L83 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Chevrolet small-block engine is a series of
 The "Turbo-Fire" V8 was the second Chevrolet small-block; the first Chevrolet V8 was produced in 1917. The 265 cu in Turbo Fire engine was designed by Ed Cole's group at Chevrolet to provide a more powerful engine for the 1955 Corvette than the model's original " Blue Flame" in-line six, the 2-barrel debut version went from drawings to production in just 15 weeks.
Cole's design borrowed the valve train design scheduled to be used at the time in the Pontiac V8. Internal GM rules at the time stated that once an automotive division had introduced a technological innovation, no other GM division could use it for a period of two years. The stud-mounted independent ball rocker arm design patented by
The "Turbo-Fire" V8 was the second Chevrolet small-block; the first Chevrolet V8 was produced in 1917. The 265 cu in Turbo Fire engine was designed by Ed Cole's group at Chevrolet to provide a more powerful engine for the 1955 Corvette than the model's original " Blue Flame" in-line six, the 2-barrel debut version went from drawings to production in just 15 weeks.
Cole's design borrowed the valve train design scheduled to be used at the time in the Pontiac V8. Internal GM rules at the time stated that once an automotive division had introduced a technological innovation, no other GM division could use it for a period of two years. The stud-mounted independent ball rocker arm design patented by
 The
The
 The V8, introduced in 1962, had a bore of 4.00in and 3.25in stroke. The exact displacement is . Power ranged from depending on the choice of carburetor or fuel injection, camshaft,
The V8, introduced in 1962, had a bore of 4.00in and 3.25in stroke. The exact displacement is . Power ranged from depending on the choice of carburetor or fuel injection, camshaft,
 The , with a stroke, first appeared as a high-performance ''L-48'' option for the 1967 Camaro. The exact displacement is . One year later it was made available in the Chevrolet Nova, and finally in 1969 the rest of the Chevrolet line could be ordered with a 350. As had been the case with earlier versions of the small-block, the 350 was available in the Beaumont sold by Pontiac Canada, which unlike its US counterparts, used Chevrolet chassis and drivelines.
Many variants followed.
The , with a stroke, first appeared as a high-performance ''L-48'' option for the 1967 Camaro. The exact displacement is . One year later it was made available in the Chevrolet Nova, and finally in 1969 the rest of the Chevrolet line could be ordered with a 350. As had been the case with earlier versions of the small-block, the 350 was available in the Beaumont sold by Pontiac Canada, which unlike its US counterparts, used Chevrolet chassis and drivelines.
Many variants followed.
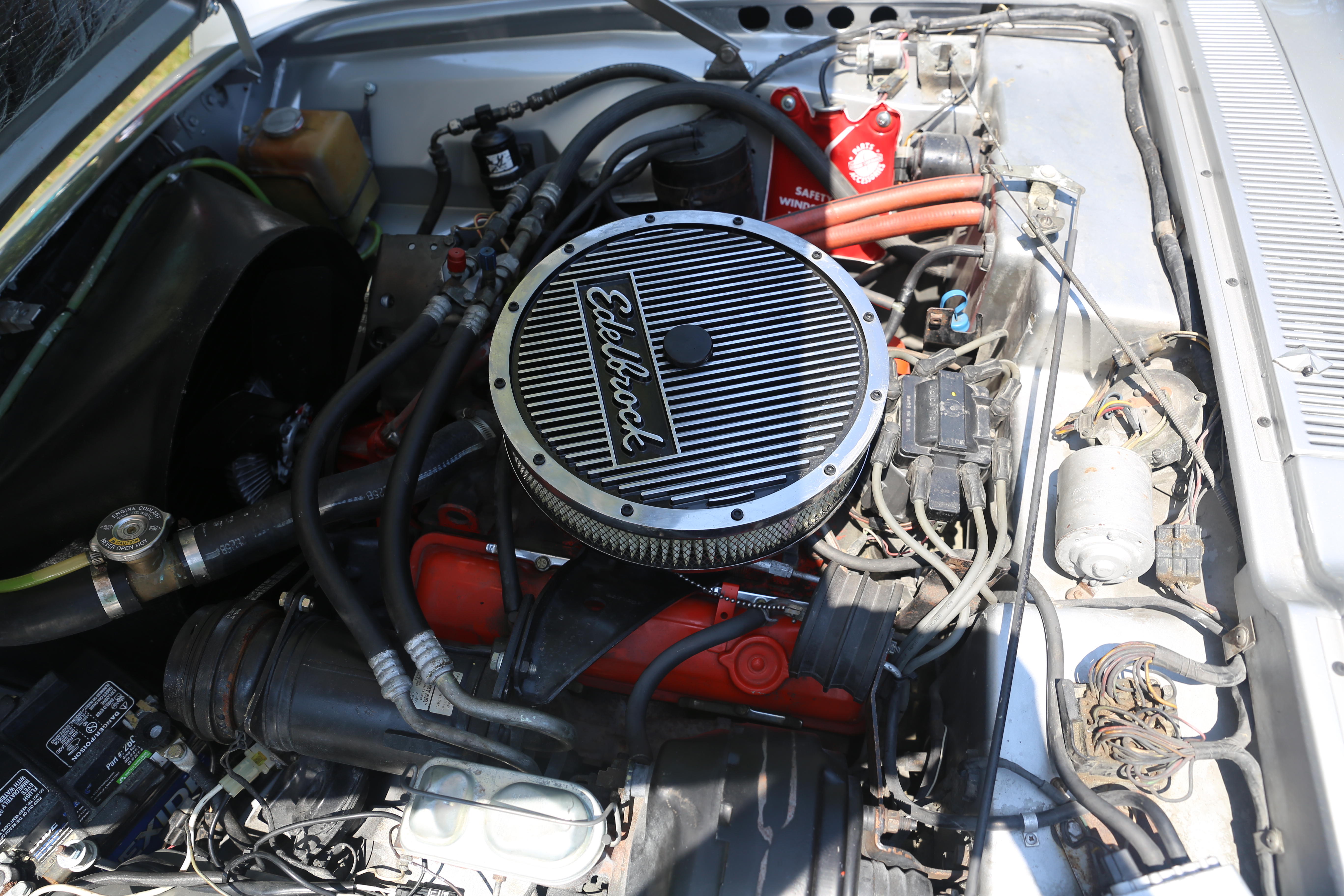 The is the only engine in this family and was introduced in 1970 and produced for 10 years. It has a bore and a stroke. The 400 differed from other small blocks in that the cylinders were siamesed and therefore required 'steam' holes in the block, head
The is the only engine in this family and was introduced in 1970 and produced for 10 years. It has a bore and a stroke. The 400 differed from other small blocks in that the cylinders were siamesed and therefore required 'steam' holes in the block, head
Mortec: Small-Block Engine Enthusiasts
Video : First start up SBC engine (& zoomies flames)
Video : Let's see Chevy first start up, and what NOT to do ! ("Dark" humor)
:
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
-powered, V-8 automobile engines, produced by the Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ), colloquially referred to as Chevy and formally the Chevrolet Motor Division of General Motors Company, is an American automobile division of the American manufacturer General Motors (GM). Louis Chevrolet (1878–1941) and ous ...
division of General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
between 1954 and 2003, using the same basic engine block. Referred to as a "small-block" for its size relative to the physically much larger Chevrolet big-block engines, the small block family spanned from to in displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
*Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
. Engineer Ed Cole
Edward Nicholas Cole (September 17, 1909 – May 2, 1977) was an American automotive executive for General Motors.
Career
Cole was the son of a dairy farmer. In his youth, he designed, built, and sold homemade radio sets, and as a teenage ...
is credited with leading the design for this engine. The engine block and cylinder heads were cast at Saginaw Metal Casting Operations
Saginaw Metal Casting Operations is an automobile engine foundry plant in Saginaw, Michigan. Opened under GM management in 1919, the factory produces engine blocks and cylinder heads for General Motors vehicles. The factory currently occupies 1.9 ...
in Saginaw, Michigan
Saginaw () is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the seat of Saginaw County. The city of Saginaw and Saginaw County are both in the area known as Mid-Michigan. Saginaw is adjacent to Saginaw Charter Township and considered part of Greater ...
.
Generation I and Generation II LT engines are distinct from subsequent LS-based small-block engines. The Generation II engine is largely an improved version of the Generation I, having many interchangeable parts and dimensions. Later generation engines have only the rod bearings, transmission-to-block bolt pattern and bore spacing in common with the Generation I and II engines.
Production of the original small-block began in late 1954 for the 1955 model year, with a displacement of , growing over time to by 1970. Among the intermediate displacements were the , , and numerous versions. Introduced as a performance engine in 1967, the 350 went on to be employed in both high- and low-output variants across the entire Chevrolet product line.
Although all of Chevrolet's siblings of the period (Buick
Buick () is a division of the American automobile manufacturer General Motors (GM). Started by automotive pioneer David Dunbar Buick in 1899, it was among the first American marques of automobiles, and was the company that established General ...
, Cadillac
The Cadillac Motor Car Division () is a division of the American automobile manufacturer General Motors (GM) that designs and builds luxury vehicles. Its major markets are the United States, Canada, and China. Cadillac models are distributed i ...
, Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile or formally the Oldsmobile Division of General Motors was a brand of American automobiles, produced for most of its existence by General Motors. Originally established as "Olds Motor Vehicle Company" by Ransom E. Olds in 1897, it produ ...
, Pontiac Pontiac may refer to:
*Pontiac (automobile), a car brand
*Pontiac (Ottawa leader) ( – 1769), a Native American war chief
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Pontiac, Quebec, a municipality
**Apostolic Vicariate of Pontiac, now the Roman Catholic D ...
, and Holden
Holden, formerly known as General Motors-Holden, was an Australian subsidiary company of General Motors. It was an Australian automobile manufacturer, importer, and exporter which sold cars under its own marque in Australia. In its last thre ...
) designed their own V8s, it was the Chevrolet small-block that became the GM corporate standard. Over the years, every GM division in America, except Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
and Geo
Geo- is a prefix derived from the Greek word ''γη'' or ''γαια'', meaning "earth", usually in the sense of "ground or land”.
GEO or Geo may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''GEO'' (magazine), a popular scientific magazine ...
, used it and its descendants in their vehicles.
Finally superseded by the Generation III LS in 1997 and discontinued in 2003, the engine is still made by a GM subsidiary in Springfield, MO as a crate engine
A crate is a large shipping container, often made of wood, typically used to transport or store large, heavy items. Steel and aluminium crates are also used. Specialized crates were designed for specific products, and were often made to be reusa ...
for replacement and hot rod
Hot rods are typically American cars that might be old, classic, or modern and that have been rebuilt or modified with large engines optimised for speed and acceleration. One definition is: "a car that's been stripped down, souped up and made ...
ding purposes. In all, over 100,000,000 small-blocks have been built in carbureted
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meterin ...
and fuel injected forms since 1955 as of November 29, 2011. The small-block family line was honored as one of the 10 Best Engines of the 20th Century by automotive magazine Ward's AutoWorld.
In February 2008 a Wisconsin businessman reported that his 1991 Chevrolet C1500 pickup had logged over 1 million miles without any major repairs to its small block V8 engine. (Source: ''The Flint Journal
''The Flint Journal'' is a quad-weekly newspaper based in Flint, Michigan, owned by Booth Newspapers, a subsidiary of Advance Publications. Published Tuesdays, Thursdays, Fridays and Sundays, it serves Genesee, Lapeer and Shiawassee Counties. ...
'', February 17, 2008).
All Chevrolet small-block engines share the same firing order that is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2.
Overview
The first generation of Chevrolet small-blocks began with the 1955 Chevrolet 265 cu in (4.3L) V8 offered in theCorvette
A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the slo ...
and Bel Air. It quickly gained popularity among stock car racers, nicknamed the " Mighty Mouse", for the then-popular cartoon character, later abbreviated to "Mouse". By 1957 it had grown to . Fitted with the optional Rochester mechanical fuel injection (FI), it was one of the first production engines to make per . The 283 was adopted by other Chevrolets, replacing the 265 V8s. A high-performance variant followed, turning out as much as (SAE gross power, not SAE net power or the current SAE certified power values) and raising horsepower per cubic inch to . From 1954 to 1974, the small-block engine was known as the "Turbo-Fire" or "High Torque" V8. But it was the series that became the best known Chevrolet small-block. Installed in everything from station wagons to sports cars, in commercial vehicles, and even in boats and (in highly modified form) airplanes, it is the most widely used small-block of all time. Though not offered in GM vehicles since 2003, the 350 series is still in production at a GM subsidiary in Springfield, MO under the company's "GM Genuine Parts" brand, and is also manufactured as an industrial and marine engine by GM Powertrain under the "Vortec
Vortec is a trademarked name for a line of gasoline engines for General Motors trucks. The name first appeared in an advertisement for the 1985 model year 4.3 L V6 that used "vortex technology" to create a vortex inside the combustion chamber ...
" name.
3.750 in. bore family (1955–1957)
All Chevrolet V8s, from the big-blocks to today's LS7 and LS9, evolved from the small-block family. Of the three engines in this family, two of them, the 265 and the 283, made automotive history. The first of this family was the 265, introduced in 1954. The 265 had abore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
. The stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
of the 265 was , like the 283.
265
 The "Turbo-Fire" V8 was the second Chevrolet small-block; the first Chevrolet V8 was produced in 1917. The 265 cu in Turbo Fire engine was designed by Ed Cole's group at Chevrolet to provide a more powerful engine for the 1955 Corvette than the model's original " Blue Flame" in-line six, the 2-barrel debut version went from drawings to production in just 15 weeks.
Cole's design borrowed the valve train design scheduled to be used at the time in the Pontiac V8. Internal GM rules at the time stated that once an automotive division had introduced a technological innovation, no other GM division could use it for a period of two years. The stud-mounted independent ball rocker arm design patented by
The "Turbo-Fire" V8 was the second Chevrolet small-block; the first Chevrolet V8 was produced in 1917. The 265 cu in Turbo Fire engine was designed by Ed Cole's group at Chevrolet to provide a more powerful engine for the 1955 Corvette than the model's original " Blue Flame" in-line six, the 2-barrel debut version went from drawings to production in just 15 weeks.
Cole's design borrowed the valve train design scheduled to be used at the time in the Pontiac V8. Internal GM rules at the time stated that once an automotive division had introduced a technological innovation, no other GM division could use it for a period of two years. The stud-mounted independent ball rocker arm design patented by Pontiac Pontiac may refer to:
*Pontiac (automobile), a car brand
*Pontiac (Ottawa leader) ( – 1769), a Native American war chief
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Pontiac, Quebec, a municipality
**Apostolic Vicariate of Pontiac, now the Roman Catholic D ...
engineer Clayton Leach, was scheduled for introduction in the Pontiac 1955 V8. GM forced the Pontiac division to share its valvetrain
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
design in Chevrolet's new 265 V8 in 1955, so that both engines were introduced the same year with the same valve train design. A side note to Pontiac's V-8 was the engine was supposed to be introduced on 1953 cars, and all 53 & 54 Pontiac's chassis and suspension were designed for the engine that didn't make it into a Pontiac until late 1954. The reason this happened is that Buick division lobbied the corporation to hold back Pontiac's release because it affected Buick's release of the new OHV Buick V8 engine.
A pushrod
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
engine with hydraulic lifters
A hydraulic tappet, also known as a hydraulic valve lifter or hydraulic lash adjuster, is a device for maintaining zero valve clearance in an internal combustion engine. Conventional solid valve lifters require regular adjusting to maintain a sma ...
, the small-block was available with an optional four-barrel Rochester carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meteri ...
, increasing engine output to , or in the Corvette. The short-stroke bore x stroke engine's bore spacing would continue in use for decades.
Also available in the Bel Air sedan, the basic passenger car version produced with a two-barrel carburetor. Upgraded to a four-barrel Rochester, dual exhaust "Power Pack" version, the engine was conservatively rated at , and with the "Super Power Pack" it was boosted up to the power level of the Corvette.
A shortcoming of the 1955 265 was its lack of any provision for oil filtration built into the block, instead relying on an add-on filter mounted on the thermostat housing, and that was an "option only". In spite of its novel green sand foundry construction, the '55 block's lack of adequate oil filtration leaves it typically only desirable to period collectors.
The 1956 Corvette introduced three versions of this engine – with a single 4-barrel carburetor, with twin 4-barrels, and with two four-barrel carburetors and a high-lift camshaft.
3.875 in. bore family (1957–1973)
The 283 had abore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
. The stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
of the 283 was , like the 265. The 283, famous for being one of the first engines to make one hp per cubic inch, is also famous for being the evolutionary stepping stone that would later give rise to small blocks and to the "W" blocks, ultimately culminating in the Chevrolet big-blocks. The last of this family was the , which was a stroked 283 with a medium journal.
283
 The
The V8 engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V8 engine was produced by the French Antoinette company in 1904, developed and us ...
was bored out to in 1957, giving it a displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
*Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
. The first 283 motors used the stock 265 blocks. However, the overbore to these blocks resulted in thin cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
walls. Future 283 blocks were cast to accept the 3.875 bore. Five different versions between and were available, depending on whether a single carb, twin carbs, or fuel injection was used.
Horsepower was up a bit each year for 1958, 1959, and 1960. The 1957 Rochester Ramjet
The Rochester Ramjet is an automotive fuel injection system developed by the Rochester Products Division of General Motors and first offered as a high-performance option on the Corvette and GM passenger cars in 1957. It was discontinued partway th ...
mechanical fuel injection version produced an even one hp per one cu in (, an impressive feat at the time. This was the second U.S.-built production V8 to produce one horsepower per cubic inch, after the 1956 Chrysler 300B.
Besides being available in the Chevrolet line, it was optional in Checker Taxis beginning in 1965.
A version of it that was built by GM Canada was also available in Studebaker
Studebaker was an American wagon and automobile manufacturer based in South Bend, Indiana, with a building at 1600 Broadway, Times Square, Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1852 and incorporated in 1868 as the Studebaker Brothers M ...
vehicles produced in Canada for 1965 and 1966.
307
A version was produced from 1968 through 1973. Engine bore and stroke was . All 307s had large journals to accept the 327'scrankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
. Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
s used with the 307 share the same pin height as the 327 but retaining the 283s bore size (prior to 1968 it was possible to stroke a 283 into a 307 where aftermarket pistons had to be used).
*1968-1971 Chevrolet Camaro
*1968-1973 Chevrolet Chevelle
The Chevrolet Chevelle is a mid-sized automobile that was produced by Chevrolet in three generations for the 1964 through 1978 model years. Part of the General Motors (GM) A-body platform, the Chevelle was one of Chevrolet's most successful ...
*1968-1969 Chevrolet Impala
The Chevrolet Impala () is a full-size car built by Chevrolet for model years 1958 to 1985, 1994 to 1996, and 2000 to 2020. The Impala was Chevrolet's popular flagship passenger car and was among the better-selling American-made automobiles in ...
*1968-1973 Chevrolet Nova
*1971-1972 Pontiac Ventura
The Pontiac Ventura was an automobile model that was produced by Pontiac. As was common practice at the time, its name was derived from Ventura, California, joining other similarly derived models such as the fellow Pontiac Catalina, the Chevrolet M ...
*1972 Chevrolet C10
C/K is a series of trucks that was manufactured by General Motors from the 1960 to 2002 model years. Marketed by both the Chevrolet and GMC (automobile), GMC divisions, the C/K series encompassed a wide range of vehicles. While most commonly assoc ...
4.000 in bore family (1962–2002)
Originally intended as the performance block, this engine family through the became an all purpose engine that saw use in many applications from Corvettes to vans. All engines in this family share the same block dimensions and sometimes even the same casting number; the latter meaning engines were of the same block, but with different strokes (e.g. the casting number 3970010 was used by all three engines: 302, 327, and 350). This engine family was updated in 1968 for the use of medium-sized journals. The first engine in this family was the small journal 327 in 1962 and the last being 2000s medium journal 350 in pickup trucks and commercial vehicles. The medium journal 350 was further developed into the Generation II LT1/4 350 in the early 1990s.302
In 1966, General Motors designed a special engine for the production Z/28 Camaro in order for it to meet the Sports Car Club of America (SCCA
The Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) is a non-profit American automobile club and sanctioning body supporting road racing, rallying, and autocross in the United States. Formed in 1944, it runs many programs for both amateur and professional r ...
) Trans-Am Series
The Trans-Am Series is a sports car racing series held in North America. Founded in 1966, it is sanctioned by the Sports Car Club of America (SCCA).
Primarily based in the United States, the series competes on a variety of track types includ ...
road racing rules limiting engine displacement to from 1967 to 1969. It was the product of placing the stroke crankshaft into a bore cylinder-block. The 1967 302 used the same crankshaft stroke as the 283, with a forged steel crank
Crank may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Crank (mechanism), in mechanical engineering, a bent portion of an axle or shaft, or an arm keyed at right angles to the end of a shaft, by which motion is imparted to or received from it
* Crankset, the compone ...
that was also produced. This block is one of three displacements, 302/327/350, that underwent a crankshaft bearing diameter transformation for 1968 when the rod-journal size was increased from the diameter small-journal to a large-journal and a main-journal size that was increased from to . DZ 302.
The large-journal connecting rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the cranksh ...
s were thicker (heavier) and used diameter cap-bolts to replace the small-journal's 11/32. 1968 blocks were made in 2-bolt and 4-bolt versions with the 4-bolt center-three main caps each fastened by two additional bolts which were supported by the addition of thicker crankcase main-web bulkheads. When the journal size increased to the standard large-journal size, the crankshaft for the 302 was specially built of tufftride
Ferritic nitrocarburizing or FNC, also known by the proprietary names Tenifer, Tufftride and Melonite as well as ARCOR,Other trade names include Tuffride/ Tuffrider, QPQ, Sulfinuz, Sursulf, Meli 1, and Nitride, among others is a range of proprie ...
-hardened forged 1053-steel and fitted with a high-rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
diameter harmonic balancer. It had a 3/4-length semi-circular windage tray, heat-treated, magnafluxed, shot-peened forged 1038-steel 'pink' connecting rods, floating-pin in '69, forged-aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
pistons with higher scuff-resistance and better sealing single-moly rings.
