|
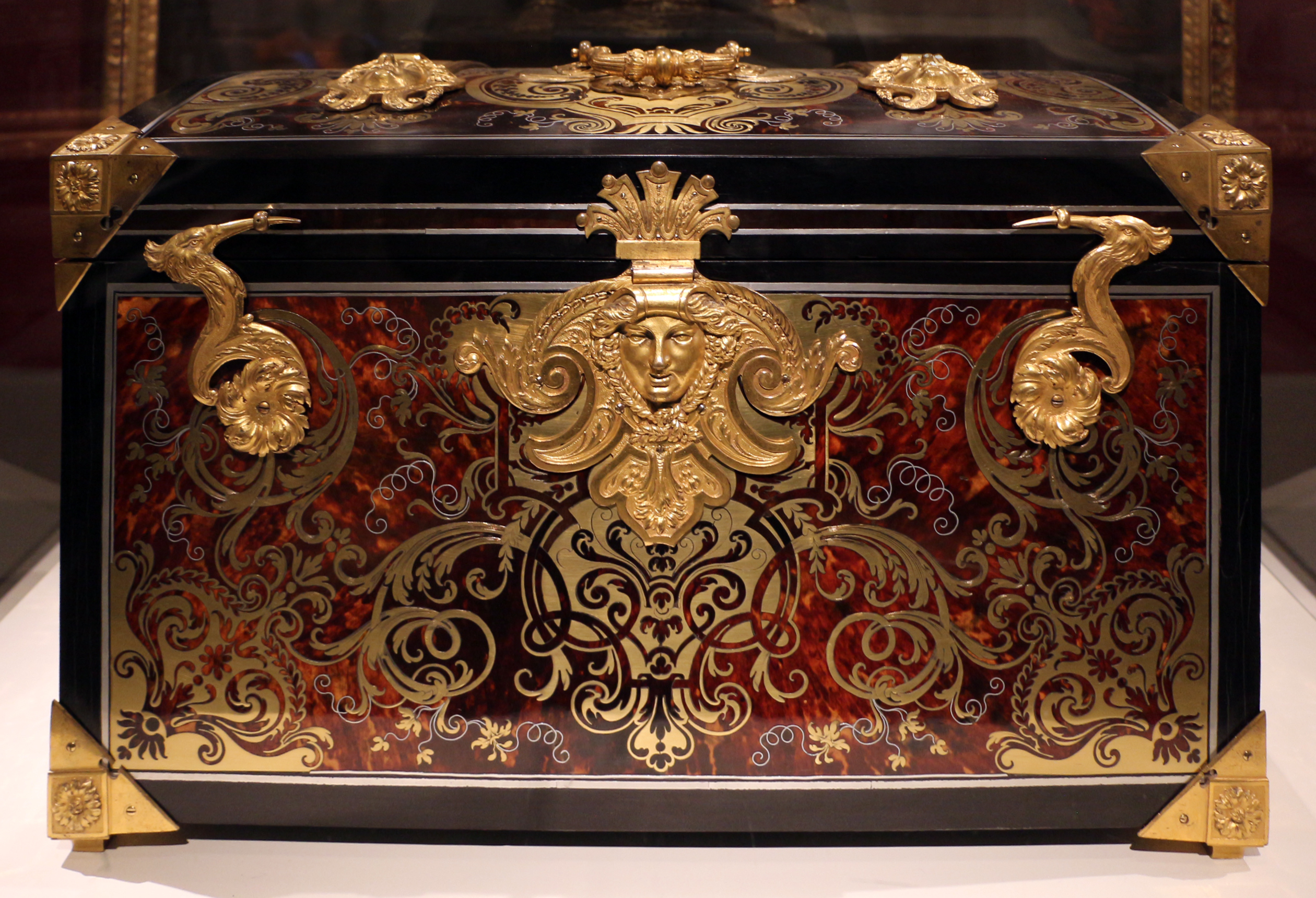
Marquetry
Marquetry (also spelled as marqueterie; from the French ''marqueter'', to variegate) is the art and craft of applying pieces of veneer to a structure to form decorative patterns, designs or pictures. The technique may be applied to case furniture or even seat furniture, to decorative small objects with smooth, veneerable surfaces or to freestanding pictorial panels appreciated in their own right. Marquetry differs from the more ancient craft of inlay, or intarsia, in which a solid body of one material is cut out to receive sections of another to form the surface pattern. The word derives from a Middle French word meaning "inlaid work". Materials The veneers used are primarily woods, but may include bone, ivory, turtle-shell (conventionally called " tortoiseshell"), mother-of-pearl, pewter, brass or fine metals. Marquetry using colored straw was a specialty of some European spa resorts from the end of the 18th century. Many exotic woods as well as common European variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straw Marquetry
Straw marquetry is a craft very similar to that of wood marquetry, except that straw replaces the wood veneer. It is thought to have first been practised in the East; examples were brought to England in the 17th century. To mimic the varying shades of wood veneer, wheat or oat straw has to be split, then soaked in cold, warm, or hot water. The strips are then ironed, and there will be a variety of tones from pale gold to deepest dark brown. There are accounts of nuns in France and Switzerland making a variety of items using straw marquetry. The most famous straw marquetry was practised by prisoners of war from the Napoleonic wars. Dartmoor and other prisons had been built for them; the prison most famous for straw marquetry was Norman Cross, Huntingdon. Easter eggs are decorated with straw applique, especially in Eastern European countries. Geometric shapes, stars and flower motifs are the most common themes. There is a slight difference in the way the straw is prepared, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intarsia
Intarsia is a form of wood inlaying that is similar to marquetry. The start of the practice dates from before the seventh century AD. The technique of intarsia inlays sections of wood (at times with contrasting ivory or bone, or mother-of-pearl) within the solid wood matrix of floors and walls or of tabletops and other furniture; by contrast marquetry assembles a pattern out of veneers glued upon the carcass. The word ''intarsia'' may derive from the Latin word '' interserere'' (to insert). Certosina is a variant also using pieces of ivory, bone or mother of pearl. Intarsia is mostly used of Italian, or at least European work. Similar techniques are found over much of Asia and the Middle East. History When Egypt came under Arab rule in the seventh century, indigenous arts of intarsia and wood inlay, which lent themselves to non-representational decors and tiling patterns, spread throughout the Maghreb. The technique of intarsia was already perfected in Islamic Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inlay
