|
Imide
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called polyimides. Inorganic imides are also known as solid state or gaseous compounds, and the imido group (=NH) can also act as a ligand. Nomenclature Most imides are cyclic compounds derived from dicarboxylic acids, and their names reflect the parent acid. Examples are succinimide, derived from succinic acid, and phthalimide, derived from phthalic acid. For imides derived from amines (as opposed to ammonia), the ''N''-substituent is indicated by a prefix. For example, N-ethylsuccinimide is derived from succinic acid and ethylamine. Isoimides are isomeric with normal imides and have the formula RC(O)OC(NR′)R″. They are often intermediates that convert to the more symmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI) is a polymer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.Wright, Walter W. and Hallden-Abberton, Michael (2002) "Polyimides" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. History The first polyimide was discovered in 1908 by Bogart and Renshaw. They found that 4-amino phthalic anhydride does not melt when heated but does release water upon the formation of a high molecular weight polyimide. The first semialiphatic polyimide was prepared by Edward and Robinson by melt fusion of diamines and tetra acids or diamines and diacids / diester. However, the first polyimide of significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI) is a polymer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.Wright, Walter W. and Hallden-Abberton, Michael (2002) "Polyimides" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. History The first polyimide was discovered in 1908 by Bogart and Renshaw. They found that 4-amino phthalic anhydride does not melt when heated but does release water upon the formation of a high molecular weight polyimide. The first semialiphatic polyimide was prepared by Edward and Robinson by melt fusion of diamines and tetra acids or diamines and diacids / diester. However, the first polyimide of significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbodiimide
In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide (systematic IUPAC name: methanediimine) is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. They are exclusively synthetic. A well known carbodiimide is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, which is used in peptide synthesis. Dialkylcarbodiimides are stable. Some diaryl derivatives tend to convert to dimers and polymers upon standing at room temperature, though this mostly occurs with low melting point carbodiimides that are liquids at room temperature. Solid diaryl carbodiimides are more stable, but can slowly undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water over time. Structure and bonding From the perspective of bonding, carbodiimides are isoelectronic with carbon dioxide. Three principal resonance structures describe carbodiimides: :RN=C=NR ↔ RN+≡C-N−R ↔ RN−-C≡N+R The N=C=N core is relatively linear and the C-N=C angles approach 120°. In the case of C(NCHPh2)2, the central N=C=N angle is 170° and the C-N=C angles are within 1° of 126°. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imide Functional Group
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called polyimides. Inorganic imides are also known as solid state or gaseous compounds, and the imido group (=NH) can also act as a ligand. Nomenclature Most imides are cyclic compounds derived from dicarboxylic acids, and their names reflect the parent acid. Examples are succinimide, derived from succinic acid, and phthalimide, derived from phthalic acid. For imides derived from amines (as opposed to ammonia), the ''N''-substituent is indicated by a prefix. For example, N-ethylsuccinimide is derived from succinic acid and ethylamine. Isoimides are isomeric with normal imides and have the formula RC(O)OC(NR′)R″. They are often intermediates that convert to the more symmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Imide
