Lactones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lactones are cyclic
 Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a
Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a
 Many methods in ester synthesis can also be applied to that of lactones. In one industrial synthesis of
Many methods in ester synthesis can also be applied to that of lactones. In one industrial synthesis of  In halolactonization, an
In halolactonization, an  The γ-lactones γ-octalactone, γ-nonalactone,
The γ-lactones γ-octalactone, γ-nonalactone,

File:Propiolactone.png,
File:GBL_chemical_structure.png,
File:Glucono-delta-lactone-2D-skeletal.png,
File:Caprolactone.png,
*Macrolides
*
carboxylic ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides a ...
s, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is usually used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecula ...
s replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.
Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
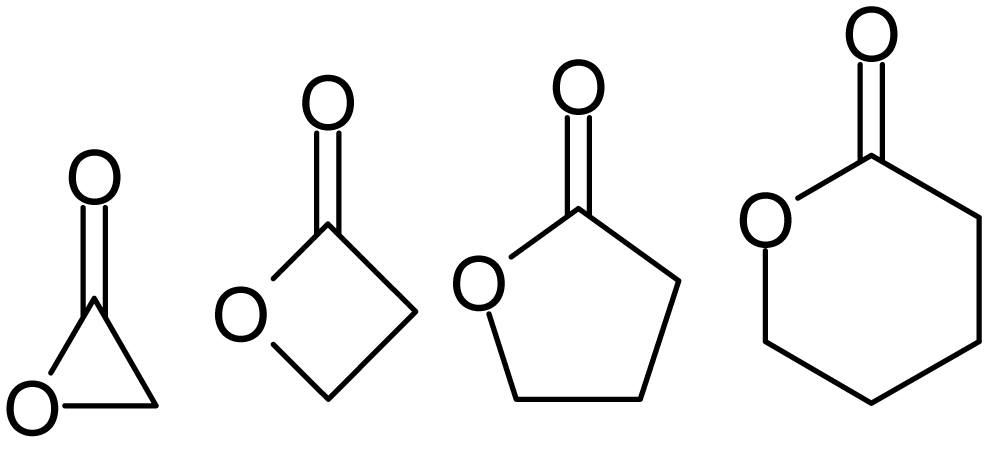
of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered.
Nomenclature
 Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a
Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as w ...
prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH and the -COOH groups along said backbone. The first carbon atom after the carbon in the -COOH group on the parent compound is labelled α, the second will be labeled β, and so forth. Therefore, the prefixes also indicate the size of the lactone ring: α-lactone = 3-membered ring, β-lactone = 4-membered, γ-lactone = 5-membered, etc. Macrocyclic
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry.
...
lactones are known as macrolactones.
The other suffix used to denote a lactone is ''-olide'', used in substance class names like ''butenolide
Butenolides are a class of lactones with a four-carbon heterocyclic ring structure.Joule JA, Mills K. (2000). Heterocyclic Chemistry 4th ed. Blackwell Science Publishing: Oxford, UK They are sometimes considered oxidized derivatives of furan. The ...
'', ''macrolide
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrol ...
'', ''cardenolide
A cardenolide is a type of steroid. Many plants contain derivatives, collectively known as cardenolides, including many in the form of cardenolide glycosides (cardenolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). Cardenolide glycoside ...
'' or ''bufadienolide
Bufadienolide is a chemical compound with steroid structure. Its derivatives are collectively known as bufadienolides, including many in the form of bufadienolide glycosides (bufadienolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). These ...
''.
To obtain the preferred IUPAC name
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among the possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choo ...
s, lactones are named as heterocyclic pseudoketones by adding the suffix ‘one’, ‘dione’, ‘thione’, etc. and the appropriate multiplicative prefixes to the name of the heterocyclic parent hydride.
Etymology
The name ''lactone'' derives from the ring compound calledlactide
Lactide is the lactone cyclic ester derived by multiple esterification between two (usually) or more molecules from lactic acid (2-hydroxypropionic acid) or other hydroxy carboxylic acid. They are designated as dilactides, trilactides, etc., accor ...
