L-mannose on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mannose is a
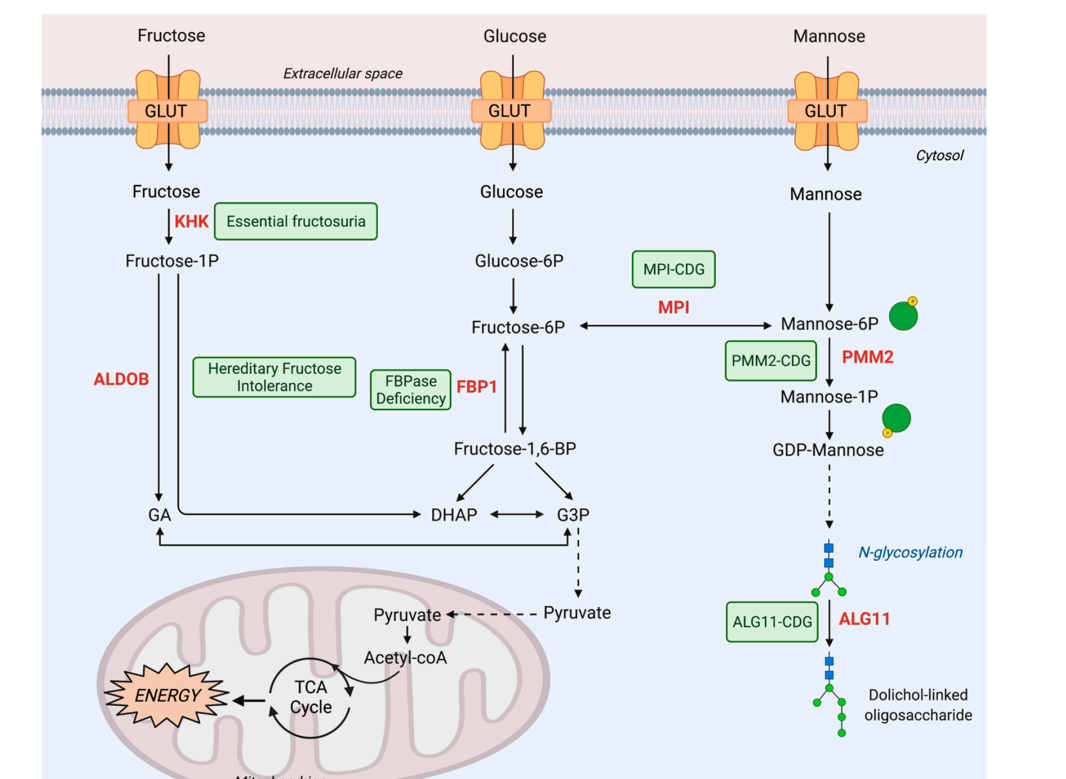 While much of the mannose used in glycosylation is believed to be derived from glucose, in cultured
While much of the mannose used in glycosylation is believed to be derived from glucose, in cultured
 The PEP-dependent sugar transporting phosphotransferase system transports and simultaneously phosphorylates its sugar substrates. Mannose XYZ permease is a member of the family, with this distinct method being used by bacteria for sugar uptake particularly exogenous hexoses in the case of mannose XYZ to release the phosphate esters into the cell cytoplasm in preparation for metabolism primarily through the route of glycolysis. The MANXYZ transporter complex is also involved in infection of ''E. coli'' by bacteriophage lambda, with subunit ManY and ManZ being sufficient for proper lambda phage infection.
MANXYZ possesses four domains in three polypeptide chains; ManX, ManY, and ManZ. The ManX subunit forms a homodimer that is localized to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. ManX contains two domains IIA and IIB linked by a hinge peptide with each domain containing a phosphorylation site and phosphoryl transfer occurs between both subunits. ManX can be membrane bound or not. The ManY and ManNZ subunits are hydrophobic integral membrane proteins with six and one transmembrane alpha helical spanner(s). The phosphoryl group of PEP is transferred to the imported sugar via Enzyme 1, histidine protein phosphate carrier, and then to the ManX, ManY, and ManZ subunits of the ManXYZ transportation complex, which phosphorylates the entering hexose sugar, creating a hexose-6-phosphate.