Inlay covers a range of techniques in sculpture and the decorative arts for inserting pieces of contrasting, often colored materials into depressions in a base object to form Ornament (art), ornament or pictures that normally are flush with the matrix. A great range of materials have been used both for the base or matrix and for the inlays inserted into it. Inlay is commonly used in the production of decorative furniture, where pieces of colored wood, precious metals or even diamonds are inserted into the surface of the carcass using various matrices including clear coats and varnishes. Lutherie inlays are frequently used as decoration and marking on musical instruments, particularly the smaller strings. Perhaps the most famous example of furniture inlay is that of Andre-Charles Boulle (11 November 1642 – 28 February 1732) which is known as Boulle Work and evolved in part from inlay produced in Italy during the late 15th century at the ''Studiolo'' for Federico da Mont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
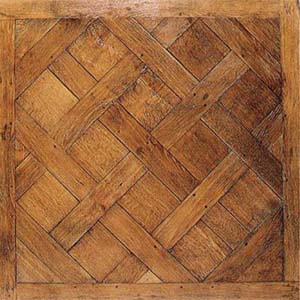
Parquetry
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Timber contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, lime, pine, maple etc. are sometimes employed, and in the more expensive kinds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortoiseshell Material
Tortoiseshell or tortoise shell is a material produced from the shells of the larger species of tortoise and turtle, mainly the hawksbill sea turtle, which is a critically endangered species according to the IUCN Red List largely because of its exploitation for this trade. The large size, fine color, and unusual form of the hawksbill's scutes make it especially suitable. The distinctive patterning is referred to in names such as the tortoiseshell cat, several breeds of guinea pig, and the common names of several species of the butterfly genera '' Nymphalis'' and '' Aglais'', and some other uses. Uses Tortoiseshell was widely used from ancient times in the North and in Asia, until the trade was banned in 2014. It was used, normally in thin slices or pieces, in the manufacture of a wide variety of items such as combs, small boxes and frames, inlays in furniture (known as Boulle Work carried out by André-Charles Boulle), and other items: frames for spectacles, guitar picks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Veneer
In woodworking, veneer refers to thin slices of wood and sometimes bark, usually thinner than 3 mm (1/8 inch), that typically are glued onto core panels (typically, wood, particle board or medium-density fiberboard) to produce flat panels such as doors, tops and panels for cabinets, parquet floors and parts of furniture. They are also used in marquetry. Plywood consists of three or more layers of veneer. Normally, each is glued with its grain at right angles to adjacent layers for strength. Veneer beading is a thin layer of decorative edging placed around objects, such as jewelry boxes. Veneer is also used to replace decorative papers in Wood Veneer HPL. Background Veneer is obtained either by "peeling" the trunk of a tree or by slicing large rectangular blocks of wood known as flitches. The appearance of the grain and figure in wood comes from slicing through the growth rings of a tree and depends upon the angle at which the wood is sliced. There are three main ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parquetry Table
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Timber contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, lime, pine, maple etc. are sometimes employed, and in the more expensive kinds the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietra Dura
''Pietra dura'' () or ''pietre dure'' () ( see below), called parchin kari or parchinkari ( fa, ) in the Indian Subcontinent, is a term for the inlay technique of using cut and fitted, highly polished colored stones to create images. It is considered a decorative art. The stonework, after the work is assembled loosely, is glued stone-by-stone to a substrate after having previously been "sliced and cut in different shape sections; and then assembled together so precisely that the contact between each section was practically invisible". Stability was achieved by grooving the undersides of the stones so that they interlocked, rather like a jigsaw puzzle, with everything held tautly in place by an encircling 'frame'. Many different colored stones, particularly marbles, were used, along with semiprecious, and even precious stones. It first appeared in Rome in the 16th century, reaching its full maturity in Florence. Pietra dura items are generally crafted on green, white or black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortoiseshell
Tortoiseshell or tortoise shell is a material produced from the shells of the larger species of tortoise and turtle, mainly the hawksbill sea turtle, which is a critically endangered species according to the IUCN Red List largely because of its exploitation for this trade. The large size, fine color, and unusual form of the hawksbill's scutes make it especially suitable. The distinctive patterning is referred to in names such as the tortoiseshell cat, several breeds of guinea pig, and the common names of several species of the butterfly genera '' Nymphalis'' and '' Aglais'', and some other uses. Uses Tortoiseshell was widely used from ancient times in the North and in Asia, until the trade was banned in 2014. It was used, normally in thin slices or pieces, in the manufacture of a wide variety of items such as combs, small boxes and frames, inlays in furniture (known as Boulle Work carried out by André-Charles Boulle), and other items: frames for spectacles, guitar picks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's administrative limits as of 2022. Metropolitan City of Naples, Its province-level municipality is the third-most populous Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 3,115,320 residents, and Naples metropolitan area, its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately 20 miles. Founded by Greeks in the 1st millennium BC, first millennium BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope ( grc, Παρθενόπη) was established on the Pizzofalcone hill. In the sixth century BC, it was refounded as Neápolis. The city was an important part of Magna Graecia, played a major role in the merging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmati
The Cosmati were a Roman family, seven members of which, for four generations, were skilful architects, sculptors and workers in decorative geometric mosaic, mostly for church floors. Their name is commemorated in the genre of Cosmatesque work, often just called "Cosmati", a technique of '' opus sectile'' ("cut work") formed of elaborate inlays of small triangles and rectangles of colored stones and glass mosaics set into stone matrices or encrusted upon stone surfaces. Bands, panels and shaped reserves of intricate mosaic alternate with contrasting bands, guilloches and simple geometric shapes of plain white marble. Pavements and revetments were executed in Cosmatesque technique, columns were inlaid with fillets and bands, and immovable church furnishings like cathedras and '' ambones'' were similarly treated. In addition, members of the Cosmati engaged in commerce in ancient sculptures, some unearthed in the course of excavating for marbles for reuse. More than one ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
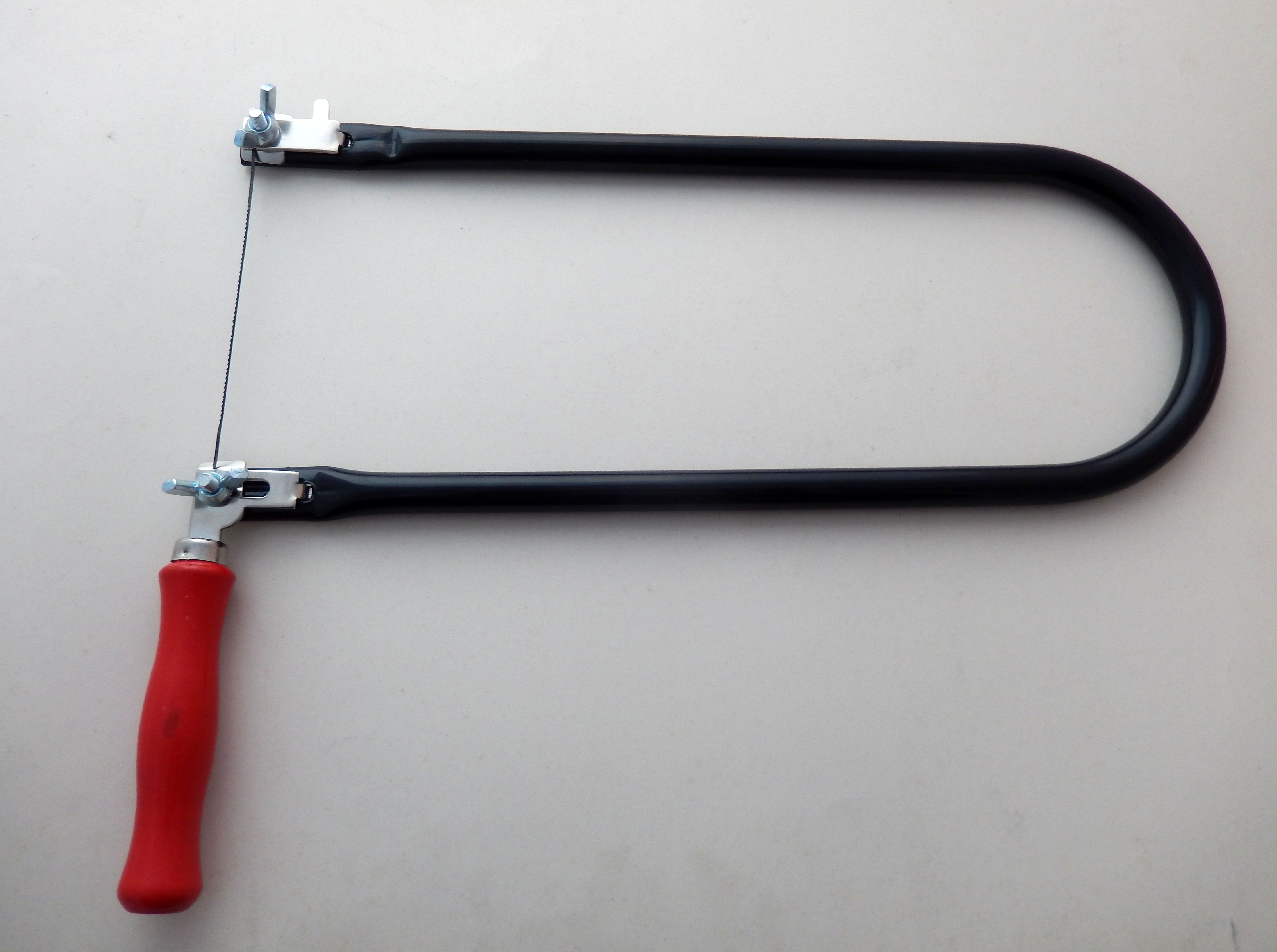
Fretsaw
The fretsaw is a bow saw used for intricate cutting work which often incorporates tight curves. Although the coping saw is often used for similar work, the fretsaw is capable of much tighter radii and more delicate work. It has a distinctive appearance due to the depth of its frame (typically between ), which together with the relatively short blade makes this tool appear somewhat out of proportion compared with most other saws. Compared with the coping saw it has much shallower blades, which are usually extra-fine, up to . This allows much tighter curves to be cut—with many blades even sharp corners are possible—but the blades are also much more fragile compared with that of a coping saw. Unlike the coping saw, the blade has a fixed orientation in relation to the frame. This means that the fretsaw is less useful when cutting long narrow components, but the increased depth of the frame does allow access much further from the edge of the board. The fretsaw is similar in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |