military. William and Mary were recognised as joint sovereigns of the British Isles, and Louis withdrew support for James II. The Dutch were given the right to garrison forts in the Spanish Netherlands that acted as a protective barrier against possible French aggression. Though in some respects the Treaty of Ryswick may appear a diplomatic defeat for Louis since he failed to place client rulers in control of the Palatinate or the Electorate of Cologne, he did in fact fulfil many of the aims laid down in his 1688 ultimatum. In any case, peace in 1697 was desirable to Louis, since France was exhausted from the costs of the war.
War of the Spanish Succession
Causes and build-up to the war
By the time of the Peace of Ryswick, the Spanish succession had been a source of concern to European leaders for well over forty years. King Charles II ruled a vast empire comprising Spain, Naples, Sicily, Milan, the Spanish Netherlands, and numerous Spanish colonies. He produced no children, however, and consequently had no direct heirs.
The principal claimants to the throne of Spain belonged to the ruling families of France and Austria. The French claim derived from Louis XIV's mother Anne of Austria (the older sister of Philip IV of Spain) and his wife Maria Theresa (Philip IV's eldest daughter). Based on the laws of primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
, France had the better claim as it originated from the eldest daughters in two generations. However, their renunciation of succession rights complicated matters. In the case of Maria Theresa, nonetheless, the renunciation was considered null and void owing to Spain's breach of her marriage contract with Louis. In contrast, no renunciations tainted the claims of Emperor Leopold I's son Charles, Archduke of Austria, who was a grandson of Philip III's youngest daughter Maria Anna Maria Anna may refer to:
* Archduchess Maria Anna of Austria (1738–1789), the second but eldest surviving daughter of Maria Theresa, Queen of Hungary and Bohemia, and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor.
* Maria Anna Adamberger (1752–1804), Vie ...
. The English and Dutch feared that a French or Austrian-born Spanish king would threaten the balance of power and thus preferred the Bavarian Prince Joseph Ferdinand, a grandson of Leopold I through his first wife Margaret Theresa of Spain (the younger daughter of Philip IV).
In an attempt to avoid war, Louis signed the Treaty of the Hague with William III of England in 1698. This agreement divided Spain's Italian territories between Louis's son ''le Grand Dauphin'' and Archduke Charles, with the rest of the empire awarded to Joseph Ferdinand. William III consented to permitting the Dauphin's new territories to become part of France when the latter succeeded to his father's throne. The signatories, however, omitted to consult the ruler of these lands, and Charles II was passionately opposed to the dismemberment of his empire. In 1699, he re-confirmed his 1693 will that named Joseph Ferdinand as his sole successor.
Six months later, Joseph Ferdinand died. Therefore, in 1700, Louis and William III concluded a fresh partitioning agreement, the Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
. This allocated Spain, the Low Countries, and the Spanish colonies to the Archduke. The Dauphin would receive all of Spain's Italian territories. Charles II acknowledged that his empire could only remain undivided by bequeathing it entirely to a Frenchman or an Austrian. Under pressure from his German wife, Maria Anna of Neuburg, Charles II named Archduke Charles as his sole heir.
Acceptance of the will of Charles II and consequences
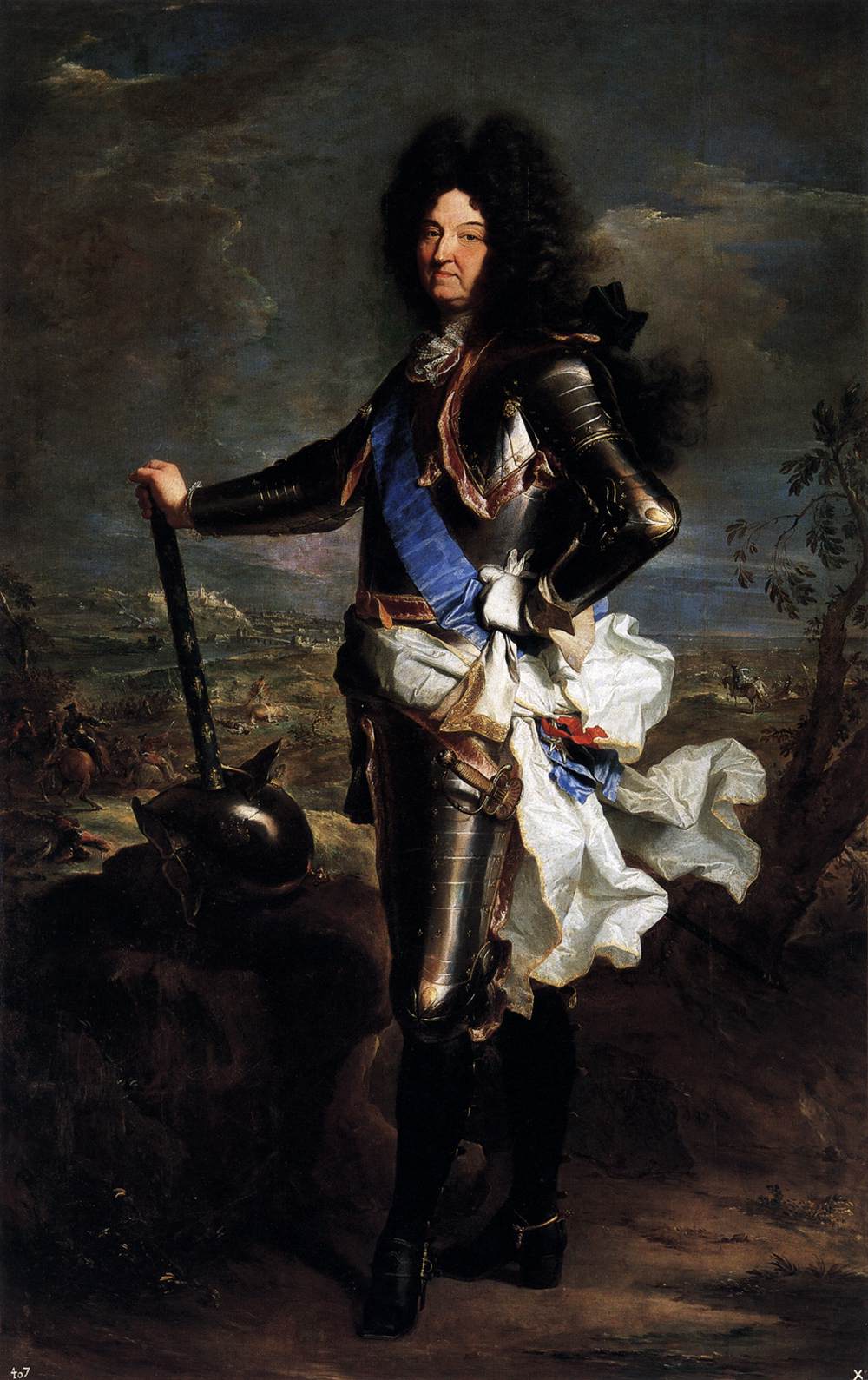 On his deathbed in 1700, Charles II of Spain unexpectedly changed his will. The clear demonstration of French military superiority for many decades before this time, the pro-French faction at the court of Spain, and even Pope Innocent XII convinced him that France was more likely to preserve his empire intact. He thus offered the entire empire to the Dauphin's second son Philip, Duke of Anjou, provided it remained undivided. Anjou was not in the direct line of French succession, thus his accession would not cause a Franco-Spanish union. If Anjou refused, the throne would be offered to his younger brother Charles, Duke of Berry. If the Duke of Berry declined it, it would go to Archduke Charles, then to the distantly related
On his deathbed in 1700, Charles II of Spain unexpectedly changed his will. The clear demonstration of French military superiority for many decades before this time, the pro-French faction at the court of Spain, and even Pope Innocent XII convinced him that France was more likely to preserve his empire intact. He thus offered the entire empire to the Dauphin's second son Philip, Duke of Anjou, provided it remained undivided. Anjou was not in the direct line of French succession, thus his accession would not cause a Franco-Spanish union. If Anjou refused, the throne would be offered to his younger brother Charles, Duke of Berry. If the Duke of Berry declined it, it would go to Archduke Charles, then to the distantly related House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
if Charles declined it.
Louis was confronted with a difficult choice. He could agree to a partition of the Spanish possessions and avoid a general war, or accept Charles II's will and alienate much of Europe. He may initially have been inclined to abide by the partition treaties, but the Dauphin's insistence persuaded him otherwise. Moreover, Louis's foreign minister, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, marquis de Torcy, pointed out that war with the Emperor would almost certainly ensue whether Louis accepted the partition treaties or Charles II's will. He emphasised that, should it come to war, William III was unlikely to stand by France since he "made a treaty to avoid war and did not intend to go to war to implement the treaty". Indeed, in the event of war, it might be preferable to be already in control of the disputed lands. Eventually, therefore, Louis decided to accept Charles II's will. Philip, Duke of Anjou, thus became Philip V, King of Spain.
Most European rulers accepted Philip as king, some reluctantly. Depending on one's views of the war's inevitability, Louis acted reasonably or arrogantly. He confirmed that Philip V retained his French rights despite his new Spanish position. Admittedly, he may only have been hypothesising a theoretical eventuality and not attempting a Franco-Spanish union. But his actions were certainly not read as disinterested. Moreover, Louis sent troops to the Spanish Netherlands to evict Dutch garrisons and secure Dutch recognition of Philip V. In 1701, Philip transferred the '' asiento'' (the right to supply slaves to Spanish colonies) to France, as a sign of the two nations' growing connections. As tensions mounted, Louis decided to acknowledge James Stuart, the son of James II, as king of England on the latter's death, infuriating William III. These actions enraged Britain and the Dutch Republic. With the Holy Roman Emperor and the petty German states, they formed another Grand Alliance and declared war on France in 1702. French diplomacy secured Bavaria, Portugal, and Savoy as Franco-Spanish allies.