The PEP-dependent sugar transporting phosphotransferase system transports and simultaneously phosphorylates its sugar substrates. Mannose XYZ permease is a member of the family, with this distinct method being used by bacteria for sugar uptake particularly exogenous hexoses in the case of mannose XYZ to release the phosphate esters into the cell cytoplasm in preparation for metabolism primarily through the route of glycolysis. The MANXYZ transporter complex is also involved in infection of ''E. coli'' by bacteriophage lambda, with subunit ManY and ManZ being sufficient for proper lambda phage infection.
MANXYZ possesses four domains in three polypeptide chains; ManX, ManY, and ManZ. The ManX subunit forms a homodimer that is localized to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. ManX contains two domains IIA and IIB linked by a hinge peptide with each domain containing a phosphorylation site and phosphoryl transfer occurs between both subunits. ManX can be membrane bound or not. The ManY and ManNZ subunits are hydrophobic integral membrane proteins with six and one transmembrane alpha helical spanner(s). The phosphoryl group of PEP is transferred to the imported sugar via Enzyme 1, histidine protein phosphate carrier, and then to the ManX, ManY, and ManZ subunits of the ManXYZ transportation complex, which phosphorylates the entering hexose sugar, creating a hexose-6-phosphate.
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
of the aldohexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
series of carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s. It is a C-2 epimer
In stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers have opposite configuration at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each. Epimerization is ...
of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
. Mannose is important in human metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, especially in the glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
of certain protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s involved in mannose metabolism.
Mannose is not an essential nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
; it can be produced in the human body from glucose, or converted into glucose. Mannose provides 2–5 kcal
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of o ...
/g. It is partially excreted in the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excretion, excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cel ...
.
Etymology
The root of both "mannose" and "mannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lower ...
" is manna
Manna ( he, מָן, mān, ; ar, اَلْمَنُّ; sometimes or archaically spelled mana) is, according to the Bible, an edible substance which God provided for the Israelites during their travels in the desert during the 40-year period follow ...
, which the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
describes as the food supplied to the Israelites during their journey in the region of Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
. Several trees and shrubs can produce a substance called manna, such as the "manna tree" (''Fraxinus ornus
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of subtropical species are evergr ...
'') from whose secretions mannitol was originally isolated.
Structure
Mannose commonly exists as two different-sized rings, thepyranose Pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring. The name derives from its similarity ...
(six-membered) form and the furanose
A furanose is a collective term for carbohydrates that have a chemical structure that includes a five-membered ring system consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The name derives from its similarity to the oxygen heterocycle furan, bu ...
(five-membered) form. Each ring closure can have either an alpha or beta configuration at the anomeric position. The chemical rapidly undergoes isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomeriz ...
among these four forms.
Metabolism
 While much of the mannose used in glycosylation is believed to be derived from glucose, in cultured
While much of the mannose used in glycosylation is believed to be derived from glucose, in cultured hepatoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
cells (cancerous cells from the liver), most of the mannose for glycoprotein biosynthesis comes from extracellular mannose, not glucose. Many of the glycoproteins produced in the liver are secreted into the bloodstream, so dietary mannose is distributed throughout the body.
Mannose is present in numerous glycoconjugates including ''N''-linked glycosylation of proteins. ''C''-Mannosylation is also abundant and can be found in collagen-like regions.
The digestion of many polysaccharides and glycoproteins yields mannose, which is phosphorylated by hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokina ...
to generate mannose-6-phosphate. Mannose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-6-phosphate, by the enzyme phosphomannose isomerase, and then enters the glycolytic pathway
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate (). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and NADH, red ...
or is converted to glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
by the gluconeogenic pathway of hepatocytes
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, b ...
.
Mannose is a dominant monosaccharide in ''N''-linked glycosylation, which is a post-translational modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosome ...
of proteins. It is initiated by the ''en bloc'' transfer on Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 to nascent glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum in a co-translational manner as the protein entered through the transport system. Glucose is hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
on fully folded protein and the mannose moieties are hydrolyzed by ER and Golgi-resident mannosidases. Typically, mature human glycoproteins only contain three mannose residues buried under sequential modification by GlcNAc, galactose, and sialic acid. This is important, as the innate immune system in mammals is geared to recognise exposed mannose residues. This activity is due to the prevalence of mannose residues, in the form of mannans, on the surfaces of yeasts. The human immunodeficiency virus displays considerable amount of mannose residues due to the tight clustering of glycans in its viral spike. These mannose residues are the target for broadly neutralizing antibodies.
