Limehouse Causeway November 1936 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Limehouse is a district in the
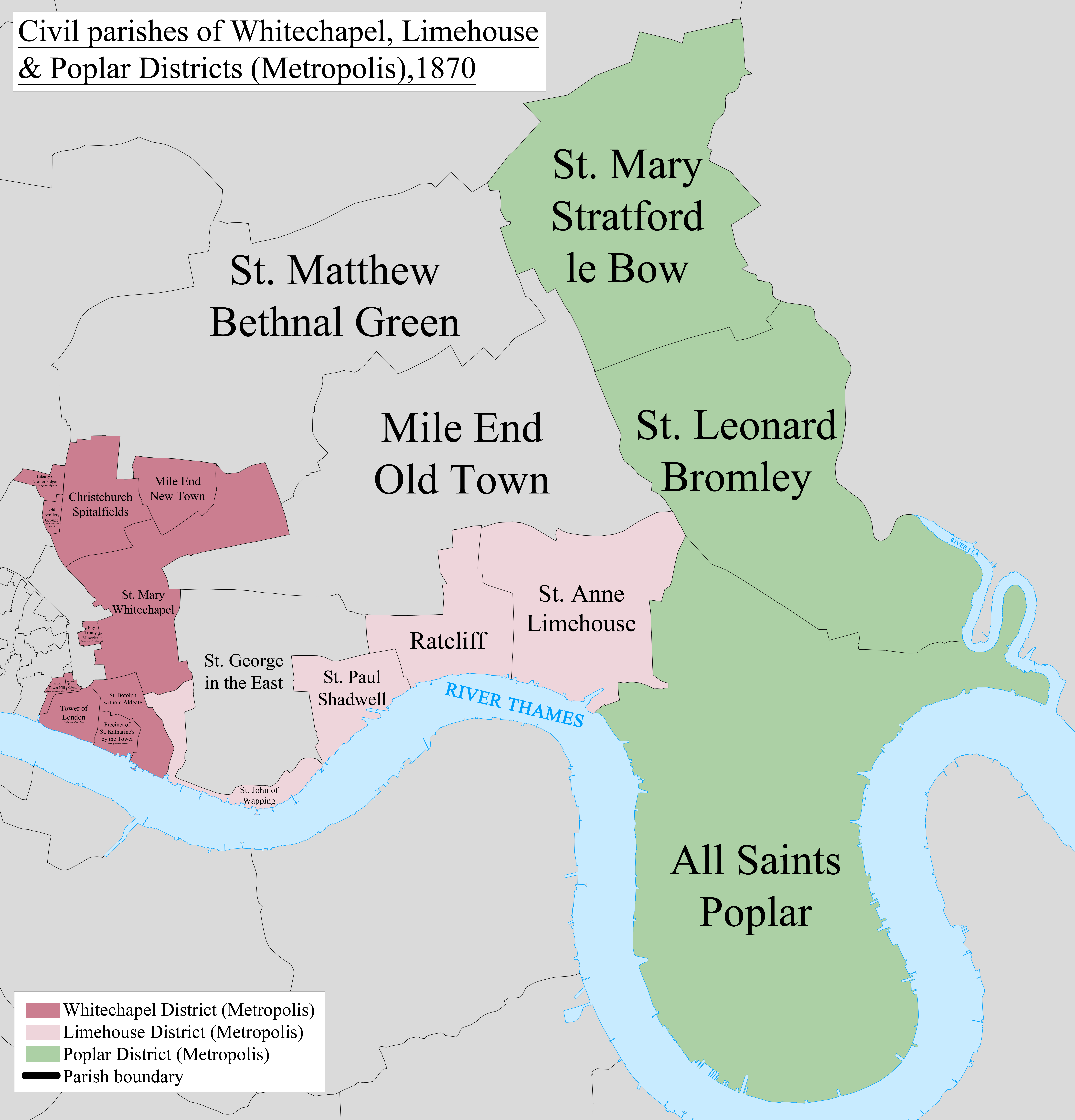
 The name relates to the local
The name relates to the local
 Limehouse Basin opened in 1820 as the ''Regent's Canal Dock''. This was an important connection between the Thames and the canal system, where cargoes could be transferred from larger ships to the shallow-draught canal boats. This mix of vessels can still be seen in the Basin:
Limehouse Basin opened in 1820 as the ''Regent's Canal Dock''. This was an important connection between the Thames and the canal system, where cargoes could be transferred from larger ships to the shallow-draught canal boats. This mix of vessels can still be seen in the Basin:
 Limehouse Basin was amongst the first docks to close in the late 1960s. By 1981, Limehouse shared the docklands-wide physical, social and economic decline which led to the setting up of the
Limehouse Basin was amongst the first docks to close in the late 1960s. By 1981, Limehouse shared the docklands-wide physical, social and economic decline which led to the setting up of the
 On 30 July 1909, the
On 30 July 1909, the
 The area inspired
The area inspired
 St Anne's Limehouse was built by Nicholas Hawksmoor. A pyramid originally planned to be put atop the tower now stands in the graveyard. The church is next door to
St Anne's Limehouse was built by Nicholas Hawksmoor. A pyramid originally planned to be put atop the tower now stands in the graveyard. The church is next door to
 Limehouse is connected to the National Road Network by the A13
Limehouse is connected to the National Road Network by the A13
 Sir Humphrey Gilbert lived here, and was an advocate of opening up the Northwest Passage. This inspired
Sir Humphrey Gilbert lived here, and was an advocate of opening up the Northwest Passage. This inspired
File:Canal lock - Regent's Canal - Limehouse Basin.jpg, Commercial Road Lock on the Regent's Canal entering the Limehouse Basin.
File:Limehouse Basin Entrance Lock - geograph.org.uk - 129004.jpg,
London Borough of Tower Hamlets
The London Borough of Tower Hamlets is a London boroughs, London borough covering much of the traditional East End of London, East End. It was formed in 1965 from the merger of the former Metropolitan boroughs of the County of London, metropol ...
in East London
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the f ...
. It is east of Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
, on the northern bank of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains through its riverside public houses and steps, such as The Grapes and Limehouse Stairs. It is part of the traditional county of Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, historic county in South East England, southeast England. Its area is almost entirely within the wider urbanised area of London and mostly within the Ceremonial counties of ...
. It became part of the ceremonial County of London
The County of London was a county of England from 1889 to 1965, corresponding to the area known today as Inner London. It was created as part of the general introduction of elected county government in England, by way of the Local Government A ...
following the passing of the Local Government Act 1888
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
* Local government, a form of public administration, usually the lowest tier of administrat ...
, and then part of Greater London
Greater may refer to:
*Greatness, the state of being great
*Greater than, in inequality (mathematics), inequality
*Greater (film), ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film
*Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record
*Greater (song), "Greate ...
in 1965. It is located between Stepney
Stepney is a district in the East End of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The district is no longer officially defined, and is usually used to refer to a relatively small area. However, for much of its history the place name appl ...
to the west and north, Mile End
Mile End is a district of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in the East End of London, England, east-northeast of Charing Cross. Situated on the London-to-Colchester road, it was one of the earliest suburbs of London. It became part of the m ...
and Bow to the northwest, Poplar to the east, and Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is an area of London, England, located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Canary Wharf is defined by the Greater London Authority as being part of London's central business district, alongside Central Lo ...
and Millwall
Millwall is a district on the western and southern side of the Isle of Dogs, in east London, England, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It lies to the immediate south of Canary Wharf and Limehouse, north of Greenwich and Deptford, east ...
to the south, and stretches from the end of Cable Street
Cable Street is a road in the East End of London, England, with several historic landmarks nearby. It was made famous by the Battle of Cable Street in 1936.
Location
Cable Street starts near the edge of London's financial district, the City ...
and Butcher Row in the west to Stainsby Road near Bartlett Park
Bartlett Park is a public open space in Poplar in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in London on Upper North Street. It is located to the south of the Limehouse Cut waterway and the Lansbury Estate to the south and east of the park. The wh ...
in the east, and from West India Dock (South Dock) and the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
in the south to Salmon Lane and Rhodeswell Road in the north.
The area gives its name to Limehouse Reach, a section of the Thames which runs south to Millwall after making a right-angled bend at Cuckold's Point
Cuckold's Point is part of a sharp bend on the River Thames on the Rotherhithe peninsula, south-east London, opposite the West India Docks and to the north of Columbia Wharf. The name comes from a post surmounted by a pair of horns that used t ...
, Rotherhithe. The west-to-east section upstream of Cuckold's Point is properly called the Lower Pool.
History
Etymology

lime kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime (material), lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this chemical reaction, reaction is
:Calcium carbonate, Ca ...
s or, more precisely, lime oast
An oast, oast house or hop kiln is a building designed for kilning (drying) hops as part of the brewing process. They can be found in most hop-growing (and former hop-growing) areas and are often good examples of vernacular architecture. Many re ...
s, by the river and operated by the large potteries that served shipping in the London Docks
London Docklands is the riverfront and former docks in London. It is located in inner east and southeast London, in the boroughs of Southwark, Tower Hamlets, Lewisham, Newham, and Greenwich. The docks were formerly part of the Port of L ...
. The name is from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
''līm-āst'' "lime-oast". The earliest reference is to ''Les Lymhostes'', in 1356.
The place appears in 1473 as "Lymehurst", with the occupation appearing as "lymebrenar"
The name 'Limehouse' is sometimes mistakenly thought to be derived from the nickname for the seamen that disembarked there, who had earned the name '' Lime-juicers'' or '' limeys'' after the obligatory ration of lime juice the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
gave their sailors to ward off scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding ...
.
The name is found used in 1417:Inquisicio capta sup' litus Thomisie apud Lymhosteys pro morte Thome Frank.
("''Inquest held on the shore of the Thames by Lymhosteys for the death of Thomas Frank''")
17 Aug, 5 Henry V. .D. 1417 inquest held before "les Lymehostes" within the liberty and franchise of the City, before Henry Bartone, the Mayor, and the King's Escheator, as to the cause of the death of Thomas Franke, of Herewich, late steersman (conductor) or "lodysman" of a ship called "la Mary Knyght" of Danzsk in Prussia. A jury sworn, viz., John Baille, Matthew Holme, Robert Marle, Henry Mark, Alexander Bryan, John Goby, Richard Hervy, Walter Steel, Peter West, Richard Stowell, John Dyse, and Walter Broun. They find that the said Thomas Franke was killed by falling on the sharp end of an anchor
Maritime links
From its foundation, Limehouse, like neighbouringWapping
Wapping () is a district in East London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Wapping's position, on the north bank of the River Thames, has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains through its riverside public houses and steps, ...
, has enjoyed better links with the river than the land, the land route being across a marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
. Limehouse became a significant port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
in late medieval times
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, with extensive docks and wharves. Although most cargoes were discharged in the Pool of London
The Pool of London is a stretch of the River Thames from London Bridge to below Limehouse.
Part of the Tideway of the Thames, the Pool was navigable by tall-masted vessels bringing coastal and later overseas goods—the wharves there were the ...
before the establishment of the docks, industries such as shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
, ship chandler
A ship chandler is a retail dealer who specializes in providing supplies or equipment for ships.
Synopsis
For traditional sailing ships, items that could be found in a chandlery
include sail-cloth, rosin, turpentine, tar, pitch, linseed oil, ...
ing and rope
A rope is a group of yarns, plies, fibres, or strands that are twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have tensile strength and so can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similarly ...
making were established in Limehouse.
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
narrowboat
A narrowboat is a particular type of canal boat, built to fit the narrow locks of the United Kingdom. The UK's canal system provided a nationwide transport network during the Industrial Revolution, but with the advent of the railways, commerc ...
s rubbing shoulders with seagoing yacht
A yacht is a sailing or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a , as opposed to a , such a pleasu ...
s.
From the Tudor era
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began with th ...
until the 20th century, ships crews were employed on a casual basis. New and replacement crews would be found wherever they were available – foreign sailors in their own waters being particularly prized for their knowledge of currents and hazards in ports around the world. Crews would be paid off at the end of their voyages and, inevitably, permanent communities of foreign sailors became established, including colonies of Lascar
A lascar was a sailor or militiaman from the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Arab world, British Somaliland, or other land east of the Cape of Good Hope, who was employed on European ships from the 16th century until the middle of the 2 ...
s and Africans from the Guinea Coast
Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the African coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.
Et ...
. Large Chinese communities developed at Shadwell
Shadwell is a district of East London, England, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets , east of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the Thames between Wapping (to the west) and Ratcliff (to the east). This riverside location has meant ...
, Limehouse and the adjoining Pennyfields area of Poplar. These were established by the crews of merchantmen
A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are us ...
in the opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
and tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and northe ...
trades, particularly Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
. The area achieved notoriety for opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
dens in the late 19th century, often featured in pulp fiction
''Pulp Fiction'' is a 1994 American crime film written and directed by Quentin Tarantino, who conceived it with Roger Avary.See, e.g., King (2002), pp. 185–7; ; Starring John Travolta, Samuel L. Jackson, Bruce Willis, Tim Roth, Ving Rhame ...
works by Sax Rohmer
Arthur Henry "Sarsfield" Ward (15 February 1883 – 1 June 1959), better known as Sax Rohmer, was an English novelist. He is best remembered for his series of novels featuring the master criminal Dr. Fu Manchu."Rohmer, Sax" by Jack Adrian in Da ...
and others. Like much of the East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
it remained a focus for immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
, but after the devastation of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
many of the Chinese community
The Chinese people or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.
Chinese people are known as Zhongguoren () or as Huaren () by speakers of s ...
relocated to Soho
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster, part of the West End of London. Originally a fashionable district for the aristocracy, it has been one of the main entertainment districts in the capital since the 19th century.
The area was develop ...
.
On 12 February 1832, the first case of cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
was reported in London at Limehouse. First described in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
in 1817, it had spread here via Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
. Although 800 people died during this epidemic, it was fewer than had died of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
in the same year. Unfortunately, cholera visited again in 1848 and 1858.
The use of Limehouse Basin as a major distribution hub declined with the growth of the railways, although the revival of canal traffic during World War I and World War II gave it a brief swansong. Today, Stepney Historical Trust works to advance the public's education in the history of the area.
Modern Limehouse
 Limehouse Basin was amongst the first docks to close in the late 1960s. By 1981, Limehouse shared the docklands-wide physical, social and economic decline which led to the setting up of the
Limehouse Basin was amongst the first docks to close in the late 1960s. By 1981, Limehouse shared the docklands-wide physical, social and economic decline which led to the setting up of the London Docklands Development Corporation
The London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) was a quango agency set up by the UK Government in 1981 to regenerate the depressed Docklands area of east London. During its seventeen-year existence it was responsible for regenerating an a ...
. In November 1982, the LDDC published its Limehouse Area Development Strategy. This built on existing plans for Limehouse Basin, and offered a discussion framework for future development, housing refurbishment and environmental improvements across the whole of Limehouse. It was based on four major projects: Limehouse Basin, Free Trade Wharf, what was then known as the Light Rapid Transit Route (DLR) and the Docklands Northern Relief Road, a road corridor between The Highway and East India Dock across the north of the Isle of Dogs.
However, it was not until the mid-1980s with the abolition of the Greater London Council that the impetus for improvements to the infrastructure was provided. The key to development in Limehouse lay next door in the Isle of Dogs. Initial development plans on the island had been modest: light industrial development and a low rise business park. The Limehouse Studios
Limehouse Studios was an independently owned television studio complex built in No. 10 Warehouse (30 Shed) of the South Quay Import Dock. This was located at the eastern end of Canary Wharf in Limehouse near the Isle of Dogs in London, which op ...
(an independent television studio built inside the shells of two old warehouses in 1983) were an early development on the island: this was, technically, a misnomer, however, as the studios were located in South Quay, not, as the name suggests, Limehouse.
By 1984, 8 million sq ft of potential commercial development was predicted. In 1985 proposals for a 10–12 million sq ft development on the of Canary Wharf were being considered. The sheer scale of the Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is an area of London, England, located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Canary Wharf is defined by the Greater London Authority as being part of London's central business district, alongside Central Lo ...
proposals, and, in due course, the rapid implementation of the first phase of development, provided the impetus to the transport improvements which completely altered prospects for Limehouse as well as for the Isle of Dogs
The Isle of Dogs is a large peninsula bounded on three sides by a large meander in the River Thames in East London, England, which includes the Cubitt Town, Millwall and Canary Wharf districts. The area was historically part of the Manor, Ham ...
. The derelict Regent's Canal Dock was converted into Limehouse Marina.
The Troxy
Troxy is a Grade II-listed Art Deco music venue on Commercial Road in Stepney, London. Built as a cinema in 1933, it closed in 1960 and became a training school for the London Opera Centre. In the 1980s the building was used as a bingo hall, an ...
concert venue is located in Limehouse on the Commercial Road.
Politics
 On 30 July 1909, the
On 30 July 1909, the Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for leading the United Kingdom during t ...
made a polemical speech in Limehouse attacking the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
for its opposition to his "People's Budget
The 1909/1910 People's Budget was a proposal of the Liberal government that introduced unprecedented taxes on the lands and incomes of Britain's wealthy to fund new social welfare programmes. It passed the House of Commons in 1909 but was bloc ...
" and speaking of the Budget's social aims. This was the origin of the verb 'to Limehouse', "To make fiery (political) speeches such as Mr. Lloyd George made at Limehouse in 1909".
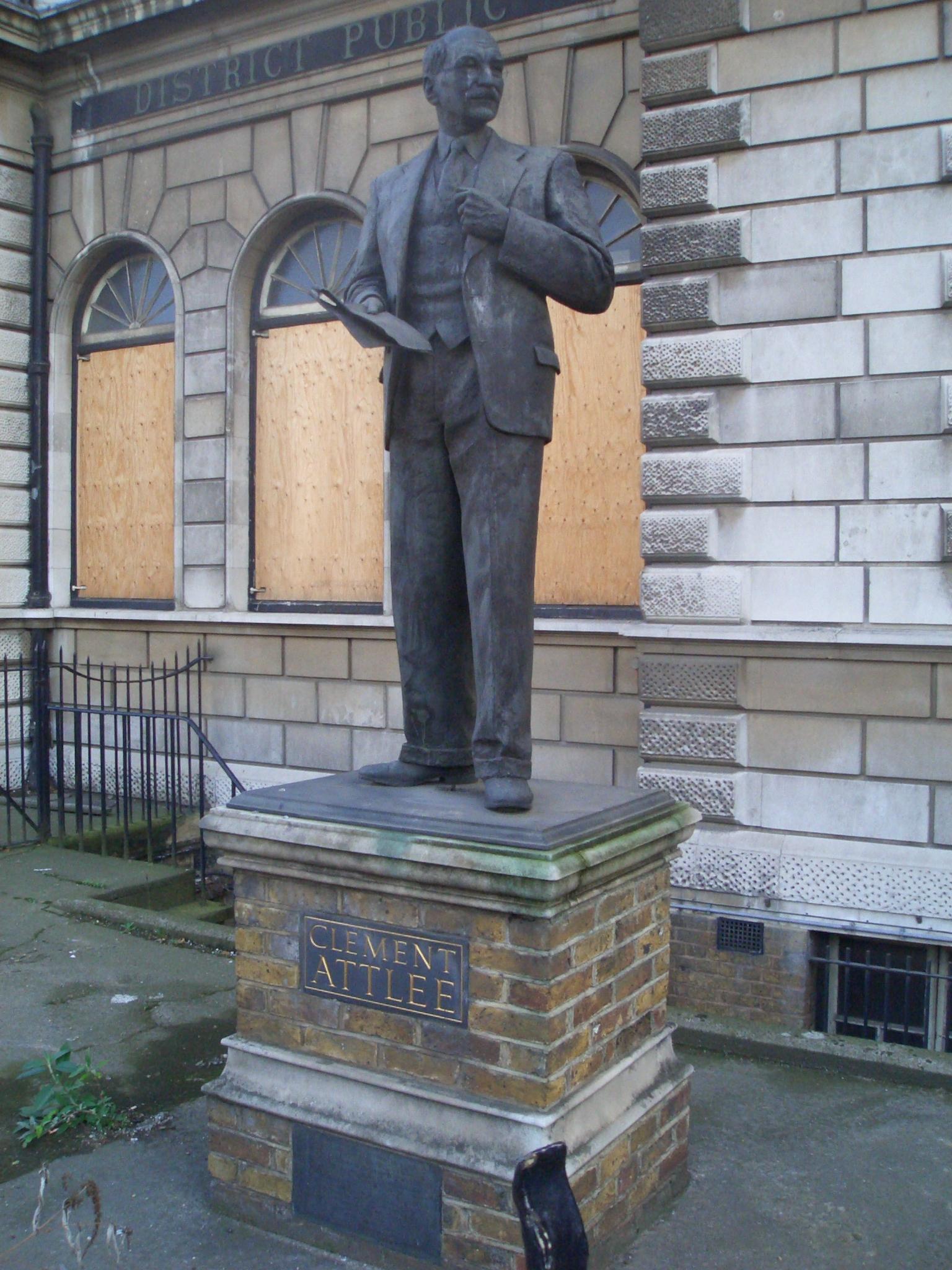
From 1906 to 1909, Clement Attlee
Clement Richard Attlee, 1st Earl Attlee, (3 January 18838 October 1967) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1945 to 1951 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1935 to 1955. He was Deputy Prime Mini ...
worked as manager of Haileybury House, a club for working class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
boys in Limehouse run by his old school. Before this, Attlee's political views had been conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization i ...
, but he was shocked by the poverty and deprivation he saw while working with slum
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily inh ...
children, and this caused him to become a socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
. He joined the Independent Labour Party
The Independent Labour Party (ILP) was a British political party of the left, established in 1893 at a conference in Bradford, after local and national dissatisfaction with the Liberals' apparent reluctance to endorse working-class candidates ...
in 1908, and became mayor of Stepney
Stepney is a district in the East End of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The district is no longer officially defined, and is usually used to refer to a relatively small area. However, for much of its history the place name appl ...
in 1919. At the 1922 general election, Attlee became Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MP) for the constituency
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger State (polity), state (a country, administrative region, ...
of Limehouse
Limehouse is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It is east of Charing Cross, on the northern bank of the River Thames. Its proximity to the river has given it a strong maritime character, which it retains throug ...
, which he represented while Deputy Prime Minister. After WWII he moved constituencies to Walthamstow West.
On 25 January 1981, MPs Shirley Williams, Roy Jenkins
Roy Harris Jenkins, Baron Jenkins of Hillhead, (11 November 1920 – 5 January 2003) was a British politician who served as President of the European Commission from 1977 to 1981. At various times a Member of Parliament (MP) for the Lab ...
, William Rodgers and David Owen
David Anthony Llewellyn Owen, Baron Owen, (born 2 July 1938) is a British politician and physician who served as Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs as a Labour Party (UK), Labour Party MP under James Callaghan from 1977 t ...
made the Limehouse Declaration from the bridge over Limehouse Cut in Narrow Street
Narrow Street is a narrow road running parallel to the River Thames through the Limehouse area of east London, England. It used to be much narrower, and is the oldest part of Limehouse, with many buildings originating from the eighteenth century ...
: it announced the formation of the Council for Social Democracy in opposition to the granting of block votes to the trade unions in the Labour Party to which they had previously belonged. They soon became leading politicians in the Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
.
Today, Limehouse is part of the constituency of Poplar and Limehouse
Poplar and Limehouse is a constituency created in 2010 and represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2019 by Apsana Begum of the Labour Party. From its creation until 2019, it was represented by Jim Fitzpatrick, also of ...
and has been represented in the House of Commons since 2019 by Apsana Begum
Apsana Begum ( bn, আফসানা বেগম; born 25 May 1990) is a British Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician serving as the Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for Poplar and Limehouse (UK Parliament ...
MP (Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
), and in the London Assembly
The London Assembly is a 25-member elected body, part of the Greater London Authority, that scrutinises the activities of the Mayor of London and has the power, with a two-thirds super-majority, to amend the Mayor's annual budget and to reject ...
since 2016 by Unmesh Desai AM (also Labour).
In popular culture
 The area inspired
The area inspired Douglas Furber
Douglas Furber (13 May 1885 – 20 February 1961) was a British lyricist and playwright.
Furber is best known for the lyrics to the 1937 song "The Lambeth Walk" and the libretto to the musical '' Me and My Girl'', composed by Noel Gay, from which ...
(lyricist) and Philip Braham
Philip Braham (18 June 1881 – 2 May 1934) was an English composer of the early twentieth century, chiefly associated with theatrical work. From 1914, he composed music for such musicals and revues as ''Theodore & Co'' (1916) and '' London Call ...
(composer) in 1921 to write the popular jazz standard " Limehouse Blues", which was introduced by Jack Buchanan and Gertrude Lawrence in the musical revue "A to Z". Much later, it was reprised in the ballet "Limehouse Blues" featuring Fred Astaire and Lucille Bremer in the musical film '' Ziegfeld Follies'' (1946) and by Julie Andrews
Dame Julie Andrews (born Julia Elizabeth Wells; 1 October 1935) is an English actress, singer, and author. She has garnered numerous accolades throughout her career spanning over seven decades, including an Academy Award, a British Academy Fi ...
in Star!
The current incarnation of E! is a Canadian English language specialty channel owned by Bell Media. Based on the American cable network of the same name, E! is devoted to entertainment programming including news, film, television, celebrities ...
(1968). In both instances the actors were in yellowface. Other notable performances on film include those by Hoagy Carmichael in ''To Have and Have Not
''To Have and Have Not'' is a novel by Ernest Hemingway published in 1937 by Charles Scribner's Sons. The book follows Harry Morgan, a fishing boat captain out of Key West, Florida. ''To Have and Have Not'' was Hemingway's second novel set in th ...
'' (1944) and by Borrah Minevich and His Harmonica Rascals in '' One in a Million'' (1936). '' Limehouse Blues'' was also the name of a 1934 film, starring George Raft
George Raft (born George Ranft; September 26, 1901 – November 24, 1980) was an American film actor and dancer identified with portrayals of gangsters in crime melodramas of the 1930s and 1940s. A stylish leading man in dozens of movies, Raft is ...
.
Thomas Burke wrote ''Limehouse Nights
''Limehouse Nights'' is a 1916 short story collection by the British writer Thomas Burke. The stories are set in and around the Chinatown that was then centred on Limehouse in the East End of London. The book was a popular success and features ...
'' (1916), a collection of stories centred around life in the poverty-stricken Limehouse district of London. Many of Burke's books feature the Chinese character Quong Lee as narrator. The area also features in the '' Fu Manchu'' books of Sax Rohmer
Arthur Henry "Sarsfield" Ward (15 February 1883 – 1 June 1959), better known as Sax Rohmer, was an English novelist. He is best remembered for his series of novels featuring the master criminal Dr. Fu Manchu."Rohmer, Sax" by Jack Adrian in Da ...
, where a Limehouse opium den serves as the hideout of the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
supervillain
A supervillain or supercriminal is a variant of the villainous stock character that is commonly found in American comic books, usually possessing superhuman abilities. A supervillain is the antithesis of a superhero.
Supervillains are oft ...
. The notion of East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
opium dens seems to have originated with a description by Charles Dickens of a visit he made to an opium den in nearby Bluegate Fields
Bluegate Fields (also known as Blue Gate Fields) was one of the worst slum areas that once existed just north of the old, east London docks during the Victorian era. Two streets in the area had actually been named Bluegate Fields at different t ...
, which inspired certain scenes in his last, unfinished, novel '' The Mystery of Edwin Drood'' (1870). More recently, the popular graphic novels of Alan Moore, '' From Hell'' (1989) and '' The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen'' (1999) contain a number of references to the notorious criminality of the area in Victorian London. Victorian-era Limehouse was also the setting of the novel ''Dan Leno and the Limehouse Golem'' (1995) by Peter Ackroyd, a fictionalized account of the notorious 'Limehouse Golem' serial murders.
The area also appeared in Anna Mae Wong's 1929 film ''Piccadilly
Piccadilly () is a road in the City of Westminster, London, to the south of Mayfair, between Hyde Park Corner in the west and Piccadilly Circus in the east. It is part of the A4 road that connects central London to Hammersmith, Earl's Court, ...
'', where, as the toughly alluring Shosho, Wong was said to embody the Limehouse Chinatown mystique. The Limehouse district of London is depicted in the silent film "Broken Blossoms
''Broken Blossoms or The Yellow Man and the Girl'', often referred to simply as ''Broken Blossoms'', is a 1919 American silent drama film directed by D. W. Griffith. It was distributed by United Artists and premiered on May 13, 1919. It stars ...
" or "The Yellow Man And The Girl" directed by D.W. Griffith
David Wark Griffith (January 22, 1875 – July 23, 1948) was an American film director. Considered one of the most influential figures in the history of the motion picture, he pioneered many aspects of film editing and expanded the art of the na ...
(1919) "where the Orient squats at the portals of the West." Limehouse is also the setting of the 1926 film "The Blackbird
''The Blackbird'' is a 1926 American silent crime film directed by Tod Browning and starring Lon Chaney. The screenplay was written by Waldemar Young, based on a story "The Mockingbird" by Tod Browning (which was originally supposed to be the ...
," directed by Tod Browning and starring Lon Chaney. The Limehouse district features prominently in the 1942 film '' Sherlock Holmes and the Voice of Terror'', when Holmes enlists the aid of rather unsavory residents to help catch a Nazi agent.
Society
 St Anne's Limehouse was built by Nicholas Hawksmoor. A pyramid originally planned to be put atop the tower now stands in the graveyard. The church is next door to
St Anne's Limehouse was built by Nicholas Hawksmoor. A pyramid originally planned to be put atop the tower now stands in the graveyard. The church is next door to Limehouse Town Hall
Limehouse Town Hall is a former town hall building on Commercial Road, in Limehouse, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is a Grade II listed building.
History
The building was commissioned by the Limehouse Board of Works as a vestry ...
and close to Limehouse Library
Limehouse Public Library is a historical building in Limehouse, London, formerly a public library. The library was first proposed for construction in 1888, but the required finances could not be raised until 1900 when John Passmore Edwards was ...
, both Grade II listed buildings, the former now used as a community centre. Across the road is the Sailors' Mission, where Situationist International
The Situationist International (SI) was an international organization of social revolutionaries made up of avant-garde artists, intellectuals, and political theorists. It was prominent in Europe from its formation in 1957 to its dissolution ...
held its conference in 1960. The building subsequently became a run-down hostel for the homeless which became notorious for its squalor, although it has since been converted into a luxury apartment block.
Further to the southwest, Narrow Street
Narrow Street is a narrow road running parallel to the River Thames through the Limehouse area of east London, England. It used to be much narrower, and is the oldest part of Limehouse, with many buildings originating from the eighteenth century ...
, Limehouse's historic spine, which runs along the back of the Thames wharves, boasts one of the few surviving early Georgian terraces in London. Next to the terrace is the historic Grapes pub, rebuilt in 1720 and well known to Charles Dickens, featuring as the ''Six Jolly Fellowship Porters'' in ''Our Mutual Friend
''Our Mutual Friend'', written in 1864–1865, is the last novel completed by Charles Dickens and is one of his most sophisticated works, combining savage satire with social analysis. It centres on, in the words of critic J. Hillis Miller, quo ...
''. A few doors along was Booty's Riverside Bar but this closed down in 2012. Almost every building on the other side of Narrow Street was destroyed by bombing in the Second World War, including hundreds of houses, Taylor Walker & Co
Taylor Walker was a large English brewery.
History
Taylor Walker & Co was founded in 1730 in Stepney as Salmon and Hare, and later became Hare and Hartford. In 1796 John Taylor acquired Hare's share, and the company took the name Taylor Walker i ...
's Barley Mow Brewery and a school. One notable exception is a former public house, known locally as 'The House They Left Behind', because it was the only Victorian terrace to survive. It still stands today, with the aid of three large supporting pillars.
Further along the street is 'The Narrow', a gastropub, now run by Gordon Ramsay
Gordon James Ramsay (; born ) is a British chef, restaurateur, television personality and writer. His restaurant group, Gordon Ramsay Restaurants, was founded in 1997 and has been awarded 17 Michelin stars overall; it currently holds a tot ...
. It is housed in the Grade II listed, former dockmaster
A dockmaster is a person in charge of a dock
A dock (from Dutch language, Dutch ''dok'') is the area of water between or next to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near ...
's and customs house, for Limehouse Dock.
Education
The Stepney Greencoat School is a Church of England primary school that was founded in 1710 by leading community members to local children, it has served the area as it transformed from an industrial to the mixed, multicultural settlement that Limehouse has become today.Transport
Rail
On 31 July 1987 the Docklands Light Railway, which operated over the old LBR line, commenced operations, with new platforms (platforms 3 and 4) built on the site of the old London and Blackwall Railway platforms; the station had been renamed Limehouse from Stepney East on 11 May that year. It is located in Limehouse, not Stepney and is served by National Rail c2c and DLR services. Between March and October 2007, West India Quay canopy was replaced in a £1.85m project funded by Transport for London. The distance from West India Quay to Canary Wharf is just , the shortest distance on the entire London Underground and Docklands Light Railway system. On 22 April 1991, two trains collided at the Delta Junction, in between Limehouse and Poplar on the West India Quay bridge during morningrush hour
A rush hour (American English, British English) or peak hour (Australian English) is a part of the day during which traffic congestion on roads and crowding on public transport is at its highest. Normally, this happens twice every weekday: on ...
, requiring a shutdown of the system and evacuation of passengers by ladder.
Buses
A number ofLondon Buses
London Buses is the subsidiary of Transport for London (TfL) that manages most bus services in London, England. It was formed following the Greater London Authority Act 1999 that transferred control of London Regional Transport (LRT) bus se ...
routes serve Limehouse, including routes 15, 115, 135 135 may refer to:
* 135 (number)
* AD 135
* 135 BC
* 135 film, better known as 35 mm film, is a format of photographic film used for still photography
*135 (New Jersey bus) 135 may refer to:
* 135 (number)
* AD 135
* 135 BC
* 135 film, better know ...
, D3 and night bus routes N15, N550 and N551.
Roads, cycling, walking
 Limehouse is connected to the National Road Network by the A13
Limehouse is connected to the National Road Network by the A13 Commercial Road
Commercial Road is a street in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in the East End of London. It is long, running from Gardiner's Corner (previously the site of Gardiners department store, and now Aldgate East Underground station), through ...
which passes west–east through Limehouse, while the A1203 Limehouse Link
The Limehouse Link tunnel is a long tunnel under Limehouse in East London on the A1203 road. The tunnel links the eastern end of The Highway to Canary Wharf in London Docklands. Built between 1989 and 1993 at a cost of £293,000,000 it has ...
tunnel passes under Limehouse Basin, linking The Highway
A highway is a long road giving a relatively fast connection between two places.
Highway may also refer to:
Roads in England
* The Highway (London) (previously Ratcliff Highway), a road in the East End of London
* The Highway, a road in Br ...
with the Docklands Northern Relief Road
Dockland or Docklands are areas occupied by, or in the neighbourhood of maritime docks, sometimes described as a Sailortown (dockland). The term is more common in Britain and British Commonwealth.
Specifically the term may refer to:
* Aarhus Do ...
. The northern entrance of the Rotherhithe Tunnel
The Rotherhithe Tunnel, designated the A101, is a road tunnel under the River Thames in East London, connecting Limehouse in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets north of the river to Rotherhithe in the London Borough of Southwark south of the ...
emerges in Limehouse, to the west of the Basin and close to Limehouse railway station.
Narrow Street
Narrow Street is a narrow road running parallel to the River Thames through the Limehouse area of east London, England. It used to be much narrower, and is the oldest part of Limehouse, with many buildings originating from the eighteenth century ...
forms a part of the north bank of the Thames Path and had previously been the principal street in Limehouse, it includes the Cycle Superhighway CS3 between Tower Gateway
Tower Gateway is a Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station in the City of London and is located near the Tower of London and Tower Bridge. It adjoins the tracks to Fenchurch Street station and is located on the site of a former station called Mino ...
to Barking and is one of London's first Cycle Superhighways
Cycle routes in London that have been waymarked with formal route signage include "Cycleways" (including "Cycle Superhighways" and "Quietways") and the older London Cycle Network, all designated by the local government body Transport for Londo ...
. Some local residents raised a petition calling for CS3 to be moved from Narrow Street onto Commercial Road, arguing that the street was too narrow and that incidents of abuse and aggression had risen sharply since the route was introduced. Transport for London (TfL) said they had no plans to move it. Former Mayor Boris Johnson defended the choice as a road that was already popular with cyclists to and from the City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
. The London Cycling Campaign
The London Cycling Campaign (LCC) is an independent membership charity lobbying for better conditions for cycling in London. Its vision is to make London "a world-class cycling city". It is one of the largest urban cycling organisations in th ...
however supported the route but called for improvements. In 2011, TfL agreed to remove logos from the road surface, but not to change the route. Vehicular access is limited, as the area is cut off by the entrance to the Limehouse link tunnel and parking is strictly controlled, however, this makes the area reasonably quiet for cyclists. Public access to the foreshore is prohibited, apparently part of the security arrangements for former Foreign Secretary
The secretary of state for foreign, Commonwealth and development affairs, known as the foreign secretary, is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom and head of the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. Seen as ...
, David Owen. The National Cycle Route 1 also runs in Limehouse north and south.
Waterways
Though no longer a working dock, Limehouse Basin with itsmarina
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : ''marina'', "coast" or "shore") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats.
A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships o ...
remains a working facility. The same is not true of the wharf buildings that have survived, most of which are now highly desirable residential properties. Limehouse Basin connects to the Regent's Canal via the Commercial Road Lock to the north, and the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
via Limehouse Basin Lock
Limehouse Basin Lock is a lock forming the exit from Limehouse Basin to the Thames, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, England. It is the final lock on the Regent's Canal. The Narrow Street swing bridge sits between the lock and the river. ...
to the south. The Limehouse Cut connects the Basin to the River Lea
The River Lea ( ) is in South East England. It originates in Bedfordshire, in the Chiltern Hills, and flows southeast through Hertfordshire, along the Essex border and into Greater London, to meet the River Thames at Bow Creek. It is one of t ...
in the east.
Notable residents
 Sir Humphrey Gilbert lived here, and was an advocate of opening up the Northwest Passage. This inspired
Sir Humphrey Gilbert lived here, and was an advocate of opening up the Northwest Passage. This inspired Martin Frobisher
Sir Martin Frobisher (; c. 1535 – 22 November 1594) was an English seaman and privateer who made three voyages to the New World looking for the North-west Passage. He probably sighted Resolution Island near Labrador in north-eastern Canada ...
to sail to Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is , slightly larger than Spain; its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadia ...
, and he returned with a mysterious black rock. Gilbert set up the Society of the New Art
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societi ...
with Lord Burghley and the Earl of Leicester, who had their alchemical laboratory in Limehouse; however, their attempts to transmute the black rock into gold proved fruitless. (Humphrey's brother Adrian Gilbert was reputed a great alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscience, protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in Chinese alchemy, C ...
and worked closely with John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, teacher, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divinatio ...
.)
Captain Christopher Newport
Christopher Newport (1561–1617) was an English seaman and privateer. He is best known as the captain of the ''Susan Constant'', the largest of three ships which carried settlers for the Virginia Company in 1607 on the way to found the settle ...
lived in Limehouse for several years up until 1595. He rose through the sailing ranks from a poor cabin boy
''Cabin Boy'' is a 1994 American fantasy comedy film, directed by Adam Resnick and co-produced by Tim Burton, which starred comedian Chris Elliott. Elliott co-wrote the film with Resnick. Both Elliott and Resnick worked for '' Late Night with Dav ...
to a wealthy English privateer and eventually one of the Masters of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
. He became rich pirating Spanish treasure vessels in the West Indies. In 1607 he sailed the '' Susan Constant'', followed by the ''Godspeed
Godspeed, a statement wishing someone a prosperous journey or success, may refer to:
Literature
* ''Godspeed'' (Sheffield novel), a 1993 science fiction novel by Charles Sheffield
* ''Godspeed'', an unpublished novel by Will Christopher Baer
* ...
'' and ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discovery ...
'', as Admiral of the Fleet to Jamestown. He helped secure England's foothold in North America through five voyages to Jamestown. He sailed his entire life, dying on a trading voyage to Bantam, on the island of Java in present-day Indonesia. His sailing experience in Limehouse made him known as Captain Christopher Newport, of Limehouse, Mariner.
Charles Dickens' godfather, Christopher Huffam, ran his sailmaking business from 12 Church Row (Newell Street). Huffam is said to be the inspiration for the Paul Dombey character in Dickens' '' Dombey and Son''.
James McNeill Whistler
James Abbott McNeill Whistler (; July 10, 1834July 17, 1903) was an American painter active during the American Gilded Age and based primarily in the United Kingdom. He eschewed sentimentality and moral allusion in painting and was a leading pr ...
and Charles Napier Hemy
Charles Napier Hemy (Newcastle-on-Tyne, 24 May 1841 – 30 September 1917, Falmouth) was a British genre and marine painter.
He was born to a musical family in Newcastle-on-Tyne, and trained in the Government School of Design, Newcastle, follo ...
sketched and painted at locations on Narrow Street's river waterfront.
Contemporary residents include the actor Sir Ian McKellen
Sir Ian Murray McKellen (born 25 May 1939) is an English actor. His career spans seven decades, having performed in genres ranging from Shakespearean and modern theatre to popular fantasy and science fiction. Regarded as a British cultural i ...
, Matthew Parris, comedy actress Cleo Rocos, actor Steven Berkoff
Steven Berkoff (born Leslie Steven Berks; 3 August 1937) is an English actor, author, playwright, theatre practitioner and theatre director.
As a theatre maker he is recognised for staging work with a heightened performance style eponymously k ...
, comedian Lee Hurst , as well as politician Lord David Owen. Limehouse was also the home of the late film director Sir David Lean
Sir David Lean (25 March 190816 April 1991) was an English film director, producer, screenwriter and editor. Widely considered one of the most important figures in British cinema, Lean directed the large-scale epics ''The Bridge on the River ...
.
Gallery
Limehouse Basin Lock
Limehouse Basin Lock is a lock forming the exit from Limehouse Basin to the Thames, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, England. It is the final lock on the Regent's Canal. The Narrow Street swing bridge sits between the lock and the river. ...
separating Limehouse Basin from the Thames
File:Limehouse development 3.jpg, Construction of apartments on Commercial Road
Commercial Road is a street in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in the East End of London. It is long, running from Gardiner's Corner (previously the site of Gardiners department store, and now Aldgate East Underground station), through ...
(now complete).
File:Docklands-Narrow Street.jpg, Taken from Narrow Street
Narrow Street is a narrow road running parallel to the River Thames through the Limehouse area of east London, England. It used to be much narrower, and is the oldest part of Limehouse, with many buildings originating from the eighteenth century ...
, this shows the proximity of Limehouse to four of the high rise buildings of Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is an area of London, England, located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Canary Wharf is defined by the Greater London Authority as being part of London's central business district, alongside Central Lo ...
.
File:Limehouse mission 1.jpg, The Mission, formerly the British Sailors Society
Sailors’ Society is an international Christian charity working in ports across the world. The organisation has chaplains and ship visitors in 91 global ports, who help seafarers and their families, from all faiths and none, with welfare and pra ...
, now apartments.
File:Limehouse Mk1.png, A picture of Limehouse D.L.R. station in 2002.
References
External links
* {{Authority control Districts of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Areas of London Districts of London on the River Thames Port of London Places formerly in Middlesex