Commencement of fighting
 Even before war was officially declared, hostilities began with Imperial aggression in Italy. Once finally declared, the War of the Spanish Succession lasted almost until Louis's death, at great cost to him and France.
The war began with French successes, but the talents of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, and Eugene of Savoy checked these victories and broke the myth of French invincibility. The duo allowed the Palatinate and Austria to occupy Bavaria after their victory at the
Even before war was officially declared, hostilities began with Imperial aggression in Italy. Once finally declared, the War of the Spanish Succession lasted almost until Louis's death, at great cost to him and France.
The war began with French successes, but the talents of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, and Eugene of Savoy checked these victories and broke the myth of French invincibility. The duo allowed the Palatinate and Austria to occupy Bavaria after their victory at the Battle of Blenheim
The Battle of Blenheim (german: Zweite Schlacht bei Höchstädt, link=no; french: Bataille de Höchstädt, link=no; nl, Slag bij Blenheim, link=no) fought on , was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied v ...
. Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, had to flee to the Spanish Netherlands. The impact of this victory won the support of Portugal and Savoy. Later, the Battle of Ramillies delivered the Low Countries to the Allies, and the Battle of Turin forced Louis to evacuate Italy, leaving it open to Allied forces. Marlborough and Eugene met again at the Battle of Oudenarde
The Battle of Oudenarde, also known as the Battle of Oudenaarde, was a major engagement of the War of the Spanish Succession, pitting a Grand Alliance force consisting of eighty thousand men under the command of the Duke of Marlborough and Prin ...
, which enabled them to invade France.
France established contact with Francis II Rákóczi and promised support if he took up the cause of Hungarian independence.
Defeats, famine, and mounting debt greatly weakened France. Between 1693 and 1710, over two million people died in two famines, made worse as foraging armies seized food supplies from the villages. In desperation, Louis ordered a disastrous invasion of the English island of Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency.
It is the second largest of the Channel Islands ...
in the autumn of 1704 with the aim of raiding their successful harvest. By the winter of 1708–09, he was willing to accept peace at nearly any cost. He agreed that the entire Spanish empire should be surrendered to Archduke Charles, and also consented to return to the frontiers of the Peace of Westphalia, giving up all the territories he had acquired over 60 years. But he could not promise that Philip V would accept these terms, so the Allies demanded that Louis single-handedly attack his grandson to force these terms on him. If he could not achieve this within the year, the war would resume. Louis could not accept these terms.
Turning point
The final phases of the War of the Spanish Succession demonstrated that the Allies could not maintain Archduke Charles in Spain just as surely as France could not retain the entire Spanish inheritance for Philip V. The Allies were definitively expelled from central Spain by the Franco-Spanish victories at the Battles of Villaviciosa and Brihuega in 1710. French forces elsewhere remained obdurate despite their defeats. The Allies suffered a Pyrrhic victory
A Pyrrhic victory ( ) is a victory that inflicts such a devastating toll on the victor that it is tantamount to defeat. Such a victory negates any true sense of achievement or damages long-term progress.
The phrase originates from a quote from P ...
at the Battle of Malplaquet with 21,000 casualties, twice that of the French. Eventually, France recovered its military pride with the decisive victory at Denain in 1712.
French military successes near the end of the war took place against the background of a changed political situation in Austria. In 1705, Emperor Leopold I died. His elder son and successor, Joseph I, followed him in 1711. His heir was none other than Archduke Charles, who secured control of all of his brother's Austrian landholdings. If the Spanish empire then fell to him, it would have resurrected a domain as vast as Holy Roman Emperor Charles V's in the 16th century. To the maritime powers of Great Britain and the Dutch Republic, this would have been as undesirable as a Franco-Spanish union.
Conclusion of peace
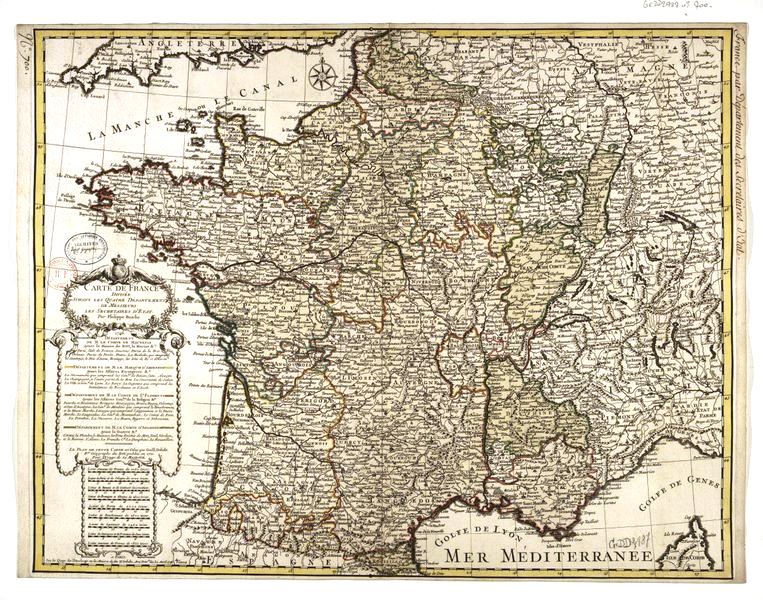 As a result of the fresh British perspective on the European balance of power, Anglo-French talks began, culminating in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht between Louis, Philip V of Spain,
As a result of the fresh British perspective on the European balance of power, Anglo-French talks began, culminating in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht between Louis, Philip V of Spain, Anne, Queen of Great Britain
Anne (6 February 1665 – 1 August 1714) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland from 8 March 1702 until 1 May 1707. On 1 May 1707, under the Acts of Union, the kingdoms of England and Scotland united as a single sovereign state known ...
, and the Dutch Republic. In 1714, after losing Landau and Freiburg, the Holy Roman Emperor also made peace with France in the Treaties of Rastatt and Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden ...
.
In the general settlement, Philip V retained Spain and its colonies, while Austria received the Spanish Netherlands and divided Spanish Italy with Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Savo ...
. Britain kept Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
and Menorca. Louis agreed to withdraw his support for James Stuart, son of James II and pretender to the throne of Great Britain, and ceded Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, Rupert's Land, and Acadia in the Americas to Anne. Britain gained the most from the treaty, but the final terms were much more favourable to France than those being discussed in peace negotiations in 1709 and 1710. France retained Île-Saint-Jean and Île Royale
The Salvation Islands (french: Îles du Salut, so called because the missionaries went there to escape plague on the mainland; sometimes mistakenly called Safety Islands) are a group of small islands of volcanic origin about off the coast of Fre ...
, and Louis acquired a few minor European territories, such as the Principality of Orange and the Ubaye Valley, which covered transalpine passes into Italy. Thanks to Louis, his allies the Electors of Bavaria and Cologne were restored to their prewar status and returned their lands.
Personal life
Marriages and children
Louis and his wife Maria Theresa of Spain had six children from the marriage contracted for them in 1660. However, only one child, the eldest, survived to adulthood: Louis, '' le Grand Dauphin'', known as ''Monseigneur''. Maria Theresa died in 1683, whereupon Louis remarked that she had never caused him unease on any other occasion.
Despite evidence of affection early on in their marriage, Louis was never faithful to Maria Theresa. He took a series of mistresses, both official and unofficial. Among the better documented are Louise de La Vallière (with whom he had five children; 1661–67), Bonne de Pons d'Heudicourt (1665), Catherine Charlotte de Gramont (1665), Françoise-Athénaïs, Marquise de Montespan (with whom he had seven children; 1667–80), Anne de Rohan-Chabot
Anne de Rohan-Chabot (Anne Julie; 1648 – 4 February 1709) was a French noble. A member of the House of Rohan, she was wife of the Prince of Soubise. It was she who brought the lordship of Soubise into the junior line of the House of Rohan. S ...
(1669–75), Claude de Vin des Œillets (one child born in 1676), Isabelle de Ludres
Marie-Élisabeth "Isabelle" de Ludres, Marquess of Ludres (1647 – 28 January 1726) was a French noblewoman and lady-in-waiting, known for being the mistress of Louis XIV, King of France between 1675 and 1676.
Early life
Marie-Élisabeth d ...
(1675–78), and Marie Angélique de Scorailles (1679–81), who died at age 19 in childbirth. Through these liaisons, he produced numerous illegitimate children, most of whom he married to members of cadet branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets—realm, ti ...
es of the royal family
A royal family is the immediate family of kings/queens, emirs/emiras, sultans/ sultanas, or raja/ rani and sometimes their extended family. The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term ...
.
Louis proved relatively more faithful to his second wife, Françoise d'Aubigné, Marquise de Maintenon. He first met her through her work caring for his children by Madame de Montespan, noting the care she gave to his favourite, Louis Auguste, Duke of Maine. The king was, at first, put off by her strict religious practice, but he warmed to her through her care for his children.
When he legitimized his children by Madame de Montespan on 20 December 1673, Françoise d'Aubigné became the royal governess at Saint-Germain. As governess, she was one of very few people permitted to speak to him as an equal, without limits. It is believed that they were married secretly at Versailles on or around 10 October 1683 or January 1684. This marriage, though never announced or publicly discussed, was an open secret and lasted until his death.
Piety and religion
 Louis was a pious and devout king who saw himself as the head and protector of the Catholic Church in France. He made his devotions daily regardless of where he was, following the liturgical calendar regularly. Under the influence of his very religious second wife, he became much stronger in the practice of his Catholic faith. This included banning opera and comedy performances during
Louis was a pious and devout king who saw himself as the head and protector of the Catholic Church in France. He made his devotions daily regardless of where he was, following the liturgical calendar regularly. Under the influence of his very religious second wife, he became much stronger in the practice of his Catholic faith. This included banning opera and comedy performances during Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke ...