, which is formed from the dehydration of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natu ...
) CH3-CH(OH)-COOH. Lactic acid, in turn, derives its name from its original isolation from soured milk (Latin: lac, lactis). The name was coined in 1844 by the French chemist Théophile-Jules Pelouze
Théophile-Jules Pelouze (also known as Jules Pelouze, Théophile Pelouze, Theo Pelouze, or T. J. Pelouze, ; 26 February 180731 May 1867) was a French chemist.
Life
He was born at Valognes, and died in Paris.
His father, Edmond Pelouze, was an ...
, who first obtained it as a derivative of lactic acid. An internal dehydration reaction
In chemistry, a dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.
Dehydration reactions in organic che ...
within the same molecule of lactic acid would have produced alpha-propiolactone, a lactone with a 3-membered ring.
In 1880 the German chemist Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig
Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig (6 December 183519 November 1910) was a German chemist. He discovered the pinacol coupling reaction, mesitylene, diacetyl and biphenyl. Fittig studied the action of sodium on ketones and hydrocarbons. He discovered the Fitt ...
extended the name "lactone" to all intramolecular carboxylic esters.
Natural sources
Naturally occurring lactones are mainly saturated and unsaturated γ- and δ-lactones, and to a lesser extent macrocyclic lactones. The γ- and δ-lactones are intramolecular esters of the corresponding hydroxy fatty acids. They contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, and other foods.Cyclopentadecanolide
Cyclopentadecanolide is a natural macrolide lactone and a synthetic musk.
Natural occurrence
Cyclopentadecanolide occurs in small quantities in angelica root essential oil and is responsible for its musklike odor.
Production
Cyclopentadecanol ...
is responsible for the musklike odor of angelica root
''Angelica archangelica'', commonly known as garden angelica, wild celery, and Norwegian angelica, is a biennial plant from the family Apiaceae, a subspecies of which is cultivated for its sweetly scented edible stems and roots. Like several oth ...
oil. Of the naturally occurring bicyclic lactones, phthalides
Phthalide is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H6O2. A white solid, it is the simplest benzo lactone. It is prepared from hydroxymethylbenzoic acid.
Phthalides
The phthalide core is found a variety of more complex chemic ...
are responsible for the odors of celery
Celery (''Apium graveolens'') is a marshland plant in the family Apiaceae that has been cultivated as a vegetable since antiquity. Celery has a long fibrous stalk tapering into leaves. Depending on location and cultivar, either its stalks, lea ...
and lovage
Lovage (), ''Levisticum officinale'', is a tall perennial plant, the sole species in the genus ''Levisticum'' in the family Apiaceae, subfamily Apioideae. It has been long cultivated in Europe, the leaves being used as a herb, the roots as a veg ...
oils, and coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered h ...
for woodruff. Lactones are present in oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
wood, and they contribute to the flavour profile of Barrel-aged beer
A barrel-aged beer is a beer that has been aged for a period of time in a wooden barrel. Typically, these barrels once housed bourbon, whisky, wine, or, to a lesser extent, brandy, sherry, or port.ascorbic acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
, kavain
Kavain is the main kavalactone found mostly in the roots of the kava plant.
Pharmacology
Kavain has anticonvulsive properties, attenuating vascular smooth muscle contraction through interactions with voltage-dependent and channels. How this ef ...
, nepetalactone
Nepetalactone is a name for multiple iridoid analog stereoisomers. Nepetalactones are produced by ''Nepeta cataria'' (catnip) and many other plants belonging to the genus ''Nepeta'', in which they protect these plants from herbivorous insects by fu ...
, gluconolactone
Glucono-delta-lactone (GDL), also known as gluconolactone, is a food additive with the E number, E-number E575 used as a sequestrant, an acidifier, or a Curing (food preservation), curing, pickling, or leavening agent. It is a lactone of D-gluconi ...
, hormones
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and beh ...
(spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood pressure ...
, mevalonolactone), enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
(lactonase
Lactonase (EC 3.1.1.81, acyl-homoserine lactonase; systematic name ''N''-acyl-L-homoserine-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a metalloenzyme, produced by certain species of bacteria, which targets and inactivates acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs). I ...
), neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
s ( butyrolactone, avermectin
The avermectins are a series of drugs and pesticides used to treat parasitic worms and insect pests. They are a group of 16-membered macrocyclic lactone derivatives with potent anthelmintic and insecticidal properties. These naturally occurring c ...
s), antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s (macrolide
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrol ...
s like erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used duri ...
; amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious mycosis, fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candida infections, candidiasis, coccidioidomy ...
), anticancer drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
(vernolepin
Vernolepin is a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from the dried fruit of ''Vernonia amygdalina''. It shows platelet anti-aggregating properties and is also an irreversible DNA polymerase inhibitor, hence may have antitumor properties.
References
, epothilones), phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonstero ...
s (resorcylic acid Resorcylic acid is a type of dihydroxybenzoic acid. It may refer to:
*3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (α-resorcylic acid) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a colorless solid.
Preparation and occurrence
It is prepared by disu ...
lactones, cardiac glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for co ...
s).
Synthesis
oxandrolone
Oxandrolone, sold under the brand names Oxandrin and Anavar, among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used to help promote weight gain in various situations, to help offset protein catabolism caused by long-term ...
the key lactone-forming step is an organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, Mechanistic Organ ...
- esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
.
alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
is attacked by a halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
via electrophilic addition
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound containing a double or triple bond has a π bond broken, with the formation of two new σ bonds.March, Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Che ...
with the cationic intermediate captured intramolecularly by an adjacent carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
(See also iodolactamization).
Specific methods include Yamaguchi esterification
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (TCBC, Yamaguchi reagent) to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric a ...
, Shiina macrolactonization, Corey-Nicolaou macrolactonization, Baeyer–Villiger oxidation
The Baeyer–Villiger oxidation is an organic reaction that forms an ester from a ketone or a lactone from a cyclic ketone, using peroxyacids or peroxides as the oxidant. The reaction is named after Adolf von Baeyer and Victor Villiger who ...
and nucleophilic abstraction
Nucleophilic abstraction is a type of an organometallic reaction which can be defined as a nucleophilic attack on a ligand which causes part or all of the original ligand to be removed from the metal along with the nucleophile.Spessard, Gary; Mie ...
.
γ-decalactone
''gamma''-Decalactone is a lactone and aroma compound with the chemical formula C10H18O2. It has an intense-peach flavor. It is present naturally in many fruits and fermented products. It is particularly important in the formulation of peach, a ...
, γ-undecalactone can be prepared in good yield in a one-step process by radical addition
In organic chemistry, free-radical addition is an addition reaction which involves free radicals. The addition may occur between a radical and a non-radical, or between two radicals.
The basic steps with examples of the free-radical addition (al ...
of primary fatty alcohols
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies ...
to acrylic acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a ...
, using di-tert-butyl peroxide
Di-''tert''-butyl peroxide or DTBP is an organic compound consisting of a peroxide group bonded to two tert-butyl groups. It is one of the most stable organic peroxides, due to the ''tert''-butyl groups being bulky. It is a colorless liquid.
...
as a catalyst.
Reactions
The most stable structure for lactones are the 5-membered γ-lactones and 6-membered δ-lactones because, as in all organic cycles, 5 and 6 membered rings minimize the strain ofbond angle
Bond or bonds may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bond (finance), a type of debt security
* Bail bond, a commercial third-party guarantor of surety bonds in the United States
* Chemical bond, the attraction of atoms, ions or molecules to form chemical ...
s. γ-lactones are so stable that, in the presence of dilute acids at room temperature, 4-hydroxy acids (R-CH(OH)-(CH2)2-COOH) immediately undergo spontaneous esterification and cyclisation to the lactone. β-lactones do exist, but can only be made by special methods. α-lactones can be detected as transient species in mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is use ...
experiments.