Biotechnology
Recombinant proteins produced in yeast may be subject to mannose addition in patterns different from those used by mammalian cells. This difference in recombinant proteins from those normally produced in mammalian organisms may influence the effectiveness of vaccines.Formation
Mannose can be formed by the oxidation ofmannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lower ...
.
It can also be formed from glucose in the Lobry-de Bruyn-van Ekenstein transformation.
Uses
Mannose (D-mannose) is used as adietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
to prevent recurrent urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney ...
s (UTIs). , one review found that taking mannose was as effective as antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s to prevent UTIs, while another review found that clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ...
quality was too low to allow any conclusion about using D‐mannose to prevent or treat UTIs.
Configuration
Mannose differs from glucose by inversion of the C-2chiral center
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups ...
. Mannose displays a pucker in the solution ring form. This simple change leads to the drastically different biochemistry of the two hexoses. This change has the same effect on the other aldohexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
s, as well.
Mannose PTS permease
 The PEP-dependent sugar transporting phosphotransferase system transports and simultaneously phosphorylates its sugar substrates. Mannose XYZ permease is a member of the family, with this distinct method being used by bacteria for sugar uptake particularly exogenous hexoses in the case of mannose XYZ to release the phosphate esters into the cell cytoplasm in preparation for metabolism primarily through the route of glycolysis. The MANXYZ transporter complex is also involved in infection of ''E. coli'' by bacteriophage lambda, with subunit ManY and ManZ being sufficient for proper lambda phage infection.
MANXYZ possesses four domains in three polypeptide chains; ManX, ManY, and ManZ. The ManX subunit forms a homodimer that is localized to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. ManX contains two domains IIA and IIB linked by a hinge peptide with each domain containing a phosphorylation site and phosphoryl transfer occurs between both subunits. ManX can be membrane bound or not. The ManY and ManNZ subunits are hydrophobic integral membrane proteins with six and one transmembrane alpha helical spanner(s). The phosphoryl group of PEP is transferred to the imported sugar via Enzyme 1, histidine protein phosphate carrier, and then to the ManX, ManY, and ManZ subunits of the ManXYZ transportation complex, which phosphorylates the entering hexose sugar, creating a hexose-6-phosphate.
The PEP-dependent sugar transporting phosphotransferase system transports and simultaneously phosphorylates its sugar substrates. Mannose XYZ permease is a member of the family, with this distinct method being used by bacteria for sugar uptake particularly exogenous hexoses in the case of mannose XYZ to release the phosphate esters into the cell cytoplasm in preparation for metabolism primarily through the route of glycolysis. The MANXYZ transporter complex is also involved in infection of ''E. coli'' by bacteriophage lambda, with subunit ManY and ManZ being sufficient for proper lambda phage infection.
MANXYZ possesses four domains in three polypeptide chains; ManX, ManY, and ManZ. The ManX subunit forms a homodimer that is localized to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. ManX contains two domains IIA and IIB linked by a hinge peptide with each domain containing a phosphorylation site and phosphoryl transfer occurs between both subunits. ManX can be membrane bound or not. The ManY and ManNZ subunits are hydrophobic integral membrane proteins with six and one transmembrane alpha helical spanner(s). The phosphoryl group of PEP is transferred to the imported sugar via Enzyme 1, histidine protein phosphate carrier, and then to the ManX, ManY, and ManZ subunits of the ManXYZ transportation complex, which phosphorylates the entering hexose sugar, creating a hexose-6-phosphate.
See also
* α-Mannosidase *Mannose receptor
The mannose receptor (Cluster of Differentiation 206, CD206) is a C-type lectin primarily present on the surface of macrophages, immature dendritic cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, but is also expressed on the surface of skin cells ...
*Mannan oligosaccharide-based nutritional supplements
Mannans are polymers containing the sugar mannose as a principal component.
They are a type of polysaccharide comprise hemicellulose, a major source of biomass found in higher plants such as softwoods. These polymers also typically contain two ot ...
* Rhamnose, 6-deoxy-L-mannose
* PTS Mannose-Fructose-Sorbose Family
References
{{Carbohydrates Aldohexoses Articles containing video clips Pyranoses Glycerols