Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second
most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
in
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
after
Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
and 26th
most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is the capital of the
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
of
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
where it is the largest city. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial and economic hubs, with an estimated GDP (
PPP) of $84 billion as of 2019.
It is the largest city as well as the historic capital and cultural centre of the wider
Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
,
[Lahore Cantonment](_blank)
globalsecurity.org and is one of Pakistan's most
socially liberal
Cultural liberalism is a social philosophy which expresses the social dimension of liberalism and advocates the freedom of individuals to choose whether to conform to cultural norms. In the words of Henry David Thoreau, it is often expressed a ...
,
progressive, and
cosmopolitan
Cosmopolitan may refer to:
Food and drink
* Cosmopolitan (cocktail), also known as a "Cosmo"
History
* Rootless cosmopolitan, a Soviet derogatory epithet during Joseph Stalin's anti-Semitic campaign of 1949–1953
Hotels and resorts
* Cosmopoli ...
cities. It is situated in
the north-east of the country, close to the
International border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
with
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.
Lahore's origins reach into antiquity. The city has been inhabited for at least two millennia, although it rose to prominence in the 10th century. Lahore was the capital of multiple empires throughout its history, including the
Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Oddiyana, Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab region, Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian ...
s,
Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
, and
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). in the medieval era. Lahore reached the height of its splendor under the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
between the late 16th and early 18th century and served as its capital city for many years.
The city was captured by the forces of the
Afsharid
Afsharid Iran ( fa, ایران افشاری), also referred as the Afsharid Empire was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, ruling Iran (Persia). The state was ruled by the ...
ruler
Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian h ...
in 1739. Although the Mughal authority was re-established, it fell into a period of decay while being contested between the Afghans and the Sikhs between 1748 and 1798. Lahore eventually became the capital of the
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahor ...
in the early 19th century, regaining some of its lost grandeur.
Lahore was annexed to the
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
in 1849 and became the capital of
British Punjab
Punjab was a province of British India. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company in 2 April 1849, and declared a province of British Rule, it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British co ...
. Lahore was central to the independence movements of both India and Pakistan, with the city being the site of both the
declaration of Indian Independence and the
resolution calling for the establishment of Pakistan. It experienced some of the worst riotings during the
Partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
period preceding Pakistan's independence.
Following the success of the
Pakistan Movement
The Pakistan Movement ( ur, , translit=Teḥrīk-e-Pākistān) was a political movement in the first half of the 20th century that aimed for the creation of Pakistan from the Muslim-majority areas of British India. It was connected to the pe ...
and the subsequent partition of British India in 1947, Lahore was declared the capital of Pakistan's Punjab province.
Lahore exerts a strong cultural influence over Pakistan.
It is a UNESCO
City of Literature
UNESCO's City of Literature programme is part of the wider Creative Cities Network.
The ''Network'' was launched in 2004, and now has member cities in seven creative fields. The other creative fields are: Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gas ...
and major center for Pakistan's publishing industry; Lahore remains the foremost center of Pakistan's literary scene. The city is also a major centre of education in
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
,
with some of Pakistan's leading universities based in the city. For many years, Lahore was home to Pakistan's film industry,
Lollywood
Lollywood ( ur, , translit=lâli vuḍ) refers to Pakistan's film industry based in Lahore, previously the base for both Punjabi and Urdu language film production.
Lahore has been the center of Pakistani cinema since the partition of ...
, though in recent years most filming has shifted to
Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
. Lahore is a major centre of
''Qawwali'' music.
The city also hosts much of
Pakistan's tourist industry,
with major attractions including the
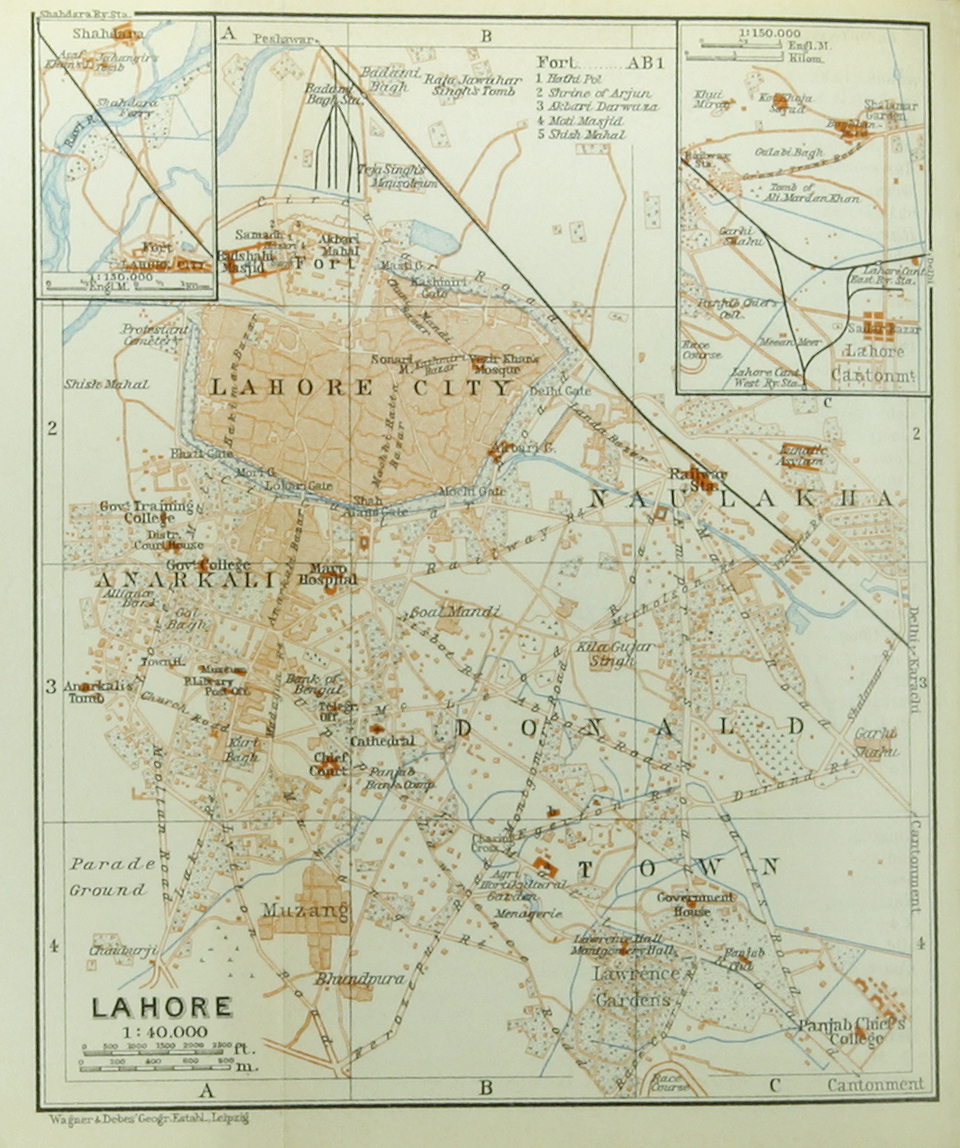
Walled City
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
, the famous
Badshahi and
Wazir Khan mosques, as well as several
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
and
Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
shrines. Lahore is also home to the
Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
and
Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
, both of which are
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s.
Etymology
The origin of Lahore's name is unclear. Lahore's name has been variously recorded by early Muslim historians as ''Luhawar'', ''Lūhār'', and ''Rahwar''.
The
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ian
polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
and
geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
,
Abu Rayhan Al-Biruni, referred to the city as ''Luhāwar'' in his 11th century work, ''Qanun,''
while the poet
Amir Khusrow
Abu'l Hasan Yamīn ud-Dīn Khusrau (1253–1325 AD), better known as Amīr Khusrau was an Indo-Persian Sufi singer, musician, poet and scholar who lived under the Delhi Sultanate. He is an iconic figure in the cultural history of the Indian s ...
, who lived during the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). period, recorded the city's name as ''Lāhanūr''.
Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) ( ar, ياقوت الحموي الرومي) was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine Greek ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th-13th centuries). He is known fo ...
records the city's name as Lawhūr, mentioning that it was famously known as Lahāwar. Persian historian
Firishta
Firishta or Ferešte ( fa, ), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi ( fa, مُحَمَّد قاسِم هِندو شاہ), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He was ...
mentions the city as ''Alahwar'' in his work, ''al-Ahwar'' being another variation.
[Briggs, J. trans. Mohammad Kasim Firishta, "History of the Rise of the Mahomedan Power in India Till the Year A.D. 1612“, Volume VI]
One theory suggests that Lahore's name is a corruption of the word ''Ravāwar,'' as R to L shifts are common in languages derived from
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
.
''Ravāwar'' is the simplified pronunciation of the name ''Iravatyāwar -'' a name possibly derived from the
Ravi River
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
, known as the Iravati River in the ''
Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
''.
Another theory suggests the city's name may derive from the word ''Lohar'', meaning "blacksmith."
According to an apocryphal Hindu legend, Lahore's name derives from ''Lavpur'' or ''Lavapuri'' ("City of ''
Lav''"), and is said to have been founded by Prince Lav, the son of
Sita
Sita (; ) also called as Janaki and Vaidehi is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic, ''Ramayana''. She is the consort of Rama, the avatar of the god Vishnu, and is regarded as a form of Vishnu's consort, Lakshmi. She ...
and
Rama
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular '' avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Bein ...
. The same account attributes the founding of nearby
Kasur
Kasur (Urdu and pa, ; also Romanization of Urdu, romanized as Qasūr; from pluralized Arabic word ''Qasr'' meaning "palaces" or "forts") is a city to south of Lahore, in the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. The city serves as th ...
to his twin brother
Kusha
Kusha was a Suryavansha
The Solar dynasty ( IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98 ...
, though it was actually established in the 16th century.
History
Origins
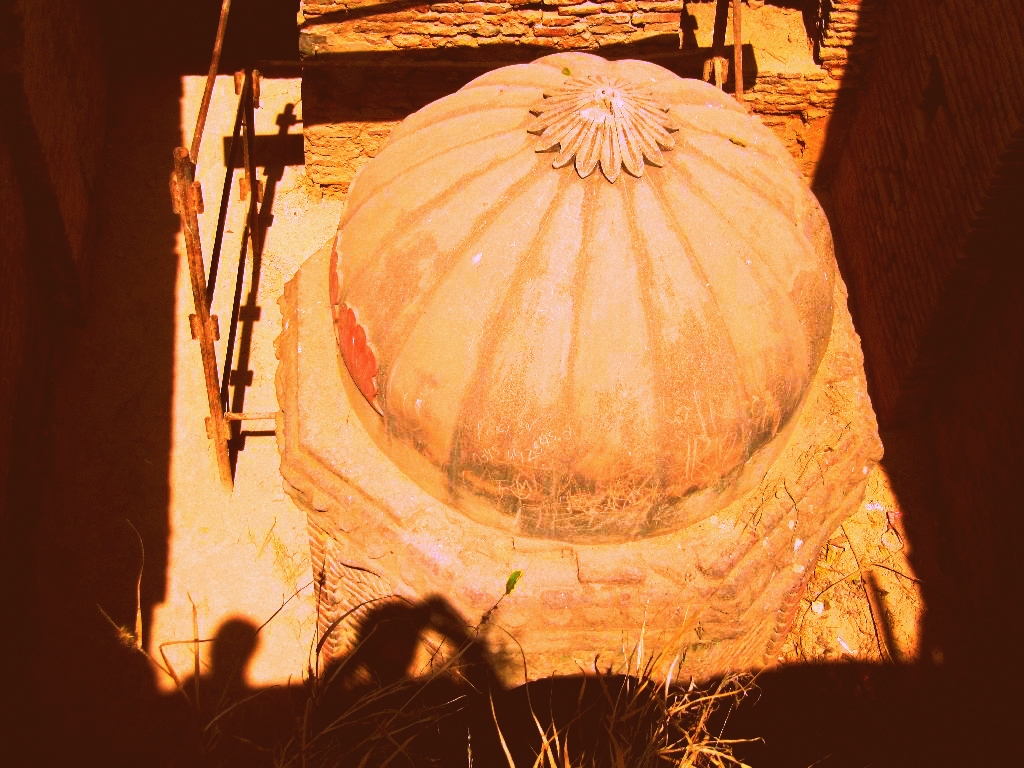

No definitive records of Lahore's earliest history exist, and Lahore's ambiguous early history has given rise to various theories about its establishment and history.
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
legend states that Keneksen, the founder of the Great
Suryavansha
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is ...
dynasty, migrated out from the city.
[Neville, p.xii] Early records of Lahore are scant, but
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
's historians make no mention of any city near Lahore's location during his invasion in 326 BCE, suggesting the city had not been founded by that point or was unimportant.
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
mentions in his ''
Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
'' a city called ''Labokla'' situated near the
Chenab
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul regi ...
and
Ravi River
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
s which may have been in reference to ancient Lahore, or an abandoned predecessor of the city. Chinese pilgrim
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
gave a vivid description of a large and prosperous unnamed city when he visited the region in 630 CE during his tour of India that may have been Lahore.
[ Xuanzang described the city, which was then under Taank rule, as a great ]Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
city.
The first document that mentions Lahore by name is the '' Hudud al-'Alam'' ("The Regions of the World"), written in 982 CE in which Lahore is mentioned as a town which had "impressive temples, large markets and huge orchards."
Lahore, previously a town first emerged as a notable city in 11th century during the era of great sufi saint Ali al-Hajvery. Few other references to Lahore remain from before its capture by the Ghaznavid
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
in the 11th century. Lahore appears to have served as the capital of north-east Punjab during this time under Anandapala
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details r ...
of the Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties in Kabul:
*Turk Shahis (665–850 CE)
*Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway ...
empire, who had moved the capital there from ''Waihind''. The capital would later be moved to Sialkot
Sialkot ( ur, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of Sialkot District and the 13th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined with Jammu (the winter capital of Indian administered Jammu and Ka ...
following Ghaznavid incursions.[
]
Medieval era
Ghaznavid
 Sultan
Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
captured Lahore, somewhere in 1020–1027. Under Ghaznavid rule, Lahore emerged effectively as the empire's second capital.[ In 1021, Sultan Mahmud appointed ]Malik Ayaz
Malik Ayaz (Persian: ملک ایاز), son of Aymāq Abu'n-Najm, was a slave from Georgia who rose to the rank of officer and general in the army of Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni (also known as ''Mahmud Ghaznavi)''. Malik Ayaz's slave-general of Mahm ...
to the Throne of Lahore—a governorship of the Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, ...
. The city was captured by Nialtigin, the rebellious Muslim Governor of Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the List ...
, in 1034, although his forces were expelled by Malik Ayaz in 1036.[ under the reign of '']Khusrau Shah
Khusrau Shah (also spelled Khosrau Shah, Khosrow Shah, and Khusraw Shah) was the last king of the Justanids from 972 to ca. 1004. He was the son and successor of Manadhar.
The words " Khosrow" and "Shah" are both Persian words that mean "king".
...
''. The city then became the sole capital of the Ghaznavid empire in 1163 after the fall of Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
. Under their patronage, poets and scholars from Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
, Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "نیشاپور" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
, Amol
Amol ( fa, آمل – ; ; also Romanized as Āmol and Amul) is a city and the administrative center of Amol County, Mazandaran Province, Iran, with a population of around 300,000 people.