.
Towards the middle and the end of his reign, the centre for the King's religious observances was usually the Chapelle Royale at Versailles. Ostentation was a distinguishing feature of daily Mass, annual celebrations, such as those of Holy Week, and special ceremonies. Louis established the Paris Foreign Missions Society, but his informal alliance with the Ottoman Empire was criticised for undermining Christendom.
Patronage of the arts
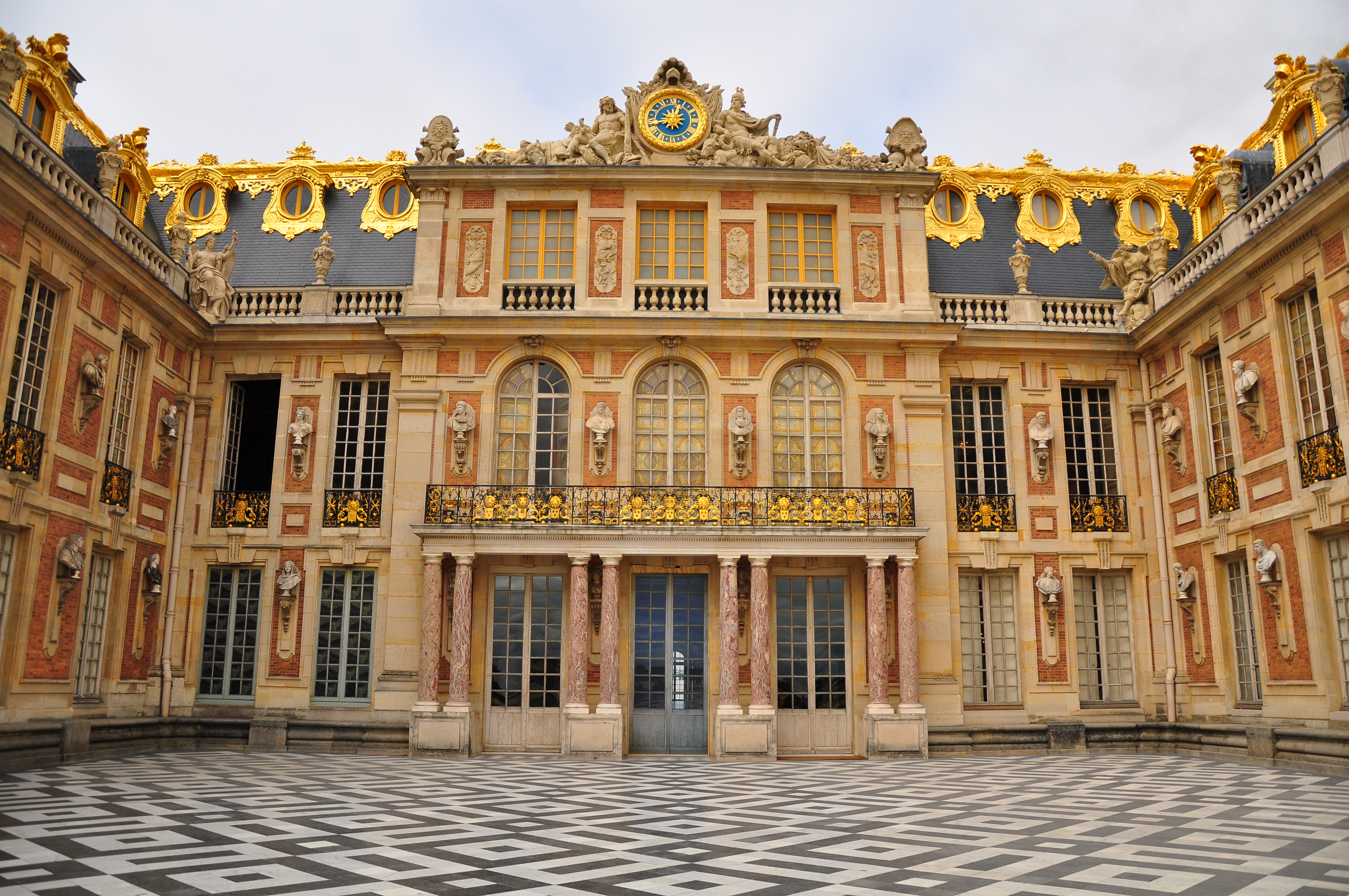
 Louis generously supported the royal court of France and those who worked under him. He brought the
Louis generously supported the royal court of France and those who worked under him. He brought the Académie Française
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
under his patronage and became its "Protector". He allowed Classical French literature to flourish by protecting such writers as Molière, Racine, and La Fontaine, whose works remain influential to this day. Louis also patronised the visual arts by funding and commissioning artists such as Charles Le Brun, Pierre Mignard, Antoine Coysevox, and Hyacinthe Rigaud, whose works became famous throughout Europe. Composers and musicians such as Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( , , ; born Giovanni Battista Lulli, ; – 22 March 1687) was an Italian-born French composer, guitarist, violinist, and dancer who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he ...
, Jacques Champion de Chambonnières, and François Couperin
François Couperin (; 10 November 1668 – 11 September 1733) was a French Baroque composer, organist and harpsichordist. He was known as ''Couperin le Grand'' ("Couperin the Great") to distinguish him from other members of the musically talented ...
thrived. In 1661, Louis founded the Académie Royale de Danse, and in 1669, the Académie d'Opéra, important driving events in the evolution of ballet. He also attracted, supported and patronized such artists as André Charles Boulle
André-Charles Boulle (11 November 164229 February 1732), ''le joailler du meuble'' (the "furniture jeweller"), became the most famous French cabinetmaker and the preeminent artist in the field of marquetry, also known as "inlay". Boulle was "t ...
, who revolutionised marquetry with his art of inlay, today known as " Boulle Work". Always on the lookout for new talent, the king launched music competitions: in 1683, Michel-Richard de Lalande thus became deputy master of the Royal Chapel, composing his ''Symphonies for the Soupers du Roy'' along with 77 large scale ''Grand Motets''.
Over the course of four building campaigns, Louis converted a hunting lodge built by Louis XIII into the spectacular Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
. With the exception of the current Royal Chapel (built near the end of his reign), the palace achieved much of its current appearance after the third building campaign, which was followed by an official move of the royal court to Versailles on 6 May 1682. Versailles became a dazzling, awe-inspiring setting for state affairs and the reception of foreign dignitaries. At Versailles, the king alone commanded attention.
 Several reasons have been suggested for the creation of the extravagant and stately palace, as well as the relocation of the monarchy's seat. The memoirist Saint-Simon speculated that Louis viewed Versailles as an isolated power centre where treasonous cabals could be more readily discovered and foiled.
Several reasons have been suggested for the creation of the extravagant and stately palace, as well as the relocation of the monarchy's seat. The memoirist Saint-Simon speculated that Louis viewed Versailles as an isolated power centre where treasonous cabals could be more readily discovered and foiled.Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
was originally to plan additions to the Louvre; however, his plans would have meant the destruction of much of the existing structure, replacing it with an Italian summer villa in the centre of Paris. Bernini's plans were eventually shelved in favour of the elegant Louvre Colonnade designed by three Frenchmen: Louis Le Vau, Charles Le Brun, and Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault (25 September 1613 – 9 October 1688) was a French physician and an amateur architect, best known for his participation in the design of the east façade of the Louvre in Paris.[portrait bust
A bust is a sculpted or cast representation of the upper part of the human figure, depicting a person's head and neck, and a variable portion of the chest and shoulders. The piece is normally supported by a plinth. The bust is generally a p ...]
of the king.
Image and depiction
Few rulers in world history have commemorated themselves in as grand a manner as Louis. He cultivated his image as the Sun King (''le Roi Soleil''), the center of the universe "without equal". Louis used court ritual and the arts to validate and augment his control over France. With his support, Colbert established from the beginning of Louis' personal reign a centralised and institutionalised system for creating and perpetuating the royal image. The King was thus portrayed largely in majesty or at war, notably against Spain. This portrayal of the monarch was to be found in numerous media of artistic expression, such as painting, sculpture, theatre, dance, music, and the almanacs that diffused royal propaganda to the population at large.
Evolution of royal portraiture
 Over his lifetime, Louis commissioned numerous works of art to portray himself, among them over 300 formal portraits. The earliest portrayals of Louis already followed the pictorial conventions of the day in depicting the child king as the majestically royal incarnation of France. This idealisation of the monarch continued in later works, which avoided depictions of the effect of smallpox that Louis contracted in 1647. In the 1660s, Louis began to be shown as a Roman emperor, the god Apollo, or
Over his lifetime, Louis commissioned numerous works of art to portray himself, among them over 300 formal portraits. The earliest portrayals of Louis already followed the pictorial conventions of the day in depicting the child king as the majestically royal incarnation of France. This idealisation of the monarch continued in later works, which avoided depictions of the effect of smallpox that Louis contracted in 1647. In the 1660s, Louis began to be shown as a Roman emperor, the god Apollo, or Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, as can be seen in many works of Charles Le Brun, such as sculpture, paintings, and the decor of major monuments.
The depiction of the king in this manner focused on allegorical or mythological attributes, instead of attempting to produce a true likeness. As Louis aged, so too did the manner in which he was depicted. Nonetheless, there was still a disparity between realistic representation and the demands of royal propaganda. There is no better illustration of this than in Hyacinthe Rigaud's frequently-reproduced ''Portrait of Louis XIV of 1701'', in which a 63-year-old Louis appears to stand on a set of unnaturally young legs.
Rigaud's portrait exemplified the height of royal portraiture during Louis' reign. Although Rigaud crafted a credible likeness of Louis, the portrait was neither meant as an exercise in realism nor to explore Louis' personal character. Certainly, Rigaud was concerned with detail and depicted the king's costume with great precision, down to his shoe buckle.
However, Rigaud's intention was to glorify the monarchy. Rigaud's original, now housed in the Louvre, was originally meant as a gift to Louis' grandson, Philip V of Spain. However, Louis was so pleased with the work that he kept the original and commissioned a copy to be sent to his grandson. That became the first of many copies, both in full and half-length formats, to be made by Rigaud, often with the help of his assistants. The portrait also became a model for French royal and imperial portraiture down to the time of Charles X over a century later. In his work, Rigaud proclaims Louis' exalted royal status through his elegant stance and haughty expression, the royal regalia and throne, rich ceremonial fleur-de-lys robes, as well as the upright column in the background, which, together with the draperies, serves to frame this image of majesty.
Other works of art
In addition to portraits, Louis commissioned at least 20 statues of himself in the 1680s, to stand in Paris and provincial towns as physical manifestations of his rule. He also commissioned "war artists" to follow him on campaigns to document his military triumphs. To remind the people of these triumphs, Louis erected permanent triumphal arches in Paris and the provinces for the first time since the decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
.
Louis' reign marked the birth and infancy of the art of medallions. Sixteenth-century rulers had often issued medals in small numbers to commemorate the major events of their reigns. Louis, however, struck more than 300 to celebrate the story of the king in bronze, that were enshrined in thousands of households throughout France.
He also used tapestries as a medium of exalting the monarchy. Tapestries could be allegorical, depicting the elements or seasons, or realist, portraying royal residences or historical events. They were among the most significant means to spread royal propaganda prior to the construction of the Hall of Mirrors at Versailles.
Ballet
 Louis loved
Louis loved ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form ...
and frequently danced in court ballets during the early half of his reign. In general, Louis was an eager dancer who performed 80 roles in 40 major ballets. This approaches the career of a professional ballet dancer.
His choices were strategic and varied. He danced four parts in three of Molière's comédies-ballets, which are plays accompanied by music and dance. Louis played an Egyptian in ''Le Mariage forcé'' in 1664, a Moorish gentleman in ''Le Sicilien'' in 1667, and both Neptune and Apollo in ''Les Amants magnifiques'' in 1670.
He sometimes danced leading roles that were suitably royal or godlike (such as Neptune, Apollo, or the Sun). At other times, he would adopt mundane roles before appearing at the end in the lead role. It is considered that, at all times, he provided his roles with sufficient majesty and drew the limelight with his flair for dancing. For Louis, ballet may not have merely been a tool for manipulation in his propaganda machinery. The sheer number of performances he gave as well as the diversity of roles he played may serve to indicate a deeper understanding and interest in the art form.
Ballet dancing was actually used by Louis as a political tool to hold power over his state. He integrated ballet deeply in court social functions and fixated his nobles' attention on upholding standards in ballet dancing, effectively distracting them from political activities. In 1661, the Royal Academy of Dance was founded by Louis to further his ambition. Pierre Beauchamp, his private dance instructor, was ordered by Louis to come up with a notation system
In linguistics and semiotics, a notation is a system of graphics or symbols, characters and abbreviated expressions, used (for example) in artistic and scientific disciplines to represent technical facts and quantities by convention. Therefore, ...
to record ballet performances, which he did with great success. His work was adopted and published by Feuillet Feuillet may refer to:
*Feuillet, Panama
*Louis Éconches Feuillée Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ...
in 1700 as ''Choregraphie''. This major development in ballet played an important role in promoting French culture and ballet throughout Europe during Louis' time.
Louis greatly emphasized etiquettes in ballet dancing, evidently seen in "La belle danse" (the French noble style). More challenging skills were required to perform this dance with movements very much resembling court behaviours, as a way to remind the nobles of the king's absolute power and their own status. All the details and rules were compressed in five positions of the bodies codified by Beauchamp.
Unofficial image
Besides the official depiction and image of Louis, his subjects also followed a non-official discourse consisting mainly of clandestine publications, popular songs, and rumours that provided an alternative interpretation of Louis and his government. They often focused on the miseries arising from poor government, but also carried the hope for a better future when Louis escaped the malignant influence of his ministers and mistresses, and took the government into his own hands. On the other hand, petitions addressed either directly to Louis or to his ministers exploited the traditional imagery and language of monarchy. These varying interpretations of Louis abounded in self-contradictions that reflected the people's amalgamation of their everyday experiences with the idea of monarchy.
In fiction
Literature
* Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (, ; ; born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie (), 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas père (where '' '' is French for 'father', to distinguish him from his son Alexandre Dumas fils), was a French writer ...
portrayed Louis in his two sequels to his 1844 novel '' The Three Musketeers'': first as a child in '' Twenty Years After'' (1845), then as a young man in '' The Vicomte de Bragelonne'' (1847–1850), in which he is a central character. The final part of the latter novel recounts the legend that a mysterious prisoner in an iron mask was actually Louis' twin brother and has spawned numerous film adaptations generally titled ''The Man in the Iron Mask''.
* In 1910, the American historical novelist Charles Major wrote ''"The Little King: A Story of the Childhood of King Louis XIV"''.
* Louis is a major character in the 1959 historical novel ''Angélique et le Roy'' ("Angélique and the King"), part of the ''Angélique'' series. The protagonist, a strong-willed lady at Versailles, rejects the King's advances and refuses to become his mistress. A later book, the 1961 ''Angélique se révolte'' ("Angélique in Revolt"), details the dire consequences of her defying this powerful monarch.
* A character based on Louis plays an important role in '' The Age of Unreason'', a series of four alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alter ...
novels written by American science fiction and fantasy author Gregory Keyes.
* Louis features significantly in Neal Stephenson
Neal Town Stephenson (born October 31, 1959) is an American writer known for his works of speculative fiction. His novels have been categorized as science fiction, historical fiction, cyberpunk, postcyberpunk, and baroque.
Stephenson's work exp ...
's Baroque Cycle, specifically in the 2003 novel ''The Confusion
''The Confusion'' is a novel by Neal Stephenson. It is the second volume in ''The Baroque Cycle'' and consists of two sections or books, ''Bonanza'' and ''The Juncto''. In 2005, ''The Confusion'' won the Locus Award, together with ''The System o ...
'', the greater part of which takes place at Versailles.
* In the ''39 Clues'' series universe, it has been noted that Louis was part of the Cahill branch, Tomas.
* He is called the son of Apollo in Rick Riordan's '' Trials of Apollo'' series.
* Louis XIV is portrayed in Vonda N. McIntyre
Vonda Neel McIntyre () was an American science fiction writer and biologist.
Early life and education
Vonda N. McIntyre was born in Louisville, Kentucky, the daughter of H. Neel and Vonda B. Keith McIntyre, who were born in Poland, Ohio. She s ...
's 1997 novel ''The Moon and the Sun
''The Moon and the Sun'' is a novel by American writer Vonda N. McIntyre, published in 1997. The book combines two major genres: science fiction (specifically the alternate history subgenre) and historical romance. It won the Nebula Award for B ...
''.
Films
* The film, ''The Taking of Power by Louis XIV
''The Taking of Power by Louis XIV'' (french: La prise de pouvoir par Louis XIV), also called ''The Rise of Louis XIV'', is a 1966 French television film by Italian film director Roberto Rossellini. The film revolves around the French king Lou ...
'' (1966), directed by Roberto Rossellini, shows Louis' rise to power after the death of Cardinal Mazarin.
* The film ''Man in the Iron Mask'' (1998), directed by Randall Wallace, focused on the identity of an anonymous masked prisoner who spent decades in the Bastille and other French prisons, and his true identity remains somewhat a mystery till date. The monarch was played by Leonardo DiCaprio.
* The film, '' Le Roi Danse'' (2000; translated: ''The King Dances''), directed by Gérard Corbiau, reveals Louis through the eyes of Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( , , ; born Giovanni Battista Lulli, ; – 22 March 1687) was an Italian-born French composer, guitarist, violinist, and dancer who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he ...
, his court musician.
* Julian Sands portrayed Louis in Roland Jaffe's '' Vatel'' (2000).
* Alan Rickman directed, co-wrote, and stars as Louis XIV in the film, '' A Little Chaos'', which centres on construction in the gardens of Versaille, at the time immediately before and after the death of Queen Maria Theresa.
* The 2016 film '' The Death of Louis XIV'', directed by Albert Serra
Albert Serra (Catalan pronunciation: �lß'ɛɾ sɛrəborn 9 October 1975) is a Spanish independent filmmaker and manager of the production company Andergraun Films, set up by Montse Triola primarily to produce Serra's films. He is best known fo ...
, is set during the last two weeks of Louis XIV's life before dying of gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
, with the monarch played by Jean-Pierre Léaud.
Television
* The 15-year-old Louis XIV, as played by the Irish actor Robert Sheehan, is a major character of the short-lived historical fantasy series '' Young Blades'' from January to June 2005.
* George Blagden portrays Louis XIV in the Canal+ series '' Versailles'' which aired for three seasons from 2015.
Musicals
*Emmanuel Moire
Emmanuel Moire (born 16 June 1979 in Le Mans) is a French singer-songwriter, best known for portraying the role of Louis XIV in the French stage musical ''Le Roi Soleil''.
Moire has released four albums ''(Là) où je pars'' (2006), '' L'Équi ...
portrayed Louis XIV in the 2005-07 Kamel Ouali
Kamel Ouali (born 15 December 1971) is a French- Algerian choreographer.
Biography
Kamel Ouali was born in Paris. He is from an Algerian Kabyle family of twelve children.
In 1989, he was spotted by Angela Lorente of TF1 and by Cédric Naimi. ...
musical Le Roi Soleil.
Health and death
Despite the image of a healthy and virile king that Louis sought to project, evidence exists to suggest that his health was not very good. He had many ailments: for example, symptoms of diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, as confirmed in reports of suppurating periostitis in 1678, dental abscesses in 1696, along with recurring boils, fainting spells, gout, dizziness, hot flushes, and headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s.
From 1647 to 1711, the three chief physicians to the king (Antoine Vallot, Antoine d'Aquin, and Guy-Crescent Fagon) recorded all of his health problems in the ''Journal de Santé du Roi'' (''Journal of the King's Health''), a daily report of his health. On 18 November 1686, Louis underwent a painful operation for an anal fistula that was performed by the surgeon Charles Felix de Tassy, who prepared a specially shaped curved scalpel for the occasion. The wound took more than two months to heal.
Louis died of gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
at Versailles on 1 September 1715, four days before his 77th birthday, after 72 years on the throne. Enduring much pain in his last days, he finally "yielded up his soul without any effort, like a candle going out", while reciting the psalm ''Deus, in adjutorium me festina'' (''O Lord, make haste to help me''). His body was laid to rest in Saint-Denis Basilica outside Paris. It remained there undisturbed for about 80 years until revolutionaries exhumed and destroyed all of the remains found in the Basilica.
Cardinal Armand Gaston Maximilien de Rohan gave Last Rites ( confession, viaticum, and unction) to king Louis XIV.
Succession
Louis outlived most of his immediate legitimate family. His last surviving legitimate son, the Dauphin, died in 1711. Barely a year later, the Duke of Burgundy, the eldest of the Dauphin's three sons and then heir-apparent to Louis, followed his father. Burgundy's elder son, Louis, Duke of Brittany, joined them a few weeks later. Thus, on his deathbed, Louis' heir-apparent was his five-year-old great-grandson, Louis, Duke of Anjou, Burgundy's younger son.
Louis foresaw an underaged successor and sought to restrict the power of his nephew Philip II, Duke of Orléans, who, as his closest surviving legitimate relative in France, would likely become regent to the prospective Louis XV. Accordingly, the king created a regency council as Louis XIII had in anticipation of Louis XIV's own minority, with some power vested in his illegitimate son Louis-Auguste de Bourbon, Duke of Maine
Louis-Auguste de Bourbon, duc du Maine (31 March 1670 – 14 May 1736) was an illegitimate son of Louis XIV and his official mistress, Madame de Montespan. The king's favourite son, he was the founder of the semi-royal House of Bourbon-Maine name ...
. Orléans, however, had Louis' will annulled by the ''Parlement of Paris'' after his death and made himself sole regent. He stripped Maine and his brother, Louis-Alexandre, Count of Toulouse, of the rank of Prince of the Blood, which Louis had granted them, and significantly reduced Maine's power and privileges.
Line of succession in 1715
Line of succession to the French throne upon the death of Louis XIV in 1715. Louis XIV's only surviving legitimate grandson, Philip V, was not included in the line of succession due to having renounced the French throne after the war of the Spanish Succession, which lasted for 13 years after the death of Charles II of Spain in 1700.
*  '' Louis XIII (1601–1643)''
**
'' Louis XIII (1601–1643)''
**  Louis XIV ''(1638–1715)''
*** '' Louis, Grand Dauphin (1661–1711)''
**** '' Louis, Duke of Burgundy (1682–1712)''
***** '' Louis, Duke of Brittany (1707–1712)''
***** (1) Louis, Duke of Anjou (1710–1774)
**** Philip V of Spain (1683–1746)
**** '' Charles, Duke of Berry (1686–1714)''
** '' Philippe I, Duke of Orléans (1640–1701)''
*** (2) Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (1674–1723)
**** (3) Louis, Duke of Chartres (1703–1752)
Further down the French line of succession in 1715 was the
Louis XIV ''(1638–1715)''
*** '' Louis, Grand Dauphin (1661–1711)''
**** '' Louis, Duke of Burgundy (1682–1712)''
***** '' Louis, Duke of Brittany (1707–1712)''
***** (1) Louis, Duke of Anjou (1710–1774)
**** Philip V of Spain (1683–1746)
**** '' Charles, Duke of Berry (1686–1714)''
** '' Philippe I, Duke of Orléans (1640–1701)''
*** (2) Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (1674–1723)
**** (3) Louis, Duke of Chartres (1703–1752)
Further down the French line of succession in 1715 was the House of Conde
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condit ...
, followed by the House of Conti (a cadet branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets—realm, ti ...
of the House of Conde). Both of these royal houses were descended in the male line from Henri II, Prince of Conde, a second cousin of French King Louis XIII (the father of Louis XIV) in the male line.
Legacy
Reputation
According to Philippe de Courcillon's ''Journal'', Louis on his deathbed advised his heir with these words: Do not follow the bad example which I have set you; I have often undertaken war too lightly and have sustained it for vanity. Do not imitate me, but be a peaceful prince, and may you apply yourself principally to the alleviation of the burdens of your subjects.
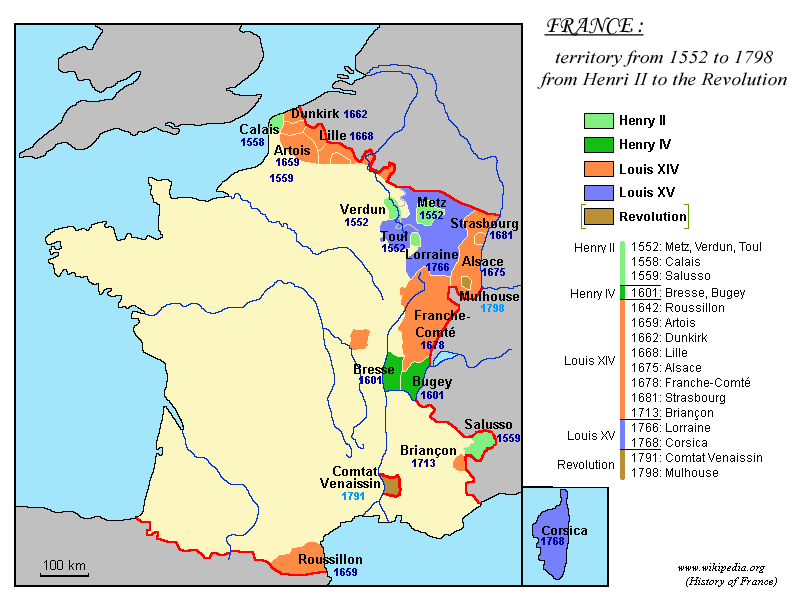 Some historians point out that it was a customary demonstration of piety in those days to exaggerate one's sins. Thus they do not place much emphasis on Louis' deathbed declarations in assessing his accomplishments. Rather, they focus on military and diplomatic successes, such as how he placed a French prince on the Spanish throne. This, they contend, ended the threat of an aggressive Spain that historically interfered in domestic French politics. These historians also emphasise the effect of Louis' wars in expanding France's boundaries and creating more defensible frontiers that preserved France from invasion until the Revolution.
Arguably, Louis also applied himself indirectly to "the alleviation of the burdens of issubjects." For example, he patronised the arts, encouraged industry, fostered trade and commerce, and sponsored the founding of an overseas empire. Moreover, the significant reduction in civil wars and aristocratic rebellions during his reign are seen by these historians as the result of Louis' consolidation of royal authority over feudal elites. In their analysis, his early reforms centralised France and marked the birth of the modern French state. They regard the political and military victories as well as numerous cultural achievements as the means by which Louis helped raise France to a preeminent position in Europe. Europe came to admire France for its military and cultural successes, power, and sophistication. Europeans generally began to emulate French manners, values, goods, and deportment. French became the universal language of the European elite.
Louis' detractors have argued that his considerable foreign, military and domestic expenditure impoverished and bankrupted France. His supporters, however, distinguish the state, which was impoverished, from France, which was not. As supporting evidence, they cite the literature of the time, such as the social commentary in Montesquieu's '' Persian Letters''.
Alternatively, Louis' critics attribute the social upheaval culminating in the French Revolution to his failure to reform French institutions while the monarchy was still secure. Other scholars counter that there was little reason to reform institutions that largely worked well under Louis. They also maintain that events occurring almost 80 years after his death were not reasonably foreseeable to Louis and that in any case, his successors had sufficient time to initiate reforms of their own.
Louis has often been criticised for his vanity. The memoirist Saint-Simon, who claimed that Louis slighted him, criticised him thus:
Some historians point out that it was a customary demonstration of piety in those days to exaggerate one's sins. Thus they do not place much emphasis on Louis' deathbed declarations in assessing his accomplishments. Rather, they focus on military and diplomatic successes, such as how he placed a French prince on the Spanish throne. This, they contend, ended the threat of an aggressive Spain that historically interfered in domestic French politics. These historians also emphasise the effect of Louis' wars in expanding France's boundaries and creating more defensible frontiers that preserved France from invasion until the Revolution.
Arguably, Louis also applied himself indirectly to "the alleviation of the burdens of issubjects." For example, he patronised the arts, encouraged industry, fostered trade and commerce, and sponsored the founding of an overseas empire. Moreover, the significant reduction in civil wars and aristocratic rebellions during his reign are seen by these historians as the result of Louis' consolidation of royal authority over feudal elites. In their analysis, his early reforms centralised France and marked the birth of the modern French state. They regard the political and military victories as well as numerous cultural achievements as the means by which Louis helped raise France to a preeminent position in Europe. Europe came to admire France for its military and cultural successes, power, and sophistication. Europeans generally began to emulate French manners, values, goods, and deportment. French became the universal language of the European elite.
Louis' detractors have argued that his considerable foreign, military and domestic expenditure impoverished and bankrupted France. His supporters, however, distinguish the state, which was impoverished, from France, which was not. As supporting evidence, they cite the literature of the time, such as the social commentary in Montesquieu's '' Persian Letters''.
Alternatively, Louis' critics attribute the social upheaval culminating in the French Revolution to his failure to reform French institutions while the monarchy was still secure. Other scholars counter that there was little reason to reform institutions that largely worked well under Louis. They also maintain that events occurring almost 80 years after his death were not reasonably foreseeable to Louis and that in any case, his successors had sufficient time to initiate reforms of their own.
Louis has often been criticised for his vanity. The memoirist Saint-Simon, who claimed that Louis slighted him, criticised him thus: There was nothing he liked so much as flattery, or, to put it more plainly, adulation; the coarser and clumsier it was, the more he relished it.
For his part, Voltaire saw Louis' vanity as the cause for his bellicosity:It is certain that he passionately wanted glory, rather than the conquests themselves. In the acquisition of Alsace and half of Flanders, and of all of Franche-Comté, what he really liked was the name he made for himself.
Nonetheless, Louis has also received praise. The anti-Bourbon Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
described him not only as "a great king", but also as "the only King of France worthy of the name". Leibniz, the German Protestant philosopher, commended him as "one of the greatest kings that ever was". And Lord Acton admired him as "by far the ablest man who was born in modern times on the steps of a throne". The historian and philosopher Voltaire wrote: "His name can never be pronounced without respect and without summoning the image of an eternally memorable age". Voltaire's history, ''The Age of Louis XIV
''The Age of Louis XIV'' (''Le Siècle de Louis XIV'', also translated ''The Century of Louis XIV'') is a historical work by the French historian, philosopher, and writer Voltaire, first published in 1751. Through it, the French 17th century beca ...
'', named Louis' reign as not only one of the four great ages in which reason and culture flourished, but the greatest ever.
In 1848, at Nuneham House, a piece of Louis' mummified heart, taken from his tomb and kept in a silver locket by Lord Harcourt, Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers ...
, was shown to the Dean of Westminster, William Buckland, who ate it.
Quotes
Numerous quotes have been attributed to Louis XIV by legend.
The well-known "I am the state" (''"L'état, c'est moi."'') was reported from at least the late 18th century. It was widely repeated but also denounced as apocryphal
Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...
by the early 19th century.
He did say, "Every time I appoint someone to a vacant position, I make a hundred unhappy and one ungrateful." Louis is recorded by numerous eyewitnesses as having said on his deathbed: "" ("I depart, but the State shall always remain.")
Arms
Order of Saint Louis
On 5 April 1693, Louis also founded the Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis (french: Ordre Royal et Militaire de Saint-Louis) is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693 by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a rewa ...
(french: Ordre Royal et Militaire de Saint-Louis), a military order of chivalry
An order of chivalry, order of knighthood, chivalric order, or equestrian order is an order (distinction), order of knights, typically founded during or inspired by the original Catholic Military order (religious society), military orders of the ...
.[* ] He named it after Louis IX and intended it as a reward for outstanding officers. It is notable as the first decoration that could be granted to non-nobles and is roughly the forerunner of the '' Légion d'honneur'', with which it shares the red ribbon (though the ''Légion d'honneur'' is awarded to military personnel and civilians alike).
Family
Ancestry
Patrilineal descent
Louis' patriline is the line from which he is descended father to son.
Patrilineal descent is the principle behind membership in royal houses, as it can be traced back through the generations - which means that if King Louis were to choose an historically accurate house name it would be Robertian, as all his male-line ancestors have been of that house.
Louis is a member of the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spanis ...
, a branch of the Capetian dynasty
The Capetian dynasty (; french: Capétiens), also known as the House of France, is a dynasty of Frankish origin, and a branch of the Robertians. It is among the largest and oldest royal houses in Europe and the world, and consists of Hugh Cape ...
and of the Robertians.
Louis' patriline is the line from which he is descended father to son. It follows the Bourbon, Kings of France, and the Counts of Paris and Worms. This line can be traced back more than 1,200 years from Robert of Hesbaye to the present day, through Kings of France & Navarre, Spain and Two-Sicilies, Dukes of Parma and Grand-Dukes of Luxembourg, Princes of Orléans and Emperors of Brazil. It is one of the oldest in Europe.
# Robert II of Worms and Rheingau ( Robert of Hesbaye), 770–807
# Robert III of Worms and Rheingau, 808–834
# Robert IV the Strong
Robert the Strong (french: Robert le Fort; c. 830 – 866) was the father of two kings of West Francia: Odo (or Eudes) and Robert I of France. His family is named after him and called the Robertians. In 853, he was named '' missus dominicus'' ...
, 820–866
# Robert I of France, 866–923
# Hugh the Great, 895–956
# Hugh Capet, 941–996
# Robert II of France, 972–1031
# Henry I of France, 1008–1060
# Philip I of France, 1053–1108
# Louis VI of France
Louis VI (late 1081 – 1 August 1137), called the Fat (french: link=no, le Gros) or the Fighter (french: link=no, le Batailleur), was King of the Franks from 1108 to 1137.
Chronicles called him "King of Saint-Denis". Louis was the first member ...
, 1081–1137
# Louis VII of France
Louis VII (1120 – 18 September 1180), called the Younger, or the Young (french: link=no, le Jeune), was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI (hence the epithet "the Young") and married Duchess ...
, 1120–1180
# Philip II of France, 1165–1223
# Louis VIII of France, 1187–1226
# Louis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the ...
, 1215–1270
# Robert, Count of Clermont, 1256–1317
# Louis I, Duke of Bourbon, 1279–1342
# James I, Count of La Marche, 1319–1362
# John I, Count of La Marche, 1344–1393
# Louis, Count of Vendôme
Louis de Bourbon (Louis I, Count of Vendôme) (1376 – December 21, 1446), younger son of John I, Count of La Marche and Catherine de Vendôme, was a French '' prince du sang'', as well as Count of Vendôme from 1393, and Count of Castres from 142 ...
, 1376–1446
# Jean VIII, Count of Vendôme, 1428–1478
# François, Count of Vendôme, 1470–1495
# Charles de Bourbon, Duke of Vendôme
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
, 1489–1537
# Antoine, King of Navarre, Duke of Vendôme, 1518–1562
# Henry IV, King of France and of Navarre, 1553–1610
# Louis XIII, King of France and Navarre, 1601–1643
# Louis XIV, King of France and Navarre, 1638–1715
Issue
This is an incomplete list of Louis XIV's illegitimate children. He reputedly had more, but the difficulty in fully documenting all such births restricts the list only to the better-known and/or legitimised.
See also
* Charles de Lorme, personal medical doctor to Louis XIV
* House of France
* Levée (ceremony)
* List of French monarchs
* Outline of France
* Style Louis XIV
* Nicolas Fouquet
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Mansel, Philip. ''King of the World: The Life of Louis XIV'' (U of Chicago Press, 2020) scholarly biography
online review
* (Fourth edition, 2019)
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Norton, Lucy (1982). ''The Sun King and His Loves''. The Folio Society.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Roosen, William J. ''The Age of Louis XIV: The Rise of Modern Diplomacy'' (1976
online
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* : a standard scholarly biography;
*
External links
* Ranum, Orest, ed. ''The Century of Louis XIV'' (1972) documents
online
*
*
Louis XIV
at ''History.com''
Full text of marriage contract
France National Archives transcription
* ''Le Siècle de Louis XIV'' by Voltaire, 1751, hosted by French Wikisource
{{DEFAULTSORT:Louis 14 of France
1638 births
1715 deaths
17th-century kings of France
18th-century kings of France
17th-century Princes of Andorra
18th-century Princes of Andorra
Ancien Régime
Burials at the Basilica of Saint-Denis
Baroque architecture in France
Dauphins of France
Deaths from gangrene
Early Modern France
French art collectors
French military personnel of the Nine Years' War
Modern child rulers
French hunters
People from Saint-Germain-en-Laye
People of the Ancien Régime
People of the Regency of Philippe d'Orléans
Princes of Andorra
Princes of France (Bourbon)
1640s in France
1650s in France
1660s in France
1670s in France
1680s in France
1690s in France
1700s in France
1710s in France
Navarrese titular monarchs
Sons of kings

 Louis XIV was born on 5 September 1638 in the
Louis XIV was born on 5 September 1638 in the  Sensing imminent death, Louis XIII decided to put his affairs in order in the spring of 1643, when Louis XIV was four years old. In defiance of custom, which would have made Queen Anne the sole regent of France, the king decreed that a regency council would rule on his son's behalf. His lack of faith in Queen Anne's political abilities was his primary rationale. He did, however, make the concession of appointing her head of the council.
Louis XIII died on 14 May 1643, and on 18 May, Queen Anne had her husband's will annulled by the '' Parlement de Paris'' (a judicial body comprising mostly nobles and high clergymen). This action abolished the regency council and made Anne the sole Regent of France. Anne exiled some of her husband's ministers (Chavigny, Bouthilier), and she nominated Brienne as her minister of foreign affairs.
Anne kept the direction of religious policy strongly in her hand until 1661; her most important political decisions were to nominate Cardinal Mazarin as her chief minister and the continuation of her late husband's and
Sensing imminent death, Louis XIII decided to put his affairs in order in the spring of 1643, when Louis XIV was four years old. In defiance of custom, which would have made Queen Anne the sole regent of France, the king decreed that a regency council would rule on his son's behalf. His lack of faith in Queen Anne's political abilities was his primary rationale. He did, however, make the concession of appointing her head of the council.