Its solid-lifter cam, known as the "30-30 Duntov" cam named after its /0.030 in hot intake/exhaust valve-lash and Zora Arkus-Duntov (the first Duntov cam was the / 1957 grind known as the '097, which referred to the last three digits of the casting number) the "Father of the Corvette", was also used in the 1964-1965 carbureted 327/365 and fuel injected 327/375 engines. It used the '202' / valve diameter high-performance 327 double-hump '186 and 461 heads, pushrod guide plates, hardened 'blue-stripe' pushrods, edge-orifice lifters to keep more valvetrain oil in the crankcase for high-rpm lubrication, and stiffer valvesprings. In 1967, a new design high-rise cast-aluminum dual-plane intake manifold with larger smoother turn runners was introduced for the Z/28 that the /370 hp 1970 LT-1 also used.
1969 Corvette and 1970 Z/28 engines were equipped with a Holley carburetor until the Q-jet carburetor returned in 1973. Unlike the Corvette, the exhaust manifold
In automotive engineering, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into one pipe. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' old and refe ...
s were the more restrictive rear outlet 'log' design to clear the Camaro chassis's front cross-member. It had a chrome oil filler tube in the front of the intake manifold next to the thermostat housing from 1967 to 1968. The first year had unique chrome valve covers with Chevrolet stamped into them without an engine displacement decal pad. In 1968, the engine had the chrome covers, but without the Chevrolet name, connected to a PCV valve and a chrome drop-base open-element air cleaner assembly fitted with a crankcase breather on a vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
secondary Holley 4-Bbl carburetor. A 'divorced' exhaust crossover port heated well-choke thermostat coil was used to provide cleaner and faster engine warm-up. Its distributor came in two styles, dual-point (Camaro) and transistorized (Corvette). The dual point had an ignition point cam designed to reduce point bounce at high rpm. Both distributors had a vacuum diaphragm to advance ignition timing at part-throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
for economy and emissions.
Pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that ...
s for the balancer, alternator, water-pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
, as well as optional power steering
A power steering is a mechanical device equipped on a motor vehicle that helps drivers steer the vehicle by reducing steering effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making it easier for the vehicle to turn or maneuver at lower speeds.
Hydraul ...
, were deep- groove to retain the drive belt(s) at high rpm. In 1969, the 302 shared the finned cast aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ...
valve cover
Rocker covers are covers that are bolted on over rocker arms in an internal combustion engine. They are called valve covers in the United States, Canada, and in situations where Rocker Arms are not present, such as some Overhead Cam, and most Du ...
s with the LT-1 350 Corvette engine. Conservatively rated at ( SAE gross) at 5800 rpm and at 4800, actual output with its production 11.0:1 compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
was around with primary x collector Sanderson tubular headers that came in the trunk when ordered with a 1967 Z/28, and associated carburetor main jet and ignition timing tuning. In 1968, the last year for factory headers, they had primaries x collectors. A stock 1968 Z/28 with the close-ratio transmission, optional transistorized-ignition and 4.88 gear, fitted with little more than the factory cowl plenum cold-air hood induction and headers, was capable of running 12.9 second/ times on street tires.
After the 1967 Trans-Am campaign with the 4-Bbl induction system producing more horsepower than the competing auto makers' 8-Bbl systems, for 1968 Chevrolet developed a factory 'cross-ram' aluminum intake-manifold package using two Holley mechanical secondary carburetors for Trans-Am racing. It was available only as off-road service parts purchased over the Chevrolet dealership parts counter. With the Chevrolet '140 1st-design off-road cam, the package increased a stock 302's horsepower from to approximately . Chevrolet went so far as to carry the positive crankcase ventilation system (PCV) over to the cross-ram induction system to retain emissions compliance mandated for US-produced cars beginning in 1967, that also provided full-throttle crankcase pressure venting to the intake air to burn its vapors.
Engines prepared for competition use were capable of producing with little more than the 8-Bbl induction, ported heads with higher pressure valvesprings, roller rocker arms, and the '754 2nd-design road-race cam. 1967/1968 models' cowl-induction system had an enclosed air-cleaner assembly ducted from its passenger side into the firewall cowl above the heater core.
In 1969, factory Z/28's could be ordered with the ZL-1 aluminum-block 427 adaption of the 1967 L-88 427 Corvette cowl-induction 'ZL-2' hood available for both single and dual four-barrel induction systems that were sealed to the air cleaner base ensuring dense cooler, high-pressure, oxygen-laiden air from the center of the base of the windshield was supplied to the engine for combustion smoothness and maximum power production.
Another popular service-parts-only component used on the 302 was the magnetic-pulse Delco transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
-ignition
Ignition may refer to:
Science and technology
* Firelighting, the human act of creating a fire for warmth, cooking and other uses
* Combustion, an exothermic chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant
* Fusion ignition, the point at which a ...
ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
distributor. Introduced in 1963 on Pontiac's drag racing
Drag racing is a type of motor racing in which automobiles or motorcycles compete, usually two at a time, to be first to cross a set finish line. The race follows a short, straight course from a standing start over a measured distance, most c ...
engines, General Motors fitted it to the 1967 Z/28 before they used it on the L88 Corvette. It eliminated the production breaker-point ignition allowing greater spark energy and more stable ignition timing at all engine speeds including idle. This was one of the least talked about yet most transformative and comprehensive performance and durability upgrades of its time. Many of the 302s off-road service parts were the development work of racers like Roger Penske
Roger Searle Penske (born February 20, 1937) is an American businessman and entrepreneur involved in professional auto racing and a retired professional auto racing driver. He is most famous for his ownership of Team Penske, DJR Team Penske, t ...
. Every part in a SCCA Trans-Am engine had to be available through local Chevrolet parts departments to encourage their use by anyone who wanted them.
While the 302 became a strong Limited Sportsman oval track racing engine in the hands of racers like Bud Lunsford in his 1966 Chevy II, its bore/stroke and rod/stroke geometries made it a natural high-rpm road-racing engine and were responsible for its being among the more reliable production street engines homologated for full competition across all the American makes, winning back-to-back Trans-Am Championships at the hands of Mark Donohue
Mark Neary Donohue Jr. (March 18, 1937 – August 19, 1975), nicknamed "Captain Nice," and later "Dark Monohue," was an American race car driver and engineer known for his ability to set up his own race car as well as driving it to victories.
D ...
in 1968 and 1969. However, with engines built by Al Bartz, Falconer & Dunn and Traco Engineering, the pinnacle of the 302's use in professional racing was its being the primary engine that powered the outstanding but overshadowed 1968-1976 Formula 5000 Championship Series, a SCCA Formula A
Formula 5000 (or F5000) was an open wheel, single seater auto-racing formula that ran in different series in various regions around the world from 1968 to 1982. It was originally intended as a low-cost series aimed at open-wheel racing cars tha ...
open-wheel class designed for lower cost.
The engine was also popular in Formula 5000 racing around the world, especially in Australia and New Zealand where it proved more powerful than the Repco-Holden V8. Weighing , with a iron block and head engine positioned near the car's polar moment of inertia for responsive turn pivoting, a Hewland 5-spd. magnesium transaxle, and wide front/ wide rear magnesium wheels, it produced incredibly exciting racing. They ran in 2.8 seconds and over .
Reminiscing about the series, mid-70s Australian F5000 driver Bruce Allison said, "We never used first gear at the start. We started in second, and even then there was so much torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
, you'd get wheelspin
A wheelspin occurs when the force delivered to the tire tread exceeds that of available tread-to-surface friction and one or more tires lose traction.This leads the wheels to "spin" and causes the driver to lose control over the tires that no lo ...
through third and fourth gears." Prepared with a Lucas-McKay mechanically timed individual-stack magnesium fuel-injection induction system that was paired with ported production car double-hump iron heads, a rev-kit fitted roller lifter camshaft, roller bearing rocker arm
In the context of an internal combustion engine, a rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod to the corresponding intake/exhaust valve.
Rocker arms in automobiles are typically made from stamped steel ...
s, and a virtually stock production crankshaft, it had a lasting impact on the series' ability to conduct high car-count finishes and close competition events by the degree of mechanical success it provided to a series filled with star international Grand Prix drivers like David Hobbs, Brian Redman, Jody Scheckter and Mario Andretti.
327
 The V8, introduced in 1962, had a bore of 4.00in and 3.25in stroke. The exact displacement is . Power ranged from depending on the choice of carburetor or fuel injection, camshaft,
The V8, introduced in 1962, had a bore of 4.00in and 3.25in stroke. The exact displacement is . Power ranged from depending on the choice of carburetor or fuel injection, camshaft, cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern ov ...
s, pistons and intake manifold. In 1962, the Duntov solid lifter cam versions produced , with single Carter
Carter(s), or Carter's, Tha Carter, or The Carter(s), may refer to:
Geography United States
* Carter, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Carter, Mississippi, an unincorporated community
* Carter, Montana, a census-designated place
* Carter, ...
4-barrel, and , with Rochester fuel-injection. In 1964, horsepower increased to for the newly named ''L-76'' version, and for the fuel injected ''L-84'', making the L-84 the most powerful naturally aspirated
Naturally may refer to:
;Albums
* ''Naturally!'', an album by Nat Adderley
* ''Naturally'' (Houston Person album)
* ''Naturally'' (J. J. Cale album)
* ''Naturally'' (John Pizzarelli album)
* ''Naturally'' (Sharon Jones album)
* ''Naturally'' ...
, single-cam, production small block V8 until the appearance of the , Generation III LS6 in 2001. This block is one of three displacements that underwent a major change in 1968 when the main journal size was increased from . In 1965 Chevrolet released the now-legendary ''L-79'', which was nothing more than an L-76 (11.0:1 forged pop-up pistons, forged steel rods and crank, 2.02 Corvette heads), but with the 30-30 Duntov cam replaced by the No. 151 hydraulic cam.
In 1966, Checker began offering the 327 as an option. The Avanti II
The Studebaker Avanti is a personal luxury coupe manufactured and marketed by Studebaker Corporation between June 1962 and December 1963. A halo car for the maker, it was marketed as "America's only four-passenger high-performance personal car ...
and its successors were powered by the 327 and later versions of the small-block V8.
The 327 was fitted in the English Gordon-Keeble
Gordon-Keeble was a British car marque, made first in Slough, then Eastleigh, and finally in Southampton (all in England), between 1964 and 1967. The marque's badge was unusual in featuring a tortoise — a pet tortoise walked into the fram ...
. 99 cars were made between 1964 and 1967. It was also installed in many Iso
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
s, until 1972 when General Motors started demanding cash in advance and the Italian manufacturer switched to the Ford Cleveland V8.
In 1968, the 327 L73 developing was part of the CKD packages exported to Australia from Canada for use in the locally assembled (by General Motors Holdens) Chevrolet Impala and Pontiac Parisienne. GMH used the same specification engine in the Holden HK Monaro GTS327. The engine was used in the Monaro GTS327 to make it the new Holden Muscle Car, and so it could compete in the local improved production (Australian Group C). The car had modified suspension just before release to also be used in local Series Production racing (Australian Group E). A special build 327 was built for GMH for the final run of the HK GTS327 by the Canadian McKinnon Industries. It was a lower compression version of the 1968 engine first used on the HK GTS327, and was dressed as a 1969 engine sporting all 1969 parts. The 327 was replaced in the mid 1969 HT Monaro by the 350 L48 developing .
350
 The , with a stroke, first appeared as a high-performance ''L-48'' option for the 1967 Camaro. The exact displacement is . One year later it was made available in the Chevrolet Nova, and finally in 1969 the rest of the Chevrolet line could be ordered with a 350. As had been the case with earlier versions of the small-block, the 350 was available in the Beaumont sold by Pontiac Canada, which unlike its US counterparts, used Chevrolet chassis and drivelines.
Many variants followed.
The , with a stroke, first appeared as a high-performance ''L-48'' option for the 1967 Camaro. The exact displacement is . One year later it was made available in the Chevrolet Nova, and finally in 1969 the rest of the Chevrolet line could be ordered with a 350. As had been the case with earlier versions of the small-block, the 350 was available in the Beaumont sold by Pontiac Canada, which unlike its US counterparts, used Chevrolet chassis and drivelines.
Many variants followed.
L46
Years: 1969-1970 The ''L46'' became an optional engine for the 1969 Chevrolet Corvette. It was a higher performance version of the base V8 with casting number 186 valve heads and had an 11.0:1 compression ratio requiring highoctane
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula , and the condensed structural formula . Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-Tri ...
gas and produced (SAE gross power). It was also available in 1970 with 4bbl Quadrajet
The Quadrajet is a four barrel carburetor, made by the Rochester Products Division of General Motors. Its first application was the new-for-1965 Chevy 396ci engine. Its last application was on the 1990 Oldsmobile 307
V8 engine, which was last us ...
carburetor and L46 hydraulic cam, dome piston (+), 186 heads, and a four-bolt block.
L48
Years: 1967–1980 The ''L48'' is the original , solely available for 1967 in the Super Sport (SS) version of Camaro (1967-up) or Chevy II/Nova in 1968–1979. In 1969 it was used in almost all car lines; Camaros, Caprices, Impalas, El Caminos, Chevelles & Novas. The 1969 L48s use a hydraulic cam, 4bbl Quadrajet carburetor, cast pistons, 4-bolt maincasting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected ...
number 010 Blocks & casting number 041 or 186 heads. Power output was SAE and torque. Compression ratio was 10.25:1. The compression ratio of the L48 was lowered to 8.5:1 in 1971.
In 1972 the L48 (4bbl V8) option for the Nova was part of the SS package. This is indicated by the fifth digit in the VIN
Vin or VIN may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Vîn TV, a Kurdish language satellite television channel founded in 2007
* ''Vos Iz Neias?'', an American Jewish online news site
* Coastal radio station VIN Geraldton (callsign), a statio ...
being a ''K''. Nineteen seventy-two was the only year the SS package could be verified by the VIN.
The L48 engine was exported to Australia, where it appeared in the Holden Monaro from 1969 through 1974, and in the Statesman
A statesman or stateswoman typically is a politician who has had a long and respected political career at the national or international level.
Statesman or Statesmen may also refer to:
Newspapers United States
* ''The Statesman'' (Oregon), a n ...
from 1971 through 1974. Towards the end of the HQ series in 1973–74, due to US emissions regulations, the performance of these engines had dropped to the same or lower than Holden's locally manufactured V8, which was not yet subject to similar regulations, so Holden discontinued using the engine.
The L48 V8 was the standard engine in the 1975–1980 Chevrolet Corvette. The L48 V8 Corvette engine produced in 1975. Power increased to in 1976 and stayed the same in 1977. The 1978 saw for California or high altitude areas and for everywhere else. Power increased to in 1979 and decreased to in 1980.
L65
The 1970 model year Camaro had a 250HP High Performance 2bbl Rochester carburetor. In 1971, it dropped to 245HP; 1972 it had 165 net HP, while 1973-1975 had 145 net HP. It was basically the 2bbl version of the L48 350. It was produced until the 1976 model year. It had 255 lb/ft (346 nm) of torque.LM1
The ''LM1'' is the base 350 cu in with a 4-barrel carburetor (usually with a Rochester Quadrajet) engine in passenger cars to 1979 as a retail option (its final use in a retail passenger car was the 1981 Camaro Z28) and police package 9C1 A/G (Malibu to 1981) and B-bodies (Caprice, Impala) until 1988 retail market GM rear wheel drive/V8s sold to the general public had a maximum 5.0 liters displacement with the exception of its muscle car survivors e.g. Corvette and F-bodies (Camaro IROC Z or Trans Am). Throughout its lifespan, it used mechanical ignition points, electronic, or computer-controlled spark system, and conventional or feedback carburetors. The LM1 was superseded by the L05 powerplant after 1988. The LM1 was first introduced for 1969 model year as a 9.0:1 255 hp engine. It was essentially an L48 engine in all ways except for 75cc combustion chambers rather than the L48's 64cc, and less spark advance to allow it to run on regular grade fuel. It was replaced at the end of December 1968 by the L65 and re-appeared again in the 1970's. This engine was fitted to automatic versions of the 1969 and 1970 Holden Monaro GTS350 in Australia where it was rated at 275 hp most likely due to the use of higher octane fuel and far more spark advance than was fitted to North American versions of the engine.ZQ3
Years: 1969-1974 The ''ZQ3'' is the standard engine in the 1969–1974 Chevrolet Corvette. In 1969 and 1970 it was a version of the small-block, with 10.25:1 compression and hydraulic lifters. It used a Rochester "4MV" Quadra-Jet 4-barrel carburetor and a L48 camshaft.Gunnell, John. Standard Catalog of Corvette, 1953-2005. Krause Publications, 2004 In 1971, power decreased to (gross) and (gross) of torque with a lower 8.5:1 compression. 1972 saw (net) and (net) of torque. In 1973 power decreased to , but increased slightly in 1974 to . Post-1971 blocks possibly had a lower nickel content but thicker cylinder deck, and post 1974 heads of the small block Chevrolet used less iron, and were lighter weight, crack-prone, and were less powerful because of the lower compression ratios used.LT-1
Years: 1970–1972 The ''LT-1'' was one of the most well-known SBC V8s, becoming available in 1970. It used solid lifters, 11.0:1 compression, the "178" high-performance camshaft, and a vacuum secondary Holley four-barrel carburetor on a special high-rise aluminum intake, with special 2.5" outlet rams' horn exhaust manifolds in the Corvette, Delco transistor ignition and a low-restriction exhaust factory rated at in the Corvette, and at 6000 rpm and at 4000 in the Camaro Z28 (theNHRA
The National Hot Rod Association (NHRA) is a drag racing governing body, which sets rules in drag racing and hosts events all over the United States and Canada. With over 40,000 drivers in its rosters, the NHRA claims to be the largest motorspo ...
rated it at for classification purposes). Redline
Redline refers to the maximum engine speed at which an internal combustion engine or traction motor and its components are designed to operate without causing damage to the components themselves or other parts of the engine. The redline of an en ...
was 6,500 rpm but power fell off significantly past 6,200 rpm. The LT-1 was available in the Corvette, and Camaro Z28. Power was down in 1971 to dual-rated (gross)/ (net) and of torque with 9.0:1 compression, and again in 1972 (the last year of the LT-1, now rated using net only, rather than gross, measurement) to and .
L82
Years: 1973–1980 The 1973–1974 ''L82'' was a "performance" version of the 350 that still used the casting number 624 76cc chamber "2.02" heads but with a Rochester Quadra-jet 4bbl carburetor and dual-plane aluminum intake manifold, the earlier L46 350 hydraulic-lifter cam, and 9.0:1 compression forged-aluminum pistons producing (1971 was the first year for SAE net hp rating, as installed in the vehicle with accessories and mufflers) and of torque. Its cast-aluminum LT-1 valvecovers were painted crinkle-black contrasting with the aluminum manifold and distributor housing. It was down to and of torque for 1975. It produced in the Corvette for 1976–1977. The 1978 L82 recovered somewhat, producing and in the Corvette and in 1979 it produced in the Corvette. In 1980, its final year, it produced a peak of . This engine was also available on the Chevrolet Camaro in 1973 and 1974.L81
Years: 1981 The ''L81'' was the only Corvette engine for 1981. It produced and of torque from 8.2:1 compression, exactly the same as the 1980 L48, but added hotter cam and computer control spark advance, replacing the vacuum advance. The L81 was the first Corvette engine to employ a "smart carburetor." The 1980 Rochester Quadrajet was modified to allow electronic mixture control, and an ECM ( Engine Control Module) supplied with data from an exhaust oxygen sensor, modified the fuel-air mixture being fed to the engine.LS9
Years: 1969-1986 The LS9 was GM's 350 cubic inch truck engine used in C/K/G 10/20 models under GVWR (gross vehicle weight rating). The LS9 used a Rochester 4 bbl carburetor, and its power ratings for 1984 were at 3800 rpm, and torque at 1600 rpm. A version using a closed-loop carburetor was used with the California emissions package in its final years. The LS9 and LT9 engines were replaced for 1987 by the L05 TBI (throttle-body fuel injection
Manifold injection is a mixture formation system for internal combustion engines with external mixture formation. It is commonly used in engines with spark ignition that use petrol as fuel, such as the Otto engine, and the Wankel engine. In a mani ...
) engines. Most of the small block engines in this timeframe were built at either the Flint engine plant in south Flint, Michigan
Flint is the largest city and seat of Genesee County, Michigan, United States. Located along the Flint River, northwest of Detroit, it is a principal city within the region known as Mid Michigan. At the 2020 census, Flint had a population of 8 ...
or at St. Catharines, Ontario
St. Catharines is the largest city in Canada's Niagara Region and the sixth largest urban area in the province of Ontario. As of 2016, it has an area of , 136,803 residents, and a metropolitan population of 406,074. It lies in Southern Ontari ...
. The Flint plant was producing about 5,200 engines per day in the mid-1980s, and had a slower, separate line for the TPI engines used in the Camaro and Corvette. (Source: 1984 Chevrolet Truck Data Book.)
LT-9
Years: 1981-1986 The ''LT-9'' served as GM's truck-based heavy emissions variant of the supplied in K20/K30 pickups, G model passenger and cargo vans (built in Lordstown, OH and later in Flint, MI) and with the P30 chassis used for motorhomes and stepvans. The LT-9's listed specifications are at 3,800 rpm and of torque at 2,800 rpm with 8.3:1 compression. LT-9's were carbureted with Rochester Quadrajets from factory and are generally 4-bolt mains. The LT-9 is often known by VIN code as the "M-code 350." The LT9 was used in models with GVWRs (gross vehicle weight ratings) over .L83
Years: 1982, 1984 The 1982 L83 was again the only Corvette engine, producing and of torque from 9.0:1 compression. Since GM did not assign a 1983 model year to production Corvettes, there was no L83 for 1983. This was also the only engine on the 1984 Corvette, at and of torque. The L83 added "Cross-Fire"fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
(twin throttle-body fuel injection).