Amol is located on the Haraz river bank. It is less than ...
and Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
congregated in Lahore.[
]
Mamluk
In 1186, the Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the ...
ruler Muhammad of Ghor
Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad ibn Sam ( fa, معز الدین محمد بن سام), also Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri ( fa, معز الدین محمد غوری) (1144 – March 15, 1206), commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor, also Gh ...
captured Lahore in third successive attempt after imprisoning the last Ghaznavid
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
ruler Khusrau Malik
Abu'l-Muzaffar Khusrau Malik ibn Khusrau-Shah ( fa, ابوالمظفر خسروملک بن خسروشاه), better simply known as Khusrau Malik (; also spelled Khosrow), was the last Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 1160 to 1186. He w ...
[ ending Ghaznavid rule over Lahore. Lahore was made an important establishment of the Mamluk Dynasty of the ]Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). following the assassination of Muhammad of Ghor
Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad ibn Sam ( fa, معز الدین محمد بن سام), also Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri ( fa, معز الدین محمد غوری) (1144 – March 15, 1206), commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor, also Gh ...
in 1206. Under the reign of Mamluk sultan Qutb ud-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak ( fa, قطبالدین ایبک), (1150 – 14 November 1210) was a Turkic peoples, Turkic general of the Ghurid king Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after ...
, Lahore attracted poets and scholars from Turkestan
Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan ( fa, ترکستان, Torkestân, lit=Land of the Turks), is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and Xinjiang.
Overview
Known as Turan to the Persians, western Turke ...
, Greater Khorasan
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plate ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
. Lahore at this time had more poets writing in Persian than any city in Persia or Khorasan.
Following the death of Aibak, Lahore came to be disputed among Ghurid officers. The city first came under the control of the Governor of Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the List ...
, Nasir ad-Din Qabacha
Nasir-ud-Din Qabacha or Kaba-cha ( fa, ناصرالدین قباچه) was the Muslim Turkic Kipchak governor of Multan, appointed by the Ghurid ruler Muhammad Ghori in 1203.
Successors of Ghori
Ghori had no offspring, but he treated thousa ...
, before being briefly captured by the sultan of the Mamluks in Delhi, Iltutmish
Shams ud-Din Iltutmish ( fa, شمس الدین ایلتتمش; died 30 April 1236, ) was the third of the Mamluk kings who ruled the former Ghurid territories in northern India. He was the first Muslim sovereign to rule from Delhi, and is thus ...
, in 1217.[
In an alliance with local ]Khokhar
Khokhar are a Punjabi community native to Pothohar Plateau of Pakistan, and the adjoining areas of India. Khokhars now predominantly follow Islam, though a minority continue to follow Hinduism. Many Khokhars converted to Islam from Hinduism a ...
s in 1223, Jalal al-Din Mangburni
Jalal al-Din Mangburni ( fa, جلال الدین مِنکُبِرنی), also known as Jalal al-Din Khwarazmshah (), Minkubirni or Mengu-Berdi (c.1199 – August 1231), was the last Khwarazmshah of the Anushteginid dynasty. The eldest son and succ ...
of the Khwarazmian dynasty
The Anushtegin dynasty or Anushteginids (English: , fa, ), also known as the Khwarazmian dynasty ( fa, ) was a Persianate C. E. BosworthKhwarazmshahs i. Descendants of the line of Anuštigin In Encyclopaedia Iranica, online ed., 2009: ''"Li ...
of modern-day Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked cou ...
captured Lahore after fleeing Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
's invasion of Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
.[ Jalal ad-Din's then fled from Lahore to capture the city of ]Uch Sharif
Uch ( pa, ;
ur, ), frequently referred to as Uch Sharīf ( pa, ;
ur, ; ''"Noble Uch"''), is a historic city in the southern part of Pakistan's Punjab province. Uch may have been founded as Alexandria on the Indus, a town founded by Alexand ...
after Iltutmish's armies re-captured Lahore in 1228.[
The threat of Mongol invasions and political instability in Lahore caused future Sultans to regard Delhi as a safer capital for medieval Islamic India,][ Under the rule of Kabir Khan Ayaz, Lahore was virtually independent from the Delhi Sultanate.][ Lahore was sacked and ruined by the Mongol army in 1241. Lahore governor Malik Ikhtyaruddin Qaraqash fled the Mongols, while the Mongols held the city for a few years under the rule of the Mongol chief ]Toghrul
Toghrul ( mn, Тоорил хан ''Tooril han''; ), also known as Wang Khan or Ong Khan ( ''Wan han''; ; died 1203) was a khan of the Keraites. He was the blood brother (anda) of the Mongol chief Yesugei and served as an important early patron ...
.Temür Khan
Öljeytü Khan ( Mongolian: Өлзийт; Mongolian script: '; ), born Temür ( mn, Төмөр ; ; October 15, 1265 – February 10, 1307), also known as Emperor Chengzong of Yuan () by his temple name ''Chengzong'', was the second emperor of th ...
,Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
. Because of Mongol invasions, Lahore region had become a city on a frontier, with the region's administrative centre shifted south to Dipalpur.[ The Mongols again invaded northern Punjab in 1298, though their advance was eventually stopped by ]Ulugh Khan
Almas Beg (died c. 1302), better known by his title Ulugh Khan, was a brother and a general of the Delhi Sultanate ruler Alauddin Khalji. He held the iqta' of Bayana in present-day India.
Ulugh Khan played an important role in Alauddin's asce ...
, brother of Sultan Alauddin Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over lar ...
of Delhi.[Neville, p.xiii]
Tughluq
Lahore briefly flourished again under the reign of Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq
Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq ) (Ghazi means 'fighter for Islam')ref name="sen2"> (died c.1325) was the Sultan of Delhi from 1320 to 1325. He was the first sultan of the Tughluq dynasty. During his reign, Ghiyath al-Din Tughlu ...
(Ghazi Malik) of the Tughluq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty ( fa, ), also referred to as Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty, was a Muslim dynasty of Indo- Turkic origin which ruled over the Delhi sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed t ...
between 1320 and 1325, though the city was again sacked in 1329, by Tarmashirin
Tarmashirin Khan (ruled 1331 AD - 1334 AD) was the khan of the Chagatai Khanate following Duwa Timur.
Biography
Tarmashirin is famous for his campaign in the Indian subcontinent in 1327 before he was enthroned. The city of Lahore was sacked by ...
of the Central Asian Chagatai Khanate, and then again by the Mongol chief Hülechü.[ ]Khokhar
Khokhar are a Punjabi community native to Pothohar Plateau of Pakistan, and the adjoining areas of India. Khokhars now predominantly follow Islam, though a minority continue to follow Hinduism. Many Khokhars converted to Islam from Hinduism a ...
s seized Lahore in 1342, but the city was retaken by Ghazi Malik's son, Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (1290 – 20 March 1351) was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from February 1325 until his death in 1351. The sultan was the eldest son of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, founder of the Tughlaq dynasty. In 1321, the youn ...
.[ The weakened city then fell into obscurity and was captured once more by the Khokhars in 1394.]Tamerlane
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
captured the city in 1398 from Shayka Khokhar, he did not loot it because it was no more wealthy.
Late Sultanates
 Mongol conqueror Timur gave control of the Lahore region to
Mongol conqueror Timur gave control of the Lahore region to Khizr Khan
Khizr Khan (reigned 28 May 1414 – 20 May 1421) was the founder of the Sayyid dynasty, the ruling dynasty of the Delhi sultanate, in northern India soon after the invasion of Timur and the fall of the Tughlaq dynasty.
Khan was Governor of Mult ...
, Governor of Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the List ...
, who later established the Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451. Founded by Khizr Khan, a former governor of Multan, they succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled the sultanate as a vassal of the Timu ...
in 1414 – the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). .Timurid Timurid refers to those descended from Timur (Tamerlane), a 14th-century conqueror:
* Timurid dynasty, a dynasty of Turco-Mongol lineage descended from Timur who established empires in Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
** Timurid Empire of C ...
Governor of Kabul in 1432–33.Bahlul Lodi
Bahlul Khan Lodi (12 July 1489) was the chief of the Pashtun Lodi tribe. Founder of the Lodi dynasty from the Delhi Sultanate upon the abdication of the last claimant from the previous Sayyid rule. Bahlul became sultan of the dynasty on 19 A ...
in 1441 by the Sayyid dynasty in Delhi, though Lodi would then displace the Sayyids in 1451 by establishing himself upon the throne of Delhi.[
Bahlul Lodi installed his cousin, Tatar Khan, to be governor of the city, though Tatar Khan died in battle with ]Sikandar Lodi
Sikandar Khan Lodi (died 21 November 1517), born Nizam Khan, was a Pashtun Sultan of the Delhi Sultanate between 1489 and 1517. He became ruler of the Lodi dynasty after the death of his father Bahlul Khan Lodi in July 1489. The second and most ...
in 1485.Daulat Khan Lodi
Daulat Khan Lodi (Pashto: دولت خان لودی) was the governor of Lahore during the reign of Ibrahim Lodi, the last ruler of the Lodi dynasty. Due to disaffection with Ibrahim, Daulat invited Babur to invade the kingdom. He was initial ...
, son of Tatar Khan and former employer of Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated wor ...
– founder of the Sikh faith.
Mughals
File:The Badshahi in all its glory during the Eid Prayers.JPG, Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
File:Naulakha Pavilion in Lahore Fort.jpg, Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
File:Tomb of Emperor Jahangir.jpg, Tomb of Jahangir
The Tomb of Jahangir ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum built for the Mughal Emperor Jahangir. The mausoleum dates from 1637, and is located in Shahdara Bagh near city of Lahore, Pakistan, along the banks of the Ravi River. The site is famous ...
File:Wazir Khan's hammams (4).JPG, Shahi Hammam
The Shahi Hammam (Urdu and pa, ; ''"Royal Baths"''), also known as the Wazir Khan Hammam, is a Turkish bath, Persian-style bath which was built in Lahore, Pakistan, in 1635 Common era, C.E. during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan. It was built by ...



Early Mughal
Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
, the founder of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, captured and sacked Lahore and Dipalpur, although he retreated after the Lodi nobles backed away from assisting him.[ The city became a refuge to ]Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northern ...
and his cousin Kamran Mirza
Kamran Mirza ( fa, ) (1512 – 5 October 1557) was the second son of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal Emperor. Kamran Mirza was born in Kabul to Babur's wife Gulrukh Begum. He was half-brother to Babur's eldest ...
when Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
rose in power on the Gangetic Plains, displacing Mughal power. Sher Shah Suri continued to rise in power, and seized Lahore in 1540, though Humayun reconquered Lahore in February 1555.[ The establishment of Mughal rule eventually led to the most prosperous era of Lahore's history.][ Lahore's prosperity and central position has yielded more Mughal-era monuments in Lahore than either ]Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
or Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is ...
.[ Only 9 of the 36 urban quarters around Lahore, known as ''guzars'', were located within the city's walls during the ]Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
period.[ During this period, Lahore was closely tied to smaller market towns known as ''qasbahs'', such as ]Kasur
Kasur (Urdu and pa, ; also Romanization of Urdu, romanized as Qasūr; from pluralized Arabic word ''Qasr'' meaning "palaces" or "forts") is a city to south of Lahore, in the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. The city serves as th ...
and Eminabad
Eminabad ( pa, ) is a town located in the south east of Gujranwala city, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous ...
, as well as Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
, and Batala
Batala is the eighth largest city in the state of Punjab, India in terms of population after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala, Bathinda, Mohali and Hoshiarpur. Batala ranks as the second-oldest city after Bathinda. It is a municipal corpo ...
in modern-day India, which in turn, linked to supply chains in villages surrounding each ''qasbah''.[
]
Akbar
Beginning in 1584, Lahore became the Mughal capital when Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
began re-fortifying the city's ruined citadel, laying the foundations for the revival of the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
.[ Akbar made Lahore one of his original twelve '']subah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''subed ...
'' provinces,[ and in 1585–86 relegated governorship of the city and ''subah'' to ]Bhagwant Das
Raja Bhagwant Das (1527 – 4 December 1589) was the 23rd Kacchwaha ruler of Amber. His sister, Mariam-uz-Zamani, was the chief consort of Emperor Akbar and mother of his successor, Emperor Jahangir. His son, Man Singh I, one of the Navaratnas ...
, brother of Mariam-uz-Zamani
Mariam-uz-Zamani (); ( – 19 May 1623), commonly known by the misnomer ' Jodha Bai', was the chief consort and principal Rajput empress consort as well as the favourite wife of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. She was also the longest-servin ...
, who was commonly known as ''Jodhabhai''.[ The Akbari Mandi ]grain market
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other ...
was set up during this era, and continues to function until the present-day.[ Akbar also established the ]Dharampura https://dharampuralahore.wordpress.com
'Dharampura'' ur, ), alternatively spelt 'Dharmapura'', is a neighbourhood located in Lahore. The Mughal emperor Akbar laid the foundation of this colony for Hindus as an alms-house in 1583. After 1947 Part ...
neighbourhood in the early 1580s, which survives today. The earliest of Lahore's many haveli
A ''haveli'' is a traditional townhouse, mansion, manor house, in the Indian subcontinent, usually one with historical and architectural significance, and located in a town or city. The word ''haveli'' is derived from Arabic ''hawali'', mean ...
s date from the Akbari era.[ Lahore's Mughal monuments were built under Akbar's reign of several emperors,][ and Lahore reached its cultural zenith during this period, with dozens of mosques, tombs, shrines, and urban infrastructure developed during this period.
]
Jahangir
During the reign of Emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
in the early 17th century, Lahore's bazaars were noted to be vibrant, frequented by foreigners, and stocked with a wide array of goods.[ In 1606, Jehangir's rebel son ]Khusrau Mirza
Khusrau Mirza (16 August 1587 – 26 January 1622) was the eldest son of the Mughal Emperor Jahangir and his first wife, Shah Begum.
He was beloved of his grandfather, Mughal Emperor Akbar and his grandmother, Mariam-uz-Zamani. The young ...
laid siege to Lahore after obtaining the blessings of the Sikh Guru Arjan Dev
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of th ...
.Shahdara Bagh
Shahdara Bagh ( ur, ; meaning “''King’s Way Garden”'') is a historic precinct located across the Ravi River from the Walled City of Lahore, Pakistan. Shahdara Bagh is the site of several Mughal era monumentally, including the Tomb of Ja ...
suburb in 1637 by his wife Nur Jahan
Nur Jahan, born Mehr-un-Nissa P ersian: نورجهان (; – 18 December 1645) was the wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Jahangir from 1620 until his death in 1627.
Nur Jahan was born Mehr-un-Nissa, as the daughter of a Mirza Ghi ...
, whose tomb is also nearby.
Shah Jahan
Jahangir's son, Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
reigned between 1628 and 1658 and was born in Lahore in 1592. He renovated large portions of the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
with luxurious white marble and erected the iconic Naulakha Pavilion
The Naulakha Pavilion () is a white marble personal chamber with a curvilinear roof, located beside the Sheesh Mahal courtyard, in the northern section of the Lahore Fort in Lahore, Pakistan. The monument is one of the 21 monuments situated ...
in 1633.Shahi Hammam
The Shahi Hammam (Urdu and pa, ; ''"Royal Baths"''), also known as the Wazir Khan Hammam, is a Turkish bath, Persian-style bath which was built in Lahore, Pakistan, in 1635 Common era, C.E. during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan. It was built by ...
in 1635, and both the Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
and the extravagantly decorated Wazir Khan Mosque
; ''Masjid Wazīr Khān'') is a 17th-century mosque located in the city of Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque was commissioned during the reign of the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan as a part of an ensemble of buildings tha ...
in 1641. The population of pre-modern Lahore probably reached its zenith during his reign, with suburban districts home to perhaps 6 times as many compared to within the Walled City
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
.[
]
Aurangzeb

 Shah Jahan's son, and last of the great Mughal Emperors,
Shah Jahan's son, and last of the great Mughal Emperors, Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
, further contributed to the development of Lahore. Aurangzeb built the ''Alamgiri Bund'' embankment along the Ravi River
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
in 1662 in order to prevent its shifting course from threatening the city's walls.[ The area near the embankment grew into a fashionable locality, with several pleasure gardens laid near the ''band'' by Lahore's gentry.][ The largest of Lahore's Mughal monuments was raised during his reign, the ]Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
in 1673, as well as the iconic ''Alamgiri'' gate of the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
in 1674.
Late Mughal
 Civil wars regarding succession to the Mughal throne following
Civil wars regarding succession to the Mughal throne following Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
's death in 1707 lead to weakening control over Lahore from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, and a prolonged period of decline in Lahore.Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
in the Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in South India, southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bou ...
eventually resulted in Lahore being governed by a series of governors who pledged nominal allegiance to the ever weaker Mughal emperors in Delhi.[
Mughal Emperor ]Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I (14 October 1643 – 27 February 1712), also known as Muhammad Mu'azzam and Shah Alam I. was the eighth Mughal Emperor who ruled from 1707 until his death in 1712. In his youth, he conspired to overthrow his father Aurangzeb, t ...
died en route to Lahore as part of a campaign in 1711 to subdue Sikh rebels under the leadership of Banda Singh Bahadur
Banda Singh Bahadur (born Lachman Dev) (27 October 1670 – 9 June 1716), was a Sikh warrior and a commander of Khalsa army. At age 15, he left home to become an ascetic, and was given the name Madho Das Bairagi. He established a monastery ...
.[ His sons fought a battle outside Lahore in 1712 for succession to the Mughal crown, with Jahandar winning the throne.][ Sikh rebels were defeated during the reign of ]Farrukhsiyar
Farrukhsiyar or Farrukh Siyar () (20 August 16839 April 1719) was the tenth emperor of the Mughal Empire from 1713 to 1719. He rose to the throne after assassinating his uncle, Emperor Jahandar Shah. Reportedly a handsome man who was easily sw ...
when Abd as-Samad and Zakariyya Khan suppressed them.[
]Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian h ...
's brief invasion of the Mughal Empire in early 1739 wrested control away from Zakariya Khan Bahadur
Zakariya Khan (died 1745) was the Mughal Empire's subahdar of Lahore Subah from 1726, succeeding his father, Abd al-Samad Khan, in the post. He was descended from the Ansari family of Panipat. He continued and extended his father's policy of sev ...
. Though Khan was able to win back control after the Persian armies had left,[ Nader Shah's invasion shifted trade routes away from Lahore, and south towards ]Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a List of cities in Afghanistan, city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population ...
instead.[ Indus ports near the Arabian Sea that served Lahore also silted up during this time, reducing the city's importance even further.][
Struggles between Zakariyya Khan's sons following his death in 1745 further weakened Muslim control over Lahore, thus leaving the city in a power vacuum, and vulnerable to foreign marauders.
]
Durrani Invasions
Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
, the founder of the Afghan Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
, captured Lahore in January 1748,[ Following Ahmed Shah Durrani's quick retreat, the Mughals entrusted Lahore to Mu’īn al-Mulk Mir Mannu.][ Ahmad Shah Durrani again invaded in 1751, forcing Mir Mannu into signing a treaty that submitted Lahore to Afghan rule.][ The Mughal Wazīr Ghazi Din Imad al-Mulk would seize Lahore in 1756, provoking Ahmad Shah Durrani to again invade in 1757, after which he placed the city under the rule of his son, ]Timur Shah Durrani
Timur Shah Durrani (; prs, ;), also known as Timur Shah Abdali or Taimur Shah Abdali (December 1746 – May 20, 1793) was the second ruler of the Afghan Durrani Empire, from November 1772 until his death in 1793. An ethnic Pashtun, he was the se ...
.[
Durrani rule was interrupted when Lahore was briefly captured by ]Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
in 1758 during their campaigns against the Afghans, under Raghunathrao
Raghunathrao Bhat (a.k.a. Ragho Ballal or Ragho Bharari) (18 August 1734 – 11 December 1783) was the 11th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire for a brief period from 1773 to 1774. He was known among the Hindus for his extremely successful North-west ...
, who drove out the Afghans,Battle of Lahore
The Battle of Lahore (Urdu: ; ''Jang-e-Lāhaur'', Hindi: लाहौर की लड़ाई; ''Lāhaur kī laḍ.āī''), also referred to as the Lahore Front, constitutes a series of battles fought in and around the Pakistani city of L ...
. Following the Third Battle of Panipat, Ahmad Shah Durrani defeated the Marathas and recaptured Lahore, Sikh forces quickly occupied the city after the Durranis withdrew from the city in 1765.[ The Durranis invaded two more times in 1797 and 1798 respectively under ]Shah Zaman
Zaman Shah Durrani, or Zaman Shah Abdali (Persian: ; 1767 – 1844), was ruler of the Durrani Empire from 1793 until 1801. He was the grandson of Ahmad Shah Durrani and the fifth son of Timur Shah Durrani. An ethnic Pashtun, Zaman Shah became th ...
, but the Sikhs re-occupied the city after both invasions.[
]
Sikh
File:Samadhi of Ranjit Singh 123.jpg, Samadhi of Ranjit Singh
The Samadhi of Ranjit Singh ( pa, , ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਮਾਧੀ ; ) is a 19th-century building in Lahore, Pakistan that houses the funerary urns of the Sikh Maharaja Ranjit Singh (1780 – 1839). It is located adjacen ...
File:Samadhi of Ranjit Singh Golden Dome.jpg, Gurdwara Dera Sahib
File:Nau Nihal Singh's haveli, now Victoria Girls High School, Lahore.jpg, Haveli of Nau Nihal Singh
The Haveli of Nau Nihal Singh (Urdu/ pa, ), officially known as Government Victoria Girls' High School, is a haveli that houses a government school located in Lahore, Pakistan. Dating from the Sikh era of the mid-19th century, the haveli is cons ...
File:Hazuri Bagh Baradari & Ground.JPG, Hazuri Bagh
Hazuri Bagh ( ur, ) is a garden in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, bounded by the Lahore Fort to the east, Badshahi Mosque to the west, the Samadhi of Ranjit Singh to the north, and the Roshnai Gate to the south. The garden was built during the rei ...
File:Gurudwara Arjun Ram (WCLA).jpg, Gurdwara Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das
The Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das ( ur, , label=Punjabi, Urdu) is a gurdwara in Lahore, Pakistan. The gurdwara was built atop the site traditionally believed to be the location of the birthplace and childhood home of Guru Ram Das, the 4th Sikh gurus. ...

Early
Expanding Sikh ''Misl
The Misls (derived from an Arabic word wikt:مثل#Etymology_3, مِثْل meaning 'equal') were the twelve sovereign states of the Sikh Confederacy, which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian ...
s'' secured control over Lahore in 1767, when the Bhangi Misl
The Bhangi Misl (Punjabi pronunciation: ə̃˨ŋɡiː mɪsəl was a large and most powerful Sikh Misl headquartered was in Amritsar. It was founded in the early 18th century by Sardar Chhajja Singh Dhillon,Sikh History (2004)"The Bhangi Misal ...
state captured the city.Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha r ...
to establish itself as the area's primary commercial centre in place of Lahore.[
Ahmad Shah Durrani's grandson, ]Zaman Shah
Zaman Shah Durrani, or Zaman Shah Abdali (Persian: ; 1767 – 1844), was ruler of the Durrani Empire from 1793 until 1801. He was the grandson of Ahmad Shah Durrani and the fifth son of Timur Shah Durrani. An ethnic Pashtun, Zaman Shah became th ...
, invaded Lahore in 1796, and again in 1798–9.[ ]Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839), popularly known as Sher-e-Punjab or "Lion of Punjab", was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire, which ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He s ...
negotiated with the Afghans for the post of ''subahdar
Subahdar, also known as Nazim or in English as a "Subah", was one of the designations of a governor of a Subah (province) during the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Khalji dynasty, Tughlaq dynasty, Mughal era ( of India who w ...
'' to control Lahore following the second invasion.[
By the end of the 18th century, the city's population drastically declined, with its remaining resident's living within the city walls, while the extramural suburbs lay abandoned, forcing travellers to pass through abandoned and ruined suburbs for a few miles before reaching the city's gates.][
]
Sikh Empire
 In the aftermath of
In the aftermath of Zaman Shah
Zaman Shah Durrani, or Zaman Shah Abdali (Persian: ; 1767 – 1844), was ruler of the Durrani Empire from 1793 until 1801. He was the grandson of Ahmad Shah Durrani and the fifth son of Timur Shah Durrani. An ethnic Pashtun, Zaman Shah became th ...
’s 1799 invasion of Punjab, Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839), popularly known as Sher-e-Punjab or "Lion of Punjab", was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire, which ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He s ...
, of nearby Gujranwala
Gujranwala ( ur, , label=none; ) is a city and capital of Gujranwala Division located in Pakistan. It is also known as "City of Wrestlers" and is quite famous for its food. It is the 5th most populous city proper after Karachi, Lahore, Faisala ...
, began to consolidate his position. Singh was able to seize control of the region after a series of battles with the Sikh ''Bhangi Misl'' chiefs who had seized Lahore in 1780.Lohari Gate
The Lahori Gate or Lohari Gate is located within Walled City of Lahore in Lahore, Pakistan. Lahori Gate is one of the 13 gates of the Walled City of Lahore.
Being one of the oldest gates of the old city, Lahori Gate is also known as Lohar ...
, Mukham Din Chaudhry, opened the gates allowing Ranjit Singh's army to enter Lahore.Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
soldiers immediately began plundering Muslim areas of the city until their actions were reined in by Ranjit Singh.
Ranjit Singh's rule restored some of Lahore's lost grandeur, but at the expense of destroying the remaining Mughal architecture for its building materials.[ He established a mint in the city in 1800,]Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
after repurposing it for his own use in governing the Sikh Empire. In 1801, he established the Gurdwara Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das
The Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das ( ur, , label=Punjabi, Urdu) is a gurdwara in Lahore, Pakistan. The gurdwara was built atop the site traditionally believed to be the location of the birthplace and childhood home of Guru Ram Das, the 4th Sikh gurus. ...
to mark the site where Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਰਾਮ ਦਾਸ, pronunciation: ; 24 September 1534 – 1 September 1581) was the fourth of the ten Ten Gurus of Sikhism, Gurus of Sikhism. He was born in a family based in Lahore. His birth n ...
was born in 1534.
Lahore became the empire's administrative capital, though the nearby economic centre of Amritsar had also been established as the empire's spiritual capital by 1802.[ By 1812 Singh had mostly refurbished the city's defences by adding a second circuit of outer walls surrounding Akbar's original walls, with the two separated by a moat. Singh also partially restored Shah Jahan's decaying Shalimar Gardens
and built the ]Hazuri Bagh Baradari
The Hazuri Bagh Baradari ( ur, ) is a baradari of white marble located in the Hazuri Bagh of Lahore, Pakistan. It was built by Maharaja Ranjit Singh, the Sikh ruler of Punjab to celebrate his capture of the ''Koh-i-Noor'' diamond from Shuja ...
in 1818 to celebrate his capture of the ''Koh-i-Noor
The Koh-i-Noor ( ; from ), also spelled Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is part of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. The diamond is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The Q ...
'' diamond from Shuja Shah Durrani
Shuja ( ar, شجاع, ur, شجاع, bn, সুজা) is a surname and male given name.
Notable people with this name include:
* Shuja al-Khwarazmi, was the mother of Abbasid caliph Al-Mutawakkil (r. 847–861)
* Ahmad Shuja Pasha (born ...
in 1813.Guru Arjan Dev
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of th ...
's 1606 death. The Sikh royal court also endowed religious architecture in the city, including a number of Sikh gurdwaras, Hindu temples, and haveli
A ''haveli'' is a traditional townhouse, mansion, manor house, in the Indian subcontinent, usually one with historical and architectural significance, and located in a town or city. The word ''haveli'' is derived from Arabic ''hawali'', mean ...
s.
While much of Lahore's Mughal era fabric lay in ruins by the time of his arrival, Ranjit Singh's rule saw the re-establishment of Lahore's glory – though Mughal monuments suffered during the Sikh period. Singh's armies plundered most of Lahore's most precious Mughal monuments, and stripped the white marble from several monuments to send to different parts of the Sikh Empire during his reign.Tomb of Asif Khan
The Tomb of Asif Khan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum located in Shahdara Bagh, in the city of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It was built for the Mughal Empire, Mughal statesman Abul-Hasan ibn Mirza Ghiyas Beg, Mirza Abul Hassan Jah, who ...
, the Tomb of Nur Jahan
The Tomb of Nur Jahan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum in Lahore, Pakistan, that was built for the Mughal empress Nur Jahan. The tomb's marble was plundered during the Sikh era in 18th century for use at the Golden Temple in Amritsar. The ...
, and the Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
.Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
by converting it into an ammunition depot and a stable for horses.Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
was also converted to a gurdwara
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths ...
, while the Mosque of Mariyam Zamani Begum was repurposed into a gunpowder factory.
Late
The Sikh royal court, or the ''Lahore Durbar'', underwent a quick succession of rulers after the death of Ranjit Singh. His son Kharak Singh
Kharak Singh (22 February 1801 – 5 November 1840) was the second Maharaja of the Sikh Empire. He was the eldest son of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, founder of the Sikh Empire and his consort, Maharani Datar Kaur. He succeeded his father on 27 June ...
died soon after taking the throne on 6 November 1840, while the next appointed successor to the throne, Nau Nihal Singh
Kunwar Nau Nihal Singh (9 March 1821 – 5 November 1840) was the third Maharaja of the Sikh Empire. He was the only son of Maharaja Kharak Singh and his consort, Maharani Chand Kaur. He was known as Yuvraj Kunwar Nau Nihal Singh. He was also kn ...
, died in an accident at Lahore's Hazuri Bagh
Hazuri Bagh ( ur, ) is a garden in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, bounded by the Lahore Fort to the east, Badshahi Mosque to the west, the Samadhi of Ranjit Singh to the north, and the Roshnai Gate to the south. The garden was built during the rei ...
on 6 November 1840, the same day Kharak Singh died.Sher Singh
Sher Singh (4 December 1807 – 15 September 1843) was the fourth Maharaja of the Sikh Empire. Elder of the twins of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, founder of the Sikh Empire and Maharani Mehtab Kaur. His reign began on 18 January 1840 following his ...
was then selected as Maharajah, though his claim to the throne was quickly challenged by Chand Kaur
Chand Kaur (1802 – 11 June 1842) was fourth ruler of the Sikh Empire, proclaimed as Malika Muqaddisa on 2 December 1840. She was born to Sardar Jaimal Singh of the Kanhaiya Misl. In 1812, she was married to Crown Prince Kharak Singh, son and ...
, widow of Kharak Singh and mother of Nau Nihal Singh, who quickly seized the throne.Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
in order to target Chand Kaur's forces in the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
, destroying the fort's historic ''Diwan-e-Aam''.[ Dhyan Singh's son, Hira Singh, sought to avenge his father's death by laying siege to Lahore in order to capture his father's assassins. The siege resulted in the capture of his father's murderer, Ajit Singh.]Duleep Singh
Maharaja Sir Duleep Singh, GCSI (4 September 1838 – 22 October 1893), or Sir Dalip Singh, and later in life nicknamed the "Black Prince of Perthshire", was the last ''Maharaja'' of the Sikh Empire. He was Maharaja Ranjit Singh's youngest son ...
was then crowned Maharajah, with Hira Singh as his ''Wazir'', but his power would be weakened by the continued infighting among Sikh nobles,
British colonial period
File:Punjab university Art & Design Dept.jpg, University of the Punjab
The University of the Punjab (Urdu, pnb, ), also referred to as Punjab University, is a public, research, coeducational higher education institution located in Lahore, Pakistan. Punjab University is the oldest public university in Pakistan. ...
File:Government College University Tower in Lahore.jpg, Government College University
File:Front View of Lahore Museum.jpg, Lahore Museum
The Lahore Museum ( pa, ; ur, ; ''"Lahore Wonder House"'') is a museum located in Lahore, Pakistan. Founded in 1865 at a smaller location and opened in 1894 at its current location on The Mall in Lahore during the British colonial period, La ...
File:Lahore High Court Building.jpg, Lahore High Court
The Lahore High Court () is based in Lahore, Pakistan. It was established as a high court on 21 March 1882. The Lahore High Court has jurisdiction over Punjab (Pakistan). The High Court's principal seat is in Lahore, but there are benches in th ...
File:King Edward Medical University.jpg, King Edward Medical University
King Edward Medical University (KEMU) () is a public medical university located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Founded in 1860, the university is named after King Edward VII.
Established by the British Raj, named as Lahore Medical School. In 1868 ...
 The
The British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
seized control of Lahore in February 1846 from the collapsing Sikh state and occupied the rest of Punjab in 1848.Battle of Gujrat
The Battle of Gujrat was a decisive battle in the Second Anglo-Sikh War, fought on 21 February 1849, between the forces of the East India Company, and a Sikh army in rebellion against the company's control of the Sikh Empire, represented by ...
, British troops formally deposed Maharaja Duleep Singh in Lahore that same year.[ Punjab was then annexed to the British Indian Empire in 1849.][
At the commencement of British rule, Lahore was estimated to have a ]population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of 120,000.Walled City
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
surrounded by plains interrupted by settlements to the south and east, such as Mozang and Qila Gujar Singh
Qila Gujar Singh (''Meaning: Fort of Gujjar Singh'') is a town located in the central part of Lahore, Pakistan. As shown by name it was the fort of a gurjar king named Gujjar Singh Banghi. Some walls and a gate still remains as a memory of the ...
, which have since been engulfed by modern Lahore. The plains between the settlements also contained the remains of Mughal gardens, tombs, and Sikh-era military structures.
The British viewed Lahore's Walled City as a bed of potential social discontent and disease epidemics, and so largely left the inner city alone, while focusing development efforts in Lahore's suburban areas, and Punjab's fertile countryside. The British instead laid out their capital city in an area south of the Walled City that would first come to be known as "Donald's Town" before being renamed "Civil Station."
Under early British rule, formerly prominent Mughal-era monuments that were scattered throughout Civil Station were also re-purposed and sometimes desecrated – including the Tomb of Anarkali
The Tomb of Anarkali ( ur, ) is an octagonal 16th century Mughal monument in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab.
Location
The tomb of Anarkali is located on the grounds of Lahore's Punjab Civil Secretariat complex near the Bri ...
, which the British had initially converted to clerical offices before re-purposing it as an Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
church in 1851. The 17th century Dai Anga Mosque
Dai Anga Mosque (Urdu: ) is a mosque situated to southeast of the Lahore Railway Station, in the city of Lahore in Pakistan's Punjab province. The mosque is said to have been built in 1635 in honour of the wetnurse of the Mughal Emperor Shah J ...
was converted into railway administration offices during this time, the tomb of Nawab Bahadur Khan was converted into a storehouse, and the tomb of Mir Mannu was used as a wine shop. The British also used older structures to house municipal offices, such as the Civil Secretariat, Public Works Department, and Accountant General's Office.
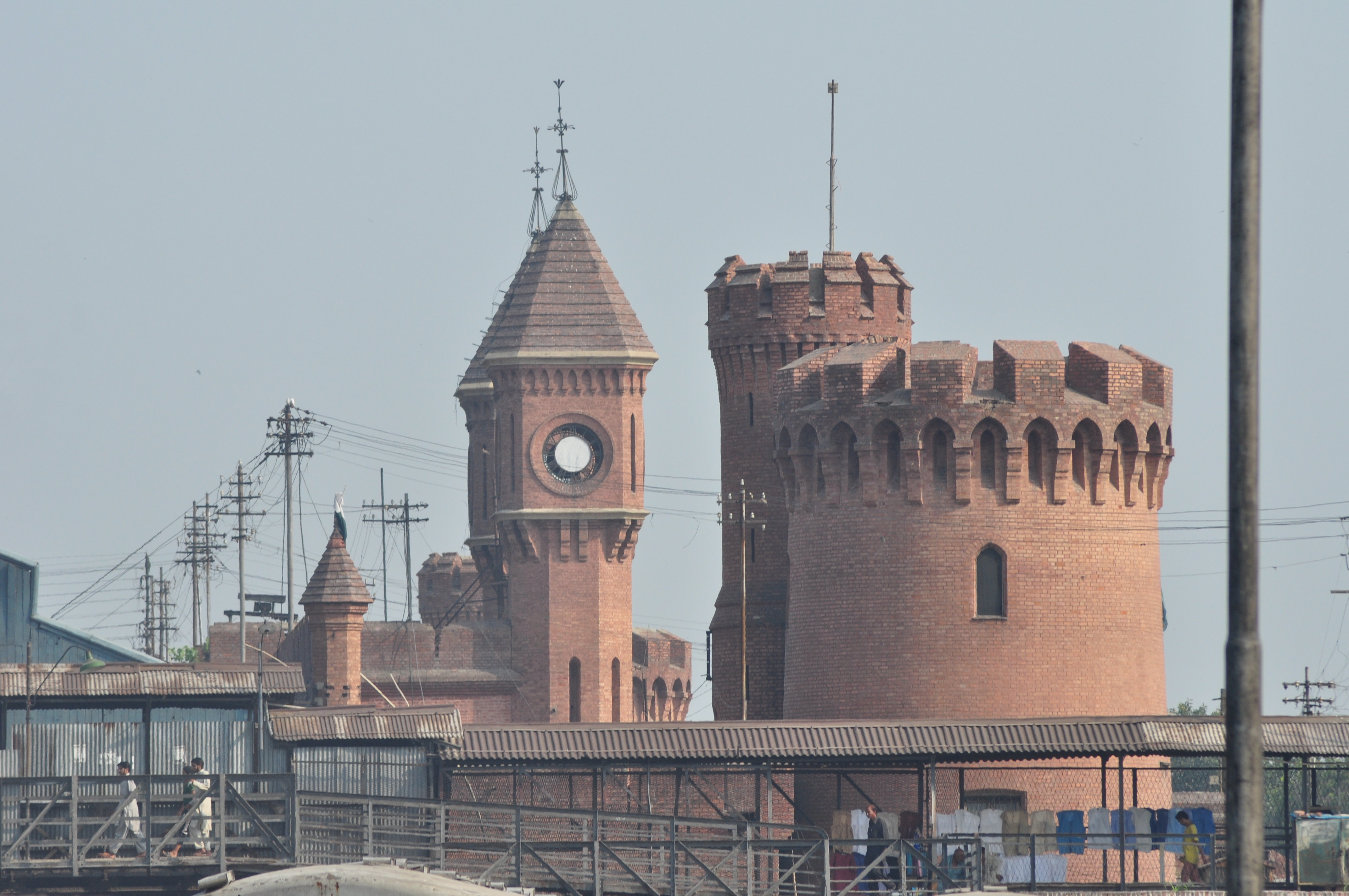 The British built the
The British built the Lahore Railway Station
Lahore Junction Railway Station (Urdu, pa, ) is the main railway station in Lahore, Pakistan. Construction commenced shortly after the 1857 War of Independence against British rule, and so was built in the style of a medieval castle with thick ...
just outside the Walled City shortly after the Mutiny of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the for ...
, and so built the station in the style of a medieval castle to ward off any potential future uprisings, with thick walls, turrets, and holes to direct gun and cannon fire for the defence of the structure. Lahore's most prominent government institutions and commercial enterprises came to be concentrated in Civil Station in a half-mile wide area flanking The Mall, where unlike in Lahore's military zone, the British and locals were allowed to mix. The Mall continues to serve as the epicentre of Lahore's civil administration, as well as one of its most fashionable commercial areas. The British also laid the spacious Lahore Cantonment
Lahore Cantonment ( ur, ) is a garrison located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Although the cantonment is located within Lahore City District (UC 152), it is an independent municipality under control of the Military Lands & Cantonments Departmen ...
to the southeast of the Walled City at the former village of Mian Mir, where unlike around The Mall, laws did exist against the mixing of different races.
Lahore was visited on 9 February 1870 by Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh
Duke of Edinburgh, named after the city of Edinburgh in Scotland, was a substantive title that has been created three times since 1726 for members of the British royal family. It does not include any territorial landholdings and does not produc ...
– a visit in which he received delegations from the Dogras
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himachal ...
of Jammu
Jammu is the winter capital of the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir. It is the headquarters and the largest city in Jammu district of the union territory. Lying on the banks of the river Tawi Ri ...
, Maharajas of Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, India, Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak, Patiala, Qila Mubarak ...
, the Nawab of Bahawalpur
Bahawalpur () is a city in the Punjab province of Pakistan. With inhabitants as of 2017, it is Pakistan's 11th most populous city.
Founded in 1748, Bahawalpur was the capital of the former princely state of Bahawalpur, ruled by the Abbasi fa ...
, and other rulers from various Punjabi states.Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria
The Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria was celebrated on 20 and 21 June 1887 to mark the 50th anniversary of Queen Victoria's accession on 20 June 1837. It was celebrated with a Thanksgiving Service at Westminster Abbey, and a banquet to which ...
in 1887 in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The Lahore Museum
The Lahore Museum ( pa, ; ur, ; ''"Lahore Wonder House"'') is a museum located in Lahore, Pakistan. Founded in 1865 at a smaller location and opened in 1894 at its current location on The Mall in Lahore during the British colonial period, La ...
and Mayo School of Industrial Arts were both established around this in this style.Krishan Nagar
Krishan Nagar is part of the Islampura neighbourhood of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan.
During British Raj, in 1930s came a change in the development of middle class localities in Lahore and areas like Krishan Nagar and Sant Nagar were established. Th ...
locality was laid in the 1930s near The Mall and Walled City.
 Lahore played an important role in the independence movements of both India and Pakistan. The
Lahore played an important role in the independence movements of both India and Pakistan. The Declaration of the Independence of India
The declaration of Purna Swaraj was made because the youth of India and many leaders of INC were not satisfied with the Dominion, Dominion Status. The word Purna Swaraj was derived , or Declaration of the Independence of India, it was promulg ...
was moved by Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat—
*
*
*
* and author who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20t ...
and passed unanimously at midnight on 31 December 1929 at Lahore's Bradlaugh Hall Bradlaugh Hall is a historic hall located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. It was founded in the memory of a British member of the parliament, Charles Bradlaugh.
History
It was founded on 30 October 1900 by Surendra Nath Banerji. After partition of In ...
. The Indian ''Swaraj flag
The national flag of India, colloquially called the tricolour, is a horizontal rectangular tricolour flag of India saffron, white and India green; with the ', a 24-spoke wheel, in navy blue at its centre. It was adopted in its present form ...
'' was adopted this time as well. Lahore's jail was used by the British to imprison independence activists such as Jatin Das
Jatindra Nath Das ( bn, যতীন্দ্রনাথ দাস; 27 October 1904 – 13 September 1929), better known as Jatin Das, was an Indian independence activist and revolutionary who worked to make India independent from the Bri ...
, and was also where Bhagat Singh
Bhagat Singh (27 September 1907 – 23 March 1931) was a charismatic Indian revolutionary*
* who participated in the mistaken murder of a junior British police officer
*
* in what was to be retaliation for the death of an Indian nationa ...
was hanged in 1931. Under the leadership of Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the ...
The All India Muslim League
The All-India Muslim League (AIML) was a political party established in Dhaka in 1906 when a group of prominent Muslim politicians met the Viceroy of British India, Lord Minto, with the goal of securing Muslim interests on the Indian subcontin ...
passed the Lahore Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
in 1940, demanding the creation of Pakistan as a separate homeland for the Muslims of India.
Sir Ganga Ram
Rai Bahadur Sir Ganga Ram (born Ganga Ram Agarwal; 13 April 1851 – 10 July 1927) was an Indian civil engineer and architect. His extensive contributions to the urban fabric of Lahore, then in colonial India and now in modern Pakistan, caused ...
is considered the 'Father of Modern Lahore'.
Partition
The 1941 census showed that city of Lahore had a population of 671,659, of which was 64.5% Muslim, with the remainder 35% being Hindu and Sikh, alongside a small Christian community.[ The population figure was disputed by Hindus and Sikhs before the Boundary Commission that would draw the ]Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab Province and Bengal Presidency of British India. It was named after Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissi ...
to demarcate the border of the two new states based on religious demography.[ In a bid to have Lahore awarded to India, they argued that the city was only 54% Muslim, and that Hindu and Sikh domination of the city's economy and educational institutions should trump Muslim demography.][ Two-thirds of shops, and 80% of Lahore's factories belonged to the Hindu and Sikh community.][ Kuldip Nayyar claimed that ]Cyril Radcliffe
Cyril John Radcliffe, 1st Viscount Radcliffe, (30 March 1899 – 1 April 1977) was a British lawyer and Law Lord best known for his role in the Partition of India. He served as the first chancellor of the University of Warwick from its foundat ...
in 1971 had told him that he originally had planned to give Lahore to the new Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
,Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of I ...
, which he saw as lacking a major city as he had already awarded Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
to India.[ Carnage ensued in which all three religious groups were both victims and perpetrators. Early riots in March and April 1947 destroyed 6,000 of Lahore 82,000 homes.][ Violence continued to rise throughout the summer, despite the presence of armoured British personnel.][ Hindus and Sikhs began to leave the city ''en masse'' as their hopes that the Boundary Commission to award the city to India came to be regarded as increasingly unlikely. By late August 1947, 66% of Hindus and Sikhs had left the city.][ The Shah Alami Bazaar, once a largely Hindu quarter of the ]Walled City
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
, was entirely burnt down during subsequent rioting.Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used by ...
'' throughout the night.[ On 17 August 1947, Lahore was awarded to Pakistan on the basis of its Muslim majority in the 1941 census and was made capital of the ]Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
province in the new state of Pakistan. The city's location near the Indian border meant that it received large numbers of refugees fleeing eastern Punjab and northern India, though it was able to accommodate them given the large stock of abandoned Hindu and Sikh properties that could be re-distributed to newly arrived refugees.[
]
Modern
File:Islamic Summit Minar.JPG, Islamic Summit Minar
The Summit Minar is an obelisk-shaped structure built in the centre of Charing Cross, Mall Road in the city of Lahore, Punjab the province of Pakistan. It was built to commemorate the second Islamic Summit Conference held in Lahore from 22 to 24 ...
File:The Minar-e-Pakistan.jpg, Minar-e-Pakistan
Minar E Pakistan ( ur, , literally "Tower of Pakistan") is a tower located in Lahore, Pakistan. The tower was built between 1960 and 1968 on the site where the All-India Muslim League passed the Lahore Resolution (which was later called the Pak ...
File:Behria Town Mosque build by Malik Riaz.jpg, Grand Jamia Mosque
Grand Jamia Mosque ( ur, گرینڈ جامع مسجد), is a cultural complex under construction in Bahria Town Karachi, Pakistan. When completed, the complex will include what would be Pakistan's largest and the world's third-largest mosque ac ...
File:Punjab Assembly as more then one decade before by Usman Ghani.jpg, Provincial Assembly of the Punjab
The Provincial Assembly of the Punjab is a unicameral legislature of elected representatives of the Pakistani provinces, Pakistani province of Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, which is located in Lahore, the provincial capital. It was established under ...
File:'Pakistan'-Islamic Summit Minar-Lahore- By @ibneazhar- Sep 2016 (72).jpg, WAPDA House
The WAPDA House (Urdu/Punjabi: ) is a nine-story office building located in Lahore, Pakistan, that serves as the headquarters of the Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA). It is one of several prominent government buildings located at Chari ...
File:Arfa Karim Tower Lahore.jpg, Arfa Karim tower in Lahore
Partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
left Lahore with a much-weakened economy, and a stymied social and cultural scene that had previously been invigorated by the city's Hindus and Sikhs.[ Industrial production dropped to one-third of pre-Partition levels by the end of the 1940s, and only 27% of its manufacturing units were operating by 1950, and usually well-below capacity.][ ]Capital flight
Capital flight, in economics, occurs when assets or money rapidly flow out of a country, due to an event of economic consequence or as the result of a political event such as regime change or economic globalization. Such events could be an increas ...
further weakened the city's economy while Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
industrialized and became more prosperous.Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
was therefore chosen to be capital on account of its relative tranquillity during the Partition period, stronger economy, and better infrastructure.[
] After independence, Lahore slowly regained its significance as an economic and cultural centre of western Punjab. Reconstruction began in 1949 of the Shah Alami Bazaar, the former commercial heart of the Walled City until it was destroyed in the 1947 riots.
After independence, Lahore slowly regained its significance as an economic and cultural centre of western Punjab. Reconstruction began in 1949 of the Shah Alami Bazaar, the former commercial heart of the Walled City until it was destroyed in the 1947 riots.[ The ]Tomb of Allama Iqbal
The Tomb of Allama Iqbal, or Mazaar-e-Iqbal ( ur, ) is a mausoleum located within the Hazuri Bagh, in the Pakistani city of Lahore, capital of Punjab province.
Background
Iqbal was one of the major inspirations behind the Pakistan Movement, a ...
was built in 1951 to honour the philosopher-poet who provided the spiritual inspiration for the Pakistan movement.[ In 1955, Lahore was selected to be the capital of all ]West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was d ...
during the single-unit period that lasted until 1970.[ Shortly afterwards, Lahore's iconic ]Minar-e-Pakistan
Minar E Pakistan ( ur, , literally "Tower of Pakistan") is a tower located in Lahore, Pakistan. The tower was built between 1960 and 1968 on the site where the All-India Muslim League passed the Lahore Resolution (which was later called the Pak ...
was completed in 1968 to mark the spot where the Pakistan Resolution
The Lahore Resolution ( ur, , ''Qarardad-e-Lahore''; Bengali: লাহোর প্রস্তাব, ''Lahor Prostab''), also called Pakistan resolution, was written and prepared by Muhammad Zafarullah Khan and was presented by A. K. Fazlul ...
was passed.[ With support from the ]United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
was able to rebuild Lahore, and most scars from the communal violence of Partition were ameliorated.
The second Islamic Summit Conference was held in the city in 1974.Babri Masjid
Babri Masjid (IAST: Bābarī Masjid; meaning ''Mosque of Babur'') was a mosque in Ayodhya, India, at a site believed by many Hindus to be the birthplace of Hindu deity Rama. It has been a focus of dispute between the Hindu and Muslim communi ...
in India, riots erupted in 1992 in which several non-Muslim monuments were targeted, including the tomb of Maharaja Sher Singh
Sher Singh (4 December 1807 – 15 September 1843) was the fourth Maharaja of the Sikh Empire. Elder of the twins of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, founder of the Sikh Empire and Maharani Mehtab Kaur. His reign began on 18 January 1840 following his ...
,[ and the former Jain temple near the Mall. In 1996, the ]International Cricket Council
The International Cricket Council (ICC) is the world governing body of cricket. Headquartered in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, its members are List of International Cricket Council members, 108 national associations, with 12 List of Internation ...
Cricket World Cup
The Cricket World Cup (officially known as ICC Men's Cricket World Cup) is the international championship of One Day International (ODI) cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council (ICC), e ...
final match was held at the Gaddafi Stadium
Gaddafi Stadium ( ur, , translit=Qaẕẕāfī Isṭeḍiyam), previously known as Lahore Stadium is a cricket stadium in Lahore, Pakistan and the home ground of Lahore Qalandars. It is owned by the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB). With a capacit ...
in Lahore.
The Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
restoration project began in 2009, when the Punjab government restored the Royal Trail from Akbari Gate
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
to the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
with money from the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
.
Geography
 Lying between 31°15′—31°45′ N and 74°01′—74°39′ E, Lahore is bounded on the north and west by the
Lying between 31°15′—31°45′ N and 74°01′—74°39′ E, Lahore is bounded on the north and west by the Sheikhupura District
Sheikhupura District ( pa, ;
ur, ), is a district located in Lahore Division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Sheikhupura is the headquarters of Sheikhupura district. According to the 1998 census of Pakistan, the district had a population of ...
, on the east by Wagah
Wagah ( ur, ) or Wagha (Shahmukhi pnb, ) is a village and union council (UC 181) located in the Wahga Zone near Lahore City District, Pakistan. The town is famous for the Wagah border ceremony and also serves as a goods transit terminal and ...
, and on the south by Kasur District
Kasur District ( Punjabi and ur, , translit=Zilā Qasūr), is a district located in Lahore Division of Punjab, Pakistan. It came into existence on 1 July 1976. Prior to its creation, it was a tehsil of the Lahore District.
The district capit ...
. The Ravi River
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
flows on the northern side of Lahore. Lahore city covers a total land area of . Lahore is in the north-eastern portion of the country.
Climate
Lahore has a semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''BSh''), not receiving enough rainfall to feature the humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
. The hottest month is June, where temperatures routinely exceed . The monsoon season starts in late July, and the wettest months are July and August,
Demographics
Population
The results of the 2017 Census determined the population to be at 11,126,285,
Ethnic Groups
According to the official census statistics, 80.9% of Lahore’s population are Punjabis
The Punjabis ( Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Panjābīs), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. The ...
, 12.6% Urdu-speaking people
Native speakers of Urdu are spread across South Asia. The vast majority of them are Muslims of the Hindi Belt, Hindi–Urdu Belt of northern India, followed by the Deccanis, Deccani people of the Deccan Plateau, Deccan plateau in south-central Ind ...
, 2.7% Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
, 1.02% Saraikis
The Saraikis ( skr, ), are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group inhabiting parts of central and southeastern Pakistan, primarily in the southern part of the Pakistani province of Punjab
They are mainly found in a region of southern Punjab known ...
and 2.78% are of other ethnicities.
Religion
The city has a Muslim majority (94.7%), Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
(5.14%) minority population, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
(0.024%). Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic on ...
community. Additionally, Lahore contains some of Sikhism's holiest sites, and is a major Sikh pilgrimage site.
According to the 1998 census, 94% of Lahore's population is Muslim, up from 60% in 1941. Other religions include Christians (5.80% of the total population, though they form around 9.0% of the rural population) and small numbers of Ahmadiyya, Ahmadis, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼís, Hindus, Parsis and Sikhs. Lahore's first church was built during the reign of Emperor Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
in the late 16th century, which was then leveled by Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
in 1632.
There is a small number of Hindus living in Lahore. The Krishna Mandir, Lahore, Shri Krishna mandir and the Valmiki Mandir are the only two functional temples in Lahore.
Languages
The Punjabi language is the most-widely spoken native language in Lahore with 80% of Lahore counting it as their first language according to the 2017 Census, Lahore is the largest Punjabi-speaking city in the world.
Urdu and English are used as official languages and as mediums of instruction and media administration. However, Punjabi is also taught at graduation level and used in theaters, films and newspapers from Lahore. Several Lahore-based prominent educational leaders, researchers and social commentators have demanded that the Punjabi language should be declared as the medium of instruction at the primary level and be used officially in the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab, Punjab Assembly, Lahore.
Cityscape
Old City

 Lahore's modern cityscape consists of the historic
Lahore's modern cityscape consists of the historic Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
in the northern part of the city, which contains several World Heritage Site, world and national heritage sites. Lahore's urban planning was not based on geometric design but was instead built piecemeal, with small cul-de-sacs, ''katrahs'' and ''galis'' developed in the context of neighbouring buildings.[ Though certain neighbourhoods were named for particular religious or ethnic communities, the neighbourhoods themselves typically were diverse and were not dominated by the namesake group.][
Lahore's urban typology is similar to other ancient cities in South Asia, such as Peshawar, ]Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the List ...
and Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
- all of which were founded near a major river, and included an old walled city, as well as a royal citadel.
By the end of the Sikh rule, most of Lahore's massive haveli
A ''haveli'' is a traditional townhouse, mansion, manor house, in the Indian subcontinent, usually one with historical and architectural significance, and located in a town or city. The word ''haveli'' is derived from Arabic ''hawali'', mean ...
compounds had been occupied by settlers. New neighbourhoods occasionally grew up entirely within the confines of an old Mughal haveli, such as the Mohallah Pathan Wali, which grew within the ruins of a haveli of the same name that was built by Mian Khan.[ By 1831, all Mughal Havelis in the Walled City had been encroached upon by the surrounding neighbourhood,][ leading to the modern-day absence of any Mughal Havelis in Lahore.
A total of thirteen gates once surrounded the historic walled city. Some of the remaining gates include the Raushnai Gate, Masti Gate, Yakki Gate, Kashmiri Gate, Khizri Gate, Shah Burj Gate, Akbari Gate and Lahori Gate. Southeast of the walled city is the spacious British-era ]Lahore Cantonment
Lahore Cantonment ( ur, ) is a garrison located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Although the cantonment is located within Lahore City District (UC 152), it is an independent municipality under control of the Military Lands & Cantonments Departmen ...
.
Architecture
 Lahore is home to numerous monuments from the Mughal Dynasty,
Lahore is home to numerous monuments from the Mughal Dynasty, Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahor ...
, and the British Raj, British Indian Raj. The architectural style of the Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
has traditionally been influenced by Mughal and Sikh styles.
Sir Ganga Ram
Rai Bahadur Sir Ganga Ram (born Ganga Ram Agarwal; 13 April 1851 – 10 July 1927) was an Indian civil engineer and architect. His extensive contributions to the urban fabric of Lahore, then in colonial India and now in modern Pakistan, caused ...
is considered the 'Father of Modern Lahore'.
Sikh period
By the arrival of the Sikh Empire, Lahore had decayed from its former glory as the Mughal capital. Rebuilding efforts under Ranjit Singh and his successors were influenced by Mughal practices, and Lahore was known as the 'City of Gardens' during the Ranjit Singh period. Later British maps of the area surrounding Lahore dating from the mid-19th century show many walled private gardens which were confiscated from the Muslim noble families bearing the names of prominent Sikh nobles – a pattern of patronage which was inherited from the Mughals.
While much of Lahore's Mughal era fabric lay in ruins by the time of his arrival, Ranjit Singh's army's plundered most of Lahore's most precious Mughal monuments, and stripped the white marble from several monuments to send to different parts of the Sikh Empire.Tomb of Asif Khan
The Tomb of Asif Khan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum located in Shahdara Bagh, in the city of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It was built for the Mughal Empire, Mughal statesman Abul-Hasan ibn Mirza Ghiyas Beg, Mirza Abul Hassan Jah, who ...
, Tomb of Nur Jahan
The Tomb of Nur Jahan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum in Lahore, Pakistan, that was built for the Mughal empress Nur Jahan. The tomb's marble was plundered during the Sikh era in 18th century for use at the Golden Temple in Amritsar. The ...
, the Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
were plundered of much of its marble and costly agate.[ and the city was left with a large number of religious monuments from this period. Several havelis were built during this era, though only a few still remain.][
]
British period

 As the capital of British Punjab, British colonialists made a lasting architectural impression on the city. Structures were built predominantly in the Indo-Gothic style – a syncretic architectural style that blends elements of Victorian architecture, Victorian and Islamic architecture, or in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The British also built Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical Montgomery Hall, which today serves as the Quaid-e-Azam Library.
Bagh-e-Jinnah, Lahore, Lawrence Gardens were also laid near Civil Station, and were paid for by donations solicited from both Lahore's European community, as well as from wealthy locals. The gardens featured over 600 species of plants, and were tended to by a horticulturist sent from London's Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew.
The British authorities built several important structures around the time of the
As the capital of British Punjab, British colonialists made a lasting architectural impression on the city. Structures were built predominantly in the Indo-Gothic style – a syncretic architectural style that blends elements of Victorian architecture, Victorian and Islamic architecture, or in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The British also built Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical Montgomery Hall, which today serves as the Quaid-e-Azam Library.
Bagh-e-Jinnah, Lahore, Lawrence Gardens were also laid near Civil Station, and were paid for by donations solicited from both Lahore's European community, as well as from wealthy locals. The gardens featured over 600 species of plants, and were tended to by a horticulturist sent from London's Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew.
The British authorities built several important structures around the time of the Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria
The Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria was celebrated on 20 and 21 June 1887 to mark the 50th anniversary of Queen Victoria's accession on 20 June 1837. It was celebrated with a Thanksgiving Service at Westminster Abbey, and a banquet to which ...
in 1887 in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The Lahore Museum
The Lahore Museum ( pa, ; ur, ; ''"Lahore Wonder House"'') is a museum located in Lahore, Pakistan. Founded in 1865 at a smaller location and opened in 1894 at its current location on The Mall in Lahore during the British colonial period, La ...
and Mayo School of Industrial Arts were both established around this in this style.Lahore High Court
The Lahore High Court () is based in Lahore, Pakistan. It was established as a high court on 21 March 1882. The Lahore High Court has jurisdiction over Punjab (Pakistan). The High Court's principal seat is in Lahore, but there are benches in th ...
), Lahore Museum
The Lahore Museum ( pa, ; ur, ; ''"Lahore Wonder House"'') is a museum located in Lahore, Pakistan. Founded in 1865 at a smaller location and opened in 1894 at its current location on The Mall in Lahore during the British colonial period, La ...
and University of the Punjab
The University of the Punjab (Urdu, pnb, ), also referred to as Punjab University, is a public, research, coeducational higher education institution located in Lahore, Pakistan. Punjab University is the oldest public university in Pakistan. ...
. Many of Lahore's most important buildings were designed by Sir Ganga Ram, who is sometimes called the "Father of modern Lahore."
Parks and gardens
 Lahore is also known as the ''City of Gardens'' due to large number of gardens. The
Lahore is also known as the ''City of Gardens'' due to large number of gardens. The Shahdara Bagh
Shahdara Bagh ( ur, ; meaning “''King’s Way Garden”'') is a historic precinct located across the Ravi River from the Walled City of Lahore, Pakistan. Shahdara Bagh is the site of several Mughal era monumentally, including the Tomb of Ja ...
was one of the earliest Mughal gardens laid in 15th century. It contains Tomb of Jahangir, tomb of Jahangir. The Shalimar Gardens (Lahore), Shalimar Gardens were laid out during the reign of Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
and were designed to mimic the Islamic paradise of the afterlife described in the Qur'an. The gardens follow the familiar charbagh layout of four squares, with three descending terraces. In 1818, Hazuri Bagh
Hazuri Bagh ( ur, ) is a garden in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, bounded by the Lahore Fort to the east, Badshahi Mosque to the west, the Samadhi of Ranjit Singh to the north, and the Roshnai Gate to the south. The garden was built during the rei ...
was built during reign of Ranjit Singh to celebrate his capture of the Koh-i-Noor
The Koh-i-Noor ( ; from ), also spelled Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is part of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. The diamond is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The Q ...
diamond from Shuja Shah Durrani.
The Bagh-e-Jinnah (Lahore), Lawrence Garden was established in 1862 and was originally named after Sir John Lawrence, late 19th-century British Viceroy to India. The Circular Garden, which surrounds on the Walled City on three sides, was established by 1892.Hazuri Bagh
Hazuri Bagh ( ur, ) is a garden in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, bounded by the Lahore Fort to the east, Badshahi Mosque to the west, the Samadhi of Ranjit Singh to the north, and the Roshnai Gate to the south. The garden was built during the rei ...
, Iqbal Park, Mochi Bagh, Gulshan-e-Iqbal Park, Model Town Park, Jilani Park, Race Course Park, Nasir Bagh Lahore, Jallo Park, Lahore Zoo Safari, Lahore Zoo Safari Park, and Changa Manga, a man-made forest near Lahore in the Kasur
Kasur (Urdu and pa, ; also Romanization of Urdu, romanized as Qasūr; from pluralized Arabic word ''Qasr'' meaning "palaces" or "forts") is a city to south of Lahore, in the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. The city serves as th ...
district. Another example is the Bagh-e-Jinnah, Lahore, Bagh-e-Jinnah, a botanical garden that houses entertainment and sports facilities as well as a library.
Economy
File:Lahore Expo Centre.jpg, Expo Centre Lahore
File:PIA Head Office, Lahore.jpg, Pakistan International Airline, PIA Head Office
File:Emporium Mall.jpg, Emporium Mall
, the city's gross domestic product (GDP) by purchasing power parity (PPP) was estimated at $40 billion with a projected average growth rate of 5.6 percent. This is at par with Pakistan's economic hub, Karachi, with Lahore (having half the population) fostering an economy that is 51% of the size of Karachi's ($78 billion in 2008).
Transport

Public transportation
 Lahore's main public transportation system is operated by the Lahore Transport Company (LTC) and Punjab Mass Transit Authority (PMTA). The backbone of its public transport network is the PMTA's Lahore Metrobus and the Orange Line (Lahore Metro), Orange Line of the Lahore Metro train. LTC and PMTA also operates an extensive network of buses, providing bus service to many parts of the city and acting as a feeder system for the Metrobus. The Orange Line metro spans 27.1 km around the city, and operates at a speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).
Lahore's main public transportation system is operated by the Lahore Transport Company (LTC) and Punjab Mass Transit Authority (PMTA). The backbone of its public transport network is the PMTA's Lahore Metrobus and the Orange Line (Lahore Metro), Orange Line of the Lahore Metro train. LTC and PMTA also operates an extensive network of buses, providing bus service to many parts of the city and acting as a feeder system for the Metrobus. The Orange Line metro spans 27.1 km around the city, and operates at a speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).
Metro Bus
The Lahore Metrobus, is a bus rapid transit service operating in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Lahore Metrobus service is integrated with Lahore Transport Company's local bus service to operate as one urban transport system, providing a connected transit service across Lahore District with connections to neighboring suburban communities.
Metro Train

Orange Line
The Orange Line (Lahore Metro), Orange Line Metro Train is an automated rapid transit system in Lahore. The Orange line is the first of the three proposed rail lines proposed for the Lahore Metro. As of 2020, it is the primary metro rail line in the city. The line spans with elevated and underground
Blue Line
The ''Blue Line'' is a proposed line from Chauburji to College Road, Township. Along the way, it will connect places like Mozang Chungi, Shadman Chowk, Jail Road, Mian Boulevard Gulberg, Mian Boulevard Garden Town and Faisal Town.
Purple Line
The ''Purple Line'' is a proposed 19 km long train. It will connect Bhaati Chowk with the Allama Iqbal International Airport. Along the way it will connect places like Brandreth Road, Railway Station, Allama Iqbal Road, Dharampura and Ghazi Road.
Taxi and Rickshaw
Ride sharing services such as Uber and Careem are available in the city. They need to be booked in advance by apps or by calling their number. Motorcycle rides are also available in the city which have been introduced by private companies. These motorcycles also need to be booked in advance by apps or by calling their number.
Auto rickshaws play an important role of public transport in Lahore. There are 246,458 auto rickshaws, often simply called ''autos'', in the city. Motorcycle rickshaws, usually called "chand gari" (moon car) or "chingchi" (after the Chinese company Jinan Qingqi Motorcycle Co. Ltd who first introduced these to the market) are also a very common means of domestic travel, though they are less common and cheaper than auto rickshaws. Chingchi rickshaw's provide a shared ride experience for multiple passengers and fares, whereas Autorick shaws cater to only one passenger or group for a fare. Since 2002, all auto rickshaws have been required to use CNG as fuel.
Urban (LOV) Wagon / Mini Bus
Medium-sized vans/wagons or LOVs (Low Occupancy Vehicle) run on routes throughout the city. They function like buses, and operate on many routes throughout the city.
Intercity transportation
Railways
Lahore Junction railway station, Lahore Junction Station serves as the main railway station for Lahore, and serves as a major hub for all Pakistan Railways services in northern Pakistan. It includes services to Peshawar and national capital Islamabad-Rawalpindi, and long-distance services to Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
and Quetta. Lahore Cantonment railway station, Lahore Cantonment Station also operates a few trains.
Buses
Lahore Badami Bagh Bus Terminal serves as a hub for intercity bus services in Lahore, served by multiple bus companies providing a comprehensive network of services in Punjab and neighboring provinces. Lahore Jinnah Bus Terminal is also a major bus stand.
Airports
 Pakistan's third busiest airport, Allama Iqbal International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA: LHE), straddles the city's eastern boundary. The new passenger terminal was opened in 2003, replacing the old terminal which now serves as a VIP and Hajj lounge. The airport was named after the national poet-philosopher, Muhammad Iqbal. and is a secondary hub for the national flag carrier, Pakistan International Airlines. Walton Airport in Askari provides general aviation facilities. In addition, Sialkot International Airport (IATA: SKT) and Faisalabad International Airport (IATA: LYP) also serve as alternate airports for the Lahore area in addition to serving their respective cities.
Allama Iqbal International Airport connects Lahore with many cities worldwide (including domestic destinations) by both passenger and cargo flight including Ras Al Khaimah International Airport, Ras al Khaimah, Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport, Guangzhou (begins 28 August 2018), Ürümqi Diwopu International Airport, Ürümqi, Abu Dhabi International Airport, Abu Dhabi, Barcelona–El Prat Airport, Barcelona, Beijing Capital International Airport, Beijing–Capital, Copenhagen Airport, Copenhagen, King Fahd International Airport, Dammam, Dera Ghazi Khan International Airport, Dera Ghazi Khan, Hamad International Airport, Doha, Dubai International Airport, Dubai–International, Islamabad International Airport, Islamabad, King Abdulaziz International Airport, Jeddah, Jinnah International Airport, Karachi, Kuala Lumpur International Airport, Kuala Lumpur–International, Heathrow Airport, London–Heathrow, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Prince Mohammad bin Abdulaziz Airport, Medina, Milan–Malpensa Airport, Milan–Malpensa, Multan Airport, Multan, Muscat International Airport, Muscat, Oslo Airport, Gardermoen, Oslo–Gardermoen, Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Bacha Khan International Airport, Peshawar, Quetta Airport, Quetta, Shaikh Zayed International Airport (Rahim Yar Khan), Rahim Yar Khan, King Khalid International Airport, Riyadh, Salalah International Airport, Salalah, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto Pearson International Airport, Toronto–Pearson, Mashhad International Airport, Mashhad, Suvarnabhumi Airport, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, and Tashkent International Airport, Tashkent.
Pakistan's third busiest airport, Allama Iqbal International Airport (International Air Transport Association airport code, IATA: LHE), straddles the city's eastern boundary. The new passenger terminal was opened in 2003, replacing the old terminal which now serves as a VIP and Hajj lounge. The airport was named after the national poet-philosopher, Muhammad Iqbal. and is a secondary hub for the national flag carrier, Pakistan International Airlines. Walton Airport in Askari provides general aviation facilities. In addition, Sialkot International Airport (IATA: SKT) and Faisalabad International Airport (IATA: LYP) also serve as alternate airports for the Lahore area in addition to serving their respective cities.
Allama Iqbal International Airport connects Lahore with many cities worldwide (including domestic destinations) by both passenger and cargo flight including Ras Al Khaimah International Airport, Ras al Khaimah, Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport, Guangzhou (begins 28 August 2018), Ürümqi Diwopu International Airport, Ürümqi, Abu Dhabi International Airport, Abu Dhabi, Barcelona–El Prat Airport, Barcelona, Beijing Capital International Airport, Beijing–Capital, Copenhagen Airport, Copenhagen, King Fahd International Airport, Dammam, Dera Ghazi Khan International Airport, Dera Ghazi Khan, Hamad International Airport, Doha, Dubai International Airport, Dubai–International, Islamabad International Airport, Islamabad, King Abdulaziz International Airport, Jeddah, Jinnah International Airport, Karachi, Kuala Lumpur International Airport, Kuala Lumpur–International, Heathrow Airport, London–Heathrow, Manchester Airport, Manchester, Prince Mohammad bin Abdulaziz Airport, Medina, Milan–Malpensa Airport, Milan–Malpensa, Multan Airport, Multan, Muscat International Airport, Muscat, Oslo Airport, Gardermoen, Oslo–Gardermoen, Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Bacha Khan International Airport, Peshawar, Quetta Airport, Quetta, Shaikh Zayed International Airport (Rahim Yar Khan), Rahim Yar Khan, King Khalid International Airport, Riyadh, Salalah International Airport, Salalah, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto Pearson International Airport, Toronto–Pearson, Mashhad International Airport, Mashhad, Suvarnabhumi Airport, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, and Tashkent International Airport, Tashkent.
Roads

 There are a number of municipal, provincial and federal Roads in Pakistan, roads that serve Lahore.
*Municipal roads
**Canal Road, Lahore, Canal Road (''serves as the major north–south artery'')
*Provincial Highways of Punjab, Provincial highways
**Lahore Ring Road
**Lahore–Kasur Road (Ferozepur Road)
**Lahore–Raiwind Road (Raiwind Road)
**Lahore–Sharaqpur Road (Sagianwala Bypass Road)
**Lahore–Wagah Road
**Grand Trunk Road (G.T Road )
*Roads in Pakistan#Federal roads, Federal highways
**M-2 motorway (Pakistan), M-2 motorway
**M3 motorway (Pakistan), M-3 motorway
**M11 motorway (Pakistan), M-11 motorway
**N-5 National Highway (Multan Road)
**N-60 National Highway (Sargodha–Lahore road)
There are a number of municipal, provincial and federal Roads in Pakistan, roads that serve Lahore.
*Municipal roads
**Canal Road, Lahore, Canal Road (''serves as the major north–south artery'')
*Provincial Highways of Punjab, Provincial highways
**Lahore Ring Road
**Lahore–Kasur Road (Ferozepur Road)
**Lahore–Raiwind Road (Raiwind Road)
**Lahore–Sharaqpur Road (Sagianwala Bypass Road)
**Lahore–Wagah Road
**Grand Trunk Road (G.T Road )
*Roads in Pakistan#Federal roads, Federal highways
**M-2 motorway (Pakistan), M-2 motorway
**M3 motorway (Pakistan), M-3 motorway
**M11 motorway (Pakistan), M-11 motorway
**N-5 National Highway (Multan Road)
**N-60 National Highway (Sargodha–Lahore road)
Government
Metropolitan Corporation
Under Punjab Local Government Act 2013, Lahore is a metropolitan area and under the authority of the Metropolitan Corporation Lahore. The district is divided into 9 zones, each with its own elected Deputy Mayor. The Metropolitan Corporation Lahore is a body of those 9 deputies, as well as the city's mayor – all of whom are elected in popular elections. The Metropolitan Corporation approves zoning and land use, urban design and planning, environmental protection laws, as well as provide municipal services.
Mayor
As per the Punjab Local Government Act 2013, the Mayor of Lahore is the elected head of the Metropolitan Corporation of Lahore. The mayor is directly elected in municipal elections every four years alongside 9 deputy List of towns in Lahore, town mayors. Mubashir Javed of the Pakistan Muslim League (N) was elected mayor of Lahore in 2016. The mayor is responsible for the administration of government services, the composition of councils and committees overseeing Lahore District, Lahore City District departments and serves as the chairperson for the meeting of the Lahore Council. The mayor also functions to help devise long-term development plans in consultation with other stakeholders and bodies to improve the condition, livability, and sustainability of urban areas.
Neighbourhoods
Lahore District is a subdivision of the Punjab, and is further divided into 9 administrative zones.
Politics
The 2015 Local Government elections for Union councils of Pakistan, Union Councils in Lahore yielded the following results:
Festivals
The people of Lahore Festivals in Lahore, celebrate many festivals and events throughout the year, including Islamic, traditional Punjabi, Christian, and national holidays and festivals.
Many people decorate their houses and light candles to illuminate the streets and houses during public holidays; roads and businesses may be lit for days. Many of Lahore's dozens of Sufi shrines hold annual festivals called urs to honour their respective saints. For example, the mausoleum of Ali Hujwiri at the Data Darbar shrine has an annual ''urs'' that attracts up to one million visitors per year.
Tourism
File:Wazir Khan Mosque by Moiz.jpg, Wazir Khan Mosque
; ''Masjid Wazīr Khān'') is a 17th-century mosque located in the city of Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque was commissioned during the reign of the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan as a part of an ensemble of buildings tha ...
File:Night View of Badshahi Mosque (King’s Mosque).jpg, Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
File:Lahore Fort.jpg, Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
(Shahi Qila)
File:Minar e Pakistan night image.jpg, Minar-e-Pakistan
Minar E Pakistan ( ur, , literally "Tower of Pakistan") is a tower located in Lahore, Pakistan. The tower was built between 1960 and 1968 on the site where the All-India Muslim League passed the Lahore Resolution (which was later called the Pak ...
at night
File:Reflection of Farah Baksh Terrace (Upper Terrace) main building.jpg, Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
Lahore remains a major tourist destination in Pakistan. The Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
was renovated in 2014 and is popular due to the presence of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s. Among the most popular sights are the Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort ( ur, , lit=Royal Fort, translit=Shāhī Qilā, label=Punjabi language, Punjabi and Urdu) is a citadel in the city of Lahore, Pakistan. The fortress is located at the northern end of Walled City of Lahore, walled city Lahore, a ...
, adjacent to the Walled City, and home to the Sheesh Mahal (Lahore), Sheesh Mahal, the Alamgiri Gate, the Naulakha pavilion, and the Moti Masjid (Lahore), Moti Masjid. The fort along with the adjoining Shalimar Gardens Shalimar or Shalamar refers to three historic royal gardens (or Baghs) of the Mughal Empire in South Asia:
* Shalimar Bagh, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; built in 1619
* Shalimar Gardens, Lahore, Pakistan; a UNESCO World Heritage Site built in ...
has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1981.
The city is home to several ancient religious sites including prominent Hindu temples, the Krishna Mandir demolition reports, Krishna Temple and Valmiki Mandir, Lahore, Valmiki Mandir. The Samadhi of Ranjit Singh
The Samadhi of Ranjit Singh ( pa, , ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਮਾਧੀ ; ) is a 19th-century building in Lahore, Pakistan that houses the funerary urns of the Sikh Maharaja Ranjit Singh (1780 – 1839). It is located adjacen ...
, also located near the Walled City, houses the Urn, funerary urns of the Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
ruler Maharaja Ranjit Singh (Punjab), Maharaja Ranjit Singh. The most prominent religious building is the Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
, constructed in 1673; it was the largest mosque in the world upon construction. Another popular sight is the Wazir Khan Mosque
; ''Masjid Wazīr Khān'') is a 17th-century mosque located in the city of Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque was commissioned during the reign of the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan as a part of an ensemble of buildings tha ...
, known for its extensive ''faience'' tile work and constructed in 1635.
Cuisine
Religious sites
Other well-known religious sites in the city are:
* Badshahi Mosque
The Badshahi Mosque (Urdu, Punjabi: ; literally ''The Royal Mosque'') is a Mughal-era congregational mosque in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque is located west of Lahore Fort along the outskirts of the Walled C ...
* Dai Anga Mosque
Dai Anga Mosque (Urdu: ) is a mosque situated to southeast of the Lahore Railway Station, in the city of Lahore in Pakistan's Punjab province. The mosque is said to have been built in 1635 in honour of the wetnurse of the Mughal Emperor Shah J ...
* Madho Lal Hussain, Darbar Madho Lal Hussain
* Data Durbar Complex, Data Darbar Complex
* Grand Jamia Mosque, Lahore
* Gurdwara Dera Sahib
* Gurdwara Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das
The Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das ( ur, , label=Punjabi, Urdu) is a gurdwara in Lahore, Pakistan. The gurdwara was built atop the site traditionally believed to be the location of the birthplace and childhood home of Guru Ram Das, the 4th Sikh gurus. ...
* Krishna Mandir, Lahore
* Lava Temple
* Lohari Gate Mosque
* Masjid of Mariyam Zamani
* Masjid Shuhada
* Moti Masjid (Lahore Fort)
* Saleh Kamboh Mosque, Muhammad Saleh Kamboh Mosque
* Neevin Mosque
* Oonchi Mosque
* Sacred Heart Cathedral, Lahore
* Shab Bhar Mosque
* Shaheed Ganj Mosque
* St. Andrew's Church, Lahore, St. Andrew's Presbyterian Church
* Suneri Mosque
* Valmiki Temple
* Wazir Khan Mosque
; ''Masjid Wazīr Khān'') is a 17th-century mosque located in the city of Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab. The mosque was commissioned during the reign of the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan as a part of an ensemble of buildings tha ...
e
Museums
*Army Museum Lahore
*Fakir Khana
*Islamic Summit Minar
The Summit Minar is an obelisk-shaped structure built in the centre of Charing Cross, Mall Road in the city of Lahore, Punjab the province of Pakistan. It was built to commemorate the second Islamic Summit Conference held in Lahore from 22 to 24 ...
*Javed Manzil
*Lahore Museum
The Lahore Museum ( pa, ; ur, ; ''"Lahore Wonder House"'') is a museum located in Lahore, Pakistan. Founded in 1865 at a smaller location and opened in 1894 at its current location on The Mall in Lahore during the British colonial period, La ...
*National History Museum
*National Museum of Science and Technology, Lahore, National Museum of Science and Technology
*Shakir Ali Museum
*Tollinton Market-Lahore City Heritage Museum
Tombs
* Tomb of Ali Mardan Khan
* Tomb of Allama Iqbal
The Tomb of Allama Iqbal, or Mazaar-e-Iqbal ( ur, ) is a mausoleum located within the Hazuri Bagh, in the Pakistani city of Lahore, capital of Punjab province.
Background
Iqbal was one of the major inspirations behind the Pakistan Movement, a ...
* Tomb of Anarkali
The Tomb of Anarkali ( ur, ) is an octagonal 16th century Mughal monument in Lahore, capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab.
Location
The tomb of Anarkali is located on the grounds of Lahore's Punjab Civil Secretariat complex near the Bri ...
* Tomb of Asif Khan
The Tomb of Asif Khan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum located in Shahdara Bagh, in the city of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It was built for the Mughal Empire, Mughal statesman Abul-Hasan ibn Mirza Ghiyas Beg, Mirza Abul Hassan Jah, who ...
* Tomb of Dai Anga
* Tomb of Jani Khan
* Tomb of Jahangir
The Tomb of Jahangir ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum built for the Mughal Emperor Jahangir. The mausoleum dates from 1637, and is located in Shahdara Bagh near city of Lahore, Pakistan, along the banks of the Ravi River. The site is famous ...
* Tomb of Nadira Begum
* Tomb of Nur Jahan
The Tomb of Nur Jahan ( ur, ) is a 17th-century mausoleum in Lahore, Pakistan, that was built for the Mughal empress Nur Jahan. The tomb's marble was plundered during the Sikh era in 18th century for use at the Golden Temple in Amritsar. The ...
*Tomb of Dai Anga
* Buddhu's Tomb
* Cypress Tomb or Sarowala Maqbara
* Tomb of Zeb-un-Nissa Begum
* Tomb of Gul Begum
* Tomb of Malik Ayaz
Malik Ayaz (Persian: ملک ایاز), son of Aymāq Abu'n-Najm, was a slave from Georgia who rose to the rank of officer and general in the army of Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni (also known as ''Mahmud Ghaznavi)''. Malik Ayaz's slave-general of Mahm ...
* Kuri Bagh
* Mai Dai
* Mian Khan
* Nusrat Khan
* Prince Pervez
* Qutb-ud-din Aibak
* Saleh Kamboh
* Mir Niamat Khan
* Rasul Shahyun
* Zafar Jang Kokaltash
Shrines
* Bibi Pak Daman
* Ali Hujwiri
* Mian Mir
* Madho Lal Hussain
* Khawaja Tahir Bandgi
* Ghazi Ilm Din Shaheed
* Sheikh Musa Ahangar
* Khawaja Mehmud
* Nizam-ud-Din
* Siraj-ud-Din Gilani
* peer makki
* Baba Shah Jamal
Samadhis
* Bhai Vasti Ram
* Samadhi of Ranjit Singh, Ranjit Singh
* Samadhi of Bhai Mani Singh
* Ganga Ram, Sir Ganga Ram
* Bhai Taru Singh
Havelis
There are many haveli
A ''haveli'' is a traditional townhouse, mansion, manor house, in the Indian subcontinent, usually one with historical and architectural significance, and located in a town or city. The word ''haveli'' is derived from Arabic ''hawali'', mean ...
s inside the Walled City of Lahore, some in good condition while others need urgent attention. Many of these havelis are fine examples of Mughal architecture, Mughal and Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
Architecture. Some of the havelis inside the Walled City include:
* Chuna Mandi Havelis
* Dina Nath Ki Haveli
* Haveli Barood Khana
* Haveli Mian Khan (Rang Mehal)
* Haveli of Nau Nihal Singh
* Haveli Shergharian (near Lal Khou)
* Haveli Sir Wajid Ali Shah (near Nisar Haveli)
* Lal Haveli beside Mochi Bagh
* Mubarak Begum Haveli Bhatti Gate
* Mubarak Haveli – Chowk Nawab Sahib, Mochi/Akbari Gate
* Mughal Haveli (residence of Maharaja Ranjeet Singh)
* Nisar Haveli
* Salman Sirhindi ki Haveli
Other landmarks
* Shahi Hammam
The Shahi Hammam (Urdu and pa, ; ''"Royal Baths"''), also known as the Wazir Khan Hammam, is a Turkish bath, Persian-style bath which was built in Lahore, Pakistan, in 1635 Common era, C.E. during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan. It was built by ...
Historic neighbourhoods
*Anarkali
*Badami Bagh
*Baghbanpura
*Begampura
*Mughalpura
*Shahdara Bagh
Shahdara Bagh ( ur, ; meaning “''King’s Way Garden”'') is a historic precinct located across the Ravi River from the Walled City of Lahore, Pakistan. Shahdara Bagh is the site of several Mughal era monumentally, including the Tomb of Ja ...
*Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
Education
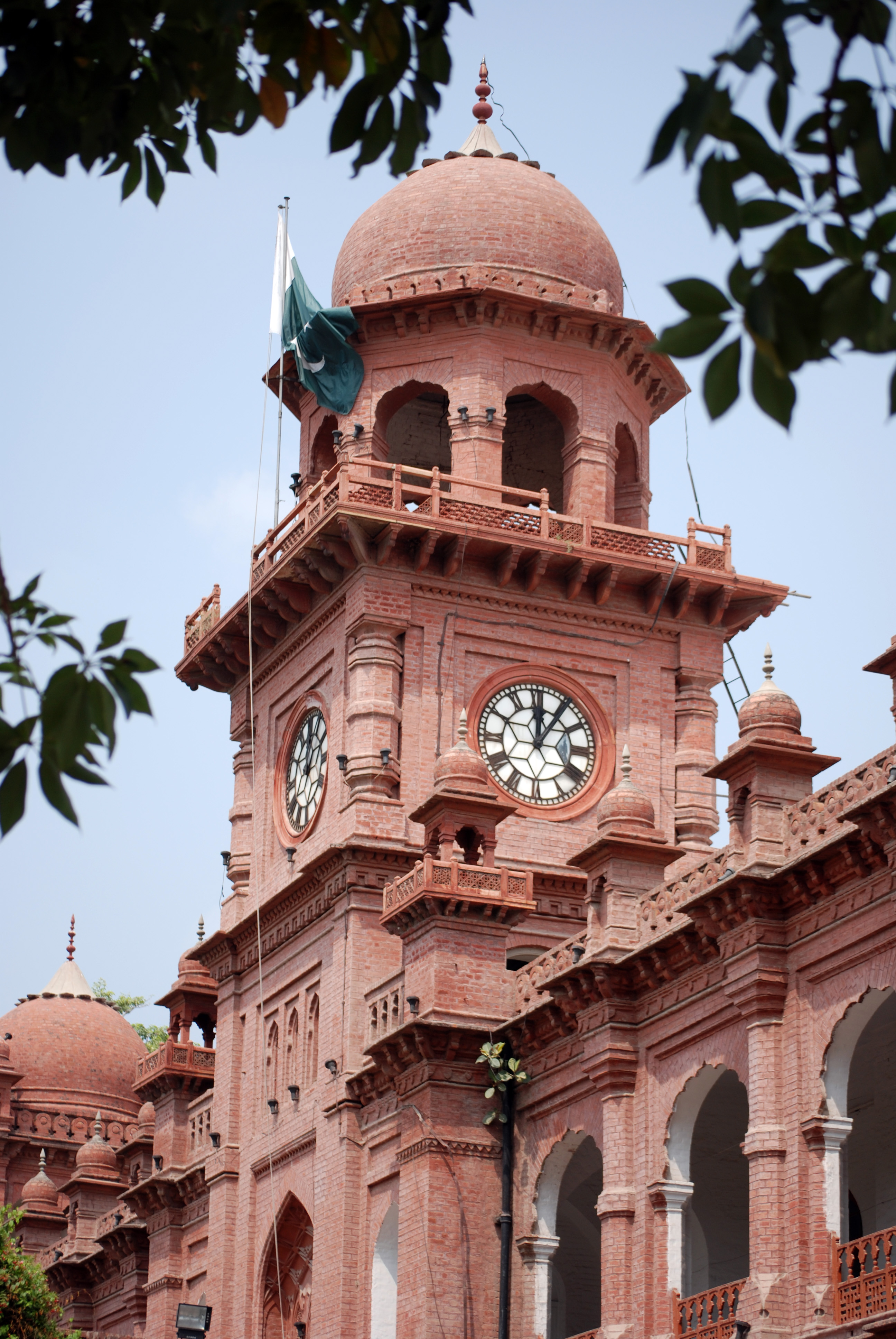



 Lahore is known as Pakistan's educational capital, with more colleges and universities than any other city in Pakistan. Lahore is Pakistan's largest producer of professionals in the fields of science, technology, IT, law, engineering, medicine, nuclear sciences, pharmacology, telecommunication, biotechnology and microelectronics, nanotechnology and the only future hyper high-tech center of Pakistan. Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities. It has the only Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business, AACSB accredited business school in Pakistan, namely, Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). The literacy rate of Lahore is 74%. Lahore hosts some of Pakistan's oldest and best educational institutes:
* Aitchison College, established in 1886
* Beaconhouse National University, established in 2003
* Central Model School, Lahore, Central Model School, established in 1883
* Crescent Model Higher Secondary School, established in 1968
* University of Home Economics Lahore, College of Home Economics, established in 1955
* College of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences, established in 1950
* Convent of Jesus and Mary, Lahore, Convent of Jesus and Mary, established in 1867
* Dayal Singh College (Lahore), Dayal Singh College, established in1910
* De'Montmorency College of Dentistry, established in 1929
* Don Bosco High School (Lahore), Don Bosco High School, established in 1956
* Fatima Jinnah Medical University, established in 1948
* Forman Christian College, established n 1864
* Garrison College for Boys, established in 2014
* GC University, Lahore, Government College University, Lahore, established in 1864
* Hailey College of Commerce, established in 1927
* Islamia College (Lahore), Islamia College, established in 1892
* Jamia Ashrafia, established in 1947
*
Lahore is known as Pakistan's educational capital, with more colleges and universities than any other city in Pakistan. Lahore is Pakistan's largest producer of professionals in the fields of science, technology, IT, law, engineering, medicine, nuclear sciences, pharmacology, telecommunication, biotechnology and microelectronics, nanotechnology and the only future hyper high-tech center of Pakistan. Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities. It has the only Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business, AACSB accredited business school in Pakistan, namely, Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). The literacy rate of Lahore is 74%. Lahore hosts some of Pakistan's oldest and best educational institutes:
* Aitchison College, established in 1886
* Beaconhouse National University, established in 2003
* Central Model School, Lahore, Central Model School, established in 1883
* Crescent Model Higher Secondary School, established in 1968
* University of Home Economics Lahore, College of Home Economics, established in 1955
* College of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences, established in 1950
* Convent of Jesus and Mary, Lahore, Convent of Jesus and Mary, established in 1867
* Dayal Singh College (Lahore), Dayal Singh College, established in1910
* De'Montmorency College of Dentistry, established in 1929
* Don Bosco High School (Lahore), Don Bosco High School, established in 1956
* Fatima Jinnah Medical University, established in 1948
* Forman Christian College, established n 1864
* Garrison College for Boys, established in 2014
* GC University, Lahore, Government College University, Lahore, established in 1864
* Hailey College of Commerce, established in 1927
* Islamia College (Lahore), Islamia College, established in 1892
* Jamia Ashrafia, established in 1947
* King Edward Medical University
King Edward Medical University (KEMU) () is a public medical university located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Founded in 1860, the university is named after King Edward VII.
Established by the British Raj, named as Lahore Medical School. In 1868 ...
, established in 1860
* Kinnaird College for Women University, established in 1913
* University of Education, Lady Maclagan Training College, established in 1933
* Lady Willingdon Hospital, Lady Willingdon Nursing School, established in 1933
* Lahore College for Women University, established in 1922
* Lahore Garrison University
* Lahore Grammar School, established in 1979
* Lahore Medical and Dental College, established in 1997
* Lahore School of Economics, established in 1993
* Lahore University of Management Sciences, established in 1986
* Govt. M.A.O College Lahore, M.A.O College, established in 1933
* Muslim Model High School, Lahore, Muslim Model High School, established in 1890
* National College of Arts, established in 1875
* Oriental College, established in 1876
* Pakistan Institute of Fashion and Design, established in 1994
* PakTurk International Schools and Colleges, established in 2006
* Queen Mary College, Lahore, Queen Mary College, established in 1908
* Sacred Heart High School for Girls, Sacred Heart High School, established in 1906
* St. Anthony's High School (Lahore), St. Anthony's High School, established in 1892
* St Francis High School, Lahore, St. Francis High School, established in 1842
* University College Lahore, established in 1994
* University College of Pharmacy, established in 1944
* University of the Punjab, University Law College, established in 1868
* University of Central Punjab, established in 2002
* University of Education, established in 2002
* University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, established in 1921
* University of Health Sciences, Lahore, established in 2002
* University of Lahore, established in 1999
* University of Management and Technology (Lahore), established in 2002
* University of the Punjab
The University of the Punjab (Urdu, pnb, ), also referred to as Punjab University, is a public, research, coeducational higher education institution located in Lahore, Pakistan. Punjab University is the oldest public university in Pakistan. ...
, established in 1882
* University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, established in 1882
Notable people
Some people born in Lahore:
*Syed Mohammad Taqweem Ahsan (born 1959), journalist
*John Bayley (writer), John O. Bayley (1925-2015), writer
*Kabir Bedi (born 1946), actor
*Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1910-1995), astrophysicist
*Javed Iqbal (serial killer), Javed Iqbal Unmayr (1956-2001), serial killer
*Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
(1592-1666), emperor
*Shekhar Kapur (born 1945), filmmaker
*Surinder Kaur (1929-2006), singer and songwriter
Sports
File:HOCKEY ARGENTINA PAKISTAN.jpg, Pakistan playing against Argentina in 2005.
File:Gaddafi stadium lahore.jpg, Gaddafi Stadium
Gaddafi Stadium ( ur, , translit=Qaẕẕāfī Isṭeḍiyam), previously known as Lahore Stadium is a cricket stadium in Lahore, Pakistan and the home ground of Lahore Qalandars. It is owned by the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB). With a capacit ...
is one of the largest List of stadiums in Pakistan, stadiums of Pakistan with a capacity of 27,000 spectators.
File:Gymkhana Club, Lahore.jpg, Lahore Gymkhana Club, Gymkhana Club
Lahore has successfully hosted many international sports events including the finals of the 1990 Men's Hockey World Cup and the 1996 Cricket World Cup. The headquarters of all major sports governing bodies are located here in Lahore including Cricket, Hockey, Rugby, Football etc. and also has the head office of Pakistan Olympic Association.
Gaddafi Stadium
Gaddafi Stadium ( ur, , translit=Qaẕẕāfī Isṭeḍiyam), previously known as Lahore Stadium is a cricket stadium in Lahore, Pakistan and the home ground of Lahore Qalandars. It is owned by the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB). With a capacit ...
is a List of Test cricket grounds, Test cricket ground in Lahore. It was completed in 1959 and later in the 1990s, renovations were carried out by Pakistani architect Nayyar Ali Dada.
Lahore is home to several golf courses. The Lahore Gymkhana Club, Lahore Gymkhana Golf Course, the Lahore Garrison Golf and Country Club, the Royal Palm Golf Club and newly built Defence Raya Golf & Country Club are well maintained Golf Courses in Lahore. In nearby Raiwind Road, a 9 holes course, Lake City, opened in 2011. The newly opened Oasis Golf and Aqua Resort is another addition to the city. It is a state-of-the-art facility featuring golf, water parks, and leisure activities such as horse riding, archery and more. The Lahore Marathon is part of an annual package of six international marathons being sponsored by Standard Chartered Bank across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. More than 20,000 athletes from Pakistan and all over the world participate in this event. It was first held on 30 January 2005, and again on 29 January 2006. More than 22,000 people participated in the 2006 race. The third marathon was held on 14 January 2007. Plans exist to build Pakistan's first sports city in Lahore, on the bank of the Ravi River
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
.
;Professional sports teams from Lahore
Twin towns and sister cities
The following international cities have been declared twin towns and sister cities of Lahore.
* Istanbul, Turkey (1975)Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
, UzbekistanSamarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, Uzbekistan (1995)Amol
Amol ( fa, آمل – ; ; also Romanized as Āmol and Amul) is a city and the administrative center of Amol County, Mazandaran Province, Iran, with a population of around 300,000 people.
Amol is located on the Haraz river bank. It is less than ...
, Iran (2010)
Awards
In 1966, the Government of Pakistan awarded a special flag, the Hilal-i-istaqlal to Lahore (also to Sargodha and Sialkot
Sialkot ( ur, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of Sialkot District and the 13th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined with Jammu (the winter capital of Indian administered Jammu and Ka ...
) for showing severe resistance to the enemy during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 as these cities were targets of the Indian aggression. Every year on Defence Day (6 September), this flag is hoisted in these cities in recognition of the will, courage and perseverance of their people.
See also
*
* Lahore Fashion Week
* Lahore Knowledge Park
* Lahore Literary Festival
* Lahore Railway Station
* Lahori cuisine
* List of cemeteries in Lahore
* List of cities proper by population
* List of films set in Lahore
* List of hospitals in Lahore
* List of largest cities in Organisation of Islamic Cooperation member countries
* List of metropolitan areas in Asia
* List of people from Lahore
* List of streets in Lahore
* List of tallest buildings in Lahore
* List of towns in Lahore
* List of urban areas by population
*Lahori chaddar
* Sikh period in Lahore
* Transport in Lahore
* Walled City of Lahore
The Walled City of Lahore (Punjabi language, Punjabi & ur, , ''"Inner City"''), also known as Old City, forms the historic core of Lahore, Pakistan. The city was established around 1000 CE in the western half of the Walled City, which was for ...
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
External links
*
{{Authority control
Lahore
Cities in Punjab (Pakistan)
Populated places in Lahore District
Capitals of Pakistan
Metropolitan areas of Pakistan
Populated places with period of establishment missing
 Sultan
Sultan  Mongol conqueror Timur gave control of the Lahore region to
Mongol conqueror Timur gave control of the Lahore region to 



 Shah Jahan's son, and last of the great Mughal Emperors,
Shah Jahan's son, and last of the great Mughal Emperors, 
 In the aftermath of
In the aftermath of 
 The
The  The British built the
The British built the  Lahore played an important role in the independence movements of both India and Pakistan. The
Lahore played an important role in the independence movements of both India and Pakistan. The  After independence, Lahore slowly regained its significance as an economic and cultural centre of western Punjab. Reconstruction began in 1949 of the Shah Alami Bazaar, the former commercial heart of the Walled City until it was destroyed in the 1947 riots. The
After independence, Lahore slowly regained its significance as an economic and cultural centre of western Punjab. Reconstruction began in 1949 of the Shah Alami Bazaar, the former commercial heart of the Walled City until it was destroyed in the 1947 riots. The  Lying between 31°15′—31°45′ N and 74°01′—74°39′ E, Lahore is bounded on the north and west by the
Lying between 31°15′—31°45′ N and 74°01′—74°39′ E, Lahore is bounded on the north and west by the 
 Lahore's modern cityscape consists of the historic
Lahore's modern cityscape consists of the historic  Lahore is home to numerous monuments from the Mughal Dynasty,
Lahore is home to numerous monuments from the Mughal Dynasty, 
 As the capital of British Punjab, British colonialists made a lasting architectural impression on the city. Structures were built predominantly in the Indo-Gothic style – a syncretic architectural style that blends elements of Victorian architecture, Victorian and Islamic architecture, or in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The British also built Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical Montgomery Hall, which today serves as the Quaid-e-Azam Library.
Bagh-e-Jinnah, Lahore, Lawrence Gardens were also laid near Civil Station, and were paid for by donations solicited from both Lahore's European community, as well as from wealthy locals. The gardens featured over 600 species of plants, and were tended to by a horticulturist sent from London's Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew.
The British authorities built several important structures around the time of the
As the capital of British Punjab, British colonialists made a lasting architectural impression on the city. Structures were built predominantly in the Indo-Gothic style – a syncretic architectural style that blends elements of Victorian architecture, Victorian and Islamic architecture, or in the distinct Indo-Saracenic style. The British also built Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical Montgomery Hall, which today serves as the Quaid-e-Azam Library.
Bagh-e-Jinnah, Lahore, Lawrence Gardens were also laid near Civil Station, and were paid for by donations solicited from both Lahore's European community, as well as from wealthy locals. The gardens featured over 600 species of plants, and were tended to by a horticulturist sent from London's Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew.
The British authorities built several important structures around the time of the  Lahore is also known as the ''City of Gardens'' due to large number of gardens. The
Lahore is also known as the ''City of Gardens'' due to large number of gardens. The 
 Lahore's main public transportation system is operated by the Lahore Transport Company (LTC) and Punjab Mass Transit Authority (PMTA). The backbone of its public transport network is the PMTA's Lahore Metrobus and the Orange Line (Lahore Metro), Orange Line of the Lahore Metro train. LTC and PMTA also operates an extensive network of buses, providing bus service to many parts of the city and acting as a feeder system for the Metrobus. The Orange Line metro spans 27.1 km around the city, and operates at a speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).
Lahore's main public transportation system is operated by the Lahore Transport Company (LTC) and Punjab Mass Transit Authority (PMTA). The backbone of its public transport network is the PMTA's Lahore Metrobus and the Orange Line (Lahore Metro), Orange Line of the Lahore Metro train. LTC and PMTA also operates an extensive network of buses, providing bus service to many parts of the city and acting as a feeder system for the Metrobus. The Orange Line metro spans 27.1 km around the city, and operates at a speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).


 There are a number of municipal, provincial and federal Roads in Pakistan, roads that serve Lahore.
*Municipal roads
**Canal Road, Lahore, Canal Road (''serves as the major north–south artery'')
*Provincial Highways of Punjab, Provincial highways
**Lahore Ring Road
**Lahore–Kasur Road (Ferozepur Road)
**Lahore–Raiwind Road (Raiwind Road)
**Lahore–Sharaqpur Road (Sagianwala Bypass Road)
**Lahore–Wagah Road
**Grand Trunk Road (G.T Road )
*Roads in Pakistan#Federal roads, Federal highways
**M-2 motorway (Pakistan), M-2 motorway
**M3 motorway (Pakistan), M-3 motorway
**M11 motorway (Pakistan), M-11 motorway
**N-5 National Highway (Multan Road)
**N-60 National Highway (Sargodha–Lahore road)
There are a number of municipal, provincial and federal Roads in Pakistan, roads that serve Lahore.
*Municipal roads
**Canal Road, Lahore, Canal Road (''serves as the major north–south artery'')
*Provincial Highways of Punjab, Provincial highways
**Lahore Ring Road
**Lahore–Kasur Road (Ferozepur Road)
**Lahore–Raiwind Road (Raiwind Road)
**Lahore–Sharaqpur Road (Sagianwala Bypass Road)
**Lahore–Wagah Road
**Grand Trunk Road (G.T Road )
*Roads in Pakistan#Federal roads, Federal highways
**M-2 motorway (Pakistan), M-2 motorway
**M3 motorway (Pakistan), M-3 motorway
**M11 motorway (Pakistan), M-11 motorway
**N-5 National Highway (Multan Road)
**N-60 National Highway (Sargodha–Lahore road)



 Lahore is known as Pakistan's educational capital, with more colleges and universities than any other city in Pakistan. Lahore is Pakistan's largest producer of professionals in the fields of science, technology, IT, law, engineering, medicine, nuclear sciences, pharmacology, telecommunication, biotechnology and microelectronics, nanotechnology and the only future hyper high-tech center of Pakistan. Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities. It has the only Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business, AACSB accredited business school in Pakistan, namely, Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). The literacy rate of Lahore is 74%. Lahore hosts some of Pakistan's oldest and best educational institutes:
* Aitchison College, established in 1886
* Beaconhouse National University, established in 2003
* Central Model School, Lahore, Central Model School, established in 1883
* Crescent Model Higher Secondary School, established in 1968
* University of Home Economics Lahore, College of Home Economics, established in 1955
* College of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences, established in 1950
* Convent of Jesus and Mary, Lahore, Convent of Jesus and Mary, established in 1867
* Dayal Singh College (Lahore), Dayal Singh College, established in1910
* De'Montmorency College of Dentistry, established in 1929
* Don Bosco High School (Lahore), Don Bosco High School, established in 1956
* Fatima Jinnah Medical University, established in 1948
* Forman Christian College, established n 1864
* Garrison College for Boys, established in 2014
* GC University, Lahore, Government College University, Lahore, established in 1864
* Hailey College of Commerce, established in 1927
* Islamia College (Lahore), Islamia College, established in 1892
* Jamia Ashrafia, established in 1947
*
Lahore is known as Pakistan's educational capital, with more colleges and universities than any other city in Pakistan. Lahore is Pakistan's largest producer of professionals in the fields of science, technology, IT, law, engineering, medicine, nuclear sciences, pharmacology, telecommunication, biotechnology and microelectronics, nanotechnology and the only future hyper high-tech center of Pakistan. Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities. It has the only Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business, AACSB accredited business school in Pakistan, namely, Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). The literacy rate of Lahore is 74%. Lahore hosts some of Pakistan's oldest and best educational institutes:
* Aitchison College, established in 1886
* Beaconhouse National University, established in 2003
* Central Model School, Lahore, Central Model School, established in 1883
* Crescent Model Higher Secondary School, established in 1968
* University of Home Economics Lahore, College of Home Economics, established in 1955
* College of Statistical and Actuarial Sciences, established in 1950
* Convent of Jesus and Mary, Lahore, Convent of Jesus and Mary, established in 1867
* Dayal Singh College (Lahore), Dayal Singh College, established in1910
* De'Montmorency College of Dentistry, established in 1929
* Don Bosco High School (Lahore), Don Bosco High School, established in 1956
* Fatima Jinnah Medical University, established in 1948
* Forman Christian College, established n 1864
* Garrison College for Boys, established in 2014
* GC University, Lahore, Government College University, Lahore, established in 1864
* Hailey College of Commerce, established in 1927
* Islamia College (Lahore), Islamia College, established in 1892
* Jamia Ashrafia, established in 1947
*