Louis XIII died on 14 May 1643, and on 18 May, Queen Anne had her husband's will annulled by the '' Parlement de Paris'' (a judicial body comprising mostly nobles and high clergymen). This action abolished the regency council and made Anne the sole Regent of France. Anne exiled some of her husband's ministers (Chavigny, Bouthilier), and she nominated Brienne as her minister of foreign affairs.
Anne kept the direction of religious policy strongly in her hand until 1661; her most important political decisions were to nominate Cardinal Mazarin as her chief minister and the continuation of her late husband's and  All this led her to advocate a forceful policy in all matters relating to the King's authority, in a manner that was much more radical than the one proposed by Mazarin. The Cardinal depended totally on Anne's support and had to use all his influence on the Queen to temper some of her radical actions. Anne imprisoned any aristocrat or member of parliament who challenged her will; her main aim was to transfer to her son an absolute authority in the matters of finance and justice. One of the leaders of the Parlement of Paris, whom she had jailed, died in prison.
The ', political heirs of the disaffected feudal aristocracy, sought to protect their traditional feudal privileges from the increasingly centralized royal government. Furthermore, they believed their traditional influence and authority was being usurped by the recently ennobled bureaucrats (the ', or "nobility of the robe"), who administered the kingdom and on whom the monarchy increasingly began to rely. This belief intensified the nobles' resentment.
In 1648, Anne and Mazarin attempted to tax members of the '. The members refused to comply and ordered all of the king's earlier financial edicts burned. Buoyed by the victory of (later known as ') at the Battle of Lens, Mazarin, on Queen Anne's insistence, arrested certain members in a show of force. The most important arrest, from Anne's point of view, concerned Pierre Broussel, one of the most important leaders in the '.
All this led her to advocate a forceful policy in all matters relating to the King's authority, in a manner that was much more radical than the one proposed by Mazarin. The Cardinal depended totally on Anne's support and had to use all his influence on the Queen to temper some of her radical actions. Anne imprisoned any aristocrat or member of parliament who challenged her will; her main aim was to transfer to her son an absolute authority in the matters of finance and justice. One of the leaders of the Parlement of Paris, whom she had jailed, died in prison.
The ', political heirs of the disaffected feudal aristocracy, sought to protect their traditional feudal privileges from the increasingly centralized royal government. Furthermore, they believed their traditional influence and authority was being usurped by the recently ennobled bureaucrats (the ', or "nobility of the robe"), who administered the kingdom and on whom the monarchy increasingly began to rely. This belief intensified the nobles' resentment.
In 1648, Anne and Mazarin attempted to tax members of the '. The members refused to comply and ordered all of the king's earlier financial edicts burned. Buoyed by the victory of (later known as ') at the Battle of Lens, Mazarin, on Queen Anne's insistence, arrested certain members in a show of force. The most important arrest, from Anne's point of view, concerned Pierre Broussel, one of the most important leaders in the '.
 People in France were complaining about the expansion of royal authority, the high rate of taxation, and the reduction of the authority of the Parlement de Paris and other regional representative entities. Paris erupted in rioting as a result, and Anne was forced, under intense pressure, to free Broussel. Moreover, on the night of 9–10 February 1651, when Louis was twelve, a mob of angry Parisians broke into the royal palace and demanded to see their king. Led into the royal bed-chamber, they gazed upon Louis, who was feigning sleep, were appeased, and then quietly departed. The threat to the royal family prompted Anne to flee Paris with the king and his courtiers.
Shortly thereafter, the conclusion of the
People in France were complaining about the expansion of royal authority, the high rate of taxation, and the reduction of the authority of the Parlement de Paris and other regional representative entities. Paris erupted in rioting as a result, and Anne was forced, under intense pressure, to free Broussel. Moreover, on the night of 9–10 February 1651, when Louis was twelve, a mob of angry Parisians broke into the royal palace and demanded to see their king. Led into the royal bed-chamber, they gazed upon Louis, who was feigning sleep, were appeased, and then quietly departed. The threat to the royal family prompted Anne to flee Paris with the king and his courtiers.
Shortly thereafter, the conclusion of the  Legal matters did not escape Louis' attention, as is reflected in the numerous " Great Ordinances" he enacted. Pre-revolutionary France was a patchwork of legal systems, with as many legal customs as there were provinces, and two co-existing legal traditions—
Legal matters did not escape Louis' attention, as is reflected in the numerous " Great Ordinances" he enacted. Pre-revolutionary France was a patchwork of legal systems, with as many legal customs as there were provinces, and two co-existing legal traditions— 
 The death of his maternal uncle King Philip IV of Spain, in 1665, precipitated the War of Devolution. In 1660, Louis had married Philip IV's eldest daughter,
The death of his maternal uncle King Philip IV of Spain, in 1665, precipitated the War of Devolution. In 1660, Louis had married Philip IV's eldest daughter,  French colonies multiplied in Africa, the Americas, and Asia during Louis' reign, and French explorers made important discoveries in North America. In 1673, Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette discovered the Mississippi River. In 1682,
French colonies multiplied in Africa, the Americas, and Asia during Louis' reign, and French explorers made important discoveries in North America. In 1673, Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette discovered the Mississippi River. In 1682,  Meanwhile, diplomatic relations were initiated with distant countries. In 1669,
Meanwhile, diplomatic relations were initiated with distant countries. In 1669,  By attaching nobles to his court at Versailles, Louis achieved increased control over the French aristocracy. According to historian Philip Mansel, the king turned the palace into:
:an irresistible combination of marriage market, employment agency and entertainment capital of aristocratic Europe, boasting the best theatre, opera, music, gambling, sex and (most important) hunting.
Apartments were built to house those willing to pay court to the king. However, the pensions and privileges necessary to live in a style appropriate to their rank were only possible by waiting constantly on Louis. For this purpose, an elaborate court ritual was created wherein the king became the centre of attention and was observed throughout the day by the public. With his excellent memory, Louis could then see who attended him at court and who was absent, facilitating the subsequent distribution of favours and positions. Another tool Louis used to control his nobility was censorship, which often involved the opening of letters to discern their author's opinion of the government and king. Moreover, by entertaining, impressing, and domesticating them with extravagant luxury and other distractions, Louis not only cultivated public opinion of him, but he also ensured the aristocracy remained under his scrutiny.
Louis's extravagance at Versailles extended far beyond the scope of elaborate court rituals. He took delivery of an African elephant as a gift from the king of Portugal. He encouraged leading nobles to live at Versailles. This, along with the prohibition of private armies, prevented them from passing time on their own estates and in their regional power bases, from which they historically waged local wars and plotted resistance to royal authority. Louis thus compelled and seduced the old military aristocracy (the "nobility of the sword") into becoming his ceremonial courtiers, further weakening their power. In their place, he raised commoners or the more recently ennobled bureaucratic aristocracy (the "nobility of the robe"). He judged that royal authority thrived more surely by filling high executive and administrative positions with these men because they could be more easily dismissed than nobles of ancient lineage and entrenched influence. It is believed that Louis's policies were rooted in his experiences during the ''Fronde'', when men of high birth readily took up the rebel cause against their king, who was actually the kinsman of some. This victory over the nobility may thus have ensured the end of major civil wars in France until the French Revolution about a century later.
By attaching nobles to his court at Versailles, Louis achieved increased control over the French aristocracy. According to historian Philip Mansel, the king turned the palace into:
:an irresistible combination of marriage market, employment agency and entertainment capital of aristocratic Europe, boasting the best theatre, opera, music, gambling, sex and (most important) hunting.
Apartments were built to house those willing to pay court to the king. However, the pensions and privileges necessary to live in a style appropriate to their rank were only possible by waiting constantly on Louis. For this purpose, an elaborate court ritual was created wherein the king became the centre of attention and was observed throughout the day by the public. With his excellent memory, Louis could then see who attended him at court and who was absent, facilitating the subsequent distribution of favours and positions. Another tool Louis used to control his nobility was censorship, which often involved the opening of letters to discern their author's opinion of the government and king. Moreover, by entertaining, impressing, and domesticating them with extravagant luxury and other distractions, Louis not only cultivated public opinion of him, but he also ensured the aristocracy remained under his scrutiny.
Louis's extravagance at Versailles extended far beyond the scope of elaborate court rituals. He took delivery of an African elephant as a gift from the king of Portugal. He encouraged leading nobles to live at Versailles. This, along with the prohibition of private armies, prevented them from passing time on their own estates and in their regional power bases, from which they historically waged local wars and plotted resistance to royal authority. Louis thus compelled and seduced the old military aristocracy (the "nobility of the sword") into becoming his ceremonial courtiers, further weakening their power. In their place, he raised commoners or the more recently ennobled bureaucratic aristocracy (the "nobility of the robe"). He judged that royal authority thrived more surely by filling high executive and administrative positions with these men because they could be more easily dismissed than nobles of ancient lineage and entrenched influence. It is believed that Louis's policies were rooted in his experiences during the ''Fronde'', when men of high birth readily took up the rebel cause against their king, who was actually the kinsman of some. This victory over the nobility may thus have ensured the end of major civil wars in France until the French Revolution about a century later.
