Lazs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Laz people, or Lazi ( lzz, ლაზი ''Lazi''; ka, ლაზი, ''lazi''; or ჭანი, ''ch'ani''; tr, Laz), are an indigenous ethnic group who mainly live in

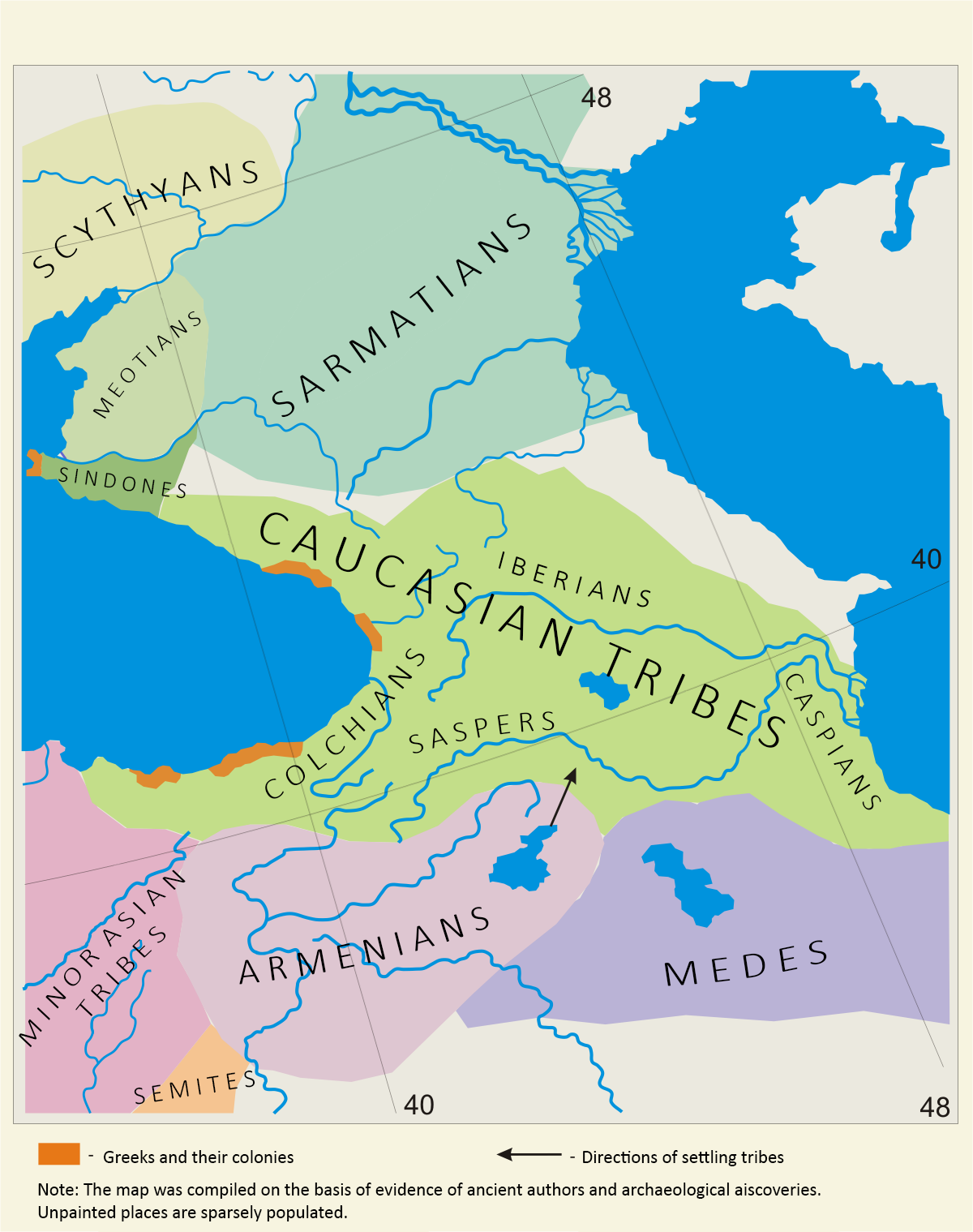 By the sixth century BC, the tribes living in the southern Colchis (
By the sixth century BC, the tribes living in the southern Colchis (
 The warlike tribes of the Chaldia, called Tzanni, the ancestors of modern Laz people lived in ''Tzanica'', the area located between the Byzantine and the Lazica. It included several settlements named: Athenae, Archabis and Apsarus; Tzanni were neither subjects of the Romans nor of the king of the Lazica, except that during the reign of the
The warlike tribes of the Chaldia, called Tzanni, the ancestors of modern Laz people lived in ''Tzanica'', the area located between the Byzantine and the Lazica. It included several settlements named: Athenae, Archabis and Apsarus; Tzanni were neither subjects of the Romans nor of the king of the Lazica, except that during the reign of the  From 542 to 562, Lazica was a scene of the protracted rivalry between the
From 542 to 562, Lazica was a scene of the protracted rivalry between the  With the Georgian intervention in Chaldia and collapse of Byzantine Empire in 1204, Empire of Trebizond was established along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea, populated by a large Kartvelian-speaking population.Mikaberidze, A. (2015). Historical dictionary of Georgia. 2nd ed. Lanham, MD, United States: ROWMAN & LITTLEFIELD, p.634. In the eastern part of the same empire, an autonomous coastal theme of Greater Lazia was established. Byzantine authors, such as
With the Georgian intervention in Chaldia and collapse of Byzantine Empire in 1204, Empire of Trebizond was established along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea, populated by a large Kartvelian-speaking population.Mikaberidze, A. (2015). Historical dictionary of Georgia. 2nd ed. Lanham, MD, United States: ROWMAN & LITTLEFIELD, p.634. In the eastern part of the same empire, an autonomous coastal theme of Greater Lazia was established. Byzantine authors, such as
 Laz populated area was often contested by different Georgian principalities, however through Battle of Murjakheti in 1535,
Laz populated area was often contested by different Georgian principalities, however through Battle of Murjakheti in 1535,
Metropolitan of Manglisi, Ananias Japaridze, nplg.gov.ge thus gradually becoming
 The majority of the Laz today live in an area they call ''Laziǩa, Lazistan, Lazeti'' or ''Lazona'' name of the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Laz people in modern northeast Turkey and southwest Georgia. Geographically, Lazistan consists of a series of narrow, rugged valleys extending northward from the crest of the
The majority of the Laz today live in an area they call ''Laziǩa, Lazistan, Lazeti'' or ''Lazona'' name of the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Laz people in modern northeast Turkey and southwest Georgia. Geographically, Lazistan consists of a series of narrow, rugged valleys extending northward from the crest of the
 Lazuri is a complex and morphologically rich tongue belonging to the South Caucasian language family whose other members are
Lazuri is a complex and morphologically rich tongue belonging to the South Caucasian language family whose other members are
 The Laz are noted for their folk dances, called the
The Laz are noted for their folk dances, called the 
 Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the leader of the early decades of the Republic, aimed to create a nation state ( tr, Ulus) from the Turkish remnants of the Ottoman Empire. During the first three decades of the Republic, efforts to Turkify geographical names were a recurring theme. Imported maps containing references to historical regions such as
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the leader of the early decades of the Republic, aimed to create a nation state ( tr, Ulus) from the Turkish remnants of the Ottoman Empire. During the first three decades of the Republic, efforts to Turkify geographical names were a recurring theme. Imported maps containing references to historical regions such as
File:Preziosi - Mustapha - Moslem from Batum circa 1852.jpg, Amedeo Preziosi: ''Mustapha, moslem from Batum'', painting,
File:Groupe de Lazes.jpg, Çürüksulu Ali Pasha with Ottoman Georgian and Laz men. Pasha was a descendant of the Georgian noble family of the Tavdgiridze, 19th century
File:Théophile Deyrolle Le Tour du Monde 1875-86.jpg, Young Laz man, engraving from ''Le Tour du Monde'', based on a drawing by
"Laz"
In: ''World Culture Encyclopedia''. Accessed on September 1, 2007.
Negele, Jolyon. ''Turkey: Laz Minority Passive In Face Of Assimilation.''
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, 25 June 1998.
Laz Culture Association
(Turkish)
Lazca.org: Culture, News and Information
(Turkish)
Lazebura.com: Culture, News and Information
(Turkish)
Lazuri.com: Culture Portal
(Turkish) {{DEFAULTSORT:Laz People People from Georgia (country) by ethnic or national origin Ethnic groups in Turkey Ancient peoples of Georgia (country) Tribes in Greco-Roman historiography Peoples of the Caucasus
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coastal regions of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. They traditionally speak the Laz language
The Laz language (; ka, ლაზური ენა/ჭანური ენა, tr; tr, Lazca, tr) is a Kartvelian language spoken by the Laz people on the southeastern shore of the Black Sea. In 2007, it was estimated that there were aroun ...
which is a member of the Kartvelian language family but has experienced a rapid language shift to Turkish. From the 103,900 ethnic Laz in Turkey, only around 20,000 speak Laz and the language is classified as threatened (6b) in Turkey and shifting (7) in Georgia on the Expanded Graded Intergenerational Disruption Scale
The Expanded Graded Intergenerational Disruption Scale (EGIDS), developed by Lewis and Simons (2010), measures a language's status in terms of endangerment or development.
The table below shows the various levels on the scale:
The EGIDS model ...
.
Etymology
The ancestors of the Laz people are cited by many classical authors fromScylax
Scylax of Caryanda ( el, Σκύλαξ ὁ Καρυανδεύς) was a Greek explorer and writer of the late 6th and early 5th centuries BCE. His own writings are lost, though occasionally cited or quoted by later Greek and Roman authors. The peri ...
to Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gen ...
and Agathias
Agathias or Agathias Scholasticus ( grc-gre, Ἀγαθίας σχολαστικός; Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), pp. 23–25582/594), of Myrina (Mysia), an Aeolian city in western Asia Minor (Turkey), was a Greek poet and the principal histo ...
, but the word Lazi in Latin language ( el, Λαζοί, Lazoí) themselves are firstly cited by Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
around the 2nd century BC.

Identity
Self-Identification
Minorsky argued in 1913 that the Laz living in Turkey and Georgia have developed different understandings of what it means to be Laz as their identity in Georgia has largely merged with a Georgian identity with the meaning of "Laz" being seen as merely a regional category. Today, most of those living in Turkey do not consider themselves Turkish, but uphold their Laz identity as a separate one.Identification by non-Laz
In a stereotyping manner, non-Laz often use the term ''Laz'' for groups that are mostly not ethnic Laz: #In Turkey, the term Laz is a 'folk' definition and exonym for anyone originating in the eastern Black Sea coast of Turkey. Sometimes, the term is extended to the western portion of the coast as well. Therefore, this term is often used mostly for ethnicPontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks ( pnt, Ρωμαίοι, Ρωμίοι, tr, Pontus Rumları or , el, Πόντιοι, or , , ka, პონტოელი ბერძნები, ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group i ...
, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Hemshins in addition to Laz in Turkey.
#The residents of the northwestern portion of the Gümüşhane
Gümüşhane () is a city and the capital district of Gümüşhane Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey. The city lies along the Harşit River, at an elevation of , about southwest of Trabzon. According to the 2010 census, population of G ...
are viewed as Laz by other people from Gümüşhane.
#The residents of Posof
Posof ( ka, ფოცხოვი, Potskhovi, formerly ka, დიღვირი, Dighviri) is a district of Ardahan Province of Turkey, in the far east of the country, 75 km from the city of Ardahan. It has a border crossing with neighborin ...
are named as Laz by neighboring communities.
#Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks ( pnt, Ρωμαίοι, Ρωμίοι, tr, Pontus Rumları or , el, Πόντιοι, or , , ka, პონტოელი ბერძნები, ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group i ...
are seen as Laz by other Greeks.
#People from İspir
İspir ( hy, Սպեր, Sper; ka, სპერი, Speri) is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, on the Çoruh River. They also appear as the Sasperi, the name Sper with a Georgian prefix of place Sa ...
and the Hemshins of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
are thought to be Laz by other people from Erzurum.
#The Pontic Greek-speakers from the village of Dönerdere in Van are called as Laz by the neighboring communities.
#A small community living in the Caspian coast of Iran is called as Laz.
History
Origins
The Lazuri-speaking ancestors of the modern Laz originally hailed from the northeast, from the southern part of Abkhazia, and settled in the present homeland of the Laz in antiquity. Modern theories suggest that theColchian tribes The following is a list of ancient Colchian
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its p ...
are direct ancestors of the Laz- Mingrelians, they constituted the dominant ethnic and cultural presence in the south-eastern Black Sea region in antiquity, and hence played a significant role in the ethnogenesis of the modern Georgians.
Antiquity
In the thirteenth century BC, the Kingdom ofColchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
was formed as a result of the increasing consolidation of the tribes inhabiting the region, which covered modern western Georgia and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
's north-eastern provinces of Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
, Rize
Rize (Greek: ρίζα, Laz: რიზინი, Georgian: რიზე,
, Ottoman Turkish: ريزه)
is the capital city of Rize Province in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey.
Rize is a typically Turkish provincial capital w ...
and Artvin
Artvin ( Laz and ; hy, Արտուին, translit=Artuin) is a city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea.
It is located on a hill overlooking the Çoruh River near the Deriner Dam. It is a former bishopric and (vacant) Armeni ...
. Colchis was an important region in Black Sea trade – rich with gold, wax, hemp, and honey. In the eighth century, several Greek trading colonies were established along the shores of the Black Sea, one of them being Trebizond ( el, Τραπεζοῦς, Trapezous) founded by Milesian traders from Sinope in 756 BC. Trebizond's trade partners included the Proto-Laz tribes of Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci (Georgian language, Georgian: მოსინიკები, grc, Μοσσύνοικοι, , modern Greek ', "dwellers in wooden towers") is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) applied to the peoples of Pontus (region ...
.
 By the sixth century BC, the tribes living in the southern Colchis (
By the sixth century BC, the tribes living in the southern Colchis (Macrones
The Macrones ( ka, მაკრონები) ( grc, Μάκρωνες, ''Makrōnes'') were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains (modern Yalnizçam Dağlari, Turkey). The name is allegedly derived fr ...
, Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci (Georgian language, Georgian: მოსინიკები, grc, Μοσσύνοικοι, , modern Greek ', "dwellers in wooden towers") is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea (Black Sea) applied to the peoples of Pontus (region ...
, Marres
The Mares ( ka, მარები ) were an ancient Colchian tribe. They entered ancient history with the writings of Hecataeus of Miletus. He gives a brief description of the tribe and mentions that they lived between closely akin Colchian trib ...
etc.) were incorporated into the nineteenth satrapy of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The Achaemenid Empire was defeated by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, however following the Alexander's death a number of separate kingdoms were established in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, including Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, in the corner of the southern Black Sea, ruled by the Persian nobleman Mithridates I. Culturally, the kingdom was Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
, with Greek as the official language. Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
conquered the Colchis, and gave it to his son Mithridates of Colchis
Mithridates () was a son of King Mithridates VI of Pontus and his sister-wife Laodice. He was made by his father ruler of Colchis on the Black Sea, but then removed and put to death on suspicion of disloyalty.
First Mithridatic War
Mithridates ...
.
As a result of the Roman campaigns between 88 and 63 BC, led by the generals Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
and Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
, the kingdom of Pontus was completely destroyed by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and all its territory, including Colchis, was incorporated into the Roman Empire. The former southern provinces of Colchis were reorganized into the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Pontus Polemoniacus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, while the northern Cholchis became the Roman province of Lazicum. Roman control remained likewise only nominal over the tribes of the interior..
The first-century historians Memnon
In Greek mythology, Memnon (; Ancient Greek: Μέμνων means 'resolute') was a king of Aethiopia and son of Tithonus and Eos. As a warrior he was considered to be almost Achilles' equal in skill. During the Trojan War, he brought an army t ...
and Strabo remark in passing that the people formerly called Macrones bore in his day the name of Sanni
The Sanni ( ka, სანები) are mentioned by Strabo (1st century BC/1st century AD), Pliny the Elder (1st century AD) and Arrian (2nd century AD) as a people settling near Trebizond (in today's Turkish Black Sea Region).
In the 1st ...
, a claim supported also by Stephanus of Byzantium. The second-century historian Arrian notes that Tzanni, same as the Sanni are neighbours of the Colchians, while the latter were now referred to as the Lazi. By the mid-third century, the Lazi tribe came to dominate most of Colchis, establishing the kingdom of Lazica
Lazica ( ka, ეგრისი, ; lzz, ლაზიკა, ; grc-gre, Λαζική, ; fa, لازستان, ; hy, Եգեր, ) was the Latin name given to the territory of Colchis during the Roman/Byzantine period, from about the 1st centur ...
.
Middle Ages
Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, to Fall of Constantinople, its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. On ...
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
(r. 527–565) they were subdued, Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
and brought to central rule. The bishops of the Lazica appointed their priests, seeing they are Christians. Tzanni began to have closer contact with the Greeks and acquired various Hellenic cultural traits, including in some cases the language.
Eastern Roman
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
empires, culminating in the Lazic War
The Lazic War, also known as the Colchidian War or in Georgian historiography as the Great War of Egrisi was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire for control of the ancient Georgian region of Lazica. The Lazic War lasted f ...
, where 1,000 Tzanni auxiliaries under Dagisthaeus
Dagisthaeus (, ''Dagisthaîos'') was a 6th-century Eastern Roman military commander, probably of Gothic origin, in the service of the emperor Justinian I.
Dagisthaeus was possibly a descendant of the Ostrogothic chieftain Dagistheus.* In 548, Da ...
participated. Emperor Heraclius's offensive in 628 AD brought victory over the Persians and ensured Roman predominance in Lazica until the invasion and conquest of the Caucasus by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
in the second half of the seventh century. As the result of Muslim invasions, the ancient metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big ci ...
, Phasis, was lost and Trebizond became the new Metropolitan bishop of Lazica, since then the name Lazi appears the general Greek name for Tzanni. According to Geography of Anania Shirakatsi
Anania Shirakatsi ( hy, Անանիա Շիրակացի, ''Anania Širakac’i'', anglicized: Ananias of Shirak) was a 7th-century Armenian polymath and natural philosopher, author of extant works covering mathematics, astronomy, geography, chronol ...
of the 7th century, Colchis (''Yeger'' in Armenian sources, same as Lazica) was subdivided into four small districts, one of them being Tzanica, that is Chaldia, and mentions Athinae, Rhizus and Trebizond among its cities. From the second half of the eight century the Trebizond area is referred to in Greek sources (namely of Epiphanius of Constantinople
Epiphanius (died June 5, 535) was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from February 25, 520 to June 5, 535, succeeding John II Cappadocia.
Biography
The Byzantine Empire was now rising to great splendour through the victories of its ge ...
) as Lazica. The 10th-century Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
geographer Abul Feda regards city of Trebizond as being largely a Lazian port.
In 780, kingdom of Abkhazia
The Kingdom of Abkhazia ( ka, აფხაზთა სამეფო, tr; lit. "Kingdom of the Abkhazians"), also known as Abasgia or Egrisi-Abkhazia, was a medieval feudal state in the Caucasus which was established in the 780s. Through dyn ...
incorporated the former territories of Lazica via a dynastic succession, thus ousting the Pontic Lazs (formerly known as Tzanni) from western Georgia; thereafter, the Tzanni lived under nominal Byzantine suzerainty in the theme
Theme or themes may refer to:
* Theme (arts), the unifying subject or idea of the type of visual work
* Theme (Byzantine district), an administrative district in the Byzantine Empire governed by a Strategos
* Theme (computing), a custom graphical ...
of Chaldia, with its capital at Trebizond, governed by the native semi-autonomous rulers, like the Gabras
Gabras or Gavras ( el, , tr, ) feminine form Gabraina (Γάβραινα), is the name of an important Byzantine aristocratic family which became especially prominent in the late 11th and early 12th centuries as the semi-independent and quasi-h ...
family,Hewsen, 47 of possibly "Greco-Laz" or simply Chaldian origin.
 With the Georgian intervention in Chaldia and collapse of Byzantine Empire in 1204, Empire of Trebizond was established along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea, populated by a large Kartvelian-speaking population.Mikaberidze, A. (2015). Historical dictionary of Georgia. 2nd ed. Lanham, MD, United States: ROWMAN & LITTLEFIELD, p.634. In the eastern part of the same empire, an autonomous coastal theme of Greater Lazia was established. Byzantine authors, such as
With the Georgian intervention in Chaldia and collapse of Byzantine Empire in 1204, Empire of Trebizond was established along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea, populated by a large Kartvelian-speaking population.Mikaberidze, A. (2015). Historical dictionary of Georgia. 2nd ed. Lanham, MD, United States: ROWMAN & LITTLEFIELD, p.634. In the eastern part of the same empire, an autonomous coastal theme of Greater Lazia was established. Byzantine authors, such as Pachymeres
George Pachymeres ( el, Γεώργιος Παχυμέρης, Geórgios Pachyméris; 1242 – 1310) was a Byzantine Greek historian, philosopher, music theorist and miscellaneous writer.
Biography
Pachymeres was born at Nicaea, in Bithynia, wher ...
, and to some extent Trapezuntines such as Lazaropoulos and Bessarion
Bessarion ( el, Βησσαρίων; 2 January 1403 – 18 November 1472) was a Byzantine Greek Renaissance humanist, theologian, Catholic cardinal and one of the famed Greek scholars who contributed to the so-called great revival of letters ...
, regarded the Trapezuntian Empire as being no more than a Lazian border state. Though Greek in higher culture, the rural areas of Trebizond empire appear to have been predominantly Laz in ethnic composition. Laz family names, with Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
terminations, are noticeable in the records of the mediaeval empire of Trebizond, and it is perhaps not too venturesome to suggest that the antagonism between the "town-party" and the "country-party," which existed in the politics of "the Empire," was in fact a national antagonism of Laz against Greek.
In 1282, kingdom of Imereti besieged Trebizond, however after the failed attempt to take the city, the Georgians occupied several provinces,Miller, ''Trebizond'', p. 30 and all the Trebizontine province of Lazia threw off its allegiance to the king of the 'Iberian' and 'Lazian' tribes and united itself with the Georgian Kingdom of Imereti
The Kingdom of Imereti ( ka, იმერეთის სამეფო, tr) was a Georgian monarchy established in 1455 by a member of the house of Bagrationi when the Kingdom of Georgia was dissolved into rival kingdoms. Before that time, Im ...
.
Early Modern era
 Laz populated area was often contested by different Georgian principalities, however through Battle of Murjakheti in 1535,
Laz populated area was often contested by different Georgian principalities, however through Battle of Murjakheti in 1535, Principality of Guria
The Principality of Guria ( ka, გურიის სამთავრო, tr) was a historical state in Georgia. Centered on modern-day Guria, a southwestern region in Georgia, it was located between the Black Sea and Lesser Caucasus, and was ...
ensured control over it, until 1547, when it was finally conquered by resurgent Ottoman forces and reorganized into the Lazistan sanjak
Lazistan ( lzz, ლაზონა / ''Lazona'', ლაზეთი / ''Lazeti'', ჭანეთი / ''Ç'aneti''; ota, لازستان, ''Lazistān'') was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administrative name for the sanjak, under Trebizond Vilayet, ...
as part of eyalet of Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
.
The Ottomans fought for three centuries to destroy
Destroy may refer to:
* ''Destroy'' (album), a 2004 album by Ektomorf
* Destroy!, a Minneapolis Crust punk band
* '' Destroy!!'', a comic book by Scott McCloud
See also
* Destroyer (disambiguation)
* Destruction (disambiguation)
* Destroy 2 ...
the Christian-Georgian consciousness of the Laz people. Due to the Ottoman Islamization
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occur ...
policy, throughout of seventeenth century Lazs gradually converted to Islam. As the Ottomans consolidated their rule, the Millet system
In the Ottoman Empire, a millet (; ar, مِلَّة) was an independent court of law pertaining to "personal law" under which a confessional community (a group abiding by the laws of Muslim Sharia, Christian Canon law, or Jewish Halakha) was ...
was brought to the newly conquered territories. Local orthodox inhabitants, once subordinated to the Georgian Orthodox Church
The Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამოციქულო ავტოკეფალური მართლმადიდებელი ეკლესია, tr), commonly ...
, had to obey Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
,ქართველთა დენაციონალიზაცია XVII-XX საუკუნეებში; ლაზეთი-თრიალეთი (ქართველთა გაბერძნება)Metropolitan of Manglisi, Ananias Japaridze, nplg.gov.ge thus gradually becoming
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, the process known as Hellenization of Laz people. Lazs who were under the control of Constantinople, soon lost their language and self-identity as they became Greeks and learned Greek, especially Pontic dialect
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from no ...
of Greek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), southe ...
, although native language was preserved by Lazs who had become Muslims. In the middle of the seventeen century, several governors of Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, who bore the title of Dey
Dey (Arabic: داي), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayı'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Tunis under the Ottoman Empire from 1671 o ...
were Laz origin, such as: Muhammad Laz (1647-1653), Mustafa Laz (1653-1665) and Ali Laz (1673).
Not only the Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitar ...
s (governors) of Trabzon until the 19th century, but real authority in many of the '' cazas'' (districts) of each sanjak by the mid-17th century lay in the hands of relatively independent native Laz derebey
A derebey ( tr, valley lord) was a feudal lord in Anatolia and the Pontic areas of Lazistan and Adjara in the 18th century, with considerable independence from the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
Derebeys were required to provide militar ...
s ("valley-lords"), or feudal chiefs who exercised absolute authority in their own districts, carried on petty warfare with each other, did not owe allegiance to a superior and never paid contributions to the sultan. In the period following the war of 1828–1829, Sultan Mahmud II
Mahmud II ( ota, محمود ثانى, Maḥmûd-u s̠ânî, tr, II. Mahmud; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the 30th Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839.
His reign is recognized for the extensive administrative, ...
attempted to break the power of the great independent derebeys of Lazistan. In the event, the Laz derebeys, led by Tahir Ağa Tuzcuoğlu of Rize, did rise in revolt in 1832. The revolt was initially successful: at its height in January 1833, but by the spring of 1834, the rising had been put down. The suppression of the rising had finally broken the power of the Laz derebeys. This state of insubordination was not really broken until the assertion of Ottoman authority during the reforms of the Osman Pasha Osman Pasha (also spelled ''Uthman Pasha'' or ''Othman Pasha'') may refer to:
* Özdemiroğlu Osman Pasha (1527–1585), Ottoman grand vizier
* Bosniak Osman Pasha (died 1685), Ottoman governor of Egypt, Damascus, and Bosnia
* Topal Osman Pasha (16 ...
in the 1850s.
In 1547, Ottomans built coastal fortress of Gonia
Gonia (Greek: ''Γωνιά'') is a village in the Rethymno regional unit in Crete, Greece, lying at an altitude of ca 222 m amsl, about 10 km southwest of the town of Rethymno
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon ...
, an important Ottoman outpost in southwestern Georgia, which served as capital of Lazistan; then Batum
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ) is the second largest city of Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's southwest. It is situated in a subtropical zone at the foot of t ...
until it was acquired according to the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at th ...
by the Russians in 1878, throughout the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
, thereafter, Rize
Rize (Greek: ρίζα, Laz: რიზინი, Georgian: რიზე,
, Ottoman Turkish: ريزه)
is the capital city of Rize Province in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey.
Rize is a typically Turkish provincial capital w ...
became the capital of the sanjak. The Muslim Lazs living in newly established Batumi Oblast
Batumi (; ka, ბათუმი ) is the second largest city of Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's southwest. It is situated in a subtropical zone at the foot of th ...
were subjected to ethnic cleansing; by 1882, approximately 40,000 Lazs had settled in the Ottoman Empire, especially to provinces in Western Anatolia such as Bursa, Yalova
Yalova is a market-gardening town located in northwestern Turkey on the eastern coast of the Sea of Marmara. The town has a population of 156,838, while the population of the surrounding Yalova Province is 291,001 . A largely modern town, it is ...
, Karamursel, Izmit, Adapazarı
Adapazarı () is a city in northwestern Turkey and the central district of Sakarya Province. The province itself was originally named Adapazarı as well. Adapazarı is a part of the densely populated region of the country known as the Marmara Re ...
and Sapanca
Sapanca is a town and district in the Sakarya Province in the Marmara region of Turkey near Lake Sapanca. The town's mayor is Özcan ÖZEN ( AKP).
Sapanca has recently become a tourist destination, due to its stunning natural environment and it ...
. With the spread of Young Turk movement in Lazistan, the short-lived autonomist national movement headed by Faik Efendişi was established. However, it was soon eliminated as the result of Abdul Hamid ʻAbd al-Ḥamīd (ALA-LC romanization of ar, عبد الحميد) is a Muslim male given name, and in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words '' ʻabd'' and ''al-Ḥamīd'', one of the names of God in the Qur'an, which gave rise t ...
's intervention. During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–18) Russians invaded the provinces of Rize and Trabzon. However, following the Bolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
in 1917, the Russian forces had to withdraw from the region and finally left the area to the Ottoman-Turkish forces in March 1918. From 1918 to 1920, the national movement swept rapidly all around Lazistan, committees and an interim government was created. It was oriented towards Soviet Russia. But as soon as, the Soviet-Turkish treaty of friendship was concluded, it helped the Turks, to integrate Lazistan. The autonomous Lazistan sanjak existed until 1923, while the designation of the term of Lazistan was officially banned in 1926, by the Kemalists. Lazistan was divided between Rize
Rize (Greek: ρίζα, Laz: რიზინი, Georgian: რიზე,
, Ottoman Turkish: ريزه)
is the capital city of Rize Province in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey.
Rize is a typically Turkish provincial capital w ...
and Artvin
Artvin ( Laz and ; hy, Արտուին, translit=Artuin) is a city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea.
It is located on a hill overlooking the Çoruh River near the Deriner Dam. It is a former bishopric and (vacant) Armeni ...
provinces.Thys-Şenocak, Lucienne. Ottoman Women Builders. Aldershot, England: Ashgate, 2006. Print.
During the beginning of the Stalinist era
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory o ...
, the Lazs living under Soviet domination had a certain cultural autonomy in the Soviet Union but after breakout of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, Soviet authorities designed a strategy to ethnically cleanse the border regions of populations it deemed unreliable. The Laz population was sent to exile in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. After the death Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
in 1953, the political climate had changed that between 1953 and 1957 the surviving Lazs were allowed to return to their homeland.
Modern
Most Laz people today live in Turkey, but the Laz minority group has no official status in Turkey. The number of the Laz speakers is decreasing, and is now limited chiefly to some areas in Rize and Artvin.Population and geographical distribution
The total population of the Laz today is only estimated, with numbers ranging widely. The majority of Laz live in Turkey, where the national census does not record ethnic data on minor populations.Settlements
Area
 The majority of the Laz today live in an area they call ''Laziǩa, Lazistan, Lazeti'' or ''Lazona'' name of the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Laz people in modern northeast Turkey and southwest Georgia. Geographically, Lazistan consists of a series of narrow, rugged valleys extending northward from the crest of the
The majority of the Laz today live in an area they call ''Laziǩa, Lazistan, Lazeti'' or ''Lazona'' name of the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Laz people in modern northeast Turkey and southwest Georgia. Geographically, Lazistan consists of a series of narrow, rugged valleys extending northward from the crest of the Pontic Alps
The Pontic Mountains or Pontic Alps ( Turkish: ''Kuzey Anadolu Dağları'', meaning North Anatolian Mountains) form a mountain range in northern Anatolia, Turkey. They are also known as the ''Parhar Mountains'' in the local Turkish and Pontic Gr ...
( tr, Anadolu Dağları), which separate it from the Çoruh
The Chorokh ( ka, ჭოროხი ''Ch'orokhi'', tr, Çoruh, hy, Չորոխ ''Ch’vorokh'', el, Άκαμψις, ''Akampsis'') is a river that rises in the Mescit Mountains in north-eastern Turkey, flows through the cities of Bayburt, İ ...
Valley, and stretches east–west along the southern shore of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. Lazistan is a virtually a forbidden term in Turkey. the name was considered to be an 'unpatriotic' invention of ancien regime.
Laz ancestral lands are not well-defined and there is no official geographic definition for the boundaries of Lazistan. However, parts of the following provinces are usually included:
* Adjara region in Georgia
* Artvin
Artvin ( Laz and ; hy, Արտուին, translit=Artuin) is a city in northeastern Turkey about inland from the Black Sea.
It is located on a hill overlooking the Çoruh River near the Deriner Dam. It is a former bishopric and (vacant) Armeni ...
province in Turkey
* Rize
Rize (Greek: ρίζα, Laz: რიზინი, Georgian: რიზე,
, Ottoman Turkish: ريزه)
is the capital city of Rize Province in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey.
Rize is a typically Turkish provincial capital w ...
province in Turkey
* Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
province in Turkey
Economy
Historically, Lazistan was known for producing hazelnuts. Lazistan also producedzinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, producing over 1,700 tons in 1901. The traditional Laz economy was based on agriculture—carried out with some difficulty in the steep mountain regions and also on the breeding of sheep, goats, and cattle. Orchards were tended and bees were kept, and the food supply was augmented by hunting. The Laz are good sailors and also practise agriculture rice, maize, tobacco and fruit-trees. The only industries were smelting, celebrated since ancient times, and the cutting of timber used for shipbuilding.
Culture
Over the past 20 years, there has been an upsurge of cultural activities aiming at revitalizing the Laz language, education and tradition. Kâzım Koyuncu, who in 1998 became the first Laz musician to gain mainstream success, contributed significantly to the identity of the Laz people, especially among their youth. The Laz Cultural Institute was founded in 1993 and the Laz Culture Association in 2008, and a Laz cultural festival was established inGemlik
Gemlik is a town and center of the Gemlik District of Bursa Province. It is located in the east of the Gulf of Gemlik. It is approximately away from Bursa. In antiquity, Gemlik was the location of the ancient Greek town of Cius.
Gemlik is an in ...
. The Laz community successfully lobbied Turkey's Education Ministry to offer Laz-language instruction in schools around the Black Sea region. In 2013, the Education Ministry added Laz as a four-year elective course for secondary students, beginning in the fifth grade.
Language
Mingrelian Mingrelian may refer to:
*the Mingrelians
*the Mingrelian language
Mingrelian or Megrelian (, ) is a Kartvelian language spoken in Western Georgia (regions of Mingrelia and Abkhazia), primarily by the Mingrelians. The language was also called kol ...
, Svan and Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
. N. Marr regarded Laz and Megrelian, two dialects of "linguistically one" language, as two languages. The Laz language does not have a written history, thus Turkish and Georgian serve as the main literary languages for the Laz people. Their folk literature has been transmitted orally and has not been systematically recorded. The first attempts at establishing a distinct Laz cultural identity and creating a literary language based on the Arabic alphabet was made by Faik Efendisi in the 1870s, but he was soon imprisoned by the Ottoman authorities, while most of his works were destroyed. During a relative cultural autonomy granted to the minorities in the 1930s, the written Laz literature—based on the Laz script—emerged in Soviet Georgia
The Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic (Georgian SSR; ka, საქართველოს საბჭოთა სოციალისტური რესპუბლიკა, tr; russian: Грузинская Советская Соц� ...
, strongly dominated by Soviet ideology. The poet Mustafa Baniṣi spearheaded this short-lived movement, but an official standard form of the tongue was never established. Since then, several attempts have been made to render the pieces of native literature in the Turkish and Georgian alphabets. A few native poets in Turkey such as Raşid Hilmi and Pehlivanoğlu have appeared later in the 20th century.
Religion
Andrew the Apostle after traveling from Trebizond into Lazica in the first century AD, built a church here. The significance of the apostle's activities was that he introduced the principle of Christian faith and thereby paved the way for later missionary activities. The Lazes were converted toChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
in the 5th century by the first Christian king, Gubazes I of Lazica
Gubazes I ( ka, გუბაზი; el, Γουβάζης) was a king of Lazica who flourished in the 450s and 460s. His relations with the Roman Empire are recorded by Priscus.Toumanoff (1963), p. 363.
Around 456 Gubazes tried to negotiate an al ...
, who declared Christianity as a state religion of Lazica. After the introduction of Christianity, Phasis was the see of a Greek diocese, one of whose bishops, Cyrus
Cyrus ( Persian: کوروش) is a male given name. It is the given name of a number of Persian kings. Most notably it refers to Cyrus the Great ( BC). Cyrus is also the name of Cyrus I of Anshan ( BC), King of Persia and the grandfather of Cyrus ...
, became a Patriarch of Alexandria between AD 630 and 641.Bury(1889), p. 458-462Holmes(1905), p. 728-730 Trebizond became the metropolitan see of Lazica when the ancient metropolis, Phasis, was lost by the Byzantine Empire. Trebizond, which was the only diocese established far in the past, Cerasous and Rizaion, both formed as upgraded bishoprics. All three dioceses survived the Ottoman conquest (1461) and generally operated until the 17th century, when the dioceses of Cerasous and Rizaion were abolished. The diocese of Rizaion and the bishopric of Of were abolished at the time due to the Islamisation
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
of the Lazs. Most of them subsequently converted to Sunni Islam. There are several ruined churches in present-day Rize and Artvin districts, such as; Jibistasi in Ardeşen, Makriali (Noghedi) in Hopa
Hopa ( Laz and , Hamshen ) is a city and district of Artvin Province in northeast Turkey. It is located on the eastern Turkish Black Sea coast about from the city of Artvin and 18 kilometres from the border with Georgia.
Geography
Hopa is on t ...
, Pironity in Arhavi
Arhavi ( Laz: არქაბი/Arǩabi; Georgian: არქაბი/arkabi) is a town and district of Artvin Province located in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. The terrain is hilly and mountainous. Area of the city center is about , and the ...
etc.
There are also a few Christian Laz in the Adjara region of Georgia who have reconverted to Christianity.
Mythology
Famous for its saga and myths and bounded by the Black Sea and the Caucasian Mountains, the ancient region of Colchis spreads out from West Georgia to Northeast Turkey. The famous tale in Greek mythology of theGolden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, where ...
in which Jason and the Argonauts stole the Golden Fleece from King Aeetes, with the help of his daughter Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason an ...
, has brought Colchis into the history books.
Festival
Kolkhoba Kolkhoba ( ka, კოლხობა, tr, Kolhoba, lzz, Ǩolxoba) is an annual Laz people, Laz festival held each year at the end of August or the beginning of September in Sarpi, Georgia, Sarpi village, Georgia (country), Georgia. It was first he ...
is an ancient Laz festival. It is held at the end of August or at the beginning of September in Sarpi village, Khelvachauri District. Festival has revived the former lifestyle of Lazeti residents and moments of human relations typical to the times of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
and Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
related to the Argonauts journey to Colchis. During the celebration of Kolkhoba theater performances are followed by a variety of activities and it is considered one of the main public festivals.
Music
The national instruments include guda (bagpipe),kemenche
Kemenche ( tr, kemençe) or Lyra is a name used for various types of stringed bowed musical instruments originating in the Eastern Mediterranean, particularly in Armenia, Greece, Iran, Turkey, and Azerbaijan. and regions adjacent to the Black S ...
(spike fiddle), zurna
The zurna ( Armenian: զուռնա zuṙna; Old Armenian: սուռնայ suṙnay; Albanian: surle/surla; Persian: karna/Kornay/surnay; Macedonian: зурла/сурла zurla/surla; Bulgarian: ''зурна/зурла''; Serbian: зурла/zu ...
(oboe), and doli (drum). In the 1990s and 2000s, the folk-rock musician Kâzım Koyuncu attained to significant popularity in Turkey and toured Georgia. Koyuncu, who died of cancer in 2005, was also an activist for the Laz people and has become a cultural hero.
Dance
 The Laz are noted for their folk dances, called the
The Laz are noted for their folk dances, called the Horon
Horon ( pnt, χορόν, khorón) is a traditional folk dance from Pontus or Eastern Black Sea Region in Turkey.
Name Etymology
The term ''horon'' derives from Greek '' choros'' ( el, χορός, khorós), which means "dance." The earliest in ...
dance of the Black Sea, originally of pagan worship which was to become a sacred ritual dance. There are many different types of this dance in different regions. Horon is related to those performed by the Ajarians known as Khorumi
The Khorumi ( ka, ხორუმი) is a war dance that originated in the region of Guria/Adjara, which is located in the southwestern region of Georgia. The dance was originally performed by only a few men. However, over time it has grown in ...
. These may be solemn and precise, performed by lines of men, with carefully executed footwork, or extremely vigorous with the men dancing erect with hands linked, making short rapid movements with their feet, punctuated by dropping to a crouch. The women's dances are graceful but more swift in movement than those encountered in Georgia. In Greece such dances are still associated with the Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks ( pnt, Ρωμαίοι, Ρωμίοι, tr, Pontus Rumları or , el, Πόντιοι, or , , ka, პონტოელი ბერძნები, ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group i ...
who emigrated from this region after 1922.

Traditional clothing
The traditional Laz men's costume consists of a peculiar bandanalike kerchief covering the entire head above the eyes, knotted on the side and hanging down to the shoulder and the upper back; a snug-fitting jacket of coarse brown homespun with loose sleeves; and baggy dark brown woolen trousers tucked into slim, knee-high leather boots. The women's costume was similar to the wide-skirted princess gown found throughout Georgia but worn with a similar kerchief to that of the men and with a rich scarf tied around the hips. Laz men crafted excellent homemade rifles and even while at the plow were usually seen bristling with arms: rifle, pistol, powder horn, cartridge belts across the chest, a dagger at the hip, and a coil of rope for trussing captives.Cuisine
Laz cuisine specialities include: * '' Muhlama'' – a filling corn meal, butter, and cheese fondue; * '' Hamsi pilavı'' – spiced rice enclosed in fried Black Sea anchovies; * ''Kuru fasulye
Kuru fasulye is a stewed bean dish in Turkish cuisine. It is made primarily with white beans and olive oil, and onion and tomato paste or tomato sauce are almost invariably used. Sometimes other vegetables or meat may also be added, especially ...
'' – white beans in a tomato sauce;
* '' Laz böreği'' – a custard filled ''baklava ''like dessert;
* '' Karadeniz pidesi'' – an elongated and closed form of the popular pide dish.
Discrimination
 Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the leader of the early decades of the Republic, aimed to create a nation state ( tr, Ulus) from the Turkish remnants of the Ottoman Empire. During the first three decades of the Republic, efforts to Turkify geographical names were a recurring theme. Imported maps containing references to historical regions such as
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the leader of the early decades of the Republic, aimed to create a nation state ( tr, Ulus) from the Turkish remnants of the Ottoman Empire. During the first three decades of the Republic, efforts to Turkify geographical names were a recurring theme. Imported maps containing references to historical regions such as Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages ...
, or Lazistan (the official name of the province of Rize
Rize (Greek: ρίζα, Laz: რიზინი, Georgian: რიზე,
, Ottoman Turkish: ريزه)
is the capital city of Rize Province in the eastern part of the Black Sea Region of Turkey.
Rize is a typically Turkish provincial capital w ...
until 1921) were prohibited (as was the case with ''Der Grosse Weltatlas'', a map published in Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
).
Cultural assimilation into the Turkish culture has been high, and Laz identity was oppressed during the days of Ottoman and Soviet Rule. One of the pivotal moments was in 1992, when the book ''Laz History'' (''Lazların tarihi'') was published. The authors had failed to have it published in 1964.
Gallery
Théophile Deyrolle
Théophile-Louis Deyrolle (16 December 1844, Paris - 14 December 1923, Concarneau) was a French painter, illustrator and ceramicist.
Biography
He came from a family of entomologists and naturalists who owned a well-known taxidermy shop in Pa ...
, who traveled in Turkey and Georgia in the 1870s, documenting, among other things, medieval Georgian monuments on the territory of the Ottoman Empire
File:Vom Kaukasus zum Persischen Meerbusen b 046.jpg, Inhabitant of Lazistan, from a German travel book, 1897
File:Lazs in 1900s.jpg, Laz men in 1900s
File:National costumes of inhabitants of Trebizond.jpg, Soldiers in traditional Trebizond clothing, Constantinople, 1900s
File:Dancers in national costume in Trebizond.jpg, Postcard featuring Laz dancers in national costume in Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
File:Lazs from Trabzon.JPG, Laz men from Trabzon, 1910s
File:Russia in Asia. Lazian Militia., ca. 1918 - ca. 1919 - NARA - 533451.tif, Lazian Militia,
File:LazesofCaucasus.jpg, Circa 1900
See also
*Adjarians
The Adjarians ( ka, აჭარლები, Ačarlebi) are an ethnographic group of Georgians living mainly in Adjara in south-western Georgia and speaking the Adjarian dialect of the Georgian language.
The Adjarians had their own terri ...
* Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks ( pnt, Ρωμαίοι, Ρωμίοι, tr, Pontus Rumları or , el, Πόντιοι, or , , ka, პონტოელი ბერძნები, ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group i ...
* Chveneburi
Georgians in Turkey ( ka, ქართველები თურქეთში) refers to citizens and denizens of Turkey who are, or descend from, ethnic Georgians.
Numbers and distribution
In the census of 1965, those who spoke Georgian ...
* Chepni people
Chepni ( az, Çəpni; tr, Çepni; tk, Çepni) is one of the 24 Oghuz Turkic tribes. History
In the legend of Oghuz Qaghan, the Chepni was stated as one of the clans of the tribe of ''Gök Han'' that consists of Pecheneg (''Beçenek''), Bayand ...
* Hemshin peoples
,
, native_name_lang =
, image =
, caption = Hamshen people by country
, population = 150,000 – 200,000
, popplace =
, regions =
, region1 =
, pop1 = 150,000
, ref1 ...
* Germakochi
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Andrews, Peter (ed.). 1989. ''Ethnic Groups in the Republic of Turkey''. Wiesbaden: Dr. Ludwig Reichert Verlag, pp. 497–501. * Benninghaus, Rüdiger. 1989. "The Laz: an example of multiple identification". In: ''Ethnic Groups in the Republic of Turkey,'' edited by P. Andrews. * Bryer, Anthony. 1969. "The last Laz risings and the downfall of the Pontic Derebeys, 1812–1840". In: ''Bedi Kartlisa
''Bedi Kartlisa. Revue de Kartvélologie'' was an international academic journal specializing in the language, literature, history and art of Georgia ( Kartvelology) published from 1948 to 1984. It derived its name from the poem ''Bedi kartlisa'' ( ...
'' 26, pp. 191–210.
* Hewsen, Robert H"Laz"
In: ''World Culture Encyclopedia''. Accessed on September 1, 2007.
Negele, Jolyon. ''Turkey: Laz Minority Passive In Face Of Assimilation.''
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, 25 June 1998.
External links
Laz Culture Association
(Turkish)
Lazca.org: Culture, News and Information
(Turkish)
Lazebura.com: Culture, News and Information
(Turkish)
Lazuri.com: Culture Portal
(Turkish) {{DEFAULTSORT:Laz People People from Georgia (country) by ethnic or national origin Ethnic groups in Turkey Ancient peoples of Georgia (country) Tribes in Greco-Roman historiography Peoples of the Caucasus