The reactions of lactones are similar to those of esters, as exemplified by gamma-lactone in the following sections:
Hydrolysis
Heating a lactone with a base (sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
) will hydrolyse
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolys ...
the lactone to its parent compound, the straight chained bifunctional compound. Like straight-chained esters, the hydrolysis-condensation reaction of lactones is a reversible reaction
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously.
: \mathit aA + \mathit bB \mathit cC + \mathit dD
A and B can react to form C and D or, in the ...
, with an equilibrium. However, the equilibrium constant
The equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is the value of its reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium, a state approached by a dynamic chemical system after sufficient time has elapsed at which its composition has no measurable tendency ...
of the hydrolysis reaction of the lactone is lower than that of the straight-chained ester i.e. the products (hydroxyacids) are less favored in the case of the lactones. This is because although the enthalpies of the hydrolysis of esters and lactones are about the same, the entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
of the hydrolysis of lactones is less than the entropy of straight-chained esters. Straight-chained esters give two products upon hydrolysis, making the entropy change more favorable than in the case of lactones which gives only a single product.
Reduction
Lactones can be reduced to diols usinglithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li Al H4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic ...
in dry ether. The reduction reaction will first break the ester bond of the lactone, and then reduce the aldehyde group (-CHO) to the alcohol group (-OH). For instance, gamma-lactones will be reduced to butane-1,4-diol, (CH2(OH)-(CH2)2-CH2(OH).
Aminolysis
Lactones also react with ethanolic ammonia, which will first break the ester bond and then react with the acidic -COOH group, because of the basic properties of ammonia, to form a difunctional group, i.e. alcohol and amide. Gamma-lactones will react to yield CH2(OH)-(CH2)2-CO-NH2.Polymerization
Lactones readily form polyesters according to the formula, and have been shown to oligomerize without catalyst as well:
Michael reaction
Sesquiterpene lactone
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are a class of sesquiterpenoids that contain a lactone ring. They are most often found in plants of the family Asteraceae (daisies, asters). Other plant families with SLs are Umbelliferae (celery, parsley, carrots) an ...
s, found in many plants, can react with other molecules via a Michael reaction
In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael addition is a reaction between a Michael donor (an enolate or other nucleophile) and a Michael acceptor (usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl) to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon ...
.
Uses
Flavors and fragrances
Lactones contribute significantly to the flavor of fruit, and of unfermented and fermented dairy products, and are therefore used as flavors and fragrances. Some examples areγ-decalactone
''gamma''-Decalactone is a lactone and aroma compound with the chemical formula C10H18O2. It has an intense-peach flavor. It is present naturally in many fruits and fermented products. It is particularly important in the formulation of peach, a ...
(4-decanolide), which has a characteristic peach flavor; δ-decalactone
δ-Decalactone (DDL) is a chemical compound, classified as a lactone, that naturally occurs in fruit and milk products in traces. It can be obtained from both chemical and biological sources. Chemically, it is produced from Baeyer–Villiger oxid ...
(5-decanolide), which has a creamy coconut/peach flavour; γ-dodecalactone (4-dodecanolide), which also has a coconut/fruity flavor, a description which also fits γ-octalactone (4-octanolide), although it also has a herbaceous character; γ-nonalactone, which has an intense coconut flavor of this series, despite not occurring in coconut, and γ-undecalactone.
Macrocyclic lactones (cyclopentadecanolide
Cyclopentadecanolide is a natural macrolide lactone and a synthetic musk.
Natural occurrence
Cyclopentadecanolide occurs in small quantities in angelica root essential oil and is responsible for its musklike odor.
Production
Cyclopentadecanol ...
, 15-pentadec-11/12-enolide) have odors similar to macrocyclic ketones of animal origin (muscone
Muscone is an organic compound that is the primary contributor to the odor of musk.
The chemical structure of muscone was first elucidated by Leopold Ružička. It consists of a 15-membered ring ketone with one methyl substituent in the 3-position ...
, civetone
Civetone is a macrocyclic ketone and the main odorous constituent of civet oil. It is a pheromone sourced from the African civet. It has a strong musky odor that becomes pleasant at extreme dilutions. Civetone is closely related to muscone, the p ...
), but they can be prepared more easily, for example, by depolymerization Depolymerization (or depolymerisation) is the process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers. This process is driven by an increase in entropy.
Ceiling temperature
The tendency of polymers to depolymerize is indicated by ...
of the corresponding linear polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
s. Replacement of a methylene unit by oxygen barely affects the odor of these compounds, and oxalactones with 15 – 17-membered rings are produced in addition to cyclopentadecanolide (e. g., 12-oxa-16-hexadecanolide).
Prebiotic chemistry
Prebiotically plausible lactones, such as ε-caprolactone and δ-valerolactone, have been shown to oligomerize without the usage of catalysts forming oligomers that may have been relevant during theorigin of life
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothes ...
.
Plastics
Polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polyester with a low melting point of around 60 °C and a glass transition temperature of about −60 °C. The most common use of polycaprolactone is in the production of speciality polyure ...
is an important plastic.
Examples
Kavalactone
Kavalactones are a class of lactone compounds found in kava roots and Alpinia zerumbet (Shell ginger). Kavalactones are under research for potential to have various psychotropic effects, including anxiolytic and sedative/ hypnotic activities.
En ...
s
Dilactones
*Ellagic acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
Name
The name comes from the French term ''acide ellagique'', from the word ''galle'' spelled backwards because it can be ob ...
(Hexahydroxydiphenic acid dilactone)
*Flavogallonic acid dilactone
Flavogallonic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in '' Rhynchosia volubilis'' seeds, in '' Shorea laevifolia'', in ''Anogeissus leiocarpus'' and ''Terminalia avicennoides
''Terminalia avicennioides'' ( bm, Wolobugun) is a ...
can be found in ''Rhynchosia volubilis
''Rhynchosia volubilis'' is a plant species in the genus '' Rhynchosia''.
Tergallic acid dilactone can be found in ''R. volubilis'' seeds.
References
External links
volubilis
Volubilis (; ar, وليلي, walīlī; ber, ⵡⵍⵉ� ...
'' seeds and in ''Shorea laeviforia''
*Lactide
Lactide is the lactone cyclic ester derived by multiple esterification between two (usually) or more molecules from lactic acid (2-hydroxypropionic acid) or other hydroxy carboxylic acid. They are designated as dilactides, trilactides, etc., accor ...
* Tergallic acid dilactone can be found in ''Rhynchosia volubilis'' seeds
*Valoneic acid dilactone
Valoneic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be isolated from the heartwood of ''Shorea laevifolia''5A-Reductase inhibitory tannin-related compounds isolated from Shorea laevifolia. Yoshio Hirano, Ryuichiro Kondo and Kokki Sakai, Jour ...
can be isolated from the heartwood of ''Shorea laeviforia''
* Ethylene brassylate (Musk T), a widely used synthetic musk
See also
*Lactam
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''.
Nomenclature
Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size:
* α-Lactam (3-atom rings)
* β-Lacta ...
, a cyclic amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
* Lactim
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''.
Nomenclature
Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size:
* α-Lactam (3-atom rings)
* β-Lacta ...
, a cyclic imide
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, ...
* Lactide
Lactide is the lactone cyclic ester derived by multiple esterification between two (usually) or more molecules from lactic acid (2-hydroxypropionic acid) or other hydroxy carboxylic acid. They are designated as dilactides, trilactides, etc., accor ...
, a cyclic diester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
* Halolactonization
* Phthalein
References and notes
{{Authority control Functional groups