 Louis decided to persecute Protestants and revoke the 1598
Louis decided to persecute Protestants and revoke the 1598  On 15 October 1685, Louis issued the
On 15 October 1685, Louis issued the  The
The  French armies were generally victorious throughout the war because of Imperial commitments in the Balkans, French logistical superiority, and the quality of French generals such as Condé's famous pupil, François Henri de Montmorency-Bouteville, duc de Luxembourg. His triumphs at the Battles of Fleurus in 1690,
French armies were generally victorious throughout the war because of Imperial commitments in the Balkans, French logistical superiority, and the quality of French generals such as Condé's famous pupil, François Henri de Montmorency-Bouteville, duc de Luxembourg. His triumphs at the Battles of Fleurus in 1690,  Although an attempt to restore James II failed at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690, France accumulated a string of victories from Flanders in the north, Germany in the east, and Italy and Spain in the south, to the high seas and the colonies. Louis personally supervised the captures of
Although an attempt to restore James II failed at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690, France accumulated a string of victories from Flanders in the north, Germany in the east, and Italy and Spain in the south, to the high seas and the colonies. Louis personally supervised the captures of  On his deathbed in 1700, Charles II of Spain unexpectedly changed his will. The clear demonstration of French military superiority for many decades before this time, the pro-French faction at the court of Spain, and even Pope Innocent XII convinced him that France was more likely to preserve his empire intact. He thus offered the entire empire to the Dauphin's second son Philip, Duke of Anjou, provided it remained undivided. Anjou was not in the direct line of French succession, thus his accession would not cause a Franco-Spanish union. If Anjou refused, the throne would be offered to his younger brother Charles, Duke of Berry. If the Duke of Berry declined it, it would go to Archduke Charles, then to the distantly related
On his deathbed in 1700, Charles II of Spain unexpectedly changed his will. The clear demonstration of French military superiority for many decades before this time, the pro-French faction at the court of Spain, and even Pope Innocent XII convinced him that France was more likely to preserve his empire intact. He thus offered the entire empire to the Dauphin's second son Philip, Duke of Anjou, provided it remained undivided. Anjou was not in the direct line of French succession, thus his accession would not cause a Franco-Spanish union. If Anjou refused, the throne would be offered to his younger brother Charles, Duke of Berry. If the Duke of Berry declined it, it would go to Archduke Charles, then to the distantly related  Even before war was officially declared, hostilities began with Imperial aggression in Italy. Once finally declared, the War of the Spanish Succession lasted almost until Louis's death, at great cost to him and France.
The war began with French successes, but the talents of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, and Eugene of Savoy checked these victories and broke the myth of French invincibility. The duo allowed the Palatinate and Austria to occupy Bavaria after their victory at the
Even before war was officially declared, hostilities began with Imperial aggression in Italy. Once finally declared, the War of the Spanish Succession lasted almost until Louis's death, at great cost to him and France.
The war began with French successes, but the talents of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, and Eugene of Savoy checked these victories and broke the myth of French invincibility. The duo allowed the Palatinate and Austria to occupy Bavaria after their victory at the  As a result of the fresh British perspective on the European balance of power, Anglo-French talks began, culminating in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht between Louis, Philip V of Spain,
As a result of the fresh British perspective on the European balance of power, Anglo-French talks began, culminating in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht between Louis, Philip V of Spain,  Louis was a pious and devout king who saw himself as the head and protector of the Catholic Church in France. He made his devotions daily regardless of where he was, following the liturgical calendar regularly. Under the influence of his very religious second wife, he became much stronger in the practice of his Catholic faith. This included banning opera and comedy performances during
Louis was a pious and devout king who saw himself as the head and protector of the Catholic Church in France. He made his devotions daily regardless of where he was, following the liturgical calendar regularly. Under the influence of his very religious second wife, he became much stronger in the practice of his Catholic faith. This included banning opera and comedy performances during 
 Louis generously supported the royal court of France and those who worked under him. He brought the
Louis generously supported the royal court of France and those who worked under him. He brought the  Several reasons have been suggested for the creation of the extravagant and stately palace, as well as the relocation of the monarchy's seat. The memoirist Saint-Simon speculated that Louis viewed Versailles as an isolated power centre where treasonous cabals could be more readily discovered and foiled. There has also been speculation that the revolt of the ''Fronde'' caused Louis to hate Paris, which he abandoned for a country retreat, but his sponsorship of many public works in Paris, such as the establishment of a police force and of street-lighting, lend little credence to this theory. As a further example of his continued care for the capital, Louis constructed the '' Hôtel des Invalides'', a military complex and home to this day for officers and soldiers rendered infirm either by injury or old age. While pharmacology was still quite rudimentary in his day, the ''Invalides'' pioneered new treatments and set new standards for hospice treatment. The conclusion of the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1668 also induced Louis to demolish Paris's northern walls in 1670 and replace them with wide tree-lined boulevards.
Louis also renovated and improved the Louvre and other royal residences.
Several reasons have been suggested for the creation of the extravagant and stately palace, as well as the relocation of the monarchy's seat. The memoirist Saint-Simon speculated that Louis viewed Versailles as an isolated power centre where treasonous cabals could be more readily discovered and foiled. There has also been speculation that the revolt of the ''Fronde'' caused Louis to hate Paris, which he abandoned for a country retreat, but his sponsorship of many public works in Paris, such as the establishment of a police force and of street-lighting, lend little credence to this theory. As a further example of his continued care for the capital, Louis constructed the '' Hôtel des Invalides'', a military complex and home to this day for officers and soldiers rendered infirm either by injury or old age. While pharmacology was still quite rudimentary in his day, the ''Invalides'' pioneered new treatments and set new standards for hospice treatment. The conclusion of the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1668 also induced Louis to demolish Paris's northern walls in 1670 and replace them with wide tree-lined boulevards.
Louis also renovated and improved the Louvre and other royal residences.  Over his lifetime, Louis commissioned numerous works of art to portray himself, among them over 300 formal portraits. The earliest portrayals of Louis already followed the pictorial conventions of the day in depicting the child king as the majestically royal incarnation of France. This idealisation of the monarch continued in later works, which avoided depictions of the effect of smallpox that Louis contracted in 1647. In the 1660s, Louis began to be shown as a Roman emperor, the god Apollo, or
Over his lifetime, Louis commissioned numerous works of art to portray himself, among them over 300 formal portraits. The earliest portrayals of Louis already followed the pictorial conventions of the day in depicting the child king as the majestically royal incarnation of France. This idealisation of the monarch continued in later works, which avoided depictions of the effect of smallpox that Louis contracted in 1647. In the 1660s, Louis began to be shown as a Roman emperor, the god Apollo, or  Louis loved
Louis loved  Some historians point out that it was a customary demonstration of piety in those days to exaggerate one's sins. Thus they do not place much emphasis on Louis' deathbed declarations in assessing his accomplishments. Rather, they focus on military and diplomatic successes, such as how he placed a French prince on the Spanish throne. This, they contend, ended the threat of an aggressive Spain that historically interfered in domestic French politics. These historians also emphasise the effect of Louis' wars in expanding France's boundaries and creating more defensible frontiers that preserved France from invasion until the Revolution.
Arguably, Louis also applied himself indirectly to "the alleviation of the burdens of issubjects." For example, he patronised the arts, encouraged industry, fostered trade and commerce, and sponsored the founding of an overseas empire. Moreover, the significant reduction in civil wars and aristocratic rebellions during his reign are seen by these historians as the result of Louis' consolidation of royal authority over feudal elites. In their analysis, his early reforms centralised France and marked the birth of the modern French state. They regard the political and military victories as well as numerous cultural achievements as the means by which Louis helped raise France to a preeminent position in Europe. Europe came to admire France for its military and cultural successes, power, and sophistication. Europeans generally began to emulate French manners, values, goods, and deportment. French became the universal language of the European elite.
Louis' detractors have argued that his considerable foreign, military and domestic expenditure impoverished and bankrupted France. His supporters, however, distinguish the state, which was impoverished, from France, which was not. As supporting evidence, they cite the literature of the time, such as the social commentary in Montesquieu's '' Persian Letters''.
Alternatively, Louis' critics attribute the social upheaval culminating in the French Revolution to his failure to reform French institutions while the monarchy was still secure. Other scholars counter that there was little reason to reform institutions that largely worked well under Louis. They also maintain that events occurring almost 80 years after his death were not reasonably foreseeable to Louis and that in any case, his successors had sufficient time to initiate reforms of their own.
Louis has often been criticised for his vanity. The memoirist Saint-Simon, who claimed that Louis slighted him, criticised him thus:
Some historians point out that it was a customary demonstration of piety in those days to exaggerate one's sins. Thus they do not place much emphasis on Louis' deathbed declarations in assessing his accomplishments. Rather, they focus on military and diplomatic successes, such as how he placed a French prince on the Spanish throne. This, they contend, ended the threat of an aggressive Spain that historically interfered in domestic French politics. These historians also emphasise the effect of Louis' wars in expanding France's boundaries and creating more defensible frontiers that preserved France from invasion until the Revolution.
Arguably, Louis also applied himself indirectly to "the alleviation of the burdens of issubjects." For example, he patronised the arts, encouraged industry, fostered trade and commerce, and sponsored the founding of an overseas empire. Moreover, the significant reduction in civil wars and aristocratic rebellions during his reign are seen by these historians as the result of Louis' consolidation of royal authority over feudal elites. In their analysis, his early reforms centralised France and marked the birth of the modern French state. They regard the political and military victories as well as numerous cultural achievements as the means by which Louis helped raise France to a preeminent position in Europe. Europe came to admire France for its military and cultural successes, power, and sophistication. Europeans generally began to emulate French manners, values, goods, and deportment. French became the universal language of the European elite.
Louis' detractors have argued that his considerable foreign, military and domestic expenditure impoverished and bankrupted France. His supporters, however, distinguish the state, which was impoverished, from France, which was not. As supporting evidence, they cite the literature of the time, such as the social commentary in Montesquieu's '' Persian Letters''.
Alternatively, Louis' critics attribute the social upheaval culminating in the French Revolution to his failure to reform French institutions while the monarchy was still secure. Other scholars counter that there was little reason to reform institutions that largely worked well under Louis. They also maintain that events occurring almost 80 years after his death were not reasonably foreseeable to Louis and that in any case, his successors had sufficient time to initiate reforms of their own.
Louis has often been criticised for his vanity. The memoirist Saint-Simon, who claimed that Louis slighted him, criticised him thus: