Liquid Neon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neon is a
 Neon was discovered in 1898 by the British chemists Sir
Neon was discovered in 1898 by the British chemists Sir
 Neon has three
Neon has three
at the
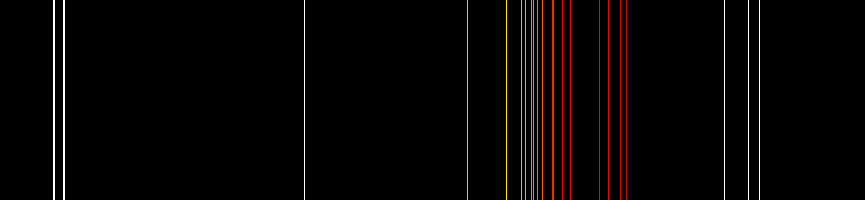 Neon plasma has the most intense light discharge at normal voltages and currents of all the noble gases. The average color of this light to the human eye is red-orange due to many lines in this range; it also contains a strong green line, which is hidden, unless the visual components are dispersed by a spectroscope.
Two quite different kinds of
Neon plasma has the most intense light discharge at normal voltages and currents of all the noble gases. The average color of this light to the human eye is red-orange due to many lines in this range; it also contains a strong green line, which is hidden, unless the visual components are dispersed by a spectroscope.
Two quite different kinds of
 Stable isotopes of neon are produced in stars. Neon's most abundant isotope 20Ne (90.48%) is created by the
Stable isotopes of neon are produced in stars. Neon's most abundant isotope 20Ne (90.48%) is created by the
 Neon is the first
Neon is the first
Neon
at ''
WebElements.com – Neon
Neon Museum, Las Vegas
{{Authority control Chemical elements Noble gases Coolants Refrigerants Laser gain media Industrial gases
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Ne and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
10. It is a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemi ...
. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas
In physics and chemistry, "monatomic" is a combination of the words "mono" and "atomic", and means "single atom". It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is a gas in which atoms are not bound to each other. Examples at standard conditions ...
under standard conditions
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union o ...
, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
and xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
) in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
, argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a atomic electron transition, transition from a high energy state to a lower energy st ...
. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, , neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic bond, ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a Chemical bond, chemical electronic bond; they are c ...
and clathrates
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word ''clathrate'' is derived from the Latin (), meaning ‘with bars, latticed’. Most clathrate compounds are polymeric and completely envelop t ...
.
During cosmic nucleogenesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
of the elements, large amounts of neon are built up from the alpha-capture fusion process in stars. Although neon is a very common element in the universe and solar system (it is fifth in cosmic abundance after hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
and carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
), it is rare on Earth. It composes about 18.2 ppm of air by volume (this is about the same as the molecular or mole fraction) and a smaller fraction in Earth's crust. The reason for neon's relative scarcity on Earth and the inner (terrestrial) planets is that neon is highly volatile and forms no compounds to fix it to solids. As a result, it escaped from the planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System a ...
s under the warmth of the newly ignited Sun in the early Solar System. Even the outer atmosphere of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
is somewhat depleted of neon, although for a different reason.
Neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in low-volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defi ...
age neon glow lamps, high-voltage discharge tubes and neon advertising signs. The red emission line from neon also causes the well known red light of helium–neon laser
A helium–neon laser or He-Ne laser, is a type of gas laser whose high energetic medium gain medium consists of a mixture of 10:1 ratio of helium and neon at a total pressure of about 1 torr inside of a small electrical discharge. The best ...
s. Neon is used in some plasma tube and refrigerant applications but has few other commercial uses. It is commercially extracted by the fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
of liquid air
Liquid air is air that has been cooled to very low temperatures ( cryogenic temperatures), so that it has condensed into a pale blue mobile liquid. To thermally insulate it from room temperature, it is stored in specialized containers ( vacuum in ...
. Since air is the only source, it is considerably more expensive than helium.
History
 Neon was discovered in 1898 by the British chemists Sir
Neon was discovered in 1898 by the British chemists Sir William Ramsay
Sir William Ramsay (; 2 October 1852 – 23 July 1916) was a Scottish chemist who discovered the noble gases and received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1904 "in recognition of his services in the discovery of the inert gaseous elements ...
(1852–1916) and Morris Travers
Morris William Travers, FRS (24 January 1872 – 25 August 1961) was an English chemist who worked with Sir William Ramsay in the discovery of xenon, neon and krypton. His work on several of the rare gases earned him the name ''Rare gas T ...
(1872–1961) in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. Neon was discovered when Ramsay chilled a sample of air until it became a liquid, then warmed the liquid and captured the gases as they boiled off. The gases nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
, and argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
had been identified, but the remaining gases were isolated in roughly their order of abundance, in a six-week period beginning at the end of May 1898. First to be identified was krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
. The next, after krypton had been removed, was a gas which gave a brilliant red light under spectroscopic discharge. This gas, identified in June, was named "neon", the Greek analogue of the Latin ''novum'' ('new') suggested by Ramsay's son. The characteristic brilliant red-orange color emitted by gaseous neon when excited electrically was noted immediately. Travers later wrote: "the blaze of crimson light from the tube told its own story and was a sight to dwell upon and never forget."
A second gas was also reported along with neon, having approximately the same density as argon but with a different spectrum – Ramsay and Travers named it ''metargon''.
However, subsequent spectroscopic analysis revealed it to be argon contaminated with carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
. Finally, the same team discovered xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
by the same process, in September 1898.
Neon's scarcity precluded its prompt application for lighting along the lines of Moore tube
Daniel McFarlan Moore (February 27, 1869 – June 15, 1936) was a U.S. electrical engineer and inventor. He developed a novel light source, the "Moore lamp", and a business that produced them in the early 1900s. The Moore lamp was the first co ...
s, which used nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and which were commercialized in the early 1900s. After 1902, Georges Claude
Georges Claude (24 September 187023 May 1960) was a French engineer and inventor. He is noted for his early work on the industrial liquefaction of air, for the invention and commercialization of neon lighting, and for a large experiment on genera ...
's company Air Liquide
Air Liquide S.A. (; ; literally "liquid air"), is a French multinational company which supplies industrial gases and services to various industries including medical, chemical and electronic manufacturers. Founded in 1902, after Linde it is ...
produced industrial quantities of neon as a byproduct of his air-liquefaction business. In December 1910 Claude demonstrated modern neon lighting
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode ...
based on a sealed tube of neon. Claude tried briefly to sell neon tubes for indoor domestic lighting, due to their intensity, but the market failed because homeowners objected to the color. In 1912, Claude's associate began selling neon discharge tubes as eye-catching advertising signs and was instantly more successful. Neon tubes were introduced to the U.S. in 1923 with two large neon signs bought by a Los Angeles Packard car dealership. The glow and arresting red color made neon advertising completely different from the competition. The intense color and vibrancy of neon equated with American society at the time, suggesting a "century of progress" and transforming cities into sensational new environments filled with radiating advertisements and "electro-graphic architecture".
Neon played a role in the basic understanding of the nature of atoms in 1913, when J. J. Thomson
Sir Joseph John Thomson (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, credited with the discovery of the electron, the first subatomic particle to be discovered.
In 1897, Thomson showed that c ...
, as part of his exploration into the composition of canal rays
An anode ray (also positive ray or canal ray) is a beam of positive ions that is created by certain types of gas-discharge tubes. They were first observed in Crookes tubes during experiments by the German scientist Eugen Goldstein, in 1886. Later ...
, channeled streams of neon ions through a magnetic and an electric field and measured the deflection of the streams with a photographic plate. Thomson observed two separate patches of light on the photographic plate (see image), which suggested two different parabolas of deflection. Thomson eventually concluded that some of the atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
s in the neon gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
were of higher mass than the rest. Though not understood at the time by Thomson, this was the first discovery of isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
s of stable
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables in use today; the ...
atoms. Thomson's device was a crude version of the instrument we now term a mass spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used ...
.
Isotopes
stable isotope
The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abundanc ...
s: 20Ne (90.48%), 21Ne (0.27%) and 22Ne (9.25%).
21Ne and 22Ne are partly primordial and partly nucleogenic A nucleogenic isotope, or nuclide, is one that is produced by a natural terrestrial nuclear reaction, other than a reaction beginning with cosmic rays (the latter nuclides by convention are called by the different term cosmogenic). The nuclear react ...
(i.e. made by nuclear reactions of other nuclides with neutrons or other particles in the environment) and their variations in natural abundance
In physics, natural abundance (NA) refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass (a weighted average, weighted by mole-fraction abundance figures) of these isotopes is the atomic ...
are well understood. In contrast, 20Ne (the chief primordial isotope
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
made in stellar nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
) is not known to be nucleogenic or radiogenic
A radiogenic nuclide is a nuclide that is produced by a process of radioactive decay. It may itself be radioactive (a radionuclide) or stable (a stable nuclide).
Radiogenic nuclides (more commonly referred to as radiogenic isotopes) form some of ...
. The causes of the variation of 20Ne in the Earth have thus been hotly debated.
The principal nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
s generating nucleogenic neon isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
s start from 24Mg and 25Mg, which produce 21Ne and 22Ne respectively, after neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, ...
and immediate emission of an alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
. The neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
s that produce the reactions are mostly produced by secondary spallation reactions from alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produce ...
s, in turn derived from uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
-series decay chain
In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to a series of radioactive decays of different radioactive decay products as a sequential series of transformations. It is also known as a "radioactive cascade". Most radioisotopes do not decay direct ...
s. The net result yields a trend towards lower 20Ne/22Ne and higher 21Ne/22Ne ratios observed in uranium-rich rocks such as granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
s.Resources on Isotopes Periodic Table--Neonat the
U.S. Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
, by Eric Caldwell, posted January 2004, retrieved February 10, 2011
In addition, isotopic analysis of exposed terrestrial rocks has demonstrated the cosmogenic
Cosmogenic nuclides (or cosmogenic isotopes) are rare nuclides (isotopes) created when a high-energy cosmic ray interacts with the nucleus of an ''in situ'' Solar System atom, causing nucleons (protons and neutrons) to be expelled from the atom ...
(cosmic ray) production of 21Ne. This isotope is generated by spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary p ...
reactions on magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
, and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
. By analyzing all three isotopes, the cosmogenic component can be resolved from magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
tic neon and nucleogenic neon. This suggests that neon will be a useful tool in determining cosmic exposure ages of surface rocks and meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
s.
Neon in solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sola ...
contains a higher proportion of 20Ne than nucleogenic and cosmogenic sources. Neon content observed in samples of volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es and diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of car ...
s is also enriched in 20Ne, suggesting a primordial, possibly solar origin.
Characteristics
Neon is the second-lightest noble gas, afterhelium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
. It glows reddish-orange in a vacuum discharge tube. It has over 40 times the refrigerating capacity (per unit volume) of liquid helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
and three times that of liquid hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
. In most applications it is a less expensive refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Ref ...
than helium.
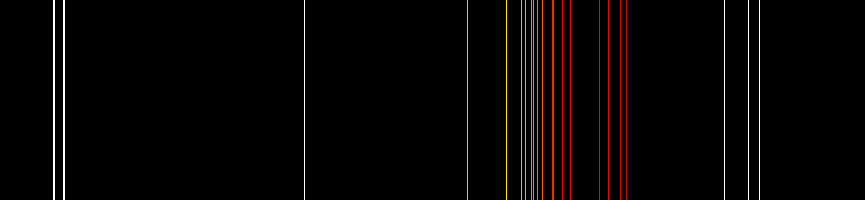 Neon plasma has the most intense light discharge at normal voltages and currents of all the noble gases. The average color of this light to the human eye is red-orange due to many lines in this range; it also contains a strong green line, which is hidden, unless the visual components are dispersed by a spectroscope.
Two quite different kinds of
Neon plasma has the most intense light discharge at normal voltages and currents of all the noble gases. The average color of this light to the human eye is red-orange due to many lines in this range; it also contains a strong green line, which is hidden, unless the visual components are dispersed by a spectroscope.
Two quite different kinds of neon lighting
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode ...
are in common use. Neon glow lamps are generally tiny, with most operating between 100 and 250 volts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Definit ...
. They have been widely used as power-on indicators and in circuit-testing equipment, but light-emitting diodes
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (cor ...
(LEDs) now dominate in those applications. These simple neon devices were the forerunners of plasma displays and plasma television screens. Paid access. Neon sign
In the signage industry, neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. They are the most common use for neon lighting, which was first demonstrated in a modern form in Decem ...
s typically operate at much higher voltages (2–15 kilovolt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defini ...
s), and the luminous tubes are commonly meters long. The glass tubing is often formed into shapes and letters for signage, as well as architectural and artistic applications.
Occurrence
 Stable isotopes of neon are produced in stars. Neon's most abundant isotope 20Ne (90.48%) is created by the
Stable isotopes of neon are produced in stars. Neon's most abundant isotope 20Ne (90.48%) is created by the nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifest ...
of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
and carbon in the carbon-burning process
The carbon-burning process or carbon fusion is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in the cores of massive stars (at least 8 \beginM_\odot\end at birth) that combines carbon into other elements. It requires high temperatures (> 5& ...
of stellar nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
. This requires temperatures above 500 megakelvin
List of orders of magnitude for temperature
Detailed list for 100 K to 1000 K
Most ordinary human activity takes place at temperatures of this order of magnitude. Circumstances where water naturally occurs in liquid form are shown in light gre ...
s, which occur in the cores of stars of more than 8 solar masses.
Neon is abundant on a universal scale; it is the fifth most abundant chemical element in the universe by mass, after hydrogen, helium, oxygen, and carbon (see chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
). Its relative rarity on Earth, like that of helium, is due to its relative lightness, high vapor pressure at very low temperatures, and chemical inertness, all properties which tend to keep it from being trapped in the condensing gas and dust clouds that formed the smaller and warmer solid planets like Earth.
Neon is monatomic, making it lighter than the molecules of diatomic nitrogen and oxygen which form the bulk of Earth's atmosphere; a balloon filled with neon will rise in air, albeit more slowly than a helium balloon.
Neon's abundance in the universe is about 1 part in 750; in the Sun and presumably in the proto-solar system nebula, about 1 part in 600. The Galileo spacecraft
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was ...
atmospheric entry probe found that even in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter, the abundance of neon is reduced (depleted) by about a factor of 10, to a level of 1 part in 6,000 by mass. This may indicate that even the ice-planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System a ...
s, which brought neon into Jupiter from the outer solar system, formed in a region which was too warm to retain the neon atmospheric component (abundances of heavier inert gases on Jupiter are several times that found in the Sun).
Neon comprises 1 part in 55,000 in the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
, or 18.2 ppm by volume (this is about the same as the molecule or mole fraction), or 1 part in 79,000 of air by mass. It comprises a smaller fraction in the crust. It is industrially produced by cryogenic fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
of liquefied air.
On 17 August 2015, based on studies with the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer
The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE; ) was a NASA lunar exploration and technology demonstration mission. It was launched on a Minotaur V rocket from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on September 7, 2013. During its sev ...
(LADEE) spacecraft, NASA scientists reported the detection of neon in the exosphere
The exosphere ( grc, ἔξω "outside, external, beyond", grc, σφαῖρα "sphere") is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the densit ...
of the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
.
Chemistry
 Neon is the first
Neon is the first p-block
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ...
noble gas, and the first element with a true octet of electrons. It is inert: as is the case with its lighter analogue, helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
, no strongly bound neutral molecules containing neon have been identified. The ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s Ar">argon.html" ;"title="eargon">Arsup>+, [Nehydrogen">H">argon">Ar">argon.html" ;"title="eargon">Arsup>+, [Nehydrogen">Hsup>+, and [HeNe]+ have been observed from optical and mass spectrometry, mass spectrometric studies. Solid neon clathrate hydrate was produced from water ice and neon gas at pressures 350–480 MPa and temperatures about −30 °C. Ne atoms are not bonded to water and can freely move through this material. They can be extracted by placing the clathrate into a vacuum chamber for several days, yielding ice XVI
Ice XVI is the least dense (0.81 g/cm) experimentally obtained crystalline form of ice. It is topologically equivalent to the empty structure of sII clathrate hydrates. It was first obtained in 2014 by removing gas molecules from a neon clathr ...
, the least dense crystalline form of water.
The familiar Pauling electronegativity scale
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
relies upon chemical bond energies, but such values have obviously not been measured for inert helium and neon. The Allen electronegativity scale, which relies only upon (measurable) atomic energies, identifies neon as the most electronegative element, closely followed by fluorine and helium.
The triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the subli ...
temperature of neon (24.5561 K) is a defining fixed point in the International Temperature Scale of 1990
The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) is an equipment calibration standard specified by the International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM) for making measurements on the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales. It is an appro ...
.
Production
Neon is produced from air incryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cr ...
air-separation plants. A gas-phase mixture mainly of nitrogen, neon, and helium is withdrawn from the main condenser at the top of the high-pressure air-separation column and fed to the bottom of a side column for rectification
Rectification has the following technical meanings:
Mathematics
* Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points
* Rectifiable curve, in mathematics
* Recti ...
of the neon. It can then be further purified from helium.
About 70% of global neon supply is produced in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
as a by-product of steel production in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. , the company Iceblick, with plants in Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
and Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, supplies 65 per cent of the world's production of neon, as well as 15% of the krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often ...
and xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
.
2022 shortage
Global neon prices jumped by about 600% after the2014 Russian annexation of Crimea
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War.
The events in Kyiv th ...
, spurring some chip manufacturers to start shifting away from Russian and Ukrainian suppliers and toward suppliers in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
also shut down two companies in Ukraine: LLC «Cryoin engineering» () and LLC «Inhaz» () located in Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
and Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russian i ...
respectively; that produced about half of the global supply. The closure was predicted to likely exacerbate COVID-19 chip shortage,Ukraine war flashes neon warning lights for chipsReuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters Corporation. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency was estab ...
, 2022-02-25 which may further shift neon production to China.
Applications
Neon is often used in signs and produces an unmistakable bright reddish-orange light. Although tube lights with other colors are often called "neon", they use differentnoble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemi ...
es or varied colors of fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
lighting.
Neon is used in vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
s, high-voltage indicators, lightning arrester
A lightning arrester (alternative spelling lightning arrestor) (also called lightning isolator) is a device, essentially an air gap between an electric wire and ground, used on electric power transmission and telecommunication systems to protect ...
s, wavemeter An absorption wavemeter is a simple electronic instrument used to measure the frequency of radio waves. It is an older method of measuring frequency, widely used from the birth of radio in the early 20th century until the 1970s, when the developmen ...
tubes, television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
tubes, and helium–neon laser
A helium–neon laser or He-Ne laser, is a type of gas laser whose high energetic medium gain medium consists of a mixture of 10:1 ratio of helium and neon at a total pressure of about 1 torr inside of a small electrical discharge. The best ...
s. Liquefied neon is commercially used as a cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cr ...
refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Ref ...
in applications not requiring the lower temperature range attainable with more extreme liquid-helium refrigeration.
Neon, as liquid or gas, is relatively expensive – for small quantities, the price of liquid neon can be more than 55 times that of liquid helium. Driving neon's expense is the rarity of neon, which, unlike helium, can only be obtained in usable quantities by filtering it out of the atmosphere.
Semiconductor industry
gas mixtures that include neon are used to power lasers forEUV lithography
Extreme ultraviolet lithography (also known as EUV or EUVL) is an optical lithography technology used in steppers, machines that make integrated circuits (ICs) for computers and other electronic devices. It uses a range of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) ...
.
See also
*Expansion ratio The expansion ratio of a liquefied and cryogenic substance is the volume of a given amount of that substance in liquid form compared to the volume of the same amount of substance in gaseous form, at room temperature and normal atmospheric pressur ...
* Neon sign
In the signage industry, neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. They are the most common use for neon lighting, which was first demonstrated in a modern form in Decem ...
* Neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and Penning mixture, other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cold ...
References
External links
Neon
at ''
The Periodic Table of Videos
''Periodic Videos'' (also known as ''The Periodic Table of Videos'') is a video project and YouTube channel on chemistry. It consists of a series of videos about chemical elements and the periodic table, with additional videos on other topics i ...
'' (University of Nottingham)
WebElements.com – Neon
Neon Museum, Las Vegas
{{Authority control Chemical elements Noble gases Coolants Refrigerants Laser gain media Industrial gases