The inorganic imides are compounds containing an ion composed of nitrogen bonded to hydrogen with formula HN2−. Organic imides have the NH group, and two single or one double covalent bond to other atoms. The imides are related to the inorganic amides (H2N−), the nitrides (N3−) and the nitridohydrides (N3−•H−). In addition to solid state imides, molecular imides are also known in dilute gases, where their spectrum can be studied. Imide can be a ligand, with a double bond to a metal such as molybdenum (e.g. Mo=NH). As a ligand it is called imido. The imido ligand is part of a nitrogen fixation cycle: Mo•N2 → Mo-N=N− → Mo-N=NH (diazenido) → Mo-N=NH2+ → Mo=N-NH2 (hydrazido) → Mo=N-NH3+ (hydrazidium) → Mo≡N (nitrido) + NH3 → Mo≡NH+ → Mo=NH (imido) → Mo=NH2+ → Mo-NH2 (amido) → Mo-NH3+ → Mo•NH3 (ammine); with the oxidation state of molybdenum varying to accommodate the number bonds from nitrogen. When the hydrogen of the imide group is sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
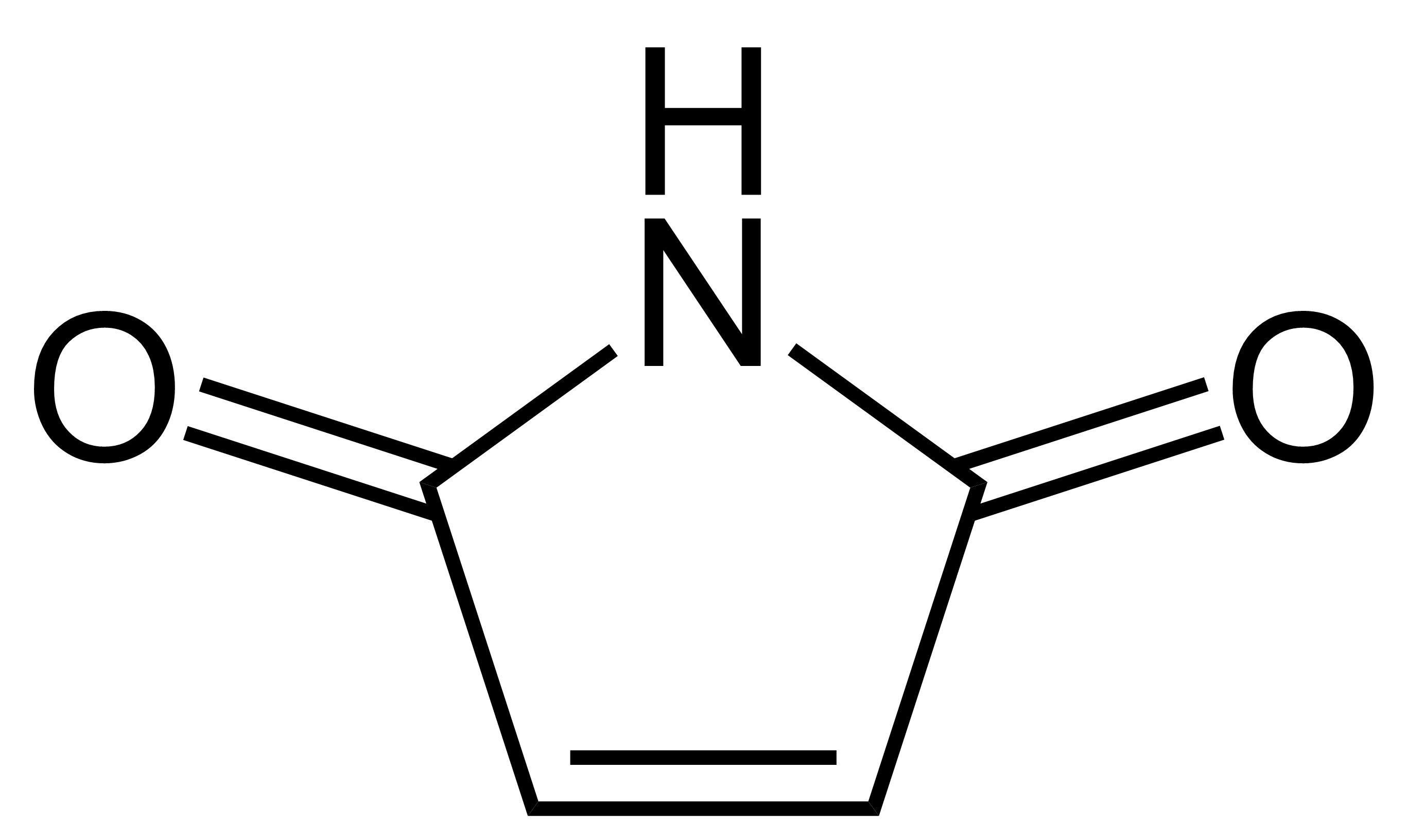
Maleimide
Maleimide is a chemical compound with the formula H2C2(CO)2NH (see diagram). This unsaturated imide is an important building block in organic synthesis. The name is a contraction of maleic acid and imide, the -C(O)NHC(O)- functional group. Maleimides also describes a ''class'' of derivatives of the parent maleimide where the N''H'' group is replaced with alkyl or aryl groups such as a methyl or phenyl, respectively. The substituent can also be a small molecule (such as biotin, a fluorescent dye, an oligosaccharide, or a nucleic acid), a reactive group, or a synthetic polymer such as polyethylene glycol. Human hemoglobin chemically modified with maleimide-polyethylene glycol is a blood substitute called MP4. Organic chemistry Maleimide and its derivatives are prepared from maleic anhydride by treatment with amines followed by dehydration. A special feature of the reactivity of maleimides is their susceptibility to additions across the double bond either by Michael additions or via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinimide
Succinimide is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)2(CO)2NH. This white solid is used in a variety of organic syntheses, as well as in some industrial silver plating processes. The compound is classified as a cyclic imide. It may be prepared by thermal decomposition of ammonium succinate. Succinimides Succinimides refers to compounds that contain the succinimide group. These compounds have some notable uses. Several succinimides are used as anticonvulsant drugs, including ethosuximide, phensuximide, and methsuximide. Succinimides are also used to form covalent bonds between proteins or peptides and plastics, which is useful in a variety of assay techniques. See also * Succinic anhydride Succinic anhydride, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2CO)2O. This colorless solid is the acid anhydride of succinic acid. Preparation In the laboratory, this material can be prepared by dehydration of succinic acid. Such dehy ... * ''N''-Hydroxysuccinimide * ''N''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthalimide
Phthalimide is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2NH. It is the imide derivative of phthalic anhydride. It is a Sublimation (phase transition), sublimable white solid that is slightly soluble in water but more so upon addition of base (chemistry), base. It is used as a precursor to other organic compounds as a masked source of ammonia. Preparation Phthalimide can be prepared by heating phthalic anhydride with alcoholic ammonia giving 95–97% yield. Alternatively, it may be prepared by treating the anhydride with ammonium carbonate or urea. It can also be produced by ammoxidation of O-Xylene, ''o''-xylene. Uses Phthalimide is used as a precursor to anthranilic acid, a precursor to azo dyes and saccharin. Alkyl phthalimides are useful precursors to amines in chemical synthesis, especially in peptide synthesis where they are used "to block both hydrogens and avoid racemization of the substrates". Alkyl halides can be converted to the N-alkylphthalimide: : C6H4( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheximide
Cycloheximide is a naturally occurring fungicide produced by the bacterium ''Streptomyces griseus''. Cycloheximide exerts its effects by interfering with the translocation step in protein synthesis (movement of two tRNA molecules and mRNA in relation to the ribosome), thus blocking eukaryotic translational elongation. Cycloheximide is widely used in biomedical research to inhibit protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells studied ''in vitro'' (''i.e.'' outside of organisms). It is inexpensive and works rapidly. Its effects are rapidly reversed by simply removing it from the culture medium. Due to significant toxic side effects, including DNA damage, teratogenesis, and other reproductive effects (including birth defects and toxicity to sperm), cycloheximide is generally used only in ''in vitro'' research applications, and is not suitable for human use as a therapeutic compound. Although it has been used as a fungicide in agricultural applications, this application is now decreasing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapton
Structure of poly-oxydiphenylene-pyromellitimide Kapton insulating pads for mounting electronic parts on a heat sink Kapton is a polyimide film used in flexible printed circuits (flexible electronics) and space blankets, which are used on spacecraft, satellites, and various space instruments. Invented by the DuPont Corporation in the 1960s, Kapton remains stable (in isolation) across a wide range of temperatures, from . History Kapton was invented by the DuPont Corporation in the 1960s. The name ''Kapton'' is a registered trademark of E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company. Chemistry and variants Kapton synthesis is an example of the use of a dianhydride in step polymerization. The intermediate polymer, known as a ''poly(amic acid)'', is soluble because of strong hydrogen bonds to the polar solvents usually employed in the reaction. The ring closure is carried out at high temperatures of . The chemical name for Kapton K and HN is ''poly (4,4'-oxydiphenylene-pyromellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutarimide
Glutarimide is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(CO)2NH. It is a white solid. The compound forms upon dehydration of the amide of glutaric acid. Glutarimide is sometimes called 2,6-piperidinedione. It is the core of a variety of medication, drugs, including thalidomide, a medication used to treat multiple myeloma and leprosy, and cycloheximide, a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. References Glutarimides, {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is a medication used to treat a number of cancers (including multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and a number of skin conditions including complications of leprosy. While it has been used in a number of HIV-associated conditions, such use is associated with increased levels of the virus. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include sleepiness, rash, and dizziness. Severe side effects include tumor lysis syndrome, blood clots, and peripheral neuropathy. Use in pregnancy may harm the fetus, including resulting in malformation of the limbs. In males who are taking the medication, contraception is essential if a partner could become pregnant. It is an immunomodulatory medication and works by a number of mechanisms, including stimulating T cells and decreasing TNF-α production. Thalidomide was first marketed in 1957 in West Germany, where it was available over the counter. When first r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_V1.png)