Lead is a
chemical element with the
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Pb (from the
Latin ) and
atomic number 82. It is a
heavy metal that is
denser
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek language, Greek letter Rho (letter), rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' ca ...
than most common materials. Lead is
soft and
malleable, and also has a relatively low
melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It
tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any
stable element
A stable is a building in which livestock, especially horses, are kept. It most commonly means a building that is divided into separate Stall (livestock), stalls for individual animals and livestock. There are many different types of stables ...
and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear
decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children.
Lead is a relatively unreactive
post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its
amphoteric nature; lead and
lead oxides react with
acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
s and
bases, and it tends to form
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
s.
Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2
oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the
carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to
organolead compound Organolead compounds are chemical compounds containing a chemical bond between carbon and lead. Organolead chemistry is the corresponding science. The first organolead compound was hexaethyldilead (Pb2(C2H5)6), first synthesized in 1858.''Main Grou ...
s. Like the lighter members of the group, lead tends to
bond with itself; it can form chains and polyhedral structures.
Since lead is easily extracted from its
ores, prehistoric people in the Near East
were aware of it.
Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
is a principal ore of lead which often bears silver. Interest in silver helped initiate widespread extraction and use of lead in
ancient Rome. Lead production declined after the
fall of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
and did not reach comparable levels until the
Industrial Revolution. Lead played
a crucial role in the development of the
printing press, as
movable type could be relatively easily cast from lead alloys. In 2014, the annual global production of lead was about ten million tonnes, over half of which was from recycling. Lead's high density, low melting point,
ductility and relative inertness to
oxidation make it useful. These properties, combined with its relative abundance and low cost, resulted in its extensive use in construction, plumbing,
batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, bullets and
shot
Shot may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Shot'' (album), by The Jesus Lizard
*''Shot, Illusion, New God'', an EP by Gruntruck
*''Shot Rev 2.0'', a video album by The Sisters of Mercy
* "Shot" (song), by The Rasmus
* ''Shot'' (2017 fi ...
, weights,
solders,
pewters,
fusible alloys,
white paints,
leaded gasoline
Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula Pb( C2H5)4. It is a fuel additive, first being mixed with gasoline beginning in the 1920s as a patented octane rating booster that all ...
, and
radiation shielding.
Lead's toxicity became widely recognized in the late 19th century, although a number of well-educated ancient Greek and Roman writers were aware of this fact and even knew some of the symptoms of lead poisoning. Lead is a
neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature ner ...
that accumulates in soft tissues and bones; it damages the
nervous system and interferes with the function of biological
enzymes, causing
neurological disorder
A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakn ...
s ranging from behavioral problems to brain damage, and also affects general health, cardiovascular, and renal systems.
Physical properties
Atomic
A lead
atom has 82
electrons, arranged in an
electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom ...
of [
Xe]4f
145d
106s
26p
2. The sum of lead's first and second
ionization energies
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
—the total energy required to remove the two 6p electrons—is close to that of
tin, lead's upper neighbor in the
carbon group. This is unusual; ionization energies generally fall going down a group, as an element's outer electrons become more distant from the
nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, and more
shielded by smaller orbitals.
The similarity of ionization energies is caused by the
lanthanide contraction—the decrease in element
radii from
lanthanum (atomic number 57) to
lutetium (71), and the relatively small radii of the elements from
hafnium (72) onwards. This is due to poor shielding of the nucleus by the
lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttr ...
4f electrons. The sum of the first four ionization energies of lead exceeds that of tin, contrary to what
periodic trends would predict.
Relativistic effects
Relativistic quantum chemistry combines relativistic mechanics with quantum chemistry to calculate elemental properties and structure, especially for the heavier elements of the periodic table. A prominent example is an explanation for the color of ...
, which become significant in heavier atoms, contribute to this behavior. One such effect is the
inert pair effect: the 6s electrons of lead become reluctant to participate in bonding, making the distance between nearest atoms in
crystalline lead unusually long.
Lead's lighter carbon group
congeners form stable or metastable
allotrope
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: the ...
s with the tetrahedrally coordinated and
covalently bonded diamond cubic structure. The energy levels of their outer
s- and
p-orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a Function (mathematics), function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electr ...
s are close enough to allow mixing into four
hybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two dif ...
sp
3 orbitals. In lead, the inert pair effect increases the separation between its s- and p-orbitals, and the gap cannot be overcome by the energy that would be released by extra bonds following hybridization. Rather than having a diamond cubic structure, lead forms
metallic bonds
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be descri ...
in which only the p-electrons are delocalized and shared between the Pb
2+ ions. Lead consequently has a
face-centered cubic structure like the similarly sized
divalent metals
calcium and
strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is ex ...
.
Bulk
Pure lead has a bright, shiny gray appearance with a hint of blue. It tarnishes on contact with moist air and takes on a dull appearance, the hue of which depends on the prevailing conditions. Characteristic properties of lead include high
density, malleability, ductility, and high resistance to
corrosion due to
passivation.

Lead's close-packed face-centered cubic structure and high atomic weight result in a density of 11.34 g/cm
3, which is greater than that of common metals such as iron (7.87 g/cm
3), copper (8.93 g/cm
3), and
zinc (7.14 g/cm
3). This density is the origin of the idiom ''to go over like a lead balloon''. Some rarer metals are denser:
tungsten and gold are both at 19.3 g/cm
3, and
osmium
Osmium (from Greek grc, ὀσμή, osme, smell, label=none) is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mos ...
—the densest metal known—has a density of 22.59 g/cm
3, almost twice that of lead.
Lead is a very soft metal with a
Mohs hardness of 1.5; it can be scratched with a fingernail. It is quite malleable and somewhat ductile. The
bulk modulus of lead—a measure of its ease of compressibility—is 45.8
GPa. In comparison, that of aluminium is 75.2 GPa; copper 137.8 GPa; and
mild steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
160–169 GPa. Lead's
tensile strength, at 12–17 MPa, is low (that of aluminium is 6 times higher, copper 10 times, and mild steel 15 times higher); it can be strengthened by adding small amounts of copper or
antimony.
The melting point of lead—at 327.5 °C (621.5 °F)—is very low compared to most metals. Its
boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envir ...
of 1749 °C (3180 °F) is the lowest among the carbon group elements. The
electrical resistivity of lead at 20 °C is 192
nanoohm-meters, almost an
order of magnitude higher than those of other industrial metals (copper at ; gold ; and aluminium at ). Lead is a
superconductor at temperatures lower than 7.19
K; this is the highest
critical temperature
Critical or Critically may refer to:
*Critical, or critical but stable, medical states
**Critical, or intensive care medicine
*Critical juncture, a discontinuous change studied in the social sciences.
*Critical Software, a company specializing in ...
of all
type-I superconductor
The interior of a bulk superconductor cannot be penetrated by a weak magnetic field, a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect. When the applied magnetic field becomes too large, superconductivity breaks down. Superconductors can be divided int ...
s and the third highest of the elemental superconductors.
Isotopes
Natural lead consists of four stable
isotopes with mass numbers of 204, 206, 207, and 208, and traces of five short-lived radioisotopes. The high number of isotopes is consistent with lead's
atomic number being even. Lead has a
magic number of protons (82), for which the
nuclear shell model accurately predicts an especially stable nucleus. Lead-208 has 126 neutrons, another magic number, which may explain why lead-208 is extraordinarily stable.
With its high atomic number, lead is the heaviest element whose natural isotopes are regarded as stable; lead-208 is the heaviest stable nucleus. (This distinction formerly fell to
bismuth, with an atomic number of 83, until its only
primordial isotope
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
, bismuth-209, was found in 2003 to decay very slowly.) The four stable isotopes of lead could theoretically undergo
alpha decay to isotopes of
mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
with a release of energy, but this has not been observed for any of them; their predicted half-lives range from 10
35 to 10
189 years (at least 10
25 times the current age of the universe).
Three of the stable isotopes are found in three of the four major
decay chains
In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to a series of radioactive decays of different radioactive decay products as a sequential series of transformations. It is also known as a "radioactive cascade". Most radioisotopes do not decay direc ...
: lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208 are the final decay products of uranium-238, uranium-235, and thorium-232, respectively. These decay chains are called the uranium chain, the actinium chain, and the thorium chain. Their isotopic concentrations in a natural rock sample depends greatly on the presence of these three parent uranium and thorium isotopes. For example, the relative abundance of lead-208 can range from 52% in normal samples to 90% in thorium ores; for this reason, the standard atomic weight of lead is given to only one decimal place. As time passes, the ratio of lead-206 and lead-207 to lead-204 increases, since the former two are supplemented by radioactive decay of heavier elements while the latter is not; this allows for
lead–lead dating. As uranium decays into lead, their relative amounts change; this is the basis for
uranium–lead dating. Lead-207 exhibits
nuclear magnetic resonance, a property that has been used to study its compounds in solution and solid state, including in human body.

Apart from the stable isotopes, which make up almost all lead that exists naturally, there are
trace quantities of a few radioactive isotopes. One of them is lead-210; although it has a half-life of only 22.2 years, small quantities occur in nature because lead-210 is produced by a long decay series that starts with uranium-238 (that has been present for billions of years on Earth). Lead-211, −212, and −214 are present in the decay chains of uranium-235, thorium-232, and uranium-238, respectively, so traces of all three of these lead isotopes are found naturally. Minute traces of lead-209 arise from the very rare
cluster decay
Cluster decay, also named heavy particle radioactivity or heavy ion radioactivity, is a rare type of nuclear decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a small "cluster" of neutrons and protons, more than in an alpha particle, but less than a typic ...
of radium-223, one of the
daughter products of natural uranium-235, and the decay chain of neptunium-237, traces of which are produced by
neutron capture in uranium ores. Lead-210 is particularly useful for helping to identify the ages of samples by measuring its ratio to lead-206 (both isotopes are present in a single decay chain).
In total, 43 lead isotopes have been synthesized, with mass numbers 178–220. Lead-205 is the most stable radioisotope, with a half-life of around 1.73 years. The second-most stable is lead-202, which has a half-life of about 52,500 years, longer than any of the natural trace radioisotopes.
Chemistry

Bulk lead exposed to moist air forms a protective layer of varying composition.
Lead(II) carbonate is a common constituent; the
sulfate or
chloride may also be present in urban or maritime settings. This layer makes bulk lead effectively chemically inert in the air. Finely powdered lead, as with many metals, is
pyrophoric, and burns with a bluish-white flame.
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
reacts with lead at room temperature, forming
lead(II) fluoride
Lead(II) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Pb F2. It is a white solid. It exists as both an orthorhombic and cubic forms.
Uses
Lead(II) fluoride is used in low melting glasses, in glass coatings to reflect infrared rays, ...
. The reaction with
chlorine is similar but requires heating, as the resulting chloride layer diminishes the reactivity of the elements. Molten lead reacts with the
chalcogens to give lead(II) chalcogenides.
Lead metal resists
sulfuric
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
and
phosphoric acid but not
hydrochloric or
nitric acid; the outcome depends on insolubility and subsequent passivation of the product salt. Organic acids, such as
acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, dissolve lead in the presence of oxygen. Concentrated
alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
s will dissolve lead and form
plumbite In chemistry, plumbite is the oxyanion or hydrated forms, or any salt containing this anion. In these salts, lead is in the oxidation state +2. It is the traditional term for the IUPAC name plumbate(II).
For example, lead(II) oxide (PbO) dissolves ...
s.
Inorganic compounds
Lead shows two main oxidation states: +4 and +2. The
tetravalent state is common for the carbon group. The divalent state is rare for
carbon and
silicon, minor for germanium, important (but not prevailing) for tin, and is the more important of the two oxidation states for lead. This is attributable to
relativistic effects
Relativistic quantum chemistry combines relativistic mechanics with quantum chemistry to calculate elemental properties and structure, especially for the heavier elements of the periodic table. A prominent example is an explanation for the color of ...
, specifically the
inert pair effect, which manifests itself when there is a large difference in
electronegativity between lead and
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
,
halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
, or
nitride anions, leading to a significant partial positive charge on lead. The result is a stronger contraction of the lead 6s orbital than is the case for the 6p orbital, making it rather inert in ionic compounds. The inert pair effect is less applicable to compounds in which lead forms covalent bonds with elements of similar electronegativity, such as carbon in organolead compounds. In these, the 6s and 6p orbitals remain similarly sized and sp
3 hybridization is still energetically favorable. Lead, like carbon, is predominantly tetravalent in such compounds.
There is a relatively large difference in the electronegativity of lead(II) at 1.87 and lead(IV) at 2.33. This difference marks the reversal in the trend of increasing stability of the +4 oxidation state going down the carbon group; tin, by comparison, has values of 1.80 in the +2 oxidation state and 1.96 in the +4 state.
Lead(II)

Lead(II) compounds are characteristic of the inorganic chemistry of lead. Even strong
oxidizing agents like fluorine and chlorine react with lead to give only PbF
2 and PbCl
2. Lead(II) ions are usually colorless in solution, and partially hydrolyze to form Pb(OH)
+ and finally
b4(OH)4sup>4+ (in which the
hydroxyl ions act as
bridging ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually r ...
s), but are not
reducing agents as tin(II) ions are.
Techniques
Technique or techniques may refer to:
Music
* The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s
*Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s
* ''Technique'' (album), by New Order, 1989
* ''Techniques'' (album), by M ...
for identifying the presence of the Pb
2+ ion in water generally rely on the precipitation of lead(II) chloride using dilute hydrochloric acid. As the chloride salt is sparingly soluble in water, in very dilute solutions the precipitation of lead(II) sulfide is instead achieved by bubbling
hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
through the solution.
Lead monoxide
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb O. PbO occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern ap ...
exists in two
polymorphs,
litharge α-PbO (red) and
massicot β-PbO (yellow), the latter being stable only above around 488 °C. Litharge is the most commonly used inorganic compound of lead. There is no lead(II) hydroxide; increasing the pH of solutions of lead(II) salts leads to hydrolysis and condensation.
Lead commonly reacts with heavier chalcogens.
Lead sulfide is a
semiconductor, a
photoconductor, and an extremely sensitive
infrared radiation detector. The other two chalcogenides,
lead selenide and
lead telluride, are likewise photoconducting. They are unusual in that their color becomes lighter going down the group.
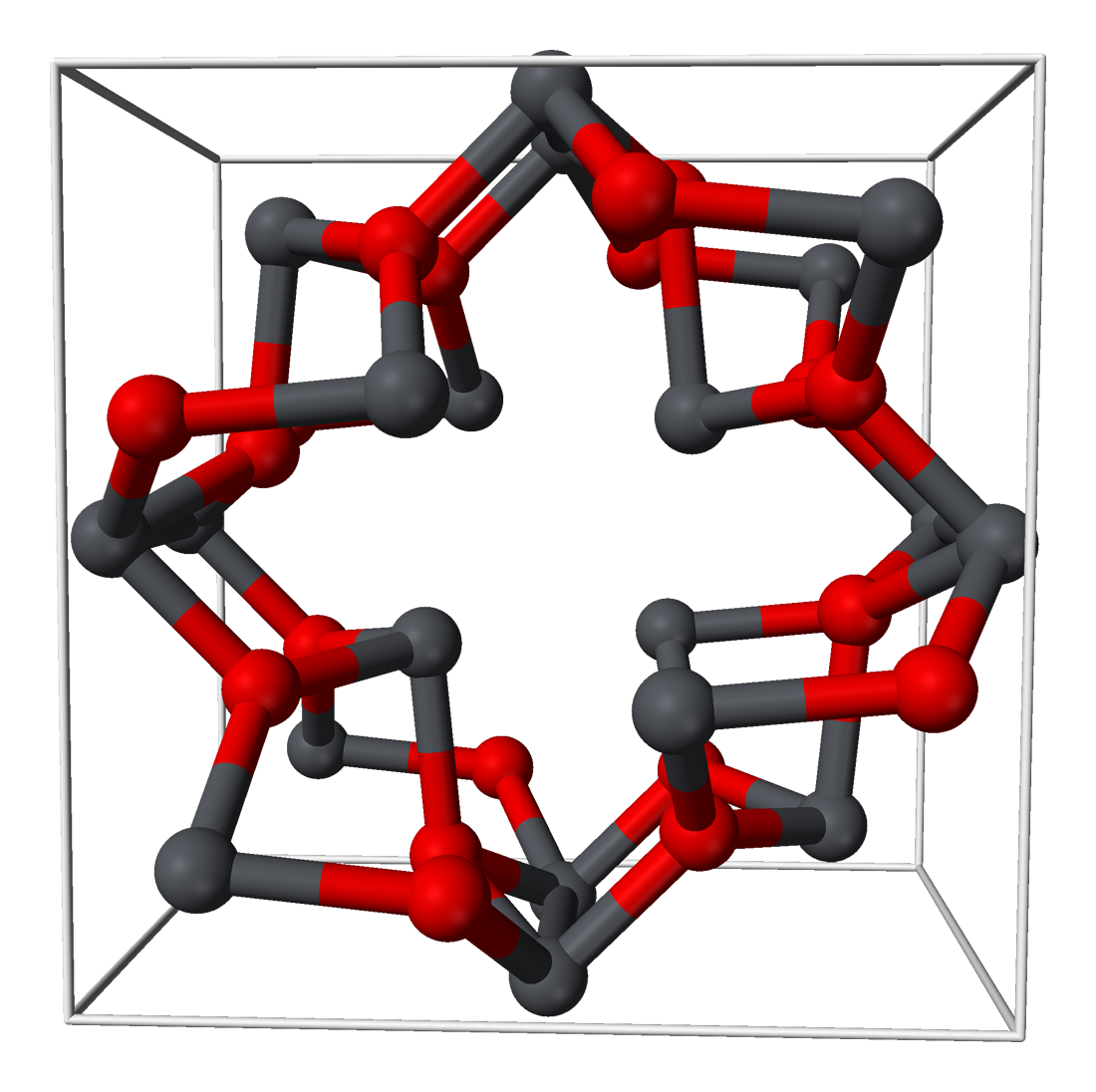
Lead dihalides are well-characterized; this includes the diastatide and mixed halides, such as PbFCl. The relative insolubility of the latter forms a useful basis for the
gravimetric determination of fluorine. The difluoride was the first solid
ionically conducting compound to be discovered (in 1834, by
Michael Faraday). The other dihalides decompose on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, especially the diiodide. Many lead(II)
pseudohalides are known, such as the
cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a ...
,
cyanate, and
thiocyanate. Lead(II) forms an extensive variety of halide
coordination complexes, such as
bCl4sup>2−,
bCl6sup>4−, and the
b2Cl9sub>''n''
5''n''− chain anion.
Lead(II) sulfate is insoluble in water, like the sulfates of other heavy divalent
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s. Lead(II) nitrate and
lead(II) acetate are very soluble, and this is exploited in the synthesis of other lead compounds.
Lead(IV)
Few inorganic lead(IV) compounds are known. They are only formed in highly oxidizing solutions and do not normally exist under standard conditions. Lead(II) oxide gives a mixed oxide on further oxidation, Pb
3O
4. It is described as
lead(II,IV) oxide, or structurally 2PbO·PbO
2, and is the best-known mixed valence lead compound.
Lead dioxide is a strong oxidizing agent, capable of oxidizing hydrochloric acid to chlorine gas. This is because the expected PbCl
4 that would be produced is unstable and spontaneously decomposes to PbCl
2 and Cl
2. Analogously to
lead monoxide
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb O. PbO occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern ap ...
, lead dioxide is capable of forming
plumbate anions.
Lead disulfide
Lead(IV) sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Pb S2. This material is generated by the reaction of the more common lead(II) sulfide, PbS, with sulfur at >600 °C and at high pressures. PbS2, like the related tin(IV) sulfide SnS2, crysta ...
and lead diselenide are only stable at high pressures.
Lead tetrafluoride
Lead tetrafluoride is a compound of lead and fluorine. The yellow solid (melting point 600 °C) is the only room-temperature stable tetrahalide of lead. Lead tetrafluoride is isostructural with tin(IV) fluoride and contains planar layers of ...
, a yellow crystalline powder, is stable, but less so than the
difluoride
Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule (or per formula unit).
Metal difluorides are all ionic. Despite being highly ionic, the alkali earth metal difluorides generally have extremely high lattice stability and ...
.
Lead tetrachloride
Lead tetrachloride, also known as lead(IV) chloride, has the molecular formula PbCl4. It is a yellow, oily liquid which is stable below 0 °C, and decomposes at 50 °C. It has a tetrahedral configuration, with lead as the central atom. ...
(a yellow oil) decomposes at room temperature, lead tetrabromide is less stable still, and the existence of lead tetraiodide is questionable.
Other oxidation states

Some lead compounds exist in formal oxidation states other than +4 or +2. Lead(III) may be obtained, as an intermediate between lead(II) and lead(IV), in larger organolead complexes; this oxidation state is not stable, as both the lead(III) ion and the larger complexes containing it are
radicals
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
. The same applies for lead(I), which can be found in such radical species.
Numerous mixed lead(II,IV) oxides are known. When PbO
2 is heated in air, it becomes Pb
12O
19 at 293 °C, Pb
12O
17 at 351 °C, Pb
3O
4 at 374 °C, and finally PbO at 605 °C. A further
sesquioxide, Pb
2O
3, can be obtained at high pressure, along with several non-stoichiometric phases. Many of them show defective
fluorite structures in which some oxygen atoms are replaced by vacancies: PbO can be considered as having such a structure, with every alternate layer of oxygen atoms absent.
Negative oxidation states can occur as
Zintl phases
In chemistry, a Zintl phase is a product of a reaction between a group 1 ( alkali metal) or group 2 (alkaline earth metal) and main group metal or metalloid (from groups 13, 14, 15, or 16). It is characterized by intermediate metallic/ ionic bon ...
, as either free lead anions, as in Ba
2Pb, with lead formally being lead(−IV), or in oxygen-sensitive ring-shaped or polyhedral cluster ions such as the
trigonal bipyramidal Pb
52− ion, where two lead atoms are lead(−I) and three are lead(0). In such anions, each atom is at a polyhedral vertex and contributes two electrons to each covalent bond along an edge from their sp
3 hybrid orbitals, the other two being an external
lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
. They may be made in
liquid ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wast ...
via the reduction of lead by
sodium.
Organolead

Lead can form
multiply-bonded chains, a property it shares with its lighter
homologs in the carbon group. Its capacity to do so is much less because the Pb–Pb
bond energy is over three and a half times lower than that of the C–C bond. With itself, lead can build metal–metal bonds of an order up to three. With carbon, lead forms organolead compounds similar to, but generally less stable than, typical organic compounds (due to the Pb–C bond being rather weak). This makes the
organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and so ...
of lead far less wide-ranging than that of tin. Lead predominantly forms organolead(IV) compounds, even when starting with inorganic lead(II) reactants; very few organolead(II) compounds are known. The most well-characterized exceptions are Pb
H(SiMe3)2sub>2 and Pb(''η''
5-C
5H
5)
2.
The lead analog of the simplest
organic compound,
methane, is
plumbane. Plumbane may be obtained in a reaction between metallic lead and
atomic hydrogen
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constit ...
. Two simple derivatives,
tetramethyllead
Tetramethyllead, also called tetra methyllead and lead tetramethyl, is a chemical compound used as an antiknock additive for gasoline. Its use is being phased out for environmental considerations.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety a ...
and
tetraethyllead, are the best-known
organolead Organolead compounds are chemical compounds containing a chemical bond between carbon and lead. Organolead chemistry is the corresponding science. The first organolead compound was hexaethyldilead (Pb2(C2H5)6), first synthesized in 1858.''Main Grou ...
compounds. These compounds are relatively stable: tetraethyllead only starts to decompose if heated or if exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet light. With sodium metal, lead readily forms an equimolar alloy that reacts with
alkyl halides to form
organometallic
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and so ...
compounds such as tetraethyllead. The oxidizing nature of many organolead compounds is usefully exploited:
lead tetraacetate
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an organometallic compound with chemical formula . It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically store ...
is an important laboratory reagent for oxidation in organic synthesis. Tetraethyllead, once added to gasoline, was produced in larger quantities than any other organometallic compound. Other organolead compounds are less chemically stable. For many organic compounds, a lead analog does not exist.
Origin and occurrence
In space
Lead's per-particle abundance in the
Solar System is 0.121
ppb (parts per billion). This figure is two and a half times higher than that of
platinum, eight times more than mercury, and seventeen times more than gold. The amount of lead in the
universe is slowly increasing as most heavier atoms (all of which are unstable) gradually decay to lead. The abundance of lead in the Solar System since its formation 4.5 billion years ago has increased by about 0.75%. The solar system abundances table shows that lead, despite its relatively high atomic number, is more prevalent than most other elements with atomic numbers greater than 40.
Primordial lead—which comprises the isotopes lead-204, lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208—was mostly created as a result of repetitive neutron capture processes occurring in stars. The two main modes of capture are the
s- and
r-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for the creation of approximately half of the atomic nuclei heavier than iron, the "heavy elements", ...
es.
In the s-process (s is for "slow"), captures are separated by years or decades, allowing less stable nuclei to undergo
beta decay. A stable thallium-203 nucleus can capture a neutron and become thallium-204; this undergoes beta decay to give stable lead-204; on capturing another neutron, it becomes lead-205, which has a half-life of around 15 million years. Further captures result in lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208. On capturing another neutron, lead-208 becomes lead-209, which quickly decays into bismuth-209. Bismuth-209 is also radioactive and eventually decays into thallium-205 if left unperturbed. On capturing another neutron, bismuth-209 becomes bismuth-210, and this beta decays to polonium-210, which alpha decays to lead-206. The cycle hence ends at lead-206, lead-207, lead-208, and thallium-205.

In the r-process (r is for "rapid"), captures happen faster than nuclei can decay. This occurs in environments with a high neutron density, such as a
supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
or the merger of two
neutron stars. The neutron flux involved may be on the order of 10
22 neutrons per square centimeter per second. The r-process does not form as much lead as the s-process. It tends to stop once neutron-rich nuclei reach 126 neutrons. At this point, the neutrons are arranged in complete shells in the atomic nucleus, and it becomes harder to energetically accommodate more of them. When the neutron flux subsides, these nuclei beta decay into stable isotopes of osmium,
iridium, and platinum.
On Earth
Lead is classified as a
chalcophile under the
Goldschmidt classification, meaning it is generally found combined with sulfur. It rarely occurs in its
native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
, metallic form. Many lead minerals are relatively light and, over the course of the Earth's history, have remained in the
crust instead of sinking deeper into the Earth's interior. This accounts for lead's relatively high
crustal abundance
The abundance of elements in Earth's crust is shown in tabulated form with the estimated crustal abundance for each chemical element shown as mg/kg, or parts per million (ppm) by mass (10,000 ppm = 1%).
Estimates of elemental abundance are diff ...
of 14 ppm; it is the 38th most
abundant element in the crust.
The main lead-bearing mineral is
galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
(PbS), which is mostly found with zinc ores. Most other lead minerals are related to galena in some way;
boulangerite, Pb
5Sb
4S
11, is a mixed sulfide derived from galena;
anglesite, PbSO
4, is a product of galena oxidation; and
cerussite or white lead ore, PbCO
3, is a decomposition product of galena.
Arsenic, tin, antimony, silver, gold, copper, and bismuth are common impurities in lead minerals.

World lead resources exceed two billion tons. Significant deposits are located in Australia, China, Ireland, Mexico, Peru, Portugal, Russia, and the United States. Global reserves—resources that are economically feasible to extract—totaled 88 million tons in 2016, of which Australia had 35 million, China 17 million, and Russia 6.4 million.
Typical background concentrations of lead do not exceed 0.1 μg/m
3 in the atmosphere; 100 mg/kg in soil; 4 mg/kg in vegetation and 5 μg/L in freshwater and seawater.
Etymology
The modern English word ''lead'' is of Germanic origin; it comes from the
Middle English and
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
(with the
macron above the "e" signifying that the vowel sound of that letter is long). The Old English word is derived from the hypothetical reconstructed
Proto-Germanic ('lead'). According to linguistic theory, this word bore descendants in multiple Germanic languages of exactly the same meaning.
There is no consensus on the origin of the Proto-Germanic . One hypothesis suggests it is derived from
Proto-Indo-European ('lead'; capitalization of the vowel is equivalent to the macron). Another hypothesis suggests it is borrowed from
Proto-Celtic ('lead'). This word is related to the
Latin , which gave the element its
chemical symbol ''Pb''. The word is thought to be the origin of Proto-Germanic (which also means 'lead'), from which stemmed the German .
The name of the chemical element is not related to the verb of the same spelling, which is derived from Proto-Germanic ('to lead').
History
Prehistory and early history

Metallic lead beads
dating back to 7000–6500 BCE have been found in
Asia Minor and may represent the first example of metal
smelting. At that time lead had few (if any) applications due to its softness and dull appearance. The major reason for the spread of lead production was its association with silver, which may be obtained by burning galena (a common lead mineral). The
Ancient Egyptians were the first to use lead minerals in cosmetics, an application that spread to
Ancient Greece and beyond; the Egyptians may have used lead for sinkers in fishing nets,
glazes, glasses,
enamels, and for ornaments. Various civilizations of the
Fertile Crescent used lead as a writing material, as
coins, and as a construction material. Lead was used in the
Ancient Chinese royal court as a
stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
, as currency, and as a
contraceptive
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
; the
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
and the
Mesoamericans used it for making amulets; and the eastern and southern African peoples used lead in
wire drawing.
Classical era
Because silver was extensively used as a decorative material and an exchange medium, lead deposits came to be worked in Asia Minor from 3000 BCE; later, lead deposits were developed in the
Aegean and
Laurion. These three regions collectively dominated production of mined lead until c. 1200 BCE. Beginning circa 2000 BCE, the
Phoenicians worked deposits in the
Iberian peninsula; by 1600 BCE, lead mining existed in
Cyprus, Greece, and
Sardinia.
 Rome's
Rome's territorial expansion in Europe and across the Mediterranean, and its development of mining, led to it becoming the greatest producer of lead during the
classical era, with an estimated annual output peaking at 80,000 tonnes. Like their predecessors, the Romans obtained lead mostly as a by-product of silver smelting.
Lead mining
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, l ...
occurred in Central Europe,
Britain, the
Balkans,
Greece,
Anatolia, and
Hispania, the latter accounting for 40% of world production.
Lead tablets were commonly used as a material for letters.
Lead coffins
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, l ...
, cast in flat sand forms, with interchangeable motifs to suit the faith of the deceased were used in ancient
Judea. Lead was used to make sling bullets from the 5th century BC. In Roman times, lead sling bullets were amply used, and were effective at a distance of between 100 and 150 meters. The Balearic slingers, used as mercenaries in Carthaginian and Roman armies, were famous for their shooting distance and accuracy.

Lead was used for making
water pipes in the
Roman Empire; the
Latin word for the metal, , is the origin of the English word "plumbing". Its ease of working, its low melting point enabling the easy fabrication of completely waterproof welded joints, and its resistance to corrosion ensured its widespread use in other applications, including pharmaceuticals, roofing, currency, and warfare. Writers of the time, such as
Cato the Elder,
Columella, and
Pliny the Elder, recommended lead (or lead-coated) vessels for the preparation of
sweeteners and preservatives added to wine and food. The lead conferred an agreeable taste due to the formation of "sugar of lead" (lead(II) acetate), whereas copper or
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
vessels could impart a bitter flavor through
verdigris
Verdigris is the common name for blue-green, copper-based pigments that form a patina on copper, bronze, and brass. The technical literature is ambiguous as to its chemical composition. Some sources refer to "neutral verdigris" as copper(II) ac ...
formation.
The Roman author
Vitruvius reported the health dangers of lead and modern writers have suggested that lead poisoning played a major role in the decline of the Roman Empire. Other researchers have criticized such claims, pointing out, for instance, that not all abdominal pain is caused by lead poisoning. According to archaeological research, Roman
lead pipe
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It ...
s increased lead levels in tap water but such an effect was "unlikely to have been truly harmful". When lead poisoning did occur, victims were called "saturnine", dark and cynical, after the ghoulish father of the gods,
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
. By association, lead was considered the father of all metals. Its status in Roman society was low as it was readily available and cheap.
Confusion with tin and antimony
Since the
Bronze Age metallurgists and engineers have understood the difference between rare and valuable
tin, essential for alloying with copper to produce tough and corrosion resistant
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
, and ‘cheap and cheerful’ lead. However the nomenclature in some languages is similar. Romans called lead ("black lead"), and tin ("bright lead"). The association of lead and tin can be seen in other languages: the word in
Czech translates to "lead", but in Russian, its
cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
() means "tin". To add to the confusion, lead bore a close relation to antimony: both elements commonly occur as sulfides (galena and
stibnite), often together. Pliny incorrectly wrote that stibnite would give lead on heating, instead of antimony. In countries such as Turkey and India, the originally Persian name came to refer to either antimony sulfide or lead sulfide, and in some languages, such as Russian, gave its name to antimony ().
Middle Ages and the Renaissance
Lead mining in Western Europe declined after the fall of the
Western Roman Empire, with
Arabian Iberia being the only region having a significant output. The largest production of lead occurred in South and East Asia, especially China and India, where lead mining grew rapidly.
In Europe, lead production began to increase in the 11th and 12th centuries, when it was again used for roofing and piping. Starting in the 13th century, lead was used to create
stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
. In the
European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
and
Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
traditions of
alchemy, lead (symbol ♄ in the European tradition) was considered an impure
base metal which, by the separation, purification and balancing of its constituent essences, could be transformed to pure and incorruptible gold. During the period, lead was used increasingly for
adulterating wine. The use of such wine was forbidden for use in Christian rites by a
papal bull in 1498, but it continued to be imbibed and resulted in mass poisonings up to the late 18th century. Lead was a key material in parts of the
printing press, and lead dust was commonly inhaled by print workers, causing lead poisoning. Lead also became the chief material for making bullets for firearms: it was cheap, less damaging to iron gun barrels, had a higher density (which allowed for better retention of velocity), and its lower melting point made the production of bullets easier as they could be made using a wood fire. Lead, in the form of
Venetian ceruse
Venetian ceruse, also known as ''blanc de ceruse de Venise'' and Spirits of Saturn, was a 16th-century cosmetic used as a skin whitener. It was in great demand and considered the best available at the time, supposedly containing the best quality ...
, was extensively used in cosmetics by Western European aristocracy as whitened faces were regarded as a sign of modesty. This practice later expanded to white wigs and eyeliners, and only faded out with the
French Revolution in the late 18th century. A similar fashion appeared in Japan in the 18th century with the emergence of the
geishas, a practice that continued long into the 20th century. The white faces of women "came to represent their feminine virtue as Japanese women", with lead commonly used in the whitener.
Outside Europe and Asia
In the
New World, lead production was recorded soon after the arrival of European settlers. The earliest record dates to 1621 in the English
Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colonial empire, English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertG ...
, fourteen years after its foundation. In Australia, the first mine opened by colonists on the continent was a lead mine, in 1841. In Africa, lead mining and smelting were known in the
Benue Trough and the lower
Congo Basin
The Congo Basin (french: Bassin du Congo) is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It con ...
, where lead was used for trade with Europeans, and as a currency by the 17th century, well before the
scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
.
Industrial Revolution

In the second half of the 18th century, Britain, and later continental Europe and the United States, experienced the
Industrial Revolution. This was the first time during which lead production rates exceeded those of Rome. Britain was the leading producer, losing this status by the mid-19th century with the depletion of its mines and the development of lead mining in Germany, Spain, and the United States. By 1900, the United States was the leader in global lead production, and other non-European nations—Canada, Mexico, and Australia—had begun significant production; production outside Europe exceeded that within. A great share of the demand for lead came from plumbing and painting—
lead paints were in regular use. At this time, more (working class) people were exposed to the metal and lead poisoning cases escalated. This led to research into the effects of lead intake. Lead was proven to be more dangerous in its fume form than as a solid metal. Lead poisoning and
gout were linked; British physician
Alfred Baring Garrod noted a third of his gout patients were plumbers and painters. The effects of chronic ingestion of lead, including mental disorders, were also studied in the 19th century. The first laws aimed at decreasing lead poisoning in factories were enacted during the 1870s and 1880s in the United Kingdom.
Modern era

Further evidence of the threat that lead posed to humans was discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Mechanisms of harm were better understood, lead blindness was documented, and the element was phased out of public use in the United States and Europe. The United Kingdom introduced mandatory factory inspections in 1878 and appointed the first Medical Inspector of Factories in 1898; as a result, a 25-fold decrease in lead poisoning incidents from 1900 to 1944 was reported. Most European countries banned lead paint—commonly used because of its opacity and water resistance—for interiors by 1930.
The last major human exposure to lead was the addition of tetraethyllead to gasoline as an
antiknock agent, a practice that originated in the United States in 1921. It was phased out in the United States and the
European Union by 2000.
In the 1970s, the United States and Western European countries introduced legislation to reduce lead air pollution. The impact was significant: while a study conducted by the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States in 1976–1980 showed that 77.8% of the population had elevated
blood lead level
Blood lead level (BLL), is a measure of the amount of lead in the blood. Lead is a toxic heavy metal and can cause neurological damage, especially among children, at any detectable level. High lead levels cause decreased vitamin D and haemoglob ...
s, in 1991–1994, a study by the same institute showed the share of people with such high levels dropped to 2.2%. The main product made of lead by the end of the 20th century was the
lead–acid battery.
From 1960 to 1990, lead output in the
Western Bloc grew by about 31%. The share of the world's lead production by the
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
increased from 10% to 30%, from 1950 to 1990, with the
Soviet Union being the world's largest producer during the mid-1970s and the 1980s, and China starting major lead production in the late 20th century. Unlike the European communist countries, China was largely unindustrialized by the mid-20th century; in 2004, China surpassed Australia as the largest producer of lead. As was the case during European industrialization, lead has had a negative effect on health in China.
Production

As of 2014, production of lead is increasing worldwide due to its use in lead–acid batteries. There are two major categories of production: primary from mined ores, and secondary from scrap. In 2014, 4.58 million metric tons came from primary production and 5.64 million from secondary production. The top three producers of mined lead concentrate in that year were China, Australia, and the United States. The top three producers of refined lead were China, the United States, and India. According to the
International Resource Panel's
Metal Stocks in Society report
The report Metal Stocks in Society: Scientific Synthesis was the first of six scientific assessments on global metals to be published by the International Resource Panel (IRP) of the United Nations Environment Programme. The IRP provides independ ...
of 2010, the total amount of lead in use, stockpiled, discarded, or dissipated into the environment, on a global basis, is 8 kg per capita. Much of this is in more developed countries (20–150 kg per capita) rather than less developed ones (1–4 kg per capita).
The primary and secondary lead production processes are similar. Some primary production plants now supplement their operations with scrap lead, and this trend is likely to increase in the future. Given adequate techniques, lead obtained via secondary processes is indistinguishable from lead obtained via primary processes. Scrap lead from the building trade is usually fairly clean and is re-melted without the need for smelting, though refining is sometimes needed. Secondary lead production is therefore cheaper, in terms of energy requirements, than is primary production, often by 50% or more.
Primary
Most lead ores contain a low percentage of lead (rich ores have a typical content of 3–8%) which must be concentrated for extraction. During initial processing, ores typically undergo crushing,
dense-medium separation,
grinding,
froth flotation, and drying. The resulting concentrate, which has a lead content of 30–80% by mass (regularly 50–60%), is then turned into (impure) lead metal.
There are two main ways of doing this: a two-stage process involving roasting followed by blast furnace extraction, carried out in separate vessels; or a direct process in which the extraction of the concentrate occurs in a single vessel. The latter has become the most common route, though the former is still significant.
roasted
Roasting is a cooking method that uses dry heat where hot air covers the food, cooking it evenly on all sides with temperatures of at least from an open flame, oven, or other heat source. Roasting can enhance the flavor through caramelization ...
in air to oxidize the lead sulfide:
: 2 PbS(s) + 3 O
2(g) → 2 PbO(s) + 2 SO
2(g)↑
As the original concentrate was not pure lead sulfide, roasting yields not only the desired lead(II) oxide, but a mixture of oxides, sulfates, and silicates of lead and of the other metals contained in the ore. This impure lead oxide is reduced in a
coke-fired blast furnace to the (again, impure) metal:
: 2 PbO(s) + C(s) → 2 Pb(s) + CO
2(g)↑
Impurities are mostly arsenic, antimony, bismuth, zinc, copper, silver, and gold. Typically they are removed in a series of
pyrometallurgical processes. The melt is treated in a
reverberatory furnace with air, steam, and sulfur, which oxidizes the impurities except for silver, gold, and bismuth. Oxidized contaminants float to the
top of the melt and are skimmed off. Metallic silver and gold are removed and recovered economically by means of the
Parkes process, in which zinc is added to lead. Zinc, which is immiscible in lead, dissolves the silver and gold. The zinc solution can be separated from the lead, and the silver and gold retrieved. De-silvered lead is freed of bismuth by the
Betterton–Kroll process
The Betterton-Kroll Process is a pyrometallurgical process for refining lead from lead bullion(lead that still contains significant amounts of impurities). Developed by William Justin Kroll in 1922, the Betterton–Kroll process is one of the fin ...
, treating it with metallic calcium and
magnesium. The resulting bismuth dross can be skimmed off.
Alternatively to the pyrometallurgical processes, very pure lead can be obtained by processing smelted lead electrolytically using the
Betts process The Betts electrolytic process is an industrial process for purification of lead from bullion. Lead obtained from its ores is impure because lead is a good solvent for many metals. Often these impurities are tolerated, but the Betts electrolytic p ...
. Anodes of impure lead and cathodes of pure lead are placed in an electrolyte of lead
fluorosilicate
Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.
Hexaflu ...
(PbSiF
6). Once electrical potential is applied, impure lead at the anode dissolves and plates onto the cathode, leaving the majority of the impurities in solution. This is a high-cost process and thus mostly reserved for refining bullion containing high percentages of impurities.
Direct process
In this process, lead bullion and
slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-prod ...
is obtained directly from lead concentrates. The lead sulfide concentrate is melted in a furnace and oxidized, forming lead monoxide. Carbon (as coke or
coal gas
Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal and supplied to the user via a piped distribution system. It is produced when coal is heated strongly in the absence of air. Town gas is a more general term referring to manufactured gaseous ...
) is added to the molten charge along with
fluxing agents
In metallurgy, a flux () is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.
Some of the earliest known fluxes we ...
. The lead monoxide is thereby reduced to metallic lead, in the midst of a slag rich in lead monoxide.
If the input is rich in lead, as much as 80% of the original lead can be obtained as bullion; the remaining 20% forms a slag rich in lead monoxide. For a low-grade feed, all of the lead can be oxidized to a high-lead slag. Metallic lead is further obtained from the high-lead (25–40%) slags via submerged fuel combustion or injection, reduction assisted by an electric furnace, or a combination of both.
Alternatives
Research on a cleaner, less energy-intensive lead extraction process continues; a major drawback is that either too much lead is lost as waste, or the alternatives result in a high sulfur content in the resulting lead metal.
Hydrometallurgical extraction, in which
anodes of impure lead are immersed into an
electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dis ...
and pure lead is deposited (
electrowound) onto a cathode, is a technique that may have potential, but is not currently economical except in cases where electricity is very cheap.
Secondary
Smelting, which is an essential part of the primary production, is often skipped during secondary production. It is only performed when metallic lead has undergone significant oxidation. The process is similar to that of primary production in either a
blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
or a
rotary furnace
A rotary kiln is a pyroprocessing device used to raise materials to a high temperature (calcination) in a continuous process. Materials produced using rotary kilns include:
* Cement
* Lime
* Refractories
* Metakaolin
* Titanium dioxide
* Alum ...
, with the essential difference being the greater variability of yields: blast furnaces produce hard lead (10% antimony) while reverberatory and rotary kiln furnaces produced semisoft lead (3–4% antimony).
The
ISASMELT process is a more recent smelting method that may act as an extension to primary production; battery paste from spent lead–acid batteries (containing lead sulfate and lead oxides) has its sulfate removed by treating it with alkali, and is then treated in a coal-fueled furnace in the presence of oxygen, which yields impure lead, with antimony the most common impurity. Refining of secondary lead is similar to that of primary lead; some refining processes may be skipped depending on the material recycled and its potential contamination.
Of the sources of lead for recycling, lead–acid batteries are the most important; lead pipe, sheet, and cable sheathing are also significant.
Applications

Contrary to popular belief, pencil leads in wooden pencils have never been made from lead. When the pencil originated as a wrapped graphite writing tool, the particular type of
graphite used was named
''plumbago'' (literally, ''act for lead'' or ''lead mockup'').
Elemental form
Lead metal has several useful mechanical properties, including high density, low melting point, ductility, and relative inertness. Many metals are superior to lead in some of these aspects but are generally less common and more difficult to extract from parent ores. Lead's toxicity has led to its phasing out for some uses.
Lead has been used for bullets since their invention in the Middle Ages. It is inexpensive; its low melting point means small arms ammunition and shotgun pellets can be cast with minimal technical equipment; and it is denser than other common metals, which allows for better retention of velocity. It remains the main material for bullets, alloyed with other metals as hardeners. Concerns have been raised that lead bullets used for hunting can damage the environment.
Lead's high density and resistance to corrosion have been exploited in a number of related applications. It is used as
ballast in sailboat keels; its density allows it to take up a small volume and minimize water resistance, thus counterbalancing the heeling effect of wind on the sails. It is used in
scuba diving weight belts to counteract the diver's buoyancy. In 1993, the base of the
Leaning Tower of Pisa was stabilized with 600 tonnes of lead. Because of its corrosion resistance, lead is used as a protective sheath for underwater cables.
Lead has many uses in the construction industry; lead sheets are used as
architectural metals in roofing material,
cladding,
flashing,
gutters and gutter joints, and on roof parapets. Lead is still used in statues and sculptures, including for
armatures. In the past it was often used to
balance the wheels of cars; for environmental reasons this use is being phased out in favor of other materials.
Lead is added to copper alloys, such as
brass and bronze, to improve
machinability and for its
lubricating qualities. Being practically insoluble in copper the lead forms solid globules in imperfections throughout the alloy, such as
grain boundaries. In low concentrations, as well as acting as a lubricant, the globules hinder the formation of
swarf
Swarf, also known as chips or by other process-specific names (such as turnings, filings, or shavings), are pieces of metal, wood, or plastic that are the debris or waste resulting from machining, woodworking, or similar subtractive (material-r ...
as the alloy is worked, thereby improving machinability. Copper alloys with larger concentrations of lead are used in
bearings. The lead provides lubrication, and the copper provides the load-bearing support.
Lead's high density, atomic number, and formability form the basis for use of lead as a barrier that absorbs sound, vibration, and radiation. Lead has no natural resonance frequencies; as a result, sheet-lead is used as a sound deadening layer in the walls, floors, and ceilings of sound studios.
Organ pipes are often made from a lead alloy, mixed with various amounts of tin to control the tone of each pipe. Lead is an established
shielding material from
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
in
nuclear science
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
and in
X-ray rooms due to its denseness and high
attenuation coefficient. Molten lead has been used as a
coolant for
lead-cooled fast reactors.
Batteries
The largest use of lead in the early 21st century is in
lead–acid batteries. The lead in batteries undergoes no direct contact with humans, so there are fewer toxicity concerns. People who work in lead battery production plants may be exposed to lead dust and inhale it. The reactions in the battery between lead, lead dioxide, and sulfuric acid provide a reliable source of
voltage.
Supercapacitor
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable ba ...
s incorporating lead–acid batteries have been installed in kilowatt and megawatt scale applications in Australia, Japan, and the United States in frequency regulation, solar smoothing and shifting, wind smoothing, and other applications. These batteries have lower energy density and charge-discharge efficiency than
lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
, but are significantly cheaper.
Coating for cables
Lead is used in high voltage power cables as shell material to prevent water diffusion into insulation; this use is decreasing as lead is being phased out. Its use in
solder for electronics is also being phased out by some countries to reduce the amount of
environmentally hazardous
An environmental hazard is a substance, state or event which has the potential to threaten the surrounding natural environment or adversely affect people's health, including pollution and natural disasters such as storms and earthquakes. It can ...
waste. Lead is one of three metals used in the
Oddy test The Oddy test is a procedure created at the British Museum by conservation scientist William Andrew Oddy in 1973, in order to test materials for safety in and around art objects.
Often, materials for construction and museum contexts (including arte ...
for museum materials, helping detect organic acids, aldehydes, and acidic gases.
Compounds


In addition to being the main application for lead metal, lead-acid batteries are also the main consumer of lead compounds. The energy storage/release reaction used in these devices involves
lead sulfate and
lead dioxide:
:(s) + (s) + 2(aq) → 2(s) + 2(l)
Other applications of lead compounds are very specialized and often fading. Lead-based coloring agents are used in
ceramic glaze
Ceramic glaze is an impervious layer or coating of a vitreous substance which has been fused to a pottery body through firing. Glaze can serve to color, decorate or waterproof an item. Glazing renders earthenware vessels suitable for holding ...
s and glass, especially for red and yellow shades. While lead paints are phased out in Europe and North America, they remain in use in less developed countries such as China, India, or Indonesia. Lead tetraacetate and lead dioxide are used as oxidizing agents in organic chemistry. Lead is frequently used in the
polyvinyl chloride coating of electrical cords. It can be used to treat candle wicks to ensure a longer, more even burn. Because of its toxicity, European and North American manufacturers use alternatives such as zinc.
Lead glass is composed of 12–28%
lead oxide, changing its optical characteristics and reducing the transmission of ionizing radiation, a property used in old TVs and computer monitors with
cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictur ...
s. Lead-based
semiconductors such as lead telluride and lead selenide are used in
photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
cells and
infrared detectors.
Biological effects
Lead has no confirmed biological role, and there is no confirmed safe level of lead exposure. A 2009 Canadian–American study concluded that even at levels that are considered to pose little to no risk, lead may cause "adverse mental health outcomes". Its prevalence in the human body—at an adult average of 120 mg—is nevertheless exceeded only by zinc (2500 mg) and iron (4000 mg) among the heavy metals. Lead
salts are very efficiently absorbed by the body. A small amount of lead (1%) is stored in bones; the rest is excreted in urine and feces within a few weeks of exposure. Only about a third of lead is excreted by a child. Continual exposure may result in the
bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated ...
of lead.
Toxicity
Lead is a highly poisonous metal (whether inhaled or swallowed), affecting almost every organ and system in the human body. At airborne levels of 100 mg/m
3, it is
immediately dangerous to life and health
The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent advers ...
. Most ingested lead is absorbed into the bloodstream. The primary cause of its toxicity is its predilection for interfering with the proper functioning of enzymes. It does so by binding to the
sulfhydryl groups found on many enzymes, or mimicking and displacing other metals which act as
cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
in many enzymatic reactions. The essential metals that lead interacts with include calcium, iron, and zinc. High levels of calcium and iron tend to provide some protection from lead poisoning; low levels cause increased susceptibility.
Effects
Lead can cause severe damage to the brain and kidneys and, ultimately, death. By mimicking calcium, lead can cross the
blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
. It degrades the
myelin sheaths of
neurons, reduces their numbers, interferes with
neurotransmission routes, and decreases neuronal growth. In the human body, lead inhibits
porphobilinogen synthase and
ferrochelatase, preventing both
porphobilinogen formation and the incorporation of iron into
protoporphyrin IX, the final step in
heme synthesis. This causes ineffective heme synthesis and
microcytic anemia.

Symptoms of lead poisoning include
nephropathy
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can ...
,
colic-like abdominal pains, and possibly weakness in the fingers, wrists, or ankles. Small blood pressure increases, particularly in middle-aged and older people, may be apparent and can cause
anemia. Several studies, mostly cross-sectional, found an association between increased lead exposure and decreased heart rate variability. In pregnant women, high levels of exposure to lead may cause miscarriage. Chronic, high-level exposure has been shown to reduce fertility in males.
In a child's developing brain, lead interferes with
synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
formation in the
cerebral cortex,
neurochemical development (including that of neurotransmitters), and the organization of
ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
s. Early childhood exposure has been linked with an increased risk of sleep disturbances and excessive daytime drowsiness in later childhood. High blood levels are associated with delayed puberty in girls. The rise and fall in exposure to airborne lead from the combustion of tetraethyl lead in gasoline during the 20th century has been linked with historical increases and
decreases in crime levels.
Exposure sources
Lead exposure is a global issue since lead mining and smelting, and battery manufacturing, disposal, and
recycling, are common in many countries. Lead enters the body via inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. Almost all inhaled lead is absorbed into the body; for ingestion, the rate is 20–70%, with children absorbing a higher percentage than adults.
Poisoning typically results from ingestion of food or water contaminated with lead, and less commonly after accidental ingestion of contaminated soil, dust, or lead-based paint. Seawater products can contain lead if affected by nearby industrial waters. Fruit and vegetables can be contaminated by high levels of lead in the soils they were grown in. Soil can be contaminated through particulate accumulation from lead in pipes, lead paint, and residual emissions from leaded gasoline.
The use of lead for water pipes is
a problem in areas with soft or acidic water. Hard water forms insoluble protective layers on the inner surface of the pipes, whereas soft and acidic water dissolves the lead pipes. Dissolved
carbon dioxide in the carried water may result in the formation of soluble lead
bicarbonate; oxygenated water may similarly dissolve lead as
lead(II) hydroxide
Lead(II) hydroxide, Pb(OH)2, is a hydroxide of lead, with lead in oxidation state +2. In 1964 it was believed that such a simple compound did not exist, as lead basic carbonate (2PbCO3·Pb(OH)2) or lead(II) oxide (PbO) was encountered where lead ...
. Drinking such water, over time, can cause health problems due to the toxicity of the dissolved lead. The
harder the water the more
calcium bicarbonate and
sulfate it will contain, and the more the inside of the pipes will be coated with a protective layer of lead carbonate or lead sulfate.

Ingestion of applied lead-based paint is the major source of exposure for children:
a direct source is chewing on old painted window sills. Alternatively, as the applied dry paint deteriorates, it peels, is pulverized into dust and then enters the body through hand-to-mouth contact or contaminated food, water, or alcohol. Ingesting certain
home remedies
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
may result in exposure to lead or its compounds.
Inhalation is the second major exposure pathway, affecting smokers and especially workers in lead-related occupations.
Cigarette smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C d ...
contains, among other toxic substances, radioactive
lead-210. "As a result of EPA's regulatory efforts, levels of lead in the air
n the United States
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
decreased by 86 percent between 2010 and 2020."
The concentration of lead in the air in the United States fell below the national standard of 0.15 μg/m
3 in 2014.
Skin exposure may be significant for people working with organic lead compounds. The rate of skin absorption is lower for inorganic lead.
Lead in plastic toys
According to the United States
Center for Disease Control, the use of lead in plastics has not been banned. Lead softens the plastic and makes it more flexible so that it can go back to its original shape. It may also be used in plastic toys to stabilize molecules from heat. Lead dust can be formed when plastic is exposed to sunlight, air, and detergents that break down the chemical bond between the lead and plastics.
Treatment
Treatment for lead poisoning normally involves the administration of
dimercaprol and
succimer
Succimer, sold under the brand name Chemet among others, is a medication used to treat lead, mercury, and arsenic poisoning. When radiolabeled with technetium-99m, it is used in a number of types of diagnostic testing. A full course is 19 days ...
. Acute cases may require the use of
disodium calcium edetate
Sodium calcium edetate (sodium calcium EDTA), also known as edetate calcium disodium among other names, is a medication primarily used to treat lead poisoning, including both short-term and long-term lead poisoning. Sodium calcium edetate came in ...
, the calcium
chelate, and the disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (
EDTA). It has a greater affinity for lead than calcium, with the result that lead chelate is formed by exchange and excreted in the urine, leaving behind harmless calcium.
Environmental effects

The extraction, production, use, and disposal of lead and its products have caused significant contamination of the Earth's soils and waters. Atmospheric emissions of lead were at their peak during the Industrial Revolution, and the leaded gasoline period in the second half of the twentieth century.
Lead releases originate from natural sources (i.e., concentration of the naturally occurring lead), industrial production, incineration and recycling, and mobilization of previously buried lead. In particular, as lead has been phased out from other uses, in the Global South, lead recycling operations designed to extract cheap lead used for global manufacturing have become a well documented source of exposure.
Elevated concentrations of lead persist in soils and sediments in post-industrial and urban areas; industrial emissions, including those arising from coal burning, continue in many parts of the world, particularly in the developing countries.
Lead can accumulate in soils, especially those with a high organic content, where it remains for hundreds to thousands of years. Environmental lead can compete with other metals found in and on plants surfaces potentially inhibiting
photosynthesis and at high enough concentrations, negatively affecting plant growth and survival. Contamination of soils and plants can allow lead to ascend the food chain affecting microorganisms and animals. In animals, lead exhibits toxicity in many organs, damaging the nervous,
renal, reproductive,
hematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. ...
, and cardiovascular systems after ingestion, inhalation, or skin absorption. Fish uptake lead from both water and sediment; bioaccumulation in the food chain poses a hazard to fish, birds, and sea mammals.
Anthropogenic lead includes lead from
shot
Shot may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Shot'' (album), by The Jesus Lizard
*''Shot, Illusion, New God'', an EP by Gruntruck
*''Shot Rev 2.0'', a video album by The Sisters of Mercy
* "Shot" (song), by The Rasmus
* ''Shot'' (2017 fi ...
and
sinkers. These are among the most potent sources of lead contamination along with lead production sites. Lead was banned for shot and sinkers in the United States in 2017, although that ban was only effective for a month, and a similar ban is being considered in the European Union.
Analytical methods for the determination of lead in the environment include
spectrophotometry,
X-ray fluorescence,
atomic spectroscopy
Atomic spectroscopy is the study of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed and emitted by atoms. Since unique elements have characteristic (signature) spectra, atomic spectroscopy, specifically the electromagnetic spectrum or mass spectrum, is appl ...
and
electrochemical methods. A specific
ion-selective electrode has been developed based on the ionophore S,S'-methylenebis (N,N-diisobutyl
dithiocarbamate). An important biomarker assay for lead poisoning is δ-aminolevulinic acid levels in plasma, serum, and urine.
Restriction and remediation
By the mid-1980s, there was significant decline in the use of lead in industry. In the United States, environmental regulations reduced or eliminated the use of lead in non-battery products, including gasoline, paints, solders, and water systems. Particulate control devices were installed in
coal-fired power plants to capture lead emissions. In 1992, U.S. Congress required the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce the blood lead levels of the country's children. Lead use was further curtailed by the European Union's 2003
Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive. A large drop in lead deposition occurred in the Netherlands after the 1993 national ban on use of lead shot for hunting and sport shooting: from 230 tonnes in 1990 to 47.5 tonnes in 1995.
In the United States, the
permissible exposure limit for lead in the workplace, comprising metallic lead, inorganic lead compounds, and lead soaps, was set at 50 μg/m
3 over an 8-hour workday, and the
blood lead level
Blood lead level (BLL), is a measure of the amount of lead in the blood. Lead is a toxic heavy metal and can cause neurological damage, especially among children, at any detectable level. High lead levels cause decreased vitamin D and haemoglob ...
limit at 5 μg per 100 g of blood in 2012. Lead may still be found in harmful quantities in stoneware,
vinyl (such as that used for tubing and the insulation of electrical cords), and Chinese brass. Old houses may still contain lead paint. White lead paint has been
withdrawn from sale in industrialized countries, but specialized uses of other pigments such as yellow
lead chromate remain. Stripping old paint by sanding produces dust which can be inhaled.
Lead abatement programs have been mandated by some authorities in properties where young children live.
Lead waste, depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the waste, may be treated as household waste (to facilitate lead abatement activities), or potentially hazardous waste requiring specialized treatment or storage. Lead is released into the environment in shooting places and a number of lead management practices have been developed to counter the lead contamination. Lead migration can be enhanced in acidic soils; to counter that, it is advised soils be treated with lime to neutralize the soils and prevent leaching of lead.
Research has been conducted on how to remove lead from biosystems by biological means: Fish bones are being researched for their ability to
bioremediate
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluent ...
lead in contaminated soil. The fungus ''
Aspergillus versicolor
''Aspergillus versicolor'' is a slow-growing filamentous fungus commonly found in damp indoor environments and on food products. It has a characteristic musty odor associated with moldy homes and is a major producer of the hepatotoxic and carcin ...
'' is effective at absorbing lead ions from industrial waste before being released to water bodies. Several bacteria have been researched for their ability to remove lead from the environment, including the
sulfate-reducing bacteria ''
Desulfovibrio'' and ''
Desulfotomaculum
''Desulfotomaculum'' is a genus of Gram-positive, obligately anaerobic soil bacteria. A type of sulfate-reducing bacteria, ''Desulfotomaculum'' can cause food spoilage in poorly processed canned foods. Their presence can be identified by the re ...
'', both of which are highly effective in aqueous solutions.
See also
*
Derek Bryce-Smith – one of the earliest campaigners against lead in petrol in the UK
*
Thomas Midgley Jr.
Thomas Midgley Jr. (May 18, 1889 – November 2, 1944) was an American mechanical and chemical engineer. He played a major role in developing leaded gasoline (tetraethyl lead) and some of the first chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), better known i ...
– discovered that the addition of
tetraethyllead to gasoline prevented
"knocking" in
internal combustion engines
*
Clair Patterson – instrumental in the banning of tetraethyllead in gasoline in the US and lead solder in food cans.
*
Robert A. Kehoe
Robert Arthur Kehoe (; November 18, 1893 – November 24, 1992) was an American toxicologist and a dominant figure in occupational health. Working on behalf of the lead industry (including the manufacturing of leaded gasoline and lead-acid batter ...
– foremost medical advocate for the use of tetraethyllead as an additive in gasoline.
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
Table of contents*
External links
The Toxicology of Heavy Metals: Getting the Lead Out American Society for Clinical Pathology The American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) is a professional association based in Chicago, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and ...
{{Authority control
Chemical elements
Post-transition metals
Native element minerals
Superconductors
Endocrine disruptors
IARC Group 2B carcinogens
Nuclear reactor coolants
Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure
 Lead's close-packed face-centered cubic structure and high atomic weight result in a density of 11.34 g/cm3, which is greater than that of common metals such as iron (7.87 g/cm3), copper (8.93 g/cm3), and zinc (7.14 g/cm3). This density is the origin of the idiom ''to go over like a lead balloon''. Some rarer metals are denser: tungsten and gold are both at 19.3 g/cm3, and
Lead's close-packed face-centered cubic structure and high atomic weight result in a density of 11.34 g/cm3, which is greater than that of common metals such as iron (7.87 g/cm3), copper (8.93 g/cm3), and zinc (7.14 g/cm3). This density is the origin of the idiom ''to go over like a lead balloon''. Some rarer metals are denser: tungsten and gold are both at 19.3 g/cm3, and  Apart from the stable isotopes, which make up almost all lead that exists naturally, there are trace quantities of a few radioactive isotopes. One of them is lead-210; although it has a half-life of only 22.2 years, small quantities occur in nature because lead-210 is produced by a long decay series that starts with uranium-238 (that has been present for billions of years on Earth). Lead-211, −212, and −214 are present in the decay chains of uranium-235, thorium-232, and uranium-238, respectively, so traces of all three of these lead isotopes are found naturally. Minute traces of lead-209 arise from the very rare
Apart from the stable isotopes, which make up almost all lead that exists naturally, there are trace quantities of a few radioactive isotopes. One of them is lead-210; although it has a half-life of only 22.2 years, small quantities occur in nature because lead-210 is produced by a long decay series that starts with uranium-238 (that has been present for billions of years on Earth). Lead-211, −212, and −214 are present in the decay chains of uranium-235, thorium-232, and uranium-238, respectively, so traces of all three of these lead isotopes are found naturally. Minute traces of lead-209 arise from the very rare  Bulk lead exposed to moist air forms a protective layer of varying composition. Lead(II) carbonate is a common constituent; the sulfate or chloride may also be present in urban or maritime settings. This layer makes bulk lead effectively chemically inert in the air. Finely powdered lead, as with many metals, is pyrophoric, and burns with a bluish-white flame.
Bulk lead exposed to moist air forms a protective layer of varying composition. Lead(II) carbonate is a common constituent; the sulfate or chloride may also be present in urban or maritime settings. This layer makes bulk lead effectively chemically inert in the air. Finely powdered lead, as with many metals, is pyrophoric, and burns with a bluish-white flame.
 Lead dihalides are well-characterized; this includes the diastatide and mixed halides, such as PbFCl. The relative insolubility of the latter forms a useful basis for the gravimetric determination of fluorine. The difluoride was the first solid ionically conducting compound to be discovered (in 1834, by Michael Faraday). The other dihalides decompose on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, especially the diiodide. Many lead(II) pseudohalides are known, such as the
Lead dihalides are well-characterized; this includes the diastatide and mixed halides, such as PbFCl. The relative insolubility of the latter forms a useful basis for the gravimetric determination of fluorine. The difluoride was the first solid ionically conducting compound to be discovered (in 1834, by Michael Faraday). The other dihalides decompose on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, especially the diiodide. Many lead(II) pseudohalides are known, such as the  Some lead compounds exist in formal oxidation states other than +4 or +2. Lead(III) may be obtained, as an intermediate between lead(II) and lead(IV), in larger organolead complexes; this oxidation state is not stable, as both the lead(III) ion and the larger complexes containing it are
Some lead compounds exist in formal oxidation states other than +4 or +2. Lead(III) may be obtained, as an intermediate between lead(II) and lead(IV), in larger organolead complexes; this oxidation state is not stable, as both the lead(III) ion and the larger complexes containing it are  Lead can form multiply-bonded chains, a property it shares with its lighter homologs in the carbon group. Its capacity to do so is much less because the Pb–Pb bond energy is over three and a half times lower than that of the C–C bond. With itself, lead can build metal–metal bonds of an order up to three. With carbon, lead forms organolead compounds similar to, but generally less stable than, typical organic compounds (due to the Pb–C bond being rather weak). This makes the
Lead can form multiply-bonded chains, a property it shares with its lighter homologs in the carbon group. Its capacity to do so is much less because the Pb–Pb bond energy is over three and a half times lower than that of the C–C bond. With itself, lead can build metal–metal bonds of an order up to three. With carbon, lead forms organolead compounds similar to, but generally less stable than, typical organic compounds (due to the Pb–C bond being rather weak). This makes the  Rome's territorial expansion in Europe and across the Mediterranean, and its development of mining, led to it becoming the greatest producer of lead during the classical era, with an estimated annual output peaking at 80,000 tonnes. Like their predecessors, the Romans obtained lead mostly as a by-product of silver smelting.
Rome's territorial expansion in Europe and across the Mediterranean, and its development of mining, led to it becoming the greatest producer of lead during the classical era, with an estimated annual output peaking at 80,000 tonnes. Like their predecessors, the Romans obtained lead mostly as a by-product of silver smelting.  Lead was used for making water pipes in the Roman Empire; the Latin word for the metal, , is the origin of the English word "plumbing". Its ease of working, its low melting point enabling the easy fabrication of completely waterproof welded joints, and its resistance to corrosion ensured its widespread use in other applications, including pharmaceuticals, roofing, currency, and warfare. Writers of the time, such as Cato the Elder, Columella, and Pliny the Elder, recommended lead (or lead-coated) vessels for the preparation of sweeteners and preservatives added to wine and food. The lead conferred an agreeable taste due to the formation of "sugar of lead" (lead(II) acetate), whereas copper or
Lead was used for making water pipes in the Roman Empire; the Latin word for the metal, , is the origin of the English word "plumbing". Its ease of working, its low melting point enabling the easy fabrication of completely waterproof welded joints, and its resistance to corrosion ensured its widespread use in other applications, including pharmaceuticals, roofing, currency, and warfare. Writers of the time, such as Cato the Elder, Columella, and Pliny the Elder, recommended lead (or lead-coated) vessels for the preparation of sweeteners and preservatives added to wine and food. The lead conferred an agreeable taste due to the formation of "sugar of lead" (lead(II) acetate), whereas copper or  In the second half of the 18th century, Britain, and later continental Europe and the United States, experienced the Industrial Revolution. This was the first time during which lead production rates exceeded those of Rome. Britain was the leading producer, losing this status by the mid-19th century with the depletion of its mines and the development of lead mining in Germany, Spain, and the United States. By 1900, the United States was the leader in global lead production, and other non-European nations—Canada, Mexico, and Australia—had begun significant production; production outside Europe exceeded that within. A great share of the demand for lead came from plumbing and painting— lead paints were in regular use. At this time, more (working class) people were exposed to the metal and lead poisoning cases escalated. This led to research into the effects of lead intake. Lead was proven to be more dangerous in its fume form than as a solid metal. Lead poisoning and gout were linked; British physician Alfred Baring Garrod noted a third of his gout patients were plumbers and painters. The effects of chronic ingestion of lead, including mental disorders, were also studied in the 19th century. The first laws aimed at decreasing lead poisoning in factories were enacted during the 1870s and 1880s in the United Kingdom.
In the second half of the 18th century, Britain, and later continental Europe and the United States, experienced the Industrial Revolution. This was the first time during which lead production rates exceeded those of Rome. Britain was the leading producer, losing this status by the mid-19th century with the depletion of its mines and the development of lead mining in Germany, Spain, and the United States. By 1900, the United States was the leader in global lead production, and other non-European nations—Canada, Mexico, and Australia—had begun significant production; production outside Europe exceeded that within. A great share of the demand for lead came from plumbing and painting— lead paints were in regular use. At this time, more (working class) people were exposed to the metal and lead poisoning cases escalated. This led to research into the effects of lead intake. Lead was proven to be more dangerous in its fume form than as a solid metal. Lead poisoning and gout were linked; British physician Alfred Baring Garrod noted a third of his gout patients were plumbers and painters. The effects of chronic ingestion of lead, including mental disorders, were also studied in the 19th century. The first laws aimed at decreasing lead poisoning in factories were enacted during the 1870s and 1880s in the United Kingdom.
 Further evidence of the threat that lead posed to humans was discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Mechanisms of harm were better understood, lead blindness was documented, and the element was phased out of public use in the United States and Europe. The United Kingdom introduced mandatory factory inspections in 1878 and appointed the first Medical Inspector of Factories in 1898; as a result, a 25-fold decrease in lead poisoning incidents from 1900 to 1944 was reported. Most European countries banned lead paint—commonly used because of its opacity and water resistance—for interiors by 1930.
The last major human exposure to lead was the addition of tetraethyllead to gasoline as an antiknock agent, a practice that originated in the United States in 1921. It was phased out in the United States and the European Union by 2000.
In the 1970s, the United States and Western European countries introduced legislation to reduce lead air pollution. The impact was significant: while a study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States in 1976–1980 showed that 77.8% of the population had elevated
Further evidence of the threat that lead posed to humans was discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Mechanisms of harm were better understood, lead blindness was documented, and the element was phased out of public use in the United States and Europe. The United Kingdom introduced mandatory factory inspections in 1878 and appointed the first Medical Inspector of Factories in 1898; as a result, a 25-fold decrease in lead poisoning incidents from 1900 to 1944 was reported. Most European countries banned lead paint—commonly used because of its opacity and water resistance—for interiors by 1930.
The last major human exposure to lead was the addition of tetraethyllead to gasoline as an antiknock agent, a practice that originated in the United States in 1921. It was phased out in the United States and the European Union by 2000.
In the 1970s, the United States and Western European countries introduced legislation to reduce lead air pollution. The impact was significant: while a study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States in 1976–1980 showed that 77.8% of the population had elevated  Contrary to popular belief, pencil leads in wooden pencils have never been made from lead. When the pencil originated as a wrapped graphite writing tool, the particular type of graphite used was named ''plumbago'' (literally, ''act for lead'' or ''lead mockup'').
Contrary to popular belief, pencil leads in wooden pencils have never been made from lead. When the pencil originated as a wrapped graphite writing tool, the particular type of graphite used was named ''plumbago'' (literally, ''act for lead'' or ''lead mockup'').

 In addition to being the main application for lead metal, lead-acid batteries are also the main consumer of lead compounds. The energy storage/release reaction used in these devices involves lead sulfate and lead dioxide:
:(s) + (s) + 2(aq) → 2(s) + 2(l)
Other applications of lead compounds are very specialized and often fading. Lead-based coloring agents are used in
In addition to being the main application for lead metal, lead-acid batteries are also the main consumer of lead compounds. The energy storage/release reaction used in these devices involves lead sulfate and lead dioxide:
:(s) + (s) + 2(aq) → 2(s) + 2(l)
Other applications of lead compounds are very specialized and often fading. Lead-based coloring agents are used in  Symptoms of lead poisoning include
Symptoms of lead poisoning include  Ingestion of applied lead-based paint is the major source of exposure for children:
a direct source is chewing on old painted window sills. Alternatively, as the applied dry paint deteriorates, it peels, is pulverized into dust and then enters the body through hand-to-mouth contact or contaminated food, water, or alcohol. Ingesting certain
Ingestion of applied lead-based paint is the major source of exposure for children:
a direct source is chewing on old painted window sills. Alternatively, as the applied dry paint deteriorates, it peels, is pulverized into dust and then enters the body through hand-to-mouth contact or contaminated food, water, or alcohol. Ingesting certain  The extraction, production, use, and disposal of lead and its products have caused significant contamination of the Earth's soils and waters. Atmospheric emissions of lead were at their peak during the Industrial Revolution, and the leaded gasoline period in the second half of the twentieth century.
Lead releases originate from natural sources (i.e., concentration of the naturally occurring lead), industrial production, incineration and recycling, and mobilization of previously buried lead. In particular, as lead has been phased out from other uses, in the Global South, lead recycling operations designed to extract cheap lead used for global manufacturing have become a well documented source of exposure. Elevated concentrations of lead persist in soils and sediments in post-industrial and urban areas; industrial emissions, including those arising from coal burning, continue in many parts of the world, particularly in the developing countries.
Lead can accumulate in soils, especially those with a high organic content, where it remains for hundreds to thousands of years. Environmental lead can compete with other metals found in and on plants surfaces potentially inhibiting photosynthesis and at high enough concentrations, negatively affecting plant growth and survival. Contamination of soils and plants can allow lead to ascend the food chain affecting microorganisms and animals. In animals, lead exhibits toxicity in many organs, damaging the nervous, renal, reproductive,
The extraction, production, use, and disposal of lead and its products have caused significant contamination of the Earth's soils and waters. Atmospheric emissions of lead were at their peak during the Industrial Revolution, and the leaded gasoline period in the second half of the twentieth century.
Lead releases originate from natural sources (i.e., concentration of the naturally occurring lead), industrial production, incineration and recycling, and mobilization of previously buried lead. In particular, as lead has been phased out from other uses, in the Global South, lead recycling operations designed to extract cheap lead used for global manufacturing have become a well documented source of exposure. Elevated concentrations of lead persist in soils and sediments in post-industrial and urban areas; industrial emissions, including those arising from coal burning, continue in many parts of the world, particularly in the developing countries.
Lead can accumulate in soils, especially those with a high organic content, where it remains for hundreds to thousands of years. Environmental lead can compete with other metals found in and on plants surfaces potentially inhibiting photosynthesis and at high enough concentrations, negatively affecting plant growth and survival. Contamination of soils and plants can allow lead to ascend the food chain affecting microorganisms and animals. In animals, lead exhibits toxicity in many organs, damaging the nervous, renal, reproductive,  By the mid-1980s, there was significant decline in the use of lead in industry. In the United States, environmental regulations reduced or eliminated the use of lead in non-battery products, including gasoline, paints, solders, and water systems. Particulate control devices were installed in coal-fired power plants to capture lead emissions. In 1992, U.S. Congress required the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce the blood lead levels of the country's children. Lead use was further curtailed by the European Union's 2003 Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive. A large drop in lead deposition occurred in the Netherlands after the 1993 national ban on use of lead shot for hunting and sport shooting: from 230 tonnes in 1990 to 47.5 tonnes in 1995.
In the United States, the permissible exposure limit for lead in the workplace, comprising metallic lead, inorganic lead compounds, and lead soaps, was set at 50 μg/m3 over an 8-hour workday, and the
By the mid-1980s, there was significant decline in the use of lead in industry. In the United States, environmental regulations reduced or eliminated the use of lead in non-battery products, including gasoline, paints, solders, and water systems. Particulate control devices were installed in coal-fired power plants to capture lead emissions. In 1992, U.S. Congress required the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce the blood lead levels of the country's children. Lead use was further curtailed by the European Union's 2003 Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive. A large drop in lead deposition occurred in the Netherlands after the 1993 national ban on use of lead shot for hunting and sport shooting: from 230 tonnes in 1990 to 47.5 tonnes in 1995.
In the United States, the permissible exposure limit for lead in the workplace, comprising metallic lead, inorganic lead compounds, and lead soaps, was set at 50 μg/m3 over an 8-hour workday, and the