L98
Years: 1985–1992 The new 1985 L98 350 added tuned-port fuel injection "TPI", which was standard on all 1985–1991 Corvettes. It was rated at for 1985–1986, for 1987-1989 ( with 3.08:1 rear axle ratio (1988-1989 only)), and in 1990-1991 ( with 3.08:1 rear axle). Aluminum cylinder heads (Corvette only) were released part way through the 1986 model run, modified for 1987 with D-ports, and continued through the end of L98 Corvette production in 1991 (still used on ZZx 350 crate engines until 2015 when the ZZ6 received the fast burn heads). The L98 V8 was optional on Jan. '87–'92 Chevrolet Camaro &Pontiac Firebird
The Pontiac Firebird is an American automobile that was built and produced by Pontiac from the 1967 to 2002 model years. Designed as a pony car to compete with the Ford Mustang, it was introduced on February 23, 1967, five months after GM's Che ...
models (rated at - and -)
The 1987 versions had and more and a change to hydraulic roller camshaft. Compression was up again in 1990 to 9.5:1 Camaro/Firebird and 10:1 Corvettes, but rated output stayed the same.
Vehicles using the L98:
*1985-1991 Chevrolet Corvette
*1987-1992 Chevrolet Camaro (optional)
*1987-1992 Pontiac Firebird
The Pontiac Firebird is an American automobile that was built and produced by Pontiac from the 1967 to 2002 model years. Designed as a pony car to compete with the Ford Mustang, it was introduced on February 23, 1967, five months after GM's Che ...
(optional)
L05
The L05 was introduced in 1987 for use in Chevrolet/GMC trucks in the GMT400 (introduced in April 1987 as 1988 models) and the R/V series trucks such as the K5 Blazer, Suburban, and rounded-era pickups formerly classed as the C/K until 1991 which includes chassis cabs and 4-door crew cabs. The L05 was also used in the G van models and the P30 step vans. Additionally, the L05 was used in 9C1-optioned police package Caprices, and in the following vehicles: *1992/1993Buick Roadmaster
The Buick Roadmaster is an automobile that was built by Buick from 1936 until 1942, from 1946 until 1958, and then again from 1991 until 1996. Roadmasters produced between 1936 and 1958 were built on Buick's longest non-limousine wheelbase and sh ...
sedan and station wagon
*1990–1992 Cadillac Brougham (optional engine)
*1993 Cadillac Fleetwood
*1989-1993 Chevrolet Caprice 9C1 police package (roller cam); 1A2-optioned special service station wagon
*1992/1993 Chevrolet Caprice wagon (optional engine)
*1993 Chevrolet Caprice LTZ
*1992 Oldsmobile Custom Cruiser wagon (optional engine)
*1995-1996 AM General Hummer H1
L05s were used primarily with casting number 14102193 (64cc combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Interna ...
s) cylinder heads with swirled intake ports - the intake ports were designed for fuel economy (the design was also shared with the 103 heads used on the 4.3L with TBI). The swirl ports (known to GM as a vortex chamber) along with the irregular shape of the combustion chambers limit the airflow and horsepower output where they did not provide a fast burn, later phased in with the 1996 Vortec heads. A majority of the L05s used with the trucks and vans had conventional flat tappet camshafts, while the Caprice 9C1 (1989–93) had a roller cam. L05 usage was replaced by the LT1 after 1993 in GM B-Bodies and D-Bodies until production ceased in 1996.
A single belt (serpentine belt) accessory drive was introduced on the L05, the 5.0L L03 and the 4.3L V6 LB4 engines used in the 1988 GMT400 models but not on the older R/V models (R/V models received the serpentine belt drive in 1989 when the front grille was facelifted in appearance to the GMT400 lineup). In mid-1996 the L05 was equipped with heads used in the 1996 G30. In February 2008, a Wisconsin businessman reported that his 1991 Chevrolet C1500 pickup had logged over 1 million miles without any major repairs to its L05 engine. (Source: ''The Flint Journal'', February 17, 2008) The article also mentioned that the Flint engine plant that built the engine, had produced 45 million engines in its 45-year history, before closing in 1999.
L31
The Vortec 5700 L31 (VIN code 8th digit "R") is a 5.7L V8 truck engine. It is Chevrolet's last production Generation I small-block. The cylinder heads feature combustion chambers and intake ports very similar to those of the LT1 V8, but lacking the LT1's reverse-flow cooling and higher compression. As such, the L31 head is compatible with all older small-blocks, and is a very popular upgrade. It offers the airflow of more expensive heads, at a much lower cost. It does, however, require a specific intake manifold (A 5.7L, 350 CI L31, Vortec engine has eight bolts attaching the intake manifold or four per head, as opposed to the "traditional" six bolts per head; twelve in total found on older Chevrolet small blocks). Chevrolet's L31 was replaced by GM's 5.3L LM7 V8. The Vortec 5700 produces to at 4,600 RPM and to of torque at 2,800 RpM. Known as the GEN 1+, the final incarnation of the 1954 era-vintage small block ended production in 2005 with the last vehicle being a Kodiak/Topkick HD truck. It is still in current production as a crate engine for marine applications and automotive hobbyists as the 'RamJet 350' with minor modifications. Volvo Penta andMercury Marine
Mercury Marine is a marine engine division of Brunswick Corporation headquartered in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin. The main product line is outboard motors. It also produces the MerCruiser line of sterndrives and inboard motors. Some manufacturing ...
also still produce the L31. The "Marine" intake, despite its cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
construction, is an L31 upgrade that allows use of common Bosch-style injectors with various flow rates while still maintaining emission compliance.
* 1996–1999 Chevrolet/GMC C/K full-size trucks
* 1996–1999 Chevrolet Suburban
The Chevrolet Suburban is a series of automobiles built by the Chevrolet division of General Motors. The name started in 1934 for the 1935 U.S. model year, making it the longest continuously used automobile nameplate in production. It has tra ...
/GMC Suburban
GMC may refer to:
Government India
* Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation, in Gujarat
* Gobichettipalayam Municipal Corporation, in Tamil Nadu
* Guntur Municipal Corporation, in Andhra Pradesh
* Guwahati Municipal Corporation, in Assam
* Gwalior ...
full-size long-wheelbase SUVs
* 1996–2000 Chevrolet Tahoe
The Chevrolet Tahoe, and its badge engineered GMC Yukon counterpart, are full-size SUVs from General Motors, offered since 1994 and 1991, respectively. Since 1982, Chevrolet and GMC sold two different-sized SUVs under their 'Blazer' and 'Jimmy ...
/ GMC Yukon (and 2000 Tahoe Limited and 2000 Tahoe Z71 models) full-size short-wheelbase SUVs
* 1999–2000 Cadillac Escalade
* 1996–2002 Chevrolet Express
Chevrolet ( ), colloquially referred to as Chevy and formally the Chevrolet Motor Division of General Motors Company, is an American automobile division of the American manufacturer General Motors (GM). Louis Chevrolet (1878–1941) and oust ...
/ GMC Savana full-size vans
TBI L31 applications
* 1996 G-Series vans over GVW w/ 4L80E transmission
Special applications
* Oscar Mayer Wienermobile
*Isuzu box trucks
4.125 in bore family (1970–1980)
400
 The is the only engine in this family and was introduced in 1970 and produced for 10 years. It has a bore and a stroke. The 400 differed from other small blocks in that the cylinders were siamesed and therefore required 'steam' holes in the block, head
The is the only engine in this family and was introduced in 1970 and produced for 10 years. It has a bore and a stroke. The 400 differed from other small blocks in that the cylinders were siamesed and therefore required 'steam' holes in the block, head gasket
Some seals and gaskets
A gasket is a mechanical seal which fills the space between two or more mating surfaces, generally to prevent leakage from or into the joined objects while under compression. It is a deformable material that is used to c ...
s, and heads to help alleviate 'hot-spots' in the cooling system at the point above the siamesed cylinders. Overheating and damage are likely if head gaskets or heads without 'steam' holes are used on a 400 block. The 400 is the only engine that uses a main bearing journal and a rod bearing journal. The connecting rod was also 400 specific being as opposed to the rod used in all other small block Chevrolet engines. The 400 was made in 4-bolt main journal from 1970 to 1972 and in 2-bolt main journal from 1973 to 1979. The 400 can have either 2 or 3 freeze-plugs per side though all 400 blocks have the provisions for a 3rd freeze-plug on each side. The 400 was rated at gross ( SAE net) through its life. The 400 saw extensive use in full-size Chevrolet and GMC trucks; K5 Blazer/Jimmy, 1/2-ton, 3/4-ton, 1-ton, and even larger 'medium duty' trucks had an option to be equipped with a 400. The engine was available in midsize A-Body and full-size B-Body
The B platform (also known as the B body) is a full-size car, full-size rear-wheel drive car platform that was produced by General Motors (GM) from 1926 to 1996. Originally made for Oldsmobile and Buick, all of General Motors's five main makes w ...
passenger cars until the end of the 1976 model year. Early models produced with a two-barrel carburetor. All 400s came with a two-barrel carburetor until 1973. A four-barrel carburetor option became available in 1974.
The 400 was never intended as a high-performance engine and never saw large factory horsepower numbers; nevertheless, it developed a reputation for creating tremendous torque (up to in 1970) and has since become popular for many types of racing, both on- and off-road. It was also used for the limited production Avanti for a few years in the 1970s.
3.671 in bore family (1975–1976)
262
The 1975–1976 262 was a 90°pushrod
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
V8 with an iron block and heads. Bore and stroke were . Power output for 1975 was at 3600 rpm and at 2000 rpm. The 262 was replaced with the 305 for the 1977 model year.
This was Chevrolet's second 4.3 L-displacement power plant; four other Chevrolet engines displaced 4.3 L: the Vortec 4300 (a V6 based on the Chevrolet , with two cylinders removed), the original V8 in 1954, a bored version of the stovebolt-era 235 inline six displacing , and a derivative of the Generation II LT engines known as the L99 (using the 305's bore, -long connecting rods, and a stroke).
This engine was used in the following cars:
*1975–1976 Chevrolet Monza
*1975 Chevrolet Nova
*Early 1977 Pontiac Ventura
The Pontiac Ventura was an automobile model that was produced by Pontiac. As was common practice at the time, its name was derived from Ventura, California, joining other similarly derived models such as the fellow Pontiac Catalina, the Chevrolet M ...
3.736 in bore family (1976–1998)
305
Designed and built during the era of the gas embargo,CAFE
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non-caf ...
mandates, and tighter emissions, this engine family was designed to become Chevrolet's cost-effective, all-purpose "economy V8" engine line. Introduced in 1976 models, it had a displacement of . It was intended to fill the gap where the venerable 283 and 307 had been. Bore and stroke were , using the 350's crankshaft throw. This new engine family would provide better gas economy than the 350, share its basic architecture and many parts with the 350 (thus reducing production costs), and provide customers with more horsepower and torque than Chevrolet's 1970s-era inline 6 and V6 engines. During the early 1980s, when GM was streamlining their engine lineups, the Chevrolet 305 would rise to prominence as General Motors' "corporate" engine, signified by being the standard (and often only) V8 in many GM vehicles. Through much of the 80's, the 305 became General Motors' most common V8, followed closely by Oldsmobile's 307. The 305 also became the standard V8 in GM's C/K truck series, and was even used in the Corvette for California in 1980.
Crankshafts used with the 305 had the same casting number as the 350 with one discernible difference - the 305 crank is lighter in weight to compensate for engine balancing. As a result, the counterweights are smaller, which makes it unsuitable for use in a 350 where metal would have to be welded back on. The medium journal 305, like its big-brother 350, would be further developed in the 1990s, although with a reduced stroke using connecting rods, into the Generation II LT engine L99 263.
*1976–1992 Chevrolet Camaro
*1977–1993 Chevrolet Caprice
*1977-1985 Chevrolet Impala
The Chevrolet Impala () is a full-size car built by Chevrolet for model years 1958 to 1985, 1994 to 1996, and 2000 to 2020. The Impala was Chevrolet's popular flagship passenger car and was among the better-selling American-made automobiles in ...
*1980 Chevrolet Corvette (California only)
*1976–1988 Chevrolet Malibu, Chevrolet El Camino/GMC Caballero, and Chevrolet Monte Carlo
*1976–1979 Chevrolet Monza
*1976–1979 Chevrolet Nova (also GM X-body clones after 1976)
*1977–2003 Chevrolet/GMC Trucks, SUVs, Vans
*1978–1987 Buick Regal
*1975–1979 Buick Skylark
*1991–1992 Cadillac Brougham
*1977–1981 Checker Marathon
The Checker Marathon is an automobile produced by the Checker Motors Corporation of Kalamazoo, Michigan, between 1961 and 1982. It was marketed as a passenger car for consumers, as opposed to the similar Taxi, which was aimed at fleet buyers.
H ...
*1991–1992 Oldsmobile Custom Cruiser
*1977 Oldsmobile Omega
The Oldsmobile Omega is a compact car manufactured and marketed from 1973-1984 by Oldsmobile, as the brand's most affordable, entry level vehicle — across three distinct generations.
The first two generations of the Omega used rear-wheel ...
*1978–1980 Oldsmobile Cutlass
The Oldsmobile Cutlass was a series of automobiles produced by General Motors' Oldsmobile division between 1961 and 1999. At its introduction, the Cutlass was Oldsmobile's entry-level model; it began as a unibody compact car, but saw its greates ...
(U.S. market only, Canadian market 1978–1987)
*1977–1981 Pontiac Catalina (B-body)
*1977–1981 Pontiac Bonneville (B-body)
*1982–1986 Pontiac Bonneville (G-body)
*1977–1992 Pontiac Firebird
The Pontiac Firebird is an American automobile that was built and produced by Pontiac from the 1967 to 2002 model years. Designed as a pony car to compete with the Ford Mustang, it was introduced on February 23, 1967, five months after GM's Che ...
*1981–1987 Pontiac Grand Prix
The Grand Prix is a line of automobiles produced by the Pontiac Division of General Motors from 1962 until 2002 for coupes and 1989–2008 for sedans.
First introduced as a full-size performance coupe for the 1962 model year, the model varied ...
*1978–1981 Pontiac Grand LeMans (A/G-body, includes Grand Am)
*1982–1986 Pontiac Parisienne (B-body)
*1982–1986 Pontiac Parisienne Safari
The Pontiac Safari is a line of station wagons that was produced by Pontiac from 1955 to 1989. Introduced as the Pontiac counterpart of the two-door Chevrolet Nomad for 1955, the nameplate was adopted across the entire full-size Pontiac station wa ...
(B-body wagon)
*1979 Pontiac Sunbird
The Pontiac Sunbird (also known as the Pontiac J2000 and Pontiac 2000) is a model line that was manufactured and marketed by Pontiac from the 1976 to the 1994 model years. Loosely deriving its name from the Pontiac Firebird, the Sunbird was intr ...
The Chevrolet 305 is a reliable, fuel efficient V8, easily capable of 200,000 miles, if maintained. From 1976 onward into the early 1980s, these engines were prone to wearing out their camshaft lobes prematurely due to a combination of improper manufacturing and poor quality controls (a result of GM cost-cutting measures). The 305 is sometimes dismissed in performance circles because of its lackluster performance, small bore size, and difficulty flowing large volumes of air at high RPM. However, two variants of the 1983 to 1992 305 were notable performers: the 1983 to 1988 L69 High Output 5.0L (only used in late 1983 to early 1986 F-body and late 1983 to 1988 Monte Carlo SS) and the 1985 to 1992 LB9 Tuned Port Injection 5.0L (F-body only).
After 1993, its usage was limited to light trucks and SUVs until the 2000 model year while vans and commercial vehicles continued until 2003. The 305 was sold as a crate motor
A replacement automobile engine is an engine or a major part of one that is sold individually without any other parts required to make a functional car (for example a drivetrain). These engines are produced either as aftermarket parts or as repro ...
under the Mr. Goodwrench
GM Certified Service, formerly GM Goodwrench, is an auto repair service for General Motors. In 2011, GM replaced the Goodwrench brand in the US with Cadillac, Buick, Chevrolet, and GMC Certified Service brands (Canada followed in 2014).
Backgrou ...
brand as a replacement motor and as a boat engine for Mercury Marine until late 2014 when it was discontinued. The cylinder block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure which contains the cylinders and other components. In an early automotive engine, the engine block consisted of just the cylinder block, to which a separate crankcase was attac ...
is still in production by GM (part number 10243869) for Sprint Car Spec Racing.
LG3
The first iteration of the 305, the LG3 was introduced in 1976. This variant used a Rochester 2GC carburetor from 1976 to 1978. In 1979, the more fuel-efficient Rochester Dual-Jet 2bbl carburetor replaced the older 2GC. This change also resulted in a drop in power to and for California emissions cars. All years had an 8.5:1 compression ratio. It was discontinued in 1982.LG4
The LG4 produced and . Introduced in 1978, the LG4 was essentially an LG3 with the addition of a 4-bbl carburetor and larger valves. The engine saw a series of gradual improvements, increasing reliability, mpg, and power output through its production run. In 1981 (1980 for California models) Chevrolet added GM's new "Computer Command Control" (CCC) engine management system to the LG4 engines (except Canadian models). The CCC system included the electronic Rochester 4-bbl E4ME Quadra-Jet, with computer-adjusted fuel metering on the primary venturis and a throttle position sensor allowing the CCC to calculate engine load. In the ignition system, CCC was fully responsible for the timing curve; mechanical and vacuum advances were eliminated from the distributor. The more precise spark timing provided by the CCC made possible a series of increases in compression ratio from a pre-CCC 8.4:1, to 8.6:1, to a knock-sensor-assisted 9.5:1, all while still only requiring 87 AKI regular unleaded fuel. In 1983, Chevrolet replaced the cast-iron intake with an aluminum version and used either 14014416 ("416") or 14022601 ("601") heads with 1.84 inch intake valves, 1.50 inch exhaust valves, 58 cc chambers, and 178 cc runners. For 1985, the 4-valve-relief, flat top pistons from the L69 were added to the LG4, which resulted in another increase in compression. Also added was a knock sensor to allow the "CCC" engine management system to compensate for the increase in compression and a more aggressive spark-timing map in the ECM. As a result, power increased for the 1985 models to from the rating in 1984. For 1986, Chevrolet changed over to a one-piece rear main seal engine block design to minimize leaks and warranty claims; however, some early 1986 blocks retained a two-piece rear main seal. For 1987, Chevrolet once again made some revisions to increase overall reliability, many of them borrowed from theTBI TBI may refer to:
Medicine
* toe-brachial index, a parameter for the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease
* Total body irradiation, a form of radiation therapy used most commonly in bone marrow transplantation
* Tracheobronchial injury, an inj ...
L03, which was to replace the LG4. The coil-in-cap HEI distributor was retired, and an all-new electronic distributor design was used. The intake manifold to head bolt pattern was redesigned to improve gasket integrity - four of the center intake manifold bolts were drilled at 72 degrees instead of 90 degrees for the cast iron cylinder heads. Changes to the valve covers were also made. Ribbing was added to the top of the valve covers to increase surface area, acting as a heat sink. To improve intake gasket sealing, the mounting bolts were relocated to the valve cover centerline, placing all sealing pressure evenly upon the mounting flange perimeter. Thus, these became known as centerbolt valve covers, first introduced in 1985 on the LB4 4.3L V6 and the Corvette a year earlier (the aluminum cylinder heads used with the Corvette were the first to have the centerbolt valve covers). Another improvement was use of a hydraulic lifter/roller camshaft on most 1987 LG4s. Some early engines have lifter retainer provisions, but use the older, non-roller camshaft. 1987 would also be the last year for the LG4 production, however a run of LG4 engines was made to supplement the carry-over production for the 1988 Monte Carlo and the 1988 Chevrolet Caprice.
LU5
Years: 1982 – 1984 The LU5 "Crossfire EFI 5.0L" featured a dual Throttle Body Injection set-up, based upon the original "Crossram Intake" supplied by Chevrolet for the 1969 Camaro Z28. Unlike, the original '69 version, Chevrolet did not place it in the trunk for owners to install. The system used a special version of GM's still-new "CCC" engine management system. Fuel was supplied by the two TBI units, set diagonally apart from each other, atop the unique, aluminum intake manifold. Unfortunately, the system was placed atop the basic LG4 and lacked any significant performance capability. The engine was originally planned for the long-awaited '82 Camaro Z28, however due to a last-minute GM-mandated cancellation of Pontiac's 301 V8 production & Turbo 4.9L Project (T301), the Crossfire 305 was made available in the '82 Trans Am. A 350 cubic inch version was also used in the Corvette from 1982 to 1984. Since it was fairly early into GM's electronic engine management development and electronic fuel injection programs, few dealerships had the technology, equipment, or properly trained mechanics capable of dealing with these engines. These problems were compounded by widely varying fuel quality standards, production issues, poor quality control by GM, & owners who tinkered with a system they did not understand. In a very short time, these engines obtained the notorious nickname; "Ceasefire Engine". Today, owners with these engines note that they are fairly reliable, and that a significant upgrade can be made by simply using the L69/LB9 TPI/L98 TPI exhaust manifolds/ exhaust systems... When combined with performance-built stock 305 heads w/larger valves or aftermarket heads, plus a camshaft upgrade, these engines can perform surprisingly well. Thanks mostly to a somewhat cult-like following, a number of aftermarket performance parts are also available through Crossfire-specialized manufacturers.L69
Years: late-1983 – 1988 The L69 High Output 5.0L was released late into the 1983 model year. It was optional in the Firebird Trans Am, Camaro Z28, and IROC-Z, and was standard in the revived Monte Carlo Super Sport. The L69 features a compression ratio of 9.5:1 and a relatively aggressive stock camshaft. It also uses a performance-tuned CCC ECM/PROM, a knock sensor, a performance-tuned E4ME Rochester Quadra-Jet 4 barrel carburetor, and a special, free-flowing exhaust system with large diameter exhaust manifolds, Y-pipe and catalytic converter. The L69 F-body exhaust system components would be revised slightly and used again on the later LB9 305 and L98 350 TPI engines. Additionally, the engines came equipped with a functional cold air induction hood on the 1983-1984 Trans Am, a dual snorkel air cleaner assembly on the 1983-1986 Camaro Z28 and IROC-Z and 1985-1986 Trans Am, a large, single snorkel on the 1983-1988 Monte Carlo SS (also, rare optional dual snorkel in 1987-1988), an aluminum intake manifold, high stall torque converter on the Monte Carlo SS and 1984 F-bodies, or a lightweight flywheel on T-5 equipped F-bodies. The L69 engine produced at 4800 and of torque at 3200 rpm in the F-Body and was rated at in the Monte SS.LE9
Years: 1981–1986 The LE9 was a truck/van/car version 4BBL that also had a 9.5:1 compression ratio, the LM1 cam and 14010201 casting heads featuring 1.84/1.50" valves and chambers. The engine produced at 4,400 and at 2,000 rpm.LB9
Years: 1985–1992 The LB9 "Tuned Port Injection 5.0L" was introduced in 1985. At its core was the stout L69 shortblock and it used the same aggressive L69 camshaft profile. The induction system was unlike any system used previously by GM. It featured a large plenum made of cast aluminum, with individual runners made of tubular aluminum, feeding air to each cylinder. And each cylinder had its own fuel injector fed by a fuel rail mounted above each bank. In 1985, this engine was optional only in the Camaro Z28, IROC-Z and Trans Am equipped with the WS6 performance suspension. The LB9 was also available in the '87-92 GTA and Firebird Formula. and and varied between (with of torque) over the years offered.L03
Years: 1987–95 The L03 produced at 4,400 rpm and of torque at 2,400 rpm in 1993–1995 GM trucks. This engine used the TBI throttle bodyfuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
, which was a hybrid between EFI and carburetor technology. It used an EFI system with electronically controlled injectors, which were mated to a twin barrel "carburetor" body. It featured "swirl port" heads (helped emissions, but severely stunted power output) and served as the base V8 engine in all C/K 1500 Series GMC/Chevrolet Trucks/Vans. It was also very common in Firebirds and Camaros because it was the only engine that offered a 5 speed manual combination. The 350 exceeded the Borg-Warner T5's input power ratings, and as such, it was cut from the 350 cars to prevent lemon law and warranty losses.
The L03 used hydraulic roller lifters, which allowed it to recover some of the lost horsepower from its factory design, while further increasing efficiency (reduced rotational drag). Despite downfalls in its aspiration restrictions, the L03 had one thing going for it: reliability (87-90 F-bodies that carry the L03 did not use a rev limiter). They used dished pistons with a 9.3:1 to 9.5:1 compression ratio The L03 TBI featured a 3.736" bore and 3.48" stroke, the same as its TPI cousin, the LB9.
L30
Years: 1996-2003 The Vortec 5000 L30 is a V8truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construction ...
engine. Displacement is 5,020 cc, (305.4 cubic inches). Bore is , stroke is . The compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
is 9.1:1. It is based on the Generation I small-block
The Chevrolet small-block engine is a series of gasoline-powered, V-8 automobile engines, produced by the Chevrolet division of General Motors between 1954 and 2003, using the same basic engine block. Referred to as a "small-block" for its size ...
from Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ), colloquially referred to as Chevy and formally the Chevrolet Motor Division of General Motors Company, is an American automobile division of the American manufacturer General Motors (GM). Louis Chevrolet (1878–1941) and ous ...
. It was replaced by the 4.8 L Vortec 4800 LR4 for the 2003 full-size vans. In C/K truck configuration it produces net flywheel at 4,600 rpm and net flywheel torque at 2,800 rpm. In van configuration it produces net flywheel at 4,600 rpm and net flywheel torque at 2,800 rpm. The engine uses a hydraulic roller cam and high flowing, fast burn style vortec heads. Differences include bore and stroke, intake valve size, and smaller combustion chambers.
L30 applications:
* Chevrolet Express
Chevrolet ( ), colloquially referred to as Chevy and formally the Chevrolet Motor Division of General Motors Company, is an American automobile division of the American manufacturer General Motors (GM). Louis Chevrolet (1878–1941) and oust ...
/ GMC Savana
* General Motors C/K full-size trucks
3.50 in bore family (1979–1982)
267
The 267 was introduced in 1979 for GM F-body (Camaro), G-bodies (Chevrolet Monte Carlo, El Camino, and Malibu Classic) and also used on GM B-body cars (Impala and Caprice models). The engine had the 350's crankshaft stroke of and the smallest bore of any small-block, , shared with the 200 V6 introduced a year earlier. It was only available with a M2ME Rochester Dualjet 210 – effectively a Rochester Quadrajet with no rear barrels. After 1980, electronic feedback carburetion was used on the 267. The 267 also saw use in 1980 to 1982Checker Marathon
The Checker Marathon is an automobile produced by the Checker Motors Corporation of Kalamazoo, Michigan, between 1961 and 1982. It was marketed as a passenger car for consumers, as opposed to the similar Taxi, which was aimed at fleet buyers.
H ...
s.''Standard Catalog of Independents'', pp. 41-42
While similar in displacement to the other V8 engines produced by General Motors (including the Oldsmobile 260 and Pontiac 265), the small bore 267 shared no parts with the other engines and was phased out after the 1982 model year due to inability to conform to emission standards. Chevrolet vehicles eventually used the as their base V8 engine.
The 267 when introduced in the GM F-Body as the L39 4.4 L it made at 3600 RPM and of torque at 2000 RPM (SAE NET). Power output would drop in subsequent years of the engine. The had a low 8.3:1 compression ratio.
Major changes
The original design of the small block remained remarkably unchanged for its production run, which began in 1954 and ended, in passenger vehicles, in 2003. The engine is still being built today for many aftermarket applications, both to replace worn-out older engines and also by many builders as high-performance applications. The principal changes to it over the years include: *1956 – Full-flow oil filtration was introduced, using a paper element filter in a canister that was mounted to a boss that was added to the left rear cylinder block casting and machined for this purpose. *1957 – The displacement of the base V8 continued at 265 cubic inches, but optional V8 engines were introduced with a displacement of 283 cubic inches. *1958 – Bosses for side motor mounts were added to the block casting, used for production mounts for this and all future model years. However, the features for front motor mounts as used in 1955–1957 remained part of the block casting in this and future years. The 265-cubic-inch version of the engine was discontinued. Also, the cylinder head valve cover mounting bolt holes were changed from the top row staggered (relative to the bottom row of bolts) to the "straight-across" pattern that remained the way of identifying the early heads from the newer ones with a valve cover design which lasted until the 1987 center-bolt-style covers. *1962 – The block's cylinder wall casting was revised to allow four-inch bores, and the 327-cubic-inch version of the engine, using this bore diameter and increased stroke, was introduced. *1967 - The oil filter mounting now came from the factory with an adapter and machining to allow the use of spin-on filters; canister mounting was possible by removing the adapter. *1968 – The main-journal diameter was increased from 2.30" (small) to 2.45" (medium), and the connecting-rod journal diameter was increased from 2.00" to 2.10". This allowed the use of cast-iron crankshafts; the previous crankshafts were made of forged steel, which was more expensive. The rod bolts were changed from 11/32" diameter to 3/8". The oil-fill location was moved from a tube on the front of the intake manifold to a cap on the left- or right-side valve cover, depending upon the application. *1970 - The "400" is introduced in September 1969 for the 1970 model year, with a bore of 4.125" and a stroke of 3.75". This engine introduced the "large-journal" crankshaft with a main journal size of 2.65" and rod bearing journals of 2.10". This engine also introduced "Siamese bores" to the Chevrolet small-block line, requiring "steam holes" in the cylinder heads and head gaskets, which were used to prevent hot spots and subsequent overheating. The connecting rods, due to the long stroke, are also shorter at 5.565", differing from the 5.7" length of all other Generation I small-block connecting rods. *1980 – Weight reduction though thinner cylinder wall block and light weight head castings. Heads are prone to cracking and blocks typically cannot tolerate an overbore more than .040". *1986 – The rear main seal was changed from a 2-piece rubber design to a 1-piece rubber design that used a mounting appliance to hold it in place. This necessitated a change in the flywheel/flexplate bolt pattern as well as requiring an externally balanced flexplate/flywheel. *1987 – The valve cover surfaces were changed so that the mounting lip was raised and the bolt location was moved from 4 bolts on the perimeter to 4 bolts along the centerline of the valve covers (this design debuted on the Corvette in 1986, and the Chevrolet 4.3L 90 degree V6 the year before). Also changed were the mounting angles of the two center bolts on each side of the intake manifold (from 90 to 73 degrees), and the lifter bosses were increased in height to accept roller lifters; the aluminum-alloy heads for use on the Corvette engines retained the non-angled bolts. Also, all carburetors(except some 1987-89 F-body and B-body models, also the 30 and 3500 model 1-ton trucks through 1989 with either the M-code 350 or W-code 454 engines, in which all retained the 4bbl rochester E4ME carbs) were replaced by TBI (throttle-body injection) fuel injection. *1996 – The cylinder heads were redesigned, using improved ports and combustion chambers similar to those in the Generation II LT1, resulting in significant power increases. The intake manifold bolt pattern was also changed to four bolts per cylinder head instead of the "traditional" six bolts. The cylinder block timing cover lip was thickened for use with the plastic timing cover (redesigned for use with a crankshaft position sensor with integrated dowel pins - cylinder blocks for 1996+ do not have dowel pins in the timing cover flange) held with 8 bolts and the water pump bypass hole on the RH deck and below the water pump passage undrilled. Also the fuel pump boss is still present but undrilled (which dates back to the 1992 model year for production engines without a fuel pump blockoff plate - some marine/industrial blocks and crate motors sold over the counter via GM dealerships e.g. Goodwrench, ZZ6, 350 H.O. retain the use of a mechanical fuel pump). :This was the last change for the Generation I engine, which continued through the end of the production run in 2003; all 1997–2003 Generation I engines were "Vortec" truck engines.Details
;Chevrolet Generation I V8 Small Block Engine Table ''note 1: depending upon vehicle application; horsepower, torque, and fuel requirements will vary. ''Generation II GM small-block (1992–1997)
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
' Generation II LT1 is a small block V8 engine. Making its debut in the 1992 Chevrolet Corvette, the new LT1 sought to draw upon the heritage of the 1970 Chevrolet LT-1.
A significant improvement over the original Generation I V8 is the Generation II LT1's "reverse cooling" system, allowing coolant to start at the heads and flow down through the block. This keeps the heads cooler, affording greater power through a higher compression ratio and greater spark advance at the same time it maintains higher and more consistent cylinder temperatures.
Some parts from the Generation II are interchangeable with the Generation I one-piece rear main seal engine. The interchangeable parts
Interchangeable parts are parts ( components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One such part can freely r ...
include the rotating assembly (crank shaft, pistons, connecting rods, and flywheel/flexplate) one piece rear main seal housing, oil pan and valve cover gaskets and valvetrain assembly (not including timing set, which includes a gear to drive the water pump). The LT1 uses a new engine block, cylinder head, timing cover, water pump, intake manifold and accessory brackets. The harmonic damper also does not interchange; it is a unique damper/pulley assembly. Engine mounts and bell housing
Bell housing or bellhousing is a colloquial/slang term for the portion of the transmission that covers the flywheel and the clutch or torque converter of the transmission on vehicles powered by internal combustion engines. This housing is bolted ...
bolt pattern remain the same, permitting a newer engine to be readily swapped into an older vehicle.
4.00 in bore blocks
5.7 L
=LT1
= In 1991, GM created a new-generation small-block engine called the "LT1 350", distinct from the high-output Generation I LT-1 of the 1970s. It displaced , and was a 2-valvepushrod
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
design. The LT1 used a reverse-flow cooling system which cooled the cylinder heads first, maintaining lower combustion chamber temperatures and allowing the engine to run at a higher compression than its immediate predecessors.
This engine was used in:
* Y-body:
** 1992–1996 Chevrolet Corvette C4
The Chevrolet Corvette (C4) is a sports car produced by American automobile manufacturer Chevrolet from 1983 until 1996. The convertible returned, as did higher performance engines, exemplified by the GM LT engine#LT5, LT5 found in the ZR-1. In ...
* F-body:
** 1993–1997 Chevrolet Camaro Z28, B4C and SS
** 1993–1997 Pontiac Firebird
The Pontiac Firebird is an American automobile that was built and produced by Pontiac from the 1967 to 2002 model years. Designed as a pony car to compete with the Ford Mustang, it was introduced on February 23, 1967, five months after GM's Che ...
Formula, Trans Am, and Firehawk
* B-body:
** 1994-1996 Buick Roadmaster
The Buick Roadmaster is an automobile that was built by Buick from 1936 until 1942, from 1946 until 1958, and then again from 1991 until 1996. Roadmasters produced between 1936 and 1958 were built on Buick's longest non-limousine wheelbase and sh ...
** 1994–1996 Chevrolet Caprice
** 1994–1996 Chevrolet Caprice Police Package
** 1994–1996 Chevrolet Impala
The Chevrolet Impala () is a full-size car built by Chevrolet for model years 1958 to 1985, 1994 to 1996, and 2000 to 2020. The Impala was Chevrolet's popular flagship passenger car and was among the better-selling American-made automobiles in ...
SS
** 1994–1996 Chevrolet Caprice Wagon
** 1994–1996 Buick Roadmaster Wagon
* D-body:
** 1994–1996 Cadillac Fleetwood
There were a few different versions of the LT1. All feature a cast iron block, with aluminum heads in the Y and F bodies, and cast iron heads in the B and D bodies. Corvette blocks had four-bolt main caps, while most other blocks were two-bolt main caps. Block castings remained the same between 2 and 4 bolt mains.
The 92–93 LT1s used speed density fuel management, batch-fire fuel injection and a dedicated Engine Control Module (ECM). In 94 the LT1 switched to a mass airflow sensor and sequential port injection. A new, more capable computer controlled the transmission as well as the engine and got a new name: Powertrain Control Module
A power-train control module, abbreviated PCM, is an automotive industry, automotive component, a control unit, used on motor vehicles. It is generally a combined controller consisting of the engine control unit (ECU) and the transmission control ...
(PCM). Where the ECM held its calibration information in a replaceable PROM chip, the 94-95 OBD1 PCMs are reprogrammable through the diagnostic port.
The early Optispark distributor had durability problems, and a revised version was introduced on the 1994 B-Bodies and on the 1995 Y and F-Bodies. Changes include a vacuum port to draw filtered air through the distributor to remove moisture and ozone and a revised drive system which uses an extended dowel pin on the camshaft rather than a separate splined shaft in the camshaft gear. 1996 saw major revisions for OBD-II: a second catalytic converter on the F-body cars, rear oxygen sensors to monitor catalyst efficiency, and a new engine front cover with a crankshaft position sensor. Some OBD-II features had been added to the Corvette starting in 1994 for testing purposes. The 1997 model year Camaro and Firebird were the last year for this engine in a GM production car before it was replaced by the LS1, which was already in the Corvette for 1997.
1992 LT1s in Corvettes were factory rated at and . 1996 LT1 Corvettes were rated at and .
The 93–95 F-bodies were rated at and , while the 96–97 cars were rated at and . The 96–97 WS6 and SS F-bodies were rated at .
The 94–96 B- and D-body version was rated at and ( with V08 mechanical fan as part of V92 or V4P towing option groups).
=LT4
= The LT4 was the special high-performance version of the new-generation LT1. It featured a slightly more aggressive camshaft profile, 1.6:1 aluminum roller rocker arms, lighter hollow intake valves and liquid-sodium filled exhaust valves, larger fuel injectors, performance crankshaft, higher 10.8:1 compression ratio and high-flow intake manifold (painted red) with extra material above the port available to allow port matching to the raised port LT4 cylinder heads. The LT4 was conservatively underrated at and . It was introduced in the 1996 model year, for the last year of the C4 Corvette, and came standard on all manual transmission ( ZF 6-speed equipped) C4 Corvettes. The engine was passed down to 1997 SLP Camaros SS and SLP Firehawks with 6-speed manual transmissions. The LT4 was available on the following vehicles: * 1996 Chevrolet Corvette only when equipped with 6-speed manual transmission (includes all Grand Sports) (Production: 6,359) * 1997 Chevrolet Camaro SLP/LT4 SS 6-speed (Production: 100 for the U.S., 6 for Canada. There were 2 prototypes) * 1997Pontiac Firebird
The Pontiac Firebird is an American automobile that was built and produced by Pontiac from the 1967 to 2002 model years. Designed as a pony car to compete with the Ford Mustang, it was introduced on February 23, 1967, five months after GM's Che ...
SLP/LT4 Firehawk 6-speed (Production: 29)
All 135 production engines for the Firehawks and SSs were completely disassembled, balanced, blueprinted and honed with stress plates. One in 5 engines was tested on a Superflow engine dyno. Every car was tested on a chassis dyno and then performed a road test.
3.90 in bore blocks
5.7 L
=LT5
= For model year 1990, Chevrolet released the Corvette ZR-1 with the radical Lotus Engineering-designed double overhead cam LT5 engine. Engineered in the UK but produced and assembled in Stillwater, Oklahoma by specialty engine builderMercury Marine
Mercury Marine is a marine engine division of Brunswick Corporation headquartered in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin. The main product line is outboard motors. It also produces the MerCruiser line of sterndrives and inboard motors. Some manufacturing ...
, the all-aluminum LT5 shared only the 4.4 inch bore spacing with any previous sbc engine. It does ''not'' have reverse cooling and is generally not considered a small block Chevrolet.
Used only in Corvettes, the LT5 was the work of a team headed by Design manager David Whitehead, and was hand built by one headed by project engineer Terry D. Stinson. It displaced and had a bore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
x stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
instead of the usual and featured Lotus-designed DOHC 4 valves per cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
rather than the usual Chevrolet 16-Valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings ...
OHV
An overhead valve (OHV) engine, sometimes called a ''pushrod engine'', is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier flathead engines, where the valves were located bel ...
Heads. The preproduction LT5 initially produced , but was reduced to and for the 1990-1992 Corvette ZR-1. The power ratings jumped to at 5800 rpm and of torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
at 5200 rpm from 1993 until its final year in 1995, thanks to cam timing changes and improvements to the engine porting. 1993 also added 4-bolt main bearing caps and an exhaust gas recirculation system.
A second generation of the LT5 was in the testing phase as early as 1993. What little information survived showed that it would have used a dual plenum system similar to the first generation Dodge Viper as well as variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with varia ...
. The next generation LT5 was set to produce between and . Unfortunately, the cost to produce the LT5 along with its weight, dimensions (would not fit the C5 pilot cars without extensive modifications) and internal GM politics over using an engine that was not designed and built in house killed the LT5 after six years of production. GM canceled the ZR-1 option beginning model year 1993. Engines that were to be installed in the as yet unbuilt ZR-1's were sealed and crated for long-term storage. After they were built at the Mercruiser plant in Stillwater, Oklahoma they were shipped to Bowling Green, Kentucky and stored in the Corvette assembly plant until the 1994 and 1995 ZR-1s went down the assembly line. A total of 6,939 cars were produced. The LT5 however wasn't an evolutionary dead end. Despite being discontinued, a new class of premium V8s for Cadillac and eventually Oldsmobile, the dual overhead cam V8 Northstar and its derivatives, drew heavily from the LT5's design and lessons learned from its production. GM also took lessons learned from producing a completely aluminum engine and applied them to the new LS series of engines.
The LT5 was available on the following vehicles:
* 1990-1995 Chevrolet Corvette C4 ZR-1 equipped with 6-speed manual transmission (Production: 6,939). Although the LT5 was never used in another production GM vehicle, it did make its way into several Corvette concepts, race cars and even into a limited run of the Lotus Elise GT1.
3.74 in bore blocks
4.3 L
=L99
= The L99 V8, produced from 1994–1996, shared a cylinder bore with the but had a stroke compared to of the . The pistons used in the 4.3 L V8 were the same as the Vortec 5000's, but longer connecting rods were used to compensate for the shorter stroke. The L99 featured updated Generation II block architecture, and is externally identical to the larger 5.7 L LT1 Generation II V8. Like the LT1, it featuressequential fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All compr ...
, reverse-flow cooling with a cam-driven water pump, and an optical ignition pickup. Output is and .
The L99 4.3 L V8 was the base engine in 1994-1996 Chevrolet Caprice sedans, including 9C1 police package sedans, and was not available in any other vehicles. The L99's smaller displacement provided slightly better EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
fuel economy than the 5.7 L LT1, but at significantly reduced horsepower and torque levels.
LT6 and LT7
The LT6 and LT7 are not part of the LT family. See Oldsmobile Diesel engine for more information.See also
* Chevrolet 90° V6 engine *GMC V8 engine
GMC has both shared engine designs and architectures with other General Motors divisions as well as having a history of developing and using its own unique engines and powertrains such as for instance its line of their straight-6 and V8 engines ...
*GMC V6 engine
GMC Truck produced a unique 60 degree V6 engine family from 1959 through 1974, in gasoline and diesel versions. V8 and V12 derivatives of the basic design were also produced. Examples of this engine family were found in pickup trucks, Suburbans, ...
* Chevrolet Series D V8
* GM LS engine – Generation III/IV/V small block
*List of GM engines
This list of GM engines encompasses all engines manufactured by General Motors and used in their cars.
Divisions
When General Motors was created in 1908, it started out with Buick and soon after acquired Oldsmobile, Cadillac and Oakland. There we ...
References
*External links
{{Commons category, Chevrolet small-block enginesMortec: Small-Block Engine Enthusiasts
Video : First start up SBC engine (& zoomies flames)
Video : Let's see Chevy first start up, and what NOT to do ! ("Dark" humor)
:
Small-Block
The Chevrolet small-block engine is a series of gasoline-powered, V-8 automobile engines, produced by the Chevrolet division of General Motors between 1954 and 2003, using the same basic engine block. Referred to as a "small-block" for its size ...
V8 engines
Gasoline engines by model